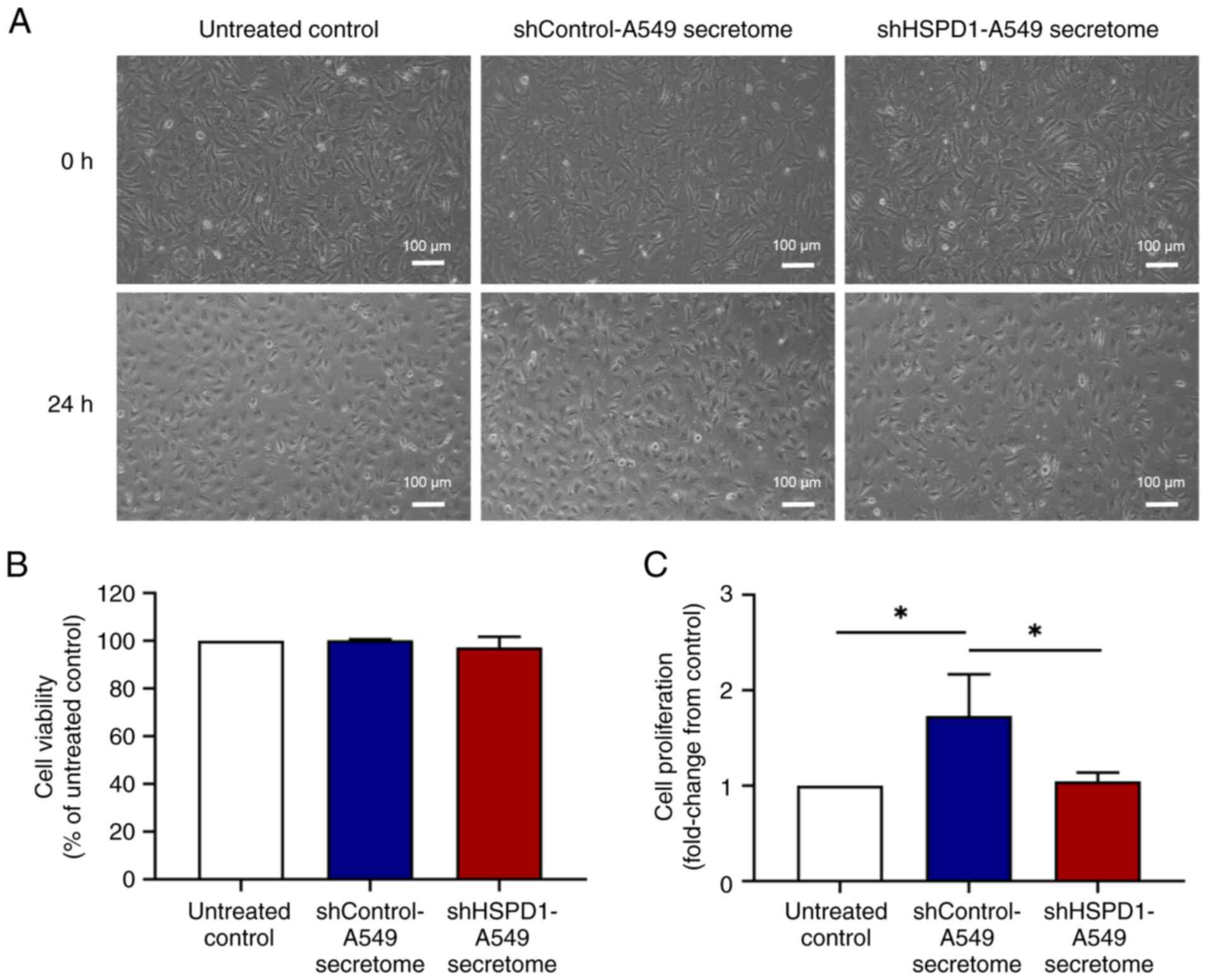
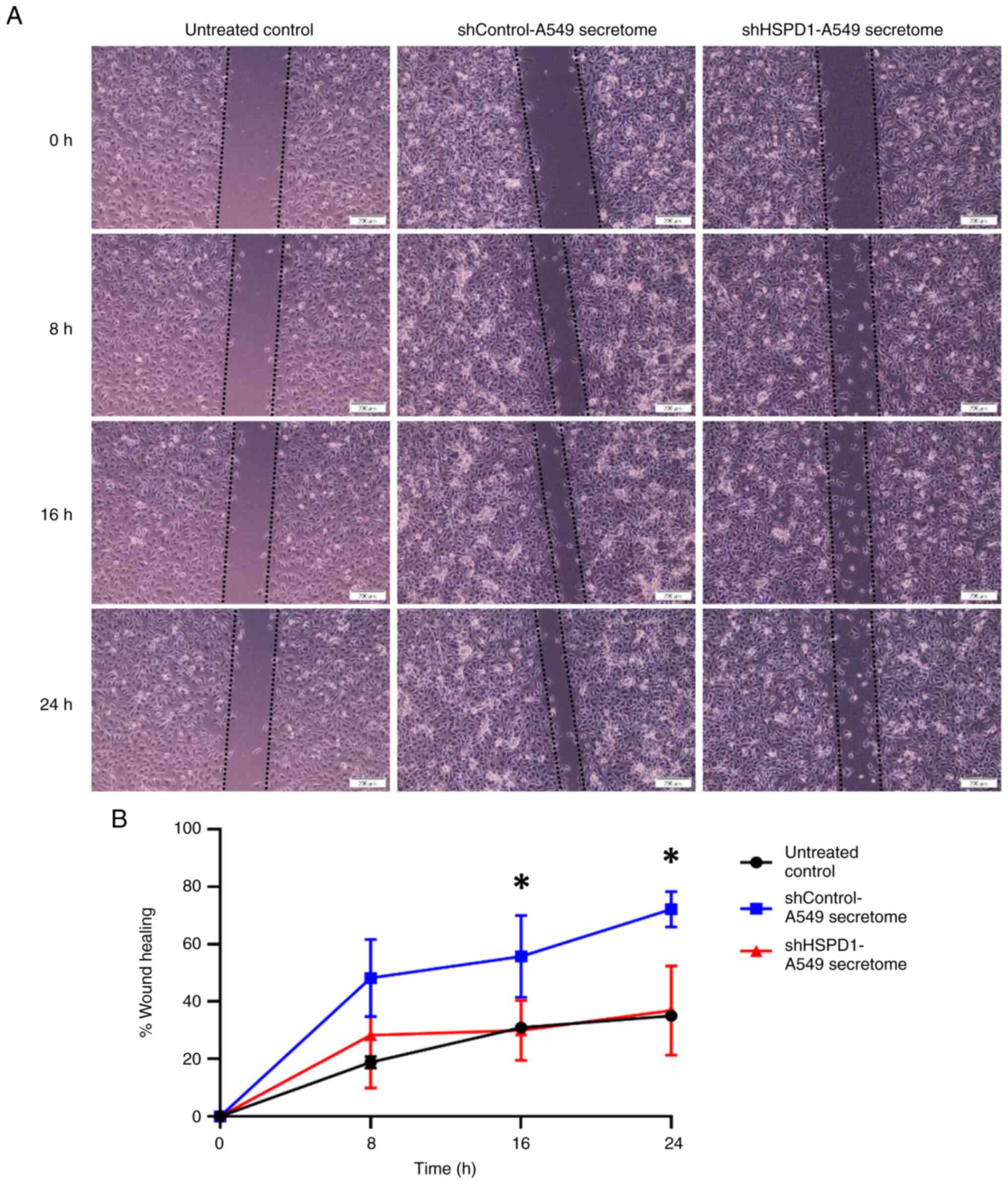
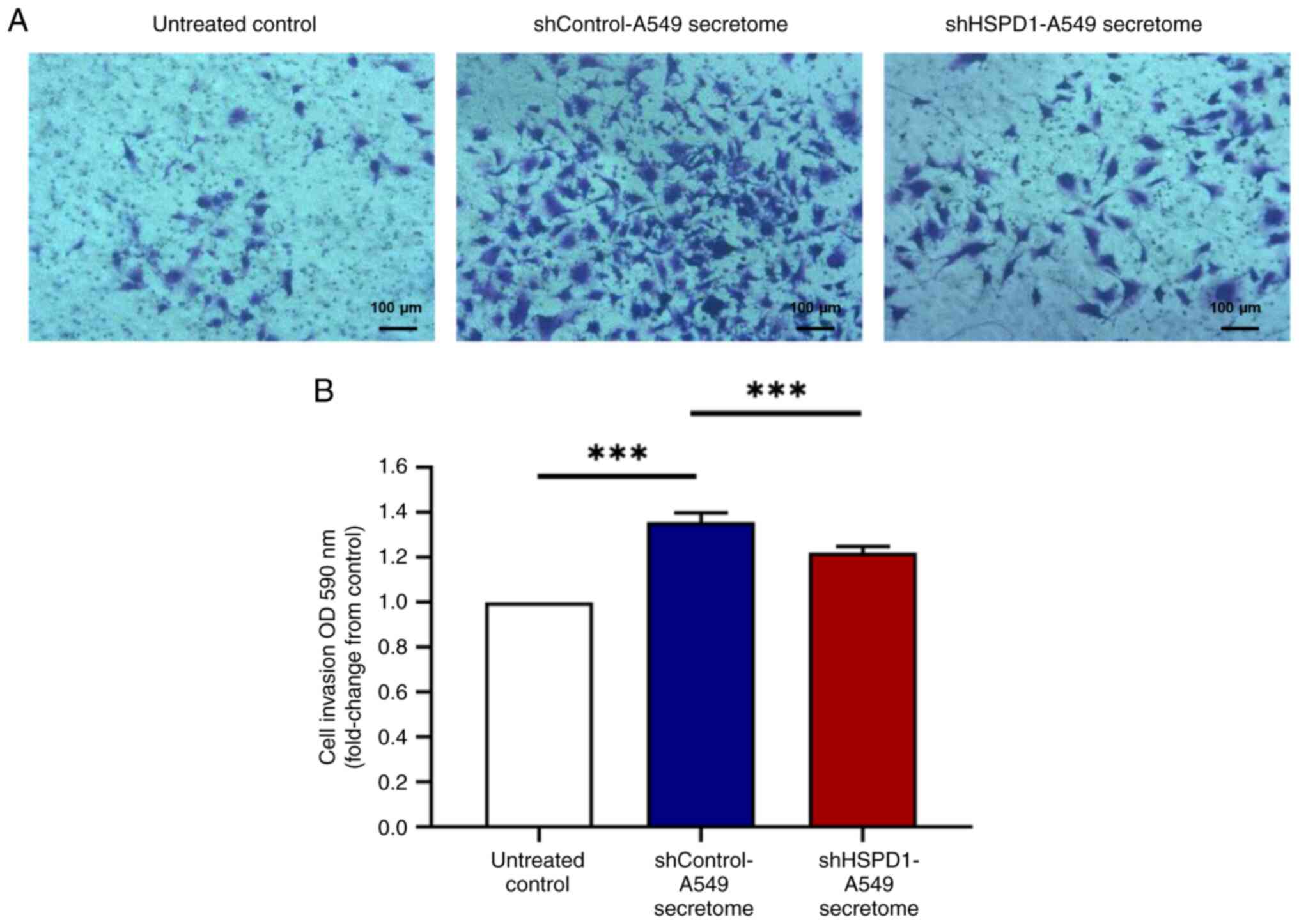
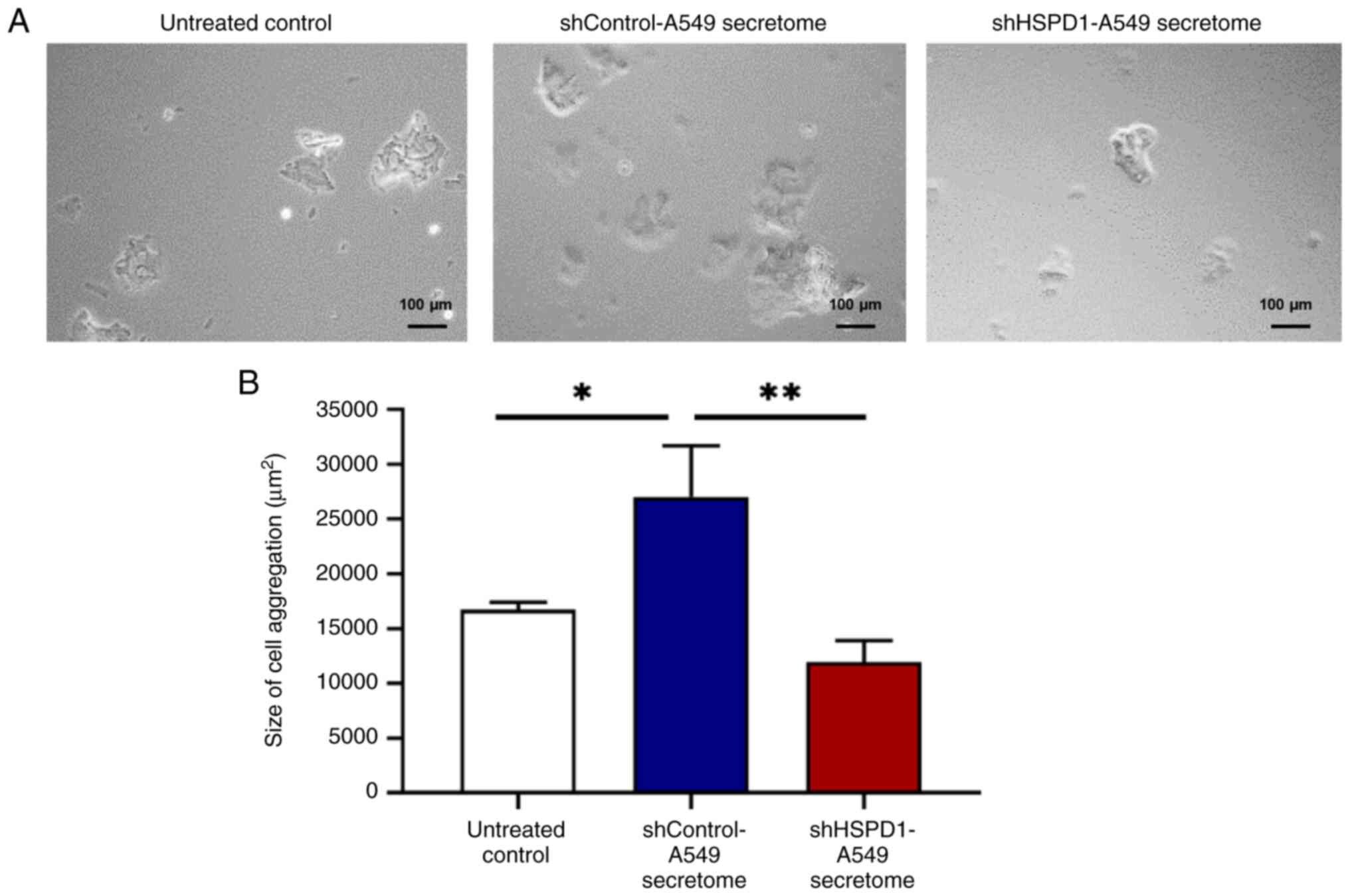
|
1
|
Folkman J: Role of angiogenesis in tumor
growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol. 29 (6 Suppl 16):S15–S18.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Li Y, Lin M, Wang S, Cao B, Li C and Li G:
Novel angiogenic regulators and anti-angiogenesis drugs targeting
angiogenesis signaling pathways: Perspectives for targeting
angiogenesis in lung cancer. Front Oncol. 12(842960)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Altorki NK, Markowitz GJ, Gao D, Port JL,
Saxena A, Stiles B, McGraw T and Mittal V: The lung
microenvironment: an important regulator of tumour growth and
metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 19:9–31. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hwang I, Kim JW, Ylaya K, Chung EJ, Kitano
H, Perry C, Hanaoka J, Fukuoka J, Chung JY and Hewitt SM:
Tumor-associated macrophage, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis
markers predict prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients. J
Transl Med. 18(443)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bremnes RM, Camps C and Sirera R:
Angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: The prognostic impact
of neoangiogenesis and the cytokines VEGF and bFGF in tumours and
blood. Lung Cancer. 51:143–158. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gu X, Chu L and Kang Y: Angiogenic
factor-based signature predicts prognosis and immunotherapy
response in non-small-cell lung cancer. Front Genet.
13(894024)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Majidpoor J and Mortezaee K: Angiogenesis
as a hallmark of solid tumors-clinical perspectives. Cell Oncol
(Dordr). 44:715–737. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ghalehbandi S, Yuzugulen J, Pranjol MZI
and Pourgholami MH: The role of VEGF in cancer-induced angiogenesis
and research progress of drugs targeting VEGF. Eur J Pharmacol.
949(175586)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lee S, Chen TT, Barber CL, Jordan MC,
Murdock J, Desai S, Ferrara N, Nagy A, Roos KP and Iruela-Arispe
ML: Autocrine VEGF signaling is required for vascular homeostasis.
Cell. 130:691–703. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu Y, Cox SR, Morita T and Kourembanas S:
Hypoxia regulates vascular endothelial growth factor gene
expression in endothelial cells. Identification of a 5' enhancer.
Circ Res. 77:638–643. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Du H, Shi H, Chen D, Zhou Y and Che G:
Cross-talk between endothelial and tumor cells via basic fibroblast
growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor signaling
promotes lung cancer growth and angiogenesis. Oncol Lett.
9:1089–1094. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhao Y, Guo S, Deng J, Shen J, Du F, Wu X,
Chen Y, Li M, Chen M, Li X, et al: VEGF/VEGFR-targeted therapy and
immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: Targeting the tumor
microenvironment. Int J Biol Sci. 18:3845–3858. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Vakhrushev IV, Nezhurina EK, Karalkin PA,
Tsvetkova AV, Sergeeva NS, Majouga AG and Yarygin KN: Heterotypic
multicellular spheroids as experimental and preclinical models of
sprouting angiogenesis. Biology (Basel). 11(18)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yun CW, Kim HJ, Lim JH and Lee SH: Heat
shock proteins: Agents of cancer development and therapeutic
targets in anti-cancer therapy. Cells. 9(60)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Quintana FJ and Cohen IR: The HSP60 immune
system network. Trends Immunol. 32:89–95. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tang Y, Yang Y, Luo J, Liu S, Zhan Y, Zang
H, Zheng H, Zhang Y, Feng J, Fan S and Wen Q: Overexpression of
HSP10 correlates with HSP60 and Mcl-1 levels and predicts poor
prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Biomark.
30:85–94. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Parma B, Ramesh V, Gollavilli PN, Siddiqui
A, Pinna L, Schwab A, Marschall S, Zhang S, Pilarsky C, Napoli F,
et al: Metabolic impairment of non-small cell lung cancers by
mitochondrial HSPD1 targeting. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
40(248)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Aluksanasuwan S, Somsuan K, Ngoenkam J,
Chutipongtanate S and Pongcharoen S: Potential association of HSPD1
with dysregulations in ribosome biogenesis and immune cell
infiltration in lung adenocarcinoma: An integrated bioinformatic
approach. Cancer Biomark. 39:155–170. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Aluksanasuwan S, Somsuan K, Ngoenkam J,
Chiangjong W, Rongjumnong A, Morchang A, Chutipongtanate S and
Pongcharoen S: Knockdown of heat shock protein family D member 1
(HSPD1) in lung cancer cell altered secretome profile and
cancer-associated fibroblast induction. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol
Cell Res. 187(119736)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Duan Y, Tang H, Mitchell-Silbaugh K, Fang
X, Han Z and Ouyang K: Heat shock protein 60 in cardiovascular
physiology and diseases. Front Mol Biosci. 7(73)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Qiu J, Gao HQ, Liang Y, Yu H and Zhou RH:
Comparative proteomics analysis reveals role of heat shock protein
60 in digoxin-induced toxicity in human endothelial cells. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1784:1857–1864. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Billack B, Heck DE, Mariano TM, Gardner
CR, Sur R, Laskin DL and Laskin JD: Induction of cyclooxygenase-2
by heat shock protein 60 in macrophages and endothelial cells. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 283:C1267–C1277. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lin CS, He PJ, Hsu WT, Wu MS, Wu CJ, Shen
HW, Hwang CH, Lai YK, Tsai NM and Liao KW: Helicobacter
pylori-derived heat shock protein 60 enhances angiogenesis via a
CXCR2-mediated signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
397:283–289. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zheng D, Zhang X, Xu J, Chen S, Wang B and
Yuan X: LncRNA LINC01503 promotes angiogenesis in colorectal cancer
by regulating VEGFA expression via miR-342-3p and HSP60 binding. J
Biomed Res: Oct 25, 2024 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
25
|
Suarez-Arnedo A, Torres Figueroa F,
Clavijo C, Arbeláez P, Cruz JC and Muñoz-Camargo C: An image J
plugin for the high throughput image analysis of in vitro scratch
wound healing assays. PLoS One. 15(e0232565)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Somsuan K, Peerapen P, Boonmark W,
Plumworasawat S, Samol R, Sakulsak N and Thongboonkerd V: ARID1A
knockdown triggers epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
carcinogenesis features of renal cells: Role in renal cell
carcinoma. FASEB J. 33:12226–12239. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:671–675. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li T, Fan J, Wang B, Traugh N, Chen Q, Liu
JS, Li B and Liu XS: TIMER: A web server for comprehensive analysis
of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Cancer Res. 77:e108–e110.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li B, Severson E, Pignon JC, Zhao H, Li T,
Novak J, Jiang P, Shen H, Aster JC, Rodig S, et al: Comprehensive
analyses of tumor immunity: Implications for cancer immunotherapy.
Genome Biol. 17(174)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Győrffy B: Transcriptome-level discovery
of survival-associated biomarkers and therapy targets in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Pharmacol. 181:362–374.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Makridakis M and Vlahou A: Secretome
proteomics for discovery of cancer biomarkers. J Proteomics.
73:2291–2305. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
da Cunha BR, Domingos C, Stefanini ACB,
Henrique T, Polachini GM, Castelo-Branco P and Tajara EH: Cellular
interactions in the tumor microenvironment: The role of secretome.
J Cancer. 10:4574–4587. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Cheng HW, Chen YF, Wong JM, Weng CW, Chen
HY, Yu SL, Chen HW, Yuan A and Chen JJ: Cancer cells increase
endothelial cell tube formation and survival by activating the
PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
36(27)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhong L, Roybal J, Chaerkady R, Zhang W,
Choi K, Alvarez CA, Tran H, Creighton CJ, Yan S, Strieter RM, et
al: Identification of secreted proteins that mediate cell-cell
interactions in an in vitro model of the lung cancer
microenvironment. Cancer Res. 68:7237–7245. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kramer N, Walzl A, Unger C, Rosner M,
Krupitza G, Hengstschläger M and Dolznig H: In vitro cell migration
and invasion assays. Mutat Res. 752:10–24. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tian J, Guo X, Liu XM, Liu L, Weng QF,
Dong SJ, Knowlton AA, Yuan WJ and Lin L: Extracellular HSP60
induces inflammation through activating and up-regulating TLRs in
cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 98:391–401. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Vabulas RM, Ahmad-Nejad P, da Costa C,
Miethke T, Kirschning CJ, Häcker H and Wagner H: Endocytosed HSP60s
use toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and TLR4 to activate the
toll/interleukin-1 receptor signaling pathway in innate immune
cells. J Biol Chem. 276:31332–31339. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Stierschneider A and Wiesner C: Shedding
light on the molecular and regulatory mechanisms of TLR4 signaling
in endothelial cells under physiological and inflamed conditions.
Front Immunol. 14(1264889)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Pei Z, Lin D, Song X, Li H and Yao H: TLR4
signaling promotes the expression of VEGF and TGFbeta1 in human
prostate epithelial PC3 cells induced by lipopolysaccharide. Cell
Immunol. 254:20–27. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Riddell JR, Maier P, Sass SN, Moser MT,
Foster BA and Gollnick SO: Peroxiredoxin 1 stimulates endothelial
cell expression of VEGF via TLR4 dependent activation of HIF-1α.
PLoS One. 7(e50394)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Voron T, Colussi O, Marcheteau E, Pernot
S, Nizard M, Pointet AL, Latreche S, Bergaya S, Benhamouda N,
Tanchot C, et al: VEGF-A modulates expression of inhibitory
checkpoints on CD8+ T cells in tumors. J Exp Med. 212:139–148.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Gabrilovich D, Ishida T, Oyama T, Ran S,
Kravtsov V, Nadaf S and Carbone DP: Vascular endothelial growth
factor inhibits the development of dendritic cells and dramatically
affects the differentiation of multiple hematopoietic lineages in
vivo. Blood. 92:4150–4166. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Song X and Luo Y: The regulatory mechanism
of Hsp90alpha secretion from endothelial cells and its role in
angiogenesis during wound healing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
398:111–117. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Schleicher M, Shepherd BR, Suarez Y,
Fernandez-Hernando C, Yu J, Pan Y, Acevedo LM, Shadel GS and Sessa
WC: Prohibitin-1 maintains the angiogenic capacity of endothelial
cells by regulating mitochondrial function and senescence. J Cell
Biol. 180:101–112. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|