|
1
|
Thipsawat S: Early detection of diabetic
nephropathy in patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review of
the literature. Diab Vasc Dis Res.
18(14791641211058856)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC,
Bragg-Gresham J, Chen X, Gipson D, Gu H, Hirth RA, Hutton D, Jin Y,
et al: US renal data system 2019 annual data report: Epidemiology
of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 75 (1
Suppl 1):A6–A7. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhou Y, Echouffo-Tcheugui JB, Gu JJ, Ruan
XN, Zhao GM, Xu WH, Yang LM, Zhang H, Qiu H, Narayan KM and Sun Q:
Prevalence of chronic kidney disease across levels of glycemia
among adults in Pudong New Area, Shanghai, China. BMC Nephrology.
14(253)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
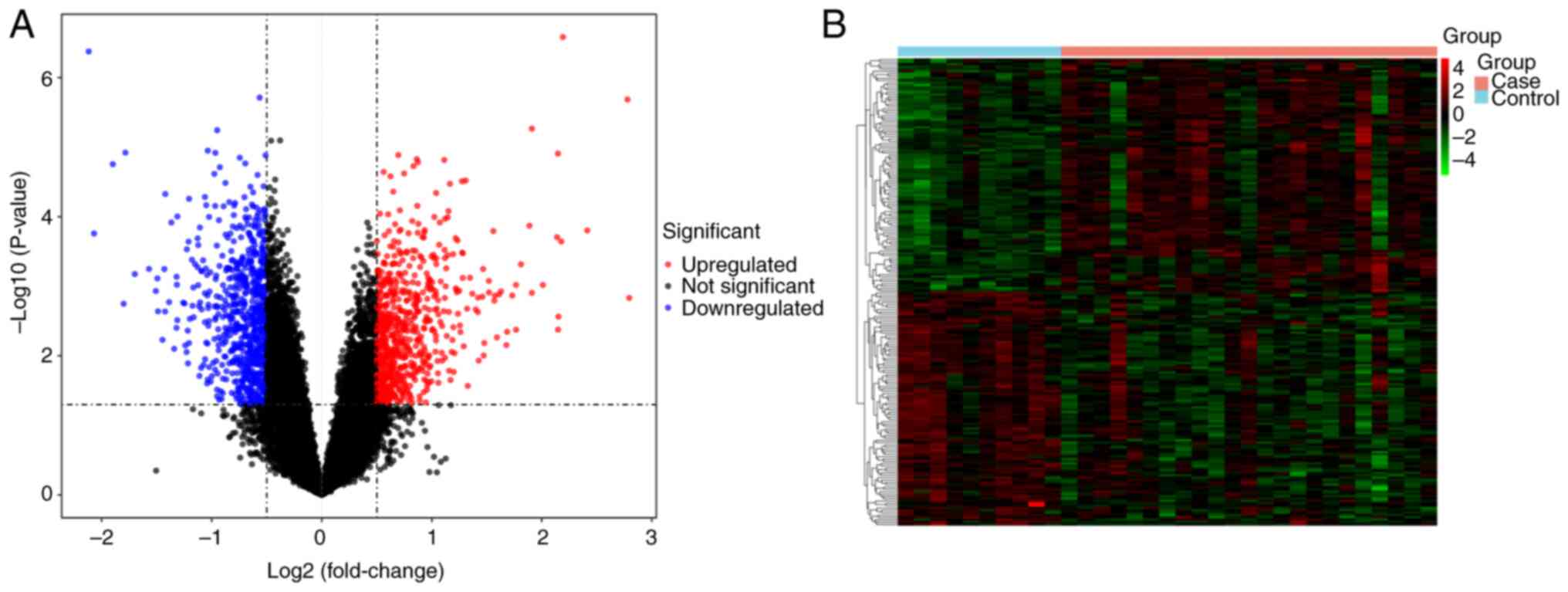
Kawanami D, Matoba K and Utsunomiya K:
Signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy. Histol Histopathol.
31:1059–1067. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Quan KY, Yap CG, Jahan NK and Pillai N:
Review of early circulating biomolecules associated with diabetes
nephropathy-Ideal candidates for early biomarker array test for DN.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 182(109122)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Samsu N: Diabetic Nephropathy: Challenges
in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Biomed Res Int.
2021(1497449)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Magee C, Grieve DJ, Watson CJ and Brazil
DP: Diabetic nephropathy: A tangled web to unweave. Cardiovasc
Drugs. 31:579–592. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Vaziri ND: Disorders of lipid metabolism
in nephrotic syndrome: Mechanisms and consequences. Kidney Int.
90:41–52. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cooper ME: Interaction of metabolic and
haemodynamic factors in mediating experimental diabetic
nephropathy. Diabetologia. 44:1957–1972. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Forbes JM, Fukami K and Cooper ME:
Diabetic nephropathy: Where hemodynamics meets metabolism. Exp Clin
Endocrinol Diabetes. 115:69–84. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Herman-Edelstein M, Scherzer P, Tobar A,
Levi M and Gafter U: Altered renal lipid metabolism and renal lipid
accumulation in human diabetic nephropathy. J Lipid Res.
55:561–572. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yang W, Luo Y, Yang S, Zeng M, Zhang S,
Liu J, Han Y, Liu Y, Zhu X, Wu H, et al: Ectopic lipid
accumulation: Potential role in tubular injury and inflammation in
diabetic kidney disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 132:2407–2422.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Vallon V and Thomson SC: The tubular
hypothesis of nephron filtration and diabetic kidney disease. Nat
Rev Nephrol. 16:317–336. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Baum P, Toyka KV, Blüher M, Kosacka J and
Nowicki M: Inflammatory mechanisms in the pathophysiology of
diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DN)-New aspects. Int J Mol Sci.
22(10835)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kawanami D, Matoba K and Utsunomiya K:
Dyslipidemia in diabetic nephropathy. Ren Replace Ther.
2(16)2016.
|
|
16
|
Lu CC, Ma KL, Ruan XZ and Liu BC: The
emerging roles of microparticles in diabetic nephropathy. Int J
Biol Sci. 13:1118–1125. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ferrara D, Montecucco F, Dallegri F and
Carbone F: Impact of different ectopic fat depots on cardiovascular
and metabolic diseases. J Cell Physiol. 234:21630–21641.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nishi H, Higashihara T and Inagi R:
Lipotoxicity in kidney, heart, and skeletal muscle dysfunction.
Nutrients. 11(1664)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xu T, Xu X, Zhang L, Zhang K, Wei Q, Zhu
L, Yu Y, Xiao L, Lin L, Qian W, et al: Lipidomics reveals serum
specific lipid alterations in diabetic nephropathy. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 12(781417)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wu L, Liu C, Chang DY, Zhan R, Zhao M, Man
Lam S, Shui G, Zhao MH, Zheng L and Chen M: The attenuation of
diabetic nephropathy by annexin A1 via regulation of lipid
metabolism through the AMPK/PPARα/CPT1b pathway. Diabetes.
70:2192–2203. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Thongnak L, Pongchaidecha A and Lungkaphin
A: Renal lipid metabolism and lipotoxicity in diabetes. Am J Med
Sci. 359:84–99. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhao YH and Fan YJ: Resveratrol improves
lipid metabolism in diabetic nephropathy rats. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 25:1913–1924. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Han Y, Xiong S, Zhao H, Yang S, Yang M,
Zhu X, Jiang N, Xiong X, Gao P, Wei L, et al: Lipophagy deficiency
exacerbates ectopic lipid accumulation and tubular cells injury in
diabetic nephropathy. Cell Death Dis. 12(1031)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Patel D and Witt SN: Ethanolamine and
Phosphatidylethanolamine: Partners in health and disease. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2017(4829180)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
van der Veen JN, Kennelly JP, Wan S, Vance
JE, Vance DE and Jacobs RL: The critical role of
phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in
health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 1859 (9 Pt
B):1558–1572. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ravandi A, Kuksis A and Shaikh NA:
Glucosylated Glycerophosphoethanolamines are the Major LDL
glycation products and increase LDL susceptibility to oxidation
evidence of their presence in atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 20:467–477. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Vlassara H and Palace MR: Glycoxidation:
The menace of diabetes and aging. Mt Sinai J Med. 70:232–241.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sur S, Nguyen M, Boada P, Sigdel TK,
Sollinger H and Sarwal MM: FcER1: A novel molecule implicated in
the progression of human diabetic kidney disease. Front Immunol.
12(769972)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43(e47)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ito K and Murphy D: Application of ggplot2
to Pharmacometric Graphics. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol.
2(e79)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hu K: Become competent in generating
RNA-Seq heat maps in one day for novices without prior R
experience. Methods Mol Biol. 2239:269–303. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chen H and Boutros PC: VennDiagram: A
package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler
diagrams in R. BMC Bioinformatics. 12(35)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tang J, Kong D, Cui Q, Wang K, Zhang D,
Gong Y and Wu G: Prognostic genes of breast cancer identified by
gene co-expression network analysis. Front Oncol.
8(374)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
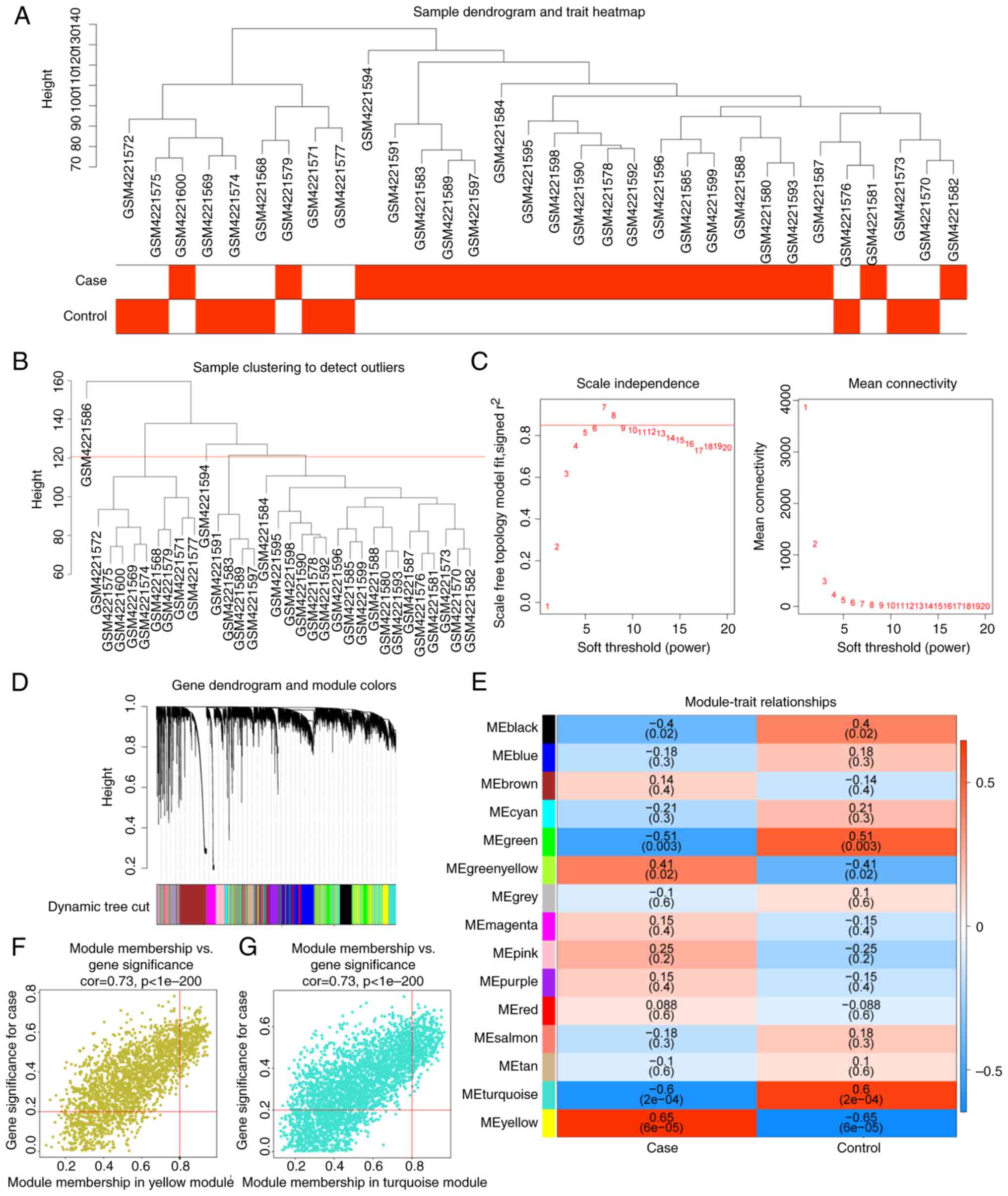
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9(559)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
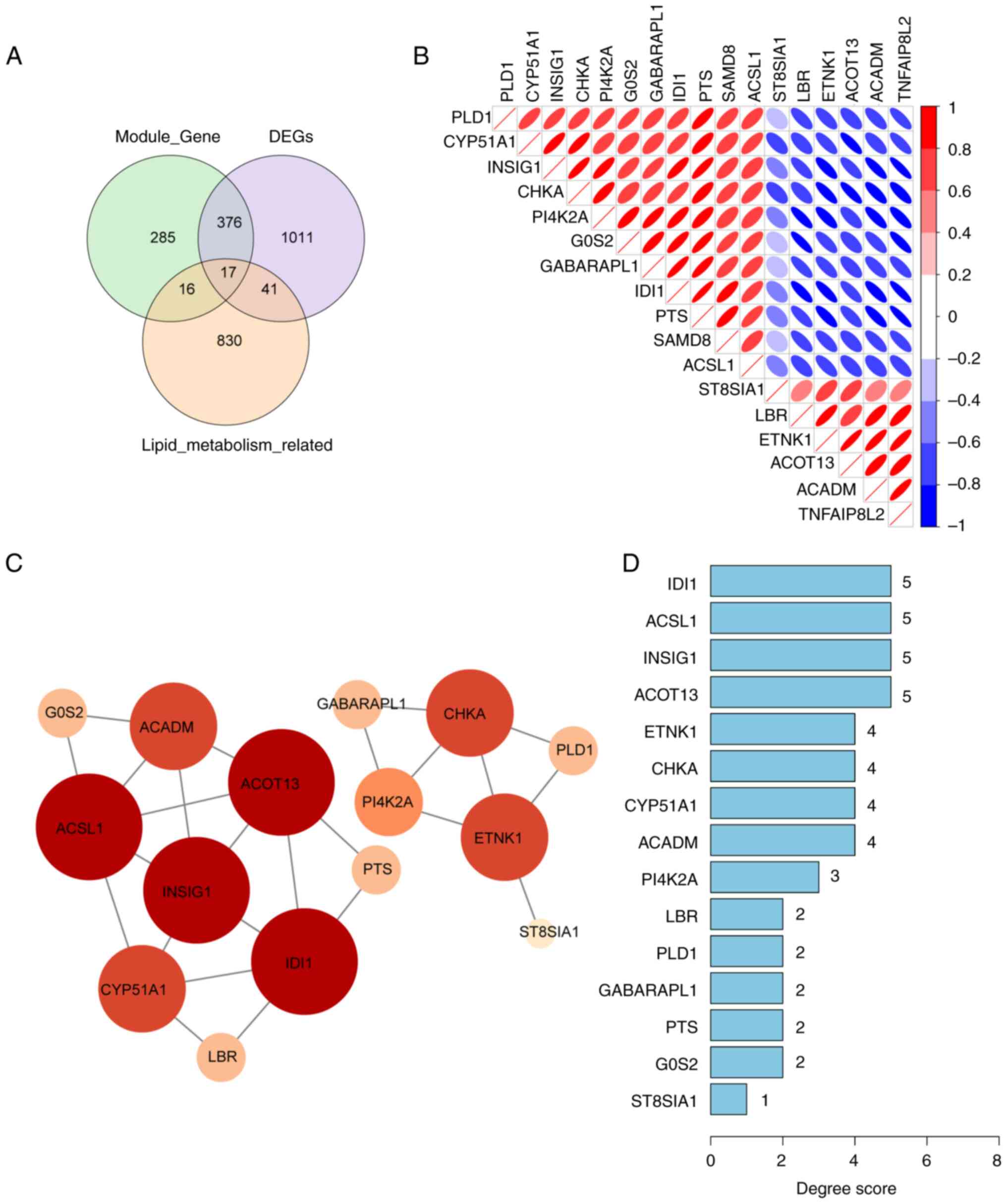
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Nastou KC, Lyon D,
Kirsch R, Pyysalo S, Doncheva NT, Legeay M, Fang T, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks,
and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement
sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 49 (D1):D605–D612. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
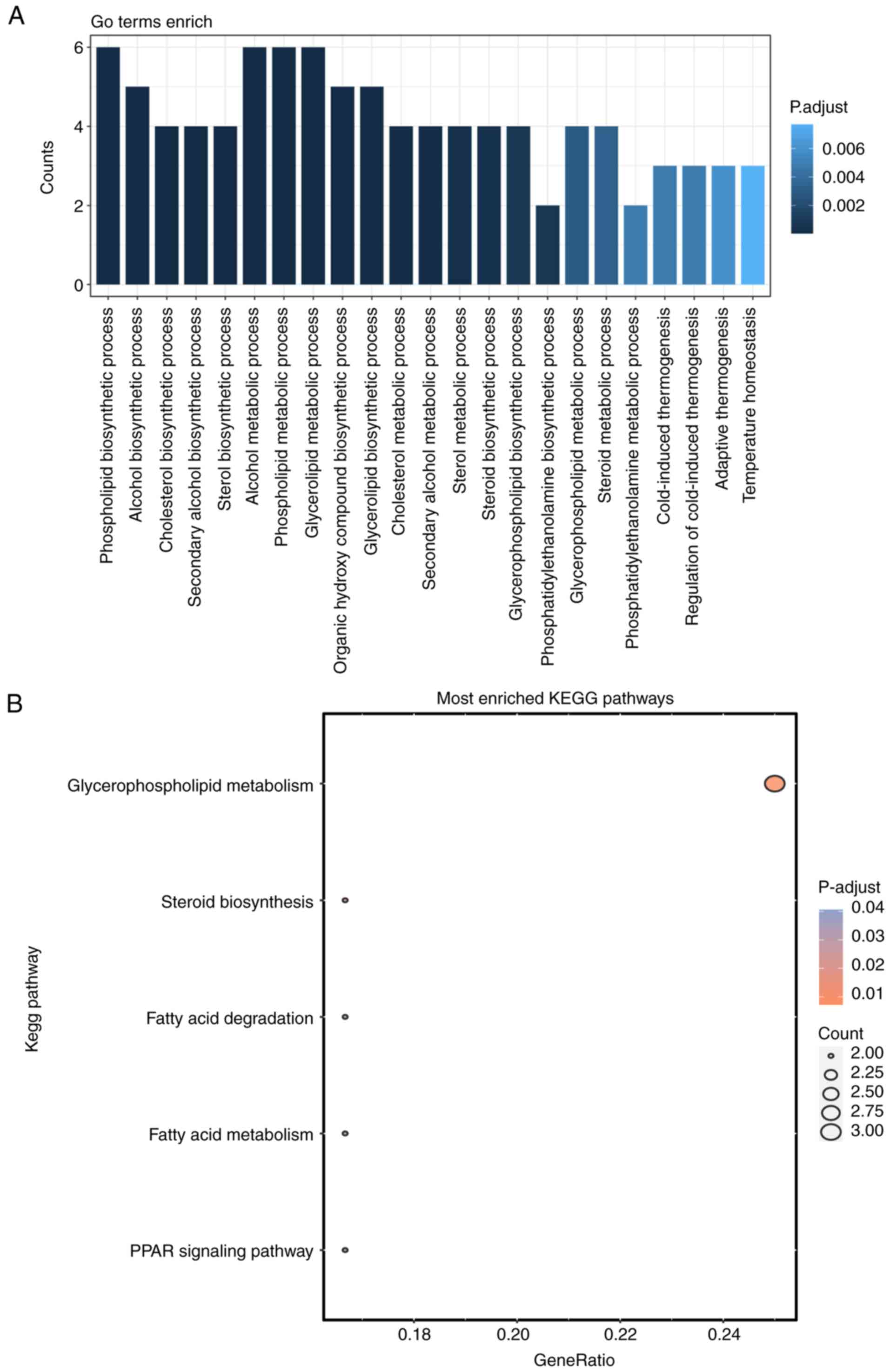
Wu T, Hu E, Xu S, Chen M, Guo P, Dai Z,
Feng T, Zhou L, Tang W, Zhan L, et al: clusterProfiler 4.0: A
universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation
(Camb). 2(100141)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Walter W, Sanchez-Cabo F and Ricote M:
GOplot: An R package for visually combining expression data with
functional analysis. Bioinformatics. 31:2912–2914. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xu Q, Xu H, Deng R, Wang Z, Li N, Qi Z,
Zhao J and Huang W: Multi-omics analysis reveals prognostic value
of tumor mutation burden in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell
Int. 21(342)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang M, Zhu K, Pu H, Wang Z, Zhao H,
Zhang J and Wang Y: An immune-related signature predicts survival
in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol.
9(1314)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sanz H, Valim C, Vegas E, Oller JM and
Reverter F: SVM-RFE: Selection and visualization of the most
relevant features through non-linear kernels. BMC Bioinformatics.
19(432)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R and Guinney J:
GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data.
BMC Bioinformatics. 14(7)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Pei L, Li J, Xu Z, Chen N, Wu X and Chen
J: Effect of high hydrostatic pressure on aroma components, amino
acids, and fatty acids of Hami melon (Cucumis melo L. var.
reticulatus naud.) juice. Food Sci Nutr. 8:1394–1405.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Strezoska Ž, Licon A, Haimes J, Spayd KJ,
Patel KM, Sullivan K, Jastrzebski K, Simpson KJ, Leake D, van
Brabant Smith A and Vermeulen A: Optimized PCR conditions and
increased shRNA fold representation improve reproducibility of
pooled shRNA screens. PLoS One. 7(e42341)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Cabukusta B, Nettebrock NT, Kol M,
Hilderink A, Tafesse FG and Holthuis JCM: Ceramide
phosphoethanolamine synthase SMSr is a target of caspase-6 during
apoptotic cell death. Biosci Rep. 37(BSR20170867)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Tafesse FG, Vacaru AM, Bosma EF,
Hermansson M, Jain A, Hilderink A, Somerharju P and Holthuis JC:
Sphingomyelin synthase-related protein SMSr is a suppressor of
ceramide-induced mitochondrial apoptosis. J Cell Sci. 127 (Pt
2):445–454. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Srivastava SP, Shi S, Koya D and Kanasaki
K: Lipid mediators in diabetic nephropathy. Fibrogenesis Tissue
Repair. 7(12)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Woodcock J: Sphingosine and ceramide
signalling in apoptosis. IUBMB Life. 58:462–466. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Tani M, Ito M and Igarashi Y:
Ceramide/sphingosine/sphingosine 1-phosphate metabolism on the cell
surface and in the extracellular space. Cell Signal. 19:229–237.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Kuzmenko DI and Klimentyeva TK: Role of
ceramide in apoptosis and development of insulin resistance.
Biochemistry (Mosc). 81:913–927. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Summers SA: The ART of lowering ceramides.
Cell Metab. 22:195–196. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Symons JD and Abel ED: Lipotoxicity
contributes to endothelial dysfunction: A focus on the contribution
from ceramide. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 14:59–68. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Chavez JA and Summers SA: A
ceramide-centric view of insulin resistance. Cell Metab.
15:585–594. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Park JW, Byrd A, Lee CM and Morgan ET:
Nitric oxide stimulates cellular degradation of human CYP51A1, the
highly conserved lanosterol 14α-demethylase. Biochem J.
474:3241–3252. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Kaluzhskiy L, Ershov P, Yablokov E, Shkel
T, Grabovec I, Mezentsev Y, Gnedenko O, Usanov S, Shabunya P,
Fatykhava S, et al: Human Lanosterol 14-Alpha Demethylase (CYP51A1)
is a putative target for natural flavonoid luteolin 7,3'-Disulfate.
Molecules. 26(2237)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Opazo-Ríos L, Mas S, Marín-Royo G, Mezzano
S, Gómez-Guerrero C, Moreno JA and Egido J: Lipotoxicity and
diabetic nephropathy: Novel mechanistic insights and therapeutic
opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. 21(2632)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Charles MA, Eschwège E, Thibult N, Claude
JR, Warnet JM, Rosselin GE, Girard J and Balkau B: The role of
non-esterified fatty acids in the deterioration of glucose
tolerance in Caucasian subjects: Results of the Paris Prospective
Study. Diabetologia. 40:1101–1106. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Meex RCR, Blaak EE and van Loon LJC:
Lipotoxicity plays a key role in the development of both insulin
resistance and muscle atrophy in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Obes Rev. 20:1205–1217. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Gai Z, Wang T, Visentin M, Kullak-Ublick
GA, Fu X and Wang Z: Lipid accumulation and chronic kidney disease.
Nutrients. 11(722)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Jaishy B and Abel ED: Lipids, lysosomes,
and autophagy. J Lipid Res. 57:1619–1635. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Pérez-Morales RE, Del Pino MD, Valdivielso
JM, Ortiz A, Mora-Fernández C and Navarro-González JF: Inflammation
in diabetic kidney disease. Nephron. 143:12–16. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Shao BY, Zhang SF, Li HD, Meng XM and Chen
HY: Epigenetics and inflammation in diabetic nephropathy. Front
Physiol. 12(649587)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Wang Y, Zhao M and Zhang Y: Identification
of fibronectin 1 (FN1) and complement component 3 (C3) as immune
infiltration-related biomarkers for diabetic nephropathy using
integrated bioinformatic analysis. Bioengineered. 12:5386–5401.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Huang M, Zhu Z, Nong C, Liang Z, Ma J and
Li G: Bioinformatics analysis identifies diagnostic biomarkers and
their correlation with immune infiltration in diabetic nephropathy.
Ann Transl Med. 10(669)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Wilson PC, Wu H, Kirita Y, Uchimura K,
Ledru N, Rennke HG, Welling PA, Waikar SS and Humphreys BD: The
single-cell transcriptomic landscape of early human diabetic
nephropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:19619–19625.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Onalan E: The relationship between
monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and diabetic
nephropathy. Pak J Med Sci. 35:1081–1086. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Huang Q, Wu H, Wo M, Ma J, Fei X and Song
Y: Monocyte-lymphocyte ratio is a valuable predictor for diabetic
nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Medicine (Baltimore).
99(e20190)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Efe FK: The association between monocyte
HDL ratio and albuminuria in diabetic nephropathy. Pak J Med Sci.
37:1128–1132. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Ancuta P, Wang J and Gabuzda D: CD16+
monocytes produce IL-6, CCL2, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 upon
interaction with CX3CL1-expressing endothelial cells. J Leukoc
Biol. 80:1156–1164. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Tang G, Li S, Zhang C, Chen H, Wang N and
Feng Y: Clinical efficacies, underlying mechanisms and molecular
targets of Chinese medicines for diabetic nephropathy treatment and
management. Acta Pharm Sin B. 11:2749–2767. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Ji L, Chen Y, Wang H, Zhang W, He L, Wu J
and Liu Y: Overexpression of Sirt6 promotes M2 macrophage
transformation, alleviating renal injury in diabetic nephropathy.
Int J Oncol. 55:103–115. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Wolf G: New insights into the
pathophysiology of diabetic nephropathy: From haemodynamics to
molecular pathology. Eur J Clin Invest. 34:785–796. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|