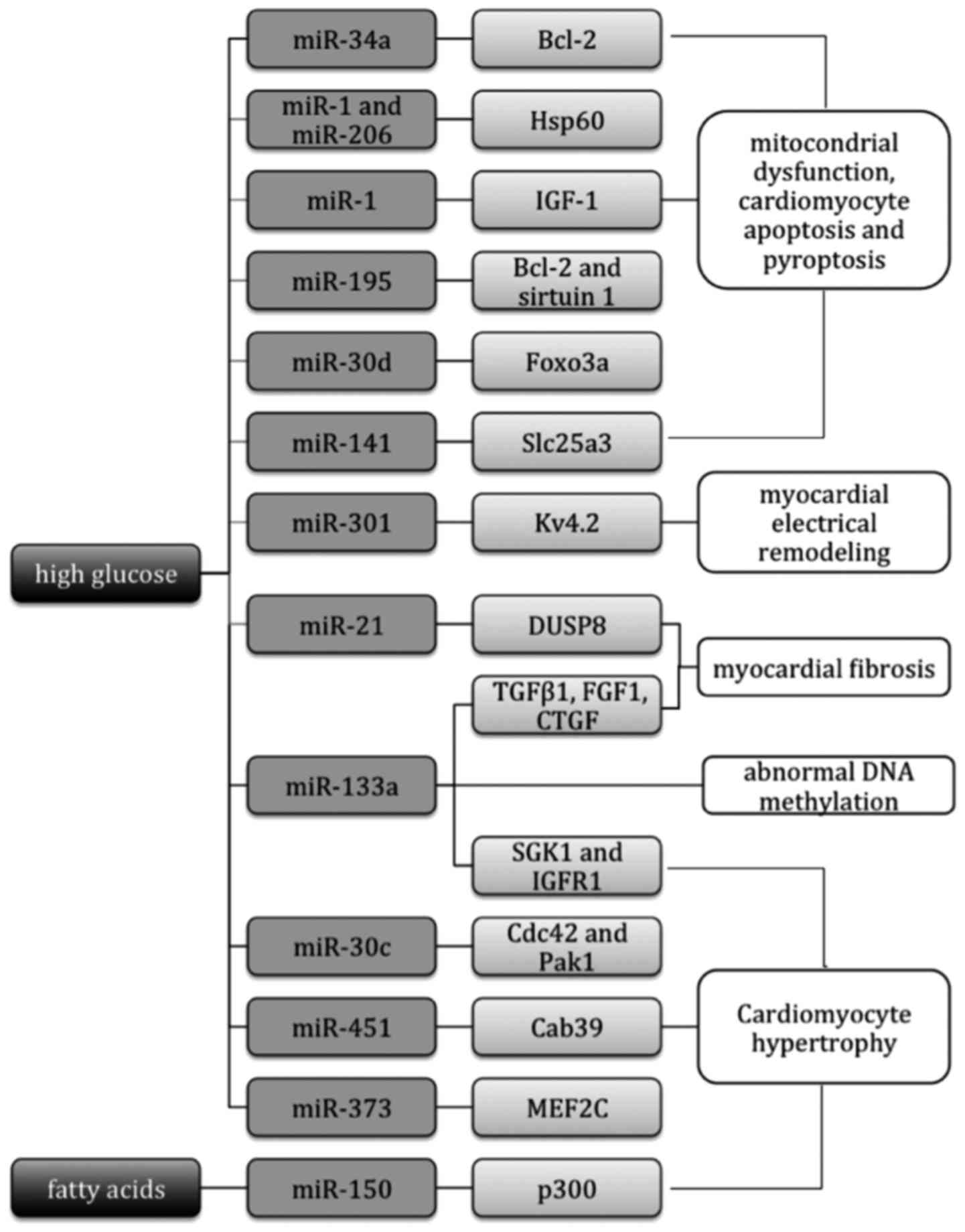
|
1
|
Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I,
Beagley J, Linnenkamp U and Shaw JE: Global estimates of diabetes
prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res Clin
Pract. 103:137–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wegner M, Neddermann D,
Piorunska-Stolzmann M and Jagodzinski PP: Role of epigenetic
mechanisms in the development of chronic complications of diabetes.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 105:164–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rawal S, Manning P and Katare R:
Cardiovascular microRNAs: As modulators and diagnostic biomarkers
of diabetic heart disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 13:442014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou Q, Lv D, Chen P, Xu T, Fu S, Li J and
Bei Y: MicroRNAs in diabetic cardiomyopathy and clinical
perspectives. Front Genet. 5:1852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Beckman JA, Creager MA and Libby P:
Diabetes and atherosclerosis: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and
management. JAMA. 287:2570–2581. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chavali V, Tyagi SC and Mishra PK:
Predictors and prevention of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes
Metab Syndr Obes. 6:151–160. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hayat SA, Patel B, Khattar RS and Malik
RA: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment.
Clin Sci (Lond). 107:539–557. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kannel WB and McGee DL: Diabetes and
glucose tolerance as risk factors for cardiovascular disease: The
Framingham study. Diabetes Care. 2:120–126. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rubler S, Dlugash J, Yuceoglu YZ, Kumral
T, Branwood AW and Grishman A: New type of cardiomyopathy
associated with diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Am J Cardiol.
30:595–602. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Trachanas K, Sideris S, Aggeli C,
Poulidakis E, Gatzoulis K, Tousoulis D and Kallikazaros I: Diabetic
cardiomyopathy: From pathophysiology to treatment. Hellenic J
Cardiol. 55:411–421. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yilmaz S, Canpolat U, Aydogdu S and Abboud
HE: Diabetic Cardiomyopathy; Summary of 41 Years. Korean Circ J.
45:266–272. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Falcão-Pires I and Leite-Moreira AF:
Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Understanding the molecular and cellular
basis to progress in diagnosis and treatment. Heart Fail Rev.
17:325–344. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Singh GB, Sharma R and Khullar M:
Epigenetics and diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
94:14–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Asrih M and Steffens S: Emerging role of
epigenetics and miRNA in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc
Pathol. 22:117–125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu JW, Liu D, Cui KZ, Xu Y, Li YB, Sun YM
and Su Y: Recent advances in understanding the biochemical and
molecular mechanism of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 427:441–443. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huynh K, Bernardo BC, McMullen JR and
Ritchie RH: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Mechanisms and new treatment
strategies targeting antioxidant signaling pathways. Pharmacol
Ther. 142:375–415. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bauersachs J and Thum T: Biogenesis and
regulation of cardiovascular microRNAs. Circ Res. 109:334–347.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Udali S, Guarini P, Moruzzi S, Choi SW and
Friso S: Cardiovascular epigenetics: From DNA methylation to
microRNAs. Mol Aspects Med. 34:883–901. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fichtlscherer S, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S and
Sessa WC: Circulating microRNAs: Biomarkers or mediators of
cardiovascular diseases? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
31:2383–2390. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fichtlscherer S, De Rosa S, Fox H,
Schwietz T, Fischer A, Liebetrau C, Weber M, Hamm CW, Röxe T,
Müller-Ardogan M, et al: Circulating microRNAs in patients with
coronary artery disease. Circ Res. 107:677–684. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Figueira MF, Monnerat-Cahli G, Medei E,
Carvalho AB, Morales MM, Lamas ME, da Fonseca RN and Souza-Menezes
J: MicroRNAs: Potential therapeutic targets in diabetic
complications of the cardiovascular and renal systems. Acta Physiol
(Oxf). 211:491–500. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Diao X, Shen E, Wang X and Hu B:
Differentially expressed microRNAs and their target genes in the
hearts of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Mol Med Rep.
4:633–640. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rawal S, Ram TP, Coffey S, Williams MJ,
Saxena P, Bunton RW, Galvin IF and Katare R: Differential
expression pattern of cardiovascular microRNAs in the human type-2
diabetic heart with normal ejection fraction. Int J Cardiol.
202:40–43. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nandi SS, Duryee MJ, Shahshahan HR, Thiele
GM, Anderson DR and Mishra PK: Induction of autophagy markers is
associated with attenuation of miR-133a in diabetic heart failure
patients undergoing mechanical unloading. Am J Transl Res.
7:683–696. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chavali V, Tyagi SC and Mishra PK:
MicroRNA-133a regulates DNA methylation in diabetic cardiomyocytes.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 425:668–672. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen S, Puthanveetil P, Feng B, Matkovich
SJ, Dorn GW II and Chakrabarti S: Cardiac miR-133a overexpression
prevents early cardiac fibrosis in diabetes. J Cell Mol Med.
18:415–421. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Duan Y, Zhou B, Su H, Liu Y and Du C:
miR-150 regulates high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by
targeting the transcriptional co-activator p300. Exp Cell Res.
319:173–184. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li X, Du N, Zhang Q, Li J, Chen X, Liu X,
Hu Y, Qin W, Shen N, Xu C, et al: MicroRNA-30d regulates
cardiomyocyte pyroptosis by directly targeting foxo3a in diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Cell Death Dis. 5:e14792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Panguluri SK, Tur J, Chapalamadugu KC,
Katnik C, Cuevas J and Tipparaju SM: MicroRNA-301a mediated
regulation of Kv4.2 in diabetes: Identification of key modulators.
PLoS One. 8:e605452013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu M, Liu Y, Zhang B, Shi Y, Cui L and
Zhao X: Inhibiting microRNA-144 abates oxidative stress and reduces
apoptosis in hearts of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice.
Cardiovasc Pathol. 24:375–381. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Feng B, Chen S, George B, Feng Q and
Chakrabarti S: miR133a regulates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in
diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 26:40–49. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kuwabara Y, Horie T, Baba O, Watanabe S,
Nishiga M, Usami S, Izuhara M, Nakao T, Nishino T, Otsu K, et al:
MicroRNA-451 exacerbates lipotoxicity in cardiac myocytes and
high-fat diet-induced cardiac hypertrophy in mice through
suppression of the LKB1/AMPK pathway. Circ Res. 116:279–288. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Raut SK, Kumar A, Singh GB, Nahar U,
Sharma V, Mittal A, Sharma R and Khullar M: miR-30c Mediates
Upregulation of Cdc42 and Pak1 in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.
Cardiovasc Ther. 33:89–97. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shen E, Diao X, Wang X, Chen R and Hu B:
MicroRNAs involved in the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades
pathway during glucose-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Am J
Pathol. 179:639–650. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu N, Bezprozvannaya S, Williams AH, Qi
X, Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R and Olson EN: MicroRNA-133a
regulates cardiomyocyte proliferation and suppresses smooth muscle
gene expression in the heart. Genes Dev. 22:3242–3254. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Barringhaus KG and Zamore PD: MicroRNAs:
Regulating a change of heart. Circulation. 119:2217–2224. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Carè A, Catalucci D, Felicetti F, Bonci D,
Addario A, Gallo P, Bang ML, Segnalini P, Gu Y, Dalton ND, et al:
MicroRNA-133 controls cardiac hypertrophy. Nat Med. 13:613–618.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ji R, Cheng Y, Yue J, Yang J, Liu X, Chen
H, Dean DB and Zhang C: MicroRNA expression signature and
antisense-mediated depletion reveal an essential role of MicroRNA
in vascular neointimal lesion formation. Circ Res. 100:1579–1588.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu S, Li W, Xu M, Huang H, Wang J and
Chen X: Micro-RNA 21Targets dual specific phosphatase 8 to promote
collagen synthesis in high glucose-treated primary cardiac
fibroblasts. Can J Cardiol. 30:1689–1699. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhao F, Li B, Wei YZ, Zhou B, Wang H, Chen
M, Gan XD, Wang ZH and Xiong SX: MicroRNA-34a regulates high
glucose-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. J Huazhong Univ
Sci Technolog Med Sci. 33:834–839. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shan ZX, Lin QX, Deng CY, Zhu JN, Mai LP,
Liu JL, Fu YH, Liu XY, Li YX, Zhang YY, et al: miR-1/miR-206
regulate Hsp60 expression contributing to glucose-mediated
apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. FEBS Lett. 584:3592–3600. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yu XY, Song YH, Geng YJ, Lin QX, Shan ZX,
Lin SG and Li Y: Glucose induces apoptosis of cardiomyocytes via
microRNA-1 and IGF-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 376:548–552.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zheng D, Ma J, Yu Y, Li M, Ni R, Wang G,
Chen R, Li J, Fan GC, Lacefield JC, et al: Silencing of miR-195
reduces diabetic cardiomyopathy in C57BL/6 mice. Diabetologia.
58:1949–1958. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P,
Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, El-Deiry WS,
Golstein P, Green DR, et al: Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death
2009: Classification of cell death: Recommendations of the
Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2009. Cell Death Differ.
16:3–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Baseler WA, Thapa D, Jagannathan R,
Dabkowski ER, Croston TL and Hollander JM: miR-141 as a regulator
of the mitochondrial phosphate carrier (Slc25a3) in the type 1
diabetic heart. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 303:C1244–C1251. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|