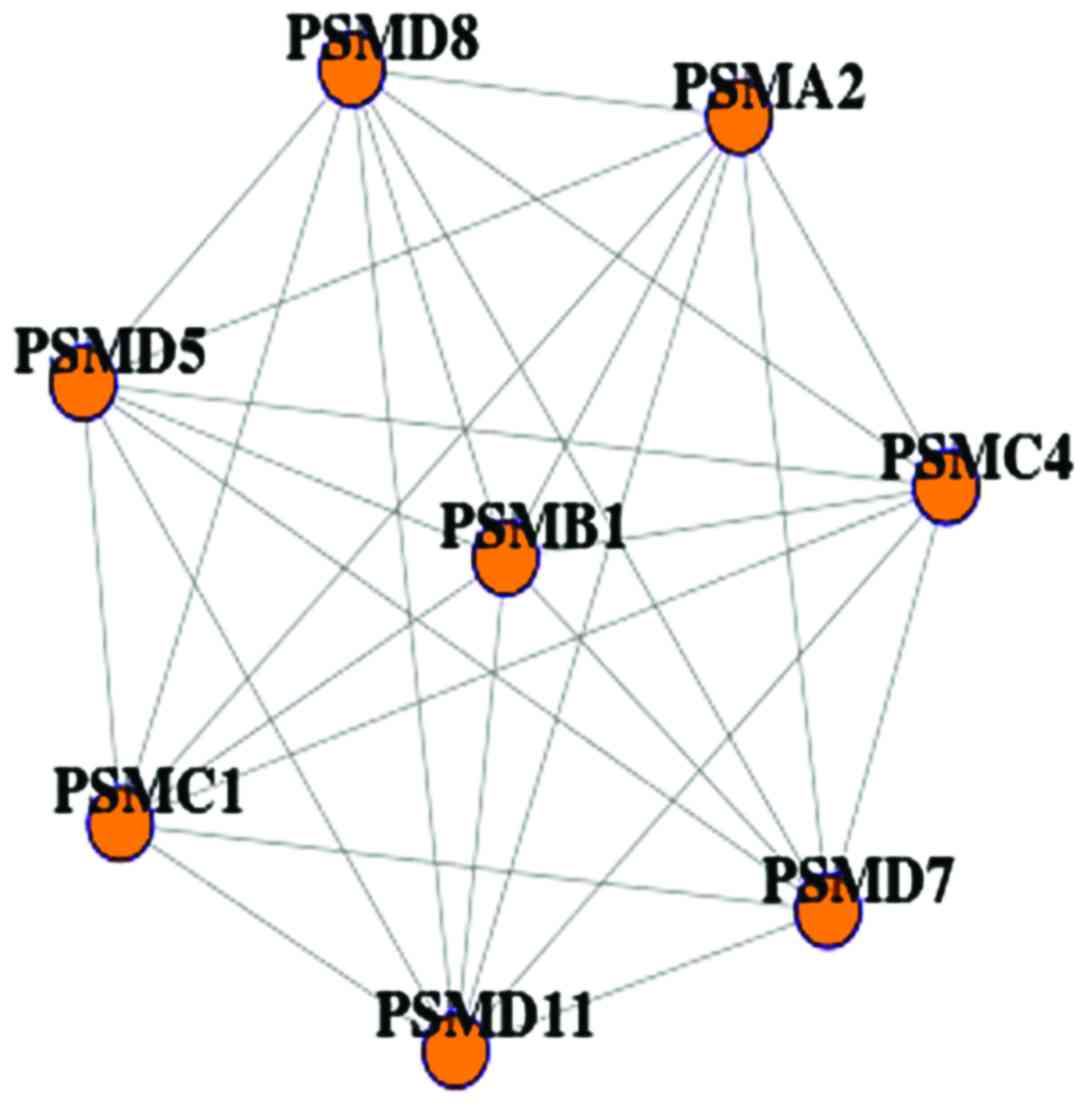
|
1
|
Czerwiński E, Badurski JE,
Marcinowska-Suchowierska E and Osieleniec J: Current understanding
of osteoporosis according to the position of the World Health
Organization (WHO) and International Osteoporosis Foundation. Ortop
Traumatol Rehabil. 9:337–356. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Heaney RP, Abrams S, Dawson-Hughes B,
Looker A, Marcus R, Matkovic V and Weaver C: Peak bone mass.
Osteoporos Int. 11:985–1009. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lei SF, Wu S, Li LM, Deng FY, Xiao SM,
Jiang C, Chen Y, Jiang H, Yang F, Tan LJ, et al: An in vivo
genome wide gene expression study of circulating monocytes
suggested GBP1, STAT1 and CXCL10 as novel risk genes for the
differentiation of peak bone mass. Bone. 44:1010–1014. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bonjour JP, Chevalley T, Ferrari S and
Rizzoli R: The importance and relevance of peak bone mass in the
prevalence of osteoporosis. Salud Publica Mex. 51 Suppl 1:S5–S17.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Akatsu T, Tanaka
H, Sasaki T, Nishihara T, Koga T, Martin TJ and Suda T: Origin of
osteoclasts: Mature monocytes and macrophages are capable of
differentiating into osteoclasts under a suitable microenvironment
prepared by bone marrow-derived stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 87:7260–7264. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fujikawa Y, Quinn JM, Sabokbar A, McGee JO
and Athanasou NA: The human osteoclast precursor circulates in the
monocyte fraction. Endocrinology. 137:4058–4060. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Quinn JM, Neale S, Fujikawa Y, McGee JO
and Athanasou NA: Human osteoclast formation from blood monocytes,
peritoneal macrophages, and bone marrow cells. Calcif Tissue Int.
62:527–531. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guasconi L, Chiapello LS and Masih DT:
Fasciola hepatica excretory-secretory products induce CD4+T
cell anergy via selective up-regulation of PD-L2 expression on
macrophages in a Dectin-1 dependent way. Immunobiology.
220:934–939. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Horton MA, Spragg JH, Bodary SC and
Helfrich MH: Recognition of cryptic sites in human and mouse
laminins by rat osteoclasts is mediated by beta 3 and beta 1
integrins. Bone. 15:639–646. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Parfitt AM: Osteonal and hemi-osteonal
remodeling: The spatial and temporal framework for signal traffic
in adult human bone. J Cell Biochem. 55:273–286. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma X, Gao L, Karamanlidis G, Gao P, Lee
CF, Garcia-Menendez L, Tian R and Tan K: Revealing pathway dynamics
in heart diseases by analyzing multiple differential networks. PLOS
Comput Biol. 11:e10043322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mine KL, Shulzhenko N, Yambartsev A,
Rochman M, Sanson GF, Lando M, Varma S, Skinner J, Volfovsky N,
Deng T, et al: Gene network reconstruction reveals cell cycle and
antiviral genes as major drivers of cervical cancer. Nat Commun.
4:18062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Barabási AL, Gulbahce N and Loscalzo J:
Network medicine: A network-based approach to human disease. Nat
Rev Genet. 12:56–68. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Greenblum S, Turnbaugh PJ and Borenstein
E: Metagenomic systems biology of the human gut microbiome reveals
topological shifts associated with obesity and inflammatory bowel
disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:594–599. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cho DY, Kim YA and Przytycka TM: Chapter
5: Network biology approach to complex diseases. PLOS Comput Biol.
8:e10028202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Scheffer M, Carpenter SR, Lenton TM,
Bascompte J, Brock W, Dakos V, van de Koppel J, van de Leemput IA,
Levin SA, van Nes EH, et al: Anticipating critical transitions.
Science. 338:344–348. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mitchell HD, Eisfeld AJ, Sims AC,
McDermott JE, Matzke MM, Webb-Robertson BJ, Tilton SC, Tchitchek N,
Josset L, Li C, et al: A network integration approach to predict
conserved regulators related to pathogenicity of influenza and
SARS-CoV respiratory viruses. PLoS One. 8:e693742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Teschendorff AE, Banerji CR, Severini S,
Kuehn R and Sollich P: Increased signaling entropy in cancer
requires the scale-free property of protein interaction networks.
Sci Rep. 5:96462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lopes FM, de Oliveira EA and Cesar RM Jr:
Inference of gene regulatory networks from time series by Tsallis
entropy. BMC Syst Biol. 5:612011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jin S, Li Y, Pan R and Zou X:
Characterizing and controlling the inflammatory network during
influenza A virus infection. Sci Rep. 4:37992014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering
C, et al: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks, with
increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res. 41(D1):
D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Srihari S and Ragan MA: Systematic
tracking of dysregulated modules identifies novel genes in cancer.
Bioinformatics. 29:1553–1561. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu G, Wong L and Chua HN: Complex
discovery from weighted PPI networks. Bioinformatics. 25:1891–1897.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Srihari S and Leong HW: A survey of
computational methods for protein complex prediction from protein
interaction networks. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 11:12300022013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hong S, Dong H, Jin L and Xiong M: Gene
co-expression network and functional module analysis of ovarian
cancer. Int J Comput Biol Drug Des. 4:147–164. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Teschendorff AE and Severini S: Increased
entropy of signal transduction in the cancer metastasis phenotype.
BMC Syst Biol. 4:1042010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
West J, Bianconi G, Severini S and
Teschendorff AE: Differential network entropy reveals cancer system
hallmarks. Sci Rep. 2:8022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Assenov Y, Ramírez F, Schelhorn SE,
Lengauer T and Albrecht M: Computing topological parameters of
biological networks. Bioinformatics. 24:282–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen B, Fan W, Liu J and Wu FX:
Identifying protein complexes and functional modules - from static
PPI networks to dynamic PPI networks. Brief Bioinform. 15:177–194.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li A, Chen M, Jiang TX, Wu P, Nie Q,
Widelitz R and Chuong CM: Shaping organs by a
wingless-int/Notch/nonmuscle myosin module which orients feather
bud elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:E1452–E1461. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shim SM, Lee WJ, Kim Y, Chang JW, Song S
and Jung YK: Role of S5b/PSMD5 in proteasome inhibition caused by
TNF-α/NFκB in higher eukaryotes. Cell Rep. 2:603–615. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Djakovic SN, Schwarz LA, Barylko B,
DeMartino GN and Patrick GN: Regulation of the proteasome by
neuronal activity and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase
II. J Biol Chem. 284:26655–26665. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kawahara H and Yokosawa H: Intracellular
calcium mobilization regulates the activity of 26 S proteasome
during the metaphase-anaphase transition in the ascidian meiotic
cell cycle. Dev Biol. 166:623–633. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li X, Yang D, Li L, Peng C, Chen S and Le
W: Proteasome inhibitor lactacystin disturbs the intracellular
calcium homeostasis of dopamine neurons in ventral mesencephalic
cultures. Neurochem Int. 50:959–965. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|