Currently, both depression and coronary heart
disease (CHD) are among the most prevalent and serious global
health issues (1). Depression is a
common mental illness that has a profound impact on physical
health, and often causes considerable suffering to patients
(2). The World Health Organization
estimates that ~3.8% of the global population suffers from this
disease (3). A lifetime prevalence
of depression was retrospectively reported through community
epidemiological surveys of adults aged between 18 and 74 years in
28 countries, and an average incidence rate of 10.6% was also
reported, comparing across various countries (4). In a prospective epidemiological study,
the findings revealed that the lifetime prevalence of major
depression ranges from 30-40% (5).
The COVID-19 pandemic that broke out around the world in 2020 led
to a surge in the incidence of mental health disorders worldwide,
with reported cases of major depression increasing by 28%, and
anxiety disorders increasing by 26% (6). In addition, the number of individuals
with depression surged by 53 million, reflecting a 27.6%
increase.
CHD, caused by an accumulation of atherosclerotic
plaques in the coronary arteries, is one of the leading causes of
mortality and disability in humans (7). In 2019, cardiovascular diseases were
responsible for ~17.9 million deaths globally, also accounting for
~32% of all cases of mortality (8).
CHD alone was responsible for ~8.5 million deaths, accounting for
almost half of all cardiovascular-associated fatalities (8). The global incidence of CHD was ~172
million in 2015, with projections estimating a rise to 234 million
cases by 2030(6). In the United
States, CHD results in an estimated 610,000 deaths annually,
accounting for ~25% of all deaths (9). Furthermore, CHD imposes a considerable
financial burden through both direct medical expenses and indirect
costs; for example, in 2010, the expenses directly associated with
CHD treatment in the United States amounted to approximately US
$108 billion, and projections suggest this figure will rise to US
$137 billion by 2030(10).
Depression serves as a risk factor leading to the
increased prevalence of various diseases (11). A systematic review of global
qualitative research on depression has revealed a significant link
between the condition and a broad spectrum of physical illnesses,
encompassing cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, obesity,
hypertension, chronic respiratory disorders and persistent pain
syndromes (12). Meta-analyses of
longitudinal studies have shown that depression consistently
forecasts the initial onset of conditions such as coronary artery
disease, stroke, diabetes and obesity (13). From a biological perspective,
various mechanisms, including the inflammation hypothesis (14), telomere theory (15), mitochondrial dysfunction (16), gut-brain axis theory (17), and epigenetic mechanisms, which also
encompass neuroendocrine-immune interactions (18), have been proposed to explain the
potential association between depression and these diseases.
Extensive evidence from cohort studies and meta-analyses points to
a robust association between depression and CHD, highlighting the
significant interrelationship between these conditions (19-21).
Depression is acknowledged not only as a standalone risk factor for
CHD, but also as a major contributor towards an increased risk of
adverse cardiovascular events in affected individuals (22). An analysis involving 22 cohort
studies found that depression increases the risk of CHD onset by
approximately 1.5 to 2 times, with prevalence rates of depression
among CHD patients estimated at 20-30% (22).
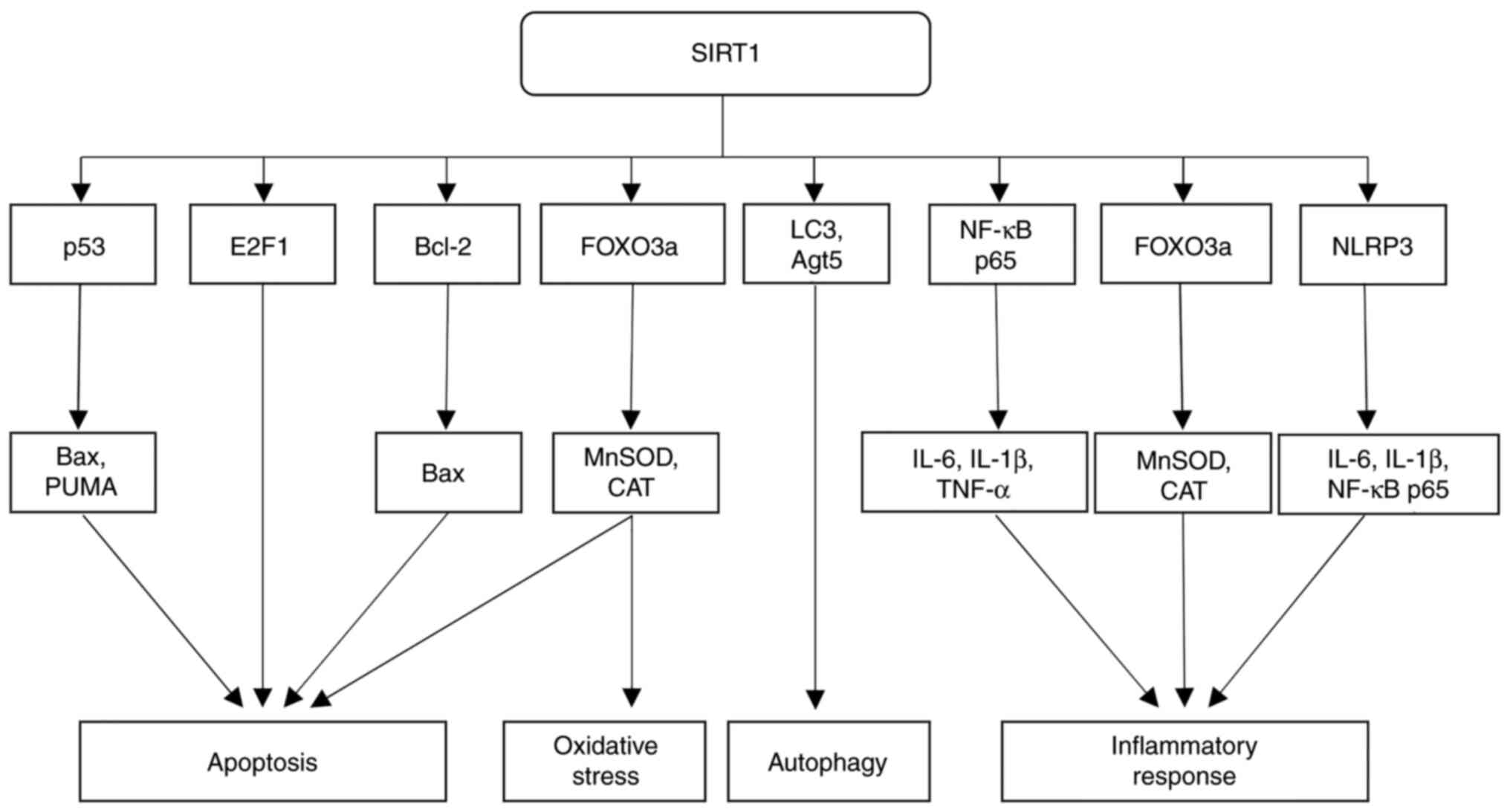
Beyond its influence on p53, SIRT1 also regulates
the activity of the forkhead box O (FOXO) transcription factor
family, the members of which are critical in the cellular response
to oxidative stress, senescence and apoptosis (35). SIRT1-mediated deacetylation
activates the FOXO3a transcription factor, thereby increasing the
expression of protective genes, such as manganese superoxide
dismutase (MnSOD) and catalase (CAT), which guard cells against
oxidative stress (36). This action
not only supports cell survival, but also leads to the inhibition
of apoptosis through the reduction of oxidative damage. In a study
wherein a mouse model of myocardial infarction was established,
through upregulation of SIRT1 expression, the deacetylation of
FOXO3a in cardiomyocytes was found to be increased, thereby
strengthening the cell defense mechanism and reducing cardiomyocyte
apoptosis during myocardial infarction. On the other hand, under
certain conditions, the upregulation of SIRT1 expression may also
inhibit the pro-apoptotic effects of FOXO (37). Through the balance of signals for
survival and apoptosis, SIRT1 ensures that cells can manage
oxidative stress without undergoing excessive apoptosis, a process
that is particularly relevant in aging and neurodegenerative
diseases (38).
The regulation of apoptosis by SIRT1, however, is
highly context-dependent, as it can also promote cell death under
specific conditions, especially in cancerous or damaged cells
(39). A previously published study
using a rat model of diabetic retinopathy revealed that SIRT1 is
able to downregulate anti-apoptotic proteins such as Bcl-2, and
increase the expression of pro-apoptotic factors such as Bax,
thereby promoting irreversible damage caused to, or the apoptosis
of, retinal cells (40). This dual
functionality of SIRT1 is critical for maintaining cellular
homeostasis, ensuring that healthy cells are preserved while they
are damaged, or that potentially cancerous cells are eliminated.
The complexity of the role of SIRT1 has been highlighted in a
number of reviews, showing that its involvement in apoptosis is
tightly regulated by the cellular environment and specific
signaling pathways, allowing for a balance between cell
proliferation and death (41).
SIRT1 fulfills another important role in influencing
the cell cycle, which is crucial for regulating cell proliferation.
In this regard, it interacts with various cyclins to promote the
progression of the cell cycle (42). The transcription factor E2F
transcription factor 1 (E2F1) is an important transcription factor
that has been shown to regulate the cell cycle, cell proliferation
and apoptosis. SIRT1 activates E2F1 through deacetylation, which
helps to promote the transition of cells from the G1 to
S phase, facilitating cell proliferation, especially in tumor cells
(43). This pathway is particularly
relevant in stem cells and cancer cells, where rapid cell division
is vital. However, a study on mouse macrophages showed that
excessive activation of SIRT1 may lead to carcinogenesis, as
unregulated cell proliferation led to tumor growth (44). This finding highlighted the
importance of carefully regulating SIRT1 activity in diverse
cellular environments.
SIRT1 also exerts a regulatory role in autophagy,
influencing the clearance of damaged organelles and proteins via
the deacetylation of key proteins, which is crucial for maintaining
cellular stress responses and the balance of energy metabolism
(45). Autophagy supports cell
survival under stress by removing damaged components and providing
essential nutrients (46). SIRT1
stimulates autophagy by deacetylating key autophagy-associated
proteins, including microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light
chain 3 (LC3) and autophagy protein 5 (Atg5), which leads to
enhanced autophagic activity (47).
In turn, autophagy is able to prevent apoptosis by eliminating
dysfunctional mitochondria, which are major sources of
pro-apoptotic signals (48).
However, when the autophagic process is insufficient to restore
cellular homeostasis, SIRT1 may shift its role towards promoting
apoptosis, especially in cells that are beyond repair (49). This dynamic interplay between
autophagy and apoptosis is fundamental to the function of SIRT1 in
regulating the cell fate, ensuring the survival of healthy cells,
while eliminating damaged ones (50).
SIRT1 has a multifaceted role in the regulation of
inflammation, which is mediated through its interactions with
several key molecular pathways to maintain cellular homeostasis and
prevent chronic inflammation, serving as a contributing factor in
numerous diseases (51). In these
molecular pathways, SIRT1 inhibits chronic inflammation by
regulating the transcription factors nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and
FOXO3a, as well as through the reduction of oxidative stress
(27). These regulatory processes
are crucial in preventing chronic inflammatory states. A key
function of SIRT1 in inflammation control is the suppression of
pro-inflammatory cytokine transcription via the deacetylation of
NF-κB; specifically, its p65 subunit (52). The transcription factor NF-κB
fulfills a crucial role in regulating inflammation through the
regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis
factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β)
(53). Research on diabetic
nephropathy in mice has shown that SIRT1 deacetylates the p65
subunit of NF-κB, leading to a reduction in its transcriptional
activity and a mitigation of diabetic renal pathology (54). These functions have been validated
in various disease models, including metabolic and
neurodegenerative disorders, where inflammation is a key driver of
disease pathology (55,56). Through the inhibition of NF-κB,
SIRT1 effectively attenuates inflammatory responses, demonstrating
its critical role in inflammation regulation (57).
Apart from modulating NF-κB, SIRT1 helps to decrease
inflammation by minimizing oxidative stress (27). Via the deacetylation of FOXO3a,
SIRT1 enhances the expression of antioxidant enzymes, including
MnSOD and CAT, thereby reducing oxidative damage and, in turn,
inflammation (58). In a
macrophage-specific mouse model, the absence of SIRT1 was found to
promote the polarization of pro-inflammatory macrophages and to
regulate the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 (TIMP3)/ADAM17
pathway, thereby facilitating the development of atherosclerosis,
demonstrating that SIRT1 activation through FOXO3a may both enhance
the proportion of anti-inflammatory macrophages and reduce
inflammatory responses (59).
Moreover, SIRT1 has been shown to regulate inflammasome activity,
notably influencing the nucleotide-binding oligomerization
domain-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3)
inflammasome, which is critically involved in inflammatory
responses (60).
Overactivation of NLRP3 inflammasomes results in
chronic low-grade inflammation, thereby promoting the production of
the cytokines IL-1β and IL-18(60).
In the airways of these mice, SIRT1 mitigates inflammation via
deacetylating components of the NLRP3 inflammasome, which restricts
the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (61). This mechanism is crucial in
preventing chronic inflammation, which is a common factor in
diseases such as atherosclerosis and type 2 diabetes, further
highlighting the pivotal role of SIRT1 in controlling inflammatory
responses (62).
Additionally, the activation of SIRT1 has been shown
to lead to an improvement in insulin sensitivity in obesity models
through inhibiting inflammation via NF-κB signaling pathways
(63). In cardiovascular diseases,
the anti-inflammatory properties of SIRT1 have been shown to
contribute towards improving vascular function through the
reduction of the expression of adhesion molecules in endothelial
cells (64). In a study involving
the overexpression of SIRT1 in mice, it was found that activation
of SIRT1 in endothelial cells could mitigate vascular inflammation,
affording protection against vascular aging and atherosclerosis
(65). Consequently, SIRT1 is a
crucial factor both in terms of regulating apoptosis, and offering
resistance to oxidative stress, autophagy and inflammation
(Fig. 1).
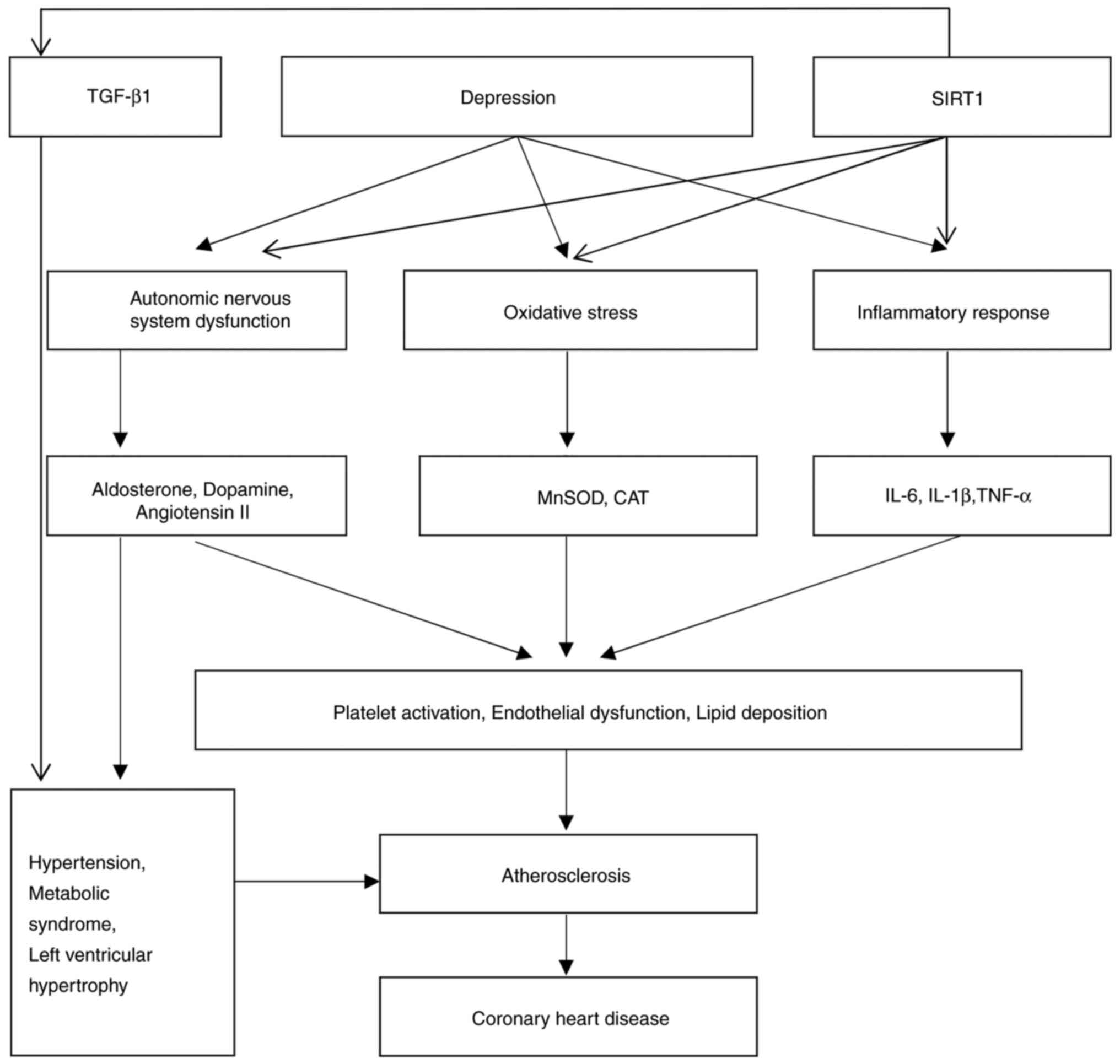
Depression, a common mood disorder, is marked by
prolonged sadness, diminished interest in activities, fatigue, poor
concentration and low self-esteem (66). Analyzing data from 22 cohort studies
involving over 500,000 individuals, researchers found that
depression has a substantial effect on both mental and physical
well-being, notably increasing the risk for CHD (67-69).
CHD is a disease caused by myocardial ischemia and hypoxia due to
coronary atherosclerosis, which, in turn, causes adverse
cardiovascular events, including angina pectoris and myocardial
infarction (70). A previous study
suggested that both acute and chronic stress disrupt the production
or activity of key neurotransmitters and hormones, including
noradrenaline, dopamine, serotonin, cortisol, aldosterone and
angiotensin II (71). These
disruptions may negatively influence mood, and contribute to
cardiovascular risk factors, such as high blood pressure, platelet
reactivity, endothelial dysfunction, diabetes and metabolic
syndrome, all of which may increase the likelihood of depression
(72). Additionally, these
biochemical imbalances cause alterations in immune function,
leading to an overproduction of cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6 and
TNF-α (73). A study based on
populations with CHD demonstrated that inflammation is a common
factor linking mood disorders and cardiovascular diseases,
potentially contributing to plaque formation and acute coronary
events (74). An additional study
suggested that shared genetic pathways across the neuroendocrine,
immune and inflammatory systems may underlie an increased risk of
both depression and CHD (21).
Brain regions involved in mood disorders and
cardiovascular regulation, particularly those associated with
stress and memory, have been shown to be altered in patients with
severe depression (75). A previous
study demonstrated that acute psychological stress reduces
baroreflex sensitivity, whereas asymmetric sympathetic signaling
from the brain to the heart may increase the risk of CHD (76). In human neuroimaging studies
analyzing the amygdala and arterial inflammation, it was found that
amygdala activity is able to independently predict cardiovascular
events, suggesting a link between emotional stress and
cardiovascular disease (77,78).
Another clinical study showed that individuals with depression face
a significantly higher CHD risk, with increased symptom severity
further elevating this risk (79).
Depression not only increases the likelihood of CHD, but also
increases the incidence of adverse cardiovascular events and
mortality among patients with CHD (80). Certain subtypes of depression, such
as new-onset depression following acute coronary syndrome,
refractory depression or depression with somatic symptoms, are more
likely to result in negative CHD outcomes and a diminished quality
of life (81). After adjusting for
factors such as functional limitations and clinical variables
(including stable angina and congestive heart failure),
improvements in depressive symptoms were found to be the strongest
predictors of improved health-associated quality of life at 1 year
(82,83). A large clinical study revealed that
depression independently predicts cardiovascular events in patients
with CHD, with the risk increasing alongside symptom severity.
Moreover, the mortality rate among patients with CHD who were
depressed was found to be more than double that of their
non-depressed counterparts (84).
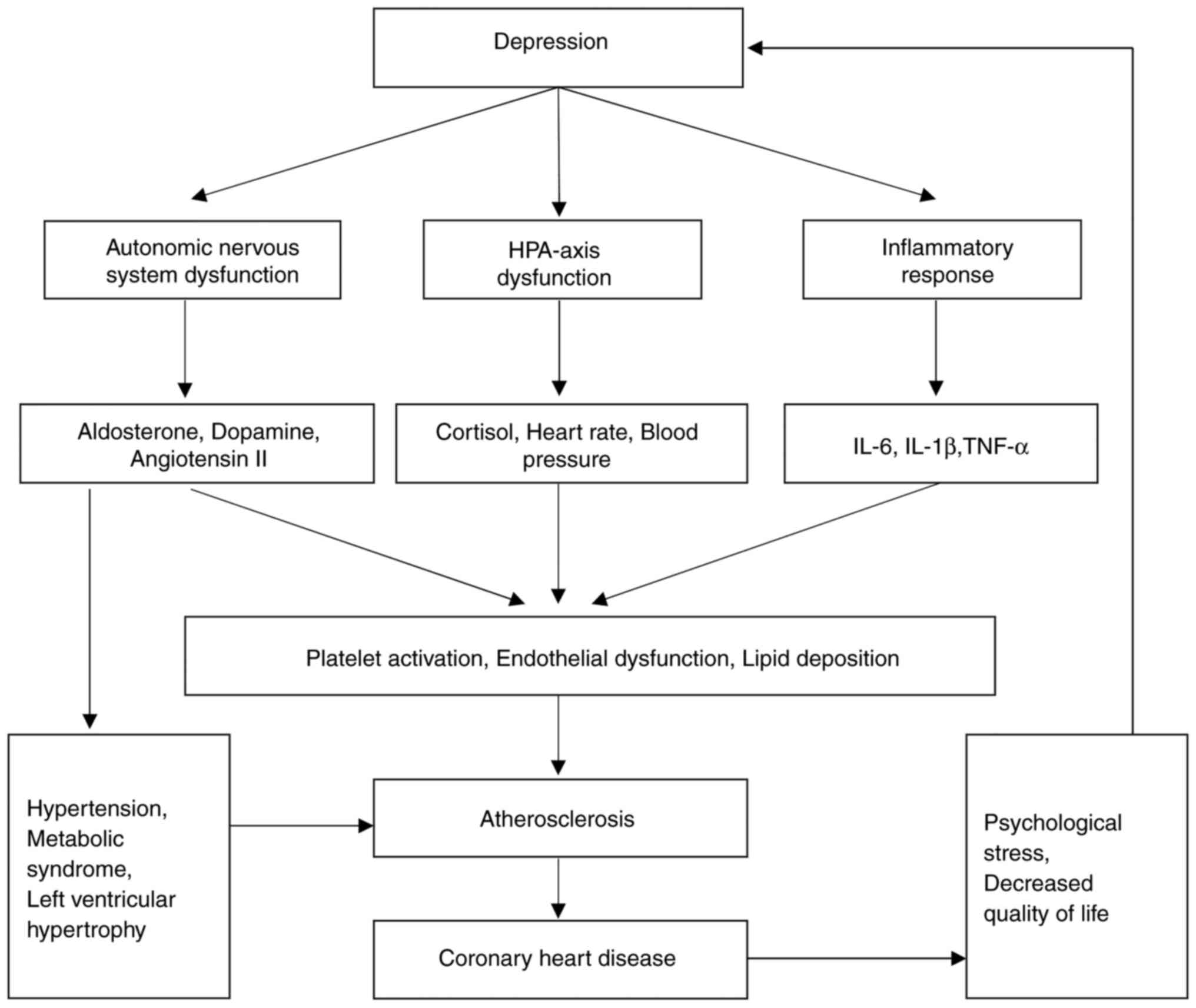
The mechanisms via which depression causes
atherosclerosis are multifaceted, although these mainly include
chronic psychological stress and the inflammatory response
(21). Depression has been shown to
be closely associated with chronic psychological stress, and this
condition is a major risk factor for atherosclerosis, which
comprises the thickening of artery walls due to the buildup of
plaque (85). A study encompassing
both animal and human studies revealed that chronic psychological
stress triggers numerous physiological shifts, including elevated
levels of stress hormones and heightened sympathetic nervous system
activity, largely driven by hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA)
axis activation (86). A clinical
study also revealed that prolonged psychological stress results in
increased cortisol levels, with resultant damage caused to vascular
endothelial cells, and other effects, including increasing vascular
wall permeability and fostering lipid accumulation in the vascular
walls, ultimately contributing to atherosclerosis (84). Persistent sympathetic nervous system
activation also leads to increases in heart rate and blood
pressure, which elevates cardiac workload and vascular wall stress,
factors that also contribute to the development of atherosclerosis
(87).
Low-grade chronic inflammation, which is common in
depressed patients, significantly contributes to atherosclerosis
onset and progression (88). High
levels of pro-inflammatory markers and oxidative stress drive this
inflammatory response (89). In
individuals with depression, markers such as C-reactive protein,
IL-6 and TNF-α are found at elevated levels (90). These inflammatory factors are able
to promote atherosclerosis through various pathways (91). Not only in human studies, but also
in animal models, inflammatory factors have been shown to activate
vascular endothelial cells, cause an upregulation of the expression
of adhesion molecules, and facilitate the adhesion of monocytes to
the vascular wall and their subsequent transformation into
macrophages, which subsequently further engulf lipids to form foam
cells, a process that is pivotal in the formation of
atherosclerotic plaques (92).
Additionally, depression has been shown to be closely associated
with oxidative stress, which not only causes direct damage to
vascular endothelial cells, but also triggers multiple inflammatory
pathways, further promoting the development of atherosclerosis
(92,93). Therefore, depression increases the
risk of CHD through multiple mechanisms (Fig. 2).
Depression is a multifaceted mental disorder, with
its causes rooted in biological, genetic and environmental factors
(94). A previous study utilizing a
mouse model of depression identified SIRT1 as performing a crucial
role in the development of depression (95). Another study also demonstrated that
SIRT1 affects neurogenesis, especially within areas of the brain
critical for emotional and cognitive processes, such as the
hippocampus and prefrontal cortex (96). Extensive studies in both animal and
human models have explored the molecular role of SIRT1 in mood
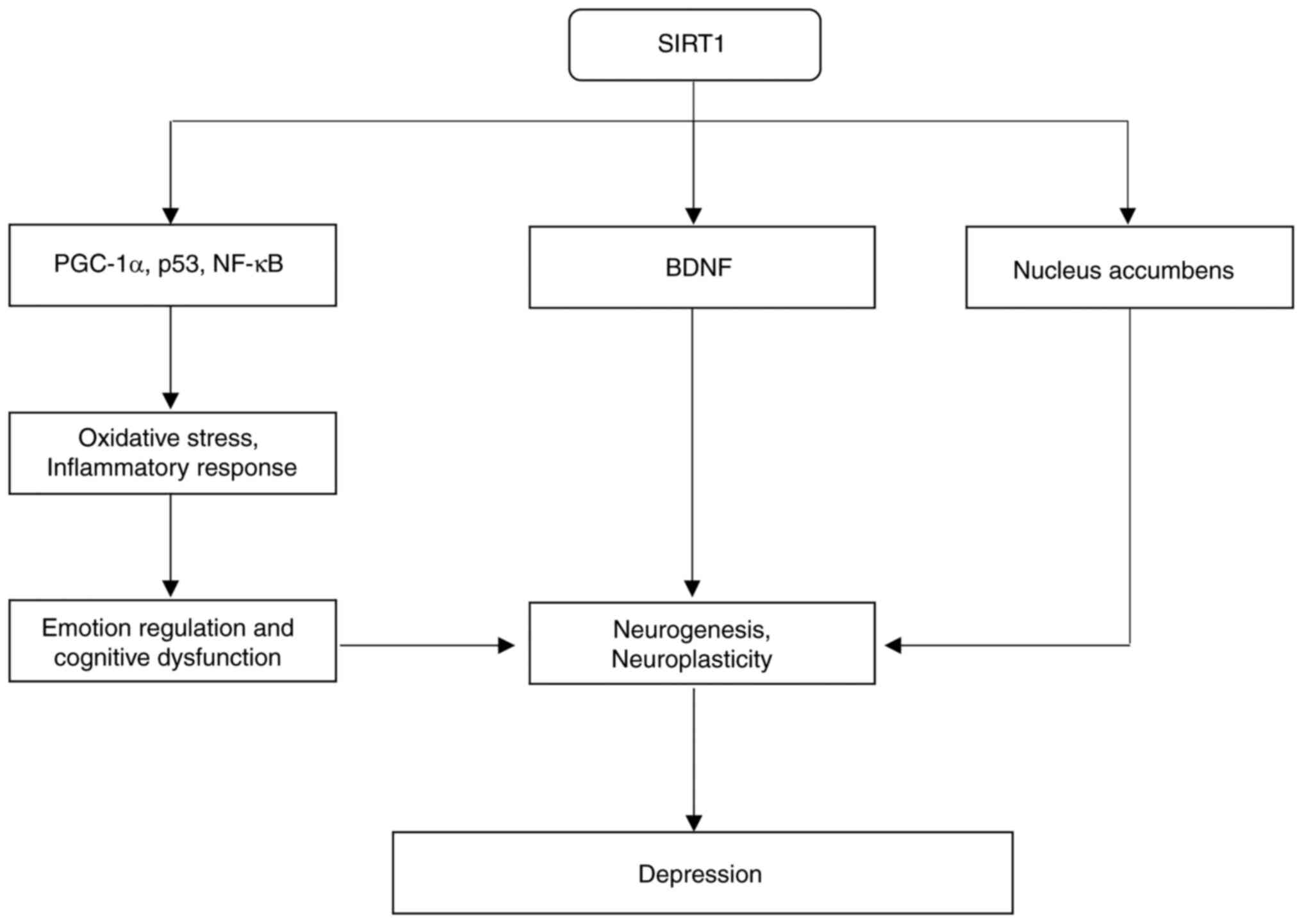
disorders (97,98). SIRT1 has been shown to regulate
multiple transcription factors, including peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1-α (PGC-1α), p53 and
NF-κB, which have crucial roles in modulating processes such as
oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis (95). These pathways are often dysregulated
in patients with depression, suggesting that SIRT1 has a pivotal
role in the pathogenesis of the disorder (99). Both SIRT1 and SIRT2 have been
implicated in regulating inflammatory responses within the brain,
indicating their potential as therapeutic targets for
anti-inflammatory treatments for depression (100). Via reduction of neuroinflammation,
SIRT1 may alleviate the biological stress that exacerbates
depressive symptoms (101).
In animal models of depression, SIRT1 expression in
hippocampal tissue has been found to be markedly reduced (102). The hippocampus, a brain region
essential for learning and memory, is often affected in the state
of depression, and its dysfunction is one of the primary
pathological features of the disorder (103). A previously published study on
hippocampal neuroplasticity in patients with depression showed that
low expression of SIRT1 may impair neuroplasticity, neurogenesis
and synaptic function, thereby exacerbating depressive symptoms
(104). Similarly, in depressive
mouse models, decreased SIRT1 expression was found to be associated
with reduced neurogenesis in the hippocampus (105). Activation of SIRT1 was also shown
to enhance the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem
cells, thereby increasing the number of new neurons and alleviating
depressive symptoms (106). In
rats subjected to chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS),
hippocampal SIRT1 expression was shown to be significantly reduced,
which correlated with depressive-like behaviors (107). In the CUMS mouse model,
overexpression of SIRT1 in the hippocampus was found to
significantly mitigate depressive-like behaviors, emphasizing the
role of SIRT1 in depression (108).
The potential antidepressant effects of SIRT1
activation have been demonstrated in numerous studies. Research in
CUMS mouse models has shown that activating SIRT1 improves neuronal
function, enhancing neuroplasticity and promoting neurogenesis,
thereby producing antidepressant-like effects (109). SIRT1 modulates the expression of
various genes through deacetylation, promoting synaptic plasticity
and the formation of functional synapses (110). In animal models of depression,
activation of SIRT1 has been shown to increase the expression of
brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein critical for
neuronal survival, synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis (111). Elevated BDNF levels were
demonstrated to improve hippocampal function and alleviate
depressive symptoms (112).
In a different study, researchers assessed
postpartum depressive-like behaviors in a depression model of
ovariectomized mice, and found that resveratrol, a SIRT1 activator,
could alleviate depressive-like behaviors in mice, drawing
significant attention to its potential role as a therapeutic agent
for treating depression (113).
Resveratrol, a natural polyphenolic compound found in fruit such as
grapes, berries and peanuts, exhibits antioxidant,
anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties (114). In animal models of depression, the
antidepressant-like effects of resveratrol have been widely
confirmed (113). Through the
activation of SIRT1, resveratrol was shown to enhance
neuroplasticity and neurogenesis in the hippocampus, thereby
mitigating depressive-like behavior (115). In CUMS models, treatment with
resveratrol also led to a marked increase in SIRT1 expression, an
elevation in the level of BDNF, and the alleviation of depressive
symptoms (116). The proposed
mechanism is that resveratrol regulates various
depression-associated molecules and pathways through SIRT1-mediated
deacetylation (116). Furthermore,
resveratrol has an important role in a variety of neurological
diseases, including depression, via activation of AMP-activated
protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of cellular energy balance.
The activation of AMPK may not only affect the behavioral effects
of antidepressants, but it may also have a role in the occurrence
of depression by regulating the expression or function of
glucocorticoids (117).
SIRT1 significantly influences depression by acting
on the nucleus accumbens, a brain region crucial for motivation and
reward processing (118). The
regulation of this region mediated by SIRT1 is considered to
influence emotional regulation and depressive-like behaviors
(25). In animal models,
manipulating SIRT1 expression in the nucleus accumbens leads to
marked changes in anxiety- and depression-associated behaviors
(119). This underscores the
potential of SIRT1 as a molecular target for novel antidepressant
therapies, especially for patients experiencing symptoms such as
anhedonia or lack of motivation (119). Chronic stress is a major
depression risk factor, and SIRT1 is pivotal in modulating the
body's stress response (120). It
affects the body's response to stress by regulating glucocorticoid
receptors, which are essential for stress responses (121). In a CUMS mouse model, numerous
studies have identified that dysregulation of SIRT1 exacerbates
stress-associated depressive behaviors (122,123). In a study conducted on male mice
with depression, it was discovered that chronic stress leads to
downregulation of SIRT1 in the amygdala. Fluoxetine, a widely used
antidepressant, is able to reverse this downregulation and
ameliorate depressive-like behaviors, demonstrating that SIRT1 may
mediate the antidepressant effects of certain medications (124). In conclusion, SIRT1 regulates
oxidative stress, inflammation, neurogenesis and neuroplasticity,
influencing both the onset and prevention of depression (Fig. 3).
A study that employed an acute myocardial infarction
rat model highlighted the role of SIRT1 in mitigating inflammation,
oxidative stress and vascular dysfunction, which all act as
contributing factors in CHD and atherosclerosis (125). A cohort study on patients
post-coronary artery bypass graft surgery and after aortic valve
replacement revealed high expression levels of SIRT1 in endothelial
cells, vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and cardiomyocytes,
where it was found to confer protective benefits (126). Its function in maintaining
endothelial homeostasis is especially important, as endothelial
dysfunction is an early event in the development of atherosclerosis
(127). A previous in vivo
study with mice revealed that activating SIRT1 boosts the
production of nitric oxide (NO), reduces oxidative stress and
decreases inflammation, thereby improving endothelial function.
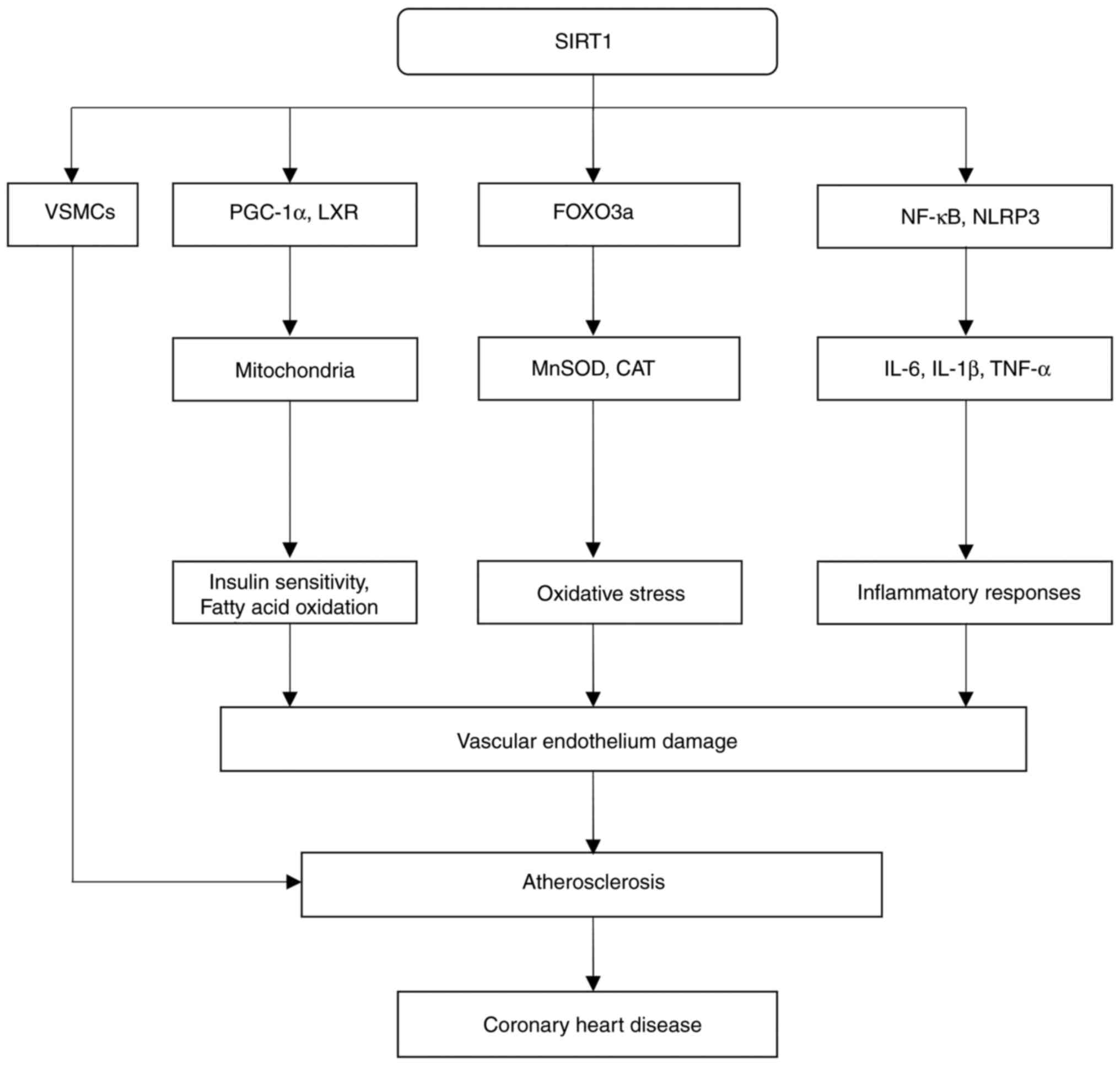
Additionally, SIRT1 protects against atherosclerosis by either
activating endothelial NO synthase or reducing NF-κB activity in
endothelial cells and macrophages (128).
These effects are crucial, as impaired NO
bioavailability and increased oxidative stress are characteristic
of endothelial dysfunction, and contribute to the progression of
atherosclerosis (129). A study
that investigated atherosclerosis using cultured human smooth
muscle cells showed that SIRT1 is able to reduce vascular wall
inflammation, a major contributor to atherosclerosis (130). In an in vitro cell culture
study, SIRT1 deacetylation was found to cause downregulation of
NF-κB, a central transcription factor in inflammatory responses,
which thereby reduced the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines,
including TNF-α and IL-6(131).
This anti-inflammatory action reduces the recruitment of immune
cells, such as monocytes and macrophages, to the arterial wall,
thereby limiting the formation of atherosclerotic plaques (132). Furthermore, moderate
overexpression of SIRT1 in mice has been shown to reduce oxidative
stress, thereby preventing lipid oxidation, which is a key step
both in terms of halting plaque formation and slowing the
progression of atherosclerosis (133).
Studies in both animals and human models have
underscored the importance of SIRT1 in lipid metabolism, directly
associating it with atherosclerosis prevention (134-136).
Experiments that analyzed SIRT1 expression in the rat hippocampus
showed that SIRT1 activates PGC-1α, a coactivator essential for
mitochondrial formation and fatty acid oxidation (137). Through the promotion of efficient
lipid utilization, SIRT1 was found to decrease the accumulation of
low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, a primary risk factor for
atherosclerosis, in the bloodstream (138). Moreover, a study on human U937
monocytes revealed that SIRT1 modulates liver X receptor (LXR)
activity, with LXRs having a key role in cholesterol clearance and
reverse transport, which are essential roles for cholesterol
removal from arterial plaques (139). The association between SIRT1 and
atherosclerosis has also been confirmed in both animal models and
human studies (140,141). SIRT1 activation has been shown to
reduce atherosclerotic plaque formation in mouse models of the
disease (142). Moreover, a
retrospective case-control study revealed an association between
gene variants of SIRT1 and a reduced risk of atherosclerotic
coronary artery disease, suggesting that the cardiovascular
protective role of SIRT1 may be genetically influenced (143). Additionally, in a rat model of
cardiac hypertrophy, another study found that activating SIRT1
using sirtuin activators such as resveratrol led to a reduction in
vascular inflammation, which caused a delay in the progression of
atherosclerosis (144).
In addition to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant
effects, SIRT1 has also been shown to have a crucial role in
regulating the proliferation and migration of VSMCs, processes that
are essential for neointimal hyperplasia and the stability of
atherosclerotic plaques (145). A
further study revealed that, in a mouse model with SIRT1
overexpression, SIRT1 helped to stabilize atherosclerotic plaques,
thereby reducing the risk of plaque rupture and subsequent
thrombotic events, such as myocardial infarction or stroke, through
inhibition of the proliferation of VSMCs and promotion of their
differentiation (146). Another
key aspect of the protective role of SIRT1 in the cardiovascular
system involves its interaction with metabolic pathways (147). SIRT1 has been shown to be able to
improve insulin sensitivity and to regulate glucose metabolism,
processes that are especially significant in metabolic diseases
such as type 2 diabetes, which is a known risk factor for CHD
(148). In diabetic patients,
SIRT1 activation was found to improve endothelial function, with a
mitigation of coronary atherosclerosis (149).
Furthermore, the cardioprotective effects of SIRT1
have been shown to extend beyond atherosclerosis; for example, it
has been shown to protect against cardiac hypertrophy, a common
complication in patients with hypertension and CHD (150). In a rat model of myocardial
hypertrophy, SIRT1 was found to regulate the hypertrophic response
of cardiomyocytes via inhibiting the transforming growth factor-β1
(TGF-β1)/p-Smad3 signaling pathway, which is implicated in cardiac
fibrosis and hypertrophy (144).
This anti-hypertrophic effect helps to preserve cardiac function
and to prevent heart failure, a frequent complication in CHD. In
conclusion, the available evidence suggests that SIRT1 exerts
protective effects against CHD by modulating the growth of VSMCs,
oxidative stress, lipid metabolism and inflammation (Fig. 4).
Studies in both animal models and humans have shown
that the role of SIRT1 in depression-induced CHD involves its
complex regulation of cardiovascular molecular pathways, including
oxidative stress, inflammation and metabolism (151). As part of the sirtuin family,
SIRT1 performs a key role in the cellular response to various forms
of stress, including emotional and psychological stressors, such as
depression (152). Extensive
longitudinal studies and meta-analyses have confirmed that
depression is a known risk factor for cardiovascular diseases,
including CHD, primarily due to its detrimental effects on the
autonomic nervous system, inflammatory processes and cardiac
function (153-155).
SIRT1 has been shown to mitigate these harmful effects by affecting
the core mechanisms underlying depression-induced CHD (156).
One of the primary mechanisms through which SIRT1
influences CHD in the context of depression is by regulating
oxidative stress (151). A
previous study using the CUMS mouse model has shown that depression
leads to an increase in the production of reactive oxygen species
and the compromise of antioxidant defenses, resulting in oxidative
damage to endothelial cells, which are critical contributors to
atherosclerosis and CHD progression (157). Furthermore, studies in
vitro have demonstrated that SIRT1 exerts protective
antioxidant and anti-apoptotic effects, which are achieved by
enhancing antioxidant gene expression and effecting the
downregulation of pro-oxidative pathways (158). SIRT1 specifically activates FOXO
transcription factors, which causes the upregulation of antioxidant
stress genes such as MnSOD, contributing to its role in oxidative
stress defense (159). A study
that utilized a mouse model of myocardial ischemia demonstrated
that SIRT1 reduces the risk of plaque formation and slows down
atherosclerosis progression through mitigation of oxidative damage
to vascular endothelial cells (160).
In addition to its role in reducing oxidative
stress, SIRT1 also regulates inflammatory pathways that are often
activated by depression (151).
Clinical evidence has shown that chronic inflammation is a shared
characteristic of depression and CHD, with SIRT1 having a crucial
role in reducing inflammatory responses (161,162). Studies in mice with overexpressed
SIRT1 have shown that the deacetylase function of SIRT1 inhibits
the activation of NF-κB, a key transcription factor that promotes
the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and
TNF-α. By dampening the inflammatory response, SIRT1 reduces immune
cell recruitment to the vessel wall, which thereby prevents
atherosclerotic plaque formation and decreases the risk of CHD in
patients with depression (163,164). Furthermore, SIRT1 regulates
disrupted metabolic processes in both depression and CHD (165). A cross-sectional study
demonstrated that depression frequently occurs concomitantly with
metabolic syndrome, which involves processes such as insulin
resistance and dyslipidemia (166)
and obesity, all of which are significant risk factors for CHD.
Analysis of cholesterol and triglyceride levels in mouse tissues
has suggested that SIRT1 regulates lipid metabolism via activation
of PGC-1α and LXRs, which are both integral to cholesterol efflux
and fatty acid oxidation (167).
Through the promotion of lipid homeostasis, SIRT1 has been shown to
reduce cholesterol accumulation in the arterial walls, thereby
decreasing the risk of atherosclerosis and CHD, especially in
individuals with depression (168).
Depression-induced CHD is also associated with
disruptions in autonomic nervous system function; specifically, an
increase in sympathetic activity and a reduction in parasympathetic
activity (169). These autonomic
imbalances may lead to increased blood pressure, an accelerated
heart rate and heightened vascular tone, all of which contribute to
the risk of CHD, especially in women with depression (170). In a study that utilized a
hypertensive rat model, activating SIRT1 in the hypothalamus led to
the regulation of sympathetic nervous activity, thereby reducing
blood pressure (171). Activation
of SIRT1 in the hypothalamus has been shown to modulate sympathetic
outflow and to reduce blood pressure, mitigating one of the key
mechanisms through which depression leads to CHD (172). Another critical role of SIRT1 in
depression-associated CHD involves its effect on cardiac remodeling
and fibrosis (173). In a clinical
observational study of hypertension, depression was often found to
be associated with increased cardiac stress and hypertrophy, which,
if left uncontrolled, may lead to heart failure (174).
In animal studies, SIRT1 was found to inhibit the
TGF-β1 signaling pathway, thereby alleviating cardiac fibrosis in
mice and leading to the protection of the heart from hypertrophic
stress, a pathway that is a significant driver of cardiac fibrosis
and remodeling (175,176). Additionally, SIRT1 was shown to
support cardiac health by limiting the accumulation of
extracellular matrix proteins in the heart, potentially lowering
the risk of heart failure in patients with depression-associated
CHD (177). Additionally, SIRT1
has been shown to have a vital role in regulating autophagy, a
cellular process essential for maintaining cardiovascular health
(178). Autophagy helps to
eliminate damaged cellular components, thereby preventing the
accumulation of toxic proteins, which can lead to cardiovascular
diseases (179). A study that
employed a mouse depression model showed that depression
compromises cardiac autophagy, increasing the likelihood of
ischemic injury and heart failure (180). SIRT1 has also been shown to
facilitate autophagy by deacetylating essential
autophagy-associated proteins, which improved the removal of
damaged mitochondria and reduced the chance of ischemia-reperfusion
injury in cardiac tissue (181).
In conclusion, a number of studies have shown that SIRT1 decreases
the risk of CHD by mitigating cardiovascular damage associated with
depression, primarily by strengthening autonomic function, boosting
antioxidant defense mechanisms and reducing inflammation (Fig. 5).
The potential of SIRT1 in managing depression and
CHD is increasingly supported by robust preclinical and clinical
data, highlighting its ability to regulate inflammation, oxidative
stress and metabolic pathways, which serve as key pathological
mechanisms implicated in both CHD and depression (104,108,128,130). As a prominent
NAD+-dependent deacetylase, SIRT1 exerts protective
effects on the cardiovascular and central nervous systems,
suggesting its suitability as a dual-targeted therapeutic
intervention. The findings from animal experiments have suggested
that natural and synthetic SIRT1 activators, such as resveratrol
and SRT1720, confer substantial cardioprotective and
neuroprotective effects, indicating their potential for use in
patients with co-morbid CHD and depression (182,183).
Similarly, SRT1720 is a synthetic SIRT1 agonist that
has shown great potential in supporting cardiac and neurological
health (186,187). Animal studies have shown that
SRT1720 may promote mitophagy, decrease oxidative stress and
regulate inflammation, which may help to slow the progression of
atherosclerosis (188,189). This is particularly beneficial in
CHD models, where atherosclerosis poses a significant risk.
Experimental evidence in vitro has demonstrated that SRT1720
exhibits neuroprotective effects by mitigating oxidative stress in
neural tissues and regulating mitochondrial function, potentially
reducing the depressive symptoms associated with chronic
neuroinflammation (190).
Other SIRT1 activators, such as quercetin, have
further underscored the therapeutic utility of SIRT1 in
cardiovascular and mental health settings (191,192). Quercetin, another polyphenol, has
been observed to activate SIRT1 and decrease lipid peroxidation,
while enhancing antioxidant enzyme activity in preclinical
cardiovascular models (188). This
modulation has been associated with improved vascular health and
reduced CHD risk (193). In a
mouse model of depression, quercetin was shown to effectively
reduce neuroinflammatory responses, suggesting that it may
alleviate depressive symptoms and improve overall neurological
resilience in patients with concurrent CHD (194).
These findings provide a strong basis for exploring
the therapeutic potential of SIRT1 in treating CHD associated with
depression. However, transitioning from preclinical to clinical
application requires extensive research. Future studies should
focus on large-scale, multi-center trials to confirm the
effectiveness of SIRT1 activators such as resveratrol and SRT1720
in diverse patient groups. Such trials should carefully evaluate
biomarkers that are associated with inflammation, oxidative stress
and mitochondrial health to better understand the impact of SIRT1
on these interlinked pathways in patients with co-occurring CHD and
depression. Additionally, identifying consistent biomarkers, such
as specific cytokines and mitochondrial activity markers, will aid
in personalizing treatment and guiding SIRT1-based interventions
for individual patients. Finally, combining SIRT1-targeted
approaches with existing cardiovascular and antidepressant
therapies may improve outcomes in both physical and mental health
for these patients.
SIRT1 is a key factor linking the pathophysiology of
depression and CHD that has shown therapeutic potential in terms of
its ability to regulate inflammation, oxidative stress and
metabolic pathways. Preclinical studies of SIRT1 activators, such
as resveratrol and SRT1720, have demonstrated their positive
effects on cardiac protection and mood improvement, laying the
foundation for further clinical research. However, the complexity
of SIRT1 signaling poses challenges for direct clinical
translation, especially in patients with co-morbid CHD and
depression. Continued advancements in SIRT1-targeted therapies are
expected to enhance the treatment outcomes for this dual
condition.
Not applicable.
Funding: This study was supported by Yichang Medical and Health
Research Project (grant no. A22-2-052).
Not applicable.
SZ and JL designed and conceived this review. SZ
wrote the manuscript. LY, QD and XL collected and analyzed the data
required for the article, and TM and JL reviewed and edited the
manuscript. The authors have carefully reviewed, analyzed, and
adapted the content of all referenced studies to ensure accuracy
and relevance within the context of this review. All authors read
and approved the final manuscript. Data authentication is
applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
|
1
|
Goldston K and Baillie AJ: Depression and
coronary heart disease: A review of the epidemiological evidence,
explanatory mechanisms and management approaches. Clin Psychol Rev.
28:288–306. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pearce M, Garcia L, Abbas A, Strain T,
Schuch FB, Golubic R, Kelly P, Khan S, Utukuri M, Laird Y, et al:
Association between physical activity and risk of depression: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 79:550–559.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li R and Odell J: Environmental, genetic
factors and depression. J Stud Res. 12:1–5. 2023.
|
|
4
|
Scott KM, de Jonge P, Stein DJ and Kessler
RC: Mental Disorders Around the World: Facts and Figures from the
WHO World Mental Health Surveys. Scott KM, de Jonge P, Stein DJ and
Kessler RC (eds). Cambridge University Press, 2018.
|
|
5
|
Moffitt TE, Caspi A, Taylor A, Kokaua J,
Milne BJ, Polanczyk G and Poulton R: How common are common mental
disorders? Evidence that lifetime prevalence rates are doubled by
prospective versus retrospective ascertainment. Psychol Med.
40:899–909. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Roth GA, Johnson C, Abajobir A, Abd-Allah
F, Abera SF, Abyu G, Ahmed M, Aksut B, Alam T, Alam K, et al:
Global, regional, and national burden of cardiovascular diseases
for 10 causes, 1990 to 2015. J Am Coll Cardiol. 70:1–25.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mensah GA, Fuster V, Murray CJL and Roth
GA: Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risks
Collaborators. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risks,
1990-2022. J Am Coll Cardiol. 82:2350–2473. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
World Health Organization: Cardiovascular
diseases (CVDs). Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds).
|
|
9
|
Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ,
Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR,
Cheng S, Delling FN, et al: Heart disease and stroke
statistics-2020 update: A report from the American Heart
Association. Circulation. 141:E139–E596. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Heidenreich PA, Trogdon JG, Khavjou OA,
Butler J, Dracup K, Ezekowitz MD, Finkelstein EA, Hong Y, Johnston
SC, Khera A, et al: Forecasting the future of cardiovascular
disease in the United States: A policy statement from the American
Heart Association. Circulation. 123:933–944. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li A, Rosella LC, Kurdyak P and Wodchis
WP: Depression as a risk factor for physical illness and
multimorbidity in a cohort with no prior comorbidity. Can J
Psychiatry. 66:726–736. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Herrman H, Patel V, Kieling C, Berk M,
Buchweitz C, Cuijpers P, Furukawa TA, Kessler RC, Kohrt BA, Maj M,
et al: Time for united action on depression: A lancet-world
psychiatric association commission. Lancet. 399:957–1022.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Penninx BW, Milaneschi Y, Lamers F and
Vogelzangs N: Understanding the somatic consequences of depression:
Biological mechanisms and the role of depression symptom profile.
BMC Med. 11(129)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Dantzer R, O'Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson
RW and Kelley KW: From inflammation to sickness and depression:
When the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci.
9:46–56. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sichko S, Bui TQ, Vinograd M, Shields GS,
Saha K, Devkota S, Olvera-Alvarez HA, Carroll JE, Cole SW, Irwin MR
and Slavich GM: Psychobiology of stress and adolescent depression
(PSY SAD) study: Protocol overview for an fMRI-based multi-method
investigation. Brain Behav Immun Health. 17(100334)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bansal Y and Kuhad A: Mitochondrial
dysfunction in depression. Curr Neuropharmacol. 14:610–618.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tan C, Yan Q, Ma Y, Fang J and Yang Y:
Recognizing the role of the vagus nerve in depression from
microbiota-gut brain axis. Front Neurol. 13(1015175)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yuan M, Yang B, Rothschild G, Mann JJ,
Sanford LD, Tang X, Huang C, Wang C and Zhang W: Epigenetic
regulation in major depression and other stress-related disorders:
Molecular mechanisms, clinical relevance and therapeutic potential.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8(309)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shen R, Zhao N, Wang J, Guo P, Shen S, Liu
D and Zou T: Association between level of depression and coronary
heart disease, stroke risk and all-cause and cardiovascular
mortality: Data from the 2005-2018 National health and nutrition
examination survey. Front Cardiovasc Med. 9(954563)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cao H, Zhao H and Shen L: Depression
increased risk of coronary heart disease: A meta-analysis of
prospective cohort studies. Front Cardiovasc Med.
9(913888)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xu L, Zhai X, Shi D and Zhang Y:
Depression and coronary heart disease: Mechanisms, interventions,
and treatments. Front Psychiatry. 15(1328048)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Harshfield EL, Pennells L, Schwartz JE,
Willeit P, Kaptoge S, Bell S, Shaffer JA, Bolton T, Spackman S,
Wassertheil-Smoller S, et al: Association between depressive
symptoms and incident cardiovascular diseases. JAMA. 324:2396–2405.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y, Cui G and Wang Y, Gong Y and Wang
Y: SIRT1 activation alleviates brain microvascular endothelial
dysfunction in peroxisomal disorders. Int J Mol Med. 44:995–1005.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Jha MK, Qamar A, Vaduganathan M, Charney
DS and Murrough JW: Screening and management of depression in
patients with cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol.
73:1827–1845. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lu G, Li J, Zhang H, Zhao X, Yan LJ and
Yang X: Role and possible mechanisms of Sirt1 in depression. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2018(8596903)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chan SH, Hung CH, Shih JY, Chu PM, Cheng
YH, Lin HC and Tsai KL: SIRT1 inhibition causes oxidative stress
and inflammation in patients with coronary artery disease. Redox
Biol. 13:301–309. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Singh V and Ubaid S: Role of silent
information regulator 1 (SIRT1) in regulating oxidative stress and
inflammation. Inflammation. 43:1589–1598. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Campagna R, Mazzanti L, Pompei V, Alia S,
Vignini A and Emanuelli M: The multifaceted role of endothelial
Sirt1 in vascular aging: An update. Cells. 13(1469)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Mao Y and Jiang P: The crisscross between
p53 and metabolism in cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
55:914–922. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mijit M, Caracciolo V, Melillo A,
Amicarelli F and Giordano A: Role of p53 in the regulation of
cellular senescence. Biomolecules. 10(420)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yi J and Luo J: SIRT1 and p53, effect on
cancer, senescence and beyond. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins
Proteom. 1804:1684–1689. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sullivan A and Lu X: ASPP: A new family of
oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes. Br J Cancer. 96:196–200.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Brockmueller A, Buhrmann C, Shayan P and
Shakibaei M: Resveratrol induces apoptosis by modulating the
reciprocal crosstalk between p53 and Sirt-1 in the CRC tumor
microenvironment. Front Immunol. 14(1225530)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sivakumar KK, Stanley JA, Behlen JC, Wuri
L, Dutta S, Wu J, Arosh JA and Banu SK: Inhibition of Sirtuin-1
hyperacetylates p53 and abrogates Sirtuin-1-p53 interaction in
Cr(VI)-induced apoptosis in the ovary. Reprod Toxicol. 109:121–134.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Dilmac S, Kuscu N, Caner A, Yildirim S,
Yoldas B, Farooqi AA and Tanriover G: SIRT1/FOXO signaling pathway
in breast cancer progression and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci.
23(10227)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Mizani S, Keshavarz A, Vazifeh Shiran N,
Bashash D and Allahbakhshian Farsani M: Expression changes of SIRT1
and FOXO3a significantly correlate with oxidative stress resistance
genes in AML patients. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 39:392–401.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen L, Li S, Zhu J, You A, Huang X, Yi X
and Xue M: Mangiferin prevents myocardial infarction-induced
apoptosis and heart failure in mice by activating the Sirt1/FoxO3a
pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 25:2944–2955. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhao X, Liu Y, Zhu G, Liang Y, Liu B, Wu
Y, Han M, Sun W, Han Y, Chen G and Jiang J: SIRT1 downregulation
mediated Manganese-induced neuronal apoptosis through activation of
FOXO3a-Bim/PUMA axis. Sci Total Environ. 646:1047–1055.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Alves-Fernandes DK and Jasiulionis MG: The
role of SIRT1 on DNA damage response and epigenetic alterations in
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 20(3153)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Qi F, Jiang X, Tong T, Chang H and Li RX:
MiR-204 inhibits inflammation and cell apoptosis in retinopathy
rats with diabetic retinopathy by regulating Bcl-2 and SIRT1
expressions. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:6486–6493.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wu QJ, Zhang TN, Chen HH, Yu XF, Lv JL,
Liu YY, Liu YS, Zheng G, Zhao JQ, Wei YF, et al: The sirtuin family
in health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
7(402)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Chen G, Zhang B, Xu H, Sun Y, Shi Y, Luo
Y, Jia H and Wang F: Suppression of Sirt1 sensitizes lung cancer
cells to WEE1 inhibitor MK-1775-induced DNA damage and apoptosis.
Oncogene. 36:6863–6872. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wang C, Chen L, Hou X, Li Z, Kabra N, Ma
Y, Nemoto S, Finkel T, Gu W, Cress WD and Chen J: Interactions
between E2F1 and SirT1 regulate apoptotic response to DNA damage.
Nat Cell Biol. 8:1025–1031. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Imperatore F, Maurizio J, Vargas Aguilar
S, Busch CJ, Favret J, Kowenz-Leutz E, Cathou W, Gentek R, Perrin
P, Leutz A, et al: SIRT1 regulates macrophage self-renewal. EMBO J.
36:2353–2372. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yang S, Moon S, Hur SC and Jeong SM: Fatty
acid oxidation regulates cellular senescence by modulating the
autophagy-SIRT1 axis. BMB Rep. 56:651–656. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Liu S, Yao S, Yang H, Liu S and Wang Y:
Autophagy: Regulator of cell death. Cell Death Dis.
14(648)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Guo H, Ding H, Tang X, Liang M, Li S,
Zhang J and Cao J: Quercetin induces pro-apoptotic autophagy via
SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway in human lung cancer cell lines A549
and H1299 in vitro. Thorac Cancer. 12:1415–1422. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Abate M, Festa A, Falco M, Lombardi A,
Luce A, Grimaldi A, Zappavigna S, Sperlongano P, Irace C, Caraglia
M and Misso G: Mitochondria as playmakers of apoptosis, autophagy
and senescence. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 98:139–153. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Ding X, Zhu C, Wang W, Li M, Ma C and Gao
B: SIRT1 is a regulator of autophagy: Implications for the
progression and treatment of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion.
Pharmacol Res. 199(106957)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Jiang Y, Botchway BOA, Hu Z and Fang M:
Overexpression of SIRT1 inhibits corticosterone-induced autophagy.
Neuroscience. 411:11–22. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Chung S, Yao H, Caito S, Hwang JW,
Arunachalam G and Rahman I: Regulation of SIRT1 in cellular
functions: Role of polyphenols. Arch Biochem Biophys. 501:79–90.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Korbecki J, Bobiński R and Dutka M:
Self-regulation of the inflammatory response by peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors. Inflamm Res. 68:443–458.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Tian Y, Ma J, Wang W, Zhang L, Xu J, Wang
K and Li D: Resveratrol supplement inhibited the NF-κB inflammation
pathway through activating AMPKα-SIRT1 pathway in mice with fatty
liver. Mol Cell Biochem. 422:75–84. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sun HJ, Xiong SP, Cao X, Cao L, Zhu MY, Wu
ZY and Bian JS: Polysulfide-mediated sulfhydration of SIRT1
prevents diabetic nephropathy by suppressing phosphorylation and
acetylation of p65 NF-κB and STAT3. Redox Biol.
38(101813)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Murphy CE, Lawther AJ, Webster MJ, Asai M,
Kondo Y, Matsumoto M, Walker AK and Weickert CS: Nuclear factor
kappa B activation appears weaker in schizophrenia patients with
high brain cytokines than in non-schizophrenic controls with high
brain cytokines. J Neuroinflammation. 17(215)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D and Sun SC: NF-κB
signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
2(17023)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Kauppinen A, Suuronen T, Ojala J,
Kaarniranta K and Salminen A: Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB
and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic
disorders. Cell Signal. 25:1939–1948. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Jalgaonkar MP, Parmar UM, Kulkarni YA and
Oza MJ: SIRT1-FOXOs activity regulates diabetic complications.
Pharmacol Res. 175(106014)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Jia D, Ping W, Wang M, Wang D, Zhang L and
Cao Y: SIRT1 mediates the inflammatory response of macrophages and
regulates the TIMP3/ADAM17 pathway in atherosclerosis. Exp Cell
Res. 442(114253)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Chen H, Deng J, Gao H, Song Y, Zhang Y,
Sun J and Zhai J: Involvement of the SIRT1-NLRP3 pathway in the
inflammatory response. Cell Commun Signal. 21(185)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Hardeland R: Aging, melatonin, and the
pro-and anti-inflammatory networks. Int J Mol Sci.
20(1223)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Rovira-Llopis S, Apostolova N, Bañuls C,
Muntané J, Rocha M and Victor VM: Mitochondria, the NLRP3
inflammasome, and sirtuins in type 2 diabetes: New therapeutic
targets. Antioxid Redox Signal. 29:749–791. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Li S, Huang K, Jiang L
and Wang Y: Metformin alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury by
regulating the SIRT1/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway and inhibiting endothelial
cell pyroptosis. Front Pharmacol. 13(801337)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Luo XY, Qu SL, Tang ZH, Zhang Y, Liu MH,
Peng J, Tang H, Yu KL, Zhang C, Ren Z and Jiang ZS: SIRT1 in
cardiovascular aging. Clin Chim Acta. 437:106–114. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Das A, Huang GX, Bonkowski MS, Longchamp
A, Li C, Schultz MB, Kim LJ, Osborne B, Joshi S, Lu Y, et al:
Impairment of an endothelial NAD+-H2S signaling network is a
reversible cause of vascular aging. Cell. 173:74–89.e20.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Zhu YJ, Huang J, Chen R, Zhang Y, He X,
Duan WX, Zou YL, Sun MM, Sun HL, Cheng SM, et al: Autophagy
dysfunction contributes to NLRP1 inflammasome-linked
depressive-like behaviors in mice. J Neuroinflammation.
21(6)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Strothers HS III: Depression in the
primary care setting. Ethn Dis. 12:S28–S30. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Schmauβ M: Depression and Parkinson's
disease. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 90:145–146. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In German).
|
|
69
|
El-Battrawy I, Behnes M and Akin I:
Depression and incident cardiovascular disease. JAMA.
325:1679–1680. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Taqueti VR and Di Carli MF: Coronary
microvascular disease pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic
options: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol.
72:2625–2641. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Halaris A: Inflammation-associated
co-morbidity between depression and cardiovascular disease. Curr
Top Behav Neurosci. 31:45–70. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Hackett RA and Steptoe A: Psychosocial
factors in diabetes and cardiovascular risk. Curr Cardiol Rep.
18(95)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Lawrence S and Scofield RH: Post traumatic
stress disorder associated hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
dysregulation and physical illness. Brain Behav Immun Health.
41(100849)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Wirtz PH and von Känel R: Psychological
stress, inflammation, and coronary heart disease. Curr Cardiol Rep.
19(111)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Tonhajzerova I, Sekaninova N, Bona Olexova
L and Visnovcova Z: Novel insight into neuroimmune regulatory
mechanisms and biomarkers linking major depression and vascular
diseases: The dilemma continues. Int J Mol Sci.
21(2317)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Ramachandruni S, Handberg E and Sheps DS:
Acute and chronic psychological stress in coronary disease. Curr
Opin Cardiol. 19:494–499. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Gianaros PJ, Hariri AR, Sheu LK, Muldoon
MF, Sutton-Tyrrell K and Manuck SB: Preclinical atherosclerosis
covaries with individual differences in reactivity and functional
connectivity of the amygdala. Biol Psychiatry. 65:943–950.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Levin A: Amygdala activity may predict
future cardiovascular events. Psychiatr News. 52:1. 2017.
|
|
79
|
Pizzi C, Manzoli L, Mancini S, Bedetti G,
Fontana F and Costa GM: Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and
preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with
coronary risk factors. Atherosclerosis. 212:292–298.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Pan Y, Chen Y, Wu S, Ying P, Zhang Z, Tan
X and Zhu J: Prevalence and management of depressive symptoms in
coronary heart disease patients and relationship with
cardiovascular prognosis: A prospective cohort study. BMC
Psychiatry. 24(644)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Compare A, Proietti R, Germani E and
Janeway D: Anxiety and depression: Risk factors for cardiovascular
disease. In: Stress Proof the Heart: Behavioral Interventions for
Cardiac Patients. Vol 9781441956507. Springer, New York, NY,
pp139-166, 2012.
|
|
82
|
Dickens C: Depression in people with
coronary heart disease: Prognostic significance and mechanisms.
Curr Cardiol Rep. 17(83)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
De Martini GA, Grisante DL, Gonçalves ALP,
D'Agostino F, Lopes JL, Santos VB and Lopes CT: Relationships
between depressive symptoms, appetite, and quality of life in heart
failure. West J Nurs Res. 45:416–424. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Xu Q, Chen C, You R, Ni L, Chen S and Peng
B: Causal association between major depressive disorder and
coronary heart disease: A two-sample bidirectional mendelian
randomization study. BMC Med Genomics. 16(183)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Meng LB, Zhang YM, Luo Y, Gong T and Liu
DP: Chronic Stress A Potential Suspect Zero of Atherosclerosis: A
Systematic Review. Front Cardiovasc Med: Dec 20, 2021 (Epub ahead
of print) doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.738654.
|
|
86
|
Mbiydzenyuy NE and Qulu LA: Stress,
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal
axis, and aggression. Metab Brain Dis. 39:1613–1636.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Hering D, Seravalle G, Grassi G and
Narkiewicz K: Sympathetic Activity in Hypertension and Heart
Failure. Springer Nature, Heidelberg, pp107-126, 2023.
|
|
88
|
Osimo EF, Baxter LJ, Lewis G, Jones PB and
Khandaker GM: Prevalence of low-grade inflammation in depression: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of CRP levels. Psychol Med.
49:1958–1970. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Correia AS, Cardoso A and Vale N:
Oxidative stress in depression: The link with the stress response,
neuroinflammation, serotonin, neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity.
Antioxidants (Basel). 12(470)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Chocano-Bedoya PO, Mirzaei F, O'Reilly EJ,
Lucas M, Okereke OI, Hu FB, Rimm EB and Ascherio A: C-reactive
protein, interleukin-6, soluble tumor necrosis factor α receptor 2
and incident clinical depression. J Affect Disord. 163:25–32.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Li G, Zhang L and Liu M: Meta-analysis on
inflammation and autonomic nervous system of coronary heart disease
combined with depression. BMJ Open. 14(e079980)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Higashi Y: Roles of oxidative stress and
inflammation in vascular endothelial dysfunction-related disease.
Antioxidants (Basel). 11(1958)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Gao F, Zhao Y, Zhang B, Xiao C, Sun Z, Gao
Y and Dou X: Orientin alleviates ox-LDL-induced oxidative stress,
inflammation and apoptosis in human vascular endothelial cells by
regulating Sestrin 1 (SESN1)-mediated autophagy. J Mol Histol.
55:109–120. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Kwong ASF, López-López JA, Hammerton G,
Manley D, Timpson NJ, Leckie G and Pearson RM: Genetic and
environmental risk factors associated with trajectories of
depression symptoms from adolescence to young adulthood. JAMA Netw
Open. 2(e196587)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Lei Y, Wang J, Wang D, Li C, Liu B, Fang
X, You J, Guo M and Lu XY: SIRT1 in forebrain excitatory neurons
produces sexually dimorphic effects on depression-related behaviors
and modulates neuronal excitability and synaptic transmission in
the medial prefrontal cortex. Mol Psychiatry. 25:1094–1111.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Abe-Higuchi N, Uchida S, Yamagata H,
Higuchi F, Hobara T, Hara K, Kobayashi A and Watanabe Y:
Hippocampal Sirtuin 1 signaling mediates depression-like behavior.
Biol Psychiatry. 80:815–826. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Singh P, Hanson PS and Morris CM: SIRT1
ameliorates oxidative stress induced neural cell death and is
down-regulated in Parkinson's disease. BMC Neurosci.
18(46)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Qiu X, Lu P, Zeng X, Jin S and Chen X:
Study on the mechanism for SIRT1 during the process of exercise
improving depression. Brain Sci. 13(719)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Wang R, Wu Y, Liu R, Liu M, Li Q, Ba Y and
Huang H: Deciphering therapeutic options for neurodegenerative
diseases: insights from SIRT1. J Mol Med (Berl). 100:537–553.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Zhang Y, Anoopkumar-Dukie S and Davey AK:
Sirt1 and sirt2 modulators: Potential anti-inflammatory treatment
for depression? Biomolecules. 11(353)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Dang R, Wang M, Li X, Wang H, Liu L, Wu Q,
Zhao J, Ji P, Zhong L, Licinio J and Xie P: Edaravone ameliorates
depressive and anxiety-like behaviors via Sirt1/Nrf2/HO-1/Gpx4
pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 19(41)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Ma Z, Feng D, Rui W and Wang Z: Baicalin
attenuates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced hippocampal
neuronal apoptosis through regulating SIRT1/PARP1 signaling
pathway. Behav Brain Res. 441(114299)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Geng M, Shao Q, Fu J, Gu J, Feng L, Zhao
L, Liu C, Mu J, Zhang X, Zhao M, et al: Down-regulation of MKP-1 in
hippocampus protects against stress-induced depression-like
behaviors and neuroinflammation. Transl Psychiatry.
14(130)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Tartt AN, Mariani MB, Hen R, Mann JJ and
Boldrini M: Dysregulation of adult hippocampal neuroplasticity in
major depression: Pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Mol
Psychiatry. 27:2689–2699. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Zhang K, Wang F, Zhai M, He M, Hu Y, Feng
L, Li Y, Yang J and Wu C: Hyperactive neuronal autophagy depletes
BDNF and impairs adult hippocampal neurogenesis in a
corticosterone-induced mouse model of depression. Theranostics.
13:1059–1075. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Saharan S, Jhaveri DJ and Bartlett PF:
SIRT1 regulates the neurogenic potential of neural precursors in
the adult subventricular zone and hippocampus. J Neurosci Res.
91:642–659. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Shen J, Hao C, Yuan S, Chen W, Tong T,
Chen Y, Shahzad Aslam M, Yan S, Li J, Zeng J, et al: Acupuncture
alleviates CUMS-induced depression-like behaviors of rats by
regulating oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and ferroptosis.
Brain Res. 1826(148715)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Li C, Wang F, Miao P, Yan L, Liu S, Wang
X, Jin Z and Gu Z: miR-138 increases depressive-like behaviors by
targeting SIRT1 in hippocampus. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat.
16:949–957. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Wu X, Zhang Y, Wang J, Qin L, Li Y, He Q,
Zhang T, Wang Y, Song L, Ji L, et al: Role of SIRT1-mediated
synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis: Sex-differences in
antidepressant-like efficacy of catalpol. Phytomedicine.
135(156120)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Michán S, Li Y, Chou MM, Parrella E, Ge H,
Long JM, Allard JS, Lewis K, Miller M, Xu W, et al: SIRT1 is
essential for normal cognitive function and synaptic plasticity. J
Neurosci. 30:9695–9707. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Guo H, Deji C, Peng H, Zhang J, Chen Y,
Zhang Y and Wang Y: The role of SIRT1 in the basolateral amygdala
in depression-like behaviors in mice. Genes Brain Behav.
20(e12765)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Erickson KI, Miller DL and Roecklein KA:
The aging hippocampus: Interactions between exercise, depression,
and BDNF. Neuroscientist. 18:82–97. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Ye S, Fang L, Xie S, Hu Y, Chen S, Amin N,
Fang M and Hu Z: Resveratrol alleviates postpartum depression-like
behavior by activating autophagy via SIRT1 and inhibiting AKT/mTOR
pathway. Behav Brain Res. 438(114208)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Wang J, Li J, Cao N, Li Z, Han J and Li L:
Resveratrol, an activator of SIRT1, induces protective autophagy in
non-small-cell lung cancer via inhibiting Akt/mTOR and activating
p38-MAPK. Onco Targets Ther. 11:7777–7786. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Tabassum S, Misrani A, Huang HX, Zhang ZY,
Li QW and Long C: Resveratrol attenuates chronic unpredictable mild
stress-induced alterations in the SIRT1/PGC1α/SIRT3 pathway and
associated mitochondrial dysfunction in mice. Mol Neurobiol.
60:5102–5116. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Shen J, Xu L, Qu C, Sun H and Zhang J:
Resveratrol prevents cognitive deficits induced by chronic
unpredictable mild stress: Sirt1/miR-134 signalling pathway
regulates CREB/BDNF expression in hippocampus in vivo and in vitro.
Behav Brain Res. 349:1–7. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Takahashi K, Kurokawa K, Hong L, Miyagawa
K, Mochida-Saito A, Takeda H and Tsuji M: Hippocampal and gut AMPK
activation attenuates enterocolitis-like symptoms and co-occurring
depressive-like behavior in ulcerative colitis model mice:
Involvement of brain-gut autophagy. Exp Neurol.
373(114671)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Kim HD, Wei J, Call T, Call T, Ma X,
Quintus NT, Summers AJ, Carotenuto S, Johnson R, Nguyen A, et al:
SIRT1 coordinates transcriptional regulation of neural activity and
modulates depression-like behaviors in the nucleus accumbens. Biol
Psychiatry. 96:495–505. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Kim HD, Hesterman J, Call T, Magazu S,
Keeley E, Armenta K, Kronman H, Neve RL, Nestler EJ and Ferguson D:
SIRT1 mediates depression-like behaviors in the nucleus accumbens.
J Neurosci. 36:8441–8452. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Nowacka-Chmielewska M, Grabowska K,
Grabowski M, Meybohm P, Burek M and Małecki A: Running from stress:
Neurobiological mechanisms of exercise-induced stress resilience.
Int J Mol Sci. 23(13348)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Yamamoto M and Takahashi Y: The essential
role of sirt1 in hypothalamic-pituitary axis. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 9(605)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Yu X, Hu Y, Huang W, Ye N, Yan Q, Ni W and
Jiang X: Role of AMPK/SIRT1-SIRT3 signaling pathway in affective
disorders in unpredictable chronic mild stress mice.
Neuropharmacology. 165(107925)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Takaba R, Ibi D, Watanabe K, Hayakawa K,
Nakasai G and Hiramatsu M: Role of sirtuin1 in impairments of
emotion-related behaviors in mice with chronic mild unpredictable
stress during adolescence. Physiol Behav.
257(113971)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Cordner ZA, Marshall-Thomas I, Boersma GJ,
Lee RS, Potash JB and Tamashiro KLK: Fluoxetine and environmental
enrichment similarly reverse chronic social stress-related
depression- and anxiety-like behavior, but have differential
effects on amygdala gene expression. Neurobiol Stress.
15(100392)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Ma B, Guo B, Chen Z and Li Y: SIRT1
regulates hypoxia-induced oxidative stress in cardiomyocytes via
PI3K/MTOR signaling. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 68:48–53.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Opstad TB, Papotti B, Åkra S, Hansen CH,
Braathen B, Tønnessen T, Solheim S and Seljeflot I: Sirtuin1, not
NAMPT, possesses anti-inflammatory effects in epicardial,
pericardial and subcutaneous adipose tissue in patients with CHD. J
Transl Med. 21(644)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Kida Y and Goligorsky MS: Sirtuins, cell
senescence, and vascular aging. Can J Cardiol. 32:634–641.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Winnik S, Auwerx J, Sinclair DA and Matter
CM: Protective effects of sirtuins in cardiovascular diseases: From
bench to bedside. Eur Heart J. 36:3404–3412. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Stein S, Schäfer N, Breitenstein A, Besler
C, Winnik S, Lohmann C, Heinrich K, Brokopp CE, Handschin C,
Landmesser U, et al: SIRT1 reduces endothelial activation without
affecting vascular function in ApoE-/-mice. Aging (Albany NY).
2:353–360. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Gorenne I, Kumar S, Gray K, Figg N, Yu H,
Mercer J and Bennett M: Vascular smooth muscle cell sirtuin 1
protects against DNA damage and inhibits atherosclerosis.
Circulation. 127:386–396. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Yang H, Zhang W, Pan H, Feldser HG, Lainez
E, Miller C, Leung S, Zhong Z, Zhao H, Sweitzer S, et al: SIRT1
activators suppress inflammatory responses through promotion of p65
deacetylation and inhibition of NF-κB activity. PLoS One.
7(e46364)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Zhu Y, Xian X, Wang Z, Bi Y, Chen Q, Han
X, Tang D and Chen R: Research progress on the relationship between
atherosclerosis and inflammation. Biomolecules.
8(80)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Kitada M, Ogura Y and Koya D: The
protective role of Sirt1 in vascular tissue: Its relationship to
vascular aging and atherosclerosis. Aging (Albany NY). 8:2290–2307.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Guarente L: Franklin H. Epstein Lecture:
Sirtuins, aging, and medicine. N Engl J Med. 364:2235–2244.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Houtkooper RH, Pirinen E and Auwerx J:
Sirtuins as regulators of metabolism and healthspan. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 13:225–238. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Yang X, Wei J, He Y, Jing T, Li Y, Xiao Y,
Wang B, Wang W, Zhang J and Lin R: SIRT1 inhibition promotes
atherosclerosis through impaired autophagy. Oncotarget.
8:51447–51461. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Wang SJ, Zhao XH, Chen W, Bo N, Wang XJ,
Chi ZF and Wu W: Sirtuin 1 activation enhances the
PGC-1α/mitochondrial antioxidant system pathway in status
epilepticus. Mol Med Rep. 11:521–526. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Dong YT, Cao K, Xiang J, Qi XL, Xiao Y, Yu
WF, He Y, Hong W and Guan ZZ: Resveratrol attenuates the disruption
of lipid metabolism observed in amyloid precursor
protein/presenilin 1 mouse brains and cultured primary neurons
exposed to Aβ. Neuroscience. 521:134–147. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Zeng HT, Fu YC, Yu W, Lin JM, Zhou L, Liu
L and Wang W: SIRT1 prevents atherosclerosis via liver-X-receptor
and NF-κB signaling in a U937 cell model. Mol Med Rep. 8:23–28.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Li L, Zhang HN, Chen HZ, Gao P, Zhu LH, Li
HL, Lv X, Zhang QJ, Zhang R, Wang Z, et al: SIRT1 acts as a
modulator of neointima formation following vascular injury in mice.
Circ Res. 108:1180–1189. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Xu W, Deng YY, Yang L, Zhao S, Liu J, Zhao
Z, Wang L, Maharjan P, Gao S, Tian Y, et al: Metformin ameliorates
the proinflammatory state in patients with carotid artery
atherosclerosis through sirtuin 1 induction. Transl Res.
166:451–458. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Chen YX, Zhang M, Cai Y, Zhao Q and Dai W:
The Sirt1 activator SRT1720 attenuates angiotensin II-induced
atherosclerosis in apoE-/-mice through inhibiting vascular
inflammatory response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 465:732–738.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Nasiri M, Rauf M, Kamfiroozie H,
Zibaeenezhad MJ and Jamali Z: SIRT1 gene polymorphisms associated
with decreased risk of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease.
Gene. 672:16–20. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Chen Y, He T, Zhang Z and Zhang J:
Activation of SIRT1 by resveratrol alleviates pressure
overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy via suppression of TGF-β1
signaling. Pharmacology. 106:667–681. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Zhang MJ, Zhou Y, Chen L, Wang X, Long CY,
Pi Y, Gao CY, Li JC and Zhang LL: SIRT1 improves VSMC functions in
atherosclerosis. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 121:11–15. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Qiang L, Lin HV, Kim-Muller JY, Welch CL,
Gu W and Accili D: Proatherogenic abnormalities of lipid metabolism
in SirT1 transgenic mice are mediated through Creb deacetylation.
Cell Metab. 14:758–767. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Liu YP, Wen R, Liu CF, Zhang TN and Yang
N: Cellular and molecular biology of sirtuins in cardiovascular
disease. Biomed Pharmacother. 164(114931)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Liang F, Kume S and Koya D: SIRT1 and
insulin resistance. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 5:367–373. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Gong H, Liu J, Xue Z, Wang W, Li C, Xu F,
Du Y and Lyu X: SIRT3 attenuates coronary atherosclerosis in
diabetic patients by regulating endothelial cell function. J Clin
Lab Anal. 36(e24586)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Yu H, Gan D, Luo Z, Yang Q, An D, Zhang H,
Hu Y, Ma Z, Zeng Q, Xu D and Ren H: α-Ketoglutarate improves
cardiac insufficiency through NAD+-SIRT1 signaling-mediated
mitophagy and ferroptosis in pressure overload-induced mice. Mol
Med. 30(15)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Rodriguez-Miguelez P and Pollock JS:
Adverse childhood events and cardiovascular diseases: The potential
role of Sirt1. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 321:H577–H579.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Lo Iacono L, Visco-Comandini F, Valzania
A, Viscomi MT, Coviello M, Giampà A, Roscini L, Bisicchia E,
Siracusano A, Troisi A, et al: Adversity in childhood and
depression: Linked through SIRT1. Transl Psychiatry.
5(e629)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Vicario A and Cerezo GH: The heart and
brain connection: Contribution of cardiovascular disease to
vascular depression-A narrative review. Heart and Mind. 7:126–131.
2023.
|
|
154
|
Piantella S, Dragano N, Marques M,
McDonald SJ and Wright BJ: Prospective increases in depression
symptoms and markers of inflammation increase coronary heart
disease risk - The Whitehall II cohort study. J Psychosom Res.
151(110657)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Liu RT, Hernandez EM, Trout ZM, Kleiman EM
and Bozzay ML: Depression, social support, and long-term risk for
coronary heart disease in a 13-year longitudinal epidemiological
study. Psychiatry Res. 251:36–40. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Yu H, Li X, Ning B, Feng L, Ren Y, Li S,
Kang Y, Ma J and Zhao M: SIRT1: A potential therapeutic target for
coronary heart disease combined with anxiety or depression. J Drug
Target: Dec 23, 2024 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
157
|
Stanley SC, Brooks SD, Butcher JT,
d'Audiffret AC, Frisbee SJ and Frisbee JC: Protective effect of sex
on chronic stress- and depressive behavior-induced vascular
dysfunction in BALB/cJ mice. J Appl Physiol. 117:959–970.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Hori YS, Kuno A, Hosoda R and Horio Y:
Regulation of FOXOs and p53 by SIRT1 modulators under oxidative
stress. PLoS One. 8(e73875)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Brunet A, Sweeney LB, Sturgill JF, Chua
KF, Greer PL, Lin Y, Tran H, Ross SE, Mostoslavsky R, Cohen HY, et
al: Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by
the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science. 303:2011–2015. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Hsu CP, Zhai P, Yamamoto T, Maejima Y,
Matsushima S, Hariharan N, Shao D, Takagi H, Oka S and Sadoshima J:
Silent information regulator 1 protects the heart from
ischemia/reperfusion. Circulation. 122:2170–2182. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Starodubtseva I, Meshkova M and Zuikova A:
Pathogenetic mechanisms of repeated adverse cardiovascular events
development in patients with coronary heart disease: The role of
chronic inflammation. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 65:863–870.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
162
|
Kofod J, Elfving B, Nielsen EH, Mors O and
Köhler-Forsberg O: Depression and inflammation: Correlation between
changes in inflammatory markers with antidepressant response and
long-term prognosis. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 54:116–125.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Pfluger PT, Herranz D, Velasco-Miguel S,
Serrano M and Tschöp MH: Sirt1 protects against high-fat
diet-induced metabolic damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:9793–9798. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
164
|
Fan J, Guang H, Zhang H, Chen D, Ding L,
Fan X, Xue F, Gan Z, Wang Y, Mao S, et al: SIRT1 mediates apelin-13
in ameliorating chronic normobaric hypoxia-induced anxiety-like
behavior by suppressing NF-κB pathway in mice hippocampus.
Neuroscience. 381:22–34. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Askin L, Tibilli H, Tanriverdi O and
Turkmen S: The relationship between coronary artery disease and
SIRT1 protein. North Clin Istanb. 7:631–635. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Sugimoto K, Yamada T, Kitazawa A and
Fukuda Y: Metabolic syndrome and depression: Evidence from a
cross-sectional study of real-world data in Japan. Environ Health
Prev Med. 29(33)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
167
|
Li X, Zhang S, Blander G, Tse JG, Krieger
M and Guarente L: SIRT1 deacetylates and positively regulates the
nuclear receptor LXR. Mol Cell. 28:91–106. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Feige JN and Auwerx J: DisSIRTing on LXR
and cholesterol metabolism. Cell Metab. 6:343–345. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Wang Y, Zhao X, O'Neil A, Turner A, Liu X
and Berk M: Altered cardiac autonomic nervous function in
depression. BMC Psychiatry. 13(187)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
170
|
Rome D, Sales A, Leeds R, Usseglio J,
Cornelius T, Monk C, Smolderen KG and Moise N: A narrative review
of the association between depression and heart disease among
women: Prevalence, mechanisms of action, and treatment. Curr
Atheroscler Rep. 24:709–720. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Yan J, Tang X, Zhou ZQ, Zhang J, Zhao Y,
Li S and Luo A: Sirtuins functions in central nervous system cells
under neurological disorders. Front Physiol.
13(886087)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Vinciguerra M, Santini MP, Martinez C,
Pazienza V, Claycomb WC, Giuliani A and Rosenthal N:
mIGF-1/JNK1/SirT1 signaling confers protection against oxidative
stress in the heart. Aging Cell. 11:139–149. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
173
|
Wang Y, Zhao R, Wu C, Liang X, He L, Wang
L and Wang X: Activation of the sirtuin silent information
regulator 1 pathway inhibits pathological myocardial remodeling.
Front Pharmacol. 14(1111320)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Shi S, Guan G, Wang J, Hui R, Zhang Y, Cui
Q, Zhao J and Zhu L: Association of depression with hypertensive
left ventricular hypertrophy in age, sex, and education
level-specific differences. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich).
25:715–724. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Liu ZH, Zhang Y, Wang X, Fan XF, Zhang Y,
Li X, Gong YS and Han LP: SIRT1 activation attenuates cardiac
fibrosis by endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Biomed
Pharmacother. 118(109227)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Piao S, Lee I, Jin SA, Kim S, Nagar H,
Choi SJ, Jeon BH and Kim CS: SIRT1 activation attenuates the
cardiac dysfunction induced by endothelial cell-specific deletion
of CRIF1. Biomedicines. 9(52)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
Pintaningrum Y, Humaera NN, Rafiq A and
Tanti A: OR10. Association between heart functional capacity with
depression severity on patient with coronary artery disease. Eur
Heart J. Suppl 23:2021.
|
|
178
|
Wang Y, Li Y, Ding H, Li D, Shen W and
Zhang X: The current state of research on sirtuin-mediated
autophagy in cardiovascular diseases. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis.
10(382)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
179
|
Luo G, Jian Z, Zhu Y, Zhu Y, Chen B, Ma R,
Tang F and Xiao Y: Sirt1 promotes autophagy and inhibits apoptosis
to protect cardiomyocytes from hypoxic stress. Int J Mol Med.
43:2033–2043. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
180
|
Jiang G, Wang Y, Liu Q, Gu T, Liu S, Yin A
and Zhang L: Autophagy: A new mechanism for esketamine as a
depression therapeutic. Neuroscience. 498:214–223. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Song X, Wei C, Huang H, Cao X, Chen Z,
Chen Y and Wu B: Effects of resveratrol on tolerance to
ischemia/reperfusion injury in aged male mice: Role of autophagy
and apoptosis. Food Sci Nutr. 11:5938–5947. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
182
|
Do GM, Kwon EY, Kim HJ, Jeon SM, Ha TY,
Park T and Choi MS: Long-term effects of resveratrol
supplementation on suppression of atherogenic lesion formation and
cholesterol synthesis in apo E-deficient mice. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 374:55–59. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
183
|
Shukla P, Akotkar L and Aswar U:
Resveratrol attenuates early life stress induced depression in
rats: Behavioural and neurochemical evidence. Neurosci Lett.
820(137606)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
184
|
Raj P, Thandapilly SJ, Wigle J, Zieroth S
and Netticadan T: A comprehensive analysis of the efficacy of
resveratrol in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, myocardial
infarction and heart failure. Molecules. 26(6600)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
185
|
Gu Z, Chu L and Han Y: Therapeutic effect
of resveratrol on mice with depression. Exp Ther Med. 17:3061–3064.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
186
|
Piao S, Kim S, Vu G, Lee M, Kim M, Jeon BH
and Kim CS: SRT1720 alleviates endothelial crif1 deficiency-induced
cardiac function. J Hypertens. 41 (Suppl 3)(e161)2023.
|
|
187
|
Wen S, Xu M, Zhang W, Song R, Zou H, Gu J,
Liu X, Bian J, Liu Z and Yuan Y: Cadmium induces mitochondrial
dysfunction via SIRT1 suppression-mediated oxidative stress in
neuronal cells. Environ Toxicol. 38:743–753. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
188
|
Sung JY, Kim SG, Kang YJ, Park SY and Choi
HC: SIRT1-dependent PGC-1α deacetylation by SRT1720 rescues
progression of atherosclerosis by enhancing mitochondrial function.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids.
1869(159453)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
189
|
Wang Q, Wang Y, Liu S, Sha X, Song X, Dai
Y, Zhao M, Cai L, Xu K and Li J: Theranostic nanoplatform to target
macrophages enables the inhibition of atherosclerosis progression
and fluorescence imaging of plaque in
ApoE(-/-) mice. J Nanobiotechnology.
19(222)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
190
|
Rabelo TK, Zeidán-Chuliá F, Caregnato FF,
Schnorr CE, Gasparotto J, Serafini MR, de Souza Araújo AA,
Quintans-Junior LJ, Moreira JCF and Gelain DP: In vitro
neuroprotective effect of shikimic acid against hydrogen
peroxide-induced oxidative stress. J Mol Neurosci. 56:956–965.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
191
|
Agrawal K, Chakraborty P, Dewanjee S,
Arfin S, Das SS, Dey A, Moustafa M, Mishra PC, Jafari SM, Jha NK,
et al: Neuropharmacological interventions of quercetin and its
derivatives in neurological and psychological disorders. Neurosci
Biobehav Rev. 144(104955)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
192
|
Korzh OM: The application of quercetin in
liposomal form for optimization of metabolic therapy of coronary
artery disease. National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, pp118-123,
2021.
|
|
193
|
Nazari-Khanamiri F and Ghasemnejad-Berenji
M: Quercetin and heart health: From molecular pathways to clinical
findings. J Food Biochem, 2023.
|
|
194
|
Ge C, Wang S, Wu X and Lei L: Quercetin
mitigates depression-like behavior via the suppression of
neuroinflammation and oxidative damage in corticosterone-induced
mice. J Chem Neuroanat. 132(102313)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|