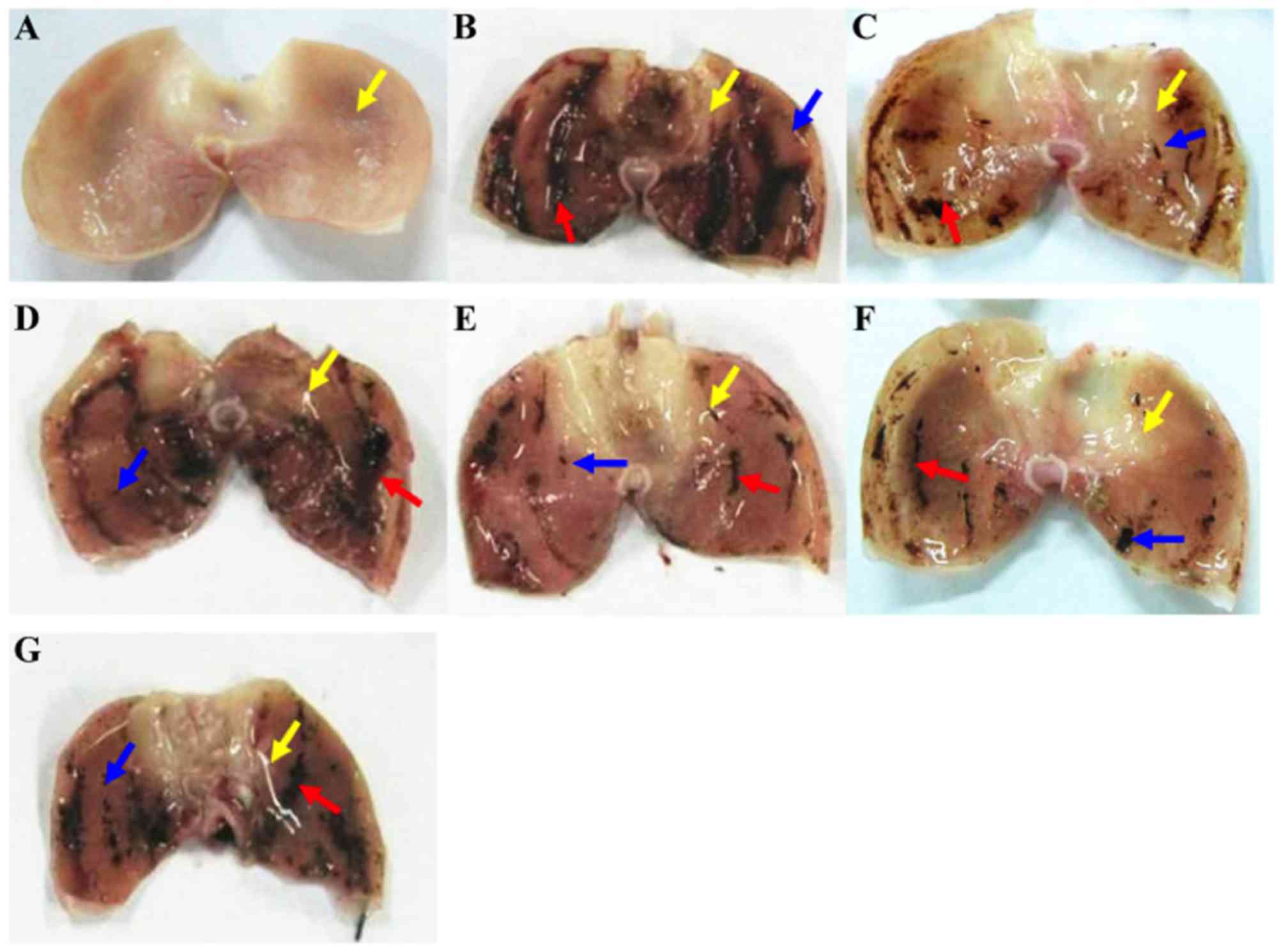
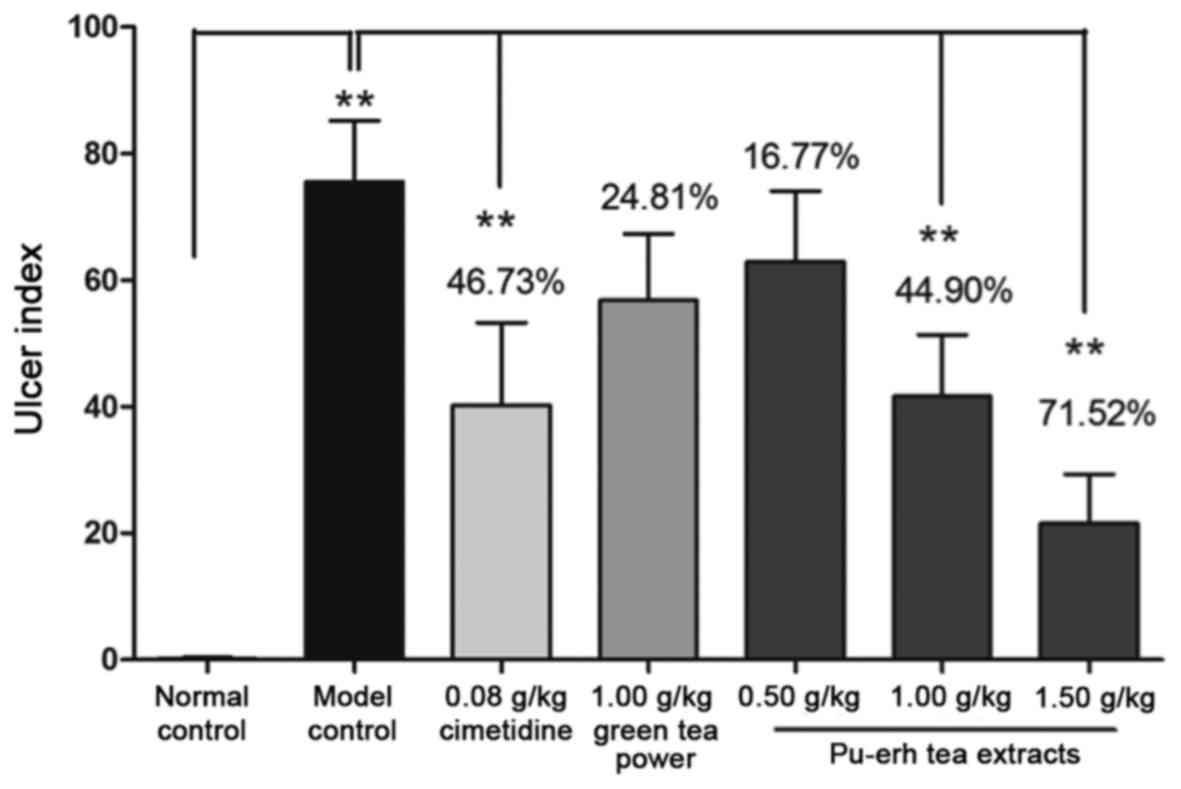
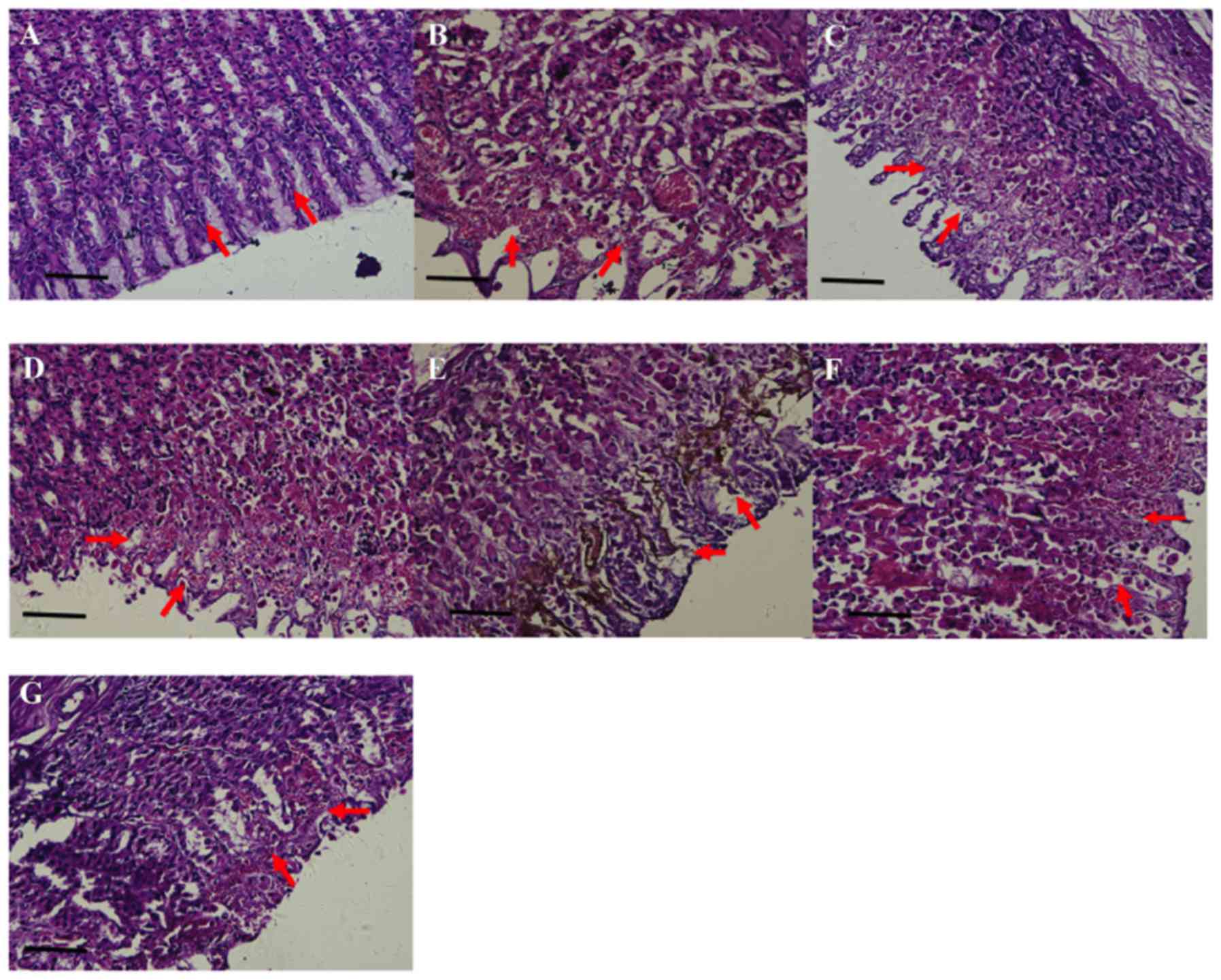
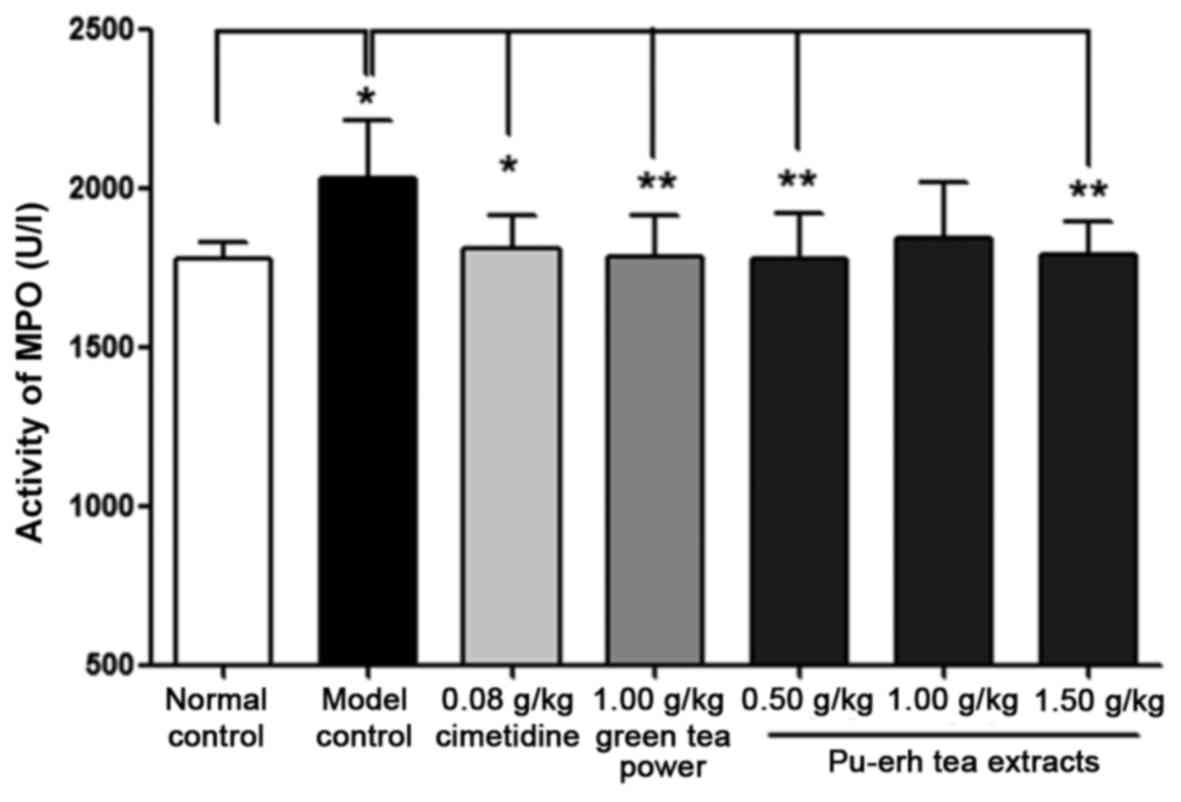
|
1
|
Zhao M, Zhang DL, Su XQ, Duan SM, Wan JQ,
Yuan WX, Liu BY, Ma Y and Pan YH: An Integrated
Metagenomics/Metaproteomics Investigation of the Microbial
Communities and Enzymes in Solid-state Fermentation of Pu-erh tea.
Sci Rep. 5:101172015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhao L, Jia S, Tang W, Sheng J and Luo Y:
Pu-erh tea inhibits tumor cell growth by down-regulating mutant
p53. Int J Mol Sci. 12:7581–7593. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Syu KY, Lin CL, Huang HC and Lin JK:
Determination of theanine, GABA, and other amino acids in green,
oolong, black, and Pu-erh teas with dabsylation and
high-performance liquid chromatography. J Agric Food Chem.
56:7637–7643. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fan JP, Fan C, Dong WM, Gao B, Yuan W and
Gong JS: Free radical scavenging and anti-oxidative activities of
an ethanol-soluble pigment extract prepared from fermented Zijuan
Pu-erh tea. Food Chem Toxicol. 59:527–533. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oi Y, Hou IC, Fujita H and Yazawa K:
Antiobesity effects of Chinese black tea (Pu-erh tea) extract and
gallic acid. Phytother Res. 26:475–481. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang L, Shao WF, Yuan LF, Tu PF and Ma
ZZ: Decreasing pro-inflammatory cytokine and reversing the
immunosenescence with extracts of Pu-erh tea in senescence
accelerated mouse (SAM). Food Chem. 135:2222–2228. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hou Y, Shao W, Xiao R, Xu K, Ma Z,
Johnstone BH and Du Y: Pu-erh tea aqueous extracts lower
atherosclerotic risk factors in a rat hyperlipidemia model. Exp
Gerontol. 44:434–439. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao X, Qian Y, Zhou YL, Wang R, Wang Q
and Li GJ: Pu-erh tea has in vitro anticancer activity in TCA8113
cells and preventive effects on buccal mucosa cancer in U14 cells
injected mice in vivo. Nutr Cancer. 66:1059–1069. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pei S, Zhang Y, Xu H, Chen X and Chen S:
Inhibition of the replication of hepatitis B virus in vitro by
pu-erh tea extracts. J Agric Food Chem. 59:9927–9934. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Su Y, Zhang C, Wang Y and Li P:
Antibacterial property and mechanism of a novel Pu-erh tea
nanofibrous membrane. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 93:1663–1671.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen H, Liao H, Liu Y, Zheng Y, Wu X and
Su Z, Zhang X, Lai Z, Lai X, Lin ZX and Su Z: Protective effects of
pogostone from Pogostemonis Herba against ethanol-induced gastric
ulcer in rats. Fitoterapia. 100:110–117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thomas D, Govindhan S, Baiju EC,
Padmavathi G, Kunnumakkara AB and Padikkala J: Cyperus rotundus L.
prevents non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastric
mucosal damage by inhibiting oxidative stress. J Basic Clin Physiol
Pharmacol. 26:485–490. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
deFoneska A and Kaunitz JD: Gastroduodenal
mucosal defense. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 26:604–610. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Laine L, Takeuchi K and Tarnawski A:
Gastric mucosal defense and cytoprotection: Bench to bedside.
Gastroenterology. 135:41–60. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tarnawski AS, Ahluwalia A and Jones MK:
The mechanisms of gastric mucosal injury: Focus on microvascular
endothelium as a key target. Curr Med Chem. 19:4–15. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brzozowski T, Ptak-Belowska A, Kwiecien S,
Krzysiek-Maczka G, Strzalka M, Drozdowicz D, Pajdo R, Olszanecki R,
Korbut R, Konturek SJ, et al: Novel concept in the mechanism of
injury and protection of gastric mucosa: Role of renin-angiotensin
system and active metabolites of angiotensin. Curr Med Chem.
19:55–62. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kuo KL, Weng MS, Chiang CT, Tsai YJ,
Lin-Shiau SY and Lin JK: Comparative studies on the hypolipidemic
and growth suppressive effects of oolong, black, pu-erh, and green
tea leaves in rats. J Agric Food Chem. 53:480–489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Antonisamy P, Kannan P, Aravinthan A,
Duraipandiyan V, Arasu MV, Ignacimuthu S, Al-Dhabi NA and Kim JH:
Gastroprotective activity of violacein isolated from
Chromobacterium violaceum on indomethacin-induced gastric lesions
in rats: Investigation of potential mechanisms of action. Sci World
J. 2014:6164322014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li L, Luo XJ, Liu YZ, Zhang YS, Yuan Q,
Tan N, Xiang DX and Peng J: The role of the DDAH-ADMA pathway in
the protective effect of resveratrol analog BTM-0512 on gastric
mucosal injury. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 88:562–567. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hou CW, Jeng KC and Chen YS: Enhancement
of fermentation process in Pu-erh tea by tea-leaf extract. J Food
Sci. 75:H44–H48. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jeng KC, Chen CS, Fang YP, Hou RC and Chen
YS: Effect of microbial fermentation on content of statin, GABA,
and polyphenols in Pu-Erh tea. J Agric Food Chem. 55:8787–8792.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Duh PD, Yen GC, Yen WJ, Wang BS and Chang
LW: Effects of pu-erh tea on oxidative damage and nitric oxide
scavenging. J Agric Food Chem. 52:8169–8176. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu Y, Zhao H, Zhang M, Li CJ, Lin XZ,
Sheng J and Shi W: Variations of antioxidant properties and NO
scavenging abilities during fermentation of tea. Int J Mol Sci.
12:4574–4590. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen YS, Liu BL and Chang YN:
Bioactivities and sensory evaluation of Pu-erh teas made from three
tea leaves in an improved pile fermentation process. J Biosci
Bioeng. 109:557–563. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Q, Gong J, Chisti Y and
Sirisansaneeyakul S: Fungal isolates from a Pu-erh type tea
fermentation and their ability to convert tea polyphenols to
theabrownins. J Food Sci. 80:M809–M817. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu Y, Wang G, Li C, Zhang M, Zhao H, Sheng
J and Shi W: Pu-erh tea reduces nitric oxide levels in rats by
inhibiting inducible nitric oxide synthase expression through
toll-like receptor 4. Int J Mol Sci. 13:7174–7185. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu CF, Lin CC, Ng LT and Lin SC:
Protection by tetramethylpyrazine in acute absolute ethanol-induced
gastric lesions. J Biomed Sci. 9:395–400. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hua HE: Application of Anaesthesia with
Combined Ether Inhalation and Sodium Pentobarbital Intraperitoneal
Injection to Rat Liver Transplantation. Chin J Comp Med. 18:30–31.
2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Halim SZ, Zakaria ZA, Omar MH, Mohtarrudin
N, Wahab IRA and Abdullah MNH: Synergistic gastroprotective
activity of methanolic extract of a mixture of Melastoma
malabathricum and Muntingia calabura leaves in rats. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 17:4882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Balan T, Sani MH, Mumtaz Ahmad SH,
Suppaiah V, Mohtarrudin N and Zakaria ZA: Antioxidant and
anti-inflammatory activities contribute to the prophylactic effect
of semi-purified fractions obtained from the crude methanol extract
of Muntingia calabura leaves against gastric ulceration in rats. J
Ethnopharmacol. 164:1–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Balan T, Mohd Sani MH, Suppaiah V,
Mohtarrudin N, Suhaili Z, Ahmad Z and Zakaria ZA: Antiulcer
activity of Muntingia calabura leaves involves the modulation of
endogenous nitric oxide and nonprotein sulfhydryl compounds. Pharm
Biol. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Technical Standards for Testing and
Assessment of Health Food: Document Guidelines of the Ministry of
health of the People's Republic of China. 23–28. 2012.
|
|
33
|
Guth PH, Aures D and Paulsen G: Topical
aspirin plus HCl gastric lesions in the rat. Cytoprotective effect
of prostaglandin, cimetidine, and probanthine. Gastroenterology.
76:88–93. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li Q, Yang LL, Fan LL, Liang C, Wang QJ,
Wen HM, Dai JW, Li X and Zhang YY: Activity of Brucea javanica oil
emulsion against gastric ulcers in rodents. Asian J Pharmaceutical
Sci. (In press).
|
|
35
|
Mei X, Xu D and Xu S, Zheng Y and Xu S:
Novel role of Zn(II)-curcumin in enhancing cell proliferation and
adjusting proinflammatory cytokine-mediated oxidative damage of
ethanol-induced acute gastric ulcers. Chem Biol Interact.
197:31–39. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Alrashdi AS, Salama SM, Alkiyumi SS,
Abdulla MA, Hadi AH, Abdelwahab SI, Taha MM, Hussiani J and Asykin
N: Mechanisms of gastroprotective effects of ethanolic leaf extract
of Jasminum sambac against HCl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal
injury in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2012:7864262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hashim H, Mughrabi FF, Ameen M, Khaledi H
and Ali HM: Cytoprotective effect of benzyl
N′-(5-chloro-indol-3-yl-methylidene)-hydrazinecarbodithioate
against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats. Molecules.
17:9306–9320. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Park CH, Nam DY, Son HU, Lee SR, Lee HJ,
Heo JC, Cha TY, Baek JH and Lee SH: Polymer fraction of Aloe vera
exhibits a protective activity on ethanol-induced gastric lesions.
Int J Mol Med. 27:511–518. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gazzieri D, Trevisani M, Springer J,
Harrison S, Cottrell GS, Andre E, Nicoletti P, Massi D, Zecchi S
and Nosi D: Substance P released by TRPV1-expressing neurons
produces reactive oxygen species that mediate ethanol-induced
gastric injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 43:581–589. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Luiz-Ferreira A, Almeida AC, Cola M,
Barbastefano V, Almeida AB, Batista LM, Farias-Silva E, Pellizzon
CH, Hiruma-Lima CA, Santos LC, et al: Mechanisms of the gastric
antiulcerogenic activity of Anacardium humile St. Hil on
ethanol-induced acute gastric mucosal injury in rats. Molecules.
15:7153–7166. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ibrahim IA, Qader SW, Abdulla MA, Nimir
AR, Abdelwahab SI and Al-Bayaty FH: Effects of Pithecellobium
jiringa ethanol extract against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal
injuries in Sprague-Dawley rats. Molecules. 17:2796–2811. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tulassay Z and Herszényi L: Gastric
mucosal defense and cytoprotection. Best Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 24:99–108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Scoparo CT, Souza LM, Dartora N, Sassaki
GL, Santana-Filho AP, Werner MF, Borato DG, Baggio CH and Iacomini
M: Chemical characterization of heteropolysaccharides from green
and black teas (Camellia sinensis) and their anti-ulcer effect. Int
J Biol Macromol. 86:772–781. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nartey ET, Ofosuhene M and Agbale CM:
Anti-ulcerogenic activity of the root bark extract of the African
laburnum ‘Cassia sieberiana’ and its effect on the anti-oxidant
defence system in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 12:2472012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhao W, Zhu F, Shen W, Fu A, Zheng L, Yan
Z, Zhao L and Fu G: Protective effects of DIDS against
ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 41:301–308. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Devi RS, Narayan S, Vani G and Shyamala
Devi CS: Gastroprotective effect of Terminalia arjuna bark on
diclofenac sodium induced gastric ulcer. Chem Biol Interact.
167:71–83. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Santos Cerqueira G, dos Santos e Silva G,
Rios Vasconcelos E, Fragoso de Freitas AP, Arcanjo Moura B,
Silveira Macedo D, Lopes Souto A, Barbosa Filho JM, de Almeida Leal
LK, de Castro Brito GA, et al: Effects of hecogenin and its
possible mechanism of action on experimental models of gastric
ulcer in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 683:260–269. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Szlachcic A, Krzysiek-Maczka G, Pajdo R,
Targosz A, Magierowski M, Jasnos K, Drozdowicz D, Kwiecien S and
Brzozowski T: The impact of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADAMA),
the endogenous nitric oxide (NO) synthase inhibitor, to the
pathogenesis of gastric mucosal damage. Curr Pharm Des. 19:90–97.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tran CT, Leiper JM and Vallance P: The
DDAH/ADMA/NOS pathway. Atheroscler Suppl. 4:33–40. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang Z, Zou YY, Li FJ and Hu CP:
Asymmetric dimethylarginine: A novel biomarker of gastric mucosal
injury? World J Gastroenterol. 17:2178–2180. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang Z, Zhou Y, Zou YY, Wang L, Yang ZC,
Guo R, Li D, Peng J and Li YJ: Detrimental effects of nicotine on
the acute gastric mucosal injury induced by ethanol: Role of
asymmetric dimethylarginine. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 86:835–840.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kwiecien S, Ptak-Belowska A,
Krzysiek-Maczka G, Targosz A, Jasnos K, Magierowski M, Szczyrk U,
Brzozowski B, Konturek SJ, Konturek PC, et al: Asymmetric
dimethylarginine, an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase,
interacts with gastric oxidative metabolism and enhances
stress-induced gastric lesions. J Physiol Pharmacol. 63:515–524.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yi R, Wang R, Sun P and Zhao X:
Antioxidant-mediated preventative effect of Dragon-pearl tea crude
polyphenol extract on reserpine-induced gastric ulcers. Exp Ther
Med. 10:338–344. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Adhikary B, Yadav SK, Chand S,
Bandyopadhyay SK and Chattopadhyay S: Black tea and theaflavins
suppress various inflammatory modulators and i-NOS mediated nitric
oxide synthesis during gastric ulcer healing. Free Radic Res.
45:767–778. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Food and Drug Administration (FDA), .
Estimating the safe starting dose in clinical trials for
therapeutics in adult healthy volunteersGuidance for Industry and
Reviewers. FDA; Rockville, MD: pp. 262002
|