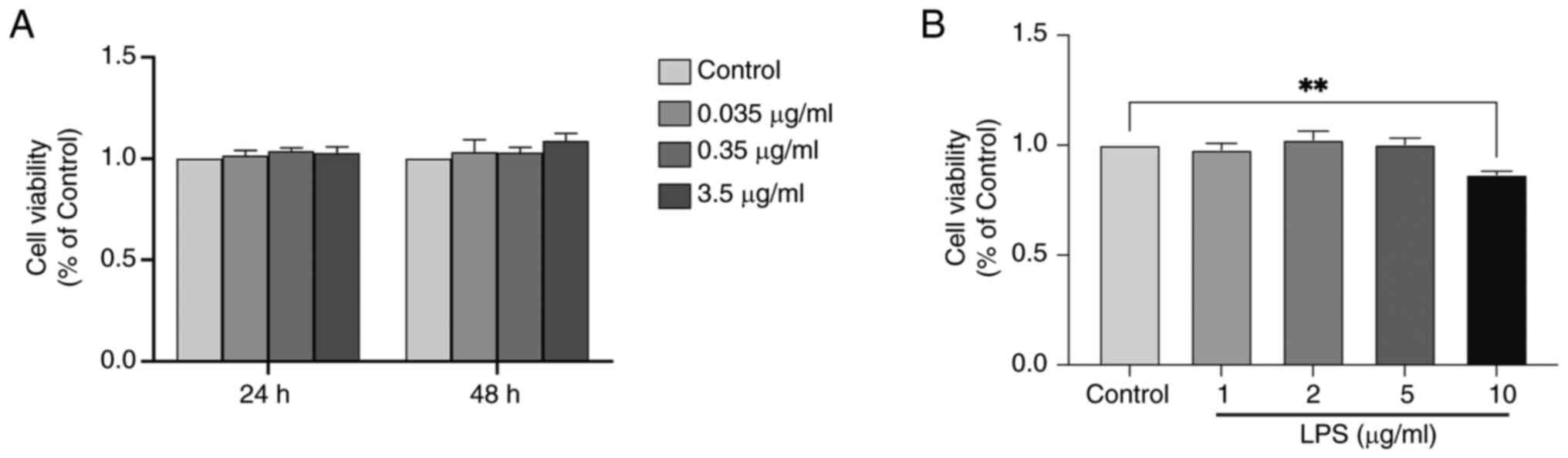
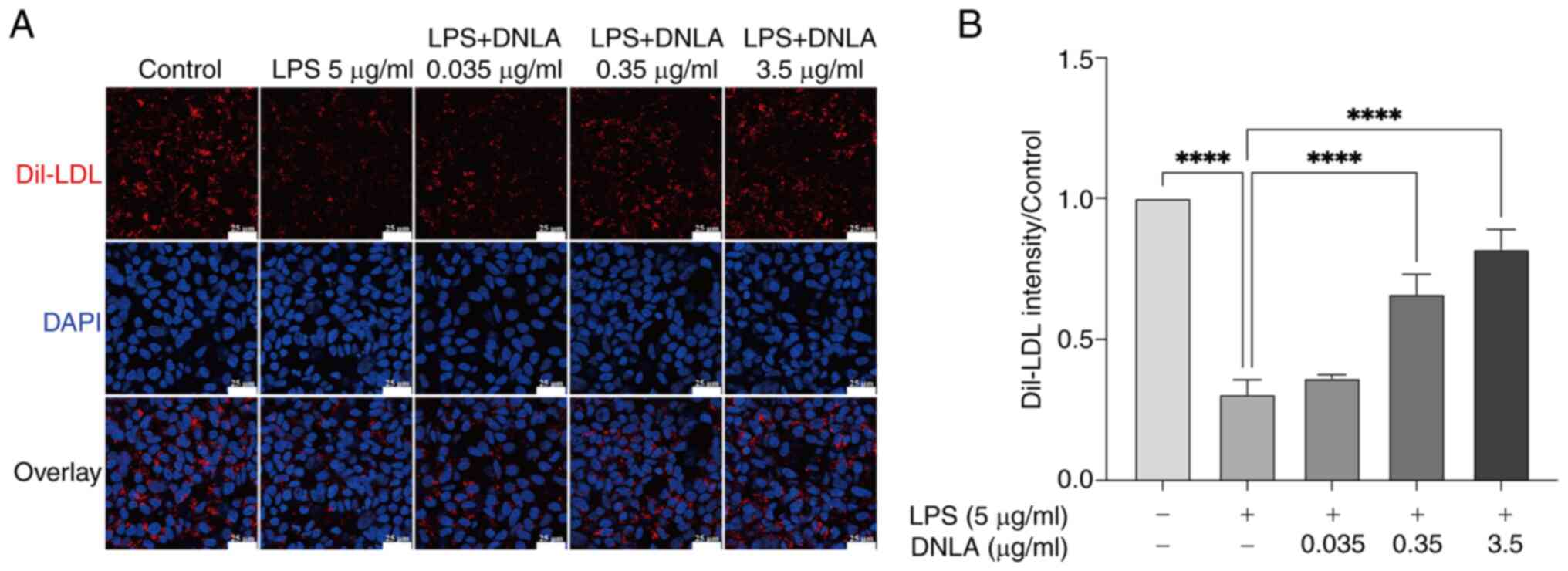
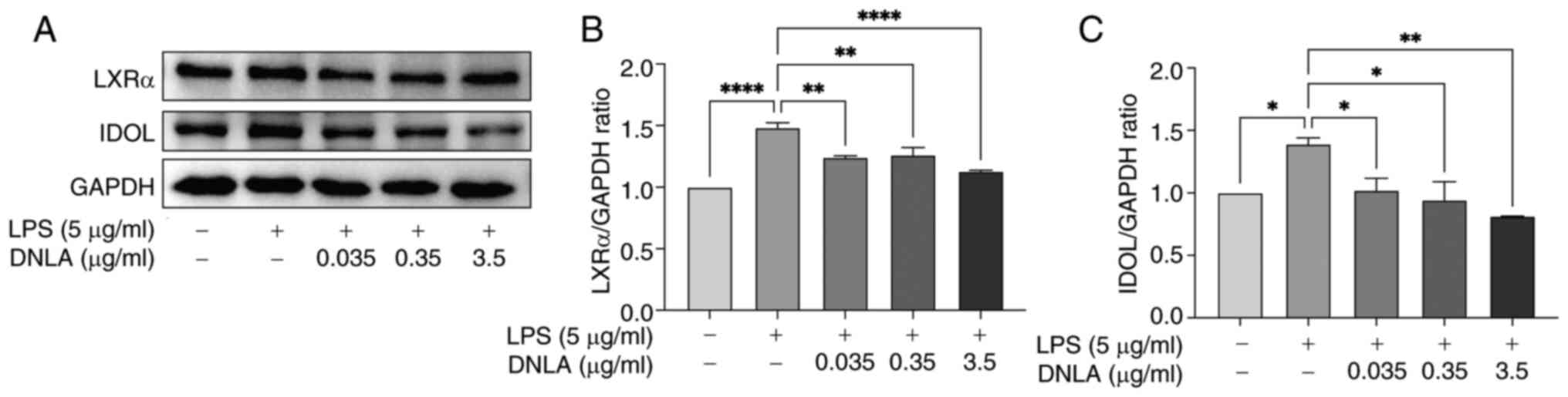
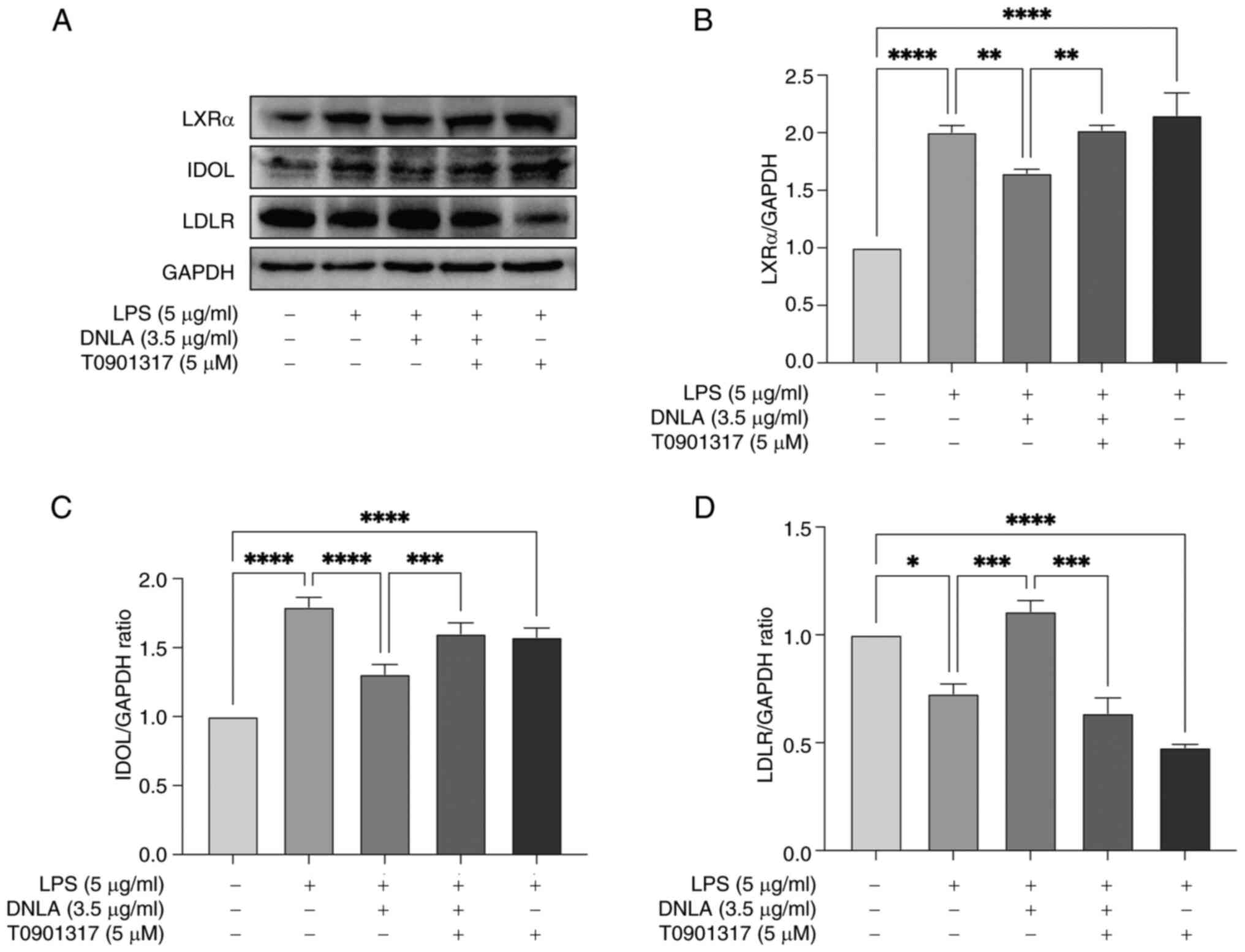
|
1
|
Kobiyama K and Ley K: Atherosclerosis.
Circ Res. 123:1118–1120. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ridker PM: LDL cholesterol: Controversies
and future therapeutic directions. Lancet. 384:607–617.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Luo J, Yang H and Song BL: Mechanisms and
regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
21:225–245. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Barale C, Melchionda E, Morotti A and
Russo I: PCSK9 biology and its role in atherothrombosis. Int J Mol
Sci. 22(5880)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Li H, Yu XH, Ou X, Ouyang XP and Tang CK:
Hepatic cholesterol transport and its role in non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease and atherosclerosis. Prog Lipid Res.
83(101109)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Brown MS and Goldstein JL: A
receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science.
232:34–47. 1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Burnett JR and Hooper AJ: MK-0616: An oral
PCSK9 inhibitor for hypercholesterolemia treatment. Expert Opin
Investig Drugs. 32:873–878. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Raschi E, Casula M, Cicero AFG, Corsini A,
Borghi C and Catapano A: Beyond statins: New pharmacological
targets to decrease LDL-cholesterol and cardiovascular events.
Pharmacol Ther. 250(108507)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
O'Donoghue ML, Fazio S, Giugliano RP,
Stroes ESG, Kanevsky E, Gouni-Berthold I, Im K, Pineda AL,
Wasserman SM, Češka R, et al: Lipoprotein(a), PCSK9 inhibition, and
cardiovascular risk. Circulation. 139:1483–1492. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Rosenson RS, Hegele RA, Fazio S and Cannon
CP: The evolving future of PCSK9 inhibitors. J Am Coll Cardiol.
72:314–329. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Goldstein JL, DeBose-Boyd RA and Brown MS:
Protein sensors for membrane sterols. Cell. 124:35–46.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hua X, Yokoyama C, Wu J, Briggs MR, Brown
MS, Goldstein JL and Wang X: SREBP-2, a second
basic-helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper protein that stimulates
transcription by binding to a sterol regulatory element. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 90:11603–11607. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shimano H, Shimomura I, Hammer RE, Herz J,
Goldstein JL, Brown MS and Horton JD: Elevated levels of SREBP-2
and cholesterol synthesis in livers of mice homozygous for a
targeted disruption of the SREBP-1 gene. J Clin Invest.
100:2115–2124. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang HX, Zhang M, Long SY, Tuo QH, Tian Y,
Chen JX, Zhang CP and Liao DF: Cholesterol in LDL receptor
recycling and degradation. Clin Chim Acta. 500:81–86.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bartolomei M, Bollati C, Li J, Arnoldi A
and Lammi C: Assessment of the cholesterol-lowering effect of
MOMAST®: Biochemical and cellular studies. Nutrients.
14(493)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ding Z, Pothineni NVK, Goel A, Lüscher TF
and Mehta JL: PCSK9 and inflammation: Role of shear stress,
pro-inflammatory cytokines, and LOX-1. Cardiovasc Res. 116:908–915.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jia Q, Cao H, Shen D, Li S, Yan L, Chen C,
Xing S and Dou F: Quercetin protects against atherosclerosis by
regulating the expression of PCSK9, CD36, PPARγ, LXRα and ABCA1.
Int J Mol Med. 44:893–902. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Olsson PA, Korhonen L, Mercer EA and
Lindholm D: MIR is a novel ERM-like protein that interacts with
myosin regulatory light chain and inhibits neurite outgrowth. J
Biol Chem. 274:36288–36292. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lagace TA: PCSK9 and LDLR degradation:
Regulatory mechanisms in circulation and in cells. Curr Opin
Lipidol. 25:387–393. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
van Loon NM, van Wouw SAE, Ottenhoff R,
Nelson JK, Kingma J, Scheij S, Moeton M and Zelcer N: Regulation of
intestinal LDLR by the LXR-IDOL axis. Atherosclerosis. 315:1–9.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zelcer N, Hong C, Boyadjian R and Tontonoz
P: LXR regulates cholesterol uptake through Idol-dependent
ubiquitination of the LDL receptor. Science. 325:100–104.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang L, Reue K, Fong LG, Young SG and
Tontonoz P: Feedback regulation of cholesterol uptake by the
LXR-IDOL-LDLR axis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:2541–2546.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
da Silva JA and Ng TB: The medicinal and
pharmaceutical importance of Dendrobium species. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 101:2227–2239. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhou J, Zhang Y, Li S, Zhou Q, Lu Y, Shi
J, Liu J, Wu Q and Zhou S: Dendrobium nobile Lindl.
alkaloids-mediated protection against CCl4-induced liver
mitochondrial oxidative damage is dependent on the activation of
Nrf2 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
129(110351)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Li DD, Fan HX, Yang R, Li YY, Zhang F and
Shi JS: Dendrobium Nobile Lindl. Alkaloid suppresses NLRP3-mediated
pyroptosis to alleviate LPS-induced neurotoxicity. Front Pharmacol.
13(846541)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Huang Q, Liao X, Wu Q, Li F, Wang LY and
Shi JS: Effects of Dendrobium nobile Lindl. alkaloids on blood
glucose and liver fatty degeneration in diabetic rats. Chin J New
Drugs Clin Rem. 32:490–493. 2013.
|
|
27
|
Xu YY, Xu YS, Wang Y, Wu Q, Lu YF, Liu J
and Shi JS: Dendrobium nobile Lindl. alkaloids regulate metabolism
gene expression in livers of mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 69:1409–1417.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Huang S, Wu Q, Liu H, Ling H, He Y, Wang
C, Wang Z and Lu Y and Lu Y: Alkaloids of dendrobium nobile lindl.
Altered hepatic lipid homeostasis via regulation of bile acids. J
Ethnopharmacol. 241(111976)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhou J, Zhang Y, Li S, Zhou Q, Lu Y, Shi
J, Liu J, Wu Q and Zhou S: Dendrobium nobile Lindl.
alkaloids-mediated protection against CCl4-induced liver
mitochondrial oxidative damage is dependent on the activation of
Nrf2 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
129(110351)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Xian S, Yang Y, Nan N, Fu X, Shi J, Wu Q
and Zhou S: Inhibition of mitochondrial ROS-mediated necroptosis by
Dendrobium nobile Lindl. alkaloids in carbon tetrachloride induced
acute liver injury. J Ethnopharmacol. 330(118253)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Nie J, Tian Y, Zhang Y, Lu YL, Li LS and
Shi JS: Dendrobium alkaloids prevent Aβ25-35-induced neuronal and
synaptic loss via promoting neurotrophic factors expression in
mice. PeerJ. 4(e2739)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li LS, Lu YL, Nie J, Xu YY, Zhang W, Yang
WJ, Gong QH, Lu YF, Lu Y and Shi JS: Dendrobium nobile Lindl
alkaloid, a novel autophagy inducer, protects against axonal
degeneration induced by Aβ25-35 in hippocampus neurons in vitro.
CNS Neurosci Ther. 23:329–340. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Huang J, Huang N, Zhang M, Nie J, Xu YY,
Wu Q and Shi J: Dendrobium alkaloids decrease Aβ by regulating α-
and β-secretases in hippocampal neurons of SD rats. PeerJ.
7(e7627)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Emmanuel UO: TNFα-Induced LDL cholesterol
accumulation involve elevated LDLR cell surface levels and SR-B1
downregulation in human arterial endothelial cells. Int J Mol Sci.
22(6236)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Scotti E, Calamai M, Goulbourne CN, Zhang
L, Hong C, Lin RR, Choi J, Pilch PF, Fong LG, Zou P, et al: IDOL
stimulates clathrin-independent endocytosis and multivesicular
body-mediated lysosomal degradation of the low-density lipoprotein
receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 33:1503–1514. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Nazih H and Bard JM: Cholesterol,
oxysterols and LXRs in breast cancer pathophysiology. Int J Mol
Sci. 21(1356)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Seidah NG and Prat A: The multifaceted
biology of PCSK9. Endocr Rev. 43:558–582. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nourse JL, Leung VM, Abuwarda H, Evans EL,
Izquierdo-Ortiz E, Ly AT, Truong N, Smith S, Bhavsar H, Bertaccini
G, et al: Piezo1 regulates cholesterol biosynthesis to influence
neural stem cell fate during brain development. J Gen Physiol.
154(e202213084)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yang T, Wang Y, Cao X, Peng Y, Huang J,
Chen L, Pang J, Jiang Z, Qian S, Liu Y, et al: Targeting mTOR/YY1
signaling pathway by quercetin through CYP7A1-mediated
cholesterol-to-bile acids conversion alleviated type 2 diabetes
mellitus induced hepatic lipid accumulation. Phytomedicine.
113(154703)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Li W, Li H, Zha C, Che B, Yu Y, Yang J and
Li T: Lipids, lipid-modified drug target genes, and the risk of
male infertility: A Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 15(1392533)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Gormley M, Yarmolinsky J, Dudding T,
Burrows K, Martin RM, Thomas S, Tyrrell J, Brennan P, Pring M,
Boccia S, et al: Using genetic variants to evaluate the causal
effect of cholesterol lowering on head and neck cancer risk: A
Mendelian randomization study. PLoS Genet.
17(e1009525)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Navarese EP, Robinson JG, Kowalewski M,
Kolodziejczak M, Andreotti F, Bliden K, Tantry U, Kubica J, Raggi P
and Gurbel PA: Association between baseline LDL-C level and total
and cardiovascular mortality after LDL-C lowering: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 319:1566–1579. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lan R, Luo H, Wu F, Wang Y and Zhao Z:
Chitosan oligosaccharides alleviate heat-stress-induced lipid
metabolism disorders by suppressing the oxidative stress and
inflammatory response in the liver of broilers. Antioxidants
(Basel). 12(1497)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Sun Y, Ishibashi M, Seimon T, Lee M,
Sharma SM, Fitzgerald KA, Samokhin AO, Wang Y, Sayers S, Aikawa M,
et al: Free cholesterol accumulation in macrophage membranes
activates Toll-like receptors and p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase and induces cathepsin K. Circ Res. 104:455–465.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wadström BN, Pedersen KM, Wulff AB and
Nordestgaard BG: Inflammation compared to low-density lipoprotein
cholesterol: Two different causes of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
disease. Curr Opin Lipidol. 34:96–104. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hussain A and Ballantyne CM: New
approaches for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular
disease: Focus on lipoproteins and inflammation. Annu Rev Med.
72:431–446. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wu YR, Li L, Sun XC, Wang J, Ma CY, Zhang
Y, Qu HL, Xu RX and Li JJ: Diallyl disulfide improves lipid
metabolism by inhibiting PCSK9 expression and increasing LDL uptake
via PI3K/Akt-SREBP2 pathway in HepG2 cells. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc
Dis. 31:322–332. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Gu B, Jiang Y, Huang Z, Li H, Yu W, Li T,
Liu C, Wang P, Chen J, Sun L, et al: MRG15 aggravates
sepsis-related liver injury by promoting PCSK9 synthesis and
secretion. Int Immunopharmacol. 140(112898)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Feingold KR, Moser AH, Shigenaga JK,
Patzek SM and Grunfeld C: Inflammation stimulates the expression of
PCSK9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 374:341–344. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Nie X, Chen Y, Li W and Lu Y: Anti-aging
properties of Dendrobium nobile Lindl.: From molecular mechanisms
to potential treatments. J Ethnopharmacol.
257(112839)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Fan C, Sun X, Wang X and Yu H: Therapeutic
potential of the chemical composition of Dendrobium nobile Lindl.
Front Pharmacol. 14(1163830)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Mou Z, Zhao Y, Ye F, Shi Y, Kennelly EJ,
Chen S and Zhao D: Identification, Biological activities and
biosynthetic pathway of dendrobium alkaloids. Front Pharmacol.
12(605994)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Horton JD, Goldstein JL and Brown MS:
SREBPs: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty
acid synthesis in the liver. J Clin Invest. 109:1125–1131.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Sorrentino V and Zelcer N:
Post-transcriptional regulation of lipoprotein receptors by the
E3-ubiquitin ligase inducible degrader of the low-density
lipoprotein receptor. Curr Opin Lipidol. 23:213–219.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Lin XL, Xiao LL, Tang ZH, Jiang ZS and Liu
MH: Role of PCSK9 in lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis. Biomed
Pharmacother. 104:36–44. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Yu Q, Zheng H and Zhang Y: Inducible
degrader of LDLR: A potential novel therapeutic target and emerging
treatment for hyperlipidemia. Vascul Pharmacol.
140(106878)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Scotti E, Hong C, Yoshinaga Y, Tu Y, Hu Y,
Zelcer N, Boyadjian R, de Jong PJ, Young SG, Fong LG and Tontonoz
P: Targeted disruption of the idol gene alters cellular regulation
of the low-density lipoprotein receptor by sterols and liver x
receptor agonists. Mol Cell Biol. 31:1885–1893. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Teslovich TM, Musunuru K, Smith AV,
Edmondson AC, Stylianou IM, Koseki M, Pirruccello JP, Ripatti S,
Chasman DI, Willer CJ, et al: Biological, clinical and population
relevance of 95 loci for blood lipids. Nature. 466:707–713.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Chasman DI, Paré G, Mora S, Hopewell JC,
Peloso G, Clarke R, Cupples LA, Hamsten A, Kathiresan S, Mälarstig
A, et al: Forty-three loci associated with plasma lipoprotein size,
concentration, and cholesterol content in genome-wide analysis.
PLoS Genet. 5(e1000730)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Isaacs A, Willems SM, Bos D, Dehghan A,
Hofman A, Ikram MA, Uitterlinden AG, Oostra BA, Franco OH, Witteman
JC and van Duijn CM: Risk scores of common genetic variants for
lipid levels influence atherosclerosis and incident coronary heart
disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 33:2233–2239.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Dong B, Wu M, Cao A, Li H and Liu J:
Suppression of Idol expression is an additional mechanism
underlying statin-induced up-regulation of hepatic LDL receptor
expression. Int J Mol Med. 27:103–110. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Hong C, Marshall SM, McDaniel AL, Graham
M, Layne JD, Cai L, Scotti E, Boyadjian R, Kim J, Chamberlain BT,
et al: The LXR-Idol axis differentially regulates plasma LDL levels
in primates and mice. Cell Metab. 20:910–918. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Lin YK, Yeh CT, Kuo KT, Yadav VK, Fong IH,
Kounis NG, Hu P and Hung MY: Pterostilbene increases LDL metabolism
in HL-1 cardiomyocytes by modulating the PCSK9/HNF1α/SREBP2/LDLR
signaling cascade, upregulating epigenetic hsa-miR-335 and
hsa-miR-6825, and LDL receptor expression. Antioxidants (Basel).
10(1280)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Lebeau PF, Byun JH, Platko K, Saliba P,
Sguazzin M, MacDonald ME, Paré G, Steinberg GR, Janssen LJ, Igdoura
SA, et al: Caffeine blocks SREBP2-induced hepatic PCSK9 expression
to enhance LDLR-mediated cholesterol clearance. Nat Commun.
13(770)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Sabatine MS: PCSK9 inhibitors: Clinical
evidence and implementation. Nat Rev Cardiol. 16:155–165.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Jeong HJ, Lee HS, Kim KS, Kim YK, Yoon D
and Park SW: Sterol-dependent regulation of proprotein convertase
subtilisin/kexin type 9 expression by sterol-regulatory element
binding protein-2. J Lipid Res. 49:399–409. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Rashid S, Curtis DE, Garuti R, Anderson
NN, Bashmakov Y, Ho YK, Hammer RE, Moon YA and Horton JD: Decreased
plasma cholesterol and hypersensitivity to statins in mice lacking
Pcsk9. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:5374–5379. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Liang J, Li W, Liu H, Li X, Yuan C, Zou W
and Qu L: Di'ao Xinxuekang capsule improves the
anti-atherosclerotic effect of atorvastatin by downregulating the
SREBP2/PCSK9 signalling pathway. Front Pharmacol.
13(857092)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Careskey HE, Davis RA, Alborn WE, Troutt
JS, Cao G and Konrad RJ: Atorvastatin increases human serum levels
of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9. J Lipid Res.
49:394–398. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Shi Q, Chen J, Zou X and Tang X:
Intracellular cholesterol synthesis and transport. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 10(819281)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Roca-Agujetas V, Barbero-Camps E, de Dios
C, Podlesniy P, Abadin X, Morales A, Marí M, Trullàs R and Colell
A: Cholesterol alters mitophagy by impairing optineurin recruitment
and lysosomal clearance in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurodegener.
16(15)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Rizzolo D, Buckley K, Kong B, Zhan L, Shen
J, Stofan M, Brinker A, Goedken M, Buckley B and Guo GL: Bile acid
homeostasis in a cholesterol 7α-Hydroxylase and sterol
27-Hydroxylase double knockout mouse model. Hepatology. 70:389–402.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|