|
1
|
Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu
Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, et al: Clinical features of patients
infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet.
395:497–506. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J,
Wang B, Xiang H, Cheng Z, Xiong Y, et al: Clinical characteristics
of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected
pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 323:1061–1069. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tall AR and Yvan-Charvet L: Cholesterol,
inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 15:104–116.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Soy M, Keser G, Atagündüz P, Tabak F,
Atagündüz I and Kayhan S: Cytokine storm in COVID-19: Pathogenesis
and overview of anti-inflammatory agents used in treatment. Clin
Rheumatol. 39:2085–2094. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kaji H: High-density lipoproteins and the
immune system. J Lipids. 2013(684903)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
McKechnie JL and Blish CA: The innate
immune system: Fighting on the front lines or fanning the flames of
COVID-19? Cell Host Microbe. 27:863–869. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kim JA, Montagnani M, Chandrasekran S and
Quon MJ: Role of lipotoxicity in endothelial dysfunction. Heart
Fail Clin. 8:589–607. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Froldi G and Dorigo P: Endothelial
dysfunction in Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Gender and age
influences. Med Hypotheses. 144(110015)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kim D, Chung H, Lee JE, Kim J, Hwang J and
Chung Y: Immunologic aspects of dyslipidemia: A critical regulator
of adaptive immunity and immune disorders. J Lipid Atheroscler.
10:184–201. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lei P, Zhang L, Han P, Zheng C, Tong Q,
Shang H, Yang F, Hu Y, Li X and Song Y: Liver injury in patients
with COVID-19: Clinical profiles, CT findings, the correlation of
the severity with liver injury. Hepatol Int. 14:733–742.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Malik J, Laique T, Ishaq U, Ashraf A,
Malik A, Ali M, Zaidi SMJ, Javaid M and Mehmood A: Effect of
COVID-19 on lipid profile and its correlation with acute phase
reactants. medRxiv: doi: https://doi.org/10.1101.
|
|
12
|
Marinakis NM, Svingou M, Veltra D, Kekou
K, Sofocleous C, Tilemis FN, Kosma K, Tsoutsou E, Fryssira H and
Traeger-Synodinos J: Phenotype-driven variant filtration strategy
in exome sequencing toward a high diagnostic yield and
identification of 85 novel variants in 400 patients with rare
Mendelian disorders. Am J Med Genet A. 185:2561–2571.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tilemis FN, Marinakis NM, Veltra D,
Svingou M, Kekou K, Mitrakos A, Tzetis M, Kosma K, Makrythanasis P,
Traeger-Synodinos J and Sofocleous C: Germline CNV detection
through whole-exome sequencing (WES) data analysis enhances
resolution of rare genetic diseases. Genes (Basel).
14(1490)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Desvignes JP, Bartoli M, Delague V, Krahn
M, Miltgen M, Béroud C and Salgado D: VarAFT: A variant annotation
and filtration system for human next generation sequencing data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 46 (W1):W545–W553. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Noreng S, Posert R, Bharadwaj A, Houser A
and Baconguis I: Molecular principles of assembly, activation, and
inhibition in epithelial sodium channel. Elife.
9(e59038)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Foloppe N and MacKerell AD Jr: All-Atom
empirical force field for nucleic Acids: 2) parameter optimization
based on small molecule and condensed phase macromolecular target
data. J Comput Chem. 21:86–104. 2000.
|
|
17
|
Yamamoto T, Uchiumi C, Suzuki N, Yoshimoto
J and Murillo-Rodriguez E: The psychological impact of ‘mild
lockdown’ in Japan during the COVID-19 pandemic: A nationwide
survey under a declared state of emergency. Int J Environ Res
Public Health. 7(9382)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li H, Xiang X, Ren H, Xu L, Zhao L, Chen
X, Long H, Wang Q and Wu Q: Serum amyloid A is a biomarker of
severe coronavirus disease and poor prognosis. J Infect.
80:646–655. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Petrilli CM, Jones SA, Yang J, Rajagopalan
H, O'Donnell L, Chernyak Y, Tobin KA, Cerfolio RJ, Francois F and
Horwitz LI: Factors associated with hospital admission and critical
illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York
City: Prospective cohort study. BMJ. 369(m1966)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chang MC, Park YK, Kim BO and Park D: Risk
factors for disease progression in COVID-19 patients. BMC Infect
Dis. 20(445)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Aparisi A, Martín-Fernández M,
Ybarra-Falcón C, Gil J, Carrasco-Moraleja M, Martinez-Paz P,
Cusacovich I, Gonzal-Benito H, Fuertes R, Marcos-Mangas M, et al:
Dyslipidemia and Inflammation as Hallmarks of oxidative stress in
COVID-19: A follow up study. Int J Mol Sci.
23(15350)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Masana L, Correig E, Ibarretxe D, Anoro E,
Arroyo JA, Jericó C, Guerrero C, Miret M, Näf S, Pardo A, et al:
Low HDL and high triglycerides predict COVID-19 severity. Sci Rep.
11(7217)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
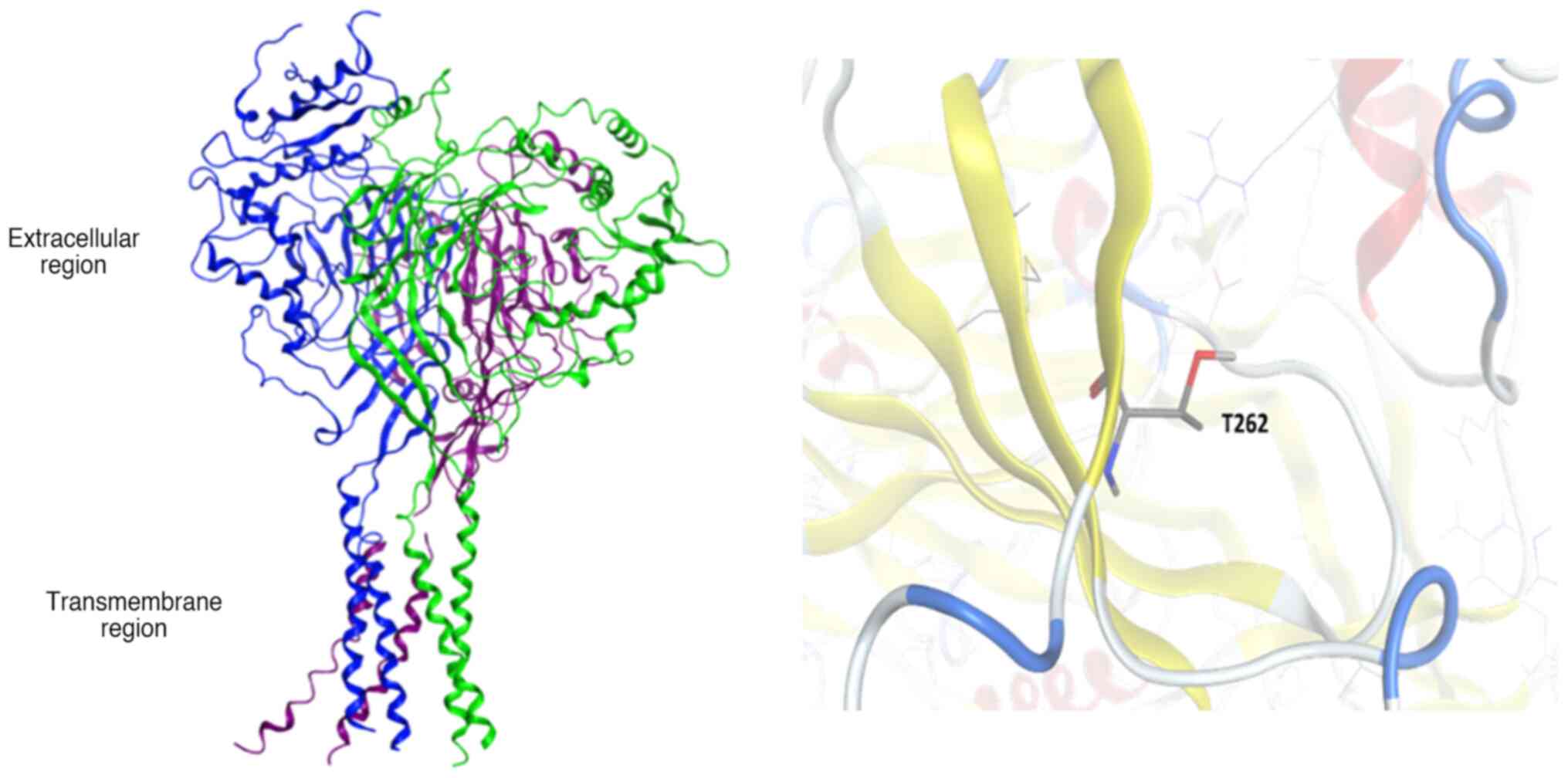
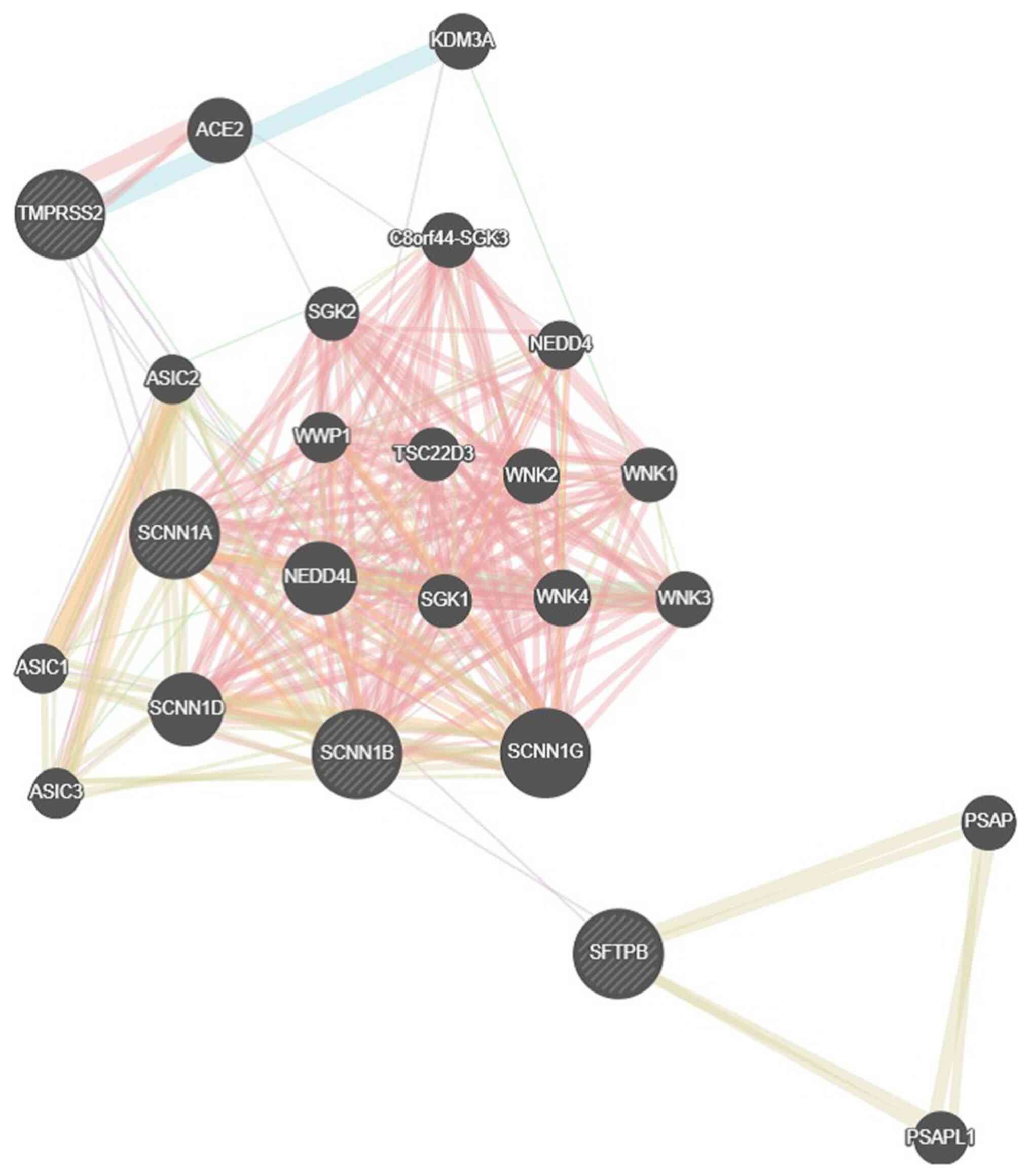
Mano I and Driscoll M: DEG/ENaC channels:
A touchy superfamily that watches its salt. Bioessays. 21:568–578.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Drummond HA, Grifoni SC and Jernigan NL: A
New Trick for an Old Dogma: ENaC proteins as mechanotransducers in
vascular smooth muscle. Physiology (Bethesda). 23:23–31.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Govindan R, Banerjee P, Dhania NK and
Senapati S: FTIR based approach to study EnaC mechanosensory
functions. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 167:79–86. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kashlan OB and Kleyman TR: ENaC structure
and function in the wake of a resolved structure of a family
member. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 301:F684–F696. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Baldin JP, Barth D and Fronius M:
Epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) formed by one or two subunits forms
functional channels that respond to shear force. Front Physiol.
11(141)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Champigny G, Voilley N, Lingueglia E,
Friend V, Barbry P and Lazdunski M: Regulation of expression of the
lung amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel by steroid hormones. EMBO J.
13:2177–2181. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hanukoglu I and Hanukoglu A: Epithelial
sodium channel (ENaC) family: Phylogeny, structure-function, tissue
distribution, and associated inherited diseases. Gene. 579:95–132.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kellenberger S and Schild L: International
Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCI. structure, function,
and pharmacology of acid-sensing ion channels and the epithelial
Na+ Channel. Pharmacol Rev. 67:1–35. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Golestaneh N, Klein C, Valamanesh F,
Suarez G, Agarwal MK and Mirshahi M: Mineralocorticoid
receptor-mediated signaling regulates the ion gated sodium channel
in vascular endothelial cells and requires an intact cytoskeleton.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 280:1300–1306. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Canessa CM, Schild L, Buell G, Thorens B,
Gautschi I, Horisberger JD and Rossier BC: Amiloride-sensitive
epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits.
Nature. 367:463–467. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Waldmann R, Champigny G, Bassilana F,
Voilley N and Lazdunski M: Molecular cloning and functional
expression of a novel amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. J Biol Chem.
270:27411–27414. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hummler E, Barker P, Gatzy J, Beermann F,
Verdumo C, Schmidt A, Boucher R and Rossier BC: Early death due to
defective neonatal lung liquid clearance in alpha-ENaC-deficient
mice. Nat Genet. 12:325–328. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Tong Q, Gamper N, Medina JL, Shapiro MS
and Stockand JD: Direct activation of the epithelial Na(+) channel
by phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate and
phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate produced by phosphoinositide
3-OH kinase. J Biol Chem. 279:22654–22663. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gründer S, Firsov D, Chang SS, Jaeger NF,
Gautschi I, Schild L, Lifton RP and Rossier BC: A mutation causing
pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1 identifies a conserved glycine that
is involved in the gating of the epithelial sodium channel. EMBO J.
16:899–907. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ruffieux-Daidié D, Poirot O, Boulkroun S,
Verrey F, Kellenberger S and Staub O: Deubiquitylation regulates
activation and proteolytic cleavage of ENaC. J Am Soc Mephrol.
19:2170–2180. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Knight KK, Wentzlaff DM and Snyder PM:
Intracellular sodium regulates proteolytic activation of the
epithelial sodium channel. J Biol Chem. 283:27477–27482.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Örd M, Faustova I and Loog M: The sequence
at Spike S1/S2 site enables cleavage by furin and
phospho-regulation in SARS-CoV2 but not in SARS-CoV1 or MERS-CoV.
Sci Rep. 10(16944)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Bonny O and Hummler E: Dysfunction of
epithelial sodium transport: From human to mouse. Kidney Int.
57:1313–1318. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
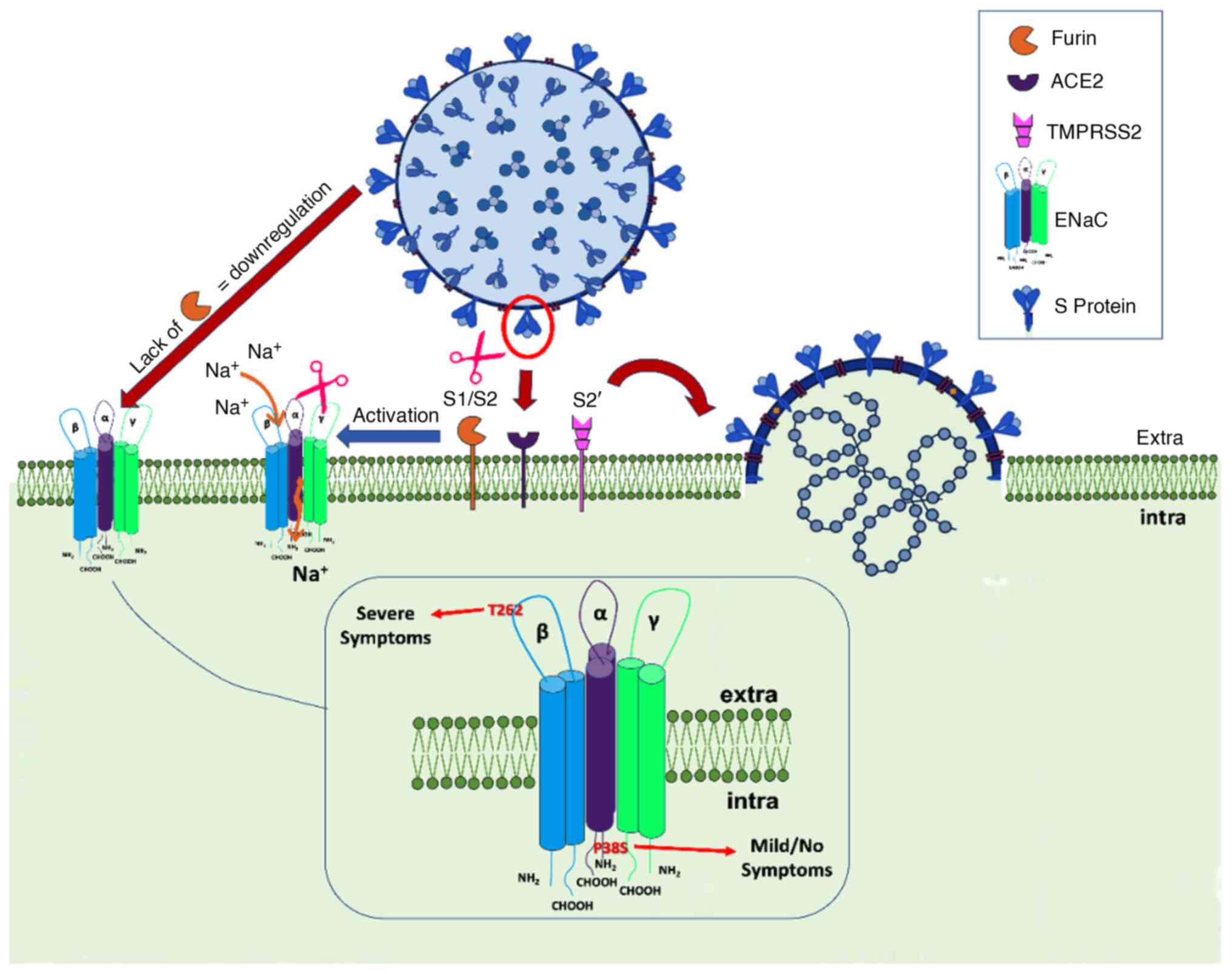
Anand P, Puranik A, Aravamudan M,
Venkatakrishnan AJ and Soundararajan V: SARS-CoV-2 strategically
mimics proteolytic activation of human ENaC. Elife.
9(e58603)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
V'kovski P, Kratzel A, Steiner S, Stalder
H and Thiel V: Coronavirus biology and replication: Implications
for SARS-CoV-2. Nat Rev Microbiol. 19:155–170. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Novelli G, Biancolella M, Mehrian-Shai R,
Colona VL, Brito AF, Grubaugh ND, Vasiliou V, Luzzatto L and
Reichardt JKV: COVID-19 one year into the pandemic: From genetics
and genomics to therapy, vaccination, and policy. Hum Genomics.
15(27)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Gandhi CK, Chen C, Wu R, Yang L, Thorenoor
N, Thomas NJ, DiAngelo SL, Spear D, Keim G, Yehya N and Floros J:
Association of SNP-SNP interactions of surfactant protein genes
with pediatric acute respiratory failure. J Clin Med.
9(1183)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Gentzsch M and Rossier BC: A
pathophysiological model for COVID-19: Critical importance of
transepithelial sodium transport upon airway infection. Function
(Oxf). 1(zqaa024)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ji HL, Song W, Gao Z, Su XF, Nie HG, Jiang
Y, Peng JB, He YX, Liao Y, Zhou YJ, et al: SARS-CoV proteins
decrease levels and activity of human ENaC via activation of
distinct PKC isoforms. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
296:L372–L383. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Quax TE, Claassens NJ, Söll D and van der
Oost J: Codon bias as a means to fine-tune gene expression. Mol
Cell. 59:149–161. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|