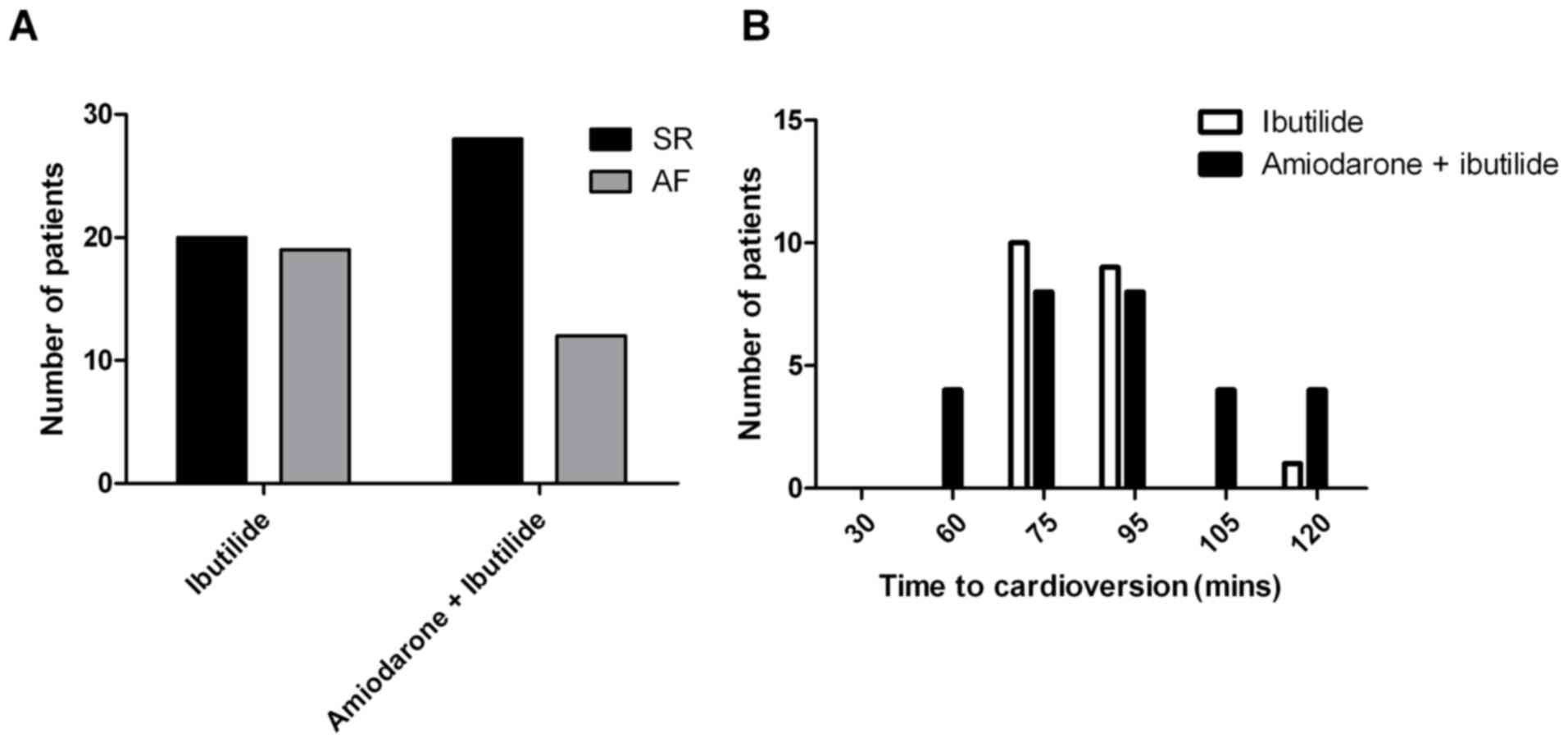
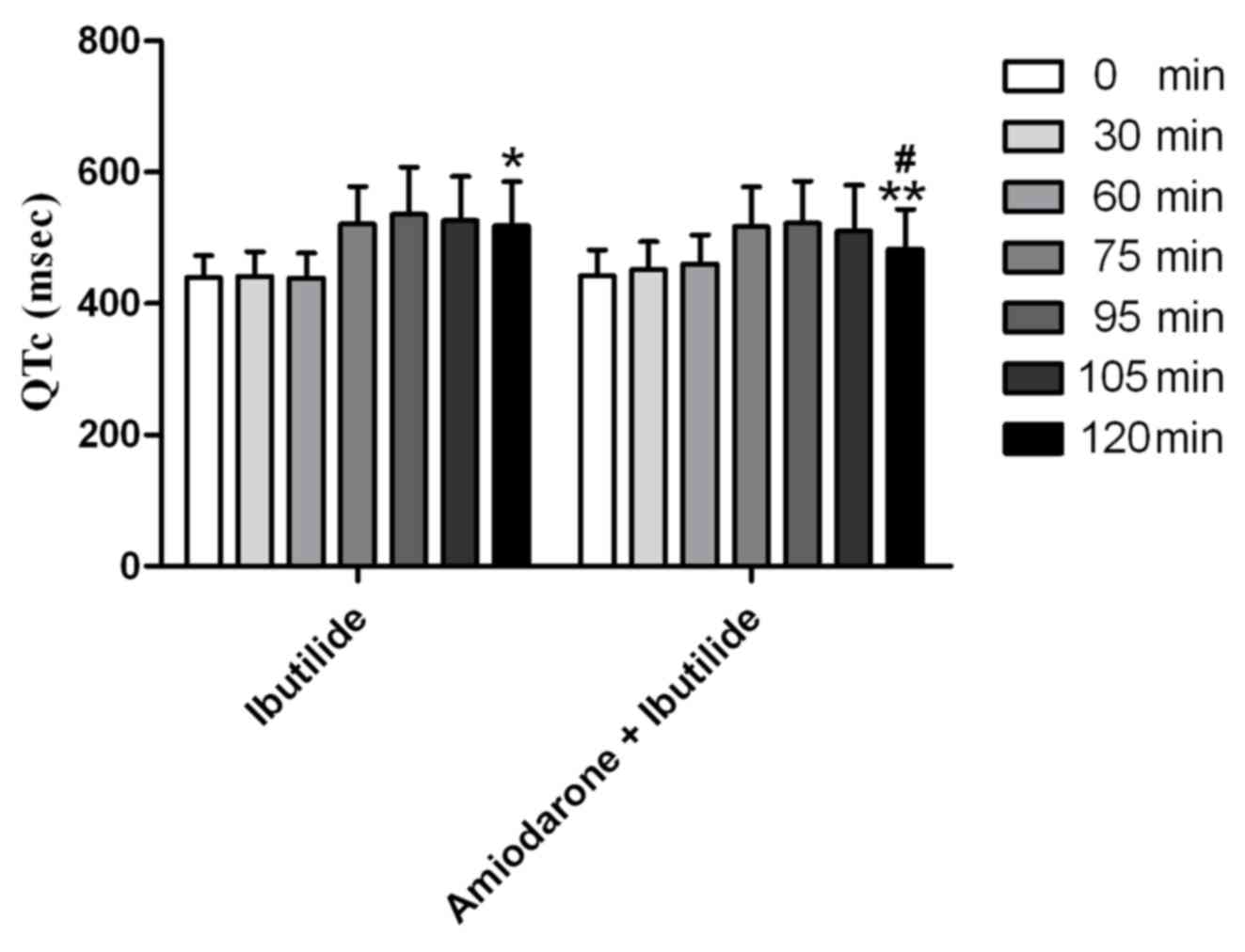
|
1
|
Waktare JE and Camm AJ: Atrial
fibrillation begets trouble. Heart. 77:393–394. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sasaki N, Watanabe I, Kogawa R, Sonoda K,
Takahashi K, Okumura Y, Ohkubo K, Nakai T and Hirayama A: Effects
of intravenous amiodarone and ibutilide on action potential
duration and atrial conduction kinetics in patients with persistent
atrial fibrillation. Int Heart J. 55:244–248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
European Heart Rhythm Association;
European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, ; Camm AJ,
Kirchof P, Lip GY, Schotten U, Savelieva I, Ernst S, van Gelder IC,
Al-Attar N, et al: Guidelines for the management of atrial
fibrillation: The task force for the management of atrial
fibrillation of the European society of cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart
J. 31:2369–2429. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Workman AJ, Smith GL and Rankin AC:
Mechanisms of termination and prevention of atrial fibrillation by
drug therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 131:221–241. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vasić NR, Milenković BA, Pešut DP, Stević
RS and Jovanović DM: Drug induced lung disease-amiodarone in focus.
Med Pregl. 67:334–337. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fadahunsi O and Krol R: Acute amiodarone
pulmonary toxicity following lung resection. Int J Biomed Sci.
10:217–220. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lafuente-Lafuente C, Mouly S,
Longás-Tejero MA, Mahé I and Bergmann JF: Antiarrhythmic drugs for
maintaining sinus rhythm after cardioversion of atrial
fibrillation: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials.
Arch Intern Med. 166:719–728. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Freemantle N, Lafuente-Lafuente C,
Mitchell S, Eckert L and Reynolds M: Mixed treatment comparison of
dronedarone, amiodarone, sotalol, flecainide, and propafenone, for
the management of atrial fibrillation. Europace. 13:329–345. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Camm J: Antiarrhythmic drugs for the
maintenance of sinus rhythm: Risks and benefits. Int J Cardiol.
155:362–371. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
de Paola AA, Figueiredo E, Sesso R, Veloso
HH and Nascimento LO: SOCES Investigators: Effectiveness and costs
of chemical versus electrical cardioversion of atrial fibrillation.
Int J Cardiol. 88:157–166. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Korantzopoulos P, Kolettis TM,
Papathanasiou A, Naka KK, Kolios P, Leontaridis I, Draganigos A,
Katsouras CS and Goudevenos JA: Propafenone added to ibutilide
increases conversion rates of persistent atrial fibrillation.
Heart. 92:631–634. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kafkas NV, Patsilinakos SP, Mertzanos GA,
Papageorgiou KI, Chaveles JI, Dagadaki OK and Kelesidis KM:
Conversion efficacy of intravenous ibutilide compared with
intravenous amiodarone in patients with recent-onset atrial
fibrillation and atrial flutter. Int J Cardiol. 118:321–325. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vos MA, Golitsyn SR, Stangl K, Ruda MY,
van Wijk LV, Harry JD, Perry KT, Touboul P, Steinbeck G and Wellens
HJ: Superiority of ibutilide (a new class III agent) over
DL-sotalol in converting atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation.
The Ibutilide/Sotalol Comparator Study Group. Heart. 79:568–575.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fragakis N, Bikias A, Delithanasis I,
Konstantinidou M, Liakopoulos N, Kozirakis M and Katsaris G: Acute
beta-adrenoceptor blockade improves efficacy of ibutilide in
conversion of atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular rate.
Europace. 11:70–74. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stambler BS, Wood MA, Ellenbogen KA, Perry
KT, Wakefield LK and VanderLugt JT: Efficacy and safety of repeated
intravenous doses of ibutilide for rapid conversion of atrial
flutter or fibrillation. Ibutilide Repeat Dose Study Investigators.
Circulation. 94:1613–1621. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang T, Snyders DJ and Roden DM:
Ibutilide, a methanesulfonanilide antiarrhythmic, is a potent
blocker of the rapidly activating delayed rectifier K+
current (IKr) in AT-1 cells. Concentration-, time-, voltage-, and
use-dependent effects. Circulation. 91:1799–1806. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stambler BS, Beckman KJ, Kadish AH, Camm
JA, Ellenbogen KA, Perry KT and VanderLugt JT: Acute hemodynamic
effects of intravenous ibutilide in patients with or without
reduced left ventricular function. Am J Cardiol. 80:458–463. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gill J, Heel RC and Fitton A: Amiodarone:
An overview of its pharmacological properties and review of its
therapeutic use in cardiac arrhythmias. Drugs. 43:69–110. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mitchell LB, Wyse DG, Gillis AM and Duff
HJ: Electropharmacology of amiodarone therapy initiation. Time
courses of onset of electrophysiologic and antiarrhythmic effects.
Circulation. 80:34–42. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stambler BS, Wood MA and Ellenbogen KA:
Antiarrhythmic actions of intravenous ibutilide compared with
procainamide during human atrial flutter and fibrillation:
Electrophysiological determinants of enhanced conversion efficacy.
Circulation. 96:4298–4306. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|