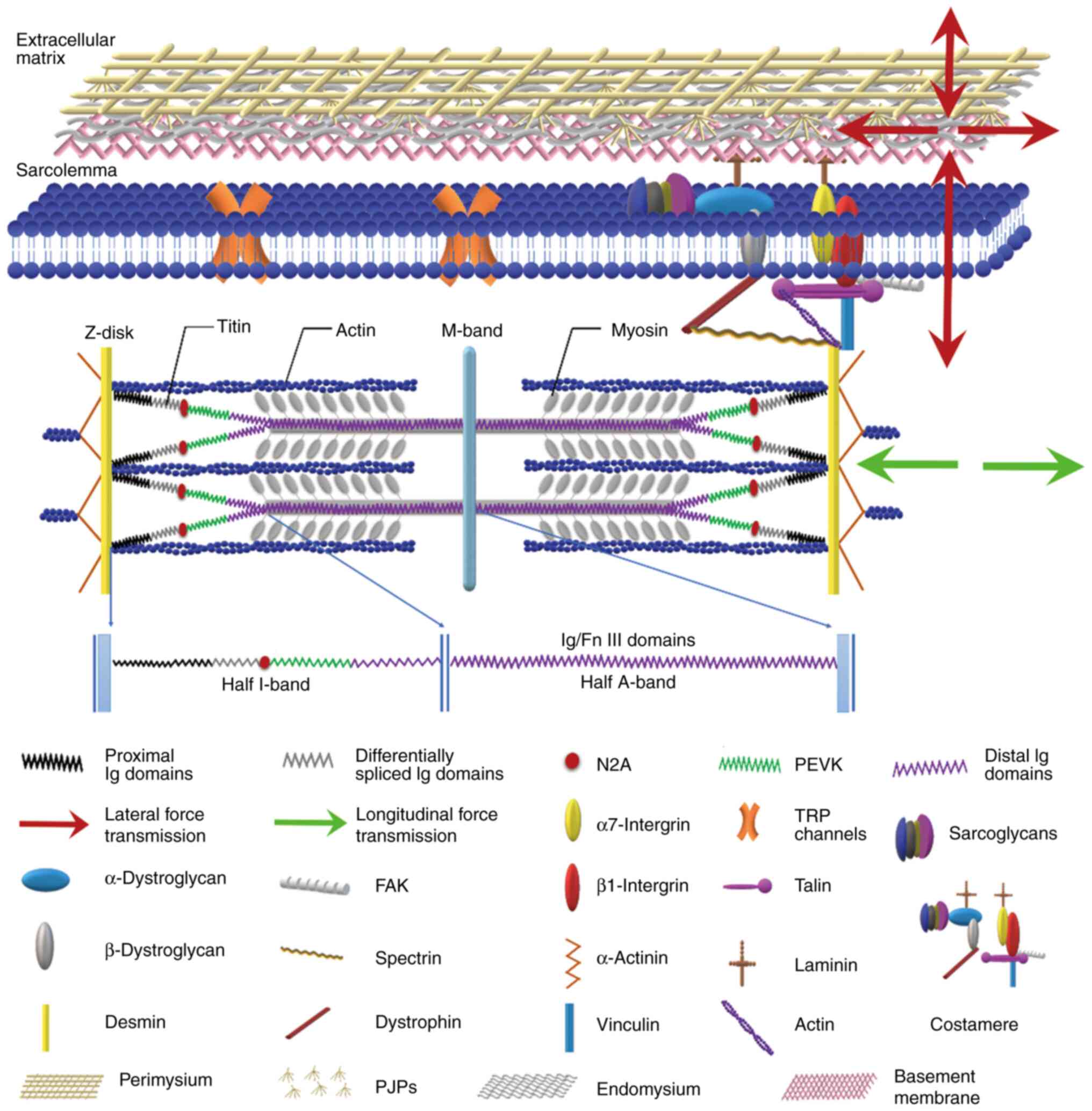
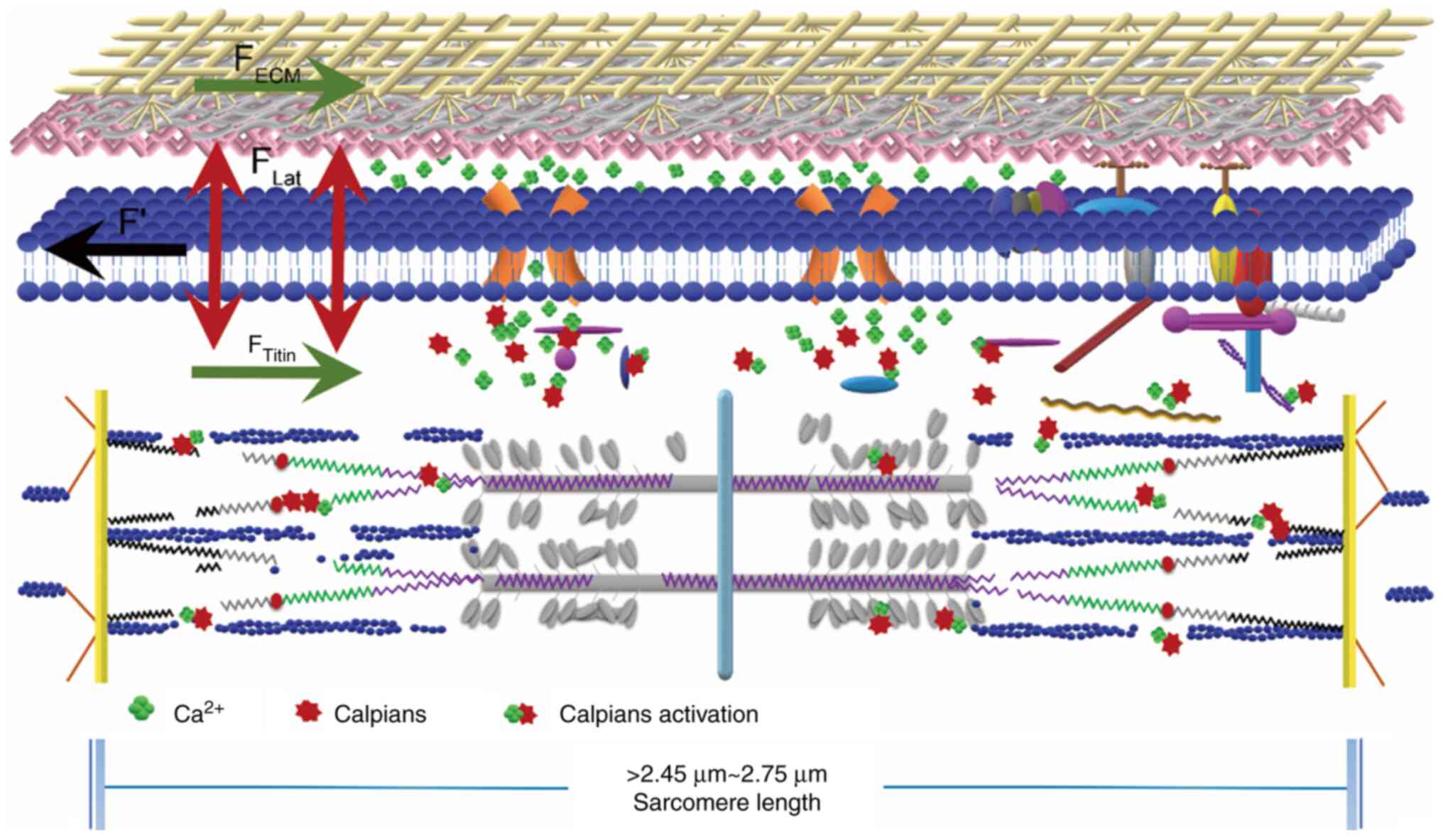
|
1
|
Hody S, Croisier JL, Bury T, Rogister B
and Leprince P: Eccentric muscle contractions: Risks and benefits.
Front Physiol. 10(536)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Liu AS and Zhang XL: Research progress of
eccentric training interventions on type 2 diabetes based on matrix
metalloproteinases 2, 9 regulating extracellular matrix
homeostasis. Chin J Sports Med. 36:1004–1011. 2017.
|
|
3
|
Tomalka A: Eccentric muscle contractions:
From single muscle fibre to whole muscle mechanics. Pflugers Arch.
475:421–435. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Douglas J, Pearson S, Ross A and McGuigan
M: Eccentric exercise: Physiological characteristics and acute
responses. Sports Med. 47:663–675. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Annibalini G, Contarelli S, Lucertini F,
Guescini M, Maggio S, Ceccaroli P, Gervasi M, Ferri Marini C,
Fardetti F, Grassi E, et al: Muscle and systemic molecular
responses to a single flywheel based iso-inertial training session
in resistance-trained men. Front Physiol. 10(554)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lovering RM and Brooks SV: Eccentric
exercise in aging and diseased skeletal muscle: Good or bad? J Appl
Physiol (1985). 116:1439–1445. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang X, Zhang XL and Xu SS: Exercise and
skeletal muscle ultrastructural changes. Chin J Sports Med.
29:109–113. 2010.
|
|
8
|
Keriven H, Sánchez-Sierra A,
Miñambres-Martín D, González de la Flor Á, García-Pérez-de-Sevilla
G and Domínguez-Balmaseda D: Effects of peripheral electromagnetic
stimulation after an eccentric exercise-induced delayed-onset
muscle soreness protocol in professional soccer players: A
randomized controlled trial. Front Physiol.
14(1206293)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhang XL, Gao XJ, Shi JP, Li JP, Zhou Y
and Wang R: The mechanism of eccentric exercise-induced skeletal
muscle overuse injuries. Chin J Sports Med. 31:1064–1074. 2012.
|
|
10
|
Thirupathi A, Freitas S, Sorato HR,
Pedroso GS, Effting PS, Damiani AP, Andrade VM, Nesi RT, Gupta RC,
Muller AP and Pinho RA: Modulatory effects of taurine on metabolic
and oxidative stress parameters in a mice model of muscle overuse.
Nutrition. 54:158–164. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhang XL and Wang RY: The mechanism of
overuse injuries: skeletal muscle tensegrity complex imbalance
theory. Chin J Sports Med. 32:646–653. 2013.
|
|
12
|
Wang RY: Skeletal muscle and exercise.
People's Sports Publishing House, Beijing, 2013.
|
|
13
|
Huxley AF and Niedergerke R: Structural
changes in muscle during contraction; interference microscopy of
living muscle fibres. Nature. 173:971–973. 1954.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Huxley H and Hanson J: Changes in the
cross-striations of muscle during contraction and stretch and their
structural interpretation. Nature. 173:973–976. 1954.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Herzog W: Mechanisms of enhanced force
production in lengthening (eccentric) muscle contractions. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 116:1407–1417. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Novak I and Truskinovsky L: Nonaffine
response of skeletal muscles on the ‘descending limb’. Math Mech
Solids. 20:697–720. 2015.
|
|
17
|
Zhang X, Zhang XL, Kong M and Ye ML:
Changes in lateral force transmission of skeletal muscle induced by
acute eccentric exercise and acupuncture intervention effect. Chin
J Sport Sci Technol. 54:94–108. 2018.
|
|
18
|
Kong M, Zhang X, Ye ML and Zhang XL:
Changes of perimysial junctional plates induced by excessive
eccentric training and the effects of acupuncture intervention.
Sheng Li Xue Bao. 69:17–32. 2017.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Hanson J and Huxley HE: Structural basis
of the cross-striations in muscle. Nature. 172:530–532.
1953.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Huxley AF: Reflections on muscle.
Liverpool UK: Liverpool University Press, 1980.
|
|
21
|
Herzog W: The role of titin in eccentric
muscle contraction. J Exp Biol. 217:2825–2833. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Horowits R and Podolsky RJ: The positional
stability of thick filaments in activated skeletal muscle depends
on sarcomere length: Evidence for the role of titin filaments. J
Cell Biol. 105:2217–2223. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhao Q and Zhang XL: Discussion on
revision of the sliding filament theory to resolve problems of
eccentric contraction mechanism. Acta Physiol Sinica. 73:143–147.
2021.
|
|
24
|
Herzog W, Schappacher G, Duvall M, Leonard
TR and Herzog JA: Residual force enhancement following eccentric
contractions: A new mechanism involving titin. Physiology
(Bethesda). 31:300–312. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Huxley HE: Electron microscope studies of
the organisation of the filaments in striated muscle. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 12:387–394. 1953.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Huxley AF: Muscle structure and theories
of contraction. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 7:255–318.
1957.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huxley HE: The mechanism of muscular
contraction. Science. 164:1356–1365. 1969.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Huxley AF and Simmons RM: Proposed
mechanism of force generation in striated muscle. Nature.
233:533–538. 1971.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Morgan DL, Whitehead NP, Wise AK, Gregory
JE and Proske U: Tension changes in the cat soleus muscle following
slow stretch or shortening of the contracting muscle. J Physiol.
522:503–513. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Iwazumi T: Molecular mechanism of muscle
contraction. Physiol Chem Phys Med NMR. 21:187–219. 1989.
|
|
31
|
Morgan DL: New insights into the behavior
of muscle during active lengthening. Biophys J. 57:209–221.
1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Morgan DL and Proske U: Popping sarcomere
hypothesis explains stretch-induced muscle damage. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 31:541–545. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Rassier DE, Herzog W and Pollack GH:
Dynamics of individual sarcomeres during and after stretch in
activated single myofibrils. Proc Biol Sci. 270:1735–1740.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Rassier DE, Herzog W and Pollack GH:
Stretch-induced force enhancement and stability of skeletal muscle
myofibrils. Adv Exp Med Biol. 538:501–515. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Dos Remedios CG: Comparative studies on
striated muscle. PhD thesis, University of Sydney, 1965.
|
|
36
|
Maruyama K: Connectin, an elastic protein
from myofibrils. J Biochem. 80:405–407. 1976.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang K, McClure J and Tu A: Titin: Major
myofibrillar components of striated muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
76:3698–3702. 1979.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Fürst DO, Osborn M, Nave R and Weber K:
The organization of titin filaments in the half-sarcomere revealed
by monoclonal antibodies in immunoelectron microscopy: A map of ten
nonrepetitive epitopes starting at the Z line extends close to the
M line. J Cell Biol. 106:1563–1572. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Linke WA and Krüger M: The giant protein
titin as an integrator of myocyte signaling pathways. Physiology
(Bethesda). 25:186–198. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Holt NC: Beyond bouncy gaits: The role of
multiscale compliance in skeletal muscle performance. J Exp Zool A
Ecol Integr Physiol. 333:50–59. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Nishikawa KC, Monroy JA, Uyeno TE, Yeo SH,
Pai DK and Lindstedt SL: Is titin a ‘winding filament’? A new twist
on muscle contraction. Proc Biol Sci. 279:981–990. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
DuVall MM, Jinha A, Schappacher-Tilp G,
Leonard TR and Herzog W: Differences in titin segmental elongation
between passive and active stretch in skeletal muscle. J Exp Biol.
220:4418–4425. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Labeit D, Watanabe K, Witt C, Fujita H, Wu
Y, Lahmers S, Funck T, Labeit S and Granzier H: Calcium-dependent
molecular spring elements in the giant protein titin. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 100:13716–13721. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Leonard TR and Herzog W: Regulation of
muscle force in the absence of actin-myosin-based cross-bridge
interaction. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 299:C14–C20.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Brynnel A, Hernandez Y, Kiss B, Lindqvist
J, Adler M, Kolb J, van der Pijl R, Gohlke J, Strom J, Smith J, et
al: Downsizing the molecular spring of the giant protein titin
reveals that skeletal muscle titin determines passive stiffness and
drives longitudinal hypertrophy. Elife. 7(e40532)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Weidner S, Tomalka A, Rode C and Siebert
T: How velocity impacts eccentric force generation of fully
activated skinned skeletal muscle fibers in long stretches. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 133:223–233. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Shi J, Watanabe D and Wada M: Eccentric
muscle contraction potentiates titin stiffness-related contractile
properties in rat fast-twitch muscles. J Appl Physiol (1985).
133:710–720. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Owens DJ, Twist C, Cobley JN, Howatson G
and Close GL: Exercise-induced muscle damage: What is it, what
causes it and what are the nutritional solutions? Eur J Sport Sci.
19:71–85. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Jørgensen A, Foster PP, Eftedal I, Wisløff
U, Paulsen G, Havnes MB and Brubakk AO: Exercise-induced
myofibrillar disruption with sarcolemmal integrity prior to
simulated diving has no effect on vascular bubble formation in
rats. Eur J Appl Physiol. 113:1189–1198. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Yu JG, Liu JX, Carlsson L, Thornell LE and
Stål PS: Re-evaluation of sarcolemma injury and muscle swelling in
human skeletal muscles after eccentric exercise. PLoS One.
8(e62056)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Powers JD, Bianco P, Pertici I, Reconditi
M, Lombardi V and Piazzesi G: Contracting striated muscle has a
dynamic I-band spring with an undamped stiffness 100 times larger
than the passive stiffness. J Physiol. 598:331–345. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Lieber RL and Binder-Markey BI: .
Biochemical and structural basis of the passive mechanical
properties of whole skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 599:3809–3823.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Ramaswamy KS, Palmer ML, van der Meulen
JH, Renoux A, Kostrominova TY, Michele DE and Faulkner JA: Lateral
transmission of force is impaired in skeletal muscles of dystrophic
mice and very old rats. J Physiol. 589:1195–1208. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Minato K, Yoshimoto Y, Kurosawa T,
Watanabe K, Kawashima H, Ikemoto-Uezumi M and Uezumi A: Measurement
of lateral transmission of force in the extensor digitorum longus
muscle of young and old mice. Int J Mol Sci.
22(12356)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Le S, Yu M, Hovan L, Zhao Z, Ervasti J and
Yan J: Dystrophin as a molecular shock absorber. ACS Nano.
12:12140–12148. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Lo HP, Hall TE and Parton RG: .
Mechanoprotection by skeletal muscle caveolae. Bioarchitecture.
6:22–27. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Boppart MD, Volker SE, Alexander N, Burkin
DJ and Kaufman SJ: . Exercise promotes alpha7 integrin gene
transcription and protection of skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Regul
Integr Comp Physiol. 295:R1623–R1630. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Zhang BT, Whitehead NP, Gervasio OL,
Reardon TF, Vale M, Fatkin D, Dietrich A, Yeung EW and Allen DG:
Pathways of Ca²+ entry and cytoskeletal damage following
eccentric contractions in mouse skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol
(1985). 112:2077–2086. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|