Introduction
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most frequent
entrapment neuropathy worldwide. The main symptoms are attributed
to the compression of the median nerve (1). The compression of this nerve is
susceptible to fibro-osseous structures surrounding the canal,
particularly in the context of increased pressures, a phenomenon
that occurs when the wrist is extended or flexed (2). Decreased epineural blood flow and
edematous changes occur when the pressure reaches 20-30 mmHg.
Sustained high pressure for extended periods of time results in
ischemia, which may lead to demyelination and further damage to the
median nerve. Notably, there are multiple risk factors for the
development of CTS, and these include the elevation of pressure
within the canal (1,2).
Clinical symptoms of CTS often involve neuropathic
pain, and this sensory impairment is classified into two groups;
namely, negative and positive. Negative symptoms refer to a loss of
sensory function, while positive sensory symptoms (PSS) refer to an
abnormal increase in the function of the sensory system (3). PSS include the following: i)
Paresthesias, when a patient experiences a tingling-like sensation;
ii) dysesthesias, when a patient experiences an unpleasant
sensation that is unlike pain, numbness or burning; and iii)
allodynia, referring to the perception of pain elicited by any
stimulus that is not otherwise pain-inflicting. Notably, the
aforementioned symptoms are sensorial abnormalities that may exist
with or without neuropathic pain (4-6).
Meyers et al (7) previously reported that the main
symptoms of CTS are paresthesia, numbness, pain and weakness, and
these are scored using different grading scales, such as the Boston
Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire (BCTQ), Disabilities of the Arm,
Shoulder and Hand and QuickDash scoring systems (7-9).
Notably, negative symptoms of CTS, such as anesthesia and
hypoesthesia, and positive sensory symptoms (PSS), such as
allodynia and dysesthesias, are rarely reported (10). The results of a previous study
conducted by the authors revealed the association between pain and
PSS in peripheral nerve neuropathy, highlighting that the
independent evaluation of all symptoms is required considering
primarily the sensitive component of each one (Fig. S1) (11). There is a gap in skilling and
assessing the clinical symptoms of CTS: Paresthesia, dysesthesia
and allodynia occasionally are underestimated in these sensitive
components, but pain is well described in literature worldwide.
The management of CTS is staged and depends on the
patient's evolution and response to treatment. Initially, patients
undergo neuro-modulatory treatments such as antidepressants,
anxiolytics and analgesics. If these treatments fail to produce
results despite dose escalation, patients are referred to
rehabilitation where thermotherapy treatments are administered. If
rehabilitation proves ineffective, wrist infiltration at the pain
clinic of the hospital is considered. Surgery is recommended if
these interventions fail.
Given the lack of established correlation between
PSS and pain intensity (11),
individual patient assessment becomes imperative. Therefore, the
present study aimed to assess PSS in CTS utilizing a standardized
clinical tool, aiming to enhance understanding of the impact of
surgery on PSS management.
Patients and methods
Study design and participants
The present study was a prospective, longitudinal,
non-randomized study that aimed to evaluate PSS in CTS following
surgical management. A total of 122 patients were evaluated in the
preoperative stage and, according to the elimination criteria and
lost patients at follow-up, 19 patients were included in the final
study [female:male, 15:4 (78.9:21.1%)], and they were admitted
between June 2007 to September 2017. Measurements were performed
both before and after surgical intervention. All patients were
evaluated at the Peripheral Nerve Clinic of the Stereotactic and
Functional Neurosurgery Service at Mexico General Hospital in
Mexico City, Mexico (Fig. 1).
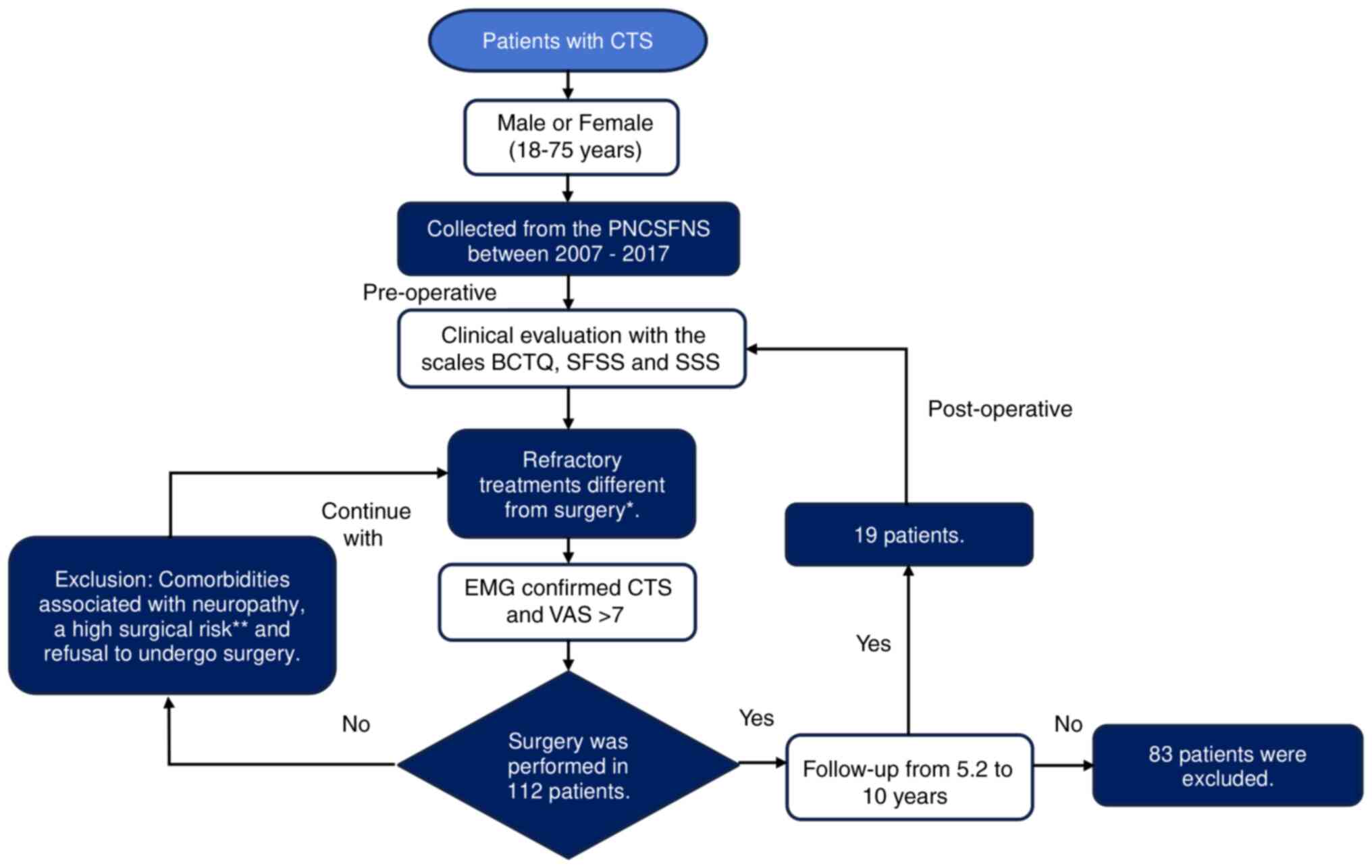 | Figure 1Flowchart.
*Pharmacological management with neuromodulators
(antidepressants, anxiolytics, and analgesics even at maximum
doses), rehabilitation with thermotherapy and electrotherapy, or
wrist infiltration. **Heart disease or coagulopathies.
CTS, carpal tunnel syndrome; PNCSFNS, Peripheral Nerve Clinic of
the Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery Service; BCTQ, Boston
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Questionnaire; SFSS, Sensory Frequency of
Symptoms Scale; SSS, Severity Symptoms Scale; EMG,
electromyography; VAS, Visual Analogue Scale. |
Inclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: Male or
female adult patients (age, 18-75 years); failure to respond to
treatment with neuromodulators (antidepressants, anxiolytics and
analgesics even at maximum doses), treatment in rehabilitation with
thermotherapy and electrotherapy, or wrist infiltration by the
hospital's pain clinic with a clinical diagnosis of CTS confirmed
via electromyography; severe CTS with >7 Visual Analogue Scale
(VAS) points.
Exclusion criteria
Patients with comorbidities associated with
neuropathy, patients with a high surgical risk (including heart
disease or coagulopathies) and refusal to undergo surgery;
continuation of other previous procedures including pharmacological
therapy, electrotherapy, thermotherapy or wrist infiltration.
Elimination criteria
Patients who missed post-operative evaluation and
those lost to follow-up or patients that declined the participation
in the present study. All patients provided written informed
consent. The present study was approved by the Mexico General
Hospital Research and Ethics Committee (approval no.
DI/16/403/03/152; Mexico City, Mexico).
Data collection
Patient characteristics, including age, sex,
location of CTS, occupation, comorbidities and average follow-up
duration, defined as the time between follow-up and the clinical
evaluation of symptoms were collected. The clinical evaluation of
patients was focused on data collection pre- and post-surgery, and
included pain as well as functional, motor and sensory
disturbances. Pain intensity was assessed according to the VAS
(12), functional components were
evaluated using BCTQ (7) and motor
status was evaluated using the classical British Medical Research
Council (BMRC) Motor Grading Scale (13), which evaluated the flexor muscles
of the hand. The present study focused on PSS, and these were
evaluated using the Severity Symptom Scale of the BCTQ, and the
Sensory Frequency of Symptoms Scale (SFSS). Notably, the SFSS
scores the frequency of sensorial manifestations from 0 to 4, with
4 corresponding to experienced symptoms >90% of the time, 3
corresponding to experienced symptoms 50-89% of the time, 2
corresponding to experienced symptoms 11-49% of the time, 1
corresponding to experienced symptoms <10% of the time and 0
corresponding to no symptoms (11). All clinical components were
evaluated by an independent surgeon. Further details of all
questionnaires are displayed in Figs.
S1 and S2 (11).
Surgical procedure
Simple open surgery was performed using the Tindall
technique (14). Briefly, the
subcutaneous tissue and superficial fascia were exposed, and the
transverse carpal ligament was fully cut, starting in the proximal
edge. This method was used to avoid damage to the flexor tendons
and led to the subsequent release of the median nerve. This type of
incision exposes the nerve and eliminates the presence of adhesions
that cannot be observed using small incisions.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
Differences in pain, and functional, motor or sensory
manifestations were compared pre- and post-surgery using a paired
Student's t-test and a Wilcoxon signed-rank test. To further
evaluate potential differences pre- and post-surgery, Cohen's D
test was used to recalculate the correction coefficient for small
sample sizes to avoid overestimation of values. Statistical
analysis was carried out using SPSS (v.25.0; IBM Corp.) α=0.05 and
β=0.2 and P<0.05 were considered to indicate a statistically
significant difference.
Results
In total, 112 patients diagnosed with CTS at the
Peripheral Nerve Clinic of the Stereotactic and Functional
Neurosurgery Service at Mexico General Hospital were screened
according to the eligibility criteria. Subsequently, 19 of 112
patients (16.9%) were included in the present study, and 93
patients were excluded due to a lack of post-operative follow-up.
In total, 79% of patients were female, with a mean age of 54±10.31
years. The main affected side was the right side (79%), where the
dominant hand was affected in 89.47% of the cases. In total, 47.36%
of patients were housewives, and 11 patients presented with
comorbidities (57.8%). The mean follow-up after surgery was
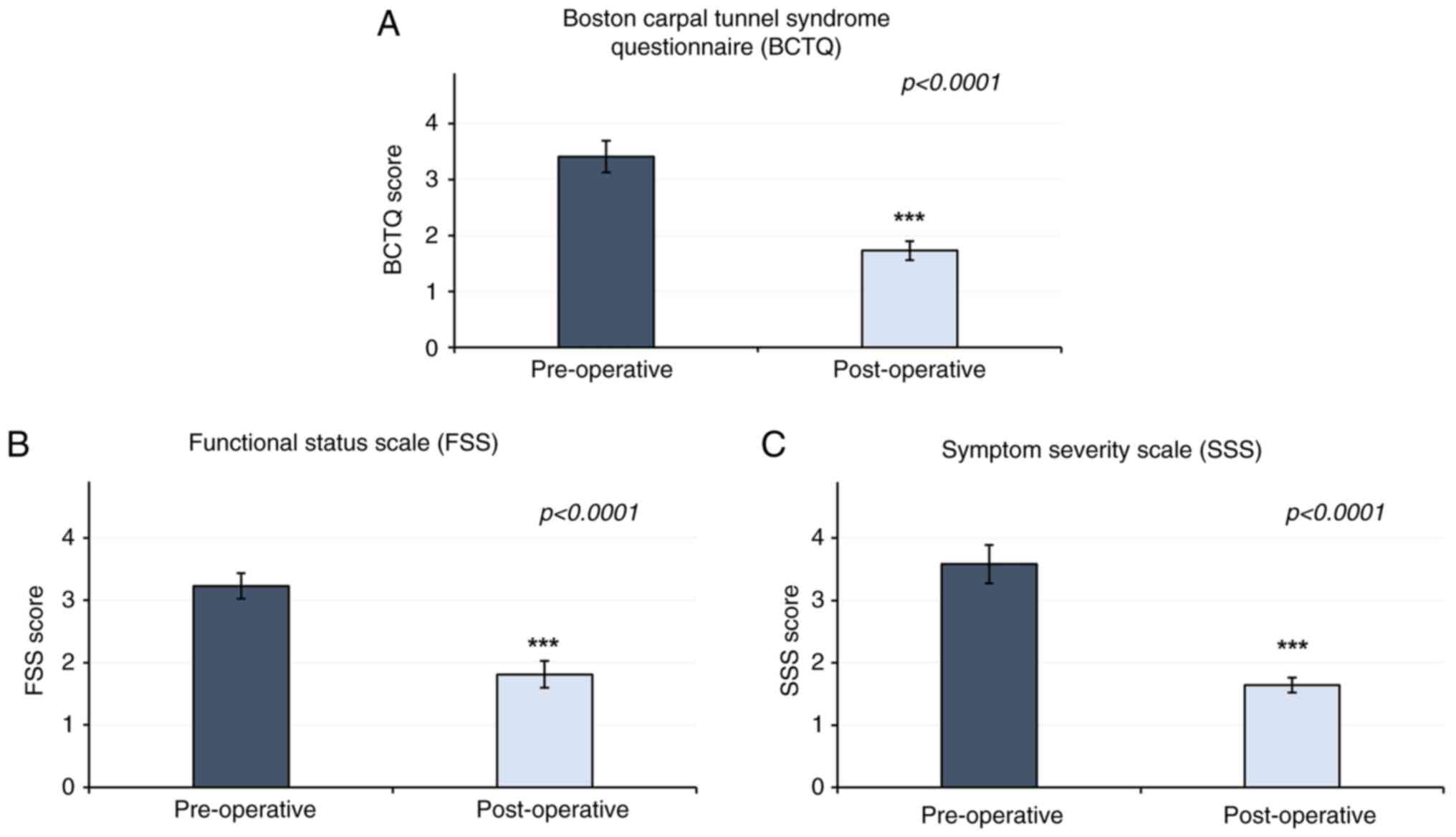
63±29.11 months. The results of the present study revealed that the
pre-surgical and post-surgical BCTQ scores were 3.52±0.63 and
1.58±0.61, respectively (P<0.0001). The FSS component of the
BCTQ demonstrated a score of 3.23±0.41 pre-surgery, compared with
1.8±0.43 post-surgery (P<0.0001). In addition, a reduction in
Symptom Severity Scale (SSS) score was observed, at 3.57±0.61
pre-surgery, compared with 1.63±0.24 post-surgery (P<0.0001)
(Fig. 2). Patient characteristics
are displayed in Table I.
 | Table IClinical and demographical
characteristics of the included patients with carpal tunnel
syndrome. |
Table I
Clinical and demographical
characteristics of the included patients with carpal tunnel
syndrome.
| | BCTQ (SSS) | VAS | BMRC |
|---|
| No. of patient
(Sex) | Age (years) | Side of injury
(Hand dominance) | Occupation | Comorbidities | Follow-up after
surgery (months) | Pre-op | Post-op | Pre-op | Post-op | Pre-op | Post-op |
|---|
| 1 (F) | 51 | L (R) | HW | V | 120 | 3.55 | 1.45 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 2 (F) | 39 | L (L) | HW | SAH, BCy | 96 | 3.82 | 1.09 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| 3 (M) | 67 | R (R) | R | - | 96 | 2.82 | 1.00 | 7 | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 (F) | 74 | R (R) | HW | G, C, SAH, CRF,
UI | 84 | 3.09 | 2.00 | 7 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 (F) | 54 | R (R) | HW | V | 84 | 2.91 | 1.27 | 7 | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 6 (F) | 48 | R (R) | BM | SAH | 72 | 3.45 | 1.09 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| 7 (F) | 38 | R (R) | BM | - | 72 | 2.45 | 1.09 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 5 |
| 8 (F) | 55 | R (R) | S | - | 72 | 2.55 | 1.00 | 7 | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| 9 (M) | 69 | L (R) | R | - | 72 | 3.36 | 1.55 | 7 | 0 | 5 | 4 |
| 10 (F) | 54 | R (R) | HW | - | 72 | 4.55 | 2.64 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| 11 (M) | 60 | R (R) | R | - | 72 | 4.00 | 1.45 | 10 | 6 | 3 | 4 |
| 12 (F) | 35 | R (R) | UE | HAS, PA | 72 | 4.27 | 1.27 | 10 | 5 | 3 | 4 |
| 13 (M) | 46 | R (R) | BM | H | 24 | 3.64 | 1.45 | 7 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 14 (F) | 56 | R (R) | UE | - | 9 | 3.91 | 1.73 | 7 | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 15 (F) | 59 | R (R) | HW | - | 36 | 2.73 | 1.00 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| 16 (F) | 54 | R (R) | HW | Sp, B | 36 | 3.64 | 1.55 | 7 | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 17 (F) | 52 | R (R) | N | GERD, St, IBS, AR,
IR, O, CSS, UF | 36 | 4.45 | 3.27 | 7 | 0 | 3 | 5 |
| 18 (F) | 67 | L (L) | HW | BCa, St | 60 | 3.73 | 1.91 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 5 |
| 19 (F) | 48 | R (R) | HW | CSS | 12 | 4.09 | 2.27 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 5 |
| Mean
(SD)/Percentage (%) | 54.00±10.31 | 89.47% (Affected
side in dominant hand) | | | 63.00±29.11 | 3.52±0.63 | 1.58±0.61 | 7.73±1.24 | 1.65±2.88 | 4.15±0.88 | 4.75±0.25 |
In addition to sensory manifestations, classical
clinical symptoms, such as pain and strength, were recorded in the
present study. According to VAS, levels of pain were significantly
decreased post-surgery, with scores of 1.65±2.88 compared with
7.73±1.24 pre-surgery (P<0.001) (Table I). According to the BMRC, motor
function was significantly increased, with a score of 4.15±0.88
pre-surgery, compared with 4.75±0.25 post-surgery (P=0.002)
(Table I).
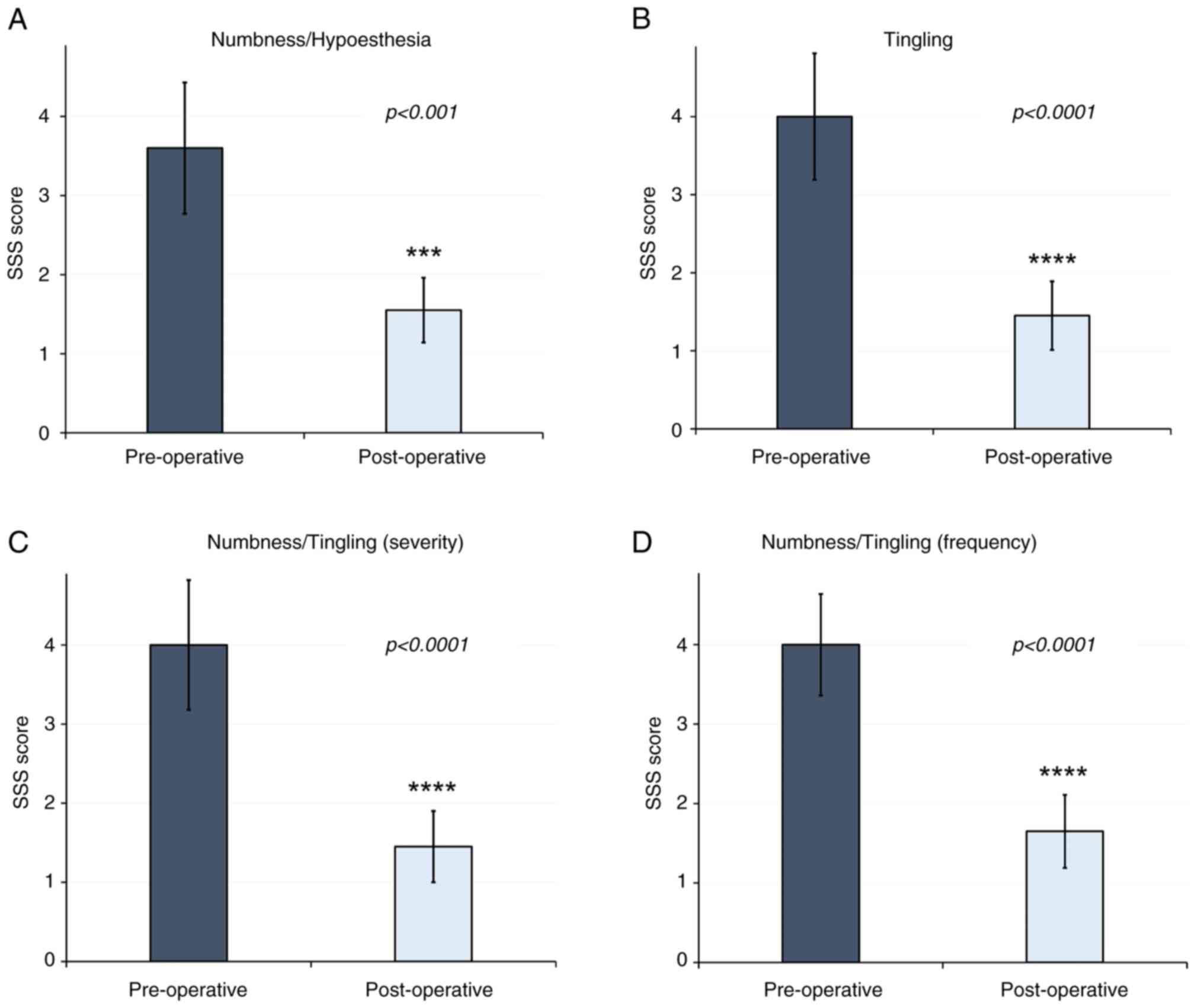
Certain sensory disturbances are considered SSS
items of the BCTQ (Fig. 3). The
results of the present study demonstrated a decrease in paresthesia
and dysesthesias in patients (P<0.001), and PSS are highlighted
in blue (Fig. 4). Allodynia is not
included in the BCTG; thus, additional scales were used to evaluate
potential changes in this symptom.
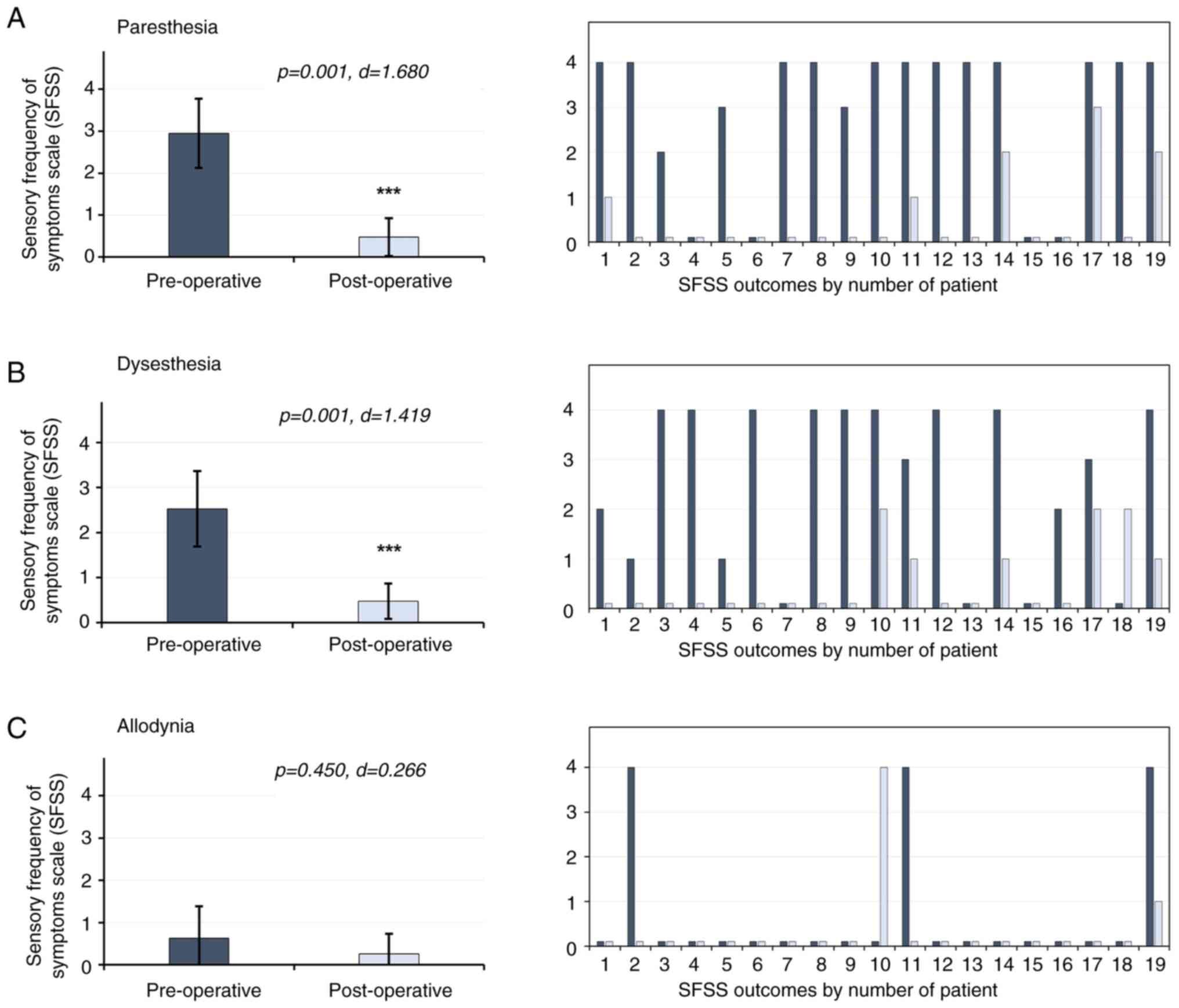
The results of the present study revealed that
levels of paresthesia decreased by 84%, with pre-surgery scores of
2.94±0.82 compared with 0.47±0.45 post-surgery (P=0.001; d=1.680).
Levels of dysesthesia decreased by 81%, with a pre-surgery score of
2.52±0.84, compared with 0.47±0.39 post-surgery (P=0.001; d=1.419).
Paresthesia and dysesthesia were decreased in 100% of the patients
who presented with these manifestations prior to surgery. Notably,
allodynia was considered an infrequent manifestation, presenting in
3 patients only (15.7%). However, allodynia levels decreased by
58%, with a pre-surgery score of 0.63±0.75, compared with a
post-surgery score of 0.26±0.47 (P=0.450; d=0.266) (Fig. 5).
Discussion
At present, there is no consensus on the criteria
used for grading paresthesia, dysesthesia and allodynia in CTS, and
treatment options are typically offered based on the severity of
pain (10). CTS surgery for the
release of the median nerve entrapment is often recommended
following electrophysiological examination (15-17).
Numerous previous studies have focused on the association between
symptom severity of pain, duration and surgical outcomes; however,
improvements in clinical symptoms are under-reported (10). Notably, patients who are treated
within three years of developing symptoms, such as pain and
paresthesia, achieve complete resolution or notable improvements in
symptoms (18-21).
However, the association between the effectiveness of surgical
management in CTS and dysesthesia or allodynia remains to be fully
elucidated (11).
PSS are under-reported, as questionnaires that
assess CTS mainly consider pain and paresthesia. Thus, further
investigations into alternate sensory impairments, such as
dysesthesia, allodynia and hypoesthesia, are required. A summary of
all scores and scales is displayed in Table II (22-31).
 | Table IINeuropathic pain and sensory symptoms
considered by the reported scales. |
Table II
Neuropathic pain and sensory symptoms
considered by the reported scales.
| Clinical scale | Pain
(Intensity) |
Paresthesiaa |
Dysesthesiaa |
Allodyniaa | Hypoesthesia | (Refs.) |
|---|
| BMRC sensory
grading scale | | | | | ✓ | (13) |
| Katz-Stirrat
diagram | ✓ | ✓ | ✓b | | ✓ | (22) |
| BCTQ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓b | | ✓ | (7) |
| Global/Katz | ✓ | ✓ | ✓b | | | (23) |
| DASH/Q-DASH | ✓ | ✓ | | | | (8,9) |
| MHQ | ✓ | | | | | (24) |
| Bland | ✓ | ✓ | | | | (25) |
| Historical | ✓ | ✓ | | | | (26) |
| Kamath &
Stothard | ✓ | ✓ | ✓b | | | (27) |
| Wainner | ✓ | ✓ | ✓b | | ✓ | (28) |
| Lo | ✓ | | | | | (29) |
| Historical-DP | ✓ | ✓ | ✓b | | | (30) |
| 6-CTS | ✓ | ✓ | ✓b | | | (31) |
| SFSS | | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | (11) |
In 1957, Garland et al (32) reported the amelioration of
paresthesia after treatment (32),
and in 1958, Giannini et al (26) demonstrated comparable results.
Subsequently, numerous previous studies have reported improvements
in paresthesia, without the use of a scale (33-35).
In 1996, Wintman et al (36) proposed a scale to assess pain,
paresthesia and numbness; however, this scale is not commonly used
in clinical practice (36).
Further investigations into factors associated with paresthesia are
required, such as timing, as nocturnal paresthesia is present in up
to 95% of patients with CTS (25-27,29).
In addition, symptoms such as hypoesthesia and allodynia are not
well represented on a common clinical scale.
The results of a previous study revealed
improvements in hypoesthesia following surgical decompression.
However, no specific percentage of change was determined. In 1984,
Duchateau and Moermans (37)
reported improvements in hypoesthesia following surgery; thus,
hypoesthesia and allodynia were recognized as clinical features of
CTS. The results of the present study revealed that hypoesthesia
was present in 42.1% of patients with CTS, and this decreased to
26.3% after surgery. Allodynia was present in 15.7% of patients;
however, no improvements were observed following surgery.
Further investigations into the impact of surgical
management on allodynia are required; however, measurements of
allodynia are complex.
The BCTQ scale is a widely used scale for the
evaluation of CTS, and includes PSS, as well as hypoesthesia and
weakness. Notably, the BCTQ scale includes paresthesias and
dysesthesias; however, it does not include allodynia. In other
scales, such as the Katz, Kamath and Stothard, Wainner, 6-CTS, and
Historical-DP, the dysesthesias component is replaced with
numbness, which does not represent the spectrum of sensory
manifestations that may be experienced with dysesthesias (7,22,27,28,31).
Symptoms of dysesthesias may also include burning, stiff skin and
subjective sensations that a patient finds difficult to describe
(5). Thus, scales that report the
evaluation of numbness were classed as reported dysesthesias
(Table II).
In the present study, a total of 2 patients
presented with allodynia following surgery. Aydin et al
(38) reported that scarring,
fibrosis and adhesion processes may cause symptoms such as PSS,
which may provide an explanation as to why novel symptoms arise
following surgery (38-41).
In addition, 1 patient exhibited fewer improvements in PSS
following surgery, which may be associated with a high number of
comorbidities in this patient, such as insulin resistance that may
be associated with nerve damage (42).
Nerve compression leads to imbalances between
excitatory and inhibitory signaling in different nerve fibers, and
these imbalances are associated with ectopic activity, which plays
a key role in the pathophysiology of pain and PSS (6). The results of a previous study
demonstrated that allodynia results from peripheral drive involving
subsets of neurons that are not classical nociceptors, leading to
the presence of proprioceptive fibers with sensory abnormalities.
Numerous mediators activate microglia, such as cytokines and
brain-derived neurotrophic factors, highlighting the involvement of
multiple molecules (43).
A previous study on peripheral nerve injury revealed
the association between PSS and pain intensity, highlighting the
requirement for independent evaluation of these factors. The
development of a standardized clinical evaluation for patients with
CTS is required, which includes the majority of symptoms
experienced (11). PSS affect the
same nerve fibers; however, these exhibit different molecular and
signaling characteristics that are complex to define. This leads to
complexities in identifying whether PSS occur simultaneously or as
isolated symptoms (6,42,43).
The SFSS was used in the present study to determine
specific patterns associated with each symptom, and to establish a
threshold of statistically significant improvements. The assessment
of paresthesia, dysesthesia and allodynia was conducted by
examining two primary components of each: The pain component and
the sensory component. While the pain component is extensively
documented in global literature as a descriptive measure (presence
or absence), the utilization of scales that could offer a more
precise understanding of the discomfort experienced is not
consistently explored. The sensory component, which is emphasized
in the present study, is significant due to its role in causing
discomfort and directly impacting the daily lives and activities of
affected patients aiming to evaluate the various symptoms present
in CTS, and to develop a scale that established the percentage of
symptom relief, referred to as ‘converting the soft data into hard
data’ (44).
The present study exhibits numerous limitations,
including study design, where randomization, blinding and
comparison with another standard therapeutic procedure have not
been performed. A convenient, self-controlled design was used in
the present study, as surgical treatment altered the natural
history of the disease (10).
Thus, evaluations performed using the SSS of the BCTQ and the SFSS
before and after surgery demonstrated the magnitude of changes,
with no ethical implications having an impact. While it may be
considered a limitation, the infrequency of the allodynia (3
patients in total in the present study) does not diminish its
importance in reporting. Similar to other sensory symptoms, it is
crucial to evaluate and report it to assess the overall condition
of the patient, as it can cause discomfort and directly impact the
daily lives and activities of patients.
The present study focused on PSS, and negative
sensory symptoms were not considered, as these are not often
present in patients with compressive neuropathy. Notably, an
exhaustive questionnaire, including pain intensity, paresthesia,
dysesthesia and allodynia must be used in the evaluation of
patients, as these symptoms are often experienced simultaneously.
In addition, further investigations into comorbidities that affect
the nervous system and the period of time before surgery are
required to determine improvements observed following surgery.
Regarding the loss of patients, 83% of them did not
continue in the study as they kept the consultation in their
hometown clinics. As a result, a total of 19 patients were
followed-up in the present study and were in line with the strict
selection criteria. The follow-up period in these patients was 5.2
years, with the highest period lasting 10 years. Notably, the
majority of previous studies reported that follow-up periods lasted
<1 year (10) (Fig. 1).
The electromyographic studies were not applied after
the surgery because the criteria for using it in the study was
mainly to diagnose the nerve lesion in CTS. In addition, they were
not performed after the surgery, because clinical improvement of
the sensitive and pain symptoms were found in all of the patients
reported.
The complexity of identifying both sensitive and
pain components needed to be elucidated as an independent
phenomenon that occasionally occurs like a symbiosis presented at
the same time. However, the special distinction between them
together with the clinical assessment is the novelty of the present
study.
In conclusion, decompression of the median nerve in
patients with CTS may lead to clinical and functional improvements.
The results of the present study demonstrated that PSS, such as
paresthesias and dysesthesias, were markedly improved following
surgery. However, the effectiveness of surgery in relieving
allodynia remains to be fully elucidated. Thus, further clinical
essays focused strictly into the association of the sensitive
components using novel clinometric scales and electrophysiological
studies are required to transform ‘soft data’ into ‘hard data’.
Supplementary Material
Sensory Frequency of Symptoms
Scale.
Boston Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Questionnaire.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
JDCR conceptualized and supervised the study,
validated and curated data, and performed formal analysis and
project administration. APCC developed methodology, and performed
software analysis and data validation. JCR and ACC confirm the
authenticity of all the raw data. AAS conceptualized the study,
curated data, performed formal analysis, conducted investigation,
developed methodology and wrote the original draft. FXCR performed
formal analysis, developed methodology, wrote the original draft
and edited the manuscript. HFGM performed formal analysis,
developed methodology, wrote the original draft and edited the
manuscript. AIGJ conducted investigation, developed methodology and
wrote the original draft. JLNO performed formal analysis and
project administration and validated the data. LGM and ASP wrote,
reviewed and edited the manuscript, and validated the data. All
authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Mexico General
Hospital Research and Ethics Committee (approval no.
DI/16/403/03/152; Mexico City, Mexico). All patients provided their
verbal and written informed consent to participate in the present
study.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Cranford CS, Ho JY, Kalainov DM and
Hartigan BJ: Carpal tunnel syndrome. J Am Acad Orthop Surg.
15:537–548. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Urits I, Gress K, Charipova K, Orhurhu V,
Kaye AD and Viswanath O: Recent Advances in the understanding and
management of carpal tunnel syndrome: A comprehensive review. Curr
Pain Headache Rep. 23(70)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Colloca L, Ludman T, Bouhassira D, Baron
R, Dickenson AH, Yarnitsky D, Freeman R, Truini A, Attal N,
Finnerup NB, et al: Neuropathic pain. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
3(17002)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Doyle JR and Carroll RE: The carpal tunnel
syndrome. A review of 100 patients treated surgically. Calif Med.
108:263–267. 1968.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pal B: 10-min consultation: Paraesthesia.
BMJ. 324(1501)2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jensen TS and Finnerup NB: Allodynia and
hyperalgesia in neuropathic pain: Clinical manifestations and
mechanisms. Lancet Neurol. 13:924–935. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Meyers A, Annunziata MJ, Rampazzo A and
Bassiri Gharb B: A systematic review of the outcomes of carpal
ligament release in severe carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Am.
48:408.e1–408.e18. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Levine D, Simmons B, Koris MJ, Daltroy LH,
Hohl GG, Fossel AH and Katz JN: A self-administered questionnaire
for the assessment of severity of symptoms and functional status in
carpal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 75:1585–1592.
1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hudak PL, Amadio PC and Bombardier C:
Development of an upper extremity outcome measure: the DASH
(disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand) [corrected]. The upper
extremity collaborative group (UECG). Am J Ind Med. 29:602–608.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Beaton DE, Wright JG and Katz JN: Upper
Extremity Collaborative Group. Development of the QuickDASH:
Comparison of three item-reduction approaches. J Bone Joint Surg
Am. 87:1038–1046. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
García-Jeronimo AI, Armas-Salazar A,
García-Muñoz L, Navarro-Olvera JL, Esqueda-Liquidano MA and
Carrillo-Ruiz JD: Neuropathic pain and positive sensory symptoms in
brachial plexus neuropathy: An exploratory study of outcomes after
surgical decompression and proposal of a new sensory frequency of
symptoms scale. J Integr Neurosci. 22(25)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chiarotto A, MaxwellL J, Ostelo RW, Boers
M, Tugwell P and Terwee CB: Measurement properties of visual
analogue scale, numeric rating scale, and pain severity subscale of
the brief pain inventory in patients with low back pain: A
systematic review. J Pain. 20:245–263. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
James MA: Use of the medical research
council muscle strength grading system in the upper extremity. J
Hand Surg Am. 32:154–156. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tindall S: Chronic injuries of periphereal
nerves entrapment. In: Youmans Neurological Surgery. Vol 3. 4th
edition. Saunders Co., Dundee OR, 1996.
|
|
15
|
Lu YT, Deol AK and Sears ED: The
association between electrodiagnostic severity and treatment
recommendations for carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Am.
46:92–98. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Keith MW, Masear V, Chung KC, Maupin K,
Andary M, Amadio PC, Watters WC III, Goldberg MJ, Haralson RH III,
Turkelson CM, et al: American academy of orthopaedic surgeons
clinical practice guideline on diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome.
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 91:2478–2479. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Maggard MA, Harness NG, Chang WT, Parikh
JA, Asch SM and Nuckols TK: Carpal Tunnel Quality Group.
Indications for performing carpal tunnel surgery: Clinical quality
measures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 126:169–179. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Choi SJ and Ahn DS: Correlation of
clinical history and electrodiagnostic abnormalities with outcome
after surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome. Plast Reconstr Surg.
102:2374–2380. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
al-Qattan MM, Bowen V and Manktelow RT:
Factors associated with poor outcome following primary carpal
tunnel release in non-diabetic patients. J Hand Surg Br.
19:622–625. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
DeStefano F, Nordstrom DL and Vierkant RA:
Long-term symptom outcomes of carpal tunnel syndrome and its
treatment. J Hand Surg Am. 22:200–210. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nau HE, Lange B and Lange S: Prediction of
outcome of decompression for carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg
Br. 13:391–394. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Katz JN, Gelberman RH, Wright EA,
Abrahamsson SO and Lew RA: A preliminary scoring system for
assessing the outcome of carpal tunnel release. J Hand Surg Am.
19:531–538. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Katz JN and Stirrat CR: A
self-administered hand diagram for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel
syndrome. J Hand Surg Am. 15:360–363. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chung KC, Hamill JB, Walters MR and
Hayward RA: The michigan hand outcomes questionnaire (MHQ):
Assessment of responsiveness to clinical change. Ann Plast Surg.
42:619–622. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bland JD: The value of the history in the
diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Am. 25:445–450.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Giannini F, Cioni R, Mondelli M, Padua R,
Gregori B, D'Amico P and Padua L: A new clinical scale of carpal
tunnel syndrome: Validation of the measurement and
clinical-neurophysiological assessment. Clin Neurophysiol.
113:71–77. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kamath V and Stothard J: A clinical
questionnaire for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand
Surg Am. 28:455–459. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wainner RS, Fritz JM, Irrgang JJ, Delitto
A, Allison S and Boninger ML: Development of a clinical prediction
rule for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Arch Phys Med
Rehabil. 86:609–618. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lo JK, Finestone HM and Gilbert K:
Prospective evaluation of the clinical prediction of
electrodiagnostic results in carpal tunnel syndrome. PM R.
1:612–619. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Caliandro P, Giannini F, Pazzaglia C,
Aprile I, Minciotti I, Granata G, Tonali P and Padua L: A new
clinical scale to grade the impairment of median nerve in carpal
tunnel syndrome. Clin Neurophysiol. 121:1066–1071. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Atroshi I, Lyrén PE, Ornstein E and
Gummesson C: The six-item CTS symptoms scale and palmar pain scale
in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Am. 36:788–794.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Garland H, Bradshaw JP and Clark JM:
Compression of median nerve in carpal tunnel and its relation to
acroparaesthesiae. Br Med J. 1:730–734. 1957.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Heathefield KW: Acroparaesthesiae and the
carpal-tunnel syndrome. Lancet. 273:663–666. 1957.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Opit LJ and Rieger RA: Acroparesthesia and
the ‘carpal tunnel syndrome’. Aust N Z J Surg. 32:59–65.
1962.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Seze D and Phankim-Koupernik M:
Acroparesthesias and carpal canal syndrome. Rev Rhum Mal
Osteoartic. 29:244–251. 1962.PubMed/NCBI(In French).
|
|
36
|
Wintman BI, Winters SC, Gelberman RH and
Katz JN: Carpal tunnel release. Correlations with preoperative
symptomatology. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 135–145. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Duchateau JA and Moermans JP: Carpal
tunnel syndrome: Postsurgical course of symptoms. Ann Chir Main.
3:227–231. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Aydin M, Argun G, Acar B, Arikan M, Toğral
G, Cinaroglu S, Mert A and Demi Rtas M: Residual symptoms after
carpal tunnel decompression and treatment with gabapentin: A
multicenter study. Cureus. 13(e17638)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Rose EH: The use of the palmaris brevis
flap in recurrent carpal tunnel syndrome. Hand Clin. 12:389–395.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Phalen GS: The carpal-tunnel syndrome.
Seventeen years' experience in diagnosis and treatment of six
hundred fifty-four hands. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 48:211–228.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Assmus H, Dombert T and Staub F:
Reoperations for CTS because of recurrence or for correction.
Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 38:306–311. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In German).
|
|
42
|
Zhou L: Small fiber neuropathy. Semin
Neurol. 39:570–577. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lolignier S, Eijkelkamp N and Wood JN:
Mechanical allodynia. Pflugers Arch. 467:133–139. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wright JG and Feinstein AR: A comparative
contrast of clinimetric and psychometric methods for constructing
indexes and rating scales. J Clin Epidemiol. 45:1201–1218.
1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|