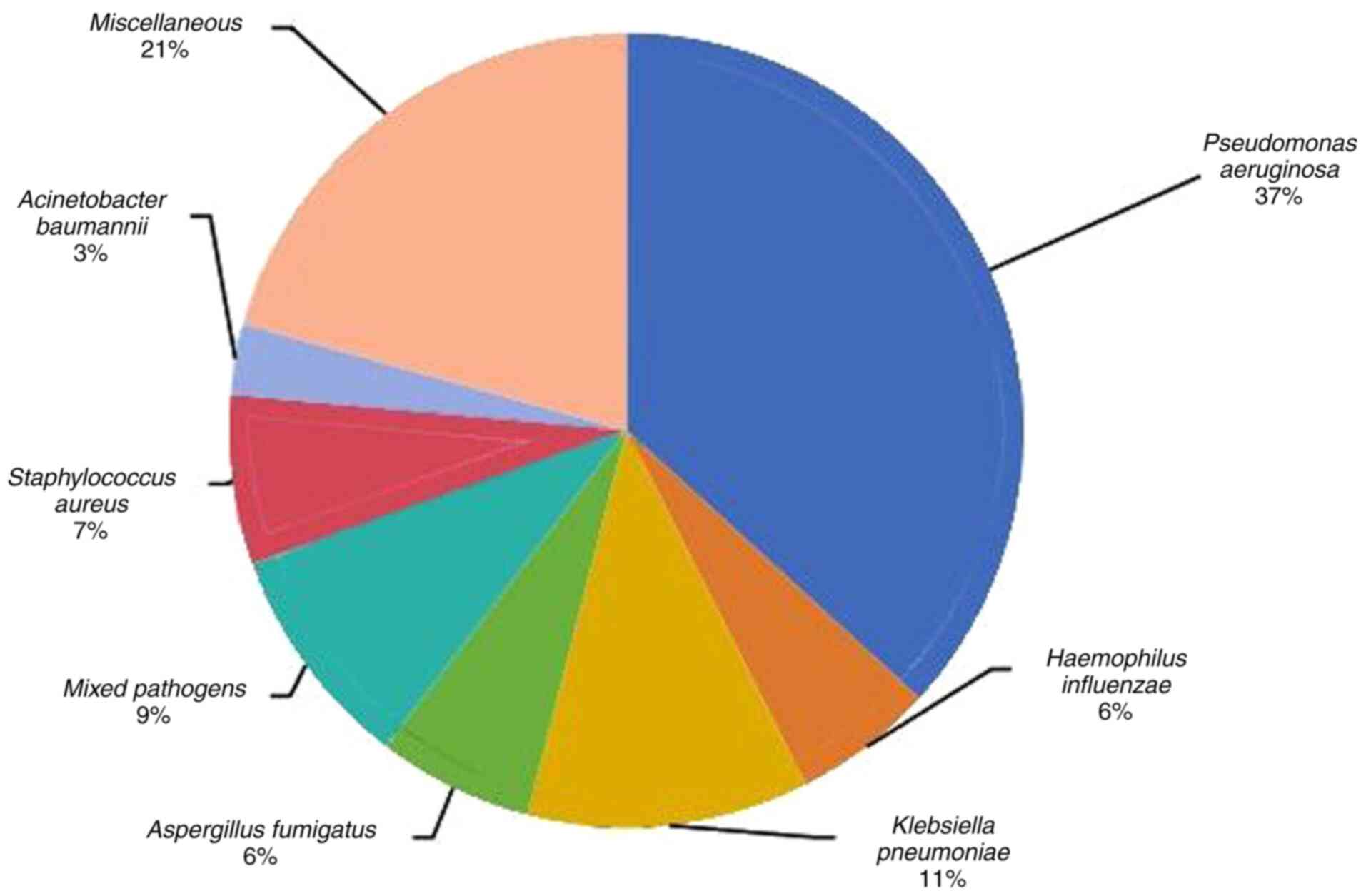
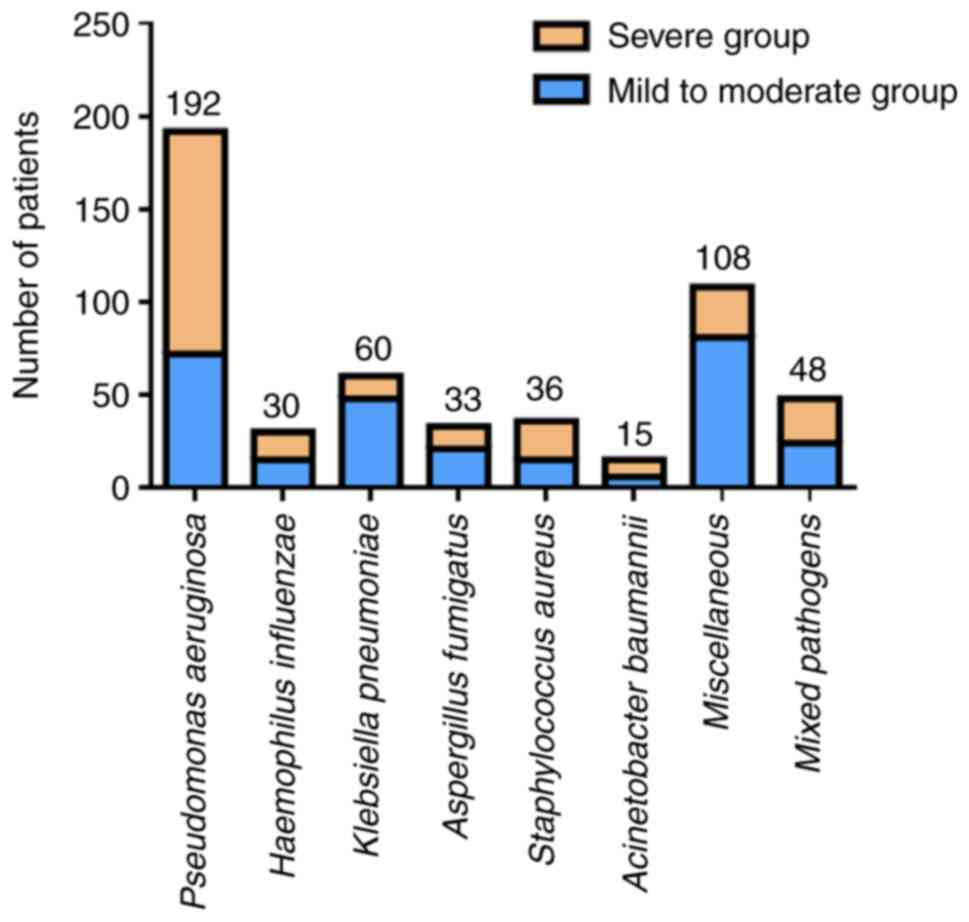
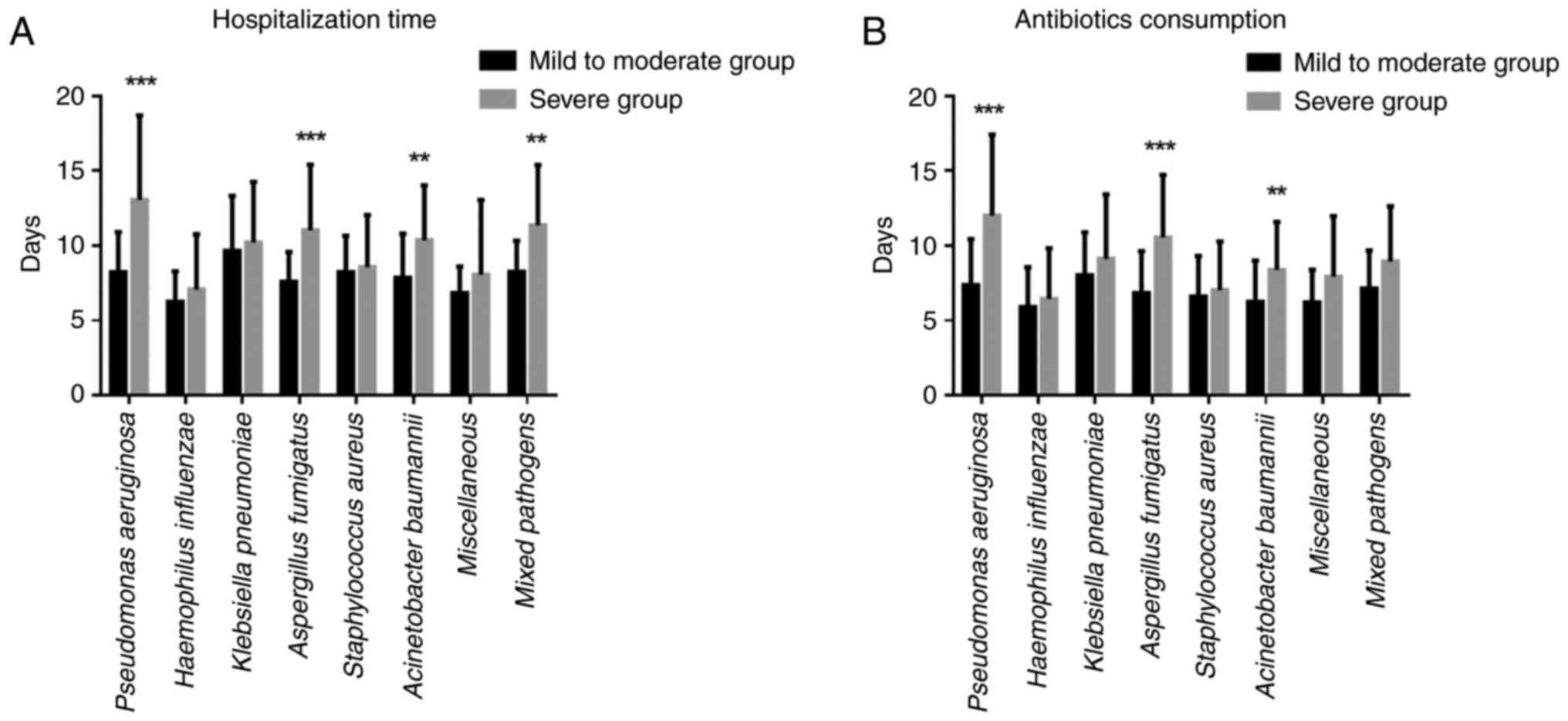
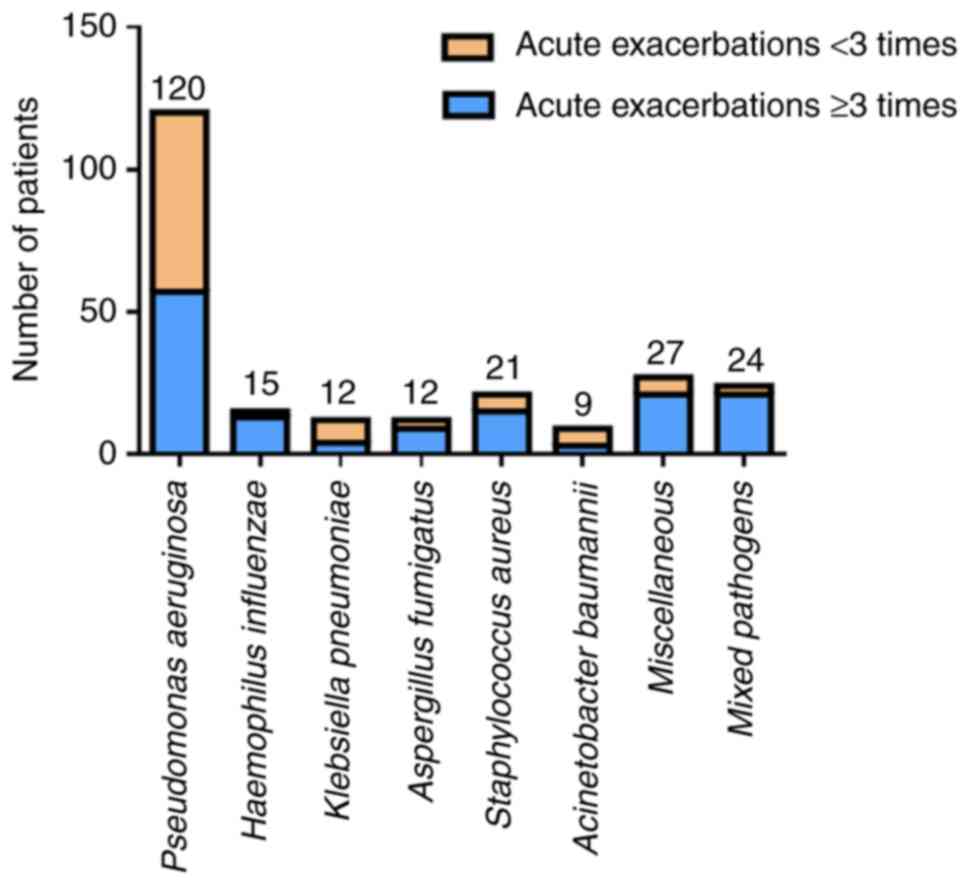
|
1
|
Shteinberg M, Flume PA and Chalmers JD: Is
bronchiectasis really a disease? Eur Respir Rev.
29(190051)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
King P, Holdsworth S, Freezer N and Holmes
P: Bronchiectasis. Intern Med J. 36:729–737. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
King PT, Holdsworth SR, Freezer NJ,
Villanueva E and Holmes PW: Characterisation of the onset and
presenting clinical features of adult bronchiectasis. Respir Med.
100:2183–2189. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Polverino E, Dimakou K, Hurst J,
Martinez-Garcia MA, Miravitlles M, Paggiaro P, Shteinberg M,
Aliberti S and Chalmers JD: The overlap between bronchiectasis and
chronic airway diseases: State of the art and future directions.
Eur Respir J. 52(1800328)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mac Aogáin M, Xaverius Ivan F, Jaggi TK,
Richardson H, Shoemark A, Narayana JK, Dicker AJ, Koh MS, Lee KCH,
Thun How O, et al: Airway ‘resistotypes’ and clinical outcomes in
bronchiectasis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 210:47–62.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Berra G, Chappuis-Gisin É, Soccal PM and
Plojoux J: Inhaled antibiotics for the management of non cystic
fibrosis bronchiectasis. Rev Med Suisse. 13:2001–2004.
2017.PubMed/NCBI(In French).
|
|
7
|
Chalmers JD, Chang AB, Chotirmall SH, Dhar
R and McShane PJ: Bronchiectasis. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
4(45)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang XX, He JH, Pan CX, He ZF, Li HM, Lin
ZH, Zhang XF, Cen LJ, Zhang RL, Shi MX and Guan WJ: Bacteria and
viruses and clinical outcomes of asthma-bronchiectasis overlap
syndrome: A cohort study. Clin Transl Allergy.
14(e12331)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yang SH, Song MJ, Kim YW, Kwon BS, Lim SY,
Lee YJ, Park JS, Cho YJ, Lee JH, Lee CT and Kim HJ: Understanding
the effects of Haemophilus influenzae colonization on
bronchiectasis: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Pulm Med.
24(7)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Loong SK, Liam CK, Karunakaran R, Tan KK,
Mahfodz NH and AbuBakar S: Non-classical Bordetella sp. (closely
related to Bordetella hinzii and Bordetella pseudohinzii) lower
respiratory tract infection in a patient with extensive
bronchiectasis: A case report. J Int Med Res.
52(3000605231214464)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
McShane PJ: Investigation and management
of bronchiectasis in nontuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary
disease. Clin Chest Med. 44:731–742. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chagas MDS, Trindade Dos Santos M, Argollo
de Menezes M and da Silva FAB: Boolean model of the gene regulatory
network of Pseudomonas aeruginosa CCBH4851. Front Microbiol.
14(1274740)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bronchiectasis Expert Consensus Writing
Group; Pulmonary Infection Assembly, Chinese Thoracic Society.
Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of adult
bronchiectasis in China. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi.
44:311–321. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Costa JC, Machado JN, Ferreira C, Gama J
and Rodrigues C: The bronchiectasis severity index and FACED score
for assessment of the severity of bronchiectasis. Pulmonology.
(S2173-5115(17)30154-9)(2018): (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
15
|
Yang B, Kim BG, Han K, Jung JH, Kim JH,
Park DW, Kim SH, Kim EG, Sohn JW, Yoon HJ, et al: Systemic
sclerosis and risk of bronchiectasis: A nationwide longitudinal
cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. 25(209)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jayaram L, King PT, Hunt J, Lim M, Park C,
Hu E, Dousha L, Ha P, Bartlett JB, Southcott AM, et al: Evaluation
of high dose N-acetylcysteine on airway inflammation and quality of
life outcomes in adults with bronchiectasis: A randomised
placebo-controlled pilot study. Pulm Pharmacol Ther.
84(102283)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen W, Ran S, Li C, Li Z, Wei N, Li J and
Li N: Elevated eosinophil counts in acute exacerbations of
bronchiectasis: Unveiling a distinct clinical phenotype. Lung.
202:53–61. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yong VFL, Soh MM, Jaggi TK, Mac Aogáin M
and Chotirmall SH: The microbial endocrinology of Pseudomonas
aeruginosa: Inflammatory and immune perspectives. Arch Immunol
Ther Exp (Warsz). 66:329–339. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shi LH, Cheng F, Gao BR, et al: Analysis
of clinical characteristics of 207 inpatients with bronchiectasis
in Hainan Province. Int J Respir. 43:595–603. 2023.
|
|
20
|
Wang R, Ding S, Lei C, Yang D and Luo H:
The contribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection to
clinical outcomes in bronchiectasis: A prospective cohort study.
Ann Med. 53:459–469. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Finney LJ, Ritchie A, Pollard E, Johnston
SL and Mallia P: Lower airway colonization and inflammatory
response in COPD: A focus on Haemophilus influenzae. Int J
Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 9:1119–1132. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Duff RM, Simmonds NJ, Davies JC, Wilson R,
Alton EW, Pantelidis P, Cox MJ, Cookson WO, Bilton D and Moffatt
MF: A molecular comparison of microbial communities in
bronchiectasis and cystic fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 41:991–993.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Miao XY, Ji XB, Lu HW, Yang JW and Xu JF:
Distribution of major pathogens from sputum and bronchoalveolar
lavage fluid in patients with noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis: A
systematic review. Chin Med J (Engl). 128:2792–2797.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sabat AJ, Pantano D, Akkerboom V, Bathoorn
E and Friedrich AW: Pseudomonas aeruginosa and
Staphylococcus aureus virulence factors as biomarkers of
infection. Biol Chem. 402:1565–1573. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Polverino E, Goeminne PC, McDonnell MJ,
Aliberti S, Marshall SE, Loebinger MR, Murris M, Cantón R, Torres
A, Dimakou K, et al: European Respiratory Society guidelines for
the management of adult bronchiectasis. Eur Respir J.
50(1700629)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chang AB, Bell SC, Torzillo PJ, King PT,
Maguire GP, Byrnes CA, Holland AE, O'Mara P and Grimwood K:
extended voting group. Chronic suppurative lung disease and
bronchiectasis in children and adults in Australia and New Zealand
Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand guidelines. Med J
Aust. 202:21–23. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pasteur MC, Bilton D and Hill AT: British
Thoracic Society Bronchiectasis non-CF Guideline Group. British
Thoracic Society guideline for non-CF bronchiectasis. Thorax. 65
(Suppl 1):i1–i58. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Alavi Foumani A, Jafari A, Tangestani
Nejad A, Jafarinejhad A, Ziyapour S, Keivanlou MH and Afzalipour M:
Effects of probiotics on clinical manifestations of bronchiectasis:
A randomized, triple blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial.
Tanaffos. 22:221–229. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Morrow LE, Kollef MH and Casale TB:
Probiotic prophylaxis of ventilator-associated pneumonia: A
blinded, randomized, controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
182:1058–1064. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sarshar M, Behzadi P, Scribano D, Palamara
AT and Ambrosi C: Acinetobacter baumannii: An ancient
commensal with weapons of a pathogen. Pathogens.
10(387)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yao Y, Chen Q and Zhou H: Virulence
factors and pathogenicity mechanisms of Acinetobacter
baumannii in respiratory infectious diseases. Antibiotics
(Basel). 12(1749)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|