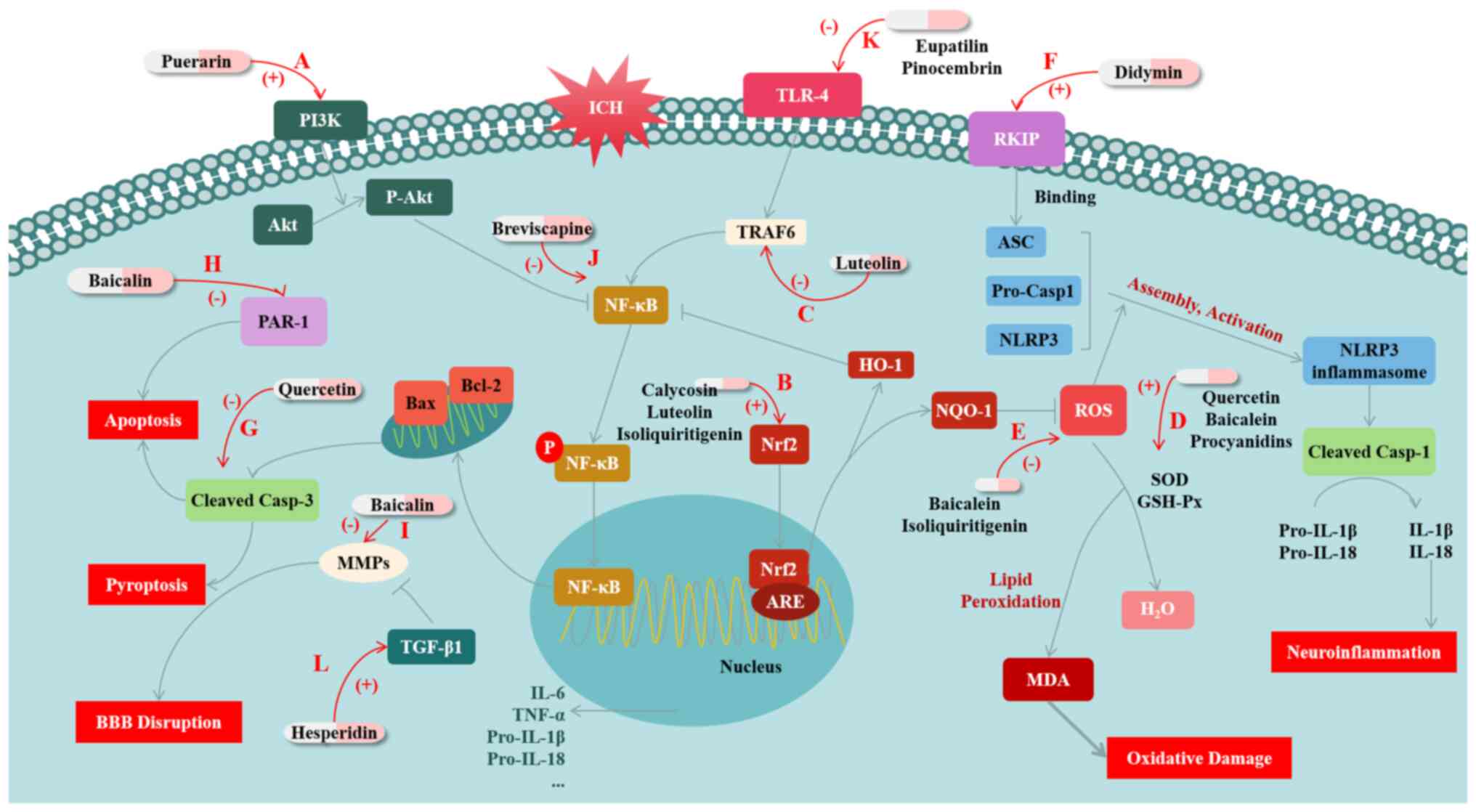
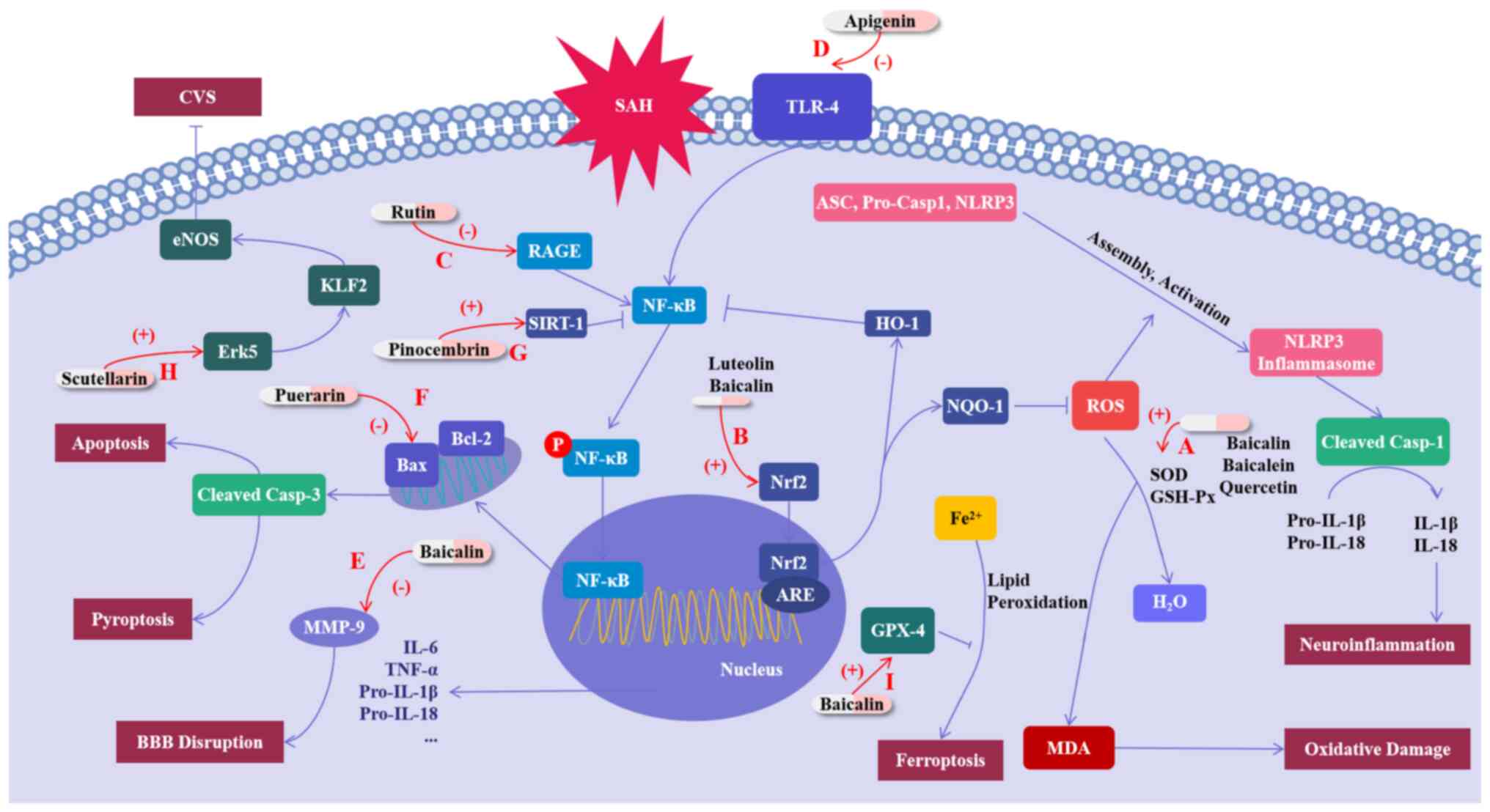
|
1
|
Magid-Bernstein J, Girard R, Polster S,
Srinath A, Romanos S, Awad IA and Sansing LH: Cerebral hemorrhage:
Pathophysiology, treatment, and future directions. Circ Res.
130:1204–1229. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Feigin VL, Lawes CM, Bennett DA,
Barker-Collo SL and Parag V: Worldwide stroke incidence and early
case fatality reported in 56 population-based studies: A systematic
review. Lancet Neurol. 8:355–369. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
van Asch CJ, Luitse MJ, Rinkel GJ, van der
Tweel I, Algra A and Klijn CJ: Incidence, case fatality, and
functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time,
according to age, sex, and ethnic origin: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 9:167–176. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chen Y, Chen S, Chang J, Wei J, Feng M and
Wang R: Perihematomal edema after intracerebral hemorrhage: An
update on pathogenesis, risk factors, and therapeutic advances.
Front Immunol. 12(740632)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Xiao L, Zheng H, Li J, Wang Q and Sun H:
Neuroinflammation mediated by NLRP3 inflammasome after
intracerebral hemorrhage and potential therapeutic targets. Mol
Neurobiol. 57:5130–5149. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Keep RF, Hua Y and Xi G: Intracerebral
haemorrhage: Mechanisms of injury and therapeutic targets. Lancet
Neurol. 11:720–731. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wan Y, Holste KG, Hua Y, Keep RF and Xi G:
Brain edema formation and therapy after intracerebral hemorrhage.
Neurobiol Dis. 176(105948)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Muehlschlegel S: Subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Continuum (Minneap Minn). 24:1623–1657. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Claassen J and Park S: Spontaneous
subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 400:846–862. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sveinsson ÓÁ, Ólafsson IH, Kjartansson Ó
and Valdimarsson EM: Spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhage-review.
Laeknabladid. 97:355–362. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Icelandic).
|
|
11
|
Lucke-Wold B, Logsdon A, Manoranjan B,
Turner RC, McConnell E, Vates GE, Huber JD, Rosen CL and Simard JM:
Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage and neuroinflammation: A
comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. 17(497)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
van Gijn J, Kerr RS and Rinkel GJ:
Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 369:306–318. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Dilli E: Thunderclap Headache. Curr Neurol
Neurosci Rep. 14(437)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hao G, Conzen-Dilger C, Schmidt TP, Harder
E, Schöps M, Clauser JC, Schubert GA and Lindauer U: Effect of
isolated intracranial hypertension on cerebral perfusion within the
phase of primary disturbances after subarachnoid hemorrhage in
rats. Front Cell Neurosci. 17(1115385)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lynch DG, Shah KA, Powell K, Wadolowski S,
Tambo W, Strohl JJ, Unadkat P, Eidelberg D, Huerta PT and Li C:
Neurobehavioral impairments predict specific cerebral damage in rat
model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res: Jul 26, 2023
(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
16
|
Ciurea AV, Palade C, Voinescu D and Nica
DA: Subarachnoid hemorrhage and cerebral vasospasm-literature
review. J Med Life. 6:120–125. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lauzier DC, Jayaraman K, Yuan JY, Diwan D,
Vellimana AK, Osbun JW, Chatterjee AR, Athiraman U, Dhar R and
Zipfel GJ: Early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage:
Incidence and mechanisms. Stroke. 54:1426–1440. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yuan B, Zhao XD, Shen JD, Chen SJ, Huang
HY, Zhou XM, Han YL, Zhou LJ, Lu XJ and Wu Q: Activation of SIRT1
alleviates ferroptosis in the early brain injury after subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022(9069825)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang Z, Fang Y, Lenahan C and Chen S: The
role of immune inflammation in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Exp Neurol. 336(113535)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Clower BR, Yamamoto Y, Cain L, Haines DE
and Smith RR: Endothelial injury following experimental
subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats: Effects on brain blood flow. Anat
Rec. 240:104–114. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen Y, Peng F, Xing Z, Chen J, Peng C and
Li D: Beneficial effects of natural flavonoids on
neuroinflammation. Front Immunol. 13(1006434)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Santos-Buelga C and Feliciano AS:
Flavonoids: From structure to health issues. Molecules.
22(477)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Liu T, Su K, Cai W, Ao H and Li M:
Therapeutic potential of puerarin against cerebral diseases: From
bench to bedside. Eur J Pharmacol. 953(175695)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zeng J, Zheng S, Chen Y, Qu Y, Xie J, Hong
E, Lv H, Ding R, Feng L and Xie Z: Puerarin attenuates
intracerebral hemorrhage-induced early brain injury possibly by
PI3K/Akt signal activation-mediated suppression of NF-κB pathway. J
Cell Mol Med. 25:7809–7824. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Franza L, Carusi V, Nucera E and Pandolfi
F: Luteolin, inflammation and cancer: Special emphasis on gut
microbiota. Biofactors. 47:181–189. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tan X, Yang Y, Xu J, Zhang P, Deng R, Mao
Y, He J, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Ding J, et al: Luteolin exerts
neuroprotection via modulation of the p62/Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in
intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Pharmacol. 10(1551)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sivandzade F, Prasad S, Bhalerao A and
Cucullo L: NRF2 and NF-κB interplay in cerebrovascular and
neurodegenerative disorders: Molecular mechanisms and possible
therapeutic approaches. Redox Biol. 21(101059)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yang Y, Tan X, Xu J, Wang T, Liang T, Xu
X, Ma C, Xu Z, Wang W, Li H, et al: Luteolin alleviates
neuroinflammation via downregulating the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB pathway
after intracerebral hemorrhage. Biomed Pharmacother.
126(110044)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yu M, Qi B, Xiaoxiang W, Xu J and Liu X:
Baicalein increases cisplatin sensitivity of A549 lung
adenocarcinoma cells via PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 90:677–685. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wei N, Wei Y, Li B and Pang L: Baicalein
promotes neuronal and behavioral recovery after intracerebral
hemorrhage via suppressing apoptosis, oxidative stress and
neuroinflammation. Neurochem Res. 42:1345–1353. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Masomi-Bornwasser J, Kurz E, Frenz C,
Schmitt J, Wesp DMA, König J, Lotz J, Ringel F, Kerz T, Krenzlin H
and Keric N: The influence of oxidative stress on neurological
outcomes in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Biomolecules.
11(1615)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chen X, Zhou Y, Wang S and Wang W:
Mechanism of baicalein in brain injury after intracerebral
hemorrhage by inhibiting the ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway.
Inflammation. 45:590–602. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Gu L, Sun M, Li R, Zhang X, Tao Y, Yuan Y,
Luo X and Xie Z: Didymin suppresses microglia pyroptosis and
neuroinflammation through the Asc/caspase-1/GSDMD pathway following
experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Immunol.
13(810582)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Di Petrillo A, Orrù G, Fais A and Fantini
MC: Quercetin and its derivates as antiviral potentials: A
comprehensive review. Phytother Res. 36:266–278. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang Y, Yi B, Ma J, Zhang L, Zhang H,
Yang Y and Dai Y: Quercetin promotes neuronal and behavioral
recovery by suppressing inflammatory response and apoptosis in a
rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurochem Res. 40:195–203.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Fu Y, Xu B, Huang S, Luo X, Deng XL, Luo
S, Liu C, Wang Q, Chen JY and Zhou L: Baicalin prevents LPS-induced
activation of TLR4/NF-κB p65 pathway and inflammation in mice via
inhibiting the expression of CD14. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 42:88–96.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Guo LT, Wang SQ, Su J, Xu LX, Ji ZY, Zhang
RY, Zhao QW, Ma ZQ, Deng XY and Ma SP: Baicalin ameliorates
neuroinflammation-induced depressive-like behavior through
inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 expression via the
PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 16(95)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhou QB, Jia Q, Zhang Y, Li LY, Chi ZF and
Liu P: Effects of baicalin on protease-activated receptor-1
expression and brain injury in a rat model of intracerebral
hemorrhage. Chin J Physiol. 55:219–226. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zeng J, Chen Y, Ding R, Feng L, Fu Z, Yang
S, Deng X, Xie Z and Zheng S: Isoliquiritigenin alleviates early
brain injury after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage via
suppressing ROS- and/or NF-κB-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome
activation by promoting Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. J
Neuroinflammation. 14(119)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chen Z, Wang C, Liu Y, Liang X, Yang C,
Zhang X and Li X: Protective effects of medicinal plant
breviscapine on postcerebral hemorrhage in rats. J Integr Neurosci.
19:101–109. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lan X, Han X, Li Q, Li Q, Gao Y, Cheng T,
Wan J, Zhu W and Wang J: Pinocembrin protects hemorrhagic brain
primarily by inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 and reducing M1
phenotype microglia. Brain Behav Immun. 61:326–339. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Fei X, Chen C, Kai S, Fu X, Man W, Ding B,
Wang C and Xu R: Eupatilin attenuates the inflammatory response
induced by intracerebral hemorrhage through the TLR4/MyD88 pathway.
Int Immunopharmacol. 76(105837)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Chen C, Yao L, Cui J and Liu B: Fisetin
protects against intracerebral hemorrhage-induced neuroinflammation
in aged mice. Cerebrovasc Dis. 45:154–161. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Singh N, Bansal Y, Bhandari R, Marwaha L,
Singh R, Chopra K and Kuhad A: Naringin reverses neurobehavioral
and biochemical alterations in intracerebroventricular
collagenase-induced intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Pharmacology.
100:172–187. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Chen C, Cui J, Ji X and Yao L:
Neuroprotective functions of calycosin against intracerebral
hemorrhage-induced oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. Future
Med Chem. 12:583–592. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Gao Y and Dong Z: Protective effect of
procyanidins on experimental rats with intracerebral hemorrhage.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 34:3078–3081. 2009.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
47
|
Pyrzynska K: Hesperidin: A review on
extraction methods, stability and biological activities. Nutrients.
14(2387)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Qin Z, Chen L, Liu M, Tan H and Zheng L:
Hesperidin reduces adverse symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage by
promoting TGF-β1 for treating ischemic stroke using tissue
plasminogen activator. Neurol Sci. 41:139–147. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Dumont AS, Dumont RJ, Chow MM, Lin CL,
Calisaneller T, Ley KF, Kassell NF and Lee KS: Cerebral vasospasm
after subarachnoid hemorrhage: Putative role of inflammation.
Neurosurgery. 53:123–135. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Erdi F, Keskin F, Esen H, Kaya B,
Feyzioglu B, Kilinc I, Karatas Y, Cuce G and Kalkan E: Telmisartan
ameliorates oxidative stress and subarachnoid haemorrhage-induced
cerebral vasospasm. Neurol Res. 38:224–231. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Xu W, Li T, Gao L, Zheng J, Yan J, Zhang J
and Shao A: Apelin-13/APJ system attenuates early brain injury via
suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated TXNIP/NLRP3
inflammasome activation and oxidative stress in a AMPK-dependent
manner after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. J Neuroinflammation.
16(247)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kuo CP, Wen LL, Chen CM, Huh B, Cherng CH,
Wong CS, Liaw WJ, Yeh CC, Lin BF and Wu CT: Attenuation of
neurological injury with early baicalein treatment following
subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. J Neurosurg. 119:1028–1037.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Hao G, Dong Y, Huo R, Wen K, Zhang Y and
Liang G: Rutin Inhibits neuroinflammation and provides
neuroprotection in an experimental rat model of subarachnoid
hemorrhage, possibly through suppressing the RAGE-NF-κB
inflammatory signaling pathway. Neurochem Res. 41:1496–1504.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Zhang T, Su J, Guo B, Wang K, Li X and
Liang G: Apigenin protects blood-brain barrier and ameliorates
early brain injury by inhibiting TLR4-mediated inflammatory pathway
in subarachnoid hemorrhage rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 28:79–87.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Shi X, Fu Y, Zhang S, Ding H and Chen J:
Baicalin attenuates subarachnoid hemorrhagic brain injury by
modulating blood-brain barrier disruption, inflammation, and
oxidative damage in mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017(1401790)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zhang H, Tu X, Song S, Liang R and Shi S:
Baicalin reduces early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage
in rats. Chin J Integr Med. 26:510–518. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Gül Ş, Aydoğmuş E, Bahadir B, Büyükuysal
MÇ and Güven B: Neuroprotective effects of quercetin on cerebral
vasospasm following experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage in rats.
Turk J Med Sci. 50:1106–1110. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Dong YS, Wang JL, Feng DY, Qin HZ, Wen H,
Yin ZM, Gao GD and Li C: Protective effect of quercetin against
oxidative stress and brain edema in an experimental rat model of
subarachnoid hemorrhage. Int J Med Sci. 11:282–290. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Tekiner A, Yilmaz MB, Bolat E, Goker T,
Sargon MF and Arat A: The therapeutic value of proanthocyanidin in
experimental cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Turk Neurosurg. 24:885–890. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Zhang ZH, Liu JQ, Hu CD, Zhao XT, Qin FY,
Zhuang Z and Zhang XS: Luteolin confers cerebroprotection after
subarachnoid hemorrhage by suppression of NLPR3 inflammasome
activation through Nrf2-dependent pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2021(5838101)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Zhang Y, Yang X, Ge X and Zhang F:
Puerarin attenuates neurological deficits via Bcl-2/Bax/cleaved
caspase-3 and Sirt3/SOD2 apoptotic pathways in subarachnoid
hemorrhage mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 109:726–733. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Zeng Y, Fang Z, Lai J, Wu Z, Lin W, Yao H,
Hu W, Chen J, Guo X and Chen X: Activation of sirtuin-1 by
pinocembrin treatment contributes to reduced early brain injury
after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2022(2242833)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Xu W, Yan J, Ocak U, Lenahan C, Shao A,
Tang J, Zhang J and Zhang JH: Melanocortin 1 receptor attenuates
early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage by controlling
mitochondrial metabolism via AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α pathway in rats.
Theranostics. 11:522–539. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Li Q, Chen Y, Zhang X, Zuo S, Ge H, Chen
Y, Liu X, Zhang JH, Ruan H and Feng H: Scutellarin attenuates
vasospasm through the Erk5-KLF2-eNOS pathway after subarachnoid
hemorrhage in rats. J Clin Neurosci. 34:264–270. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Sun Y, Chen P, Zhai B, Zhang M, Xiang Y,
Fang J, Xu S, Gao Y, Chen X, Sui X and Li G: The emerging role of
ferroptosis in inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother.
127(110108)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Wang F, He J, Xing R, Sha T and Sun B:
Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and their role in inflammation.
Int Rev Immunol. 42:71–81. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao
N, Sun B and Wang G: Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell
Death Dis. 11(88)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Yu Y, Yan Y, Niu F, Wang Y, Chen X, Su G,
Liu Y, Zhao X, Qian L, Liu P and Xiong Y: Ferroptosis: A cell death
connecting oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiovascular
diseases. Cell Death Discov. 7(193)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Gao S, Zhou L, Lu J, Fang Y, Wu H, Xu W,
Pan Y, Wang J, Wang X, Zhang J and Shao A: Cepharanthine attenuates
early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in mice via
inhibiting 15-lipoxygenase-1-mediated microglia and endothelial
cell ferroptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2022(4295208)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Zheng B, Zhou X, Pang L, Che Y and Qi X:
Baicalin suppresses autophagy-dependent ferroptosis in early brain
injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Bioengineered. 12:7794–7804.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Chen D, Chen JJ, Yin Q, Guan JH and Liu
YH: Role of ERK1/2 and vascular cell proliferation in cerebral
vasospasm after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta
Neurochir (Wien). 151:1127–1134. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Curson JEB, Liu L, Luo L, Muusse TW, Lucas
RM, Gunther KS, Vajjhala PR, Abrol R, Jones A, Kapetanovic R, et
al: TLR4 phosphorylation at tyrosine 672 activates the ERK/c-FOS
signaling module for LPS-induced cytokine responses in macrophages.
Eur J Immunol. 53(e2250056)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Lin CW, Chen PN, Chen MK, Yang WE, Tang
CH, Yang SF and Hsieh YS: Kaempferol reduces matrix
metalloproteinase-2 expression by down-regulating ERK1/2 and the
activator protein-1 signaling pathways in oral cancer cells. PLoS
One. 8(e80883)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Zong J, Zhang DP, Zhou H, Bian ZY, Deng W,
Dai J, Yuan Y, Gan HW, Guo HP and Tang QZ: Baicalein protects
against cardiac hypertrophy through blocking MEK-ERK1/2 signaling.
J Cell Biochem. 114:1058–1065. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Cheng Y, Zhang Z, Tang H, Chen B, Cai Y,
Wei Y, Zhao W, Wu ZB and Shang H: Mitochondrial inhibitor rotenone
triggers and enhances neuronal ferroptosis following intracerebral
hemorrhage. ACS Chem Neurosci. 14:1071–1079. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Li N, Ragheb K, Lawler G, Sturgis J, Rajwa
B, Melendez JA and Robinson JP: Mitochondrial complex I inhibitor
rotenone induces apoptosis through enhancing mitochondrial reactive
oxygen species production. J Biol Chem. 278:8516–8525.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Li K, Liang Y, Cheng A, Wang Q, Li Y, Wei
H, Zhou C and Wan X: Antiviral properties of baicalin: A concise
review. Rev Bras Farmacogn. 31:408–419. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Yao C, Dai S, Wang C, Fu K, Wu R, Zhao X,
Yao Y and Li Y: Luteolin as a potential hepatoprotective drug:
Molecular mechanisms and treatment strategies. Biomed Pharmacother.
167(115464)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Choi EJ, Lee BH, Lee K and Chee KM:
Long-term combined administration of quercetin and daidzein
inhibits quercetin-induced suppression of glutathione antioxidant
defenses. Food Chem Toxicol. 43:793–798. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Di Lorenzo C, Colombo F, Biella S,
Stockley C and Restani P: Polyphenols and human health: The role of
bioavailability. Nutrients. 13(273)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Galho AR, Cordeiro MF, Ribeiro SA, Marques
MS, Antunes MF, Luz DC, Hädrich G, Muccillo-Baisch AL, Barros DM,
Lima JV, et al: Protective role of free and quercetin-loaded
nanoemulsion against damage induced by intracerebral haemorrhage in
rats. Nanotechnology. 27(175101)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Waki T, Nakanishi I, Matsumoto K, Kitajima
J, Chikuma T and Kobayashi S: Key role of chemical hardness to
compare 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging power of
flavone and flavonol O-glycoside and C-glycoside derivatives. Chem
Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 60:37–44. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Cassidy A, O'Reilly ÉJ, Kay C, Sampson L,
Franz M, Forman JP, Curhan G and Rimm EB: Habitual intake of
flavonoid subclasses and incident hypertension in adults. Am J Clin
Nutr. 93:338–347. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Elijovich L, Patel PV and Hemphill JC III:
Intracerebral hemorrhage. Semin Neurol. 28:657–667. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Sung B, Chung HY and Kim ND: Role of
apigenin in cancer prevention via the induction of apoptosis and
autophagy. J Cancer Prev. 21:216–226. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Ganeshpurkar A and Saluja AK: The
pharmacological potential of rutin. Saudi Pharm J. 25:149–164.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Jäger A and Saaby L: Flavonoids and the
CNS. Molecules. 16:1471–1485. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Parrella E, Gussago C, Porrini V, Benarese
M and Pizzi M: From preclinical stroke models to humans:
Polyphenols in the prevention and treatment of stroke. Nutrients.
13(85)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|