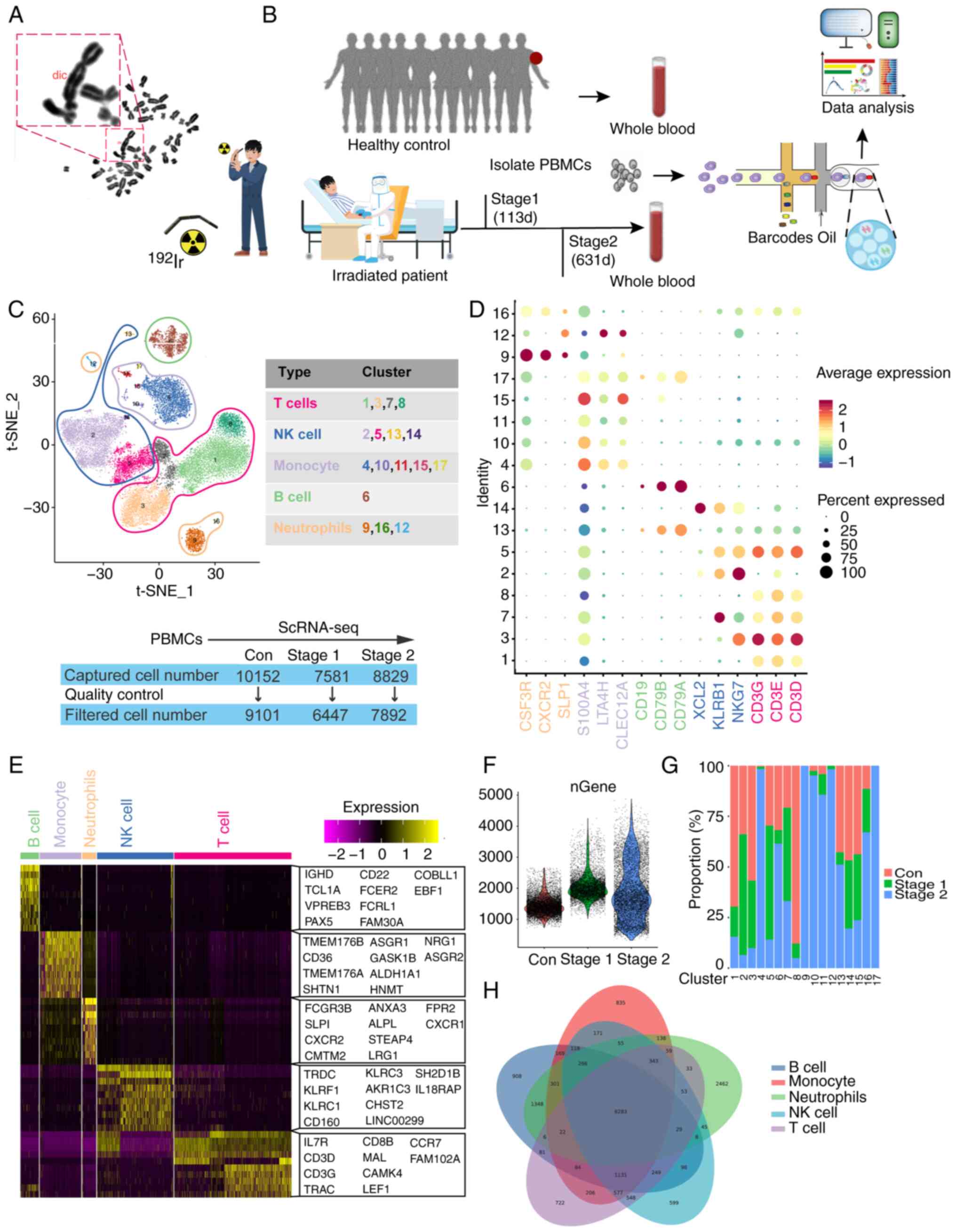
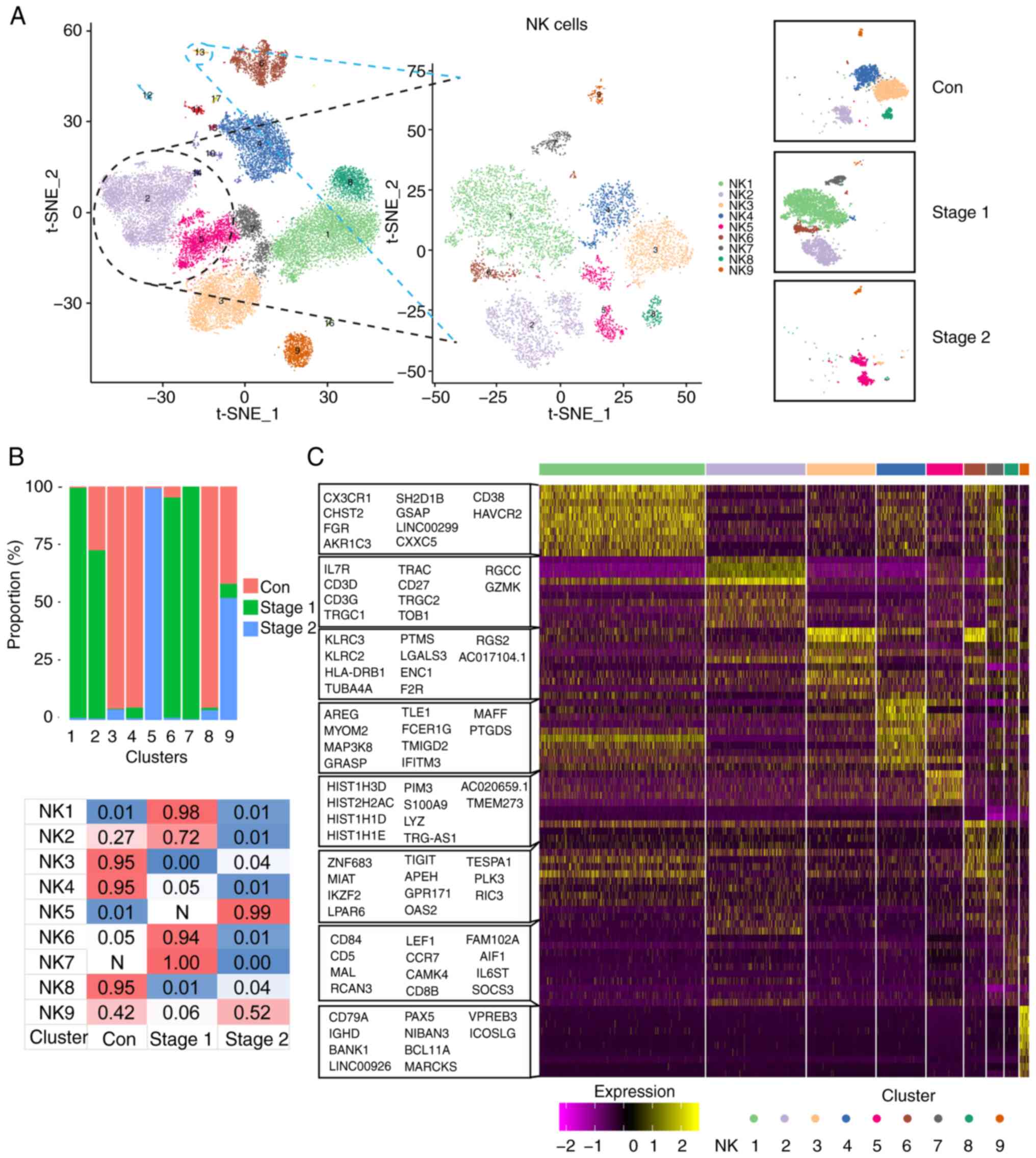
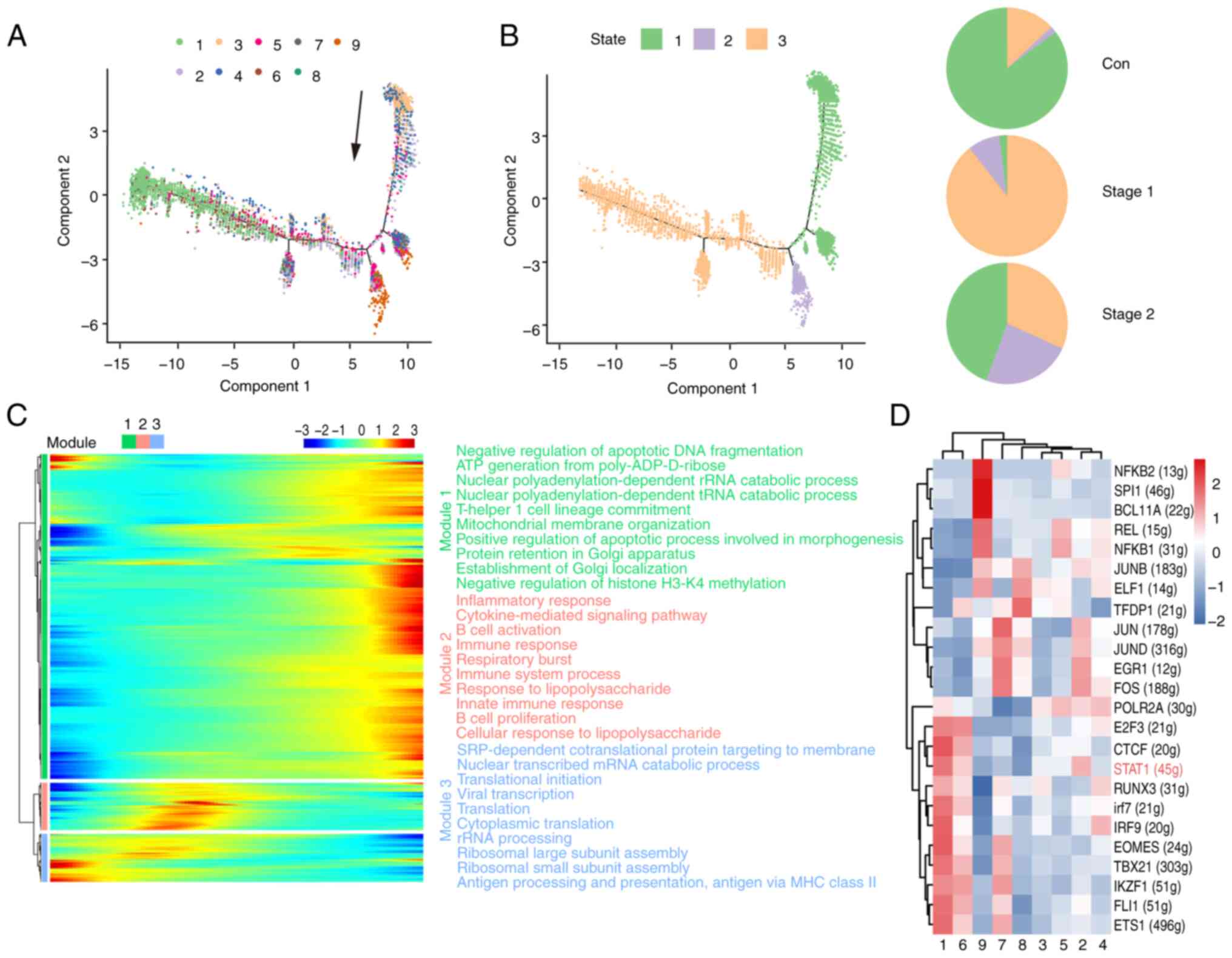
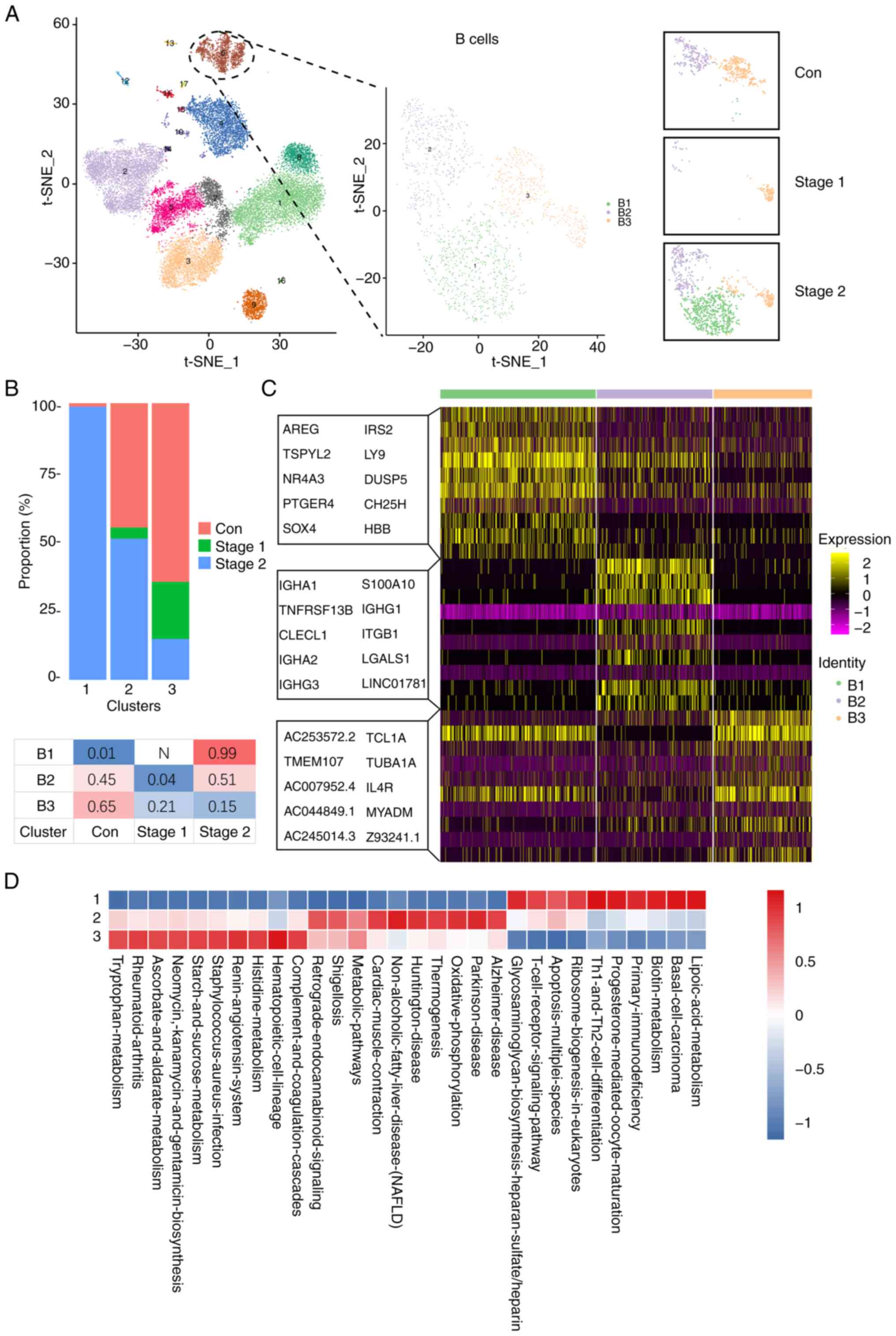
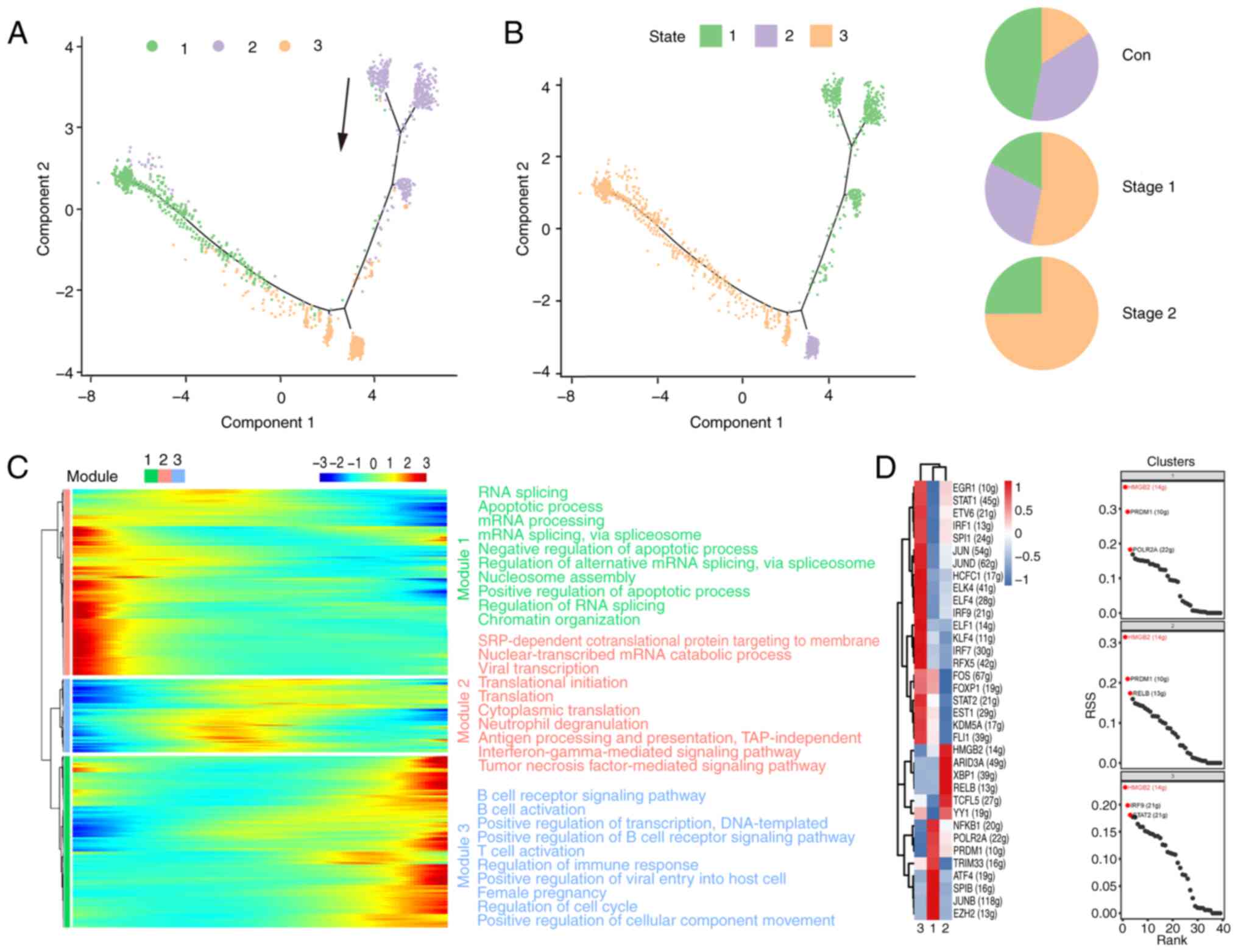
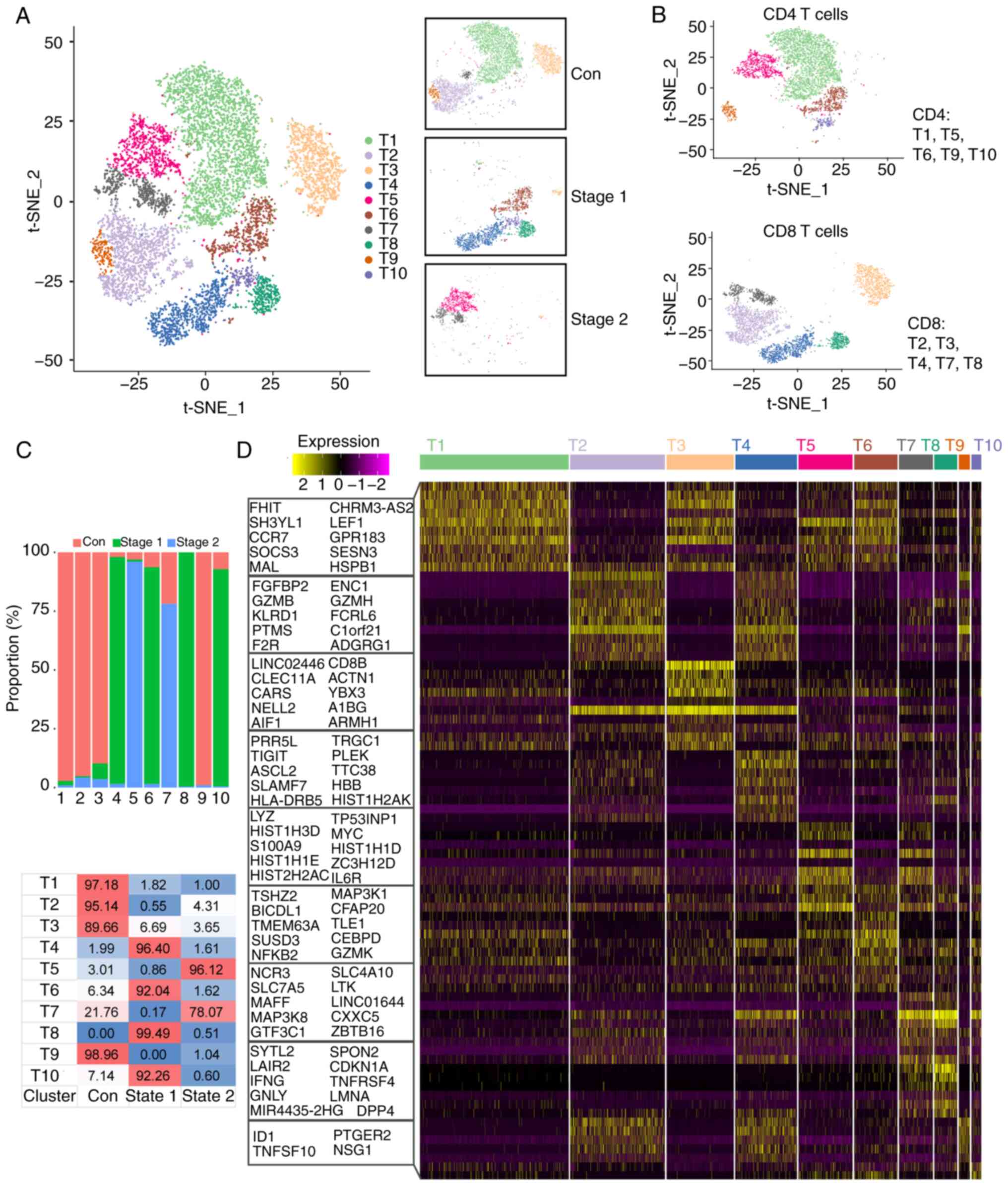
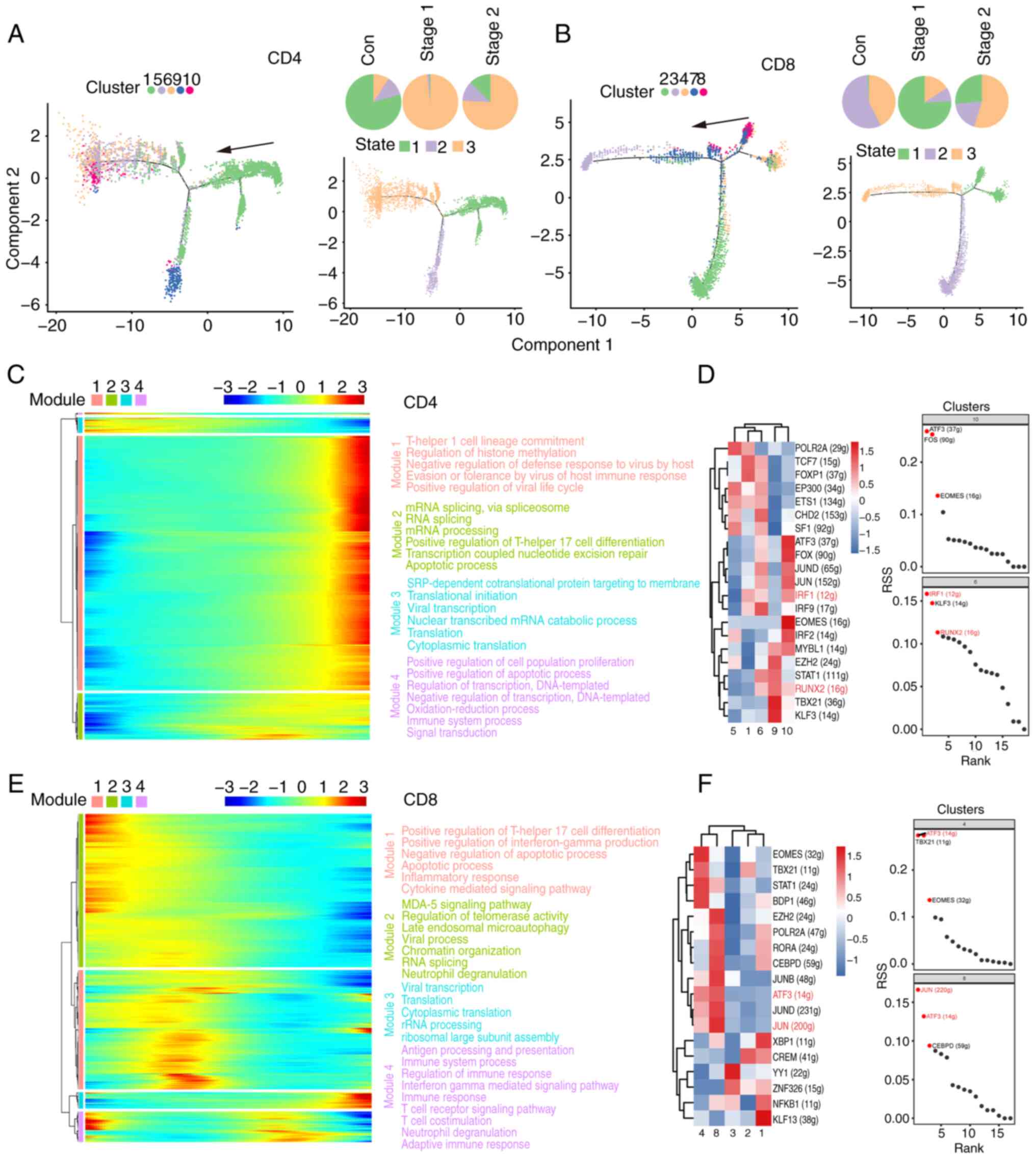
|
1
|
Fushiki S: Radiation hazards in
children-lessons from chernobyl, three mile island and fukushima.
Brain Dev. 35:220–227. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ohnishi T: The disaster at Japan's
Fukushima-Daiichi nuclear power plant after the March 11, 2011
earthquake and tsunami, and the resulting spread of radioisotope
contamination. Radiat Res. 177:1–14. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Densow D, Kindler H, Baranov AE, Tibken B,
Hofer EP and Fliedner TM: Criteria for the selection of radiation
accident victims for stem cell transplantation. Stem Cells. 15
(Suppl 2):S287–S297. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Schaue D: A century of radiation therapy
and adaptive immunity. Front Immunol. 8(431)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kusunoki Y and Hayashi T: Long-lasting
alterations of the immune system by ionizing radiation exposure:
Implications for disease development among atomic bomb survivors.
Int J Radiat Biol. 84:1–14. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hekim N, Cetin Z, Nikitaki Z, Cort A and
Saygili EI: Radiation triggering immune response and inflammation.
Cancer Lett. 368:156–163. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhou Y, Yu N, Wang J, Chen W and Cai P:
Review of the 5·7 nanjing 192Ir source radiological accident.
Radiat Med Protect. 3:190–195. 2022.
|
|
8
|
Fielder E, Weigand M, Agneessens J,
Griffin B, Parker C, Miwa S and von Zglinicki T: Sublethal
whole-body irradiation causes progressive premature frailty in
mice. Mech Ageing Dev. 180:63–69. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Berger ME, Hurtado R, Dunlap J, Mutchinick
O, Velasco MG, Tostado RA, Tostado RA, Valenzuela J and Ricks RC:
Accidental radiation injury to the hand: Anatomical and
physiological considerations. Health Phys. 72:343–348.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shao L, Luo Y and Zhou D: Hematopoietic
stem cell injury induced by ionizing radiation. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 20:1447–1462. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Dainiak N, Waselenko JK, Armitage JO,
MacVittie TJ and Farese AM: The hematologist and radiation
casualties. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program: 473-496, 2003.
|
|
12
|
Paul S and Amundson SA: Development of
gene expression signatures for practical radiation biodosimetry.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 71:1236–1244. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Dressman HK, Muramoto GG, Chao NJ, Meadows
S, Marshall D, Ginsburg GS, Nevins JR and Chute JP: Gene expression
signatures that predict radiation exposure in mice and humans. PLoS
Med. 4(e106)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bauer M, Goldstein M, Christmann M, Becker
H, Heylmann D and Kaina B: Human monocytes are severely impaired in
base and DNA double-strand break repair that renders them
vulnerable to oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:21105–21110. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sasaki Y, Darmochwal-Kolarz D, Suzuki D,
Sakai M, Ito M, Shima T, Shiozaki A, Rolinski J and Saito S:
Proportion of peripheral blood and decidual CD4(+) CD25(bright)
regulatory T cells in pre-eclampsia. Clin Exp Immunol. 149:139–145.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Soto-Peña GA, Luna AL, Acosta-Saavedra L,
Conde P, López-Carrillo L, Cebrián ME, Bastida M, Calderón-Aranda
ES and Vega L: Assessment of lymphocyte subpopulations and cytokine
secretion in children exposed to arsenic. FASEB J. 20:779–781.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Autissier P, Soulas C, Burdo TH and
Williams KC: Evaluation of a 12-color flow cytometry panel to study
lymphocyte, monocyte, and dendritic cell subsets in humans.
Cytometry A. 77:410–409. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Corkum CP, Ings DP, Burgess C, Karwowska
S, Kroll W and Michalak TI: Immune cell subsets and their gene
expression profiles from human PBMC isolated by Vacutainer Cell
Preparation Tube (CPT™) and standard density gradient. BMC Immunol.
16(48)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hromadnikova I, Li S, Kotlabova K and
Dickinson AM: Influence of in vitro IL-2 or IL-15 alone or in
combination with hsp 70 derived 14-mer peptide (TKD) on the
expression of NK cell activatory and inhibitory receptors on
peripheral blood T cells, B cells and NKT cells. PLoS One.
11(e0151535)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Regev A, Teichmann SA, Lander ES, Amit I,
Benoist C, Birney E, Bodenmiller B, Campbell P, Carninci P,
Clatworthy M, et al: The human cell atlas. Elife.
6(e27041)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tang F, Barbacioru C, Wang Y, Nordman E,
Lee C, Xu N, Wang X, Bodeau J, Tuch BB, Siddiqui A, et al: mRNA-Seq
whole-transcriptome analysis of a single cell. Nat Methods.
6:377–382. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Papalexi E and Satija R: Single-cell RNA
sequencing to explore immune cell heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol.
18:35–45. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Griffiths JA, Scialdone A and Marioni JC:
Using single-cell genomics to understand developmental processes
and cell fate decisions. Mol Syst Biol. 14(e8046)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Fan X, Zhou Y, Guo X and Xu M: Utilizing
single-cell RNA sequencing for analyzing the characteristics of
PBMC in patients with kawasaki disease. BMC Pediatr.
21(277)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhu W, Liu J, Nie J, Sheng W, Cao H, Shen
W, Dong A, Zhou J, Jiao Y, Zhang S and Cao J: MG132 enhances the
radiosensitivity of lung cancer cells in vitro and in
vivo. Oncol Rep. 34:2083–2089. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yan T, Yang P, Bai H, Song B, Liu Y, Wang
J, Zhang Y, Tu W, Yu D and Zhang S: Single-cell RNA-Seq analysis of
molecular changes during radiation-induced skin injury: The
involvement of Nur77. Theranostics. 14:5809–5825. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Butler A, Hoffman P, Smibert P, Papalexi E
and Satija R: Integrating single-cell transcriptomic data across
different conditions, technologies, and species. Nat Biotechnol.
36:411–420. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
McGinnis CS, Murrow LM and Gartner ZJ:
DoubletFinder: Doublet detection in single-cell RNA sequencing data
using artificial nearest neighbors. Cell Syst. 8:329–337.e4.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Macosko EZ, Basu A, Satija R, Nemesh J,
Shekhar K, Goldman M, Tirosh I, Bialas AR, Kamitaki N, Martersteck
EM, et al: Highly parallel Genome-wide expression profiling of
individual cells using nanoliter droplets. Cell. 161:1202–1214.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Haghverdi L, Lun ATL, Morgan MD and
Marioni JC: Batch effects in single-cell RNA-sequencing data are
corrected by matching mutual nearest neighbors. Nat Biotechnol.
36:421–427. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Aran D, Looney AP, Liu L, Wu E, Fong V,
Hsu A, Chak S, Naikawadi RP, Wolters PJ, Abate AR, et al:
Reference-based analysis of lung single-cell sequencing reveals a
transitional profibrotic macrophage. Nat Immunol. 20:163–172.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Aibar S, González-Blas CB, Moerman T,
Huynh-Thu VA, Imrichova H, Hulselmans G, Rambow F, Marine JC,
Geurts P, Aerts J, et al: SCENIC: Single-cell regulatory network
inference and clustering. Nat Methods. 14:1083–1086.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Suo S, Zhu Q, Saadatpour A, Fei L, Guo G
and Yuan GC: Revealing the critical regulators of cell identity in
the mouse cell atlas. Cell Rep. 25:1436–1445.e3. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Trapnell C, Cacchiarelli D, Grimsby J,
Pokharel P, Li S, Morse M, Lennon NJ, Livak KJ, Mikkelsen TS and
Rinn JL: The dynamics and regulators of cell fate decisions are
revealed by pseudotemporal ordering of single cells. Nat
Biotechnol. 32:381–386. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R and Guinney J:
GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data.
BMC Bioinformatics. 14(7)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Team RC: R: A language and environment for
statistical computing. MSOR connections 1, 2014.
|
|
37
|
Zhang J, Tessier SN, Biggar KK, Wu CW,
Pifferi F, Perret M and Storey KB: Regulation of torpor in the gray
mouse lemur: Transcriptional and translational controls and role of
AMPK signaling. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 13:103–110.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kabilan U, Graber TE, Alain T and Klokov
D: Ionizing radiation and translation control: A link to radiation
hormesis? Int J Mol Sci. 21(6650)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Mabbott NA, Baillie JK, Brown H, Freeman
TC and Hume DA: An expression atlas of human primary cells:
Inference of gene function from coexpression networks. BMC
Genomics. 14(632)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yu X, Wang Y, Deng M, Li Y, Ruhn KA, Zhang
CC and Hooper LV: The basic leucine zipper transcription factor
NFIL3 directs the development of a common innate lymphoid cell
precursor. Elife. 3(e04406)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Nwabo Kamdje AH, Tagne Simo R, Fogang
Dongmo HP, Bidias AR and Masumbe Netongo P: Role of signaling
pathways in the interaction between microbial, inflammation and
cancer. Holistic Integrative Oncol. 2(42)2023.
|
|
42
|
Gou M, Zhang Y, Wang Z and Qian N: Changes
in the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as predictive values
for metastatic gastric cancer patients with PD-1 inhibitors.
Holistic Integrative Oncol. 3(5)2024.
|
|
43
|
Min JY, Kim HM, Lee H, Cho MY, Park HS,
Lee SY, Park MS, Ha SK, Kim D, Jeong HG, et al: STAT1 as a tool for
non-invasive monitoring of NK cell activation in cancer. Commun
Biol. 7(1222)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Neubert EN, DeRogatis JM, Lewis SA,
Viramontes KM, Ortega P, Henriquez ML, Buisson R, Messaoudi I and
Tinoco R: HMGB2 regulates the differentiation and stemness of
exhausted CD8(+) T cells during chronic viral infection and cancer.
Nat Commun. 14(5631)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Tian S, Zheng N, Zu X, Wu G, Zhong J,
Zhang J, Sheng L, Liu W, Wang C, Ge G, et al: Integrated hepatic
single-cell RNA sequencing and untargeted metabolomics reveals the
immune and metabolic modulation of Qing-Fei-Pai-Du decoction in
mice with coronavirus-induced pneumonia. Phytomedicine.
97(153922)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zenke K, Muroi M and Tanamoto KI: IRF1
supports DNA binding of STAT1 by promoting its phosphorylation.
Immunol Cell Biol. 96:1095–1103. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Lopes-Ramos CM, Chen CY, Kuijjer ML,
Paulson JN, Sonawane AR, Fagny M, Platig J, Glass K, Quackenbush J
and DeMeo DL: Sex differences in gene expression and regulatory
networks across 29 human tissues. Cell Rep.
31(107795)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Sykes SM, Di Marcantonio D, Martinez E,
Huhn J, Gupta A and Mistry R: JUN and ATF3 regulate the
transcriptional output of the unfolded protein response to support
acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 132(1327)2018.
|
|
49
|
Zhou Y, Zhao L, Cai M, Luo D, Pang Y, Chen
J, Luo Q and Lin Q: Utilizing sc-linker to integrate single-cell
RNA sequencing and human genetics to identify cell types and driver
genes associated with non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer.
25(130)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Lahoz-Beneytez J, Elemans M, Zhang Y,
Ahmed R, Salam A, Block M, Niederalt C, Asquith B and Macallan D:
Human neutrophil kinetics: Modeling of stable isotope labeling data
supports short blood neutrophil half-lives. Blood. 127:3431–3438.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lefranc MP: Immunoglobulin and T cell
receptor genes: IMGT(®) and the birth and rise of
immunoinformatics. Front Immunol. 5(22)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Nielsen MM, Witherden DA and Havran WL: γδ
T cells in homeostasis and host defence of epithelial barrier
tissues. Nature reviews Immunology. 17:733–745. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Vantourout P and Hayday A:
Six-of-the-best: Unique contributions of γδ T cells to immunology.
Nat Rev Immunol. 13:88–100. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Willmarth NE and Ethier SP: Autocrine and
juxtacrine effects of amphiregulin on the proliferative, invasive,
and migratory properties of normal and neoplastic human mammary
epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 281:37728–37737. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Ishikawa N, Daigo Y, Takano A, Taniwaki M,
Kato T, Hayama S, Murakami H, Takeshima Y, Inai K, Nishimura H, et
al: Increases of amphiregulin and transforming growth factor-alpha
in serum as predictors of poor response to gefitinib among patients
with advanced non-small cell lung cancers. Cancer Res.
65:9176–9184. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Jing C, Jin YH, You Z, Qiong Q and Jun Z:
Prognostic value of amphiregulin and epiregulin mRNA expression in
metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Oncotarget. 7:55890–55899.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Son B, Kim TR, Park JH, Yun SI, Choi H,
Choi JW, Jeon C and Park HO: SAMiRNA targeting amphiregulin
alleviate total-body-irradiation-induced renal fibrosis. Radiat
Res. 197:471–479. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Prince LR, Prosseda SD, Higgins K,
Carlring J, Prestwich EC, Ogryzko NV, Rahman A, Basran A, Falciani
F, Taylor P, et al: NR4A orphan nuclear receptor family members,
NR4A2 and NR4A3, regulate neutrophil number and survival. Blood.
130:1014–1025. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
McMorrow JP and Murphy EP: Inflammation: A
role for NR4A orphan nuclear receptors? Biochem Soc Trans.
39:688–693. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Son B, Jeon J, Lee S, Kim H, Kang H, Youn
H, Jo S and Youn B: Radiotherapy in combination with hyperthermia
suppresses lung cancer progression via increased NR4A3 and KLF11
expression. Int J Radiat Biol. 95:1696–1707. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Ilienko IM, Golyarnik NA, Lyaskivska OV,
Belayev OA and Bazyka DA: Expression of biological markers induced
by ionizing radiation at the late period after exposure in a wide
range of doses. Probl Radiac Med Radiobiol. 23:331–350.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Kusunoki Y, Kyoizumi S, Hirai Y, Suzuki T,
Nakashima E, Kodama K and Seyama T: Flow cytometry measurements of
subsets of T, B and NK cells in peripheral blood lymphocytes of
atomic bomb survivors. Radiat Res. 150:227–236. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Paganetti H: A review on lymphocyte
radiosensitivity and its impact on radiotherapy. Front Oncol.
13(1201500)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|