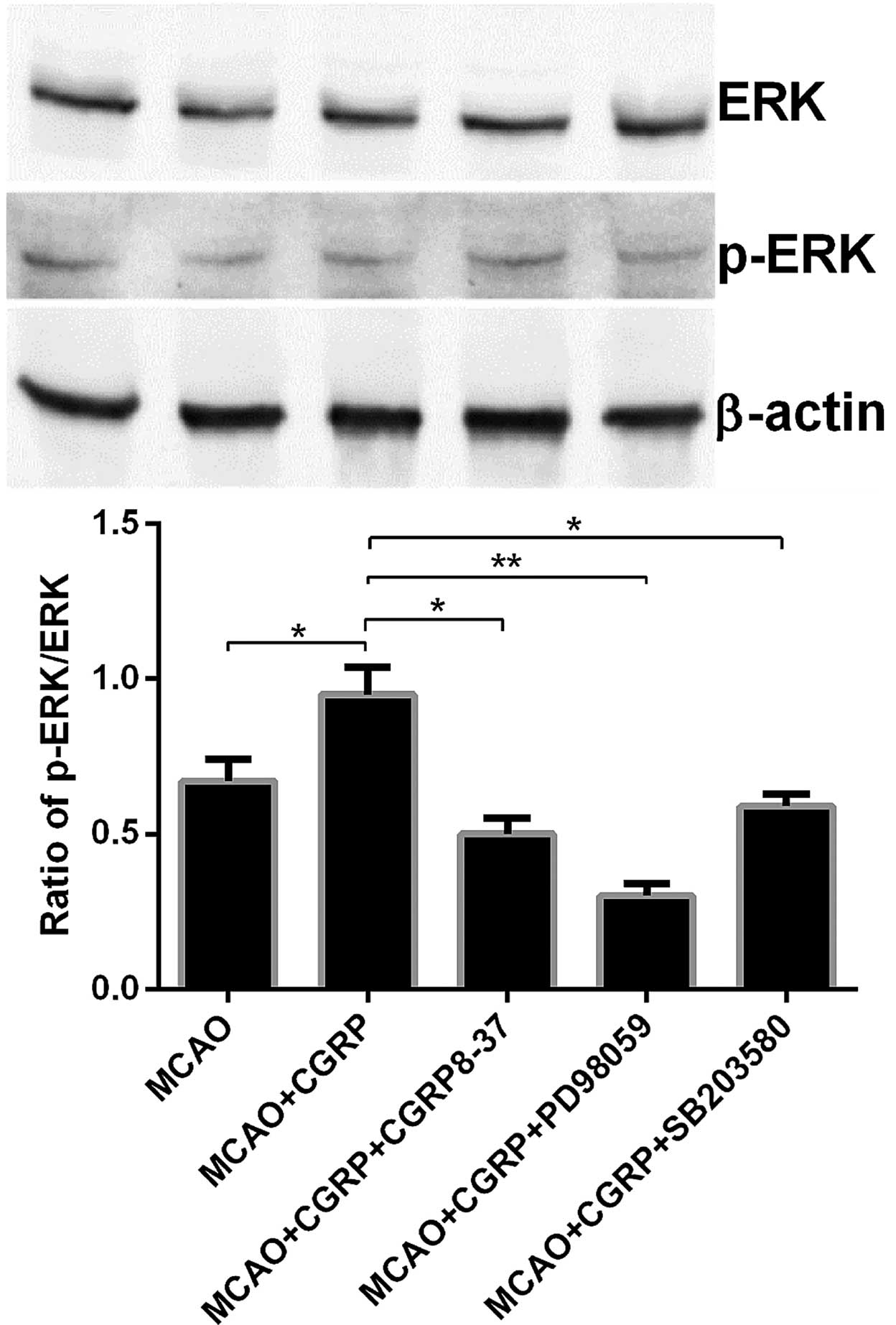
|
1
|
Zhang ZH, Fang XB, Xi GM, Li WC, Ling HY
and Qu P: Calcitonin gene-related peptide enhances CREB
phosphorylation and attenuates tau protein phosphorylation in rat
brain during focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Biomed
Pharmacother. 64:430–436. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu Z, Liu Q, Cai H, Xu C, Liu G and Li Z:
Calcitonin gene-related peptide prevents blood-brain barrier injury
and brain edema induced by focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion.
Regul Pept. 171:19–25. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shao B, Zhou YL, Wang H and Lin YS: The
role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in post-stroke depression
in chronic mild stress-treated ischemic rats. Physiol Behav.
139:224–230. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou J, Du T, Li B, Rong Y, Verkhratsky A
and Peng L: Crosstalk between MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signal pathways
during brain ischemia/reperfusion. ASN Neuro. 7:72015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wei SG, Yu Y, Weiss RM and Felder RB:
Inhibition of brain mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling
reduces central endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation and
sympathetic nerve activity in heart failure rats. Hypertension.
67:229–236. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nagasawa H and Kogure K: Correlation
between cerebral blood flow and histologic changes in a new rat
model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke. 20:1037–1043.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Germano SM,
Nishimura MC, Davis RL and Bartkowski HM: Evaluation of
2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride as a stain for detection and
quantification of experimental cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke.
17:1304–1308. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:671–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mistrova E, Wiegand S, Sviglerova J, Pfeil
U, Kuncova J, Slavikova J, Kummer W and Chottova Dvorakova M:
Adrenomedullin and the calcitonin receptor-like receptor system
mRNA expressions in the rat heart and sensory ganglia in
experimentally-induced long-term diabetes. Gen Physiol Biophys.
33:215–225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hagner S, Stahl U, Knoblauch B, McGregor
GP and Lang RE: Calcitonin receptor-like receptor: Identification
and distribution in human peripheral tissues. Cell Tissue Res.
310:41–50. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cai H, Xu X, Liu Z, Wang Q, Feng G, Li Y,
Xu C, Liu G and Li Z: The effects of calcitonin gene-related
peptide on bFGF and AQP4 expression after focal cerebral ischemia
reperfusion in rats. Pharmazie. 65:274–278. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang CX, Liu JX, Li D, Li L, Fu JH, Hou
JC, Du XM and Zhang FC: Effect of guanmaitong tablet on ERK and p38
protein of TLR2 pathway expression in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
rats: An experimental study. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi.
35:712–716. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nozaki K, Nishimura M and Hashimoto N:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases and cerebral ischemia. Mol
Neurobiol. 23:1–19. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun X, Liu C, Qian M, Zhao Z and Guo J:
Ceramide from sphingomyelin hydrolysis differentially mediates
mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) activation following
cerebral ischemia in rat hippocampal CA1 subregion. J Biomed Res.
24:132–137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Piao CS, Kim JB, Han PL and Lee JK:
Administration of the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 affords brain
protection with a wide therapeutic window against focal ischemic
insult. J Neurosci Res. 73:537–544. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bonny C, Borsello T and Zine A: Targeting
the JNK pathway as a therapeutic protective strategy for nervous
system diseases. Rev Neurosci. 16:57–67. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Haddad JJ: The role of Bax/Bcl-2 and
pro-caspase peptides in hypoxia/reperfusion-dependent regulation of
MAPK(ERK): Discordant proteomic effect of MAPK(p38). Protein Pept
Lett. 14:361–371. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shen CP, Tsimberg Y, Salvadore C and
Meller E: Activation of Erk and JNK MAPK pathways by acute swim
stress in rat brain regions. BMC Neurosci. 5:362004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Piao CS, Che Y, Han PL and Lee JK: Delayed
and differential induction of p38 MAPK isoforms in microglia and
astrocytes in the brain after transient global ischemia. Brain Res
Mol Brain Res. 107:137–144. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang M, Wang L and Jiang HH: Role of
spinal MAPK-ERK signal pathway in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 15:387–391. 2013.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Anfuso CD, Motta C, Giurdanella G, Arena
V, Alberghina M and Lupo G: Endothelial PKCα-MAPK/ERK-phospholipase
A2 pathway activation as a response of glioma in a triple culture
model. A new role for pericytes? Biochimie. 99:77–87. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim TK, Lee JS, Jung HS, Ha TK, Kim SM,
Han N, Lee EJ, Kim TN, Kwon MJ, Lee SH, et al: Triiodothyronine
induces proliferation of pancreatic β-cells through the MAPK/ERK
pathway. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 122:240–245. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|