Introduction
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is among the fastest
growing global health emergencies at present, reaching alarming
levels. Globally, >10% of adults are now living with diabetes.
In 2021, the number of individuals living with diabetes was
estimated to be 537 million (10.5% of the global population)
worldwide, with an expected rise to 783 million (12.2% of the
global population) by 2045(1). The
prevalence of T2DM in Jordan is the second highest DM prevalence
worldwide, where it was 14.0% in 1990 and is expected to rise to
20.6% in 2050(2). T2DM is a
lifelong progressive chronic metabolic disease characterized by
chronic hyperglycemia due to either impaired insulin action in
peripheral target tissues, declined insulin secretion due to β-cell
failure, or both (3). Indeed, T2DM
increases the risk of developing various microvascular and
macrovascular complications, resulting in a significant financial
burden on the patients, their families, and the healthcare system
(4,5).
The American Diabetes Association has classified
T2DM based on the level of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c)
into controlled T2DM where the HbA1c is maintained at
≤7%, and uncontrolled T2DM where the HbA1c level exceeds
7% (6,7). Of note, several studies reported that
large percentage (30-83%) of diabetic patients are unable to
control their blood glucose levels despite treatment with different
glucose-lowering medications (8-10).
Poor glycemic control among T2DM increases the risk of development
of diabetic complications irrespective of the main treatment.
Therefore, glycemic control is considered the main therapeutic
objective to improve the quality of life and to prevent organ
damage in diabetic patients.
Chronic systemic inflammation and disordered
abundance of various growth factors are a prominent feature of T2DM
and are suggested to play a role in the pathogenesis and
progression of diabetes-related complications (11,12).
Importantly, several growth factors such as the epidermal growth
factor (EGF) are involved in numerous biological processes, such as
cell proliferation, differentiation, migration and wound healing,
are also involved in the pancreatic β cell function, development,
glucose regulation and insulin secretion (13,14).
Moreover, EGF was shown to exert anti-inflammatory effects on the
pancreas in animal models of pancreatitis (15). EGF is produced in different tissues
such as the pancreas, kidney and the digestive system, and its
circulating level is reduced in diabetic patients and animal models
of diabetes (13,16). Therefore, the intricate relationship
between poor glycemic control, altered EGF levels, and insulin
resistance creates a complex feedback loop of metabolic
dysregulation that has not been fully elucidated. This gap in
understanding highlights the need for further investigation to
uncover the underlying mechanisms and their potential implications
for more effective management of T2DM.
This study aimed to estimate the relative abundance
of various inflammatory markers and growth factors in patients with
controlled and uncontrolled T2DM in Jordan, to assess their
correlation with the glycemic status and insulin resistance and to
evaluate their value in predicting disease progression. This
research is crucial for the Jordanian population, where T2DM
prevalence is rising, and the progression of insulin resistance and
glycemic dysregulation often appears inevitable. Elucidating this
relationship could unveil novel therapeutic strategies to mitigate
diabetic complications, addressing the distinct metabolic factors
influencing diabetes in the Jordanian population.
Materials and methods
Study design
An observational case-control design was used in the
present study. Ethical approval to recruit subjects to participate
in the study was received from The Institutional Review Boards of
the Jordan University of Science and Technology (approval no.
7/114/2018; Irbid, Jordan). All study subjects were informed about
the procedures and data collection prior to the start of study.
Signed written consent forms were obtained from all participants
followed by whole blood sampling. Recruitment of study subjects
took place between December 2018 and December 2019 at the
endocrinology clinics at King Abdullah University Hospital (KAUH),
a tertiary hospital affiliated with Jordan University of Science
and Technology in the northern part of Jordan. All research
procedures were conducted following the Principle of Good Clinical
Practice and the Declaration of Helsinki.
Study population
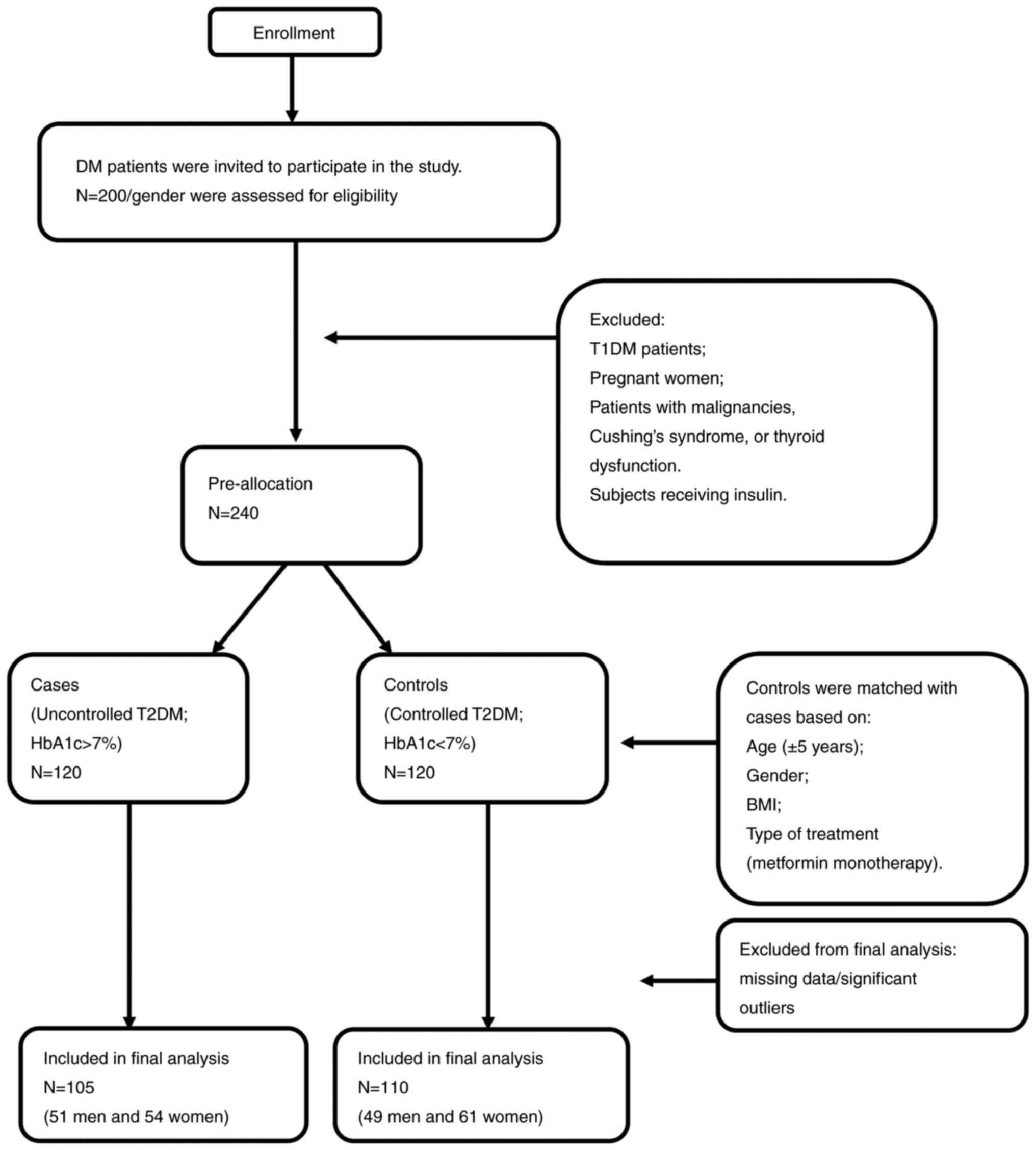
A total of 200 male and 200 female diabetic patients
were invited to participate in the study. Inclusion criteria were
as follows: Age >18 years-old and previous diagnosis with T2DM,
whereas exclusion criteria were: patients with T1DM, pregnant
women, patients with malignancies, Cushing's syndrome, or thyroid
dysfunction. Subjects receiving insulin were also excluded from the
study since it could affect HOMA-IR measurements. Of the invited
patients, 240 agreed to participate and were pre-allocated for the
study. Cases were defined as patients with uncontrolled T2DM (HbA1c
>7%, n=120) and 1:1 matched them with controls (HbA1c ≤7%,
n=120) based on age (±5 years), sex, body mass index (BMI) (±2
kg/m2), and treatment type (metformin monotherapy).
After data collection, outliers were identified using the z-score
method, where values exceeding a z-score of 3.3 were flagged for
further examination. These were then confirmed through box-plot
analysis and outliers' analysis in SPSS. Since all statistical
tests used in the present study require data normality, outliers
that compromised the normal distribution were removed to ensure an
acceptable level of skewness. Patients with missing data or
significant outliers were excluded from analysis, and eventually
105 patients with uncontrolled T2DM and 110 patients with
controlled T2DM were included in the final analysis.
Anthropometric measurements
Patients who met the eligibility criteria were
interviewed by the attending physician during their visit to the
clinic, and relevant information was obtained into a structured
data collection sheet. Medical history, family history, height
(cm), and weight (kg), waist circumference (cm) of the patients
were recorded during their visit. BMI was calculated based on the
aforementioned measurements using the following equation:
BMI=weight (kg)/height2 (m2). The age of the
patient was recovered from the patients' electronic medical
records.
Blood sampling and handling
A certified phlebotomist withdrew two blood samples
(5 ml each) by venipuncture from each participant after a 12-h
fast. One blood sample was collected into an
ethylene-diamine-tetra-acetic acid (EDTA) tube (AFCO) and then kept
at 4˚C to be used for HbA1c measurement. The second
sample was collected into a plain tube containing a gel clot
activator (AFCO) and allowed to clot at room temperature. This
sample was then centrifuged at 4˚C at 4,000 x g for 5 min to
separate the serum. The serum was immediately aliquoted into
smaller volumes to prevent degradation due to repeated freeze-thaw
cycles. The aliquoted serum samples were then deep-frozen at -80˚C
and subsequently used for biochemical measurements, including
glucose, total cholesterol, triglycerides and cytokine levels.
HbA1c measurement
The blood samples stored in EDTA tubes were used to
measure HbA1c levels using an automated cobas c 513
analyzer system which is an in vitro diagnostic test system
designed to quantitatively determine the percentage of
HbA1c in human capillary and venous whole blood by
photometric transmission measurement (Roche Diagnostics) at the
laboratories of KAUH. Patients having HbA1c level >7%
were considered to have an uncontrolled T2DM, whereas patients
having HbA1c ≤7% were considered to have controlled
T2DM.
Biochemical measurements
To evaluate differential cytokines and growth
factors level in the serum samples, a human cytokine antibody
membrane array targeting 42 proteins (cat. no. ab133997; Abcam) was
used according to the manufacturer's protocol. Briefly, 20 µl of
serum samples from each patient of controlled T2DM and uncontrolled
T2DM groups were pooled into two pools (labeled controlled and
uncontrolled T2DM), then 1 ml of each pool was incubated overnight
into a designated well at 4˚C containing the membrane array. After
24 h, serum samples were aspirated, and the membranes were washed
with wash buffer and then incubated with 1 ml of biotin-conjugated
anti-cytokines overnight at 4˚C. Then the biotin-conjugated
anti-cytokines were aspirated and washed. Finally, 2 ml of
horseradish peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin was added into each
well and incubated overnight at 4˚C; then it was aspirated, and the
membranes were washed again by the previously described method.
Detection buffer was used to develop a chemiluminescent signal and
the C-DIGIT blot scanner (LI-COR Biosciences) was used to detect
the signal intensity. The blots were visually assessed for relative
differences in the abundance of inflammatory mediators and growth
factors between the controlled and uncontrolled T2DM groups. The
EGF, CXCL5/epithelial cell-derived neutrophil-activating peptide
(ENA-78), stem cell factor (SCF), and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand
1 (CXCL1/GRO alpha, GRO-α) showed relative difference between
groups, therefore their serum levels were evaluated using a
commercially available DuoSet ELISA kits purchased from R&D
Systems, Inc. The ELISA kits used in the present study are based on
the solid-phase sandwich ELISA technique. The Human EGF ELISA (cat.
no. DY236) has an assay range of 3.9-250 pg/ml. The Human
CXCL5/ENA-78 ELISA (cat. no. DY254) provides an assay range of
15.6-1,000 pg/ml. The Human SCF ELISA (cat. no. DY255) and the
Human CXCL1/GRO alpha ELISA (cat. no. DY275) both have assay ranges
of 31.2-2,000 pg/ml. In addition, serum insulin levels were
assessed by a solid phase sandwich Quantikine ELISA kit (cat. no.
DINS00; R&D Systems, Inc.; sensitivity: 2.15 pmol/l, assay
range: 15.6-500 pmol/l). Moreover, serum levels of tumor necrosis
factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1α) and interleukin-1
beta (IL-1β) were measured using ELISA kits from R&D Systems,
Inc. The TNF-α assay (cat. no. DTA00D) had a sensitivity of 6.23
pg/ml and a measurement range of 15.6-1,000 pg/ml. The IL-1α assay
(cat. no. DLA50) had a sensitivity of 1 pg/ml and a range of
3.9-250 pg/ml. Similarly, the IL-1β assay (cat. no. DLB50) had a
sensitivity of 1 pg/ml with the same assay range of 3.9-250 pg/ml.
Briefly, the ELISA was carried out in duplicates of 100 µl aliquots
of the serum samples, diluted accordingly to comply with the
detection range of the relevant assay. A total of 100 µl of the
standard solution was added to the wells of a 96-well plate
pre-coated with a monoclonal antibody. Following the appropriate
incubation period, the plate was washed, and an enzyme-labeled
antibody, supplied as part of the assay kit, was added, followed by
the substrate. The reaction was stopped by adding the stop solution
after the development of color. The optical density of each well
was determined by measuring the absorbance at 450 nm using an
absorption spectrophotometer (Bio-Tek Instruments, Inc.).
Furthermore, the serum samples were submitted to the laboratories
of KAUH to measure glucose, total cholesterol and triglyceride
levels using a high throughput automated analyzer system
(cobas® modular analyzer series; Roche Diagnostics).
Insulin resistance score (HOMA-IR) was calculated according to the
formula: Fasting serum insulin (µU/l) x fasting serum glucose
(nmol/l)/22.5.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using the IBM
SPSS software ver. 22.0 (IBM Corp.). The unpaired Student's
t-test was used to test for significant differences in serum
cytokine levels, age, BMI, weight circumference total cholesterol,
triglyceride and glucose levels between patients with controlled
and uncontrolled T2DM. The binary logistic model was used to
predict the likelihood of being uncontrolled diabetic based on EGF
and HOMA-IR; factors that were significant on the t-test. A P-value
of <0.05 was used as a cut-off for significance. Additionally, a
Pearson's product-moment correlation was run to assess the
relationship between serum EGF levels, HOMA-IR, fasting blood sugar
(FBS) and HbA1c indicative of glycemic control using
SigmaPlot 12 software (Systat Software, Inc.).
Results
Patient characteristics and
biochemical profile
During the course of the present study, 110 patients
with controlled T2DM and 105 patients with uncontrolled T2DM were
eligible to participate in the study. A schematic diagram that
summarizes recruitment of study subjects is demonstrated in
Fig. 1. Those patients were
previously diagnosed with T2DM by a specialist endocrinologist
according to the American Diabetes Association guidelines.
The percentage of women was 53% among controlled
T2DM and 54% among uncontrolled T2DM with no significant
differences existing in sex distribution between controlled and
uncontrolled T2DM groups. The biochemical profile of the patients
showed that patients with uncontrolled T2DM had significantly
higher levels of fasting blood sugar (FBS), higher HbA1c
percentage, higher serum insulin levels, HOMA-IR score, and serum
triglycerides level, with no difference in cholesterol levels
between study groups.
The relative abundance of various cytokines and
growth factor levels was evaluated using a human antibody cytokine
membrane array. Surprisingly, a large number of prominent cytokines
such as the interleukins were not detected on the array, and this
was confirmed with ELISA (Table
SI). However, certain chemokines and growth factors such as
EGF, ENA-78, GRO-α and SCF were detected and revealed a visual
difference in the cytokine array and therefore the results were
assessed with ELISA (Fig. 2).
Compared with the controlled T2DM subjects, the uncontrolled group
had significantly lower EGF levels (95.9±82.7 vs. 158.77±111.7
pg/ml, P=0.002), representing ~40% reduction, while GRO-α showed a
tendency for significant increase in the uncontrolled T2DM subjects
(P=0.06). However, ENA-78 and SCF levels were not significantly
different between study groups. The baseline characteristics of the
study subjects and their biochemical profile are included in
Table I.
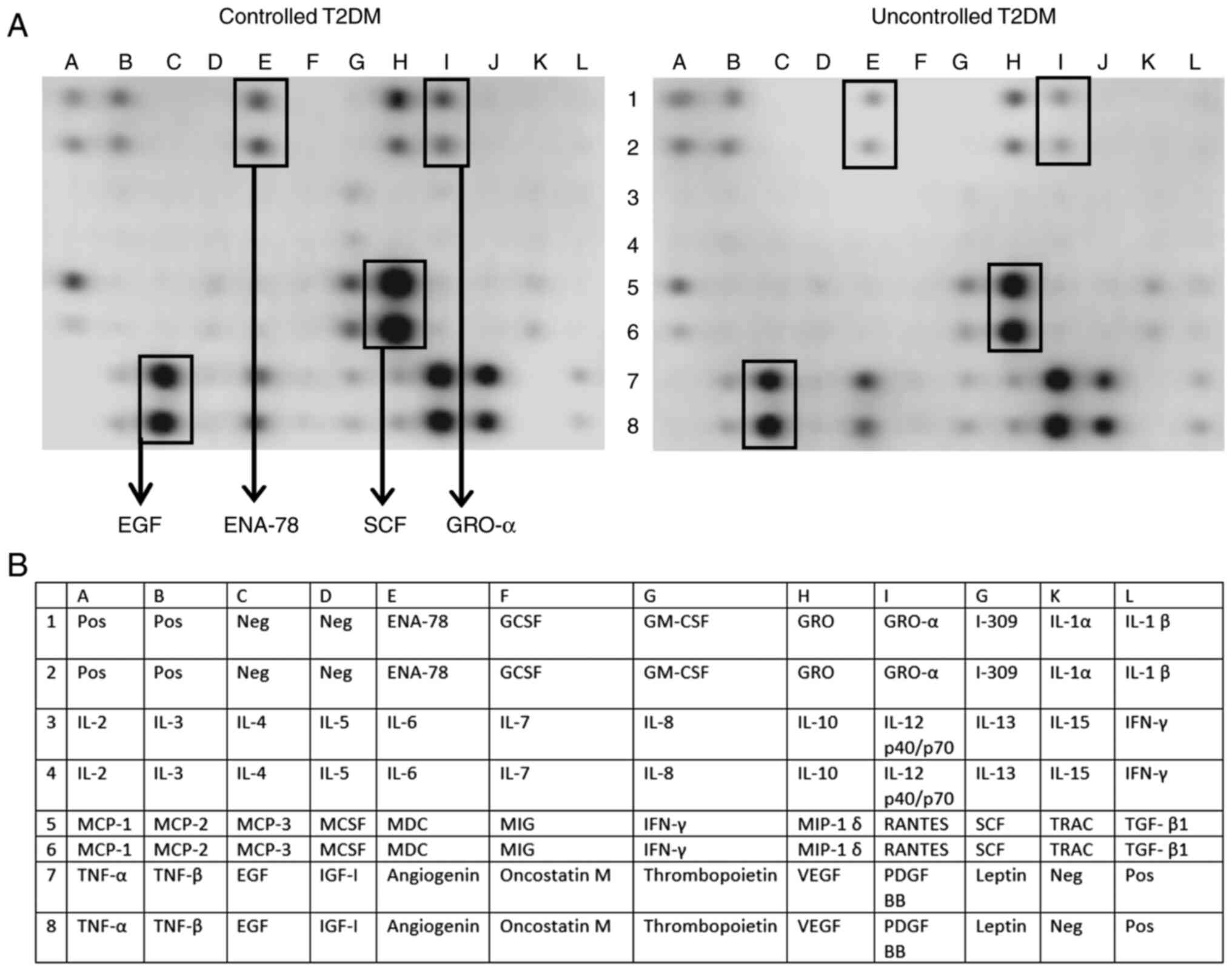 | Figure 2Relative abundance of different
inflammatory mediators and growth factors in patients with
controlled and uncontrolled T2DM. (A) To evaluate differential
cytokines and growth factors level in the serum samples, a human
cytokine antibody membrane array targeting 42 proteins was used
according to the manufacturer's protocol. Briefly, 20 µl of serum
samples from each patient of controlled T2DM and uncontrolled T2DM
groups were pooled into two pools (labeled controlled and
uncontrolled T2DM), then 1 ml of each pool was incubated overnight
into a designated well at 4˚C containing the membrane array. A
visual comparison between the two arrays performed by two
independent investigators revealed that five cytokines were
different between groups: The EGF, ENA-78, SCF and GRO-α. (B) List
of cytokines and chemokines represented by the antibody array
membrane. T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; EGF, epidermal growth
factor; ENA-78, CXCL5/epithelial cell-derived neutrophil-activating
peptide; SCF, stem cell factor; GRO-α, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand
1. |
 | Table IBaseline characteristics of
controlled and uncontrolled diabetic participants. |
Table I
Baseline characteristics of
controlled and uncontrolled diabetic participants.
|
Characteristics | Controlled T2DM,
n=110 | Uncontrolled T2DM
n=105 | P-value |
|---|
| Sex | | | 0.557 |
|
Males, n
(%) | 49(49) | 51(51) | |
|
Females, n
(%) | 61(53) | 54(47) | |
| Age (years) | 60.12±9.27 | 60.89±10.82 | 0.56 |
| Weight (Kg) | 83.94±16.54 | 83.74±15.46 | 0.71 |
| Height (cm) | 166.3±8.6 | 167.2±8.7 | 0.79 |
| Waist circumference
(cm) | 106.6±11.3 | 108.8±12.43 | 0.46 |
| Body mass
index | 30.3±5.47 | 29.9±5.01 | 0.63 |
| Glycated
hemoglobin | 6.25±0.46 | 8.97±1.41 | <0.001 |
| Glucose
(mg/dl) | 138.2±38.86 | 202.8±68.56 | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol
(mg/dl) | 207.8±58.39 | 211.1±56.7 | 0.89 |
| Triglyceride
(mg/dl) | 140.32±75.35 | 179.46±131.13 | 0.025 |
| GRO-α (pg/ml) | 194.98+81.9 | 229.1±123.47 | 0.06 |
| EGF (pg/ml) | 158.77±111.7 | 95.9±82.7 | 0.002 |
| ENA-78 (pg/ml) | 489.13±326.31 | 548.4±318.27 | 0.99 |
| SCF (pg/ml) | 66±26.57 | 61.3±25.1 | 0.33 |
| HOMA-IR | 9.6±8.2 | 16±10.5 | 0.001 |
| Insulin
(pmol/l) | 163.37±123.68 | 209.22±182.68 | 0.02 |
| All continuous
variables are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (Mean ±
SD) |
Association between EGF, insulin
resistance and glycemic control in T2DM
The binary logistic model was used to predict the
likelihood of being uncontrolled diabetic based on EGF and HOMA-IR;
factors that were significant on the t-test. After controlling for
age, sex, and BMI both factors were statistically associated with
diabetes control; higher HOMA-IR scores and lower EGF levels
predicted uncontrolled diabetes, as shown in Table II. The underlying assumptions of
the binary logistic regression were the normality of data
distribution, independence of observations and errors, and the
absence of extremely high correlation between any 2 predictors that
could suspect collinearity was assessed using variance inflation
factors. The goodness-of-fit of the model was evaluated using the
Hosmer-Lemeshow test, which assesses how well the observed data fit
the model. A non-significant P-value (>0.05) from this test
indicates that the model's predicted probabilities align well with
the observed outcomes, suggesting a favorable fit.
 | Table IIBinary logistic regression model
predicting the likelihood of uncontrolled diabetes based on EGF and
HOMA-IR levels, adjusted for age, sex and BMI. |
Table II
Binary logistic regression model
predicting the likelihood of uncontrolled diabetes based on EGF and
HOMA-IR levels, adjusted for age, sex and BMI.
| | 95% CI for odds
ratio |
|---|
| | B | SE | Wald | df | P | Odds ratio | Lower | Upper |
|---|
| EGF | -0.006 | 0.002 | 13.747 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.994 | 0.991 | 0.997 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.073 | 0.018 | 16.747 | 1 | 0.000 | 1.075 | 1.039 | 1.114 |
| Constant | -0.262 | 0.321 | 0.666 | 1 | 0.414 | 0.770 | | |
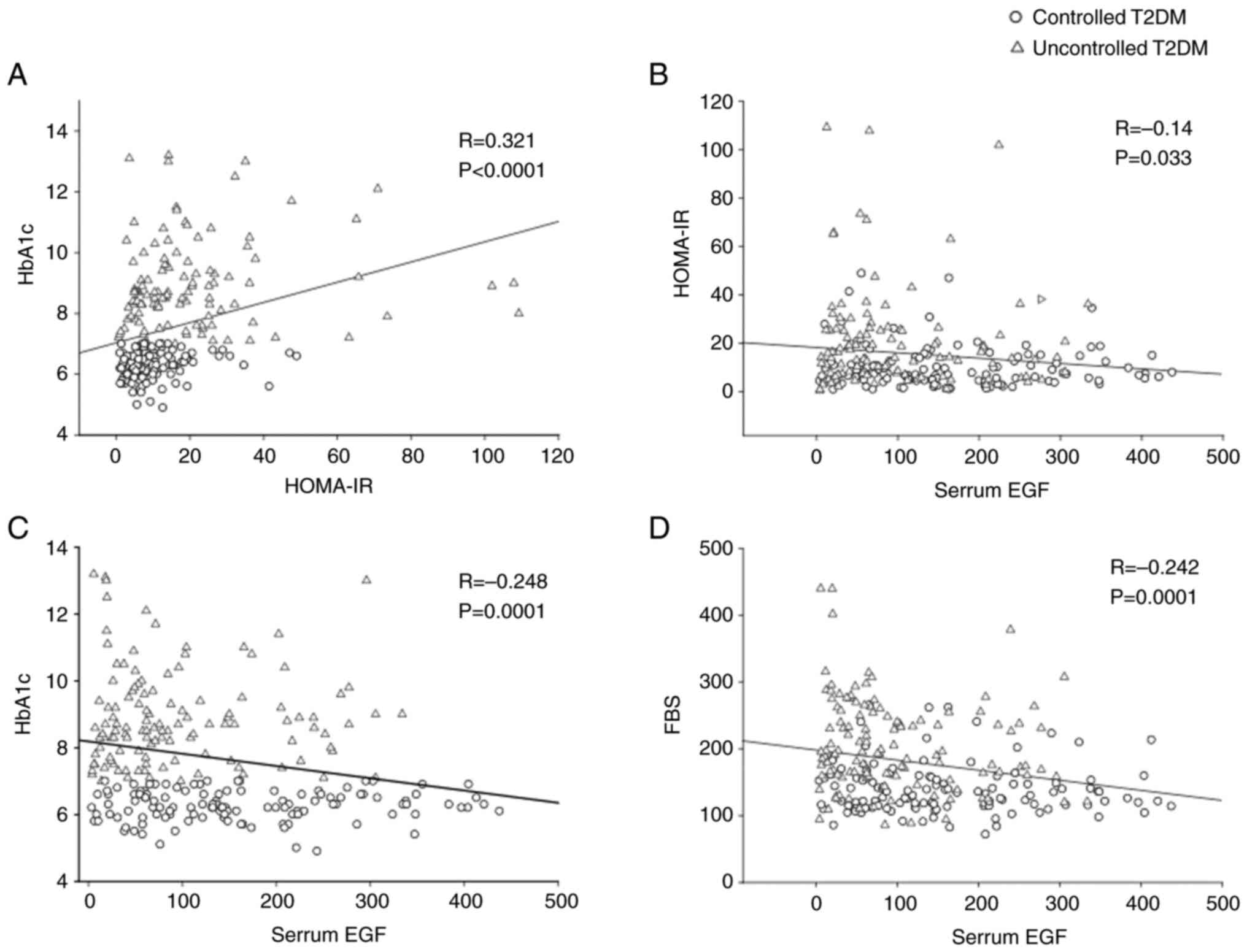
Additionally, a Pearson's product-moment correlation
was run to assess the relationship between serum EGF levels,
HOMA-IR and HbA1c indicative of glycemic control. There
was a statistically significant positive correlation between
HOMA-IR and HBA1c (R=0.321; P<0.001), significant negative
correlation between EGF and HOMA-IR (R=-0.14; P=0.03), negative
correlation between EGF and HbA1c, (R=-0.248,
P<0.001) and a negative correlation between EGF and FBS
(R=-0.242, P<0.001) (Fig.
3).
Discussion
Despite the scientific advances in the management of
T2DM, it remains a major threat to public health globally due to
its epidemic nature and its effect on the wellbeing of the patients
(17,18). It is well known that T2DM increases
the risk of developing various health problems such as
cardiovascular diseases, dyslipidemia, neuropathy, loss of vision,
nephropathy, diabetic foot ulcers and leg amputations. The
hyperglycemic state and disturbed endocrine milieu are usually
associated with increased serum levels of various inflammatory
markers and growth factors, which are considered to mediate these
diabetic complications (19,20).
Moreover, T2DM is considered as a progressive disease, that can
lead over time to irreversible complications due to chronic
hyperglycemia, oxidative stress, metabolic derangements and
glucolipotoxicity (21,22).
HbA1c, which reflects the cumulative
glycemic history of the preceding 2-3 months, is considered as an
indicator of overall glycemic control and the potential long-term
diabetic complications. Several studies reported increasing loss of
glycemic control over time in patients with T2DM, despite the use
of various glucose-lowering medications such as metformin and
sulfonylureas (10,23,24).
Therefore, regular follow up of the patients, adopting an active
lifestyle and exercise to maintain adequate glycemic control in
T2DM is crucial to reduce the mortality and morbidity of
diabetes.
The association between serum levels of inflammatory
markers and the glycemic state in T2DM was not previously
investigated in diabetic patients in Jordan. In the current study,
the role of glycemic control on the relative abundance of
inflammatory markers and growth factors was investigated in
patients with T2DM sub-grouped into age-sex-, and BMI-matched
controlled diabetic group (HbA1c ≤7%) and uncontrolled
diabetic group (HbA1c >7%) using an observational
case-control study design. It was found that patients with
uncontrolled T2DM had significantly lower levels of serum EGF
compared with patients with controlled T2DM. Moreover, patients
with uncontrolled T2DM had significantly higher levels of FBS,
serum triglycerides, serum insulin, HOMA-IR and a slight increase
in GRO-α, compared with patients with controlled T2DM. Furthermore,
the binary logistic regression demonstrated that higher HOMA-IR
scores and lower EGF levels predicted an increased likelihood of
being an uncontrolled diabetic.
The negative correlation between EGF and
HbA1c in these study subjects indicates that EGF may
exert direct effects or is involved in the regulation of glucose
homeostasis and overall glycemic control in the body. EGF, a small
transmembrane polypeptide secreted by a variety of tissues such as
the loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule in the kidney, salivary
glands and duodenum and the pancreas, is a potent mitogen and
regulator of a wide range of cellular processes (25,26).
After binding to its receptor (EGFR), a member of the tyrosine
kinase receptor superfamily, it activates various signaling
pathways that regulate cellular proliferation, differentiation,
secretion and apoptosis. EGFR activation results in the activation
of phosphatidylinositol pathway through the activation of protein
kinase C and inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate [Ins(1,4,5)P3] as
well as by increasing the intracellular cytoplasmic calcium
concentration (27).
In fact, EGF is proposed to have a role in the
development of the pancreas, pancreatic β cells regeneration,
insulin and glucagon secretion and glucose homeostasis (28). Moreover, EGFR is expressed
throughout the human fetal pancreas, and its absence in mice
resulted in abnormal pancreatic islets development (14). Additionally, it has been shown that
EGF has a vital role in generating β-cells, regulation of their
insulin content, and maintenance of their mass through stimulation
of the anti-apoptotic protein survivin (29,30).
Moreover, studies have identified that EGF acts as secretagogue
that lowers plasma glucose levels in normal and diabetic mice via a
Ca2+ influx-and PLD2-dependent mechanism by regulation
of glucose transporters' activity and expression (13). Interestingly, EGF deficiency is
associated with diabetes mellitus in animals, where EGF or EGFR
levels are decreased in various organs or fluids, such as the
liver, the submandibular gland, plasma and milk (31). Furthermore, reduced EGF levels are
associated with chronicity and severity of diabetic foot ulcers,
therefore topical and intralesional EGF administration have been
implemented to improve and speed ulcer healing (32,33).
Previous research showed that EGF A61G polymorphism
(rs4444903) is a genetic variation associated with various types of
cancer (34). This single
nucleotide change shows significant differences in frequency across
ethnic groups (35). Interestingly,
research by Trimal et al (36) revealed that EGF A61G gene single
nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) was associated with increased risk of
developing T2DM in Indian population, and low EGF mRNA expression
in T2DM when compared with healthy controls. The aforementioned
study demonstrated that individuals with the A/G genotype have a
substantially higher risk (~4-fold) of developing T2DM compared
with those with the G/G genotype. The study also found that the ‘A’
allele was more common in patients with T2DM than in healthy
controls, suggesting it increases the risk of T2DM by 1.91-fold
compared with the ‘G’ allele. Additionally, both AG and AA
genotypes were linked to notably reduced EGF mRNA expression levels
when compared with the GG genotype (36). Furthermore, reduced concentrations
of EGF have been observed in other conditions such as diabetic
nephropathy, IgA nephropathy, adult polycystic kidney disease and
children with chronic renal failure (37).
EGF's actions extend to diverse molecular and
biochemical pathways at both local and systemic levels such as
neural maturation, myelination, immunomodulation, inhibition of
inflammatory mediators, reduction-oxidation balance, decreased
toxic glycation products, and intestinal development and barrier
function through regulation of tight junction protein expression,
autophagy, and apoptosis of epithelial cells (38-40).
Kawaguchi et al (41) reported a significant positive
correlation between urinary EGF excretion and HbA1c
levels in diabetic patients with inadequate glycemic control when
the HbA1c level is >8%, and lack of correlation in
these parameters when the HbA1c is <8%, possibly due
to increased glomerular filtration rate due to hyperglycemia. On
the other hand, previous studies in diabetic patients and animal
models of diabetes reported reduced urinary EGF expression and
secretion in case of diabetes reflecting diabetes-induced renal
tubular injury (42). Notably,
several studies demonstrated that urinary EGF (uEGF) levels
decrease across various kidney diseases, including diabetic
nephropathy. Importantly, uEGF has been validated as a predictor of
kidney damage in patients with type 2 diabetes and as a
non-invasive prognostic biomarker for chronic kidney disease even
in the absence of albuminuria (43). Therefore, it is plausible to
postulate that loss of glycemic control and elevated
HbA1c level reduces serum EGF levels possibly through
affecting renal EGF handling and expression, and this may lead to
further decline in β cell mass and further deterioration in glucose
homeostasis.
The positive correlation between HOMA-IR and
HbA1c in the present study is in accordance with
previous published studies, emphasizing the role of glycemic
control on the status of insulin resistance, which has been
postulated to be an important and independent risk factor for the
development of cardiovascular diseases, retinopathy and diabetic
foot (19,44). Although the glucose clamp technique
and HOMA-IR are the standard methods to measure insulin resistance,
the present study revealed that HbA1c can also be a
valuable assist to predict insulin resistance and potential
long-term complications (45-47).
The current study identified a significant negative correlation
between serum EGF levels and HbA1c, indicating that higher HbA1c
levels are associated with lower serum EGF levels, which may impair
wound healing and vascular health due to reduced cellular repair
and endothelial function. Additionally, a significant positive
correlation between HOMA-IR and HbA1c suggests that higher insulin
resistance correlates with poorer glycemic control, exacerbating
metabolic dysfunction and beta-cell stress. Moreover, it was
hypothesized that the observed 40% reduction in serum EGF levels in
patients with uncontrolled T2DM has significant biological
implications, particularly in terms of wound healing, vascular
health and metabolic regulation. The potential mechanisms behind
this finding include hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress,
chronic inflammation, disrupted insulin signaling, renal function
impairment and the impact of advanced glycation end products. These
findings highlight the impact of chronic hyperglycemia on growth
factor levels and the central role of insulin resistance in T2DM,
emphasizing the need for comprehensive management strategies that
address both glycemic control and insulin sensitivity to mitigate
complications and improve patient outcomes. Understanding these
mechanisms can provide insights into the pathophysiology of T2DM
and inform targeted therapeutic strategies to mitigate these
effects.
Despite previous studies indicating increased serum
levels of various cytokines and inflammatory markers in diabetic
patients, a lack of detectable cytokine expression of the majority
of inflammatory mediators such IL-1α, IL-1β and TNF-α was observed
in this cohort of patients, with both controlled and uncontrolled
T2DM (Table SI). Possible
explanations of this intriguing observation include the fact that
those patients were treated with metformin, which is reported to
have anti-inflammatory effects which could potentially normalize
interleukin and TNF-α levels across different patient groups
(48). This uniformity in
medication might have mitigated any expected variations in
inflammatory markers, thereby contributing to the observed lack of
significant differences. Additionally, the relatively moderate BMI
of the cohort, with an average ~30, along with the ethnic
background of the patients, may have further contributed to the
absence of significant variations in cytokine levels.
The present study has several limitations that
should be acknowledged. Firstly, the cross-sectional design
restricts our ability to establish causal relationships between
glycemic control, serum EGF levels and insulin resistance; while
the observed associations offer valuable insights, they do not
confirm causation. Additionally, data on some variables were not
collected, such as the duration of diabetes, stages of diabetic
nephropathy, or other comorbid conditions, which may have an
influence on the study outcomes. Moreover, the sample size may
limit the generalizability of the present findings to the broader
Jordanian population, especially across its diverse ethnic and
demographic groups. The results of the current study were adjusted
for key well-established demographic confounding factors known to
influence glycemic control and associated health outcomes. Focus
was addressed on these global confounders as they are among the
most significant determinants in this context. It is acknowledged
that other factors could also potentially influence the outcomes;
however, based on the present study design and the available data,
it was determined that age, sex and BMI were the most critical
factors to control for to ensure the validity of our findings.
Moreover, while the statistical methods were appropriate and
justified for the present study, it is acknowledged that they do
have limitations. Specifically, these methods may not fully capture
complex interactions between variables. Nonetheless, they were
effective in exploring the associations between glycemic control,
serum EGF levels and insulin resistance. Future studies with
longitudinal designs, larger sample sizes, and more comprehensive
data collection are necessary to address these limitations and
provide a clearer understanding of the complex interactions
involved in EGF's role in insulin resistance and glycemic control.
Such studies could provide valuable insights into how changes in
glycemic control over time impact EGF levels and, conversely, how
EGF levels might influence the progression of diabetes and its
complications. In addition, since multiple statistical tests were
conducted in the present study, it is important to acknowledge that
multiplicity could occur, increasing the risk of Type I errors, or
false positives. While the results were carefully interpreted, the
potential for inflated significance due to the number of
comparisons cannot be fully excluded. Future studies with larger
sample sizes and more stringent correction methods, such as
Bonferroni adjustment or false discovery rate control, are
recommended to confirm the findings and ensure the robustness of
the observed associations.
In conclusion, the present study identified a
significant negative association between serum EGF levels and
glycemic control in patients with T2DM, suggesting that EGF may
play a crucial role in the metabolic dysregulation observed in
T2DM. This finding offers new insights into the pathophysiology of
T2DM and underscores the potential use of serum EGF levels as a
novel biomarker for assessing and monitoring glycemic control in
clinical settings. Incorporating EGF into a panel of biomarkers
could help identify patients with T2DM at risk of developing poor
glycemic control, providing a more comprehensive approach to
disease management and facilitating personalized treatment
strategies. Furthermore, targeting EGF-related pathways may open up
new therapeutic avenues to improve glycemic control and optimize
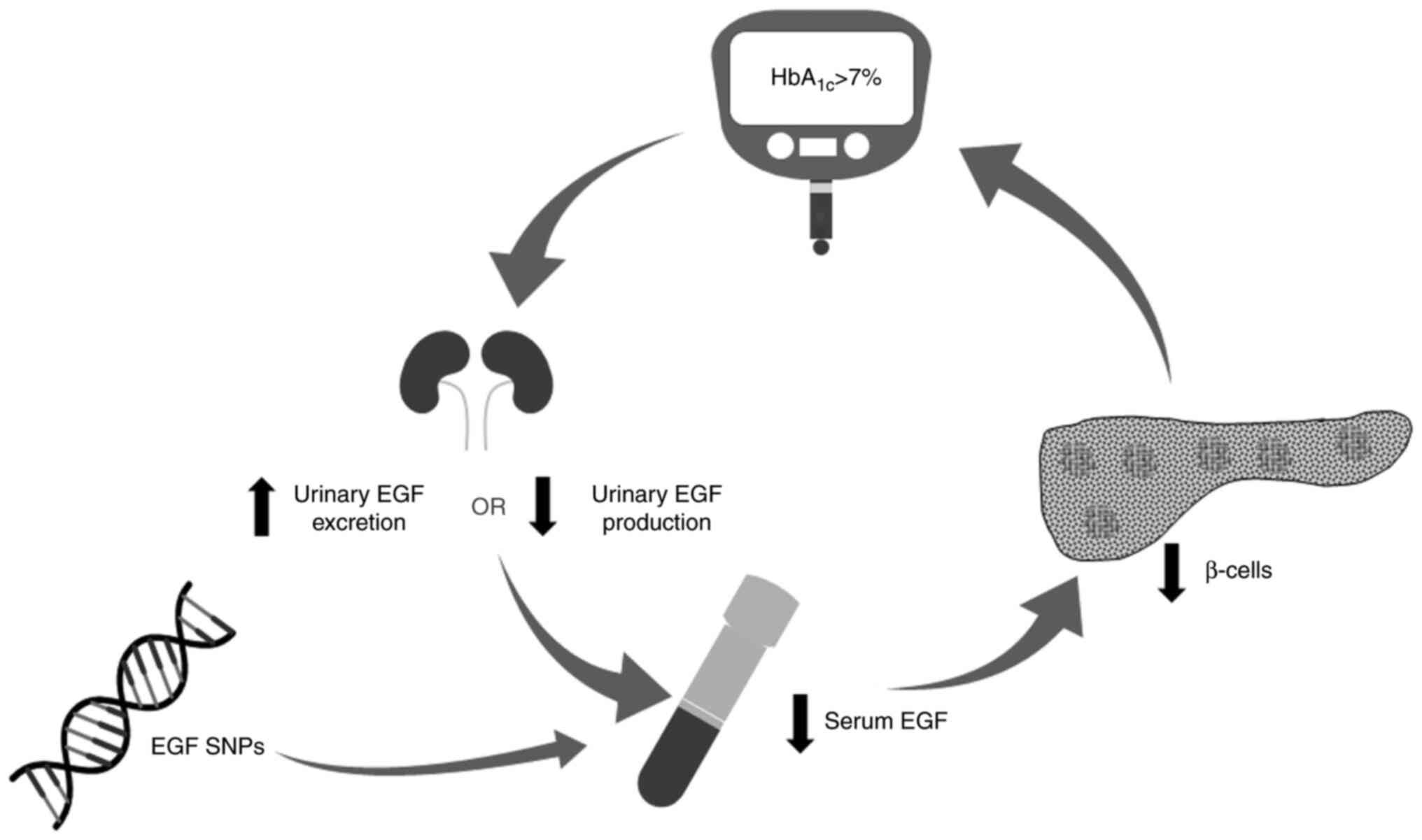
the overall management of T2DM. An integrative model of the
possible role of EGF in regulating insulin levels and glycemic
control is proposed in Fig. 4,
based on the findings from the present study and previous studies.
It is hypothesized that loss of glycemic control in patients with
T2DM decreases urinary EGF production or increases urinary EGF
excretion due to hyperfiltration through the kidneys, ultimately
leading to reduced serum EGF levels, which in turn causes further
deterioration of β-cell function and insulin secretion.
Furthermore, variation in the genetic makeup of the patients such
as a SNPs in EGF gene may lead to reduced EGF levels. It is
acknowledged that there is currently limited epidemiological data
on EGF SNPs within the Jordanian population. As a result, any
comparison between Jordanian and other populations, such as Indian
individuals, carries a degree of speculation. The outcomes of the
present study emphasize the importance of recognizing individuals
with uncontrolled T2DM lies in the fact that early intervention may
delay or prevent the progression of the disease and development of
complications.
Supplementary Material
Serum levels of IL-1α, IL-1β and TNF-α
in the controlled and uncontrolled patients with T2DM.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: The present study was supported by the Deanship of
Research at Jordan University of Science and Technology (grant no.
20180162).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
AAD performed experimental design, acquired funding
and wrote the manuscript. MAA and OA performed experimental design
and data analysis. RAS conducted statistical analysis and wrote the
manuscript. MA wrote the manuscript and performed data analysis. MK
collected data. AK performed experimental design and interpretation
of the data. AAD and OA confirm the authenticity of all the raw
data. All authors read and approved the final version of the
manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual
participants included in the study. All procedures performed in
studies involving human participants were in accordance with the
ethical standards of Jordan University of Science and Technology
and King Abdullah University Hospital Institutional Review Board
(approval no. 7/114/2018; Irbid Jordan), and with the 1964 Helsinki
Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical
standards.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Use of artificial intelligence tools
During the preparation of this work, artificial
intelligence tools were used to improve the readability and
language of the manuscript or to generate images, and subsequently,
the authors revised and edited the content produced by the
artificial intelligence tools as necessary, taking full
responsibility for the ultimate content of the present
manuscript.
References
|
1
|
International Diabetes Federation. IDF
Diabetes Atlas, 10th edition. Brussels, Belgium: 2021. Available
at: https://www.diabetesatlas.org.
|
|
2
|
Awad SF, Huangfu P, Dargham SR, Ajlouni K,
Batieha A, Khader YS, Critchley JA and Abu-Raddad LJ:
Characterizing the type 2 diabetes mellitus epidemic in Jordan up
to 2050. Sci Rep. 10(21001)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kahn SE, Cooper ME and Del Prato S:
Pathophysiology and treatment of type 2 diabetes: Perspectives on
the past, present, and future. Lancet. 383:1068–1083.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tomic D, Shaw JE and Magliano DJ: The
burden and risks of emerging complications of diabetes mellitus.
Nat Rev Endocrinol. 18:525–539. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Trikkalinou A, Papazafiropoulou AK and
Melidonis A: Type 2 diabetes and quality of life. World J Diabetes.
8:120–129. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Aschner P: New IDF clinical practice
recommendations for managing type 2 diabetes in primary care.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 132:169–170. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
American Diabetes Association. 6. Glycemic
targets: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care.
43 (Suppl 1):S66–S76. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Fiagbe J, Bosoka S, Opong J, Takramah W,
Axame WK, Owusu R, Parbey PA, Adjuik M, Tarkang E and Kweku M:
Prevalence of controlled and uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and
associated factors of controlled diabetes among diabetic adults in
the hohoe municipality of Ghana. Diabetes Manag. 7:343–354.
2017.
|
|
9
|
Siddiqui FJ, Avan BI, Mahmud S, Nanan DJ,
Jabbar A and Assam PN: Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus: Prevalence
and risk factors among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus in an
Urban District of Karachi, Pakistan. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
107:148–156. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cook MN, Girman CJ, Stein PP, Alexander CM
and Holman RR: Glycemic control continues to deteriorate after
sulfonylureas are added to metformin among patients with type 2
diabetes. Diabetes Care. 28:995–1000. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Mirza S, Hossain M, Mathews C, Martinez P,
Pino P, Gay JL, Rentfro A, McCormick JB and Fisher-Hoch SP: Type
2-diabetes is associated with elevated levels of TNF-alpha, IL-6
and adiponectin and low levels of leptin in a population of Mexican
Americans: A cross-sectional study. Cytokine. 57:136–142.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rohm TV, Meier DT, Olefsky JM and Donath
MY: Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders.
Immunity. 55:31–55. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lee HY, Yea K, Kim J, Lee BD, Chae YC, Kim
HS, Lee DW, Kim SH, Cho JH, Jin CJ, et al: Epidermal growth factor
increases insulin secretion and lowers blood glucose in diabetic
mice. J Cell Mol Med. 12:1593–1604. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Song Z, Fusco J, Zimmerman R, Fischbach S,
Chen C, Ricks DM, Prasadan K, Shiota C, Xiao X and Gittes GK:
Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling regulates β cell
proliferation in adult mice. J Biol Chem. 291:22630–22637.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Warzecha Z, Dembiński A, Konturek PC,
Ceranowicz P and Konturek SJ: Epidermal growth factor protects
against pancreatic damage in cerulein-induced pancreatitis.
Digestion. 60:314–323. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ledeganck KJ, den Brinker M, Peeters E,
Verschueren A, De Winter BY, France A, Dotremont H and Trouet D:
The next generation: Urinary epidermal growth factor is associated
with an early decline in kidney function in children and
adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
178(108945)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M,
Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, Stein C, Basit A, Chan JCN, Mbanya JC, et
al: IDF diabetes atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes
prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes
Res Clin Pract. 183(109119)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang J, Lin C, Jin S, Wang H, Wang Y, Du
X, Hutchinson MR, Zhao H, Fang L and Wang X: The pharmacology and
therapeutic role of cannabidiol in diabetes. Exploration (Beijing).
3(20230047)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Forbes JM and Cooper ME: Mechanisms of
diabetic complications. Physiol Rev. 93:137–188. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cheng HT, Xu X, Lim PS and Hung KY:
Worldwide epidemiology of diabetes-related end-stage renal disease,
2000-2015. Diabetes Care. 44:89–97. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Galindo RJ, Trujillo JM, Low Wang CC and
McCoy RG: Advances in the management of type 2 diabetes in adults.
BMJ Med. 2(e000372)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sun YM, Qu W, Liao JB, Chen L, Cao YJ and
Li HL: Jiangtangjing ameliorates type 2 diabetes through effects on
the gut microbiota and cAMP/PKA pathway. Tradit Med Res.
7(7)2022.
|
|
23
|
Riedel AA, Heien H, Wogen J and
Plauschinat CA: Loss of glycemic control in patients with type 2
diabetes mellitus who were receiving initial metformin,
sulfonylurea, or thiazolidinedione monotherapy. Pharmacotherapy.
27:1102–1110. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Boye KS, Lage MJ and Kiljański J: Time to
failure on oral glucose-lowering agents for patients with type 2
diabetes: A retrospective cohort study. Diabetes Ther.
12:1463–1474. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Meybosch S, De Monie A, Anné C,
Bruyndonckx L, Jürgens A, De Winter BY, Trouet D and Ledeganck KJ:
Epidermal growth factor and its influencing variables in healthy
children and adults. PLoS One. 14(e0211212)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Isaka Y: Epidermal growth factor as a
prognostic biomarker in chronic kidney diseases. Ann Transl Med. 4
(Suppl 1)(S62)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Roskoski R Jr: The ErbB/HER family of
protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Pharmacol Res. 79:34–74.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Jansen C, Lundquist I, Salehi A, Axelson J
and Ohlsson B: Does epidermal growth factor participate in the
regulation of glucose, insulin and glucagon levels? Eur Surg Res.
38:377–384. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Baeyens L, De Breuck S, Lardon J, Mfopou
JK, Rooman I and Bouwens L: In vitro generation of
insulin-producing beta cells from adult exocrine pancreatic cells.
Diabetologia. 48:49–57. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang H, Gambosova K, Cooper ZA, Holloway
MP, Kassai A, Izquierdo D, Cleveland K, Boney CM and Altura RA: EGF
regulates survivin stability through the Raf-1/ERK pathway in
insulin-secreting pancreatic β-cells. BMC Mol Biol.
11(66)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kasayama S, Ohba Y and Oka T: Epidermal
growth factor deficiency associated with diabetes mellitus. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 86:7644–7648. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Armstrong DG, Boulton AJM and Bus SA:
Diabetic foot ulcers and their recurrence. N Engl J Med.
376:2367–2375. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wu X, He W, Mu X, Liu Y, Deng J, Liu Y and
Nie X: Macrophage polarization in diabetic wound healing. Burns
Trauma. 10(tkac051)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Araújo AP, Ribeiro R, Pereira D, Pinto D,
Sousa B, Catarino R and Medeiros R: Exp Biol Med. (Maywood).
234:241–245. 2009.
|
|
35
|
Cacina C, Arikan S, Düzköylü Y, Doğan MB,
Okay E, Turan S, Yaylim I and Isbir T: Analyses of EGF A61G gene
variation and serum EGF level on gastric cancer susceptibility and
clinicopathological parameters. Anticancer Res. 35:2709–2713.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Trimal K, Shah T, Joshi K and Mulla G:
Association of EGF A61G polymorphism and EGF expression with type 2
diabetes mellitus in Indian population. Gene Rep.
15(100384)2019.
|
|
37
|
Ju W, Nair V, Smith S, Zhu L, Shedden K,
Song PXK, Mariani LH, Eichinger FH, Berthier CC, Randolph A, et al:
Tissue transcriptome-driven identification of epidermal growth
factor as a chronic kidney disease biomarker. Sci Transl Med.
7(316ra193)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wong RW and Guillaud L: The role of
epidermal growth factor and its receptors in mammalian CNS.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:147–156. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jung N, Kong T, Yu Y, Park H, Lee E, Yoo
S, Baek S, Lee S and Kang KS: Immunomodulatory effect of epidermal
growth factor secreted by human umbilical cord blood-derived
mesenchymal stem cells on atopic dermatitis. Int J Stem Cells.
15:311–323. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Tang X, Liu H, Yang S, Li Z, Zhong J and
Fang R: Epidermal growth factor and intestinal barrier function.
Mediators Inflamm. 2016(1927348)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kawaguchi M, Kamiya Y, Ito J, Fujii T,
Hayakawa F, Sakuma N and Fujinami T: Excretion of urinary epidermal
growth factor in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Life Sci.
52:1181–1186. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Akhtar S and Benter IF: The role of
epidermal growth factor receptor in diabetes-induced cardiac
dysfunction. Bioimpacts. 3:5–9. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Cortvrindt C, Speeckaert R, Delanghe JR
and Speeckaert MM: Urinary epidermal growth factor: A promising
‘next generation’ biomarker in kidney disease. Am J Nephrol.
53:372–387. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Borai A, Livingstone C, Abdelaal F,
Bawazeer A, Keti V and Ferns G: The relationship between
glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) and measures of insulin resistance
across a range of glucose tolerance. Scand J Clin Lab Invest.
71:168–172. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Liu Y, Yu Q, Luo X, Ye L, Yang L and Cui
Y: A microtube-based wearable closed-loop minisystem for diabetes
management. Research (Wash D C). 2022(9870637)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Liu Y, Wang H, Wang Y and Xue LX: Annual
advances of integrative pharmacology in 2021. Tradit Med Re.
7(57)2022.
|
|
47
|
Fu LH, Qi C, Sun T, Huang K, Lin J and
Huang P: Glucose oxidase-instructed biomineralization of
calcium-based biomaterials for biomedical applications. Exploration
(Beijing). 3(20210110)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Kristófi R and Eriksson JW: Metformin as
an anti-inflammatory agent: A short review. J Endocrinol.
251:R11–R22. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|