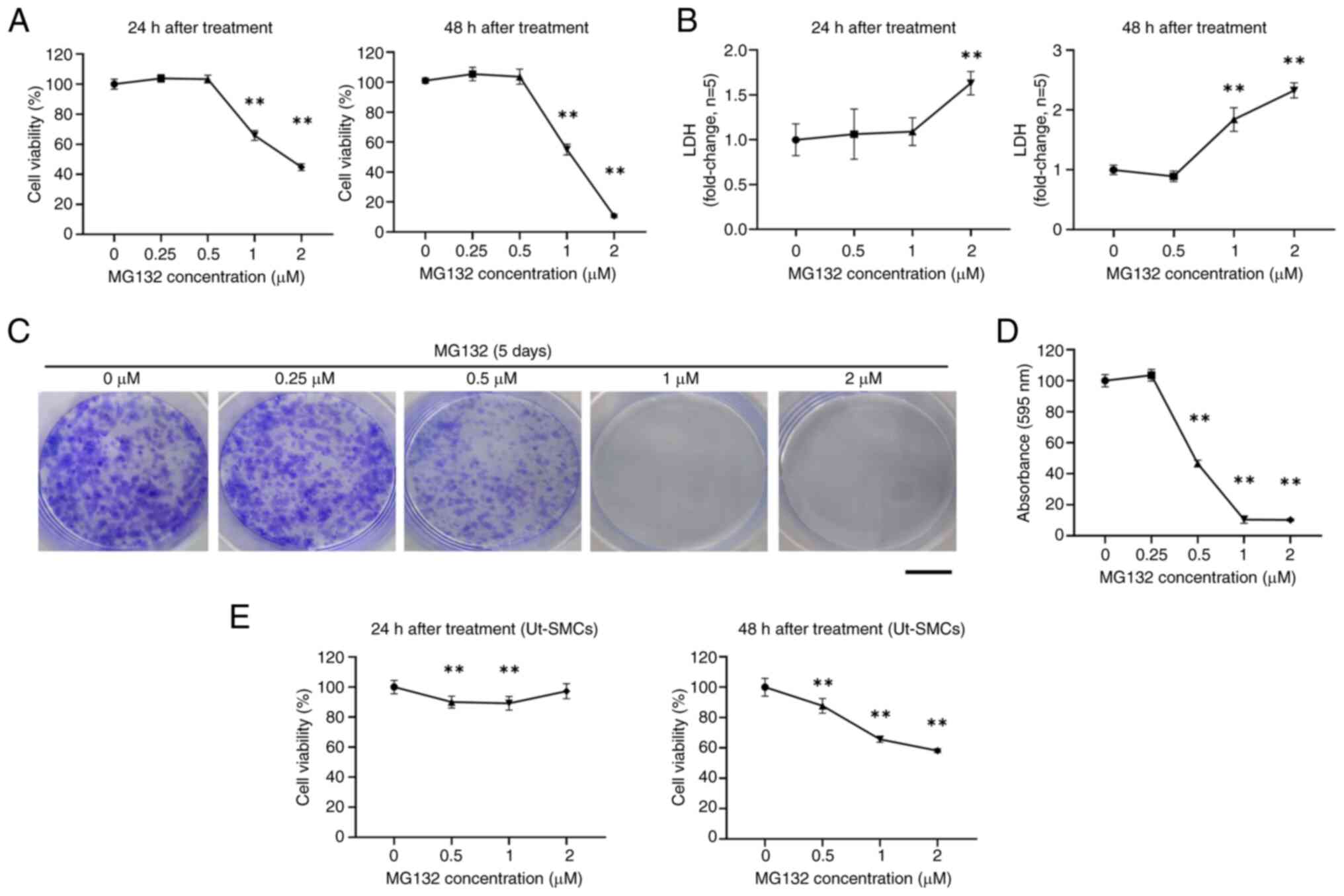
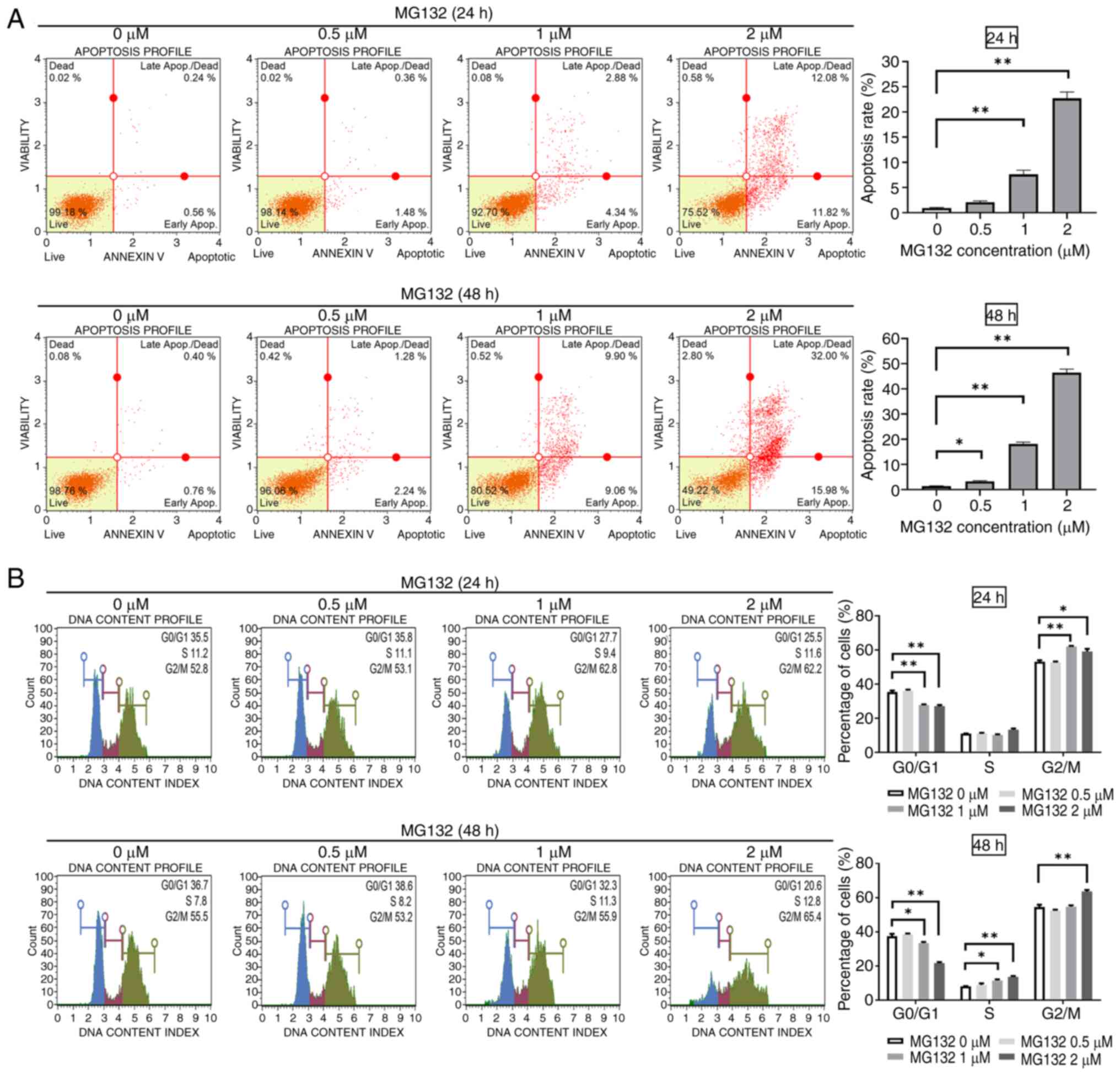
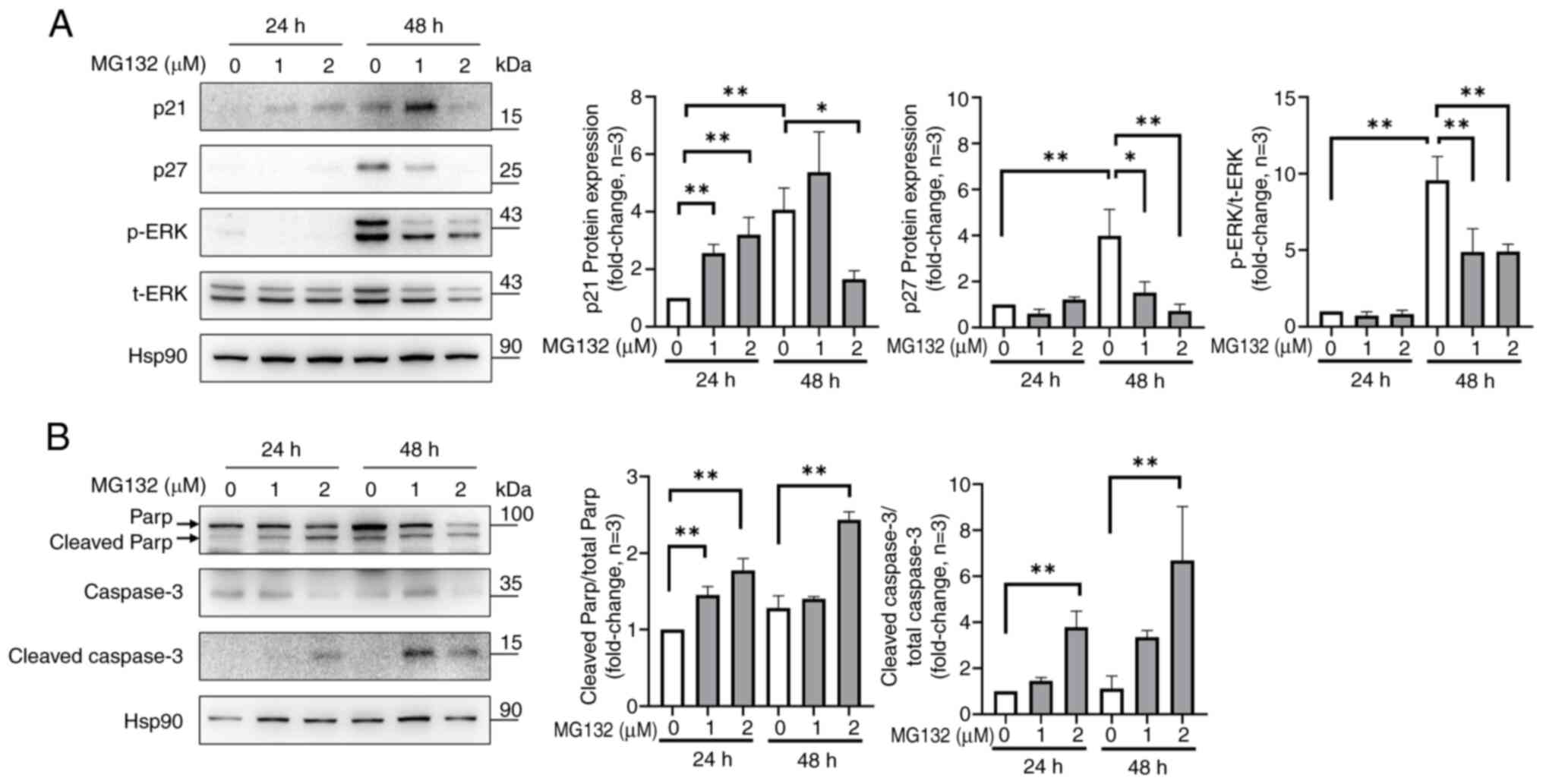
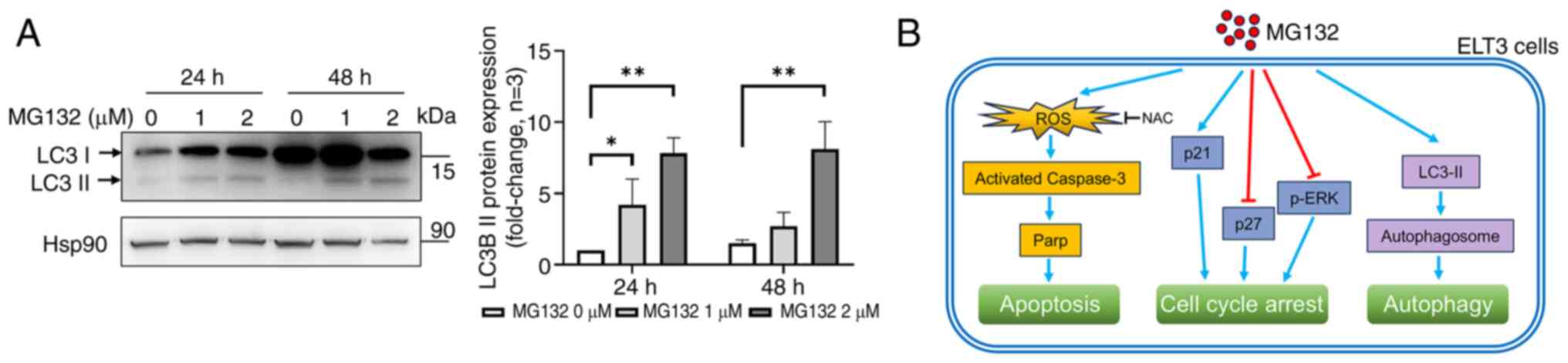
|
1
|
Stewart EA, Laughlin-Tommaso SK, Catherino
WH, Lalitkumar S, Gupta D and Vollenhoven B: Uterine fibroids. Nat
Rev Dis Primers. 2(16043)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sohn GS, Cho S, Kim YM, Cho CH, Kim MR and
Lee SR: Working Group of Society of Uterine Leiomyoma. Current
medical treatment of uterine fibroids. Obstet Gynecol Sci.
61:192–201. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cermik D, Arici A and Taylor HS:
Coordinated regulation of HOX gene expression in myometrium and
uterine leiomyoma. Fertil Steril. 78:979–984. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Okoro CC, Ikpeze OC, Eleje GU, Udigwe GO,
Ezeama CO, Ugboaja JO, Enechukwu CI, Umeononihu OS, Ogabido CA,
Oguejiofor CB, et al: Association between serum vitamin D status
and uterine leiomyomas: A case-control study. Obstet Gynecol Sci.
67:101–111. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
De La Cruz MS and Buchanan EM: Uterine
fibroids: Diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 95:100–107.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee MJ, Yun BS, Seong SJ, Kim ML, Jung YW,
Kim MK, Bae HS, Kim DH and Hwang JY: Uterine fibroid shrinkage
after short-term use of selective progesterone receptor modulator
or gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist. Obstet Gynecol Sci.
60:69–73. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Navarro A, Bariani MV, Yang Q and Al-Hendy
A: Understanding the impact of uterine fibroids on human
endometrium function. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9(633180)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Angioni S, D'Alterio MN and Daniilidis A:
Highlights on medical treatment of uterine fibroids. Curr Pharm
Des. 27:3821–3832. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lee S and Stewart EA: New treatment
options for nonsurgical management of uterine fibroids. Curr Opin
Obstet Gynecol. 35:288–293. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Duhan N: Current and emerging treatments
for uterine myoma-an update. Int J Womens Health. 3:231–241.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Choe YS, Lee WM, Choi JS, Bae J, Eom JM
and Choi E: Clinical characteristics of patients with leiomyoma who
undergo surgery after high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU).
Obstet Gynecol Sci. 62:258–263. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yerezhepbayeva M, Terzic M, Aimagambetova
G and Crape B: Comparison of two invasive non-surgical treatment
options for uterine myomas: Uterine artery embolization and
magnetic resonance guided high intensity focused
ultrasound-systematic review. BMC Womens Health.
22(55)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yang CH, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Reuben JM,
Booser DJ, Pusztai L, Krishnamurthy S, Esseltine D, Stec J, Broglio
KR, Islam R, et al: Bortezomib (VELCADE) in metastatic breast
cancer: Pharmacodynamics, biological effects, and prediction of
clinical benefits. Ann Oncol. 17:813–817. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Engel RH, Brown JA, Von Roenn JH, O'Regan
RM, Bergan R, Badve S, Rademaker A and Gradishar WJ: A phase II
study of single agent bortezomib in patients with metastatic breast
cancer: A single institution experience. Cancer Invest. 25:733–737.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cresta S, Sessa C, Catapano CV, Gallerani
E, Passalacqua D, Rinaldi A, Bertoni F, Viganò L, Maur M, Capri G,
et al: Phase I study of bortezomib with weekly paclitaxel in
patients with advanced solid tumours. Eur J Cancer. 44:1829–1834.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ramirez PT, Landen CN Jr, Coleman RL,
Milam MR, Levenback C, Johnston TA and Gershenson DM: Phase I trial
of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in combination with
carboplatin in patients with platinum- and taxane-resistant ovarian
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 108:68–71. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yang H, Zonder JA and Dou QP: Clinical
development of novel proteasome inhibitors for cancer treatment.
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 18:957–971. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lee DH and Goldberg AL: Proteasome
inhibitors: Valuable new tools for cell biologists. Trends Cell
Biol. 8:397–403. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Han YH, Moon HJ, You BR and Park WH: The
effect of MG132, a proteasome inhibitor on HeLa cells in relation
to cell growth, reactive oxygen species and GSH. Oncol Rep.
22:215–221. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guo N and Peng Z: MG132, a proteasome
inhibitor, induces apoptosis in tumor cells. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol.
9:6–11. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tarjányi O, Haerer J, Vecsernyés M, Berta
G, Stayer-Harci A, Balogh B, Farkas K, Boldizsár F, Szeberényi J
and Sétáló G Jr: Prolonged treatment with the proteasome inhibitor
MG-132 induces apoptosis in PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cells. Sci
Rep. 12(5808)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yang W, Monroe J, Zhang Y, George D,
Bremer E and Li H: Proteasome inhibition induces both pro- and
anti-cell death pathways in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
243:217–227. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yan H, Ma YL, Gui YZ, Wang SM, Wang XB,
Gao F and Wang YP: MG132, a proteasome inhibitor, enhances LDL
uptake in HepG2 cells in vitro by regulating LDLR and PCSK9
expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:994–1004. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Yang B, Zhao J, Li X, Zhang L and
Zhai Z: Proteasome inhibitor
carbobenzoxy-L-Leucyl-L-leucyl-L-leucinal (MG132) enhances
therapeutic effect of paclitaxel on breast cancer by inhibiting
nuclear factor (NF)-κB signaling. Med Sci Monit. 24:294–304.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Han YH and Park WH: MG132 as a proteasome
inhibitor induces cell growth inhibition and cell death in A549
lung cancer cells via influencing reactive oxygen species and GSH
level. Hum Exp Toxicol. 29:607–614. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Duan W, Guo Y, Jiang H, Yu X and Li C:
MG132 enhances neurite outgrowth in neurons overexpressing mutant
TAR DNA-binding protein-43 via increase of HO-1. Brain Res.
1397:1–9. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Joung H and Liu H: 2-D08 mediates notable
anticancer effects through multiple cellular pathways in uterine
leiomyosarcoma cells. Oncol Rep. 52(97)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Cenini G, Lloret A and Cascella R:
Oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage in neurodegenerative
diseases: From molecular mechanisms to targeted therapies. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2020(1270256)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhitkovich A: N-acetylcysteine:
Antioxidant, aldehyde scavenger, and more. Chem Res Toxicol.
32:1318–1319. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Aman Y, Schmauck-Medina T, Hansen M,
Morimoto RI, Simon AK, Bjedov I, Palikaras K, Simonsen A, Johansen
T, Tavernarakis N, et al: Autophagy in healthy aging and disease.
Nat Aging. 1:634–650. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ortiz-Lazareno PC, Hernandez-Flores G,
Dominguez-Rodriguez JR, Lerma-Diaz JM, Jave-Suarez LF,
Aguilar-Lemarroy A, Gomez-Contreras PC, Scott-Algara D and
Bravo-Cuellar A: MG132 proteasome inhibitor modulates
proinflammatory cytokines production and expression of their
receptors in U937 cells: Involvement of nuclear factor-kappaB and
activator protein-1. Immunology. 124:534–541. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Park HS, Jun do Y, Han CR, Woo HJ and Kim
YH: Proteasome inhibitor MG132-induced apoptosis via ER
stress-mediated apoptotic pathway and its potentiation by protein
tyrosine kinase p56lck in human Jurkat T cells. Biochem Pharmacol.
82:1110–1125. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Westerberg CM, Hägglund H and Nilsson G:
Proteasome inhibition upregulates Bim and induces
caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in human mast cells expressing the
Kit D816V mutation. Cell Death Dis. 3(e417)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kim OH, Lim JH, Woo KJ, Kim YH, Jin IN,
Han ST, Park JW and Kwon TK: Influence of p53 and p21Waf1
expression on G2/M phase arrest of colorectal carcinoma HCT116
cells to proteasome inhibitors. Int J Oncol. 24:935–941.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zanotto-Filho A, Braganhol E, Battastini
AM and Moreira JC: Proteasome inhibitor MG132 induces selective
apoptosis in glioblastoma cells through inhibition of PI3K/Akt and
NFkappaB pathways, mitochondrial dysfunction, and activation of
p38-JNK1/2 signaling. Invest New Drugs. 30:2252–2262.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Jung S, Jeong H and Yu SW: Autophagy as a
decisive process for cell death. Exp Mol Med. 52:921–930.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Liu S, Yao S, Yang H, Liu S and Wang Y:
Autophagy: Regulator of cell death. Cell Death Dis.
14(648)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Bao W, Gu Y, Ta L, Wang K and Xu Z:
Induction of autophagy by the MG-132 proteasome inhibitor is
associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress in MCF-7 cells. Mol
Med Rep. 13:796–804. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wang D, Xu Q, Yuan Q, Jia M, Niu H, Liu X,
Zhang J, Young CY and Yuan H: Proteasome inhibition boosts
autophagic degradation of ubiquitinated-AGR2 and enhances the
antitumor efficiency of bevacizumab. Oncogene. 38:3458–3474.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Guo F, He XB, Li S and Le W: A central
role for phosphorylated p38α in linking proteasome
inhibition-induced apoptosis and autophagy. Mol Neurobiol.
54:7597–7609. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|