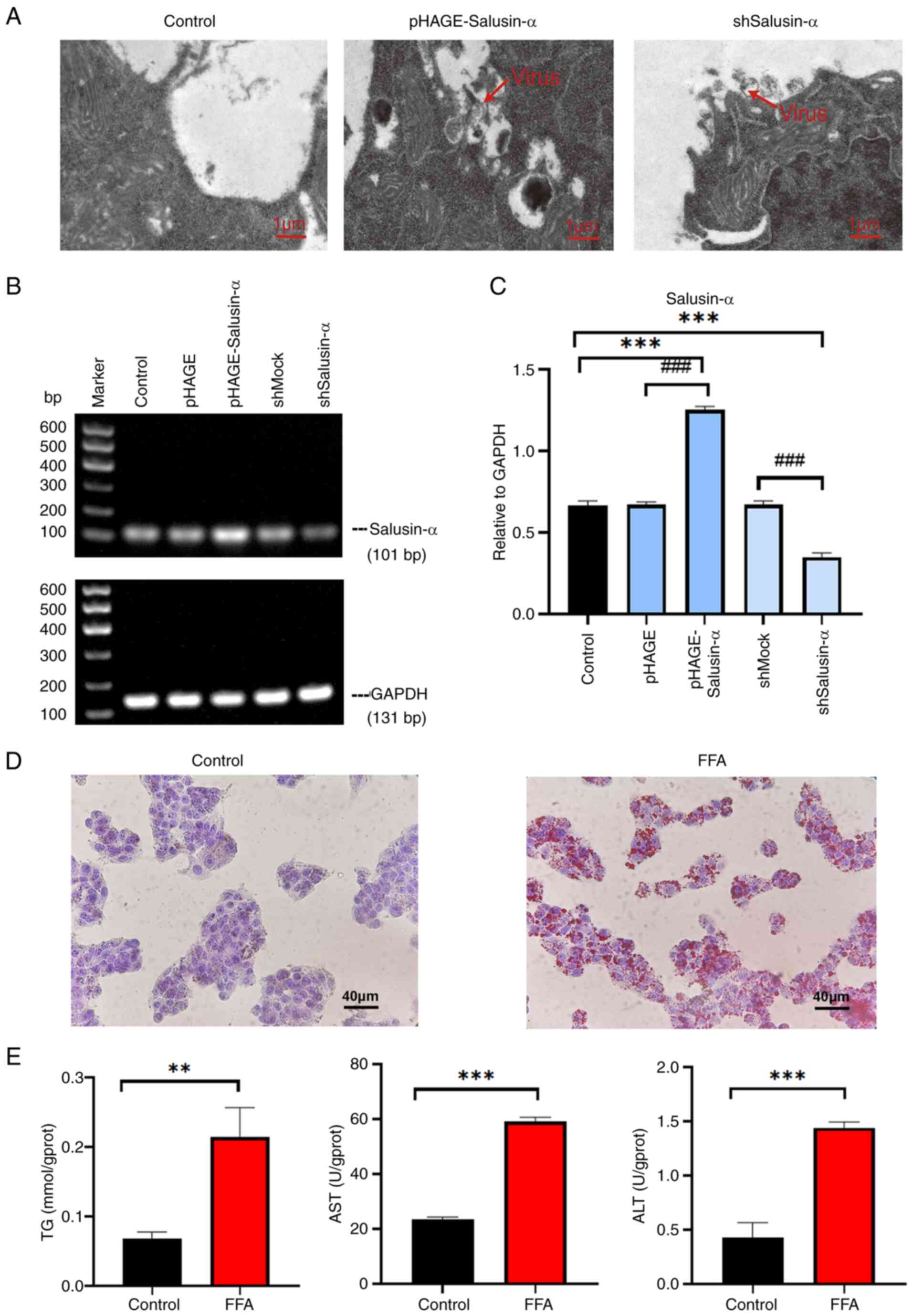
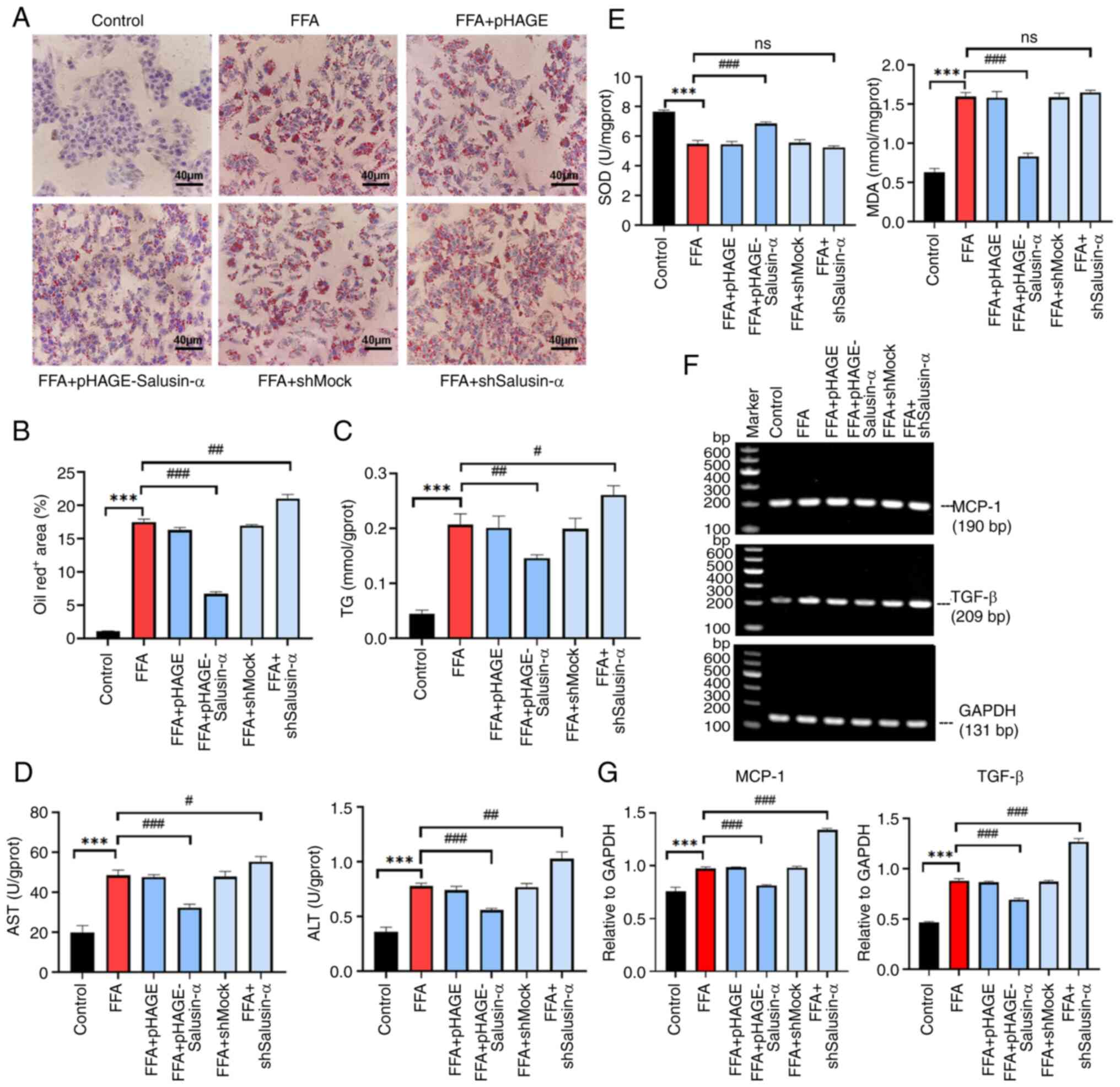
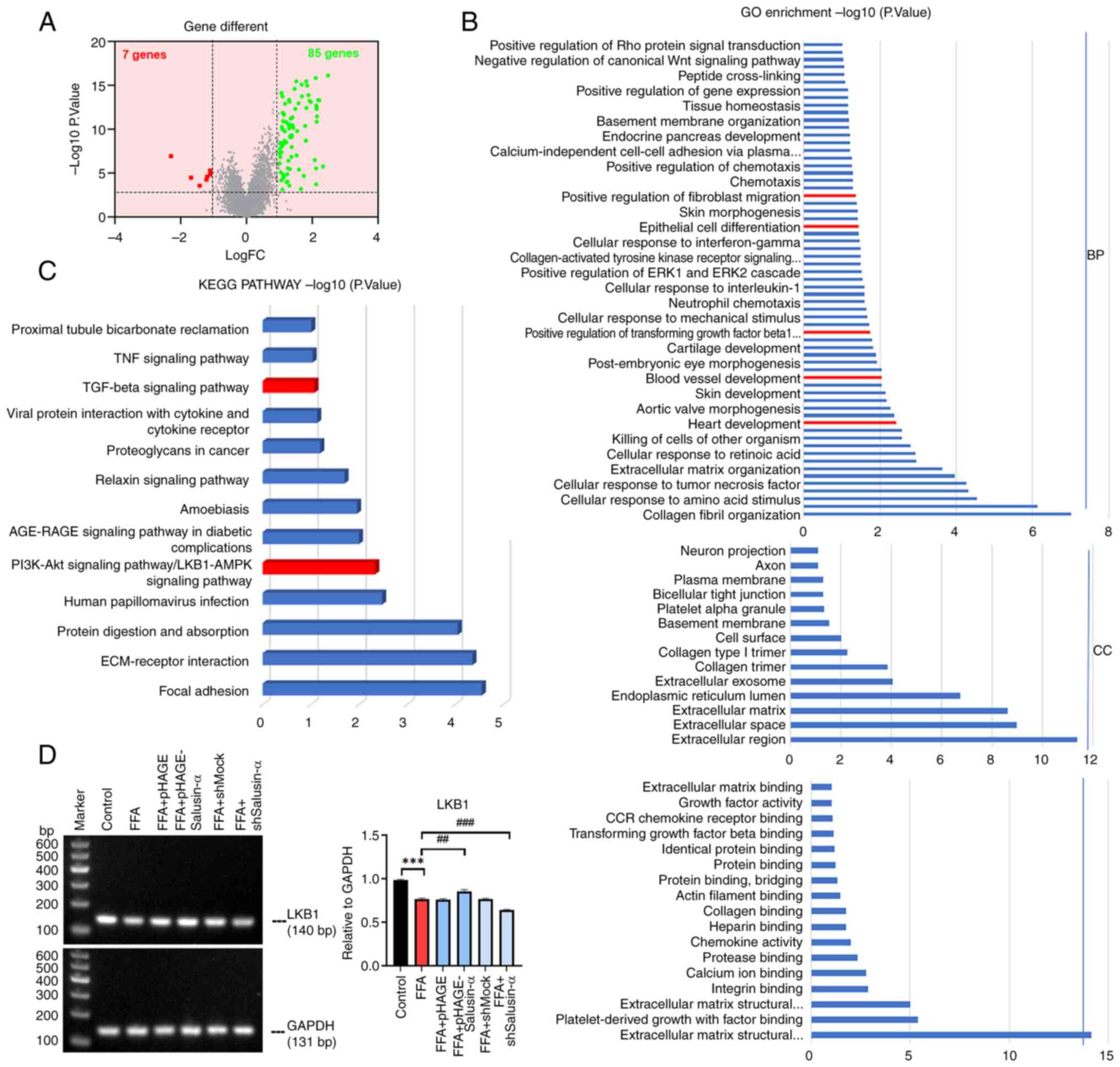
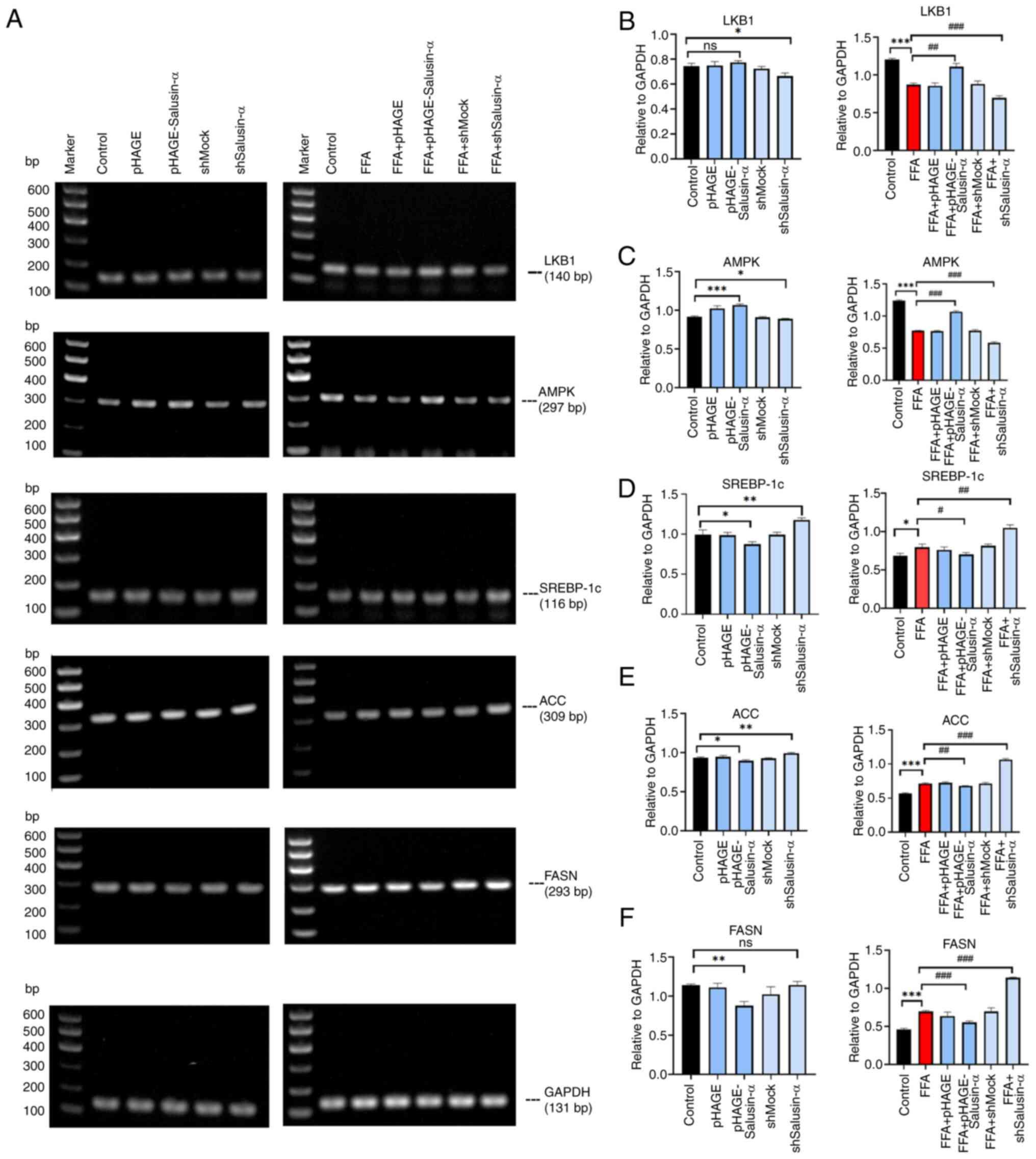
|
1
|
Chen M, Zhu J, Luo H, Mu W and Guo L: The
journey towards physiology and pathology: Tracing the path of
neuregulin 4. Genes Dis. 11:687–700. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guo YY, Li BY, Xiao G, Liu Y, Guo L and
Tang QQ: Cdo1 promotes PPARγ-mediated adipose tissue lipolysis in
male mice. Nat Metab. 4:1352–1368. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang DQ, El-serag HB and Loomba R: Global
epidemiology of NAFLD-related HCC: Trends, predictions, risk
factors and prevention. J Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
18:223–238. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhou F, Zhou J, Wang W, Zhang XJ, Ji YX,
Zhang P, She ZG, Zhu L, Cai J and Li H: Unexpected rapid increase
in the burden of NAFLD in China from 2008 to 2018: A systematic
review and meta analysis. Hepatology. 70:1119–1133. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Powell EE, Wong VW and Rinella M:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Lancet. 397:2212–2224. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wong VW, Adams LA, de Lédinghen V, Wong GL
and Sookoian S: Noninvasive biomarkers in NAFLD and NASH-current
progress and future promise. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
15:461–478. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jin C, Zhou T, Duan Z, Deng Y, Zhang X,
Xiao C, He J, He G, Zhou Y and Li S: Effect of chin brick tea
[Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze] on lipid metabolism and
inflammation by modulating intestinal flora and bile acids in mice
with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Ethnopharmacol.
318:1169502024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Stefan N, Häring HU and Cusi K:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Causes, diagnosis,
cardiometabolic consequences, and treatment strategies. Lancet
Diabetes Endocrinol. 7:313–324. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Shichiri M, Ishimaru S, Ota T, Nishikawa
T, Isogai T and Hirata Y: Salusins: Newly identified bioactive
peptides with hemodynamic and mitogenic activities. Nat Med.
9:1166–1172. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nakayama C, Shichiri M, Sato K and Hirata
Y: Expression of proSalusin in human neuroblastoma cells. Peptide.
30:1362–1367. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nagashima M, Watanabe T, Shiraishi Y,
Morita R, Terasaki M, Arita S, Hongo S, Sato K, Shichiri M,
Miyazaki A and Hirano T: Chronic infusion of Salusin-alpha and
-beta exerts opposite effects on atherosclerotic lesion development
in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis. 212:70–77.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Murphy SK, Yang H, Moylan CA, Pang H,
Dellinger A, Abdelmalek MF, Garrett ME, Ashley-Koch A, Suzuki A,
Tillmann HL, et al: Relationship between methylome and
transcriptome in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Gastroenterology. 145:1076–1087. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen M, Wang Z and Wang S: Research
progress of Salusin-α in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Chem Life. 42:326–331. 2022.In Chinese.
|
|
14
|
Yang C and Yang J: Research progress on
the role of salusins in the development of atherosclerosis. J Pract
Med. 30:1663–1665. 2014.In Chinese.
|
|
15
|
Niepolski L and Grzegorzewska AE: Salusins
and adropin: New peptides potentially involved in lipid metabolism
and atherosclerosis. Adv Med Sci. 61:282–287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tang K, Wang F, Zeng Y, Chen X and Xu X:
Salusin-α attenuates hepatic steatosis and atherosclerosis in high
fat diet-fed low density lipoprotein receptor deficient mice. Eur J
Pharmacol. 830:76–86. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Luo M, Mao X, Shi X and Liu X:
Targeted delivery of salusin-α into rabbit carotid arterial
endothelium using SonoVue. J Ultrasound Med. 41:365–376. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang H, Yan C, Wang S, Xu A, Zhang Q,
Duan X, Gong G and Wang Y: Overexpression of Salusin-α upregulates
AdipoR2 and activates the PPARα/ApoA5/SREBP-1c pathway to inhibit
lipid synthesis in HepG2 cells. Int J Mol Med. 51:412023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xu A, Wang L, Luo M, Zhang H, Ning M, Pan
J, Duan X, Wang Y and Liu X: Overexpression of salusin-β
downregulates adipoR1 expression to prevent fatty acid oxidation in
HepG2 cells. Mol Med Rep. 29:182024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kuang X, Lu F and Yi P: Effect of
berberine on LKB1-AMPK-TORC2 signaling network in HepG2 insulin
resistance cell model. Chin J Integr Chin West Med Dig. 23:467–471.
2015.In Chinese.
|
|
21
|
Watanabe T, Nishio K, Kanome T, Matsuyama
TA, Koba S, Sakai T, Sato K, Hongo S, Nose K, Ota H, et al: Impact
of salusin-alpha and -beta on human macrophage foam cell formation
and coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation. 117:638–648. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Y, Guo Z, Wang J, Yue Y, Yang Y, Wen
Y, Luo Y and Zhang X: Qinlian hongqu decoction ameliorates
hyperlipidemia via the IRE1-α/IKKB-β/NF-κb signaling pathway:
Network pharmacology and experimental validation. J Ethnopharmacol.
318:1168562024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Poznyak A, Grechko AV, Poggio P,
Myasoedova VA, Alfieri V and Orekhov AN: The diabetes
mellitus-atherosclerosis connection: The role of lipid and glucose
metabolism and chronic inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 21:18352020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sweeney NP and Vink CA: The impact of
lentiviral vector genome size and producer cell genomic to gag-pol
mRNA ratios on packaging efficiency and titre. Mol Ther Methods
Clin Dev. 21:574–584. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yi J, Zhou Q, Huang J, Niu S, Ji G and
Zheng T: Lipid metabolism disorder promotes the development of
intervertebral disc degenerate. Biomed Pharmacother.
166:1154012023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zechner R, Zimmermann R, Eichmann TO,
Kohlwein SD, Haemmerle G, Lass A and Madeo F: FAT SIGNALS-lipases
and lipolysis in lipid metabolism and signaling. Cell Metab.
15:279–291. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Koh IU, Lim JH, Joe MK, Kim WH, Jung MH,
Yoon JB and Song J: AdipoR2 is transcriptionally regulated by ER
stress inducible ATF3 in HepG2 human hepatocyte cells. FEBS J.
277:2304–2317. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li J, Wang S, Yao L, Ma P, Chen Z, Han TL,
Yuan C, Zhang J, Jiang L, Liu L, et al: 6-gingerol ameliorates
age-related hepatic steatosis: Association with regulating
lipogenesis, fatty acid oxidation, oxidative stress and
mitochondrial dysfunction. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 362:125–135.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Xu N, Luo H, Li M, Wu J, Wu X, Chen L, Gan
Y, Guan F, Li M, Su Z, et al: β-patchoulene improves lipid
metabolism to alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via
activating AMPK signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
134:1111042021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gong P, Long H, Guo Y, Wang Z, Yao W, Wang
J, Yang W, Li N, Xie J and Chen F: Chinese herbal medicines: The
modulator of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease targeting oxidative
stress. J Ethnopharmacol. 318:1169272024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang J, Ma X and Fan D: Ginsenoside CK
ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation via activating the LKB1/AMPK
pathway in vitro and in vivo. Food Funct. 13:1153–1167. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li BY, Guo YY, Xiao G, Guo and Tang QQ:
SERPINA3C ameliorates adipose tissue inflammation through the
cathepsin G/Integrin/AKT pathway. Mol Metabol. 61:1015002022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Saravia J, Raynor JL, Chapman NM, Lim SA
and Chi H: Signaling networks in immunometabolism. Cell Res.
30:328–334. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li Q, Tan JX, He Y, Bai F, Li SW, Hou YW,
Ji LS, Gao YT, Zhang X, Zhou ZH, et al: Atractylenolide III
ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by activating hepatic
adiponectin receptor 1-mediated AMPK pathway. Int J Biol Sci.
18:1594–1611. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qiu B, Lawan A, Xirouchaki CE, Yi JS,
Robert M, Zhang L, Brown W, Fernández-Hernando C, Yang X, Tiganis T
and Bennett AM: MKP1 promotes nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by
suppressing AMPK activity through LKB1 nuclear retention. Nat
Commun. 14:54052023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jang HJ, Lee YH, Dao T, Jo Y, Khim KW, Eom
HJ, Lee JE, Song YJ, Choi SS, Park K, et al: Thrap3 promotes
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by suppressing AMPK-mediated
autophagy. Exp Mol Med. 55:1720–1733. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yin X, Liu Z and Wang J:
Tetrahydropalmatine ameliorates hepatic steatosis in nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease by switching lipid metabolism via
AMPK-SREBP-1c-Sirt1 signaling axis. Phytomedicine. 119:1550052023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ruolan Z and Bo N: The pathogenesis and
treatment progress of NAFLD targeted by SREBP-1 related path-way. J
Progr Clin Med. 12:4210–4220. 2022.
|
|
39
|
Li C, Zhang L, Qiu Z, Deng W and Wang W:
Key molecules of fatty acid metabolism in gastric cancer.
Biomolecules. 12:7062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang Z, Ye Z and Chen Y: Research
progress on the role of AMPK signaling pathway in the development
of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Nanjing Med Univ (Nat Sci).
39:1252–1256. 2019.In Chinese.
|
|
41
|
Zhou CH, Pan J, Huang H, Zhu Y, Zhang M,
Liu L and Wu Y: Salusin-β, but not salusin-α, promotes human
umbilical vein endothelial cell inflammation via the p38
MAPK/JNK-NF-κB pathway. PLoS One. 9:e1075552014. View Article : Google Scholar
|