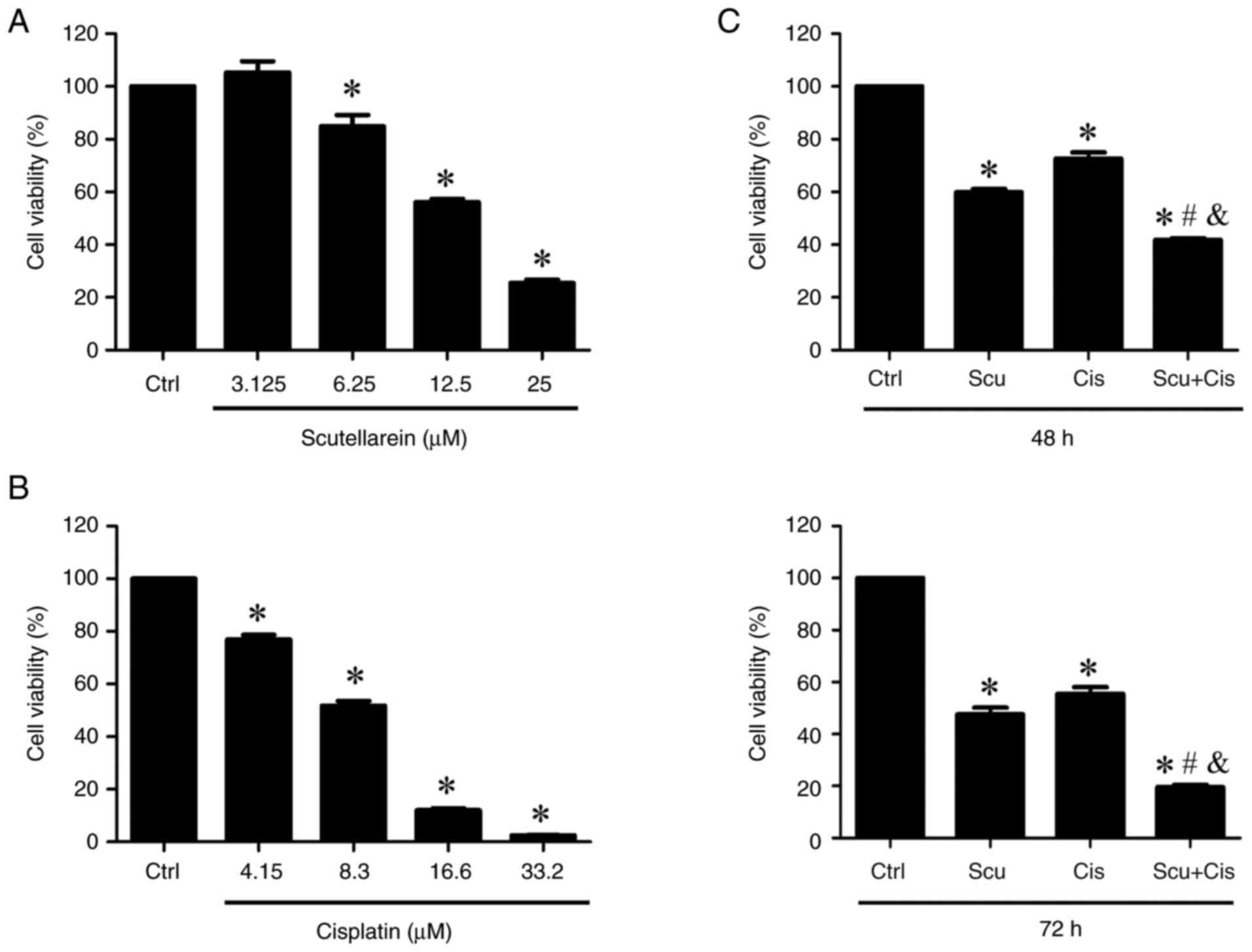
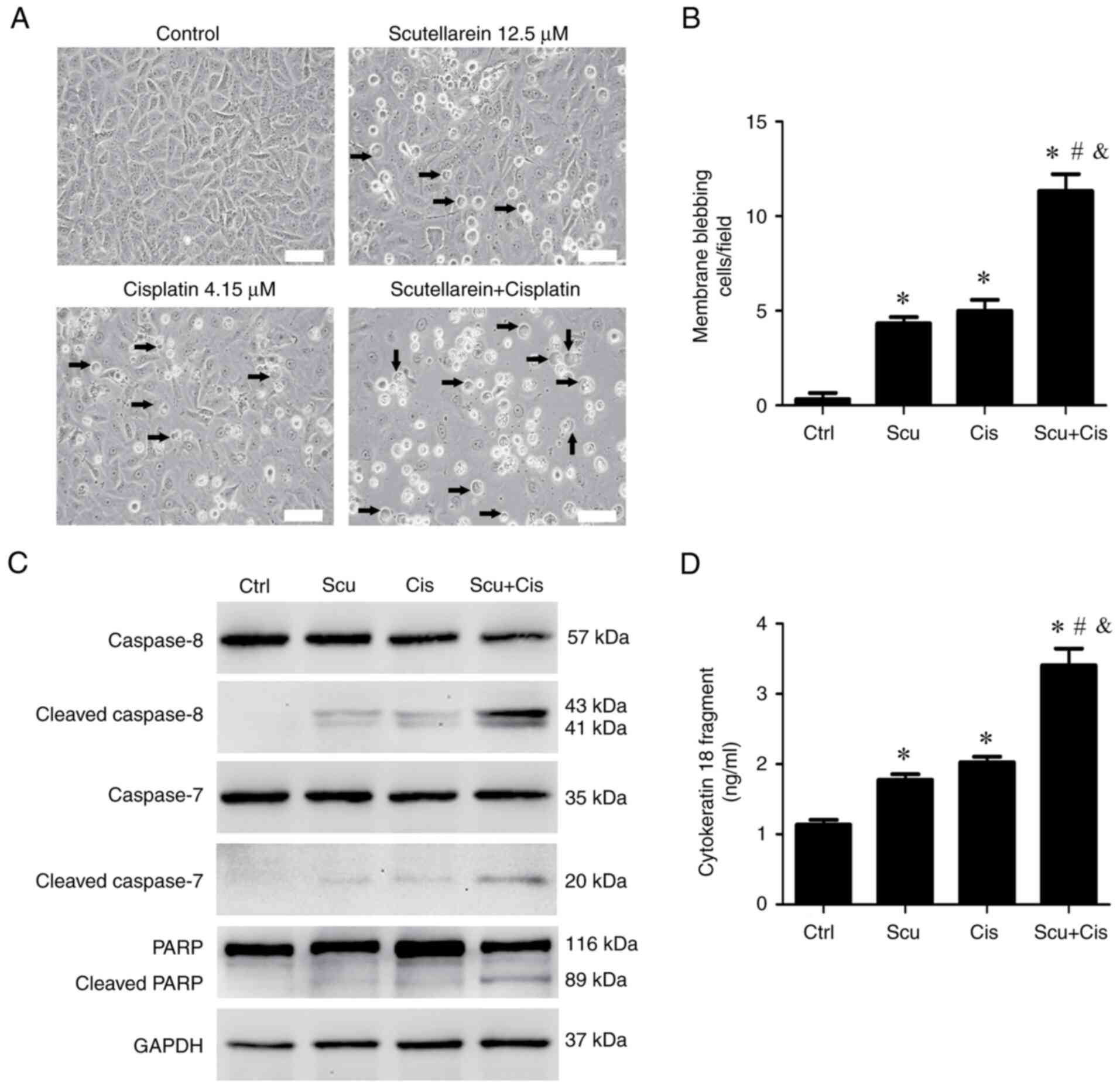
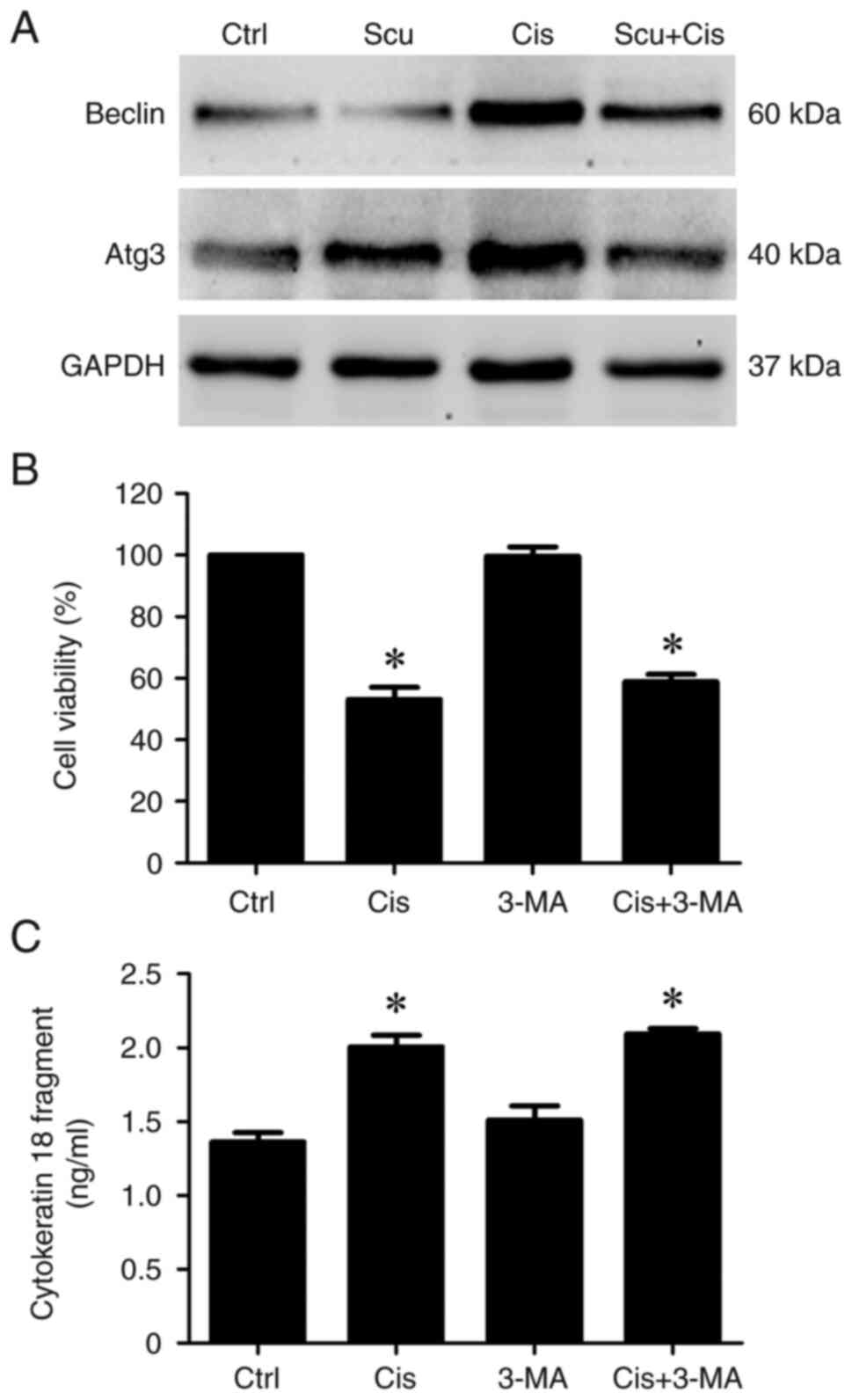
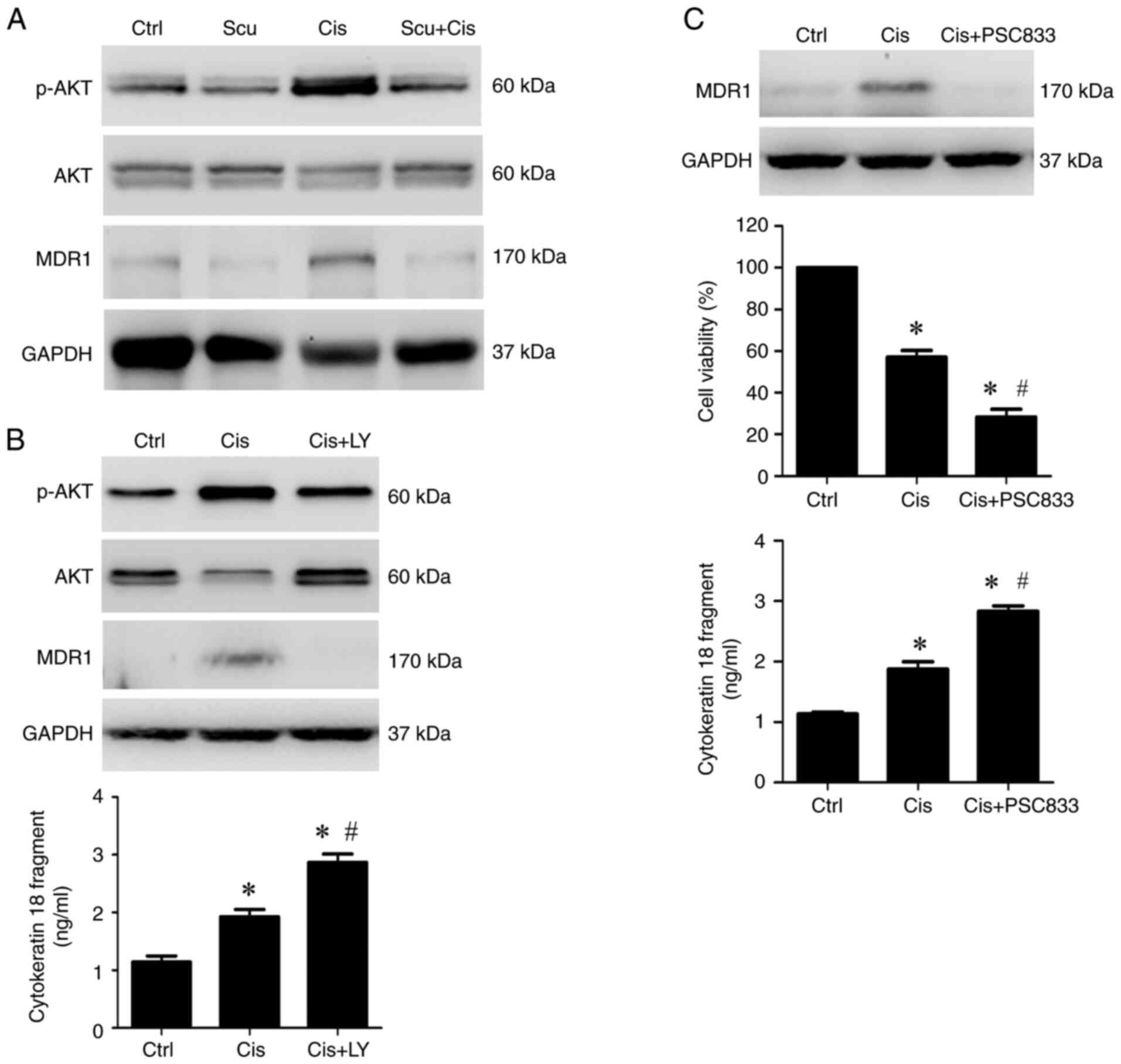
|
1
|
Jicman Stan D, Niculet E, Lungu M, Onisor
C, Rebegea L, Vesa D, Bezman L, Bujoreanu FC, Sarbu MI, Mihailov R,
et al: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A new synthesis of literature data
(Review). Exp Ther Med. 23(136)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yang XR, Diehl S, Pfeiffer R, Chen CJ, Hsu
WL, Dosemeci M, Cheng YJ, Sun B, Goldstein AM and Hildesheim A:
Chinese and American Genetic Epidemiology of NPC Study Team.
Evaluation of risk factors for nasopharyngeal carcinoma in
high-risk nasopharyngeal carcinoma families in Taiwan. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 14:900–905. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Feng H, Zhou Y, Wang L, Wang Y, Zhou S and
Tian F: Consumption of processed food and risk of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl Cancer
Res. 11:872–879. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bai R, Sun J, Xu Y, Sun Z and Zhao X:
Incidence and mortality trends of nasopharynx cancer from 1990 to
2019 in China: An age-period-cohort analysis. BMC Public Health.
22(1351)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yu H, Yin X, Mao Y, Chen M, Tang Q and Yan
S: The global burden of nasopharyngeal carcinoma from 2009 to 2019:
An observational study based on the global burden of disease study
2019. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 279:1519–1533. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Blanchard P, Lee A, Marguet S, Leclercq J,
Ng WT, Ma J, Chan AT, Huang PY, Benhamou E, Zhu G, et al:
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An
update of the MAC-NPC meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 16:645–655.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wu J, Zhou Q, Pan Z, Wang Y, Hu L, Chen G,
Wang S and Lyu J: Development and validation of a nomogram for
predicting long-term overall survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma:
A population-based study. Medicine (Baltimore).
99(e18974)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wu P, Tang Y, He J, Qi L, Jiang W and Zhao
S: ARC is highly expressed in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and confers
X-radiation and cisplatin resistance. Oncol Rep. 30:1807–1813.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Song Y, Zhou X, Bai W and Ma X: FBW7
increases drug sensitivity to cisplatin in human nasopharyngeal
carcinoma by downregulating the expression of multidrug
resistance-associated protein. Tumour Biol. 36:4197–4202.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yang CH, Chang YC, Hsu CC, Lin CH, Chen
IJ, Wu YT and Lan YY: Fucoidan enhances cisplatin-induced effects
on SCC-25 human oral cancer cells by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT
pathway. Anticancer Res. 43:4015–4022. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liu Z, Peng Q, Li Y and Gao Y: Resveratrol
enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma cells via
glutamine metabolism inhibition. BMB Rep. 51:474–479.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Park BH, Lim JE, Jeon HG, Seo SI, Lee HM,
Choi HY, Jeon SS and Jeong BC: Curcumin potentiates antitumor
activity of cisplatin in bladder cancer cell lines via ROS-mediated
activation of ERK1/2. Oncotarget. 7:63870–63886. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liao XZ, Gao Y, Zhao HW, Zhou M, Chen DL,
Tao LT, Guo W, Sun LL, Gu CY, Chen HR, et al: Cordycepin reverses
cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by activating
AMPK and Inhibiting AKT signaling pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol.
8(609285)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Xu Y, Kong W, Zhao S, Xiong D and Wang Y:
Capsaicin enhances cisplatin-induced anti-metastasis of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma by inhibiting EMT and ERK signaling via
serpin family B member 2. Carcinogenesis. 45:556–568.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lai J and Li C: Review on the
pharmacological effects and pharmacokinetics of scutellarein. Arch
Pharm (Weinheim). 357(e2400053)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Guo F, Yang F and Zhu YH: Scutellarein
from Scutellaria barbata induces apoptosis of human colon cancer
HCT116 cells through the ROS-mediated mitochondria-dependent
pathway. Nat Prod Res. 33:2372–2375. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lang X, Chen Z, Yang X, Yan Q, Xu M, Liu
W, He Q, Zhang Y, Cheng W and Zhao W: Scutellarein induces
apoptosis and inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion in
ovarian cancer via inhibition of EZH2/FOXO1 signaling. J Biochem
Mol Toxicol. 35(e22870)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shi X, Chen G and Liu X, Qiu Y, Yang S,
Zhang Y, Fang X, Zhang C and Liu X: Scutellarein inhibits cancer
cell metastasis in vitro and attenuates the development of
fibrosarcoma in vivo. Int J Mol Med. 35:31–38. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang Y, Chen X, Gueydan C and Han J:
Plasma membrane changes during programmed cell deaths. Cell Res.
28:9–21. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Costigan A, Hollville E and Martin SJ:
Discriminating between apoptosis, necrosis, necroptosis, and
ferroptosis by microscopy and flow cytometry. Curr Protoc.
3(e951)2023.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hsu M, Wu SY, Chang SS, Su IJ, Tsai CH,
Lai SJ, Shiau AL, Takada K and Chang Y: Epstein-Barr virus lytic
transactivator Zta enhances chemotactic activity through induction
of interleukin-8 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. J Virol.
82:3679–3688. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Carneiro BA and El-Deiry WS: Targeting
apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:395–417.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mishra AP, Salehi B, Sharifi-Rad M,
Pezzani R, Kobarfard F, Sharifi-Rad J and Nigam M: Programmed cell
death, from a cancer perspective: An overview. Mol Diagn Ther.
22:281–295. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ulukaya E, Karaagac E, Ari F, Oral AY,
Adim SB, Tokullugil AH and Evrensel T: Chemotherapy increases
caspase-cleaved cytokeratin 18 in the serum of breast cancer
patients. Radiol Oncol. 45:116–122. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Khandia R, Dadar M, Munjal A, Dhama K,
Karthik K, Tiwari R, Yatoo MI, Iqbal HMN, Singh KP, Joshi SK and
Chaicumpa W: A comprehensive review of autophagy and its various
roles in infectious, non-infectious, and lifestyle diseases:
Current knowledge and prospects for disease prevention, novel drug
design, and therapy. Cells. 8(674)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhou Y, Manghwar H, Hu W and Liu F:
Degradation mechanism of autophagy-related proteins and research
progress. Int J Mol Sci. 23(7301)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chen J, Zhang L, Zhou H, Wang W, Luo Y,
Yang H and Yi H: Inhibition of autophagy promotes cisplatin-induced
apoptotic cell death through Atg5 and Beclin 1 in A549 human lung
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 17:6859–6865. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kim A, Yim NH and Ma JY: Samsoeum, a
traditional herbal medicine, elicits apoptotic and autophagic cell
death by inhibiting Akt/mTOR and activating the JNK pathway in
cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 13(233)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang T, Yu J, Cheng S, Zhang Y, Zhou CH,
Qin J and Luo H: Research progress on the anticancer molecular
mechanism of targets regulating cell autophagy. Pharmacology.
108:224–237. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Rascio F, Spadaccino F, Rocchetti MT,
Castellano G, Stallone G, Netti GS and Ranieri E: The pathogenic
role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer onset and drug resistance: An
updated review. Cancers (Basel). 13(3949)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Morgensztern D and McLeod HL:
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as a target for cancer therapy. Anticancer
Drugs. 16:797–803. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Navaei ZN, Khalili-Tanha G, Zangouei AS,
Abbaszadegan MR and Moghbeli M: PI3K/AKT signaling pathway as a
critical regulator of Cisplatin response in tumor cells. Oncol Res.
29:235–250. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu R, Chen Y, Liu G, Li C, Song Y, Cao Z,
Li W, Hu J, Lu C and Liu Y: PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link
modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers. Cell Death Dis.
11(797)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sun Y, Guan Z, Liang L, Cheng Y, Zhou J,
Li J and Xu Y: HIF-1α/MDR1 pathway confers chemoresistance to
cisplatin in bladder cancer. Oncol Rep. 35:1549–1556.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
He C, Sun Z, Hoffman RM, Yang Z, Jiang Y,
Wang L and Hao Y: P-Glycoprotein overexpression is associated with
cisplatin resistance in human osteosarcoma. Anticancer Res.
39:1711–1718. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chen L, Li YC, Hu M, Zhao SJ and Yang QW:
Efficacy and safety of weekly versus triweekly cisplatin concurrent
with radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A meta-analysis.
Medicine (Baltimore). 101(e31842)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Singh Bhangu J, Macher-Beer A, Schimek V,
Garmroudi B, Tamandl D, Unger LW, Bachleitner-Hofmann T and Oehler
R: Circulating caspase-cleaved cytokeratin 18 correlates with
tumour burden and response to therapy in patients with colorectal
cancer liver metastasis. Clin Chim Acta. 538:53–59. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wang J and Wu GS: Role of autophagy in
cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
289:17163–17173. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|