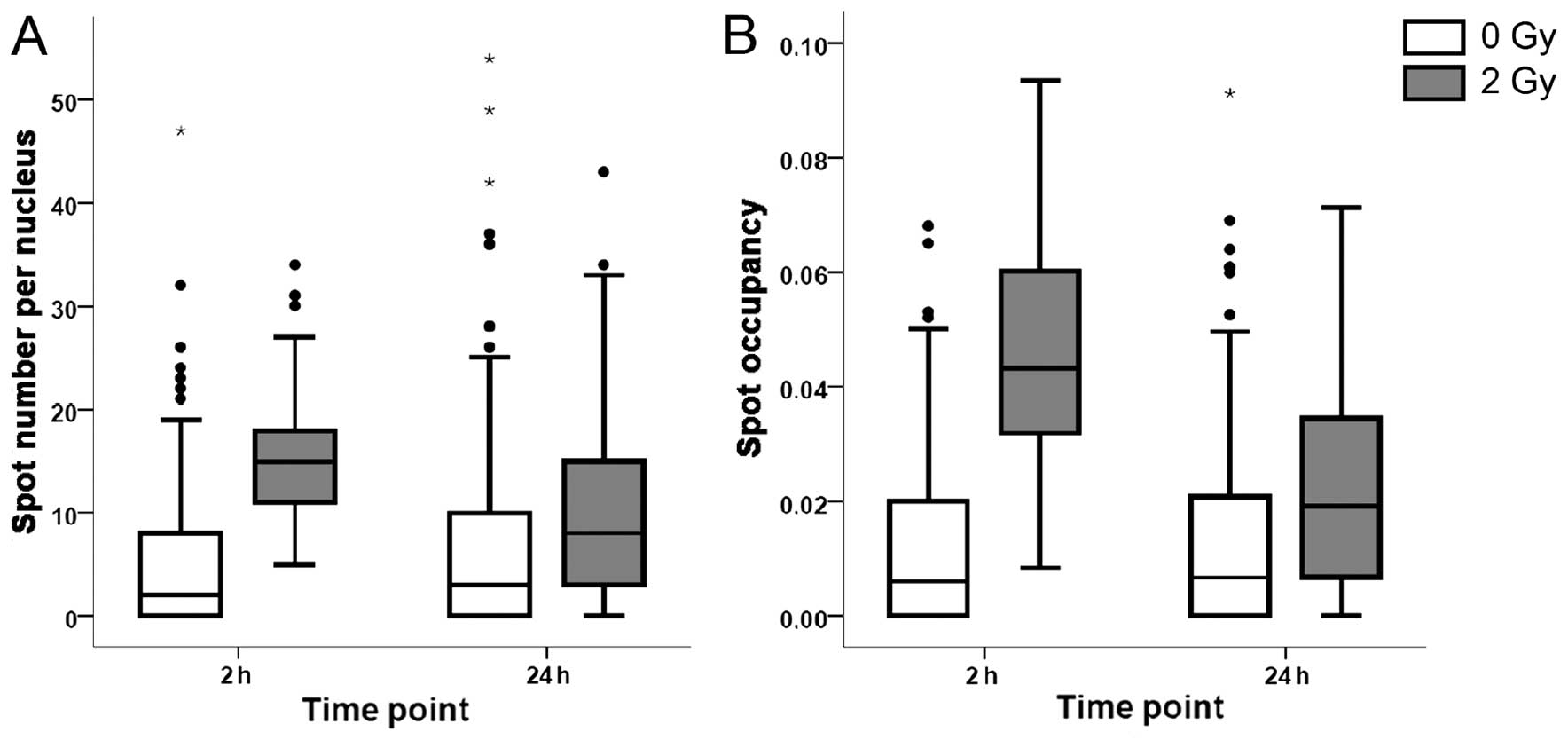
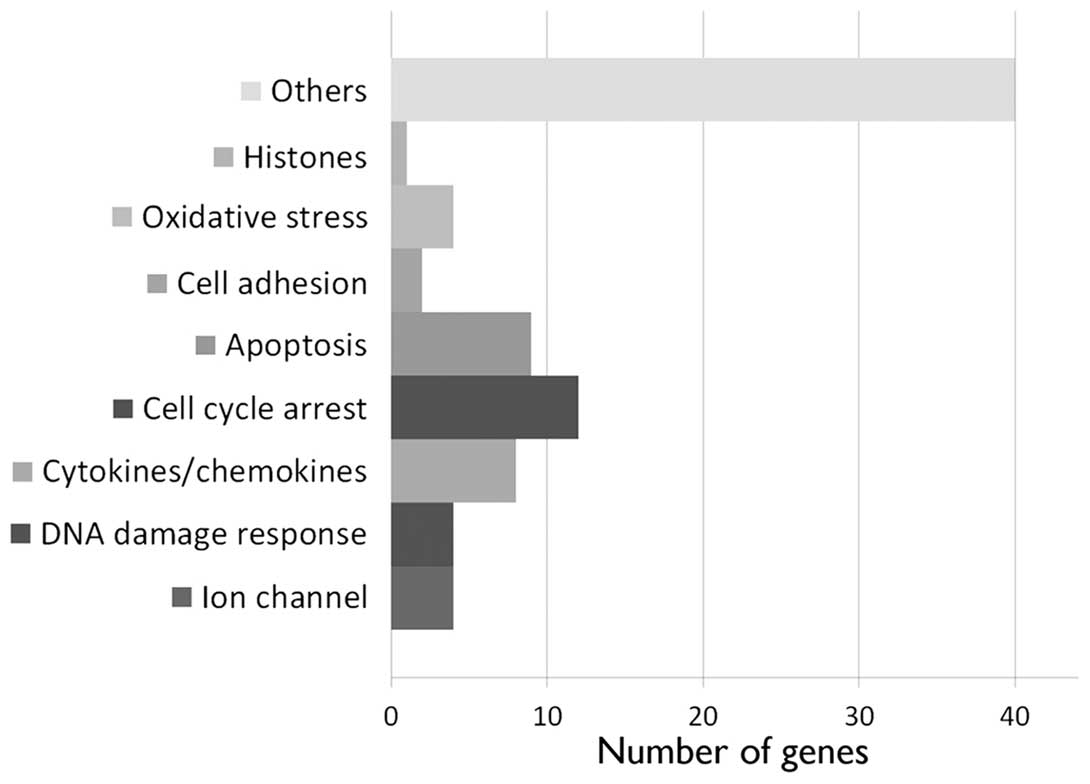
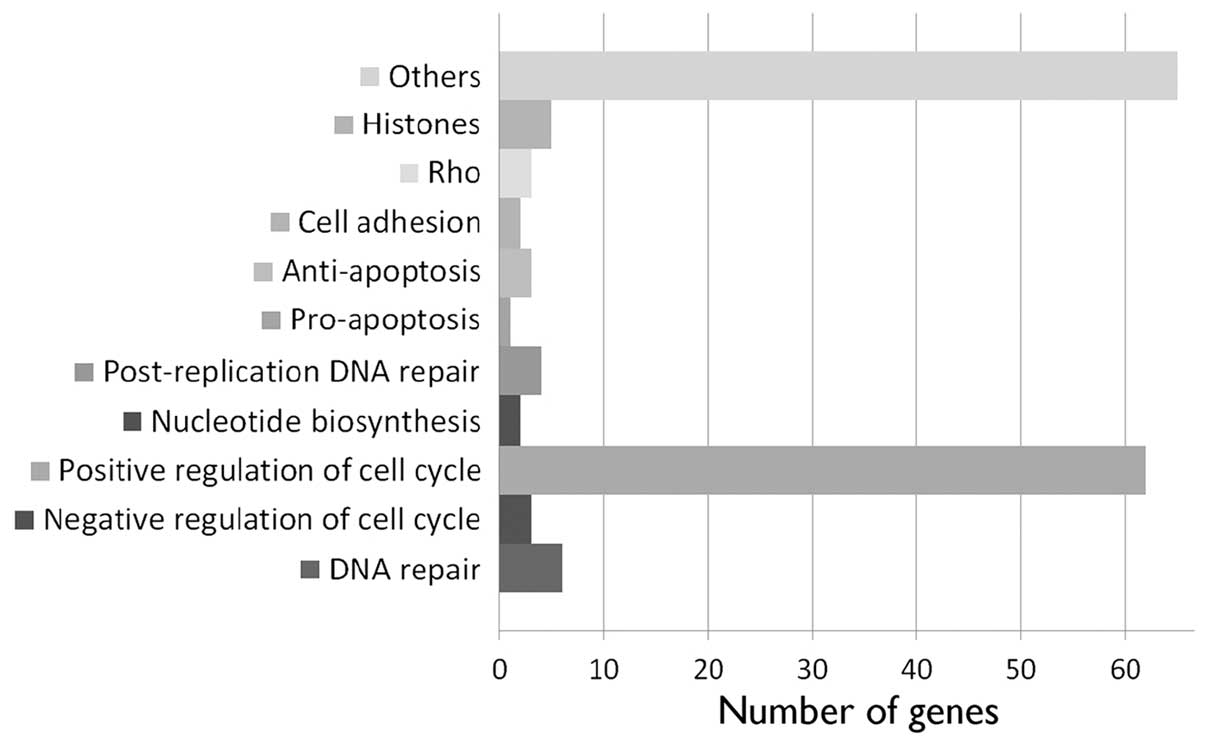
|
1
|
Schultz-Hector S and Trott KR:
Radiation-induced cardiovascular diseases: is the epidemiologic
evidence compatible with the radiobiologic data? Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 67:10–18. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blaber E, Marçal H and Burns BP:
Bioastronautics: the influence of microgravity on astronaut health.
Astrobiology. 10:463–473. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brinckmann E: Biology in Space and Life on
Earth: Effects of Spaceflight on Biological Systems. WILEY-VCH
Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA; Weinheim: 2007, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rong Y and Welsh J: Basics of particle
therapy II biologic and dosimetric aspects of clinical hadron
therapy. Am J Clin Oncol. 33:646–649. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Blakely EA and Chang PY: Biology of
charged particles. Cancer J. 15:271–284. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Halle M, Hall P and Tornvall P:
Cardiovascular disease associated with radiotherapy: Activation of
nuclear factor kappa-B. J Intern Med. 269:469–477. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hildebrandt G: Non-cancer diseases and
non-targeted effects. Mutat Res. 687:73–77. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rödel F, Frey B, Capalbo G, et al:
Discontinuous induction of x-linked inhibitor of apoptosis in ea.
Hy926 endothelial cells is linked to NF-κB activation and mediates
the anti-inflammatory properties of low-dose ionising-radiation.
Radiother Oncol. 97:346–351. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rödel F, Hofmann D, Auer J, et al: The
anti-inflammatory effect of low-dose radiation therapy involves a
diminished CCL20 chemokine expression and granulocyte/endothelial
cell adhesion. Strahlenther Onkol. 184:41–47. 2008.
|
|
10
|
Rödel F, Keilholz L, Herrmann M, Sauer R
and Hildebrandt G: Radiobiological mechanisms in inflammatory
diseases of low-dose radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Biol.
83:357–366. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rödel F, Schaller U, Schultze-Mosgau S, et
al: The induction of TGF-beta(1) and NF-kappaB parallels a biphasic
time course of leukocyte/endothelial cell adhesion following
low-dose X-irradiation. Strahlenther Onkol. 180:194–200.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ando K, Ishibashi T, Ohkawara H, et al:
Crucial role of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP)
in Rhoa/Rac1-dependent signaling pathways in thrombin-stimulated
endothelial cells. J Atheroscler Thromb. 18:762–773. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kantak SS, Diglio CA and Onoda JM: Low
dose radiation-induced endothelial cell retraction. Int J Radiat
Biol. 64:319–328. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Onoda JM, Kantak SS and Diglio CA:
Radiation induced endothelial cell retraction in vitro: correlation
with acute pulmonary edema. Pathol Oncol Res. 5:49–55. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gabrys D, Greco O, Patel G, Prise KM,
Tozer GM and Kanthou C: Radiation effects on the cytoskeleton of
endothelial cells and endothelial monolayer permeability. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 69:1553–1562. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pluder F, Barjaktarovic Z, Azimzadeh O, et
al: Low-dose irradiation causes rapid alterations to the proteome
of the human endothelial cell line EA. hy926. Radiat Environ
Biophys. 50:155–166. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Grabham P, Hu B, Sharma P and Geard C:
Effects of ionizing radiation on three-dimensional human vessel
models: differential effects according to radiation quality and
cellular development. Radiat Res. 175:21–28. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Takahashi Y, Teshima T, Kawaguchi N,
Hamada Y, Mori S, Madachi A, Ikeda S, Mizuno H, Ogata T, Nojima K,
Furusawa Y and Matsuura N: Heavy ion irradiation inhibits in vitro
angiogenesis even at sublethal dose. Cancer Res. 63:4253–4257.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kiyohara H, Ishizaki Y, Suzuki Y, Katoh H,
Hamada N, Ohno T, Takahashi T, Kobayashi Y and Nakano T:
Radiation-induced ICAM-1 expression via TGF-β1 pathway on human
umbilical vein endothelial cells; comparison between X-ray and
carbon-ion beam irradiation. J Radiat Res. 52:287–292.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Haberer T, Becher W, Schardt D and Kraft
G: Magnetic scanning system for heavy ion therapy. Nucl Instrum
Methods Phys Res A. 330:296–305. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
De Vos WH, Van Neste L, Dieriks B, Joss GH
and Van Oostveldt P: High content image cytometry in the context of
subnuclear organization. Cytometry A. 77:64–75. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zambelli F, Pesole G and Pavesi G: Pscan:
finding over-represented transcription factor binding site motifs
in sequences from co-regulated or co-expressed genes. Nucleic Acids
Res. 37:W247–W252. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fokas E, Kraft G, An H and
Engenhart-Cabillic R: Ion beam radiobiology and cancer: time to
update ourselves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:216–229.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Held KD: Effects of low fluences of
radiations found in space on cellular systems. Int J Radiat Biol.
85:379–390. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Costes SV, Boissière A, Ravani S, Romano
R, Parvin B and Barcellos-Hoff MH: Imaging features that
discriminate between foci induced by high- and low-let radiation in
human fibroblasts. Radiat Res. 165:505–515. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Blakely EA and Kronenberg A: Heavy-ion
radiobiology: new approaches to delineate mechanisms underlying
enhanced biological effectiveness. Radiat Res. 150:S126–S145. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chappell LJ, Whalen MK, Gurai S, Ponomarev
A, Cucinotta FA and Pluth JM: Analysis of flow cytometry DNA damage
response protein activation kinetics after exposure to x rays and
high-energy iron nuclei. Radiat Res. 174:691–702. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dyson N: The regulation of E2F by
pRB-family proteins. Genes Dev. 12:2245–2262. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Biswas AK and Johnson DG: Transcriptional
and nontranscriptional functions of E2F1 in response to DNA damage.
Cancer Res. 72:13–17. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Costa A and Onesti S: The MCM complex:
(just) a replicative helicase? Biochem Soc Trans. 36:136–140. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Forsburg SL: The MCM helicase: Linking
checkpoints to the replication fork. Biochem Soc Trans. 36:114–119.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chuang CH, Yang D, Bai G, Freeland A,
Pruitt SC and Schimenti JC: Post-transcriptional homeostasis and
regulation of MCM2-7 in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:4914–4924. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dejana E, Orsenigo F, Molendini C, Baluk P
and McDonald DM: Organization and signaling of endothelial
cell-to-cell junctions in various regions of the blood and
lymphatic vascular trees. Cell Tissue Res. 335:17–25. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Prasain N and Stevens T: The actin
cytoskeleton in endothelial cell phenotypes. Microvasc Res.
77:53–63. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Bogatcheva NV and Verin AD: The role of
cytoskeleton in the regulation of vascular endothelial barrier
function. Microvasc Res. 76:202–207. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oeckinghaus A and Ghosh S: The NF-kappaB
family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Biol. 1:a0000342009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Karin M: NF-kappaB as a critical link
between inflammation and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1:a0001412009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dieriks B, De Vos WH, Derradji H, Baatout
S and Van Oostveldt P: Medium-mediated DNA repair response after
ionizing radiation is correlated with the increase of specific
cytokines in human fibroblasts. Mutat Res. 687:40–48. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|