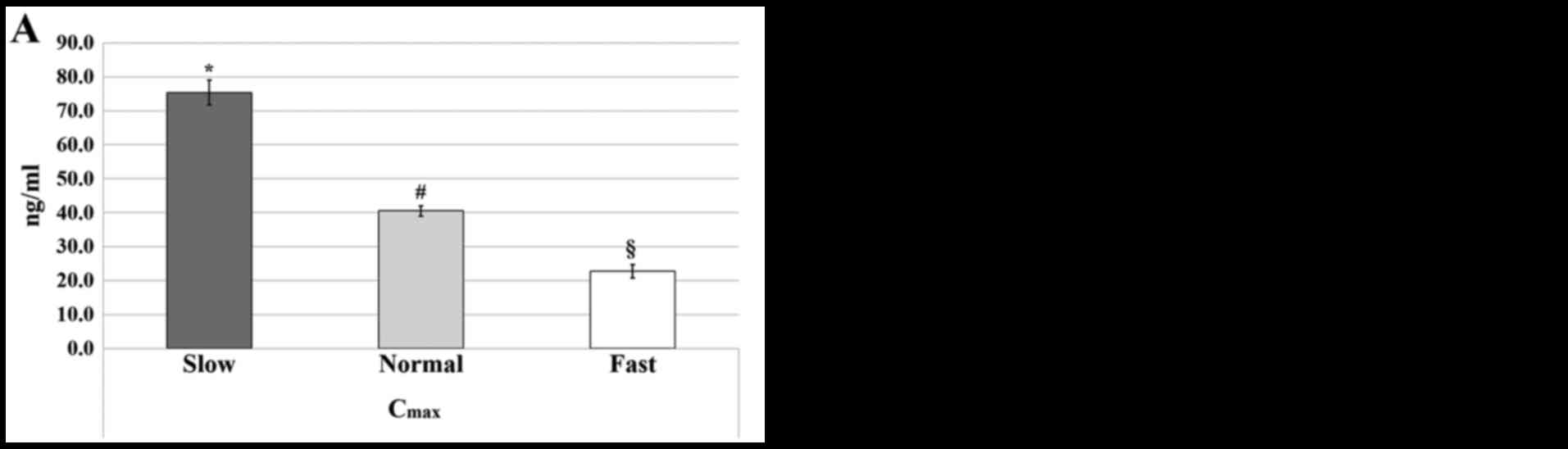
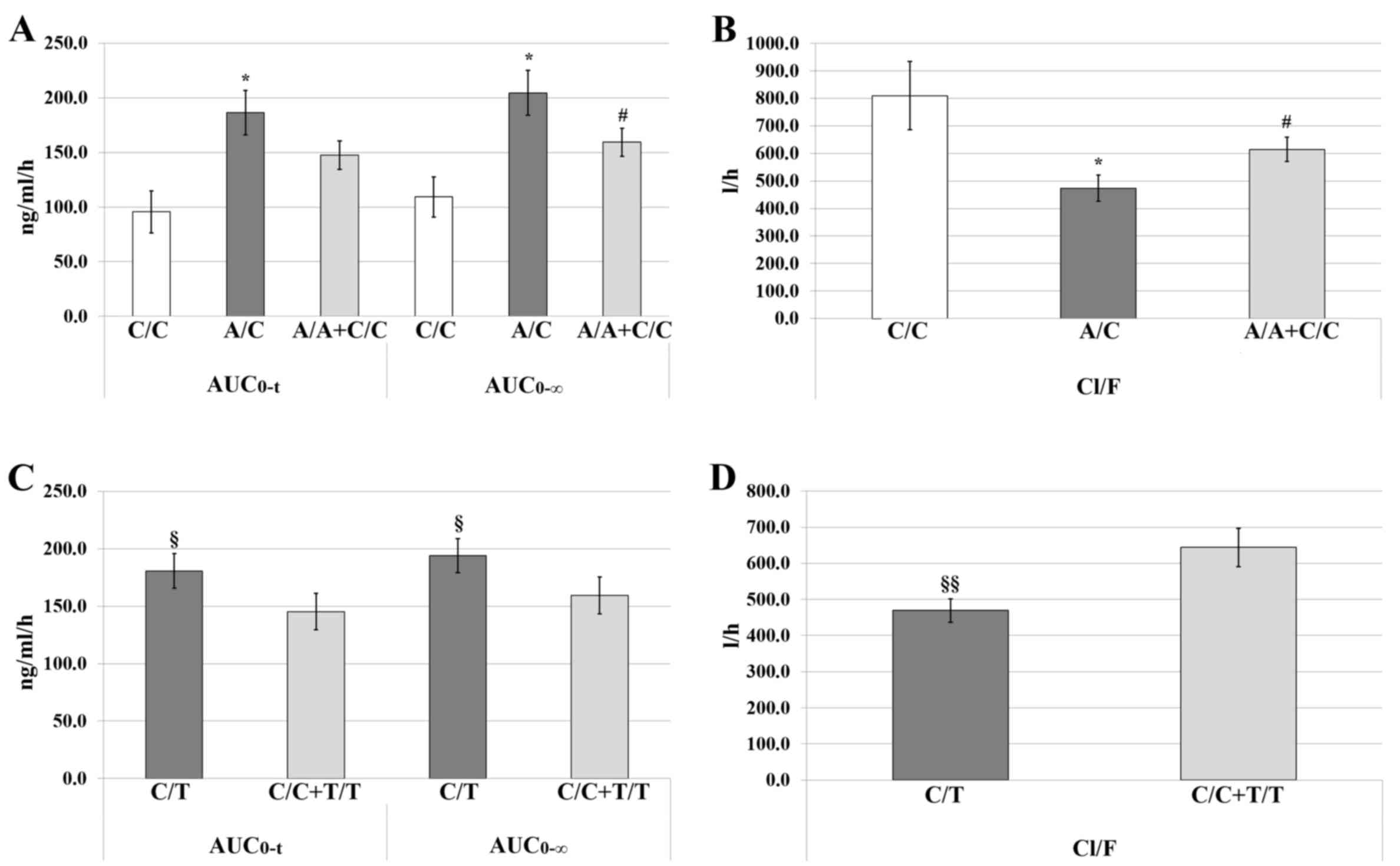
|
1
|
Valdez Morales M, Medina Godoy S, Chacón
López MA and Espinosa Alonso LG: Comprehensive approach of diet
importance on health status of the Mexican population. Biotecnia.
18:102016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kuri-Morales PA: La transición en salud y
su impacto en la demanda de servicios. Gac Med Mex. 147:451–454.
2011.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
National Institute of Statistics and
Geography (INEGI), . Mortality Statistics. INEGI, Mexico City.
2015.http://www.beta.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/proyectos/registros/vitales/mortalidad/doc/presentacion.pdfJune
15–2016(In Spanish).
|
|
4
|
Escobedo-de la Peña J, de Jesús-Pérez R,
Schargrodsky H and Champagne B: Prevalence of dyslipidemias in
Mexico city and Its relation to other cardiovascular risk factors.
Results from the CARMELA study. Gac Med Mex. 150:128–136. 2014.(In
Spanish).
|
|
5
|
Canalizo-Miranda E, Favela-Pérez EA,
Salas-Anaya JA, Gómez-Díaz R, Jara-Espino R, Del Pilar
Torres-Arreola L and Viniegra-Osorio A: Clinical practice
guideline. Diagnosis and treatment of dyslipidemia. Rev Med Inst
Mex Seguro Soc. 51:700–709. 2013.(In Spanish).
|
|
6
|
McFarland AJ, Anoopkumar-Dukie S, Arora
DS, Grant GD, McDermott CM, Perkins AV and Davey AK: Molecular
mechanisms underlying the effects of statins in the central nervous
system. Int J Mol Sci. 15:20607–20637. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
León-Cachón RBR, Ascacio-Martínez JA,
Gamino-Peña ME, Cerda-Flores RM, Meester I, Gallardo-Blanco HL,
Gómez-Silva M, Piñeyro-Garza E and Barrera-Saldaña HA: A
pharmacogenetic pilot study reveals MTHFR, DRD3, and MDR1
polymorphisms as biomarker candidates for slow atorvastatin
metabolizers. BMC Cancer. 16:742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
León-Cachón RBR, Ascacio-Martínez JAI,
Gómez-Silva M, Piñeyro-Garza E, González-González JG, Pogue G,
Simón-Buela L and Barrera-Saldaña HA: Application of genomic
technologies in clinical pharmacology research. Rev Inves Clin.
67:212–218. 2015.
|
|
9
|
US Food and Drug Administration, . Draft
guidance on atorvastatin calcium and ezetimibe. US Department of
Health and Human Services; Silver Spring, MD: 2014
|
|
10
|
León-Cachón RB1, Ascacio-Martínez JA and
Barrera-Saldaña HA: Individual response to drug therapy: Bases and
study approaches. Rev Invest Clin. 64:364–376. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cruz-Correa OF, León-Cachón RB,
Barrera-Saldaña HA and Soberón X: Prediction of atorvastatin
plasmatic concentrations in healthy volunteers using integrated
pharmacogenetics sequencing. Pharmacogenomics. 18:121–131. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma Y, Chen Z, Zou Y and Ge J: Atorvastatin
represses the angiotensin 2-induced oxidative stress and
inflammatory response in dendritic cells via the PI3K/Akt/Nrf 2
pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014:1487982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ruaño G, Thompson PD, Windemuth A, Smith
A, Kocherla M, Holford TR, Seip R and Wu AH: Physiogenomic analysis
links serum creatine kinase activities during statin therapy to
vascular smooth muscle homeostasis. Pharmacogenomics. 6:865–872.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Peters BJ, Klungel OH, de Boer A, Ch
Stricker BH and Maitland-van der Zee AH: Pharmacogenetics of
cardiovascular drug therapy. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 6:55–65.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Frazier L, Turner ST, Schwartz GL, Chapman
AB and Boerwinkle E: Multilocus effects of the
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system genes on blood pressure
response to a thiazide diuretic. Pharmacogenomics J. 4:17–23. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang X, Sheng HH, Lin G, Li J, Lu XZ,
Cheng YL, Huang J, Xiao HS and Zhan YY: Effect of
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system gene polymorphisms on blood
pressure response to antihypertensive treatment. Chin Med J (Engl).
120:782–786. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bryant JW and Shariat-Madar Z: Human
plasma kallikrein-kinin system: Physiological and biochemical
parameters. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 7:234–250. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bentley JP, Asselbergs FW, Coffey CS,
Hebert PR, Moore JH, Hillege HL and van Gilst WH: Cardiovascular
risk associated with interactions among polymorphisms in genes from
the renin-angiotensin, bradykinin, and fibrinolytic systems. PLoS
One. 5:e127572010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pal GK, Adithan C, Umamaheswaran G, Pal P,
Nanda N, Indumathy J and Syamsunder AN: Endothelial nitric oxide
synthase gene polymorphisms are associated with cardiovascular
risks in prehypertensives. J Am Soc Hypertens. 10:865–872. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Luo K, Kang W and Xu G: The risk of
bradykinin B2 receptor-58T/C gene polymorphism on hypertension: A
meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:19917–19927. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Silva PS, Fontana V, Luizon MR, Lacchini
R, Silva WA Jr, Biagi C and Tanus-Santos JE: eNOS and BDKRB2
genotypes affect the antihypertensive responses to enalapril. Eur J
Clin Pharmacol. 69:167–177. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
World Medical Association, . World Medical
Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. JAMA. 310:2191–2194. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
World Medical Association, . WMA
Declaration of Tokyo - Guidelines for physicians concerning torture
and other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment in
relation to detention and imprisonment. 29th WMA General Assembly.
Tokyo, Japan. 1975;
|
|
24
|
Solorzano-Flores LI: Official Mexican
Standard NOM-177-SSA1-1998, establishing tests and procedures to
demonstrate that a drug is interchangeable. Requirements must be
subject to third party authorized to perform the tests. Secretaria
de Salud, Mexico. 1999.
|
|
25
|
Briggs GG, Freeman RK, Towers CV and
Forinash AB: Drugs in Pregnancy and Lactation. 11th. Williams &
Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA: 2017
|
|
26
|
Sambrook J and Russell DW: Preparation and
analysis of eukaryotic genomic DNAMolecular Cloning: A Laboratory
Manual. 3rd. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; New York, NY:
2001
|
|
27
|
Ahmed T, Kollipara S, Gautam A, Gigras R,
Kothari M, Saha N, Batra V and Paliwal J: Bioavailability and
interaction potential of atorvastatin and losartan on
co-administration in healthy human subjects. J Bioequiv Availab.
1:18–27. 2009.
|
|
28
|
Stanisz B and Kania L: Validation of HPLC
method for determination of atorvastatin in tablets and for
monitoring stability in solid phase. Acta Pol Pharm. 63:471–476.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rowland M and Tozer TN: Clinical
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: Concepts and Applications.
4th. Williams & Willkins; Philadelphia, PA: 2017
|
|
30
|
Ward JH Jr: Hierarchical grouping to
optimize an objective function. J Am Stat Assoc. 58:236–244. 1963.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Reed TE and Schull WJ: A general maximum
likelihood estimation program. Am J Hum Genet. 20:579–580.
1968.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Horita N and Kaneko T: Genetic model
selection for a case-control study and a meta-analysis. Meta Gene.
5:1–8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang Q, Aa J, Jia H, Xin X, Tao C, Liu L,
Zou B, Song Q, Shi J, Cao B, et al: A Pharmacometabonomic approach
to predicting metabolic phenotypes and pharmacokinetic parameters
of atorvastatin in healthy volunteers. J Proteome Res.
14:3970–3981. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Niemi M: Transporter pharmacogenetics and
statin toxicity. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 87:130–133. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kadam P, Ashavaid TF, Ponde CK and Rajani
RM: Genetic determinants of lipid-lowering response to atorvastatin
therapy in an Indian population. J Clin Pharm Ther. 41:329–333.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Prado Y, Zambrano T and Salazar LA:
Transporter genes ABCG2 rs2231142 and ABCB1 rs1128503 polymorphisms
and atorvastatin response in Chilean subjects. J Clin Pharm Ther.
Aug 19–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yap RWK, Shidoji Y, Yap WS and Masaki M:
Association and interaction effect of AGTR1 and AGTR2 gene
polymorphisms with dietary pattern on metabolic risk factors of
cardiovascular disease in Malaysian adults. Nutrients. 9:E8532017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Isley WL, Miles JM, Patterson BW and
Harris WS: The effect of high-dose simvastatin on triglyceride-rich
lipoprotein metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J
Lipid Res. 47:193–200. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chandra S, Narang R, Sreenivas V, Bhatia
J, Saluja D and Srivastava K: Association of angiotensin II type 1
receptor (A1166C) gene polymorphism and its increased expression in
essential hypertension: A case-control study. PLoS One.
9:e1015022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Moreno M, Ramalho LN, Sancho-Bru P,
Ruiz-Ortega M, Ramalho F, Abraldes JG, Colmenero J, Dominguez M,
Egido J, Arroyo V, et al: Atorvastatin attenuates angiotensin
II-induced inflammatory actions in the liver. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 296:G147–G156. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Morgado M, Rolo S, Macedo AF and
Castelo-Branco M: Association of statin therapy with blood pressure
control in hypertensive hypercholesterolemic outpatients in
clinical practice. J Cardiovasc Dis Res. 2:44–49. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|