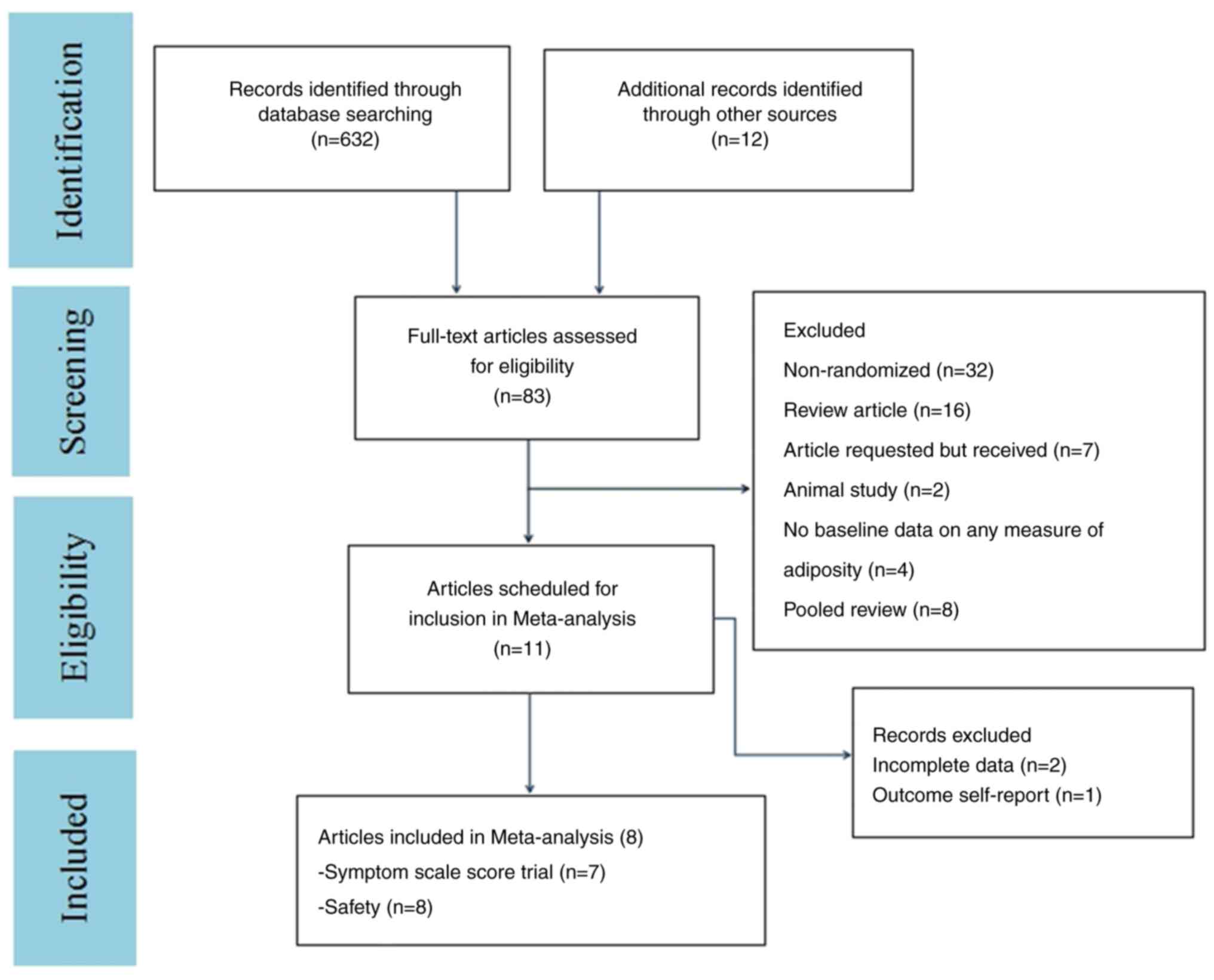
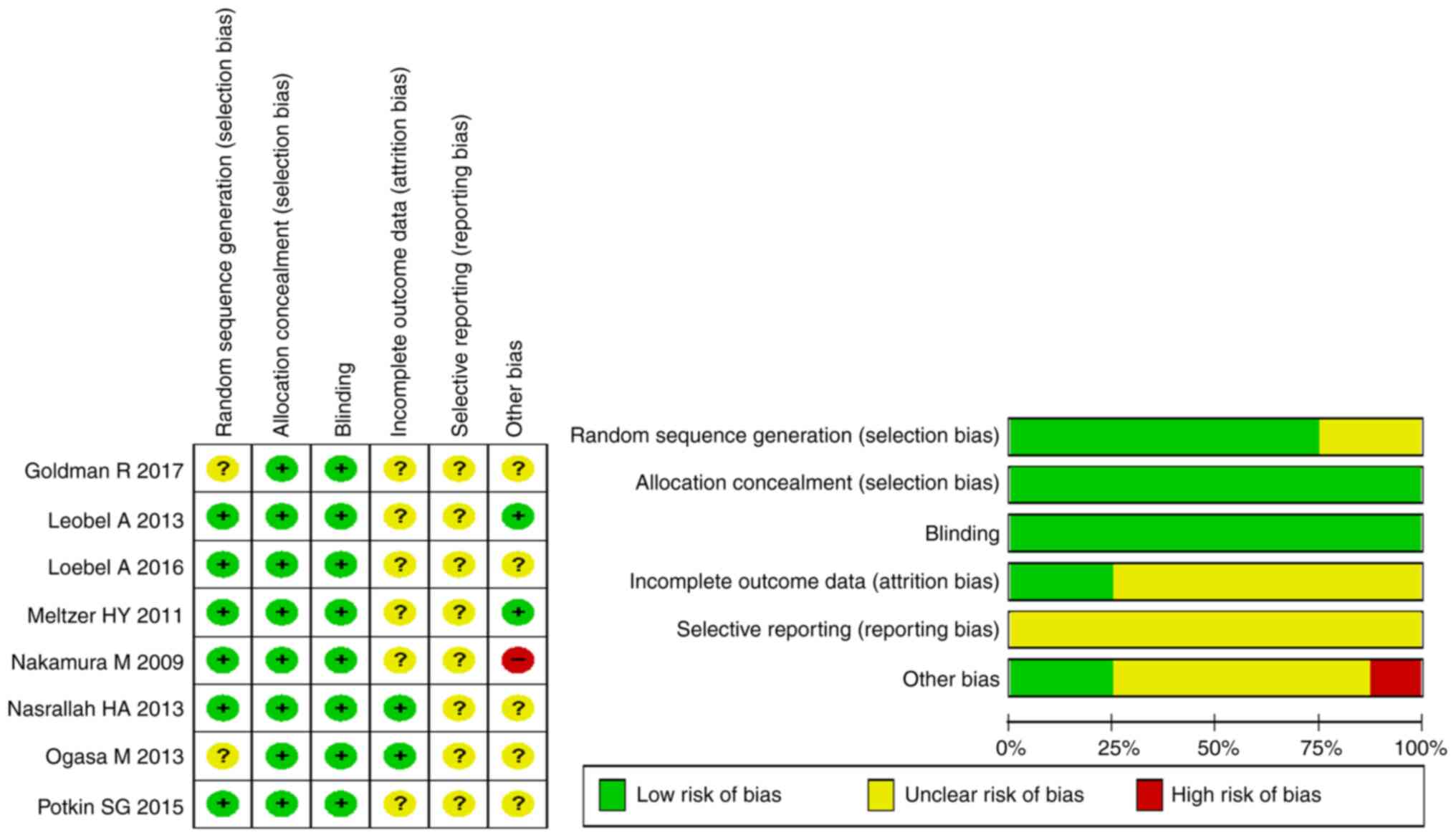
|
1
|
Henson P, D'Mello R, Vaidyam A, Keshavan M
and Torous J: Anomaly detection to predict relapse risk in
schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry. 11(28)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hálfdánarson Ó, Zoëga H, Aagaard L,
Bernardo M, Brandt L, Fusté AC, Furu K, Garuoliené K, Hoffmann F,
Huybrechts KF, et al: International trends in antipsychotic use: A
study in 16 countries, 2005-2014. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol.
27:1064–1076. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sun ZW, Shi TT and Fu PX: Characteristics
of schizophrenia patients' homicide behaviors and their
correlations with criminal capacity. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi. 33:32–35.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
4
|
Maggioni E, Crespo-Facorro B, Nenadic I,
Benedetti F, Gaser C, Sauer H, Roiz-Santiañez R, Poletti S,
Marinelli V, Bellani M, et al: Common and distinct structural
features of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: The European
network on psychosis, affective disorders and cognitive trajectory
(ENPACT) study. PLoS One. 12(e0188000)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wimberley T, MacCabe JH, Laursen TM,
Sørensen HJ, Astrup A, Horsdal HT, Gasse C and Støvring H:
Mortality and self-harm in association with clozapine in
treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 174:990–998.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Cai C and Yu L: Quality of life in
patients with schizophrenia in China: Relationships among
demographic characteristics, psychosocial variables, and symptom
severity. J Psychosoc Nurs Ment Health Serv. 55:48–54.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li W, Zhou FC, Zhang L, Ng CH, Ungvari GS,
Li J and Xiang YT: Comparison of cognitive dysfunction between
schizophrenia and bipolar disorder patients: A meta-analysis of
comparative studies. J Affect Disord. 274:652–661. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang LJ, Lin SK, Chen YC, Huang MC, Chen
TT, Ree SC and Chen CK: Differences in clinical features of
methamphetamine users with persistent psychosis and patients with
schizophrenia. Psychopathology. 49:108–115. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tan EJ, Neill E and Rossell SL: Assessing
the relationship between semantic processing and thought disorder
symptoms in schizophrenia. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 21:629–638.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kurtz M, Mohring P, Förster K, Bauer M and
Kanske P: Deficits in explicit emotion regulation in bipolar
disorder: A systematic review. Int J Bipolar Disord.
9(15)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Reutfors J, Cesta CE, Cohen JM, Bateman
BT, Brauer R, Einarsdóttir K, Engeland A, Furu K, Gissler M, Havard
A, et al: Antipsychotic drug use in pregnancy: A multinational
study from ten countries. Schizophr Res. 220:106–115.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bruijnzeel D, Yazdanpanah M, Suryadevara U
and Tandon R: Lurasidone in the treatment of schizophrenia: A
critical evaluation. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 16:1559–1565.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Citrome L: Schizophrenia relapse, patient
considerations, and potential role of lurasidone. Patient Prefer
Adherence. 10:1529–1537. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Horisawa T, Ishibashi T, Nishikawa H,
Enomoto T, Toma S, Ishiyama T and Taiji M: The effects of selective
antagonists of serotonin 5-HT7 and 5-HT1A receptors on
MK-801-induced impairment of learning and memory in the passive
avoidance and morris water maze tests in rats: Mechanistic
implications for the benefcial effects of the novel atypical
antipsychotic lurasidone. Behav Brain Res. 220:83–90.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Srisurapanont M, Suttajit S, Likhitsathian
S, Maneeton B and Maneeton N: A network meta-analysis of the
dose-response effects of lurasidone on acute schizophrenia. Sci
Rep. 11(5571)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kishi T, Nosaka T, Sakuma K, Okuya M and
Iwata N: Efficacy, tolerability, and safety of lurasidone for acute
schizophrenia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of
phase 3 trials in Japan. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 40:314–322.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Braga VL, Rocha LPDS, Bernardo DD, Cruz CO
and Riera R: What do Cochrane systematic reviews say about
probiotics as preventive interventions? Sao Paulo Med J.
135:578–586. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J and Altman
DG: PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews
and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med.
6(e1000097)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Page MJ and Moher D: Evaluations of the
uptake and impact of the preferred reporting items for systematic
reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) statement and extensions: A
scoping review. Syst Rev. 6(263)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Knobloch K, Yoon U and Vogt PM: Preferred
reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA)
statement and publication bias. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 39:91–92.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Panic N, Leoncini E, de Belvis G,
Ricciardi W and Boccia S: Evaluation of the endorsement of the
preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis
(PRISMA) statement on the quality of published systematic review
and meta-analyses. PLoS One. 8(e83138)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Durak S, Ercan ES, Ardic UA, Yuce D, Ercan
E and Ipci M: Effect of methylphenidate on neurocognitive test
battery: An evaluation according to the diagnostic and statistical
manual of mental disorders, fourth edition, subtypes. J Clin
Psychopharmacol. 34:467–474. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Shabsigh R and Rowland D: The diagnostic
and statistical manual of mental disorders, fourth edition, text
revision as an appropriate diagnostic for premature ejaculation. J
Sex Med. 4:1468–1478. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Faiad Y, Khoury B, Daouk S, Maj M, Keeley
J, Gureje O and Reed G: Frequency of use of the international
classification of diseases ICD-10 diagnostic categories for mental
and behavioural disorders across world regions. Epidemiol Psychiatr
Sci. 9:568–576. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Janca A, Ustün TB, Early TS and Sartorius
N: The ICD-10 symptom checklist: A companion to the ICD-10
classification of mental and behavioural disorders. Soc Psychiatry
Psychiatr Epidemiol. 28:239–242. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
International Advisory Group for the
Revision of ICD-10 Mental and Behavioural Disorders. A conceptual
framework for the revision of the ICD-10 classification of mental
and behavioural disorders. World Psychiatry. 10:86–92.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Khan A, Lewis C and Lindenmayer JP: Use of
non-parametric item response theory to develop a shortened version
of the positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS). BMC
Psychiatry. 11(178)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Pinna F, Deriu L, Diana E, Perra V,
Randaccio RP, Sanna L, Tusconi M and Carpiniello B: Cagliari
Recovery Study Group. Clinical global impression-severity score as
a reliable measure for routine evaluation of remission in
schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorders. Ann Gen Psychiatry.
14(6)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Health Quality Ontario. Psychotherapy for
Major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder: A
health technology assessment. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser.
17:1–167. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Higgins JPT and Green S (eds): Cochrane
handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0
[updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available
from. http://handbook.cochrane.org.
|
|
31
|
Loebel A, Cucchiaro J, Sarma K, Xu L, Hsu
C, Kalali AH, Pikalov A and Potkin SG: Efficacy and safety of
lurasidone 80 and 160 mg/day in the treatment of schizophrenia: A
randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled trial.
Schizophr Res. 145:101–109. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ogasa M, Kimura T, Nakamura M and Guarino
J: Lurasidone in the treatment of schizophrenia: A 6-week,
placebo-controlled study. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 225:519–530.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Goldman R, Loebel A, Cucchiaro J, Deng L
and Findling RL: Efficacy and safety of lurasidone in adolescents
with schizophrenia: A 6-week, randomized placebo-controlled study.
J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 27:516–525. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Meltzer HY, Cucchiaro J, Silva R, Ogasa M,
Phillips D, Xu J, Kalali AH, Schweizer E, Pikalov A and Loebel A:
Lurasidone in the treatment of schizophrenia: A randomized,
double-blind, placebo- and olanzapine-controlled study. Am J
Psychiatry. 168:957–967. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Nasrallah HA, Silva R, Phillips D,
Cucchiaro J, Hsu J, Xu J and Loebel A: Lurasidone for the treatment
of acutely psychotic patients with schizophrenia: A 6-week,
randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Psychiatr Res. 47:670–677.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Nakamura M, Ogasa M, Guarino J, Phillips
D, Severs J, Cucchiaro J and Loebel A: Lurasidone in the treatment
of acute schizophrenia: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J
Clin Psychiatry. 70:829–836. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Potkin SG, Kimura T and Guarino J: A
6-week, double-blind, placebo- and haloperidol-controlled, phase II
study of lurasidone in patients with acute schizophrenia. Ther Adv
Psychopharmacol. 5:322–331. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Loebel A, Silva R, Goldman R, Watabe K,
Cucchiaro J, Citrome L and Kane JM: Lurasidone dose escalation in
early nonresponding patients with schizophrenia: A randomized,
placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychiatry. 77:1672–1680.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sanford M: Lurasidone: In the treatment of
schizophrenia. CNS Drugs. 27:67–80. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Owen RT: Lurasidone: A new treatment
option for schizophrenia. Drugs Today (Barc). 47:807–816.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Latuda. (lurasidone HCl) Tablets US
Prescribing Information, 2012. http://www.latuda.com/LatudaPrescribingInformation.pdf.
|
|
42
|
Kane JM: Lurasidone: A clinical overview.
J Clin Psychiatry. 72 (Suppl 1):S24–S28. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ishibashi T, Horisawa T, Tokuda K,
Ishiyama T, Ogasa M, Tagashira R, Matsumoto K, Nishikawa H, Ueda Y,
Toma S, et al: Pharmacological profile of lurasidone, a novel
antipsychotic agent with potent 5-hydroxytryptamine 7 (5-HT7) and
5-HT1A receptor activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 334:171–181.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Stahl SM, Morrissette DA, Citrome L,
Saklad SR, Cummings MA, Meyer JM, O'Day JA, Dardashti LJ and
Warburton KD: ‘Meta-guidelines’ for the management of patients with
schizophrenia. CNS Spectr. 18:150–162. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Stahl SM: Stahl's essential
psychopharmacology: Neuroscientific basis and practical
applications. 5th edition. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University
Press, 2021.
|
|
46
|
De Hert M, Yu W, Detraux J, Sweers K, van
Winkel R and Correll CU: Body weight and metabolic adverse effects
of asenapine, iloperidone, lurasidone and paliperidone in the
treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: A systematic
review and exploratory meta-analysis. CNS Drugs. 26:733–759.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Fukuyama K, Motomura E, Shiroyama T and
Okada M: Impact of 5-HT7 receptor inverse agonism of lurasidone on
monoaminergic tripartite synaptic transmission and pathophysiology
of lower risk of weight gain. Biomed Pharmacother.
148(112750)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Tarzian M, Soudan M, Alhajji M, Ndrio M
and Fakoya AO: Lurasidone for treating schizophrenia and bipolar
depression: A review of its efficacy. Cureus.
15(e38071)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Higuchi T, Ishigooka J, Iyo M, Yeh CB,
Ebenezer EG, Liang KY, Lee JS, Lee SY, Lin SK, Yoon BH, et al:
Lurasidone in the treatment of schizophrenia: Results of a
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in Asian patients. Asia Pac
Psychiatry. 11(e12352)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Stahl SM, Cucchiaro J, Simonelli D, Hsu J,
Pikalov A and Loebel A: Effectiveness of lurasidone for patients
with schizophrenia following 6 weeks of acute treatment with
lurasidone, olanzapine, or placebo: A 6-month, open-label,
extension study. J Clin Psychiatry. 74:507–515. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Miura I, Horikoshi S, Ichinose M, Suzuki Y
and Watanabe K: Lurasidone for the treatment of schizophrenia:
Design, development, and place in therapy. Drug Des Devel Ther.
17:3023–3031. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Harvey PD, Ogasa M, Cucchiaro J, Loebel A
and Keefe RS: Performance and interview-based assessments of
cognitive change in a randomized, double-blind comparison of
lurasidone vs ziprasidone. Schizophr Res. 127:188–194.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Zheng W, Cai DB, Yang XH, Li L, Zhang QE,
Ng CH, Ungvari GS, Li XB, Ning YP and Xiang YT: Short-term efficacy
and tolerability of lurasidone in the treatment of acute
schizophrenia: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J
Psychiatr Res. 103:244–251. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|