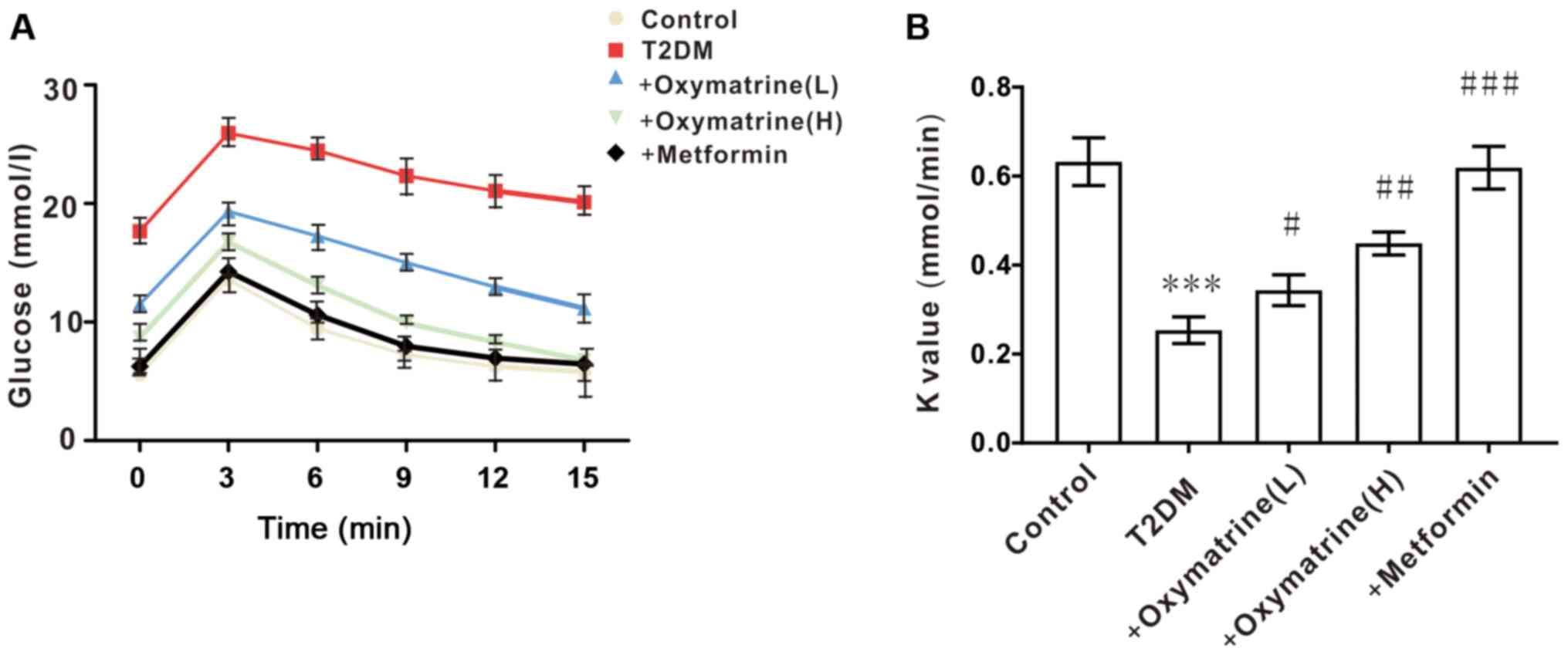
|
1
|
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis
and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 37 (Suppl
1):S81–S90. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ma RCW: Epidemiology of diabetes and
diabetic complications in China. Diabetologia. 61:1249–1260.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wu Y, Ding Y, Tanaka Y and Zhang W: Risk
factors contributing to type 2 diabetes and recent advances in the
treatment and prevention. Int J Med Sci. 11:1185–1200.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rines AK, Sharabi K, Tavares CD and
Puigserver P: Targeting hepatic glucose metabolism in the treatment
of type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 15:786–804.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rui L: Energy metabolism in the liver.
Compr Physiol. 4:177–197. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
De Meyts P: The insulin receptor and its
signal transduction network. [Updated 2016 Apr 27]. In. Feingold
KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K,
Dungan K, Grossman A, Hershman JM, Hofland J, et al (eds).
Endotext (Internet). South Dartmouth (MA), MDText.com, Inc.,
2000. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK378978. Accessed
April 27, 2016.
|
|
7
|
Muoio DM and Newgard CB: Mechanisms of
disease: Molecular and metabolic mechanisms of insulin resistance
and beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
9:193–205. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Fan H, Li L, Zhang X, Liu Y, Yang C, Yang
Y and Yin J: Oxymatrine downregulates TLR4, TLR2, MyD88 and
NF-kappa B and protects rat brains against focal ischemia.
Mediators Inflamm. 2009(704706)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liu Y, Xu Y, Ji W, Li X, Sun B, Gao Q and
Su C: Anti-tumor activities of matrine and oxymatrine: Literature
review. Tumour Biol. 35:5111–5119. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chen XS, Wang GJ, Cai X, Yu HY and Hu YP:
Inhibition of hepatitis B virus by oxymatrine in vivo. World J
Gastroenterol. 7:49–52. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wu XL, Zeng WZ, Jiang MD, Qin JP and Xu H:
Effect of oxymatrine on the TGF beta-Smad signaling pathway in rats
with CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol.
14:2100–2105. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chan SM and Ye JM: Strategies for the
discovery and development of anti-diabetic drugs from the natural
products of traditional medicines. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 16:207–216.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang L, Li X, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Zhang Y
and Ma Q: Oxymatrine ameliorates diabetes-induced aortic
endothelial dysfunction via the regulation of eNOS and NOX4. J Cell
Biochem, Nov 19, 2018 (Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1002/jcb.28006.
|
|
14
|
Wang SB and Jia JP: Oxymatrine attenuates
diabetes-associated cognitive deficits in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
35:331–338. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lu ML, Xiang XH and Xia SH: Potential
signaling pathways involved in the clinical application of
oxymatrine. Phytother Res. 30:1104–1112. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. National Academicals Press, Washington, DC, 2011.
|
|
17
|
Ma C, Yu H, Xiao Y and Wang H: Momordica
charantia extracts ameliorate insulin resistance by regulating the
expression of SOCS-3 and JNK in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats.
Pharm Biol. 55:2170–2177. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zuo ML, Wang AP, Tian Y, Mao L, Song GL
and Yang ZB: Oxymatrine ameliorates insulin resistance in rats with
type 2 diabetes by regulating the expression of KSRP, PETN, and AKT
in the liver. J Cell Biochem. 120:16185–16194. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yoshioka K, Saito M, Oh KB, Nemoto Y,
Matsuoka H, Natsume M and Abe H: Intracellular fate of 2-NBDG, a
fluorescent probe for glucose uptake activity, in Escherichia coli
cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 60:1899–1901. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zdychova J and Komers R: Emerging role of
AKT kinase/protein kinase B signaling in pathophysiology of
diabetes and its complications. Physiol Res. 54:1–16.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang X, Liu G, Guo J and Su Z: The
PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int J Biol Sci.
14:1483–1496. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Vinayagam A, Kulkarni MM, Sopko R, Sun X,
Hu Y, Nand A, Villalta C, Moghimi A, Yang X, Mohr SE, et al: An
integrative analysis of the InR/PI3K/AKT network identifies the
dynamic response to insulin signaling. Cell Rep. 16:3062–3074.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bathina S and Das UN: Dysregulation of
PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway in brain of streptozotocin-induced type 2
diabetes mellitus in Wistar rats. Lipids Health Dis.
17(168)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Burgess SC, Hausler N, Merritt M, Jeffrey
FM, Storey C, Milde A, Koshy S, Lindner J, Magnuson MA, Malloy CR
and Sherry AD: Impaired tricarboxylic acid cycle activity in mouse
livers lacking cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. J Biol
Chem. 279:48941–48949. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mutel E, Abdul-Wahed A, Ramamonjisoa N,
Stefanutti A, Houberdon I, Cavassila S, Pilleul F, Beuf O,
Gautier-Stein A, Penhoat A, et al: Targeted deletion of liver
glucose-6 phosphatase mimics glycogen storage disease type l a
including development of multiple adenomas. J Hepatol. 54:529–537.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jiang WJ, Wang S, Xiao M, Lin Y, Zhou L,
Lei Q, Xiong Y, Guan KL and Zhao S: Acetylation regulates
gluconeogenesis by promoting PEPCK1 degradation via recruiting the
UBR5 ubiquitin ligase. Mol Cell. 43:33–44. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Koo SH, Flechner L, Qi L, Zhang X,
Screaton RA, Jeffries S, Hedrick S, Xu W, Boussouar F, Brindle P,
et al: The CREB coactivator TORC2 is a key regulator of fasting
glucose metabolism. Nature. 437:1109–1111. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Matsumoto M, Pocai A, Rossetti L, Depinho
RA and Accili D: Impaired regulmion of hepatic glucose production
in mice lacking the forkhead transcription factor Foxol in liver.
Cell Metab. 6:208–216. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhou XY, Shibusawa N, Naik K, Porras D,
Temple K, Ou H, Kaihara K, Roe MW, Brady MJ and Wondisford FE:
Insulin regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis through
phosphorylation of CREB-binding protein. Nat Med. l0:633–637.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Erion DM, Ignatova ID, Yonemitsu S, Nagai
Y, Chatterjee P, Weismann D, Hsiao JJ, Zhang D, 1wasaki T, Stark R,
et al: Prevention of hepatic steatosis and hepatic insulin
resistance by knockdown of cAMP response element-binding protein.
Cell Metab. 10:499–506. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cypess AM, Zhang H, Schulz TJ, Huang TL,
Espinoza DO, Kristiansen K, Unterman TG and Tseng YH: Insulin/IGF-I
regulation of necdin and brown adipocyte differentiation via CREB-
and FoxO1-associated pathways. Endocrinology. 152:3680–3689.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li X, Monks B, Ge Q and Birnbaum MJ:
AKT/PKB regulates hepatic metabolism by directly inhibiting
PGC-1alpha transcription coactivator. Nature. 447:1012–1016.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Abdul-Ghani MA, Puckett C, Triplitt C,
Maggs D, Adams J, Cersosimo E and DeFronzo RA: Initial combination
therapy with metformin, pioglitazone and exenatide is more
effective than sequential add-on therapy in subjects with new-onset
diabetes. Results from the efficacy and durability of initial
combination therapy for Type 2 Diabetes (EDICT): A randomized
trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 17:268–275. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Guo C, Zhang C, Li L, Wang Z, Xiao W and
Yang Z: Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of oxymatrine in
high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
Phytomedicine. 21:807–814. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yu XH, Zhu JS and Gu GM: Clinical effect
of oxymatrine combined with metformin on insulin resistance and
serum TNF-α in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver. Chin J Clin
Hepatol. 23:195. 2007.
|