Introduction
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic,
caused by infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome
coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has led to millions of infections and
deaths worldwide since it was first reported at the end of
2019(1). The clinical symptoms of
COVID-19 are diverse and range from asymptomatic to critical
illness and even fatal outcomes. With the global administration of
COVID-19 vaccines, the severity and mortality of COVID-19 has
markedly decreased (2). The
‘dynamic COVID-zero’ strategy of China has effectively maintained
low morbidity and mortality rates in the country over the past 3
years (3). Reinfection may have
contributed to the lower morbidity and mortality, as a survey
revealed that 96.03% of reinfected individuals took medication on
their own, while only 3.97% sought medical attention. No critical
or hospitalized cases were found compared with the initial
infection (4). During the period
from December 2022 to February 2023, the prevention and control
measures associated with COVID-19 were relaxed, most Chinese
individuals had been infected and the reinfection incidence among
primary cases increased, with only a small proportion requiring
medical attention (3). Currently,
the majority of infected individuals with COVID-19 are asymptomatic
or have mild COVID-19. The most common symptoms in patients with
COVID-19 are fever or chills, headache, muscle or body aches, dry
cough, myalgia or fatigue, loss of sense of taste and rhinorrhea
(5).
As SARS-CoV-2 infections continue to occur
worldwide, the influenza A virus is also prevalent in China.
Influenza can also be characterized by a variety of respiratory
symptoms, including high fever, chills, headache, myalgia,
discomfort, anorexia, cough, congestion and sore throat (6). In the early days of COVID-19, it was
difficult to differentiate influenza A from COVID-19 because of the
similar clinical characteristics. However, there were numerous
differences between them. The age range of patients with COVID-19
was between 44 and 56 years and males were more easily infected
than females (6). By contrast, the
average age of patients with influenza A was 23.4 years (7) and children aged <14 years were
more susceptible to influenza than COVID-19. Furthermore, 53.8% of
patients with influenza were male (7). In addition, compared with patients
with influenza, patients with COVID-19 had a higher incidence of
chemosensory dysfunction, rash and non-productive coughs (8). However, patients with influenza had a
higher prevalence of high fever, with their body temperature
exceeding 41˚C within the first 24 h, compared with patients with
COVID-19(6). It was difficult to
distinguish influenza A from COVID-19 via patient age, sex and
symptoms. As the treatment regimens and prognoses differ between
COVID-19 and influenza A, it is important for clinicians to
accurately differentiate between these two respiratory infections
on the basis of their respective characteristics in the early
stages. Since the diagnostic criteria and definitions for both
COVID-19 and influenza A include fever, entry screening at the
fever clinic tends to start with a routine blood test and a nucleic
acid PCR test. The average time of the nucleic acid PCR test to
detect the virus with an instrument for PCR is 2-4 h. A routine
blood test takes 10-15 min to obtain results, and every hospital
can accomplish it. Therefore, if a routine blood test can help in
the diagnosis of COVID-19, it may help interrupt the spread of the
disease in the shortest amount of time and at the lowest cost
(9,10).
Lymphopenia is commonly observed in patients with
COVID-19 (5,11), SARS (12) and influenza virus infections
(7,13). Although lymphopenia appears to be
associated with illness severity for both influenza and
COVID-19(14), it does not appear
to be a unique marker of COVID-19 and may not be useful in
distinguishing viral pneumonia caused by SARS-CoV-2 and influenza
virus (15). Eosinophils, a type
of white blood cells, have been well-known to play an important
role in combating parasitic infections (16). Recent research has found that
eosinophils contribute to healthy homeostasis and have pathological
roles in bacterial and viral infections, as well as certain cancers
(17). A study reported that
eosinopenia may be a useful biomarker for the diagnosis and
prognosis of COVID-19(18).
However, to date, no study has reported that eosinopenia may be
useful for the differential diagnosis of COVID-19, to the best of
our knowledge. Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate
the clinical significance of eosinophils in fever clinic
outpatients infected with SARS-CoV-2 or influenza virus.
Patients and methods
Patients
Starting from January 2023, China has downgraded the
management of COVID-19 from category A to category B (19) in accordance with the country's law
on prevention and treatment of infectious disease, and removed it
from quarantinable infectious disease management carried out in
accordance with the Frontier Health and Quarantine Law of the
People's Republic of China, in the same category as HIV and bird
flu. Since February 2023, influenza A has been spreading rapidly
throughout China (20), just like
it is occurring in every cold season every year. To date, the
epidemic of influenza A has not stopped. In the present study,
fever clinic outpatients of the First Affiliated Hospital of
University of South China (Hengyang, China) with confirmed COVID-19
and influenza A without any chronic underlying medical conditions
were included between April 2023 and June 2023. The present study
was approved by the Medical Ethical Committee of the First
Affiliated Hospital of the University of South China (Hengyang,
China). The diagnosis of COVID-19 was made according to the World
Health Organization guidelines (21) and treatment was performed in
accordance with evidence-based guidelines (22). The diagnosis and antiviral
treatment of influenza A were guided by clinical practice
guidelines from the Infectious Diseases Society of America and
China for treating influenza in adult patients with Chinese patent
medicines (23,24). All patients were newly diagnosed
and did not have any other diseases, such as chronic heart or lung
disease, diabetes mellitus or chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease. In addition, pregnant women and minors younger than 14
years old were excluded. All outpatients at the fever clinic
recruited into the present study received oral medication and did
not require any further treatment. Patients who were diagnosed with
COVID-19 and required hospitalization were excluded from the
present study. Those outpatients who needed further treatment and
were admitted to the hospital during the follow-up were also
excluded from the current study. All patients enrolled in the
present study were living in Hengyang (China) during the outbreak
period of COVID-19 and influenza A (April 2023 to June 2023). The
clinical outcomes were monitored up until the end of June 2023,
which was the time-point of final follow-up.
A total of 447 outpatients, including 201 with
COVID-19 [median, interquartile range (IQR), 25.0 (19.0-41.5);
men/women, 112/89] and 246 with influenza A [median (IQR), 29.5
(19.0-51.0); men/women, 124/122] were randomly enrolled in the
present study. Clinical data, including demographic information,
medical history, exposure history, comorbidities, symptoms, signs,
laboratory examinations and treatment measures, were obtained from
the electronic medical record system of the First Affiliated
Hospital of the University of South China. All patients developed
fever ranging from 2 h to 2 days, accompanied by cough, sore
throat, dizziness and fatigue, and presented to the fever clinic.
Only a minority of patients received chest computed tomography
scans because they had severe cough and expectoration, or the scans
were requested by the patients. A total of two independent trained
physicians (RH and CH) from the research team collected and
verified the data from the electronic medical record system. The
onset date was defined as the day when the symptoms were noticed by
the patients.
Reverse transcription-quantitative
(RT-q)PCR assay for SARS-CoV-2
The throat swab samples of the patients were
collected for SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid detection using a RT-qPCR
assay. Nucleic acid testing was conducted at the clinical
laboratory of the First Affiliated Hospital of the University of
South China using the Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Dual Probes
qRT-PCR Kit by Wuhan Easy Diagnosis Biomedicine Co. Ltd. with a
QPT1000 real-time PCR system. Specific primers and probes for the
detection of the 2019 novel coronavirus were designed on the basis
of recently available data from the National Institute for Viral
Disease Control and Prevention, China. The designed forward primer
for Target 1 (ORF1ab gene) was 5'-CCCTGTGGGTTTTACACTTAA-3', the
reverse primer was 5'-ACGATTGTGCATCAGCTGA-3' and the probe was
5'-FAM-CCGTCTGCGGTATGTGGAAAGGTTATGG-BHQ1-3'. For Target 2 (N gene),
the forward primer used was 5'-GGGGAACTTCTCCTGCTAGAAT-3, the
reverse primer was 5'-CAGACATTTTGCTCTCAAGCTG-3' and the probe was
5'-FAM-TTGCTGCTGCTTGACAGATT-TAMRA-3'. An aliquot of 5.0 µl of the
viral RNA extract, which was extracted with the RNAeasy™
Viral RNA Isolation Kit with Spin Column (cat. no. R0035L; Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology) was mixed with 20.0 µl of a 2019-nCoV
RT-qPCR mixture according to the manufacturer's protocol. The
RT-qPCR conditions were as follows: 50˚C for 15 min (RT), 95˚C for
30 sec (initial denaturation), followed by 40 cycles of 3 sec of
denaturation at 95˚C and 40 sec of annealing and extension at 60˚C.
The results from each sample were normalized to the internal
control, 2019-nCoV RNA control. The RT-qPCR was performed in
triplicate, and the mean Cq value of three independent experiments
was used (25). A cycle threshold
value (Ct-value) <40 for all three target genes was used to
distinguish positive from negative test results.
Rapid influenza diagnostic test with
antigen detection
Direct antigen detection tests in nasopharyngeal
aspirates (Nanjing Synthgene Medical Technology Co., Ltd.) were
used to detect the presence of influenza viruses. The detection
process was carried out in strict accordance with the instruction
manual of the Flu A/Flu B antigen rapid test kit (colloidal gold
method).
Statistical analyses
Continuous variables are presented as the mean ±
standard deviation or the median (25th percentile, 75th
percentile), and categorical variables are presented as numbers
(percentages). Statistical analyses of the data were performed with
SPSS version 23.0 (IBM Corp.). An unpaired Student's t-test was
used to compare the quantitative variables. The χ2 test
or Fisher's exact test was used to compare the categorical
variables (men/women). The predictive factors for discriminating
COVID-19 from influenza A, such as the white blood cell (WBC) count
(x109/l), neutrophil percentage, lymphocyte percentage,
monocyte percentage, eosinophil percentage, neutrophil count
(x109/l), lymphocyte count (x109/l), monocyte
count (x109/l), eosinophil count (x109/l) and
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) (calculated as neutrophil
counts/lymphocyte counts), were computed via univariate analysis
and a multivariate logistic regression model with Cox's
proportional hazards model. The diagnostic value of eosinophils and
lymphocytes for distinguishing early COVID-19 from influenza A was
assessed using the area under the receiver operating characteristic
(ROC) curve (AUC) performed with MedCalc statistical software
(version 20.0; MedCalc Software Ltd.). Cut-off points with best
sensitivity and specificity were selected. Diagnostic accuracy was
assessed by sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio and
negative likelihood ratio. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Results
Demographic characteristics
A total of 447 outpatients were included in the
present study, comprising 201 patients with confirmed COVID-19 and
246 patients with influenza A. The median age of the patients with
COVID-19 and influenza A was 25.0 (19.0-41.5) and 29.5 (19.0-51.0)
years, respectively. The percentage of men was 55.72% (112/201) and
50.41% (124/246) in the COVID-19 and influenza A group,
respectively. There was no significant difference between these two
groups in terms of age (P=0.394) and sex (P=0.263). Demographics
and characteristics of all patients are presented in Table I.
 | Table IClinical and laboratory parameters of
the enrolled outpatients with COVID-19 and influenza A in the
present study. |
Table I
Clinical and laboratory parameters of
the enrolled outpatients with COVID-19 and influenza A in the
present study.
| Parameter | COVID-19 (n=201) | Influenza A
(n=246) | P-value |
|---|
| Age, years | 25.0 (19.0-41.5) | 29.5 (19.0-51.0) | 0.394 |
| Men/women | 112/89 | 124/122 | 0.263 |
| WBC,
x109/l | 6.48±1.90 | 6.18±2.17 | 0.122 |
| Neutrophil
percentage | 74.58±10.11 | 73.65±10.69 | 0.348 |
| Lymphocyte
percentage | 14.59±9.03 | 16.48±9.28 | 0.031 |
| Monocyte
percentage | 9.63±3.99 | 9.03±3.28 | 0.078 |
| Eosinophil
percentage | 0.95±1.12 | 0.56±0.95 | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil count,
x109/l | 4.96±1.74 | 4.64±1.97 | 0.075 |
| Lymphocyte count,
x109/l | 0.86±0.43 | 0.94±0.51 | 0.109 |
| Monocyte count,
x109/l | 0.61±0.31 | 0.55±0.27 | 0.018 |
| Eosinophil count,
x109/l | 0.06±0.07 | 0.04±0.09 | 0.002 |
| NLR | 7.59±5.47 | 6.38±4.51 | 0.012 |
Laboratory parameters
Laboratory testing of the patients was performed at
the fever clinic (Table I).
Complete blood cell counts were compared between patients with
confirmed COVID-19 and those with influenza A. The lymphocyte
percentage was lower in patients with confirmed COVID-19 than in
those with influenza A (P=0.031); no differences with respect to
lymphocyte counts (absolute count) were found between these two
groups. The absolute monocyte count was significantly lower in the
influenza A group compared with the confirmed COVID-19 group
(P=0.018). However, patients with influenza A presented with
significantly lower eosinophils (absolute count and percentage)
than patients with confirmed COVID-19 (P=0.002 and P<0.001,
respectively). In addition, the NLR, which is an indicator of
systemic inflammation, was higher in patients with confirmed
COVID-19 compared with those with influenza A (P=0.012). There were
no significant differences in the WBC count or neutrophils
(P>0.05). The detailed information is shown in Table I.
Treatment and clinical outcomes
Both groups of patients received therapy according
to the aforementioned clinical practice guidelines; they received
antiviral therapy (Azvudine prescribed for COVID-19 at 5 mg once a
day for 5 days; Oseltamivir for influenza A at 75 mg twice a day
for 5 days; Baloxavir for influenza A at 40 mg 1 dose), antipyretic
medication (acetaminophen or salicylates) and Chinese patent drugs
(Lianhua Qingwen granule, three capsules three times a day for 5
days). As of the final date of follow-up, only one patient with
confirmed COVID-19 required admission to the hospital to receive
oxygen therapy and respiratory support, and no patient died. On the
other hand, none of the patients with influenza A were
hospitalized.
Univariate and multivariate analyses
of factors for discriminating COVID-19 from influenza A
Logistic regression analysis was performed to
identify which clinical parameters were able to discriminate
COVID-19 from influenza A. As shown in Table II, the lymphocyte percentage
(P=0.033), eosinophil percentage (P<0.001), monocyte count
(P=0.020), eosinophil count (P=0.004) and NLR (P=0.012) were able
to distinguish COVID-19 from influenza A in the univariate
analysis. According to the multivariate analysis, the eosinophil
percentage [hazard ratio (HR), 3.62; 95% CI, 1.96-6.67;
P<0.001], eosinophil count (HR, 0.00; 95% CI,
3.33x10-9-0.01; P=0.002) and monocyte count (HR, 3.00;
95% CI, 1.34-6.72; P=0.008) were the independent risk factors for
the early distinction of COVID-19 from influenza A among
outpatients. The results are presented in Table II.
 | Table IIUnivariate and multivariate logistic
regression analyses of factors in discriminating coronavirus
disease 2019 from influenza A. |
Table II
Univariate and multivariate logistic
regression analyses of factors in discriminating coronavirus
disease 2019 from influenza A.
| | Univariate
analysis | Multivariate
analysis |
|---|
| Variable | HR (95% CI) | P-value | HR (95% CI) | P-value |
|---|
| WBC | 1.07
(0.98-1.18) | 0.123 | ND | ND |
| Neutrophil
percentage | 1.01
(0.99-1.03) | 0.348 | ND | ND |
| Lymphocyte
percentage | 0.98
(0.96-1.00) | 0.033 | 0.98
(0.94-1.01) | 0.232 |
| Monocytes
percentage | 1.045
(1.00-1.10) | 0.080 | ND | ND |
| Eosinophil
percentage | 1.50
(1.21-1.86) | <0.001 | 3.62
(1.96-6.67) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil
count | 1.10
(1.00-1.21) | 0.077 | ND | ND |
| Lymphocyte
count | 0.71
(0.47-1.09) | 0.113 | ND | ND |
| Monocyte count | 2.23
(1.13-4.39) | 0.020 | 3.00
(1.34-6.72) | 0.008 |
| Eosinophil
count | 91.14
(4.21-1974.21) | 0.004 | 0.00
(3.33x10-9-0.01) | 0.002 |
| NLR | 1.05
(1.01-1.09) | 0.012 | 1.04
(0.98-1.10) | 0.227 |
Eosinophils as a biomarker for the
early distinction of COVID-19 from influenza A in outpatients
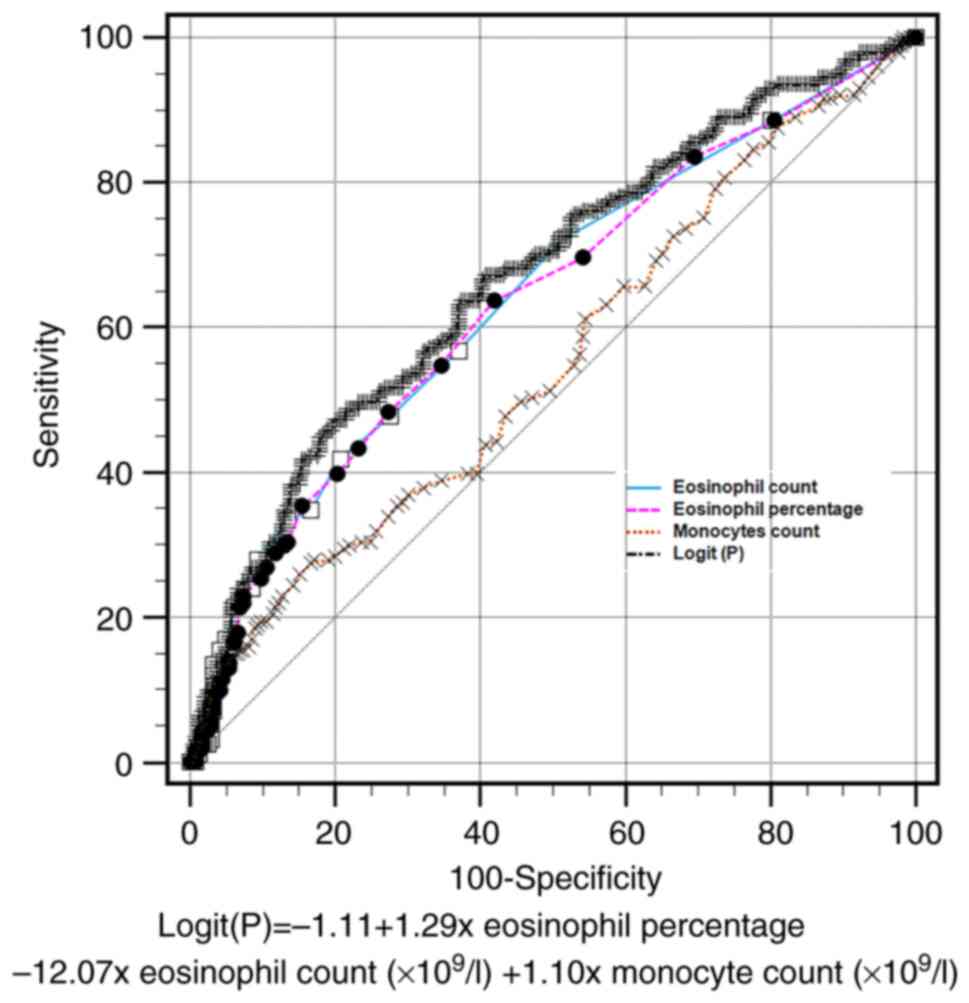
A ROC curve of combined parameters was constructed
to discriminate between COVID-19 and influenza A among the
outpatients. According to the multivariate analysis results, a new
parameter was deduced, which was automatically generated by MedCalc
statistical software (version 20.0): Logit(P)=-1.11 + 1.29 x
eosinophil percentage -12.07 x eosinophil count (x109/l)
+ 1.10 x monocyte count (x109/l). The eosinophil count,
with a cut-off value <0.04x109/l, had a sensitivity
of 41.8%, specificity of 79.3%, positive likelihood ratio of 2.02
and negative likelihood ratio of 0.73. The AUC was 0.64 [standard
error (SE)=0.03; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.60-0.68]. The AUC
of the eosinophil percentage (cut-off value <0.30%) was 0.64
(SE=0.03; 95% CI, 0.60-0.68), that of the monocyte count (cut-off
value >0.74 x109/l) was 0.55 (SE=0.03; 95% CI,
0.50-0.60) and that the AUC of the Logit(P) (cut-off value
>0.50) was 0.67 (SE=0.03; 95% CI, 0.63-0.71). No significant
differences associated with the AUC were found among the eosinophil
percentage, eosinophil count or Logit(P). However, compared with
the monocyte count, the AUC of the eosinophil percentage,
eosinophil count and Logit(P) were significantly higher (P=0.028,
P=0.012 and P<0.001, respectively; results shown in Table SI). These results indicate that
eosinophils may serve as a potential biomarker to help physicians
distinguish COVID-19 from influenza A in fever clinics. These
results are presented in Table
III and Fig. 1.
 | Table IIIAUC of factors in discriminating
coronavirus disease 2019 from influenza A at the fever outpatient
clinic. |
Table III
AUC of factors in discriminating
coronavirus disease 2019 from influenza A at the fever outpatient
clinic.
| Variable | AUC | 95% CI | Sensitivity, % | Specificity, % | Cut-off value | +LR | -LR |
|---|
| Eosinophil
count | 0.64 | 0.60-0.68 | 41.8 | 79.3 |
<0.04x109/l | 2.02 | 0.73 |
| Eosinophil
percentage | 0.64 | 0.60-0.68 | 63.7 | 58.1 | <0.30% | 1.52 | 0.62 |
| Monocyte count | 0.55 | 0.50-0.60 | 25.9 | 85.0 |
>0.74x109/l | 1.72 | 0.87 |
| Logit(P) | 0.67 | 0.63-0.71 | 47.3 | 80.1 | >0.50 | 2.37 | 0.66 |
Discussion
COVID-19 and influenza A have numerous similarities
and differ in several aspects. For instance, COVID-19 show mild
upper respiratory symptom similar to the common cold in early
stages (26), nonproductive cough
and shortness of breath are relatively large (27); high fever and cough is the common
symptom of influenza (7). Besides,
other clinical symptoms, including fever, chemical sensory
disturbance, damage to the reproductive system, constitutional
symptoms and rash, were developed in COVID-19(28); hyperthermia, photophobia and
conjunctivitis was caused by influenza A (6).
But the mortality rate of COVID-19 is higher than
that of influenza A; thus, clinicians and epidemiologists should
differentiate between them as early as possible. Blood cell count
analysis is a simple, effective and rapid laboratory test that has
been widely used in clinical practice. Although hematological
parameters associated with lymphocytopenia in patients with
influenza and COVID-19 are similar, the situation is different
regarding eosinophils: Patients with confirmed COVID-19 presented
with small but significantly increased eosinophil counts than those
with influenza A, which may help distinguish COVID-19 from
influenza A in a short amount of time. This insight may be helpful
for identifying factors that may aid in making a definitive
diagnosis.
Eosinophils are white blood cells that play a
homeostatic role in the body's immune response and are involved in
combating various parasitic, bacterial and viral infections, as
well as certain cancers (17). It
has been indicated that human eosinophils contribute to viral
clearance (29) and are present in
patients with moderate-to-severe COVID-19(30). Eosinophil counts have been used in
several algorithms to predict the severity of COVID-19. Eosinopenia
is a presenting sign of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and an association
between eosinopenia and disease severity has been reported
(18). Low peripheral eosinophil
counts returned to normal levels when patients recovered from
severe COVID-19(31). The value of
peripheral blood eosinophil counts at patient presentation has been
examined for its ability to distinguish between COVID-19 and
influenza virus infection. Compared with that of patients with
influenza A, the mean eosinophil count was significantly increased
in patients with COVID-19 Univariate and multivariate logistic
regression analyses were also performed. The results suggested that
an eosinophil count <0.04x109/l or eosinophil
percentage <0.3% and a clear epidemiological exposure history
are primary significant factors that distinguish COVID-19 from
influenza A. The role of eosinophils in antiviral responses in the
pathophysiology of COVID-19 remains to be elucidated. Additional
studies are needed to uncover the interplay of eosinophils with
coronavirus and influenza virus.
In the present study, it was found that the monocyte
count was significantly higher in patients with COVID-19 compared
with patients with influenza A. However, when the ROC curve was
used to calculate the AUC, the AUC for monocytes was lower than
that for the eosinophil percentage, eosinophil count and
Logit(P).
The NLR is an indicator of the systematic
inflammatory response and is used to predict the prognosis of
patients with viral pneumonia (32). An elevated NLR was associated with
COVID-19 progression and the return to normal levels may be
associated with improved prognosis (32). The present findings indicate that
an elevated NLR level may be beneficial for the early distinction
of COVID-19 from influenza A, but it is not of greater value than
the eosinophil percentage and eosinophil count.
There are several limitations to the present study.
First, the data were obtained from a single clinical research
center, and the conclusion of the present study should be validated
in a multicenter, large-scale cohort. Furthermore, the experimental
data are limited. The participants enrolled were newly diagnosed
with COVID-19 and influenza A from epidemic seasons in the fever
clinic. General information, such as the lifestyles, family
history, smoking or smoking environment history of the patients,
was not collected, and these factors may affect the conclusions as
potential confounding factors. The relatively small sample size may
affect the accuracy of the conclusions. Furthermore, the
outpatients included in the present study had mild conditions, not
moderate or severe conditions, and the progression of
mild-to-moderate or severe illness was not evaluated. In most
cases, the symptoms gradually alleviate after 2-3 days. When the
patients were contacted by phone, they did not accept any
follow-up. Therefore, the present study investigated only a single
blood count test. Finally, the present study only focused on the
count and percentage of eosinophils and monocytes from a regular
blood test, and further research should be conducted to explore the
phenotype of eosinophils, monocytes and other blood cells, such as
the cytokine levels secreted by these cells, granzyme B, perforin
and T-cell subpopulations. These findings will offer promising
guidelines for further experimental and clinical studies to
distinguish between COVID-19 and influenza A.
In conclusion, the present study revealed that the
monocyte count and NLR were significantly higher and that the
eosinophil count/percentage was higher in outpatients with COVID-19
compared with those with influenza A from a fever clinic. These
features may help significantly differentiate early COVID-19 from
influenza A.
Supplementary Material
Comparison of receiver operating
characteristic curves of eosinophil percentage, eosinophil count
and Logit(P) with the monocyte count.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: The present study was supported by scholarships from
the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (grant no.
2023JJ60052) and the Education Foundation of Hunan Province, China
(grant no. 21C0294). The funders had no role in the study design,
data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of
the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
CC performed the experiments, analysed the data and
edited the manuscript. HX checked and confirmed the authenticity of
the raw data and analysed the data. RG collected clinical and
laboratory parameters of every enrolled patient and interpreted
data for this work. CD designed and complemented this work and
reviewed the manuscript. JT designed the present study, solved
related questions and approved the final version to be published.
CD and JT confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors
have read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Medical
Ethical Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of the
University of South China (Hengyang, China; approval no.
2023110103002). The requirement for informed consent was waived for
this study.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Cucinotta D and Vanelli M: WHO declares
COVID-19 a pandemic. Acta Biomed. 91:157–160. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Thompson MG, Stenehjem E, Grannis S, Ball
SW, Naleway AL, Ong TC, DeSilva MB, Natarajan K, Bozio CH, Lewis N,
et al: Effectiveness of covid-19 vaccines in ambulatory and
inpatient care settings. N Engl J Med. 385:1355–1371.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cai C, Li Y, Hu T, Liang R, Wang K, Guo C,
Li Y, Zhang M and Kang M: The associated factors of SARS-CoV-2
reinfection by Omicron variant-guangdong province, China, December
2022 to January 2023. China CDC Weekly. 5:391–396. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang Y, Liang J, Yang H, Zhu L, Hu J, Xiao
L, Huang Y, Dong Y, Wu C, Zhang J and Zhou X: Epidemiological and
clinical characteristics of COVID-19 reinfection during the
epidemic period in Yangzhou city, Jiangsu province. Front Public
Health. 11(1256768)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chilamakuri R and Agarwal S: COVID-19:
Characteristics and therapeutics. Cells. 10(206)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bai Y and Tao X: Comparison of COVID-19
and influenza characteristics. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 22:87–98.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Cao B, Li XW, Mao Y, Wang J, Lu HZ, Chen
YS, Liang ZA, Liang L, Zhang SJ, Zhang B, et al: Clinical features
of the initial cases of 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus
infection in China. N Engl J Med. 361:2507–2517. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yan CH, Faraji F, Prajapati DP, Boone CE
and DeConde AS: Association of chemosensory dysfunction and
COVID-19 in patients presenting with influenza-like symptoms. Int
Forum Allergy Rhinol. 10:806–813. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xu J, Kirtek T, Xu Y, Zheng H, Yao H,
Ostman E, Oliver D, Malter JS, Gagan JR and SoRelle JA: Digital
droplet PCR for SARS-CoV-2 resolves borderline cases. Am J Clin
Pathol. 155:815–822. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Alon R, Sportiello M, Kozlovski S, Kumar
A, Reilly EC, Zarbock A, Garbi N and Topham DJ: Leukocyte
trafficking to the lungs and beyond: Lessons from influenza for
COVID-19. Nat Rev Immunol. 21:49–64. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wu J, Li J, Zhu G, Zhang Y, Bi Z, Yu Y,
Huang B, Fu S, Tan Y, Sun J and Li X: Clinical features of
maintenance hemodialysis patients with 2019 novel
coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. Clin J Am Soc
Nephrol. 15:1139–1145. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lee N, Hui D, Wu A, Chan P, Cameron P,
Joynt GM, Ahuja A, Yung MY, Leung CB, To KF, et al: A major
outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. N Engl
J Med. 348:1986–1994. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sharon N, Talnir R, Lavid O, Rubinstein U,
Niven M, First Y, Tsivion AJ and Schachter Y: Transient lymphopenia
and neutropenia: Pediatric influenza A/H1N1 infection in a primary
hospital in Israel. Isr Med Assoc J. 13:408–412. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z,
Xiang J, Wang Y, Song B, Gu X, et al: Clinical course and risk
factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan,
China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 395:1054–1062.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cobb NL, Sathe NA, Duan KI, Seitz KP, Thau
MR, Sung CC, Morrell ED, Mikacenic C, Kim HN, Liles WC, et al:
Comparison of clinical features and outcomes in critically ill
patients hospitalized with COVID-19 versus influenza. Ann Am Thorac
Soc. 18:632–640. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Klion AD, Ackerman SJ and Bochner BS:
Contributions of eosinophils to human health and disease. Annu Rev
Pathol. 15:179–209. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wechsler ME, Munitz A, Ackerman SJ, Drake
MG, Jackson DJ, Wardlaw AJ, Dougan SK, Berdnikovs S, Schleich F,
Matucci A, et al: Eosinophils in health and disease: A
state-of-the-art review. Mayo Clin Proc. 96:2694–2707.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rosenberg HF and Foster PS: Eosinophils
and COVID-19: Diagnosis, prognosis, and vaccination strategies.
Semin Immunopathol. 43:383–392. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
China NHCotPsRo: Notice on the issuance of
the overall plan for the implementation of ‘Category B and B
Management’ for the novel coronavirus infection, 2022.
|
|
20
|
Mi J, Wang J, Chen L, Guo Z, Lei H, Chong
MK, Talifu J, Yang S, Luotebula K, Ablikemu M, et al: Real-world
effectiveness of influenza vaccine against medical-attended
influenza infection during 2023/24 season in Ili Kazakh autonomous
prefecture, China: A test-negative, case-control study. Hum Vaccin
Immunother. 20(2394255)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sohrabi C, Alsafi Z, O'Neill N, Khan M,
Kerwan A, Al-Jabir A, Iosifidis C and Agha R: World Health
Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel
coronavirus (COVID-19). Int J Surg. 76:71–76. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ye Z, Rochwerg B, Wang Y, Adhikari NK,
Murthy S, Lamontagne F, Fowler RA, Qiu H, Wei L, Sang L, et al:
Treatment of patients with nonsevere and severe coronavirus disease
2019: An evidence-based guideline. CMAJ. 192:E536–E545.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wu L, Chen Y, Ma Y, Yang Z, Yang N, Deng
W, Chen Y, Sun Y, Li Y and Lin L: Clinical practice guideline on
treating influenza in adult patients with Chinese patent medicines.
Pharmacol Res. 160(105101)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Uyeki TM, Bernstein HH, Bradley JS,
Englund JA, File TM, Fry AM, Gravenstein S, Hayden FG, Harper SA,
Hirshon JM, et al: Clinical practice guidelines by the infectious
diseases society of America: 2018 Update on diagnosis, treatment,
chemoprophylaxis, and institutional outbreak management of seasonal
influenzaa. Clin Infect Dis. 68:895–902. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chan KW, Wong VT and Tang SCW: COVID-19:
An update on the epidemiological, clinical, preventive and
therapeutic evidence and guidelines of integrative Chinese-western
medicine for the management of 2019 novel coronavirus disease. Am J
Chin Med. 48:737–762. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tang X, Du RH, Wang R, Cao TZ, Guan LL,
Yang CQ, Zhu Q, Hu M, Li XY, Li Y, et al: Comparison of
hospitalized patients with ARDS caused by COVID-19 and H1N1. Chest.
158:195–205. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tersalvi G, Veronese G and Winterton D:
Emerging evidence of myocardial injury in COVID-19: A path through
the smoke. Theranostics. 10:9888–9889. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sabogal Piñeros YS, Bal SM, Dijkhuis A,
Majoor CJ, Dierdorp BS, Dekker T, Hoefsmit EP, Bonta PI, Picavet D,
van der Wel NN, et al: Eosinophils capture viruses, a capacity that
is defective in asthma. Allergy. 74:1898–1909. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liao D, Zhou F, Luo L, Xu M, Wang H, Xia
J, Gao Y, Cai L, Wang Z, Yin P, et al: Haematological
characteristics and risk factors in the classification and
prognosis evaluation of COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study.
Lancet Haematol. 7:e671–e678. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chen R, Sang L, Jiang M, Yang Z, Jia N, Fu
W, Xie J, Guan W, Liang W, Ni Z, et al: Longitudinal hematologic
and immunologic variations associated with the progression of
COVID-19 patients in China. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 146:89–100.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yang AP, Liu JP, Tao WQ and Li HM: The
diagnostic and predictive role of NLR, d-NLR and PLR in COVID-19
patients. Int Immunopharmacol. 84(106504)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|