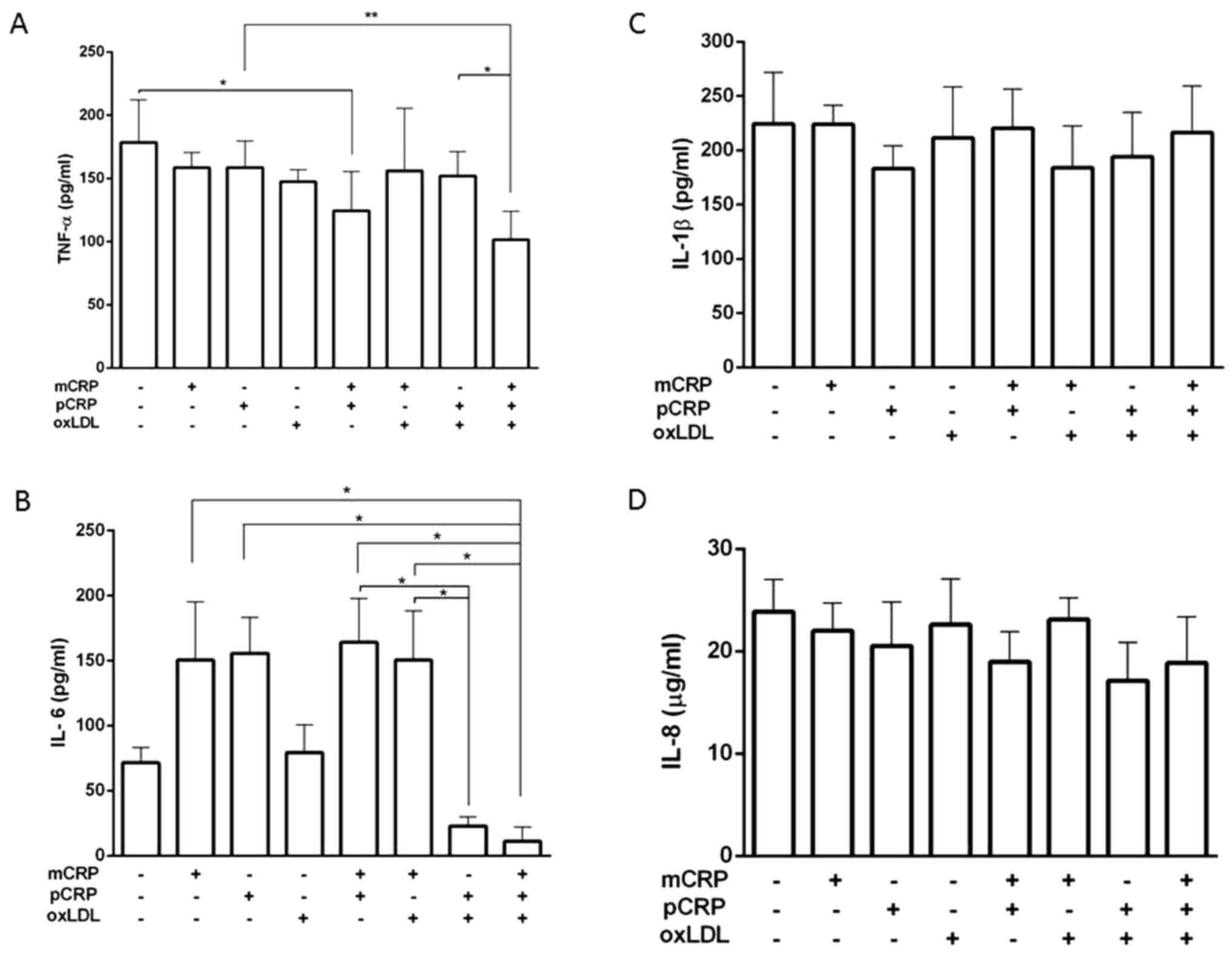
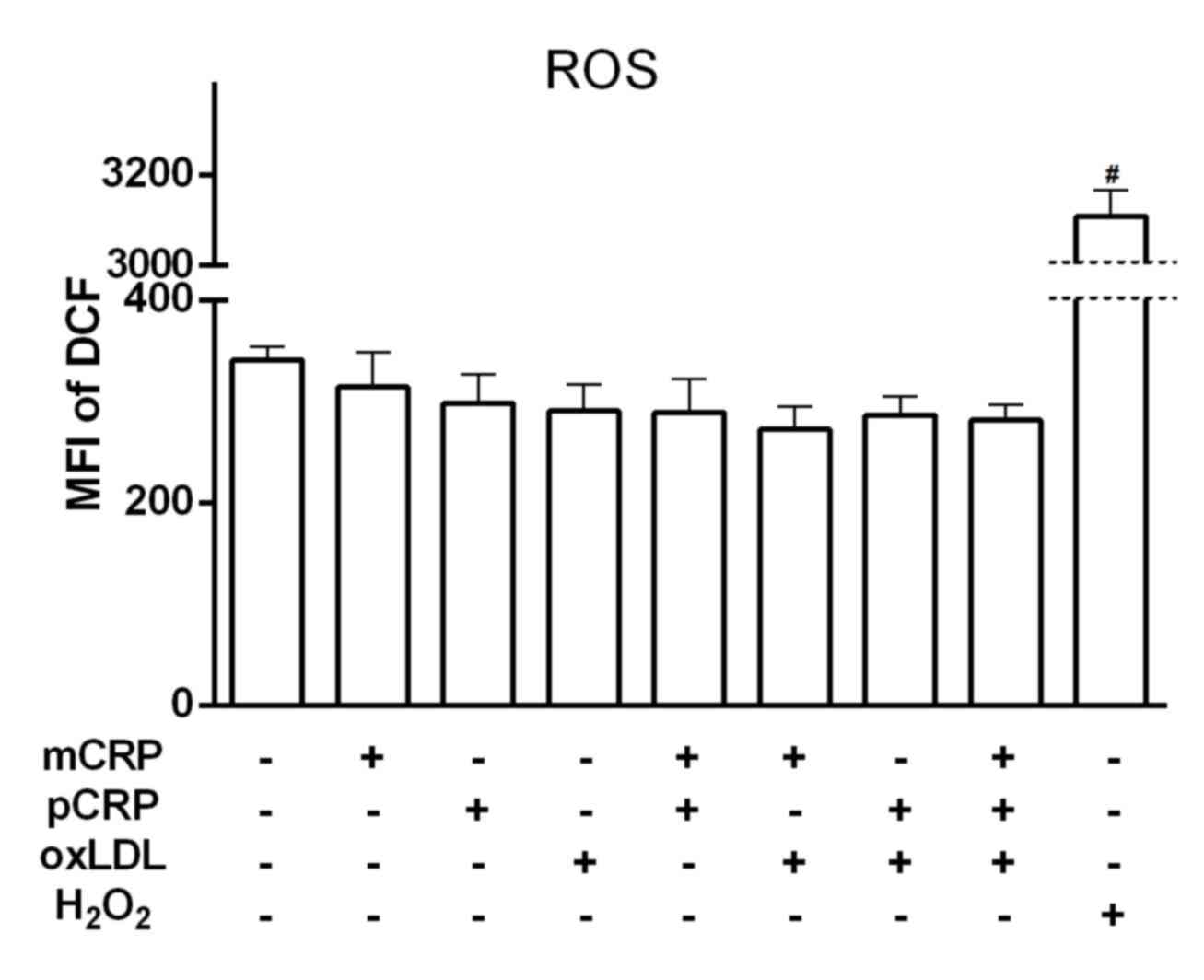
|
1
|
Barquera S, Pedroza-Tobías A, Medina C,
Hernández-Barrera L, Bibbins-Domingo K, Lozano R and Moran AE:
Global overview of the epidemiology of atherosclerotic
cardiovascular disease. Arch Med Res. 46:328–338. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hattori Y, Matsumura M and Kasai K:
Vascular smooth muscle cell activation by C-reactive protein.
Cardiovasc Res. 58:186–195. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eisenhardt SU, Thiele JR, Bannasch H,
Stark GB and Peter K: C-reactive protein: How conformational
changes influence inflammatory properties. Cell Cycle. 8:3885–3892.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Eisenhardt SU, Habersberger J, Murphy A,
Chen YC, Woollard KJ, Bassler N, Qian H, von Zur Muhlen C,
Hagemeyer CE, Ahrens I, et al: Dissociation of pentameric to
monomeric C-reactive protein on activated platelets localizes
inflammation to atherosclerotic plaques. Circ Res. 105:128–137.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Khreiss T, József L, Potempa LA and Filep
JG: Conformational rearrangement in C-reactive protein is required
for proinflammatory actions on human endothelial cells.
Circulation. 109:2016–2022. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schwedler SB, Amann K, Wernicke K, Krebs
A, Nauck M, Wanner C, Potempa LA and Galle J: Native C-reactive
protein increases whereas modified C-reactive protein reduces
atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice. Circulation.
112:1016–1023. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eisenhardt SU, Habersberger J and Peter K:
Monomeric C-reactive protein generation on activated platelets: The
missing link between inflammation and atherothrombotic risk. Trends
Cardiovasc Med. 19:232–237. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Filep JG: Platelets affect the structure
and function of C-reactive protein. Circ Res. 105:109–111. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Khreiss T, József L, Potempa LA and Filep
JG: Loss of pentameric symmetry in C-reactive protein induces
interleukin-8 secretion through peroxynitrite signaling in human
neutrophils. Circ Res. 97:690–697. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Libby P, Ridker PM and Maseri A:
Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 105:1135–1143. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tabuchi M, Inoue K, Usui-Kataoka H,
Kobayashi K, Teramoto M, Takasugi K, Shikata K, Yamamura M, Ando K,
Nishida K, et al: The association of C-reactive protein with an
oxidative metabolite of LDL and its implication in atherosclerosis.
J Lipid Res. 48:768–781. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chang MK, Hartvigsen K, Ryu J, Kim Y and
Han KH: The pro-atherogenic effects of macrophages are reduced upon
formation of a complex between C-reactive protein and
lysophosphatidylcholine. J Inflamm (Lond). 9:422012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Frostegard J, Ulfgren AK, Nyberg P, Hedin
U, Swedenborg J, Andersson U and Hansson GK: Cytokine expression in
advanced human atherosclerotic plaques: Dominance of
pro-inflammatory (Th1) and macrophage-stimulating cytokines.
Atherosclerosis. 145:33–43. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qiu G, Ho AC, Yu W and Hill JS:
Suppression of endothelial or lipoprotein lipase in THP-1
macrophages attenuates proinflammatory cytokine secretion. J Lipid
Res. 48:385–394. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jovinge S, Ares MP, Kallin B and Nilsson
J: Human monocytes/macrophages release TNF-alpha in response to
Ox-LDL. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 16:1573–1579. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eruslanov E and Kusmartsev S:
Identification of ROS using oxidized DCFDA and flow-cytometry.
Methods Mol Biol. 594:57–72. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Uzui H, Harpf A, Liu M, Doherty TM, Shukla
A, Chai NN, Tripathi PV, Jovinge S, Wilkin DJ, Asotra K, et al:
Increased expression of membrane type 3-matrix metalloproteinase in
human atherosclerotic plaque: Role of activated macrophages and
inflammatory cytokines. Circulation. 106:3024–3030. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kaneto H, Katakami N, Matsuhisa M and
Matsuoka TA: Role of reactive oxygen species in the progression of
type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis. Mediators Inflamm.
2010:4538922010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chávez-Sánchez L, Chávez-Rueda K,
Legorreta-Haquet MV, Zenteno E, Ledesma-Soto Y, Montoya-Díaz E,
Tesoro-Cruz E, Madrid-Miller A and Blanco-Favela F: The activation
of CD14, TLR4, and TLR2 by mmLDL induces IL-1beta, IL-6, and IL-10
secretion in human monocytes and macrophages. Lipids Health Dis.
9:1172010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Galve-de Rochemonteix B, Wiktorowicz K,
Kushner I and Dayer JM: C-reactive protein increases production of
IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, and TNF-alpha and expression of mRNA by
human alveolar macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 53:439–445.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pue CA, Mortensen RF, Marsh CB, Pope HA
and Wewers MD: Acute phase levels of C-reactive protein enhance
IL-1 beta and IL-1ra production by human blood monocytes but
inhibit IL-1 beta and IL-1ra production by alveolar macrophages. J
Immunol. 156:1594–1600. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gershov D, Kim S, Brot N and Elkon KB:
C-Reactive protein binds to apoptotic cells, protects the cells
from assembly of the terminal complement components, and sustains
an antiinflammatory innate immune response: Implications for
systemic autoimmunity. J Exp Med. 192:1353–1364. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Taylor KE and van den Berg CW: Structural
and functional comparison of native pentameric, denatured monomeric
and biotinylated C-reactive protein. Immunology. 120:404–411. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Adan A, Kiraz Y and Baran Y: Cell
proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. Curr Pharm Biotechnol.
17:1213–1221. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bruunsgaard H, Andersen-Ranberg K, Jeune
B, Pedersen AN, Skinhoj P and Pedersen BK: A high plasma
concentration of TNF-αlpha is associated with dementia in
centenarians. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 54:M357–M364. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hansson GK and Hermansson A: The immune
system in atherosclerosis. Nat Immunol. 12:204–212. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Devaraj S, Davis B, Simon SI and Jialal I:
CRP promotes monocyte-endothelial cell adhesion via Fcgamma
receptors in human aortic endothelial cells under static and shear
flow conditions. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 291:H1170–H1176.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bruunsgaard H, Skinhøj P, Pedersen AN,
Schroll M and Pedersen BK: Ageing, tumour necrosis factor-alpha
(TNF-alpha) and atherosclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 121:255–260.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huber SA, Sakkinen P, Conze D, Hardin N
and Tracy R: Interleukin-6 exacerbates early atherosclerosis in
mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 19:2364–2367. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Branen L, Hovgaard L, Nitulescu M,
Bengtsson E, Nilsson J and Jovinge S: Inhibition of tumor necrosis
factor-alpha reduces atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E knockout
mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:2137–2142. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hansson GK and Libby P: The immune
response in atherosclerosis: A double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol.
6:508–519. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Harada A, Sekido N, Akahoshi T, Wada T,
Mukaida N and Matsushima K: Essential involvement of interleukin-8
(IL-8) in acute inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 56:559–564.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao XQ, Zhang MW, Wang F, Zhao YX, Li JJ,
Wang XP, Bu PL, Yang JM, Liu XL, Zhang MX, et al: CRP enhances
soluble LOX-1 release from macrophages by activating TNF-α
converting enzyme. J Lipid Res. 52:923–933. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Thiele JR, Zeller J, Bannasch H, Stark GB,
Peter K and Eisenhardt SU: Targeting C-reactive protein in
inflammatory disease by preventing conformational changes.
Mediators Inflamm. 2015:3724322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|