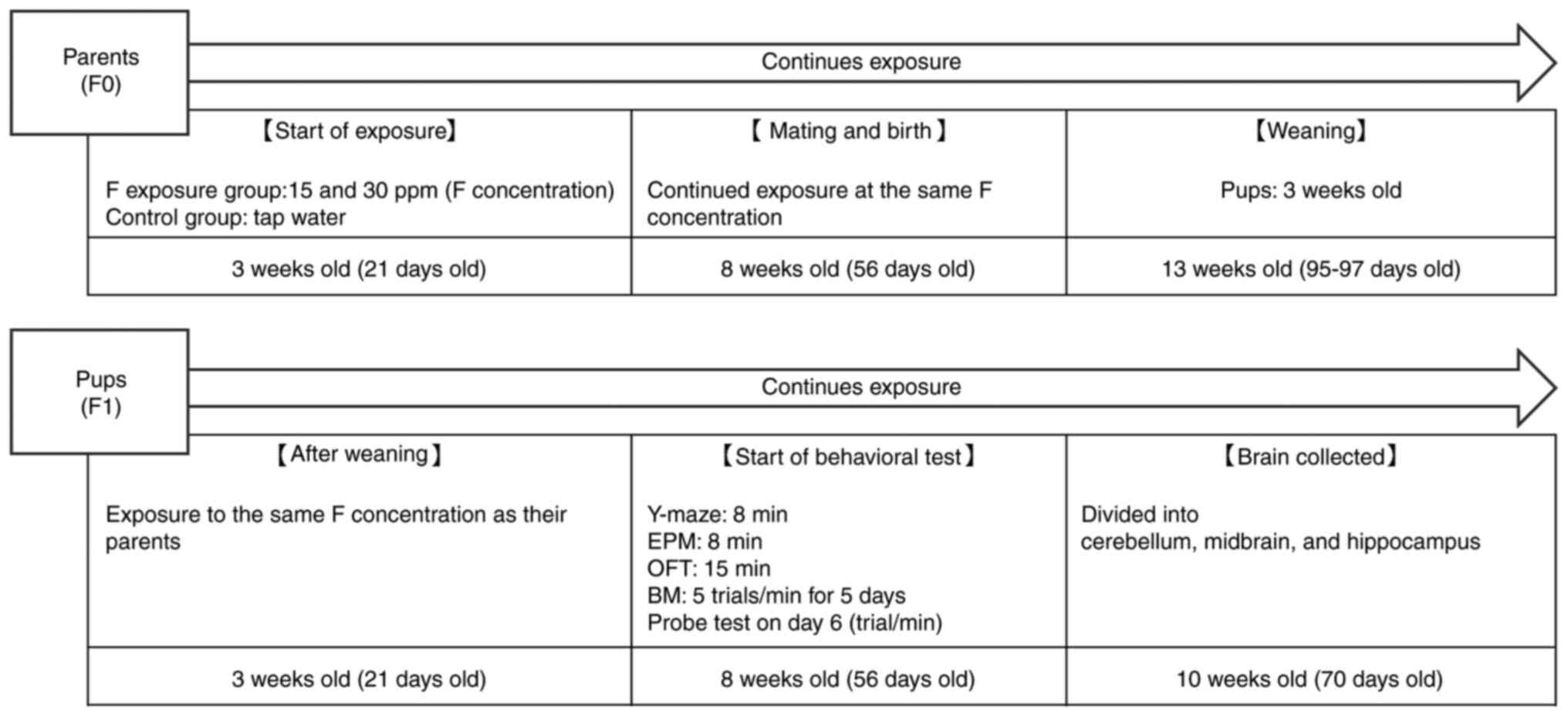
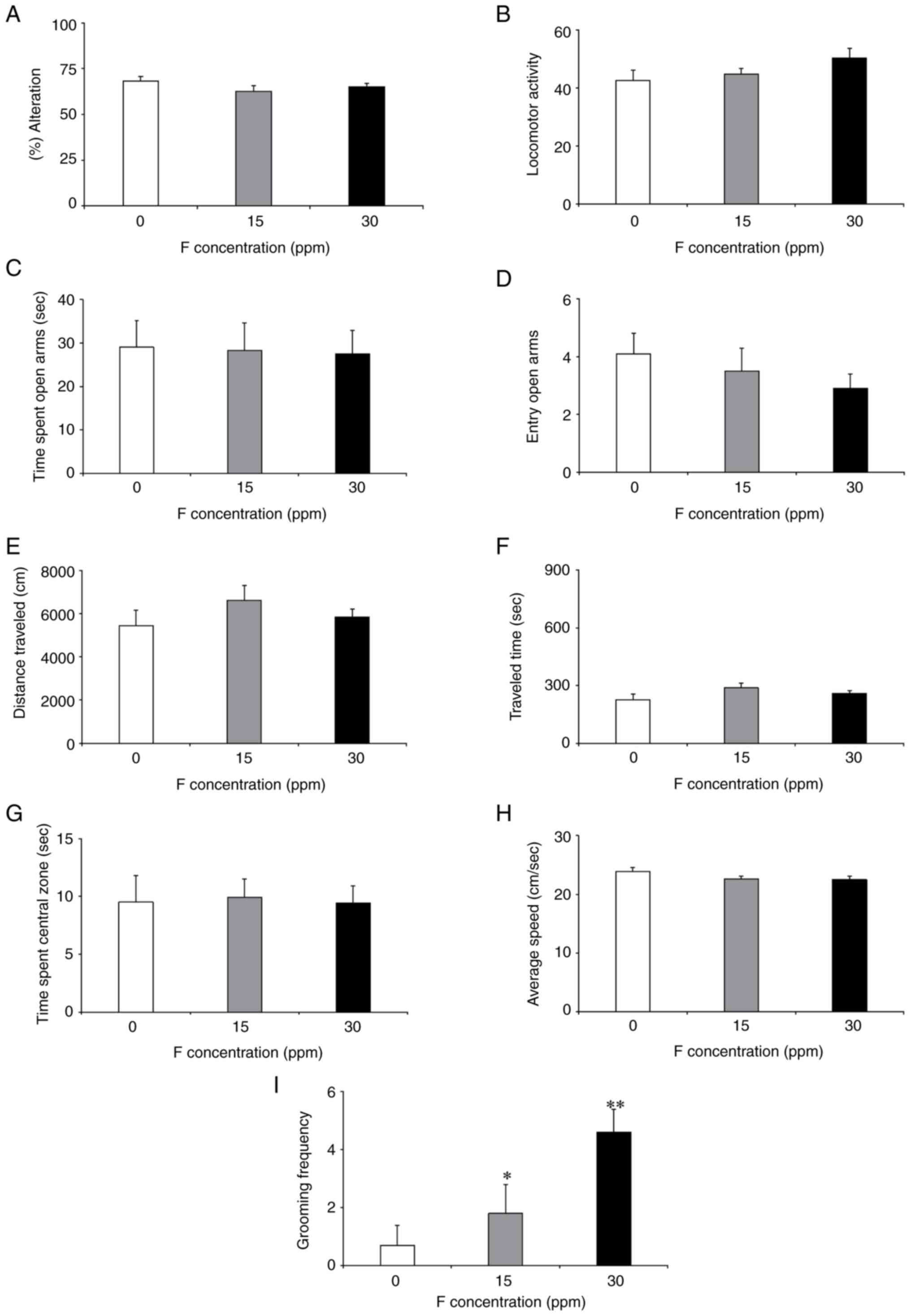
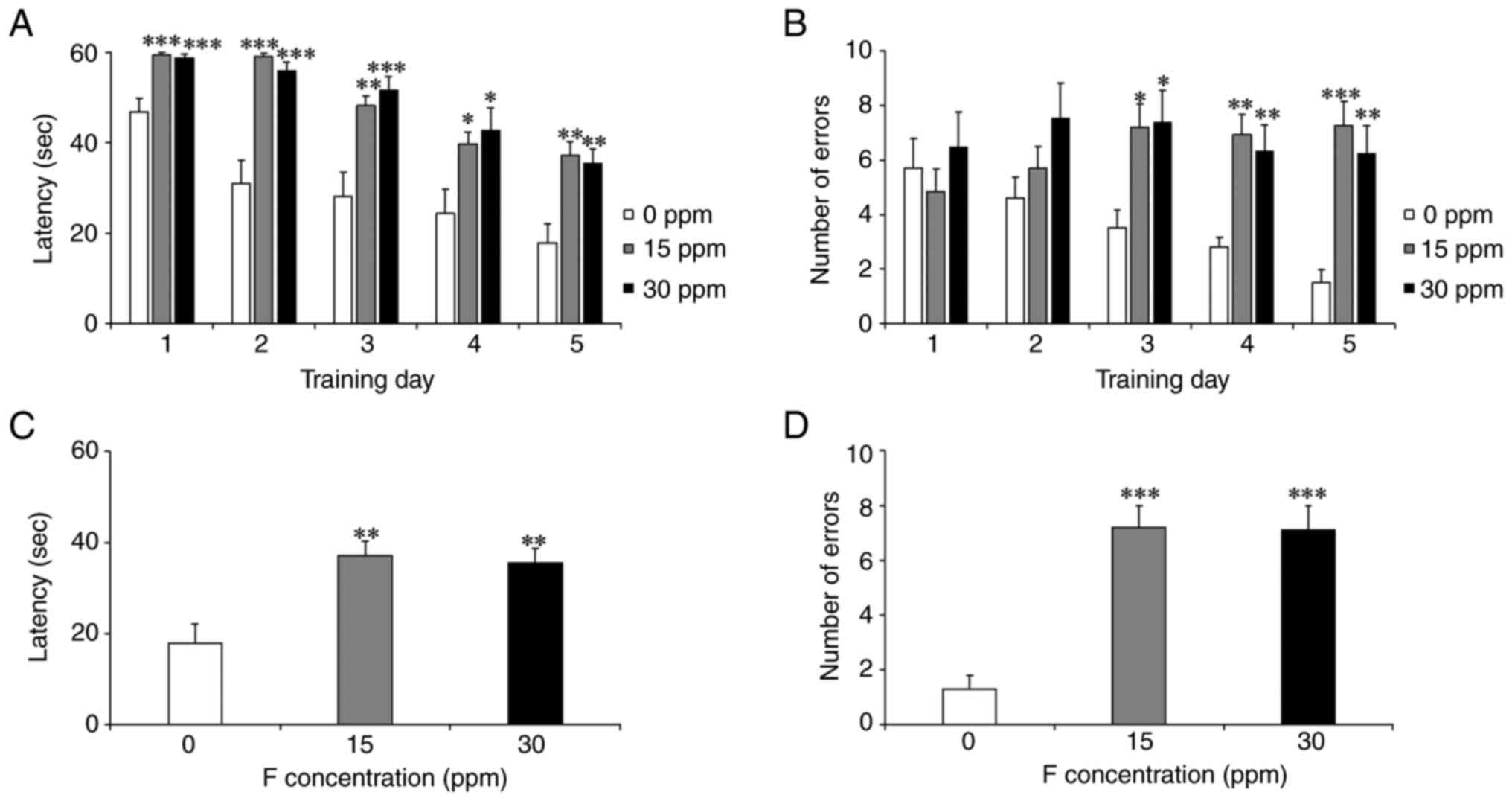
|
1
|
Srivastava S and Flora SJS: Fluoride in
drinking water and skeletal fluorosis: A Review of the global
impact. Curr Environ Health Rep. 7:140–146. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Strunecka A and Strunecky O: Chronic
fluoride exposure and the risk of autism spectrum disorder. Int J
Environ Res Public Health. 16(3431)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Green R, Lanphear B, Hornung R, Flora D,
Martinez-Mier EA, Neufeld R, Ayotte P, Muckle G and Till C:
Association between maternal fluoride exposure during pregnancy and
IQ scores in offspring in Canada. JAMA Pediatr. 173:940–948.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
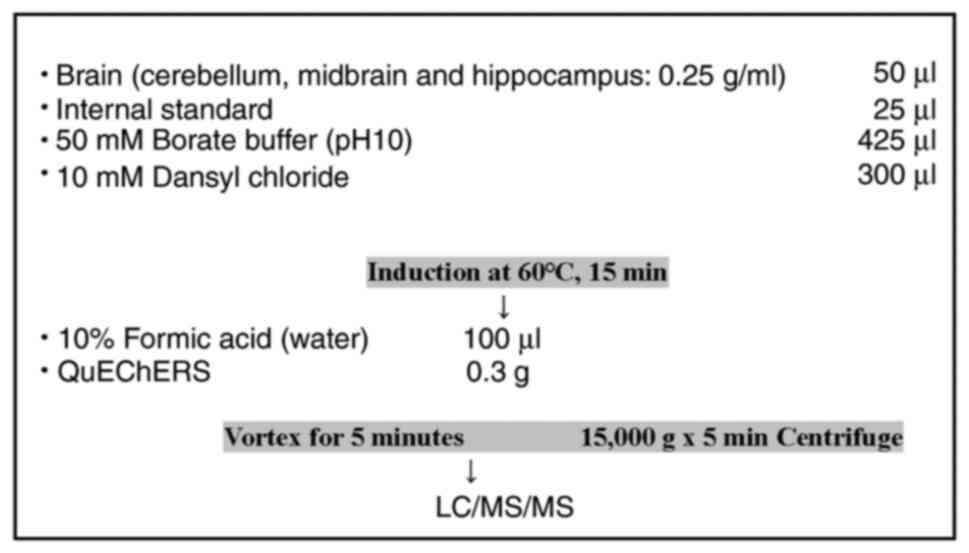
|
4
|
Bashash M, Marchand M, Hu H, Till C,
Martinez-Mier EA, Sanchez BN, Basu N, Peterson KE, Green R, Schnaas
L, et al: Prenatal fluoride exposure and attention deficit
hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms in children at 6-12 years of
age in Mexico City. Environ Int. 121(Pt 1):658–666. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Nilsson EE, Sadler-Riggleman I and Skinner
MK: Environmentally induced epigenetic transgenerational
inheritance of disease. Environ Epigenet. 4(dvy016)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Elsabbagh M, Divan G, Koh YJ, Kim YS,
Kauchali S, Marcín C, Montiel-Nava C, Patel V, Paula CS, Wang C, et
al: Global prevalence of autism and other pervasive developmental
disorders. Autism Res. 5:160–179. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Olusanya BO, Smythe T, Ogbo FA, Nair MKC,
Scher M and Davis AC: Global prevalence of developmental
disabilities in children and adolescents: A systematic umbrella
review. Front Public Health. 11(1122009)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Khairkar P, Palicarp SM, Kamble A, Alladi
S, Thomas S, Bommadi R, Mohanty S, Reddy R, Jothula KY, Anupama K,
et al: Outcome of systemic fluoride effects on developmental
neurocognitions and psychopathology in adolescent children. Indian
J Pediatr. 88(1264)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kuru R, Balan G, Yilmaz S, Taslı PN, Akyuz
S, Yarat A and Sahin F: The level of two trace elements in carious,
non-carious, primary, and permanent teeth. Eur Oral Res. 54:77–80.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Żwierełło W, Maruszewska A,
Skórka-Majewicz M and Gutowska I: Fluoride in the central nervous
system and its potential influence on the development and
invasiveness of brain tumours-a research hypothesis. Int J Mol Sci.
24(1558)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Abduweli Uyghurturk D, Goin DE,
Martinez-Mier EA, Woodruff TJ and DenBesten PK: Maternal and fetal
exposures to fluoride during mid-gestation among pregnant women in
northern California. Environ Health. 19(38)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Thippeswamy HM, Nanditha Kumar M, Girish
M, Prashanth SN and Shanbhog R: Linear regression approach for
predicting fluoride concentrations in maternal serum, urine and
cord blood of pregnant women consuming fluoride containing drinking
water. Clin Epidemiol Global Health. 10(100685)2021.
|
|
13
|
Bartos M, Gumilar F, Gallegos CE, Bras C,
Dominguez S, Cancela LM and Minetti A: Effects of perinatal
fluoride exposure on short- and long-term memory, brain antioxidant
status, and glutamate metabolism of young rat pups. Int J Toxicol.
38:405–414. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
National Toxicology Program (NTP): NTP
monograph on the state of the science concerning fluoride exposure
and neurodevelopment and cognition: a systematic review. NTP,
Research Triangle Park, NC, 2024.
|
|
15
|
Morabia A: Community water fluoridation:
Open discussions strengthen public health. Am J Public Health.
106:209–210. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
McGrady MG, Ellwood RP and Pretty IA:
Water fluoridation as a public health measure. Dent Update.
37:658–660, 662-664. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lu F, Zhang Y, Trivedi A, Jiang X, Chandra
D, Zheng J, Nakano Y, Abduweli Uyghurturk D, Jalai R, Onur SG, et
al: Fluoride related changes in behavioral outcomes may relate to
increased serotonin. Physiol Behav. 206:76–83. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bittencourt LO, Dionizio A, Ferreira MKM,
Aragão WAB, de Carvalho Cartágenes S, Puty B, do Socorro Ferraz
Maia C, Zohoori FV, Buzalaf MAR and Lima RR: Prolonged exposure to
high fluoride levels during adolescence to adulthood elicits
molecular, morphological, and functional impairments in the
hippocampus. Sci Rep. 13(11083)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ran LY, Xiang J, Zeng XX, Tang JL, Dong
YT, Zhang F, Yu WF, Qi XL, Xiao Y, Zou J, et al: Integrated
transcriptomic and proteomic analysis indicated that neurotoxicity
of rats with chronic fluorosis may be in mechanism involved in the
changed cholinergic pathway and oxidative stress. J Trace Elem Med
Biol. 64(126688)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Reddy YP, Tiwari S, Tomar LK, Desai N and
Sharma VK: Fluoride-induced expression of neuroinflammatory markers
and neurophysiological regulation in the brain of wistar rat model.
Biol Trace Elem Res. 199:2621–2626. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Pereira M, Dombrowski PA, Losso EM, Chioca
LR, Da Cunha C and Andreatini R: Memory impairment induced by
sodium fluoride is associated with changes in brain monoamine
levels. Neurotox Res. 19:55–62. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zeidan J, Fombonne E, Scorah J, Ibrahim A,
Durkin MS, Saxena S, Yusuf A, Shih A and Elsabbagh M: Global
prevalence of autism: A systematic review update. Autism Res.
15:778–790. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Iwasaki Y, Matsumoto H, Okumura M, Inoue
H, Kaji Y, Ando C and Kamei J: Determination of neurotransmitters
in mouse brain using miniaturized and tableted QuEChERS for the
sample preparation. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 217(114809)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Murayama C, Iwabuchi T, Kato Y, Yokokura
M, Harada T, Goto T, Tamayama T, Kameno Y, Wakuda T, Kuwabara H, et
al: Extrastriatal dopamine D2/3 receptor binding, functional
connectivity, and autism socio-communicational deficits: A PET and
fMRI study. Mol Psychiatry. 27:2106–2113. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Saleh MG, Prescot A, Chang L, Cloak C,
Cunningham E, Subramaniam P, Renshaw PF, Yurgelun-Todd D, Zöllner
HJ, Roberts TPL, et al: Glutamate measurements using edited MRS.
Magn Reson Med. 91:1314–1322. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu F, Ma J, Zhang H, Liu P, Liu YP, Xing
B and Dang YH: Fluoride exposure during development affects both
cognition and emotion in mice. Physiol Behav. 124:1–7.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Fiore G, Veneri F, Di Lorenzo R, Generali
L, Vinceti M and Filippini T: Fluoride exposure and ADHD: A
systematic review of epidemiological studies. Medicina (Kaunas).
59(797)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li X, Zhang J, Niu R, Manthari RK, Yang K
and Wang J: Effect of fluoride exposure on anxiety- and
depression-like behavior in mouse. Chemosphere. 215:454–460.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ottappilakkil H, Babu S, Balasubramanian
S, Manoharan S and Perumal E: Fluoride induced neurobehavioral
impairments in experimental animals: A brief review. Biol Trace
Elem Res. 201:1214–1236. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Izídio GS, Lopes DM, Spricigo L Jr and
Ramos A: Common variations in the pretest environment influence
genotypic comparisons in models of anxiety. Genes Brain Behav.
4:412–419. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Berridge CW and Waterhouse BD: The locus
coeruleus-noradrenergic system: Modulation of behavioral state and
state-dependent cognitive processes. Brain Res Brain Res Rev.
42:33–84. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Robinson TE and Berridge KC: Review. The
incentive sensitization theory of addiction: Some current issues.
Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 363:3137–3146. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
McCall C and Singer T: The animal and
human neuroendocrinology of social cognition, motivation and
behavior. Nat Neurosci. 15:681–688. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lord C, Elsabbagh M, Baird G and
Veenstra-Vanderweele J: Autism spectrum disorder. Lancet.
392:508–520. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Landrigan PJ: What causes autism?
Exploring the environmental contribution. Curr Opin Pediatr.
22:219–225. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hodges H, Fealko C and Soares N: Autism
spectrum disorder: Definition, epidemiology, causes, and clinical
evaluation. Transl Pediatr. 9 (Suppl 1):S55–S65. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Eden AS, Schreiber J, Anwander A, Keuper
K, Laeger I, Zwanzger P, Zwitserlood P, Kugel H and Dobel C:
Emotion regulation and trait anxiety are predicted by the
microstructure of fibers between amygdala and prefrontal cortex. J
Neurosci. 35:6020–6027. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Gold AL, Shechner T, Farber MJ, Spiro CN,
Leibenluft E, Pine DS and Britton JC: Amygdala-cortical
connectivity: Associations with anxiety, development, and threat.
Depress Anxiety. 33:917–926. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Rudolph S, Badura A, Lutzu S, Pathak SS,
Thieme A, Verpeut JL, Wagner MJ, Yang YM and Fioravante D:
Cognitive-affective functions of the cerebellum. J Neurosci.
43:7554–7564. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Pal MM: Glutamate: The master
neurotransmitter and its implications in chronic stress and mood
disorders. Front Hum Neurosci. 15(722323)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
An L and Sun W: Prenatal melamine exposure
impairs spatial cognition and hippocampal synaptic plasticity by
presynaptic and postsynaptic inhibition of glutamatergic
transmission in adolescent offspring. Toxicol Lett. 269:55–64.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Fendt M, Imobersteg S, Peterlik D,
Chaperon F, Mattes C, Wittmann C, Olpe HR, Mosbacher J, Vranesic I,
van der Putten H, et al: Differential roles of mGlu(7) and mGlu(8)
in amygdala-dependent behavior and physiology. Neuropharmacology.
72:215–223. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Mapelli L, Soda T, D'Angelo E and Prestori
F: The cerebellar involvement in autism spectrum disorders: From
the social brain to mouse models. Int J Mol Sci.
23(3894)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Cramb KML, Beccano-Kelly D, Cragg SJ and
Wade-Martins R: Impaired dopamine release in Parkinson's disease.
Brain. 146:3117–3132. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Chen Y, Chen T and Hou R: Locus coeruleus
in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: A systematic review.
Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 8(e12257)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Borodovitsyna O, Flamini M and Chandler D:
Noradrenergic modulation of cognition in health and disease. Neural
Plast. 2017(6031478)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sara SJ: The locus coeruleus and
noradrenergic modulation of cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci.
10:211–223. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Jenkins TA, Nguyen JC, Polglaze KE and
Bertrand PP: Influence of tryptophan and serotonin on mood and
cognition with a possible role of the gut-brain axis. Nutrients.
8(56)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Thorstensen JR, Henderson TT and Kavanagh
JJ: Serotonergic and noradrenergic contributions to motor cortical
and spinal motoneuronal excitability in humans. Neuropharmacology.
242(109761)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Brown PL, Shepard PD, Elmer GI, Stockman
S, McFarland R, Mayo CL, Cadet JL, Krasnova IN, Greenwald M,
Schoonover C and Vogel MW: Altered spatial learning, cortical
plasticity and hippocampal anatomy in a neurodevelopmental model of
schizophrenia-related endophenotypes. Eur J Neurosci. 36:2773–2781.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Pae CU, Marks DM, Han C, Patkar AA and
Steffens D: Does neurotropin-3 have a therapeutic implication in
major depression? Int J Neurosci. 118:1515–1522. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Hong SM, Liu Z, Fan Y, Neumann M, Won SJ,
Lac D, Lum X, Weinstein PR and Liu J: Reduced hippocampal
neurogenesis and skill reaching performance in adult Emx1 mutant
mice. Exp Neurol. 206:24–32. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Richards SEV and Van Hooser SD: Neural
architecture: From cells to circuits. J Neurophysiol. 120:854–866.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Institute of Medicine Committee on
Assessing Interactions Among Social B and Genetic Factors in H: The
National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National
Institutes of Health. In: Genes, behavior, and the social
environment: Moving beyond the nature/nurture debate. Hernandez LM
and Blazer DG (eds). National Academies Press (US), National
Academy of Sciences, Washington (DC), 2006.
|
|
55
|
Rodriguez PJ, Goodwin Cartwright BM,
Gratzl S, Brar R, Baker C, Gluckman TJ and Stucky NL: Semaglutide
vs tirzepatide for weight loss in adults with overweight or
obesity. JAMA Intern Med. 184:1056–1064. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|