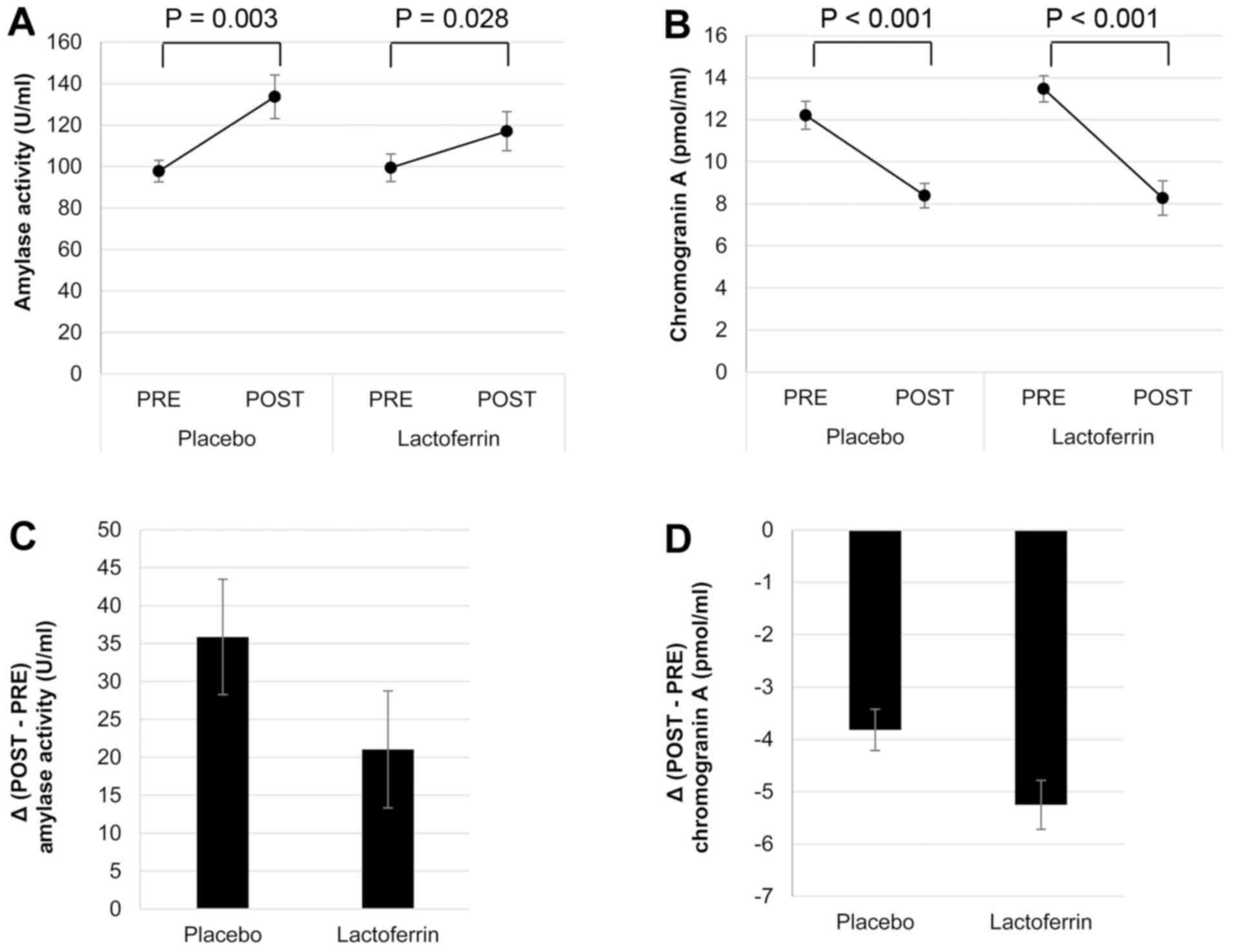
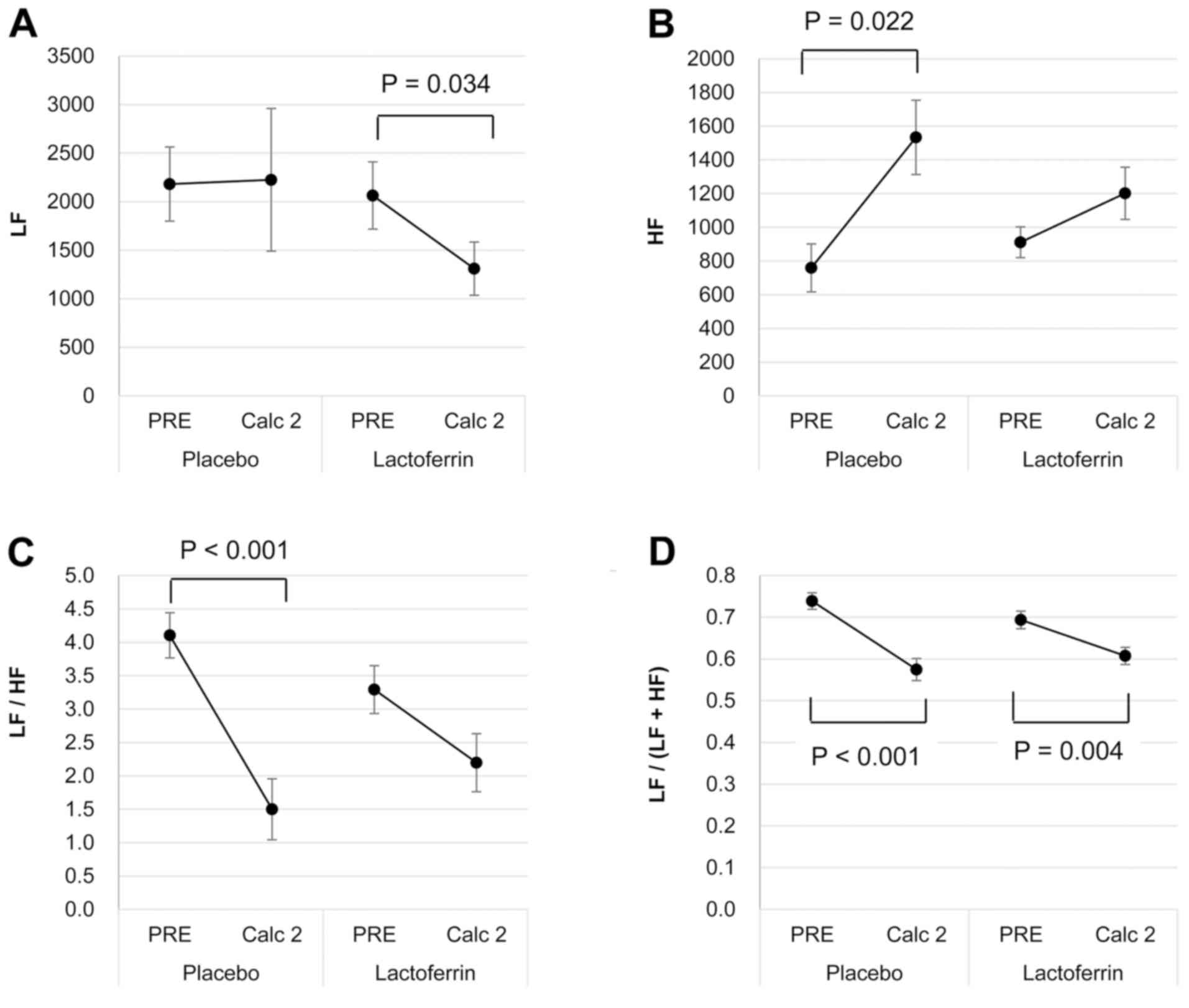
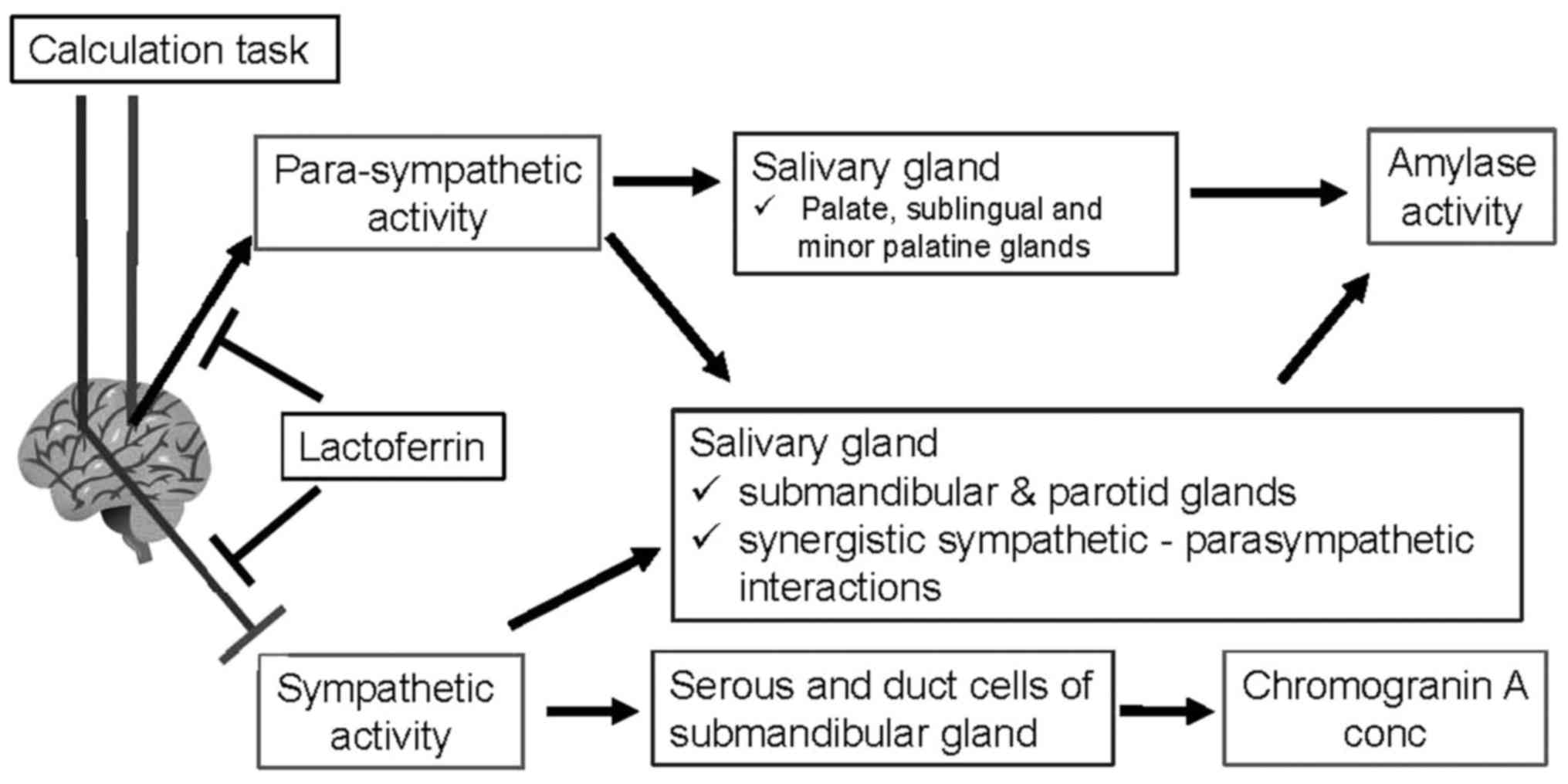
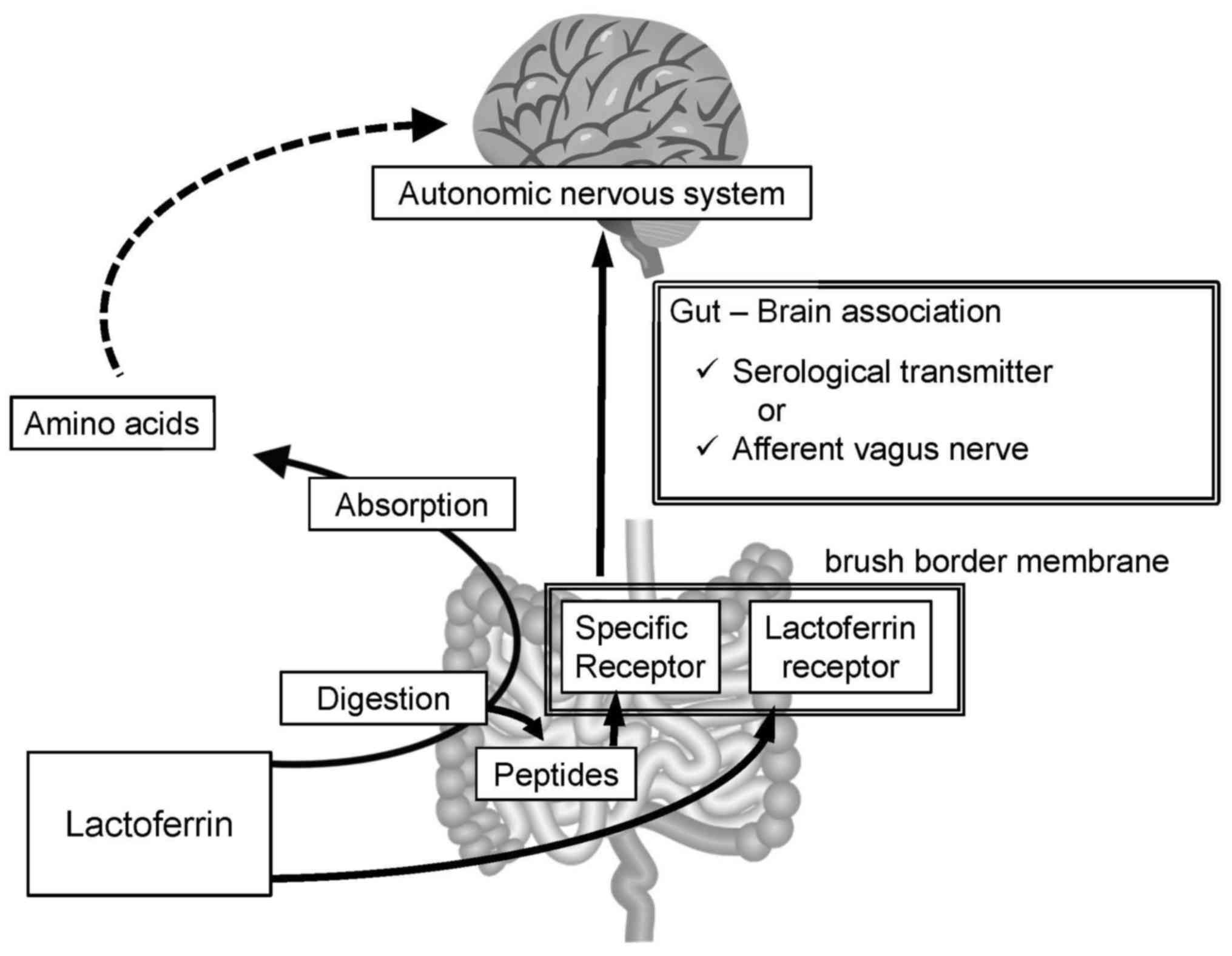
|
1
|
Arnold RR, Cole MF and McGhee JR: A
bactericidal effect for human lactoferrin. Science. 197:263–265.
1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arnold RR, Brewer M and Gauthier JJ:
Bactericidal activity of human lactoferrin: Sensitivity of a
variety of microorganisms. Infect Immun. 28:893–898.
1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kalmar JR and Arnold RR: Killing of
Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans by human lactoferrin. Infect
Immun. 56:2552–2557. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yamauchi K, Tomita M, Giehl TJ and Ellison
RT III: Antibacterial activity of lactoferrin and a pepsin-derived
lactoferrin peptide fragment. Infect Immun. 61:719–728.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vitetta L, Coulson S, Beck SL, Gramotnev
H, Du S and Lewis S: The clinical efficacy of a bovine
lactoferrin/whey protein Ig-rich fraction (Lf/IgF) for the common
cold: A double blind randomized study. Complement Ther Med.
21:164–171. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ishikado A, Uesaki S, Suido H, Nomura Y,
Sumikawa K, Maeda M, Miyauchi M, Takata T and Makino T: Human trial
of liposomal lactoferrin supplementation for periodontal disease.
Biol Pharm Bull. 33:1758–1762. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kuhara T, Iigo M, Itoh T, Ushida Y, Sekine
K, Terada N, Okamura H and Tsuda H: Orally administered lactoferrin
exerts an antimetastatic effect and enhances production of IL-18 in
the intestinal epithelium. Nutr Cancer. 38:192–199. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Koikawa N, Nagaoka I, Yamaguchi M, Hamano
H, Yamauchi K and Sawaki K: Preventive effect of lactoferrin intake
on anemia in female long distance runners. Biosci Biotechnol
Biochem. 72:931–935. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Paesano R, Torcia F, Berlutti F, Pacifici
E, Ebano V, Moscarini M and Valenti P: Oral administration of
lactoferrin increases hemoglobin and total serum iron in pregnant
women. Biochem Cell Biol. 84:377–380. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kamemori N, Takeuchi T, Hayashida K and
Harada E: Suppressive effects of milk-derived lactoferrin on
psychological stress in adult rats. Brain Res. 1029:34–40. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rohleder N, Wolf JM, Maldonado EF and
Kirschbaum C: The psychosocial stress-induced increase in salivary
alpha-amylase is independent of saliva flow rate. Psychophysiology.
43:645–652. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Granger DA, Kivlighan KT, el-Sheikh M,
Gordis EB and Stroud LR: Salivary α-amylase in biobehavioral
research: Recent developments and applications. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1098:122–144. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Haririan H, Bertl K, Laky M, Rausch WD,
Böttcher M, Matejka M, Andrukhov O and Rausch-Fan X: Salivary and
serum chromogranin A and α-amylase in periodontal health and
disease. J Periodontol. 83:1314–1321. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee T, Shimizu T, Iijima M, Obinata K,
Yamashiro Y and Nagasawa S: Evaluation of psychosomatic stress in
children by measuring salivary chromogranin A. Acta Paediatr.
95:935–939. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kanno T, Asada N, Yanase H, Iwanaga T and
Yanaihara N: Salivary Secretion of Chromogranin A Control by
Autonomic Nervous SystemChromogranins: Functional and Clinical
Aspects. Helle KB and Aunis D: Springer US; Boston, MA: pp.
143–151. 2002, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Koibuchi E and Suzuki Y: Exercise
upregulates salivary amylase in humans (Review). Exp Ther Med.
7:773–777. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chatterton RT Jr, Vogelsong KM, Lu YC,
Ellman AB and Hudgens GA: Salivary alpha-amylase as a measure of
endogenous adrenergic activity. Clin Physiol. 16:433–448. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nater UM, La Marca R, Florin L, Moses A,
Langhans W, Koller MM and Ehlert U: Stress-induced changes in human
salivary alpha-amylase activity - associations with adrenergic
activity. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 31:49–58. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakane H, Asami O, Yamada Y, Harada T,
Matsui N, Kanno T and Yanaihara N: Salivary chromogranin A as an
index of psychosomatic stress response. Biomed Res. 19:401–406.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Malik M, Bigger J, Camm A, Kleiger R,
Malliani A, Moss AJ and Schwartz PJ: Task Force of the European
Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and
Electrophysiology: Heart rate variability. Standards of
measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Eur
Heart J. 17:354–381. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Acharya Rajendra U, Joseph Paul K,
Kannathal N, Lim CM and Suri JS: Heart rate variability: A review.
Med Biol Eng Comput. 44:1031–1051. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bosch JA, Veerman ECI, de Geus EJ and
Proctor GB: α-Amylase as a reliable and convenient measure of
sympathetic activity: Don't start salivating just yet!
Psychoneuroendocrinology. 36:449–453. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Morse DR, Schacterle GR, Furst ML,
Esposito JV and Zaydenburg M: Stress, relaxation and saliva:
Relationship to dental caries and its prevention, with a literature
review. Ann Dent. 42:47–54. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kanno T, Asada N, Yanase H, Iwanaga T and
Yanaihara N: Salivary secretion of chromogranin A. Control by
autonomic nervous system. Adv Exp Med Biol. 482:143–151. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takeuchi T, Hayashida K, Inagaki H,
Kuwahara M, Tsubone H and Harada E: Opioid mediated suppressive
effect of milk-derived lactoferrin on distress induced by maternal
separation in rat pups. Brain Res. 979:216–224. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zimecki M and Kruzel ML: Milk-derived
proteins and peptides of potential therapeutic and nutritive value.
J Exp Ther Oncol. 6:89–106. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mohanty DP, Mohapatra S, Misra S and Sahu
PS: Milk derived bioactive peptides and their impact on human
health - A review. Saudi J Biol Sci. 23:577–583. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Marcone S, Belton O and Fitzgerald DJ:
Milk-derived bioactive peptides and their health promoting effects:
A potential role in atherosclerosis. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
83:152–162. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kawakami H and Lönnerdal B: Isolation and
function of a receptor for human lactoferrin in human fetal
intestinal brush-border membranes. Am J Physiol. 261:G841–G846.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Suzuki YA, Shin K and Lönnerdal B:
Molecular cloning and functional expression of a human intestinal
lactoferrin receptor. Biochemistry. 40:15771–15779. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Perez-Burgos A, Wang B, Mao YK, Mistry B,
McVey Neufeld KA, Bienenstock J and Kunze W: Psychoactive bacteria
Lactobacillus rhamnosus (JB-1) elicits rapid frequency
facilitation in vagal afferents. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 304:G211–G220. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Steinert RE, Feinle-Bisset C, Asarian L,
Horowitz M, Beglinger C and Geary N: Ghrelin, CCK, GLP-1, and
PYY(3-36): Secretory Controls and Physiological Roles in Eating and
Glycemia in Health, Obesity, and After RYGB. Physiol Rev.
97:411–463. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Takai N, Yamaguchi M, Aragaki T, Eto K,
Uchihashi K and Nishikawa Y: Effect of psychological stress on the
salivary cortisol and amylase levels in healthy young adults. Arch
Oral Biol. 49:963–968. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nater UM, Rohleder N, Schlotz W, Ehlert U
and Kirschbaum C: Determinants of the diurnal course of salivary
alpha-amylase. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 32:392–401. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Den R, Toda M, Nagasawa S, Kitamura K and
Morimoto K: Circadian rhythm of human salivary chromogranin A.
Biomed Res. 28:57–60. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Grenham S, Clarke G, Cryan JF and Dinan
TG: Brain-gut-microbe communication in health and disease. Front
Physiol. 2:942011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bengmark S: Gut microbiota, immune
development and function. Pharmacol Res. 69:87–113. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Forsythe P and Kunze WA: Voices from
within: Gut microbes and the CNS. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:55–69.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|