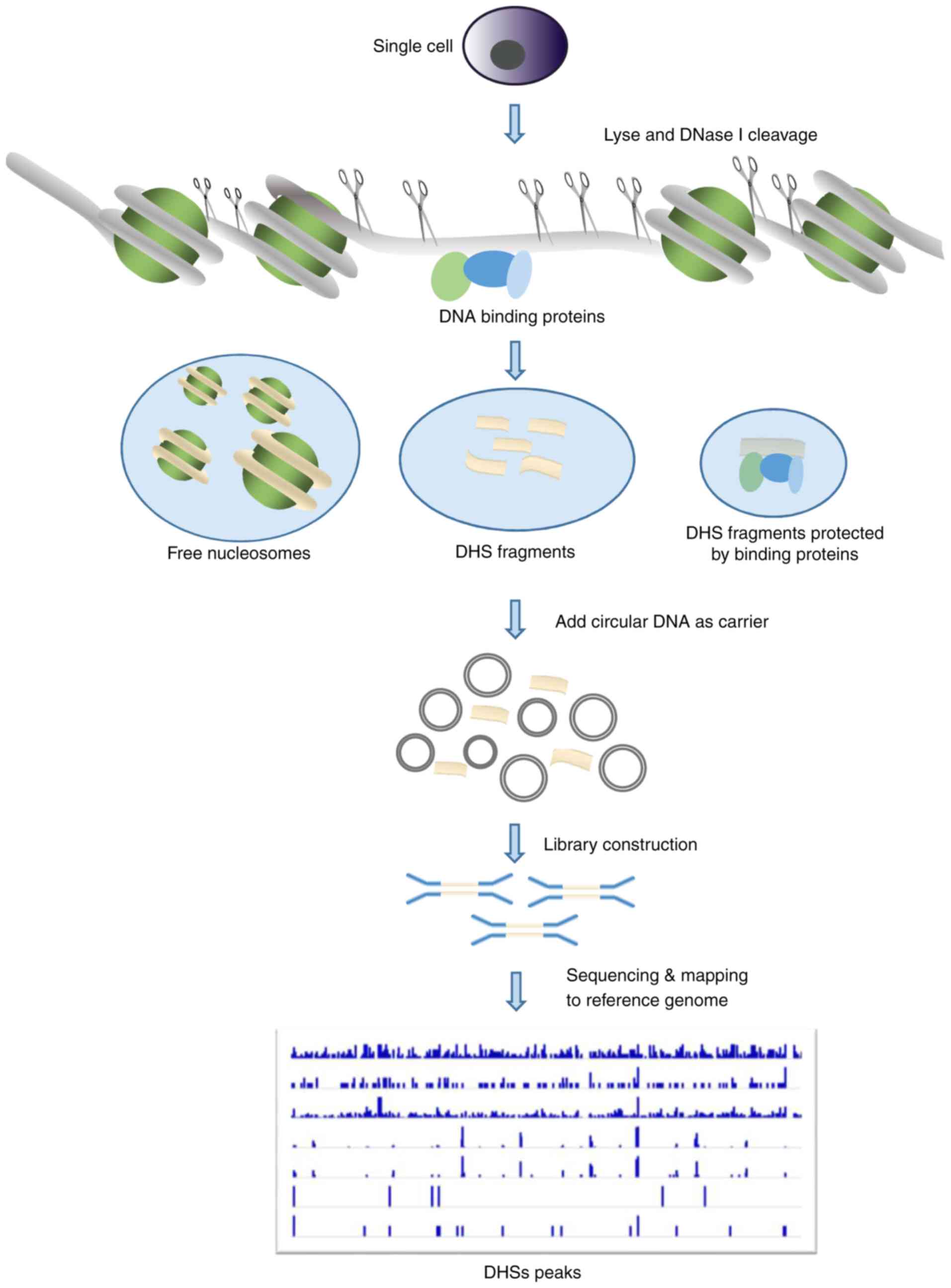
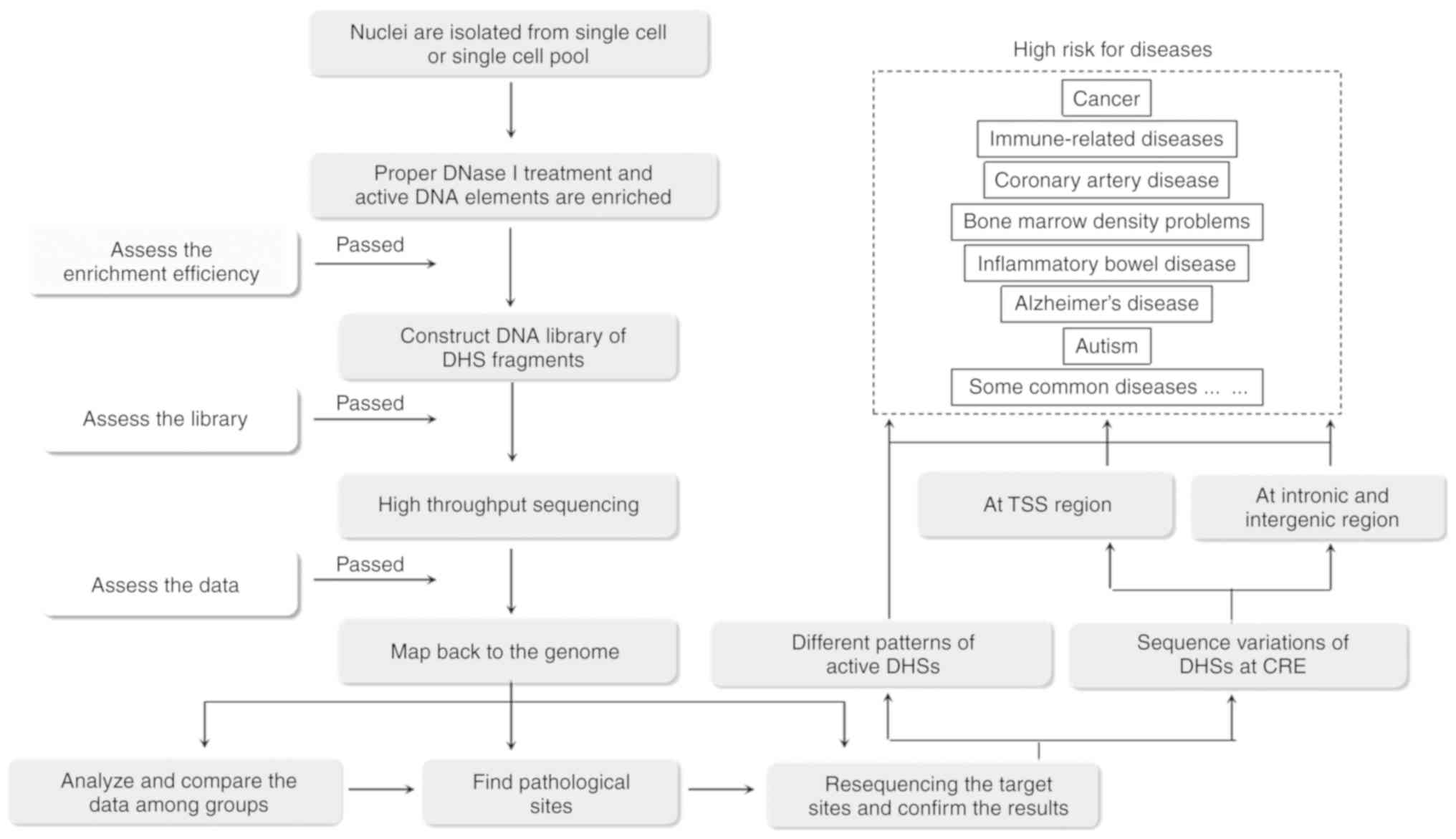
|
1
|
Elgin SC: DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of
chromatin. Cell. 27:413–415. 1981.
|
|
2
|
Meisterernst M, Roy AL, Lieu HM and Roeder
RG: Activation of class II gene transcription by regulatory factors
is potentiated by a novel activity. Cell. 66:981–993.
1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Weintraub H and Groudine M: Chromosomal
subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science.
193:848–856. 1976.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Felsenfeld G, Boyes J, Chung J, Clark D
and Studitsky V: Chromatin structure and gene expression. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 93:9384–9388. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wu C: The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock
genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature.
286:854–860. 1980.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Martinez-Balbas MA, Dey A, Rabindran SK,
Ozato K and Wu C: Displacement of sequence-specific transcription
factors from mitotic chromatin. Cell. 83:29–38. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hebbes TR, Clayton AL, Thorne AW and
Crane-Robinson C: Core histone hyperacetylation co-maps with
generalized DNase I sensitivity in the chicken beta-globin
chromosomal domain. EMBO J. 13:1823–1830. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kleff S, Andrulis ED, Anderson CW and
Sternglanz R: Identification of a gene encoding a yeast histone H4
acetyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 270:24674–24677. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Peterson CL and Tamkun JW: The SWI-SNF
complex: A chromatin remodeling machine? Trends Biochem Sci.
20:143–146. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Roeder RG: The role of general initiation
factors in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Trends Biochem Sci.
21:327–335. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kim YJ, Bjorklund S, Li Y, Sayre MH and
Kornberg RD: A multiprotein mediator of transcriptional activation
and its interaction with the C-terminal repeat domain of RNA
polymerase II. Cell. 77:599–608. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Koleske AJ and Young RA: An RNA polymerase
II holoenzyme responsive to activators. Nature. 368:466–469.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Dynlacht BD, Hoey T and Tjian R: Isolation
of coactivators associated with the TATA-binding protein that
mediate transcriptional activation. Cell. 66:563–576.
1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Verrijzer CP and Tjian R: TAFs mediate
transcriptional activation and promoter selectivity. Trends Biochem
Sci. 21:338–342. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lefevre P, Witham J, Lacroix CE, Cockerill
PN and Bonifer C: The LPS-induced transcriptional upregulation of
the chicken lysozyme locus involves CTCF eviction and noncoding RNA
transcription. Mol Cell. 32:129–139. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ishii H, Du H, Zhang Z, Henderson A, Sen R
and Pazin MJ: Mi2beta shows chromatin enzyme specificity by erasing
a DNase I-hypersensitive site established by ACF. J Biol Chem.
284:7533–7541. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zeng WP and McFarland MM: Rapid and
unambiguous detection of DNase I hypersensitive site in rare
population of cells. PLoS One. 9(e85740)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Trynka G, Sandor C, Han B, Xu H, Stranger
BE, Liu XS and Raychaudhuri S: Chromatin marks identify critical
cell types for fine mapping complex trait variants. Nat Genet.
45:124–130. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Frank CL, Manandhar D, Gordan R and
Crawford GE: HDAC inhibitors cause site-specific chromatin
remodeling at PU.1-bound enhancers in K562 cells. Epigenetics
Chromatin. 9(15)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Choi YC and Chae CB: DNA hypomethylation
and germ cell-specific expression of testis-specific H2B histone
gene. J Biol Chem. 266:20504–20511. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ngo V, Gourdji D and Laverriere JN:
Site-specific methylation of the rat prolactin and growth hormone
promoters correlates with gene expression. Mol Cell Biol.
16:3245–3254. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang T, Marand AP and Jiang J: PlantDHS:
A database for DNase I hypersensitive sites in plants. Nucleic
Acids Res. 44:D1148–D1153. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Deng T, Zhu ZI, Zhang S, Postnikov Y,
Huang D, Horsch M, Furusawa T, Beckers J, Rozman J, Klingenspor M,
et al: Functional compensation among HMGN variants modulates the
DNase I hypersensitive sites at enhancers. Genome Res.
25:1295–1308. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kodama Y, Nagaya S, Shinmyo A and Kato K:
Mapping and characterization of DNase I hypersensitive sites in
Arabidopsis chromatin. Plant Cell Physiol. 48:459–470.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Boyle AP, Davis S, Shulha HP, Meltzer P,
Margulies EH, Weng Z, Furey TS and Crawford GE: High-resolution
mapping and characterization of open chromatin across the genome.
Cell. 132:311–322. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Crawford GE, Davis S, Scacheri PC, Renaud
G, Halawi MJ, Erdos MR, Green R, Meltzer PS, Wolfsberg TG and
Collins FS: DNase-chip: A high-resolution method to identify DNase
I hypersensitive sites using tiled microarrays. Nat Methods.
3:503–509. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Crawford GE, Holt IE, Mullikin JC, Tai D,
Blakesley R, Bouffard G, Young A, Masiello C, Green ED, Wolfsberg
TG, et al: Identifying gene regulatory elements by genome-wide
recovery of DNase hypersensitive sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:992–997. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Crawford GE, Holt IE, Whittle J, Webb BD,
Tai D, Davis S, Margulies EH, Chen Y, Bernat JA, Ginsburg D, et al:
Genome-wide mapping of DNase hypersensitive sites using massively
parallel signature sequencing (MPSS). Genome Res. 16:123–131.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Thurman RE, Rynes E, Humbert R, Vierstra
J, Maurano MT, Haugen E, Sheffield NC, Stergachis AB, Wang H,
Vernot B, et al: The accessible chromatin landscape of the human
genome. Nature. 489:75–82. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Vierstra J, Rynes E, Sandstrom R, Zhang M,
Canfield T, Hansen RS, Stehling-Sun S, Sabo PJ, Byron R, Humbert R,
et al: Mouse regulatory DNA landscapes reveal global principles of
cis-regulatory evolution. Science. 346:1007–1012. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Morin A, Kwan T, Ge B, Letourneau L, Ban
M, Tandre K, Caron M, Sandling JK, Carlsson J, Bourque G, et al:
Immunoseq: The identification of functionally relevant variants
through targeted capture and sequencing of active regulatory
regions in human immune cells. BMC Med Genomics.
9(59)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cooper J, Ding Y, Song J and Zhao K:
Genome-wide mapping of DNase I hypersensitive sites in rare cell
populations using single-cell DNase sequencing. Nat Protoc.
12:2342–2354. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jin W, Tang Q, Wan M, Cui K, Zhang Y, Ren
G, Ni B, Sklar J, Przytycka TM, Childs R, et al: Genome-wide
detection of DNase I hypersensitive sites in single cells and FFPE
tissue samples. Nature. 528:142–146. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lu F, Liu Y, Inoue A, Suzuki T, Zhao K and
Zhang Y: Establishing chromatin regulatory landscape during mouse
preimplantation development. Cell. 165:1375–1388. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Gross DS and Garrard WT: Nuclease
hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 57:159–197.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gaszner M and Felsenfeld G: Insulators:
Exploiting transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms. Nat Rev
Genet. 7:703–713. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li Q, Harju S and Peterson KR: Locus
control regions: Coming of age at a decade plus. Trends Genet.
15:403–408. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Huang WY and Liew CC: A conserved GATA
motif in a tissue-specific DNase I hypersensitive site of the
cardiac alpha-myosin heavy chain gene. Biochem J. 325:47–51.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bell O, Tiwari VK, Thoma NH and Schubeler
D: Determinants and dynamics of genome accessibility. Nat Rev
Genet. 12:554–564. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Pan Z, Lichtler AC and Upholt WB: DNase I
hypersensitive sites in the chromatin of the chicken Msx2 gene
differ in anterior and posterior limb mesenchyme, calvarial
osteoblasts and embryonic fibroblasts. Biochem Mol Biol Int.
46:549–557. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Grünweller A, Purschke WG, Kügler S, Kruse
C and Müller PK: Chicken vigilin gene: A distinctive pattern of
hypersensitive sites is characteristic for its transcriptional
activity. Biochem J. 326:601–607. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Heintzman ND, Stuart RK, Hon G, Fu Y,
Ching CW, Hawkins RD, Barrera LO, Van Calcar S, Qu C, Ching KA, et
al: Distinct and predictive chromatin signatures of transcriptional
promoters and enhancers in the human genome. Nat Genet. 39:311–318.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sheffield NC, Thurman RE, Song L, Safi A,
Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Lenhard B, Crawford GE and Furey TS:
Patterns of regulatory activity across diverse human cell types
predict tissue identity, transcription factor binding, and
long-range interactions. Genome Res. 23:777–788. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liu Y, Ding D, Liu H and Sun X: The
accessible chromatin landscape during conversion of human embryonic
stem cells to trophoblast by bone morphogenetic protein 4. Biol
Reprod. 96:1267–1278. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Dong X, Wang X, Zhang F and Tian W:
Genome-wide identification of regulatory sequences undergoing
accelerated evolution in the human genome. Mol Biol Evol.
33:2565–2575. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Mokry M, Harakalova M, Asselbergs FW, de
Bakker PI and Nieuwenhuis EE: Extensive association of common
disease variants with regulatory sequence. PLoS One.
11(e0165893)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
D'Antonio M and Ciccarelli FD: Integrated
analysis of recurrent properties of cancer genes to identify novel
drivers. Genome Biol. 14(R52)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Perera D, Poulos RC, Shah A, Beck D,
Pimanda JE and Wong JW: Differential DNA repair underlies mutation
hotspots at active promoters in cancer genomes. Nature.
532:259–263. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Peterson RE, Cai N, Bigdeli TB, Li Y,
Reimers M, Nikulova A, Webb BT, Bacanu SA, Riley BP, Flint J and
Kendler KS: The genetic architecture of major depressive disorder
in han chinese women. JAMA Psychiatry. 74:162–168. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Turner TN, Hormozdiari F, Duyzend MH,
McClymont SA, Hook PW, Iossifov I, Raja A, Baker C, Hoekzema K,
Stessman HA, et al: Genome sequencing of autism-affected families
reveals disruption of putative noncoding regulatory DNA. Am J Hum
Genet. 98:58–74. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Yuen RK, Merico D, Cao H, Pellecchia G,
Alipanahi B, Thiruvahindrapuram B, Tong X, Sun Y, Cao D, Zhang T,
et al: Genome-wide characteristics of de novo mutations in autism.
NPJ Genom Med. 1:160271–1602710. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Wang K, Sturt-Gillespie B, Hittle JC,
Macdonald D, Chan GK, Yen TJ and Liu ST: Thyroid hormone receptor
interacting protein 13 (TRIP13) AAA-ATPase is a novel mitotic
checkpoint-silencing protein. J Biol Chem. 289:23928–23937.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Rafnar T, Sulem P, Stacey SN, Geller F,
Gudmundsson J, Sigurdsson A, Jakobsdottir M, Helgadottir H,
Thorlacius S, Aben KK, et al: Sequence variants at the TERT-CLPTM1L
locus associate with many cancer types. Nat Genet. 41:221–227.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Abdelzaher E and MostafaM F:
Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 1 (LPCAT1) upregulation in
breast carcinoma contributes to tumor progression and predicts
early tumor recurrence. Tumour Biol. 36:5473–5483. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
D Antonio M, Weghorn D, D
Antonio-Chronowska A, Coulet F, Olson KM, DeBoever C, Drees F,
Arias A, Alakus H, Richardson AL, et al: Identifying DNase I
hypersensitive sites as driver distal regulatory elements in breast
cancer. Nat Commun. 8(436)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Guo X, Long J, Zeng C, Michailidou K,
Ghoussaini M, Bolla MK, Wang Q, Milne RL, Shu XO, Cai Q, et al:
Fine-scale mapping of the 4q24 locus identifies two independent
loci associated with breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 24:1680–1691. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Jiang T, Du F, Qin N, Lu Q, Dai J, Shen H
and Hu Z: Systematical analyses of variants in DNase I
hypersensitive sites to identify hepatocellular carcinoma
susceptibility loci in a Chinese population. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 32:1887–1894. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Nakaoka H, Gurumurthy A, Hayano T,
Ahmadloo S, Omer WH, Yoshihara K, Yamamoto A, Kurose K, Enomoto T,
Akira S, et al: Allelic imbalance in regulation of ANRIL through
chromatin interaction at 9p21 endometriosis risk locus. PLoS Genet.
12(e1005893)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
He HH, Meyer CA, Chen MW, Jordan VC, Brown
M and Liu XS: Differential DNase I hypersensitivity reveals
factor-dependent chromatin dynamics. Genome Res. 22:1015–1025.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Wei X, Yu L, Jin X, Song L, Lv Y and Han
Y: Identification of open chromosomal regions and key genes in
prostate cancer via integrated analysis of DNase-seq and RNA-seq
data. Mol Med Rep. 18:2245–2252. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Kallioniemi A: Bone morphogenetic protein
4-a fascinating regulator of cancer cell behavior. Cancer Genet.
205:267–277. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Ampuja M, Rantapero T, Rodriguez-Martinez
A, Palmroth M, Alarmo EL, Nykter M and Kallioniemi A: Integrated
RNA-seq and DNase-seq analyses identify phenotype-specific BMP4
signaling in breast cancer. BMC Genomics. 18(68)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
de Boer B, Prick J, Pruis MG, Keane P,
Imperato MR, Jaques J, Brouwers-Vos AZ, Hogeling SM, Woolthuis CM,
Nijk MT, et al: Prospective isolation and characterization of
genetically and functionally distinct AML subclones. Cancer Cell.
34:674–689. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Stergachis AB, Neph S, Reynolds A, Humbert
R, Miller B, Paige SL, Vernot B, Cheng JB, Thurman RE, Sandstrom R,
et al: Developmental fate and cellular maturity encoded in human
regulatory DNA landscapes. Cell. 154:888–903. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Wei C and Dong X, Lu H, Tong F, Chen L,
Zhang R, Dong J, Hu Y, Wu G and Dong X: LPCAT1 promotes brain
metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma by up-regulating PI3K/AKT/MYC
pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38(95)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|