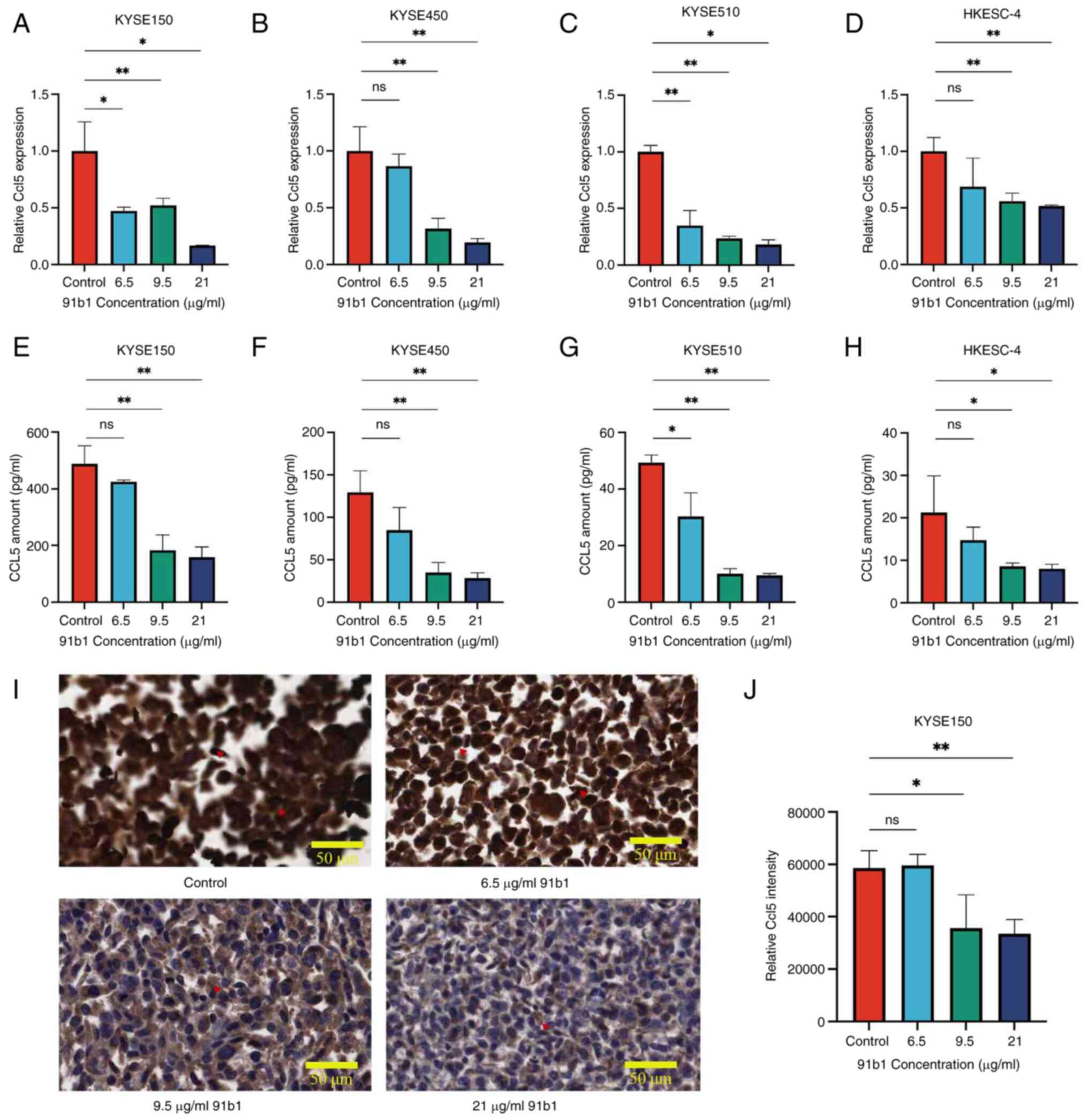
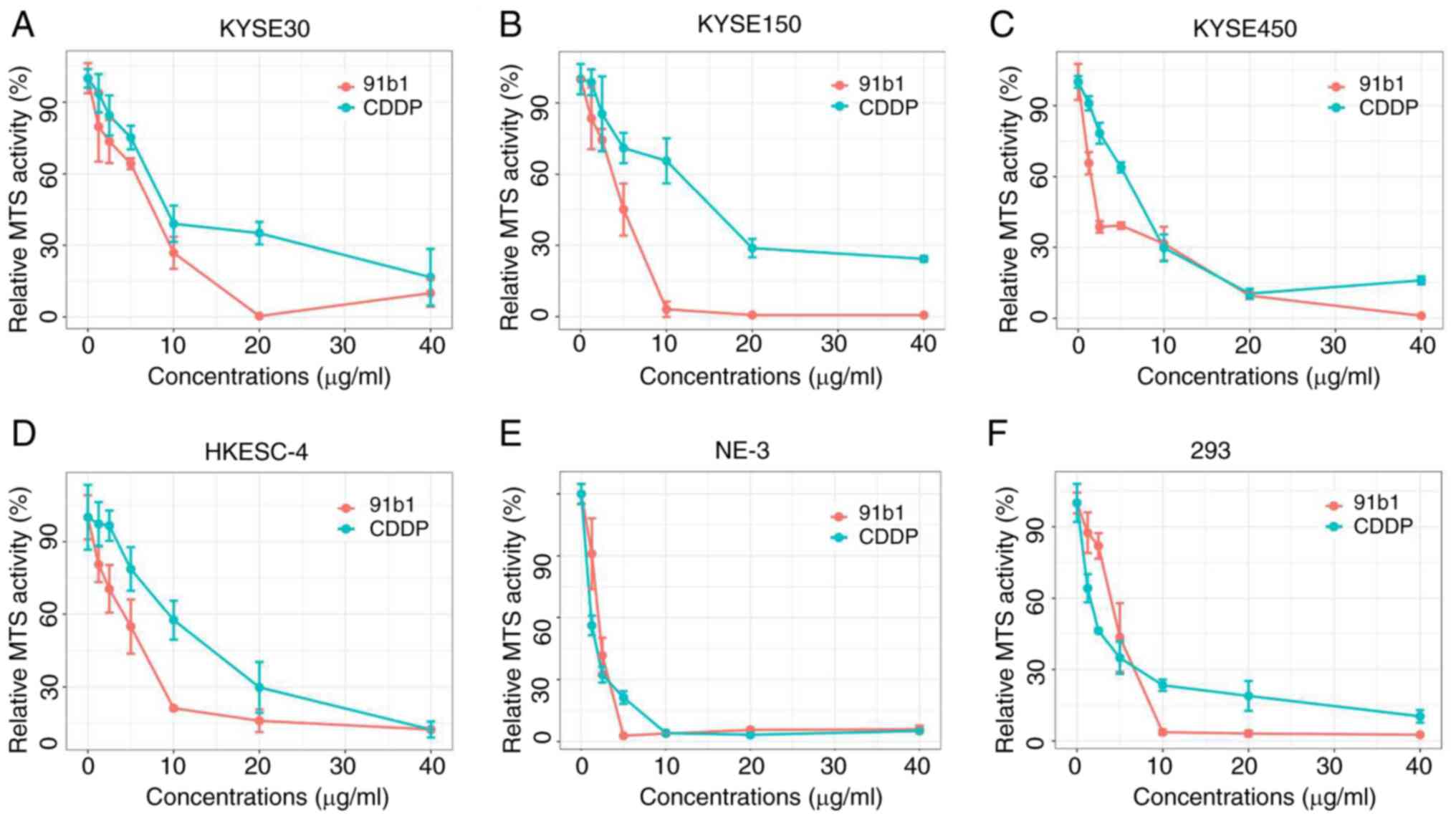
|
1
|
Then EO, Lopez M, Saleem S, Gayam V,
Sunkara T, Culliford A and Gaduputi V: Esophageal cancer: An
updated surveillance epidemiology and end results database
analysis. World J Oncol. 11:55–64. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tong D and Law S: Hong Kong experience.
Ando N: Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Springer; Tokyo: pp.
261–278. 2015, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chan D, Zhou Y, Chui CH, Lam KH, Law S,
Chan AS, Li X, Lam AK and Tang JCO: Expression of insulin-like
growth factor binding protein-5 (IGFBP5) reverses
cisplatin-resistance in esophageal carcinoma. Cells. 7:1432018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aldinucci D, Borghese C and Casagrande N:
The CCL5/CCR5 axis in cancer progression. Cancers (Basel).
12:17652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schall TJ, Bacon K, Toy KJ and Goeddel DV:
Selective attraction of monocytes and T lymphocytes of the memory
phenotype by cytokine RANTES. Nature. 347:669–671. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brett E, Duscher D, Pagani A, Daigeler A,
Kolbenschlag J and Hahn M: Naming the barriers between Anti-CCR5
therapy, breast cancer and its microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci.
23:141592022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ding H, Zhao L, Dai S, Li L, Wang F and
Shan B: CCL5 secreted by tumor associated macrophages may be a new
target in treatment of gastric cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
77:142–149. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang XF, Zhang XL, Wang YJ, Fang Y, Li
ML, Liu XY, Luo HY and Tian Y: The regulatory network of the
chemokine CCL5 in colorectal cancer. Ann Med. 55:22051682023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu H, Zhao J, Li J, Zhu Z, Cui Z, Liu R,
Lu R, Yao Z and Xu Q: Cancer associated fibroblast-derived CCL5
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through activating
HIF1α/ZEB1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 13:4782022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang R, Wang S, Wang N, Zheng Y, Zhou J,
Yang B, Wang X, Zhang J, Guo L, Wang S, et al: CCL5 derived from
tumor-associated macrophages promotes prostate cancer stem cells
and metastasis via activating β-catenin/STAT3 signaling. Cell Death
Dis. 11:2342020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chen K, Wang Y, Hou Y, Wang Q, Long D, Liu
X, Tian X and Yang Y: Single cell RNA-seq reveals the CCL5/SDC1
receptor-ligand interaction between T cells and tumor cells in
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 545:2158342022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Michael JP: Quinoline, quinazoline and
acridone alkaloids. Nat Prod Rep. 15:595–606. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Balaraman K, Vieira NC, Moussa F, Vacus J,
Cojean S, Pomel S, Bories C, Figadère B, Kesavan V and Loiseau PM:
In vitro and in vivo antileishmanial properties of a
2-n-propylquinoline hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin formulation and
pharmacoki-netics via intravenous route. Biomed Pharmacother.
76:127–133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vivanco JM, Bais HP, Stermitz FR, Thelen
GC and Callaway RM: Biogeographical variation in community response
to root allelochemistry: Novel weapons and exotic invasion. Ecol
Lett. 7:285–292. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Huang XQ, Wu RC, Liang JM, Zhou Z, Qin QP
and Liang H: Anticancer activity of
8-hydroxyquinoline-triphenylphosphine rhodium(III) complexes
targeting mitophagy pathways. Eur J Med Chem. 272:1164782024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Prajapati AK, Bhattacharya A and Choudhary
S: Inhibiting the activity of malarial drug target Plasmepsin V by
quinolines in aqueous medium. J Mol Liq. 397:1241582024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Joaquim AR, Gionbelli MP, Gosmann G,
Fuentefria AM, Lopes MS and Fernandes de Andrade S: Novel
antimicrobial 8-hydroxyquinoline-based agents: Current development,
structure-activity relationships, and perspectives. J Med Chem.
64:16349–16379. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chan SH, Chui CH, Chan SW, Kok SH, Chan D,
Tsoi MY, Leung PH, Lam AK, Chan AS, Lam KH and Tang JC: Synthesis
of 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives as novel antitumor agents. ACS
Med Chem Lett. 4:170–174. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lam KH, Lee KK, Gambari R, Kok SH, Kok TW,
Chan AS, Bian ZX, Wong WY, Wong RS, Lau FY, et al: Anti-tumour and
pharmacokinetics study of 2-Formyl-8-hydroxy-quinolinium chloride
as Galipea longiflora alkaloid analogue. Phytomedicine. 21:877–882.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lam KH, Lee KK, Kok SH, Wong RS, Lau FY,
Cheng GY, Wong WY, Tong SW, Chan KW, Chan RY, et al: Antiangiogenic
activity of 2-formyl-8-hydroxy-quinolinium chloride. Biomed
Pharmacother. 80:145–150. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pun IH, Chan D, Chan SH, Chung PY, Zhou
YY, Law S, Lam AK, Chui CH, Chan AS, Lam KH and Tang JC:
Anti-cancer Effects of a Novel Quinoline Derivative 83b1 on human
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through down-regulation of COX-2
mRNA and PGE2. Cancer Res Treat. 49:219–229. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lam KH, Lee KK, Gambari R, Wong RS, Cheng
GY, Tong SW, Chan KW, Lau FY, Lai PB, Wong WY, et al: Preparation
of Galipea officinalis Hancock type tetrahydroquinoline alkaloid
analogues as anti-tumour agents. Phytomedicine. 20:166–171. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chan ASC, Tang JCO, Lam KH, Chui CH, Kok
SHL, Chan SH, Cheung F, Chor RG and Cheng H: Method of making and
administering quinoline derivatives as anti-cancer agents. The Hong
Kong Polytechnic University; 2016
|
|
25
|
Tang JCO, Chan ASC, Lam KH and Chan SH:
Quinoline derivatives as anti-cancer agents. Hong Kong Polytechnic
University; 2016
|
|
26
|
Chung PY, Lam PL, Zhou YY, Gasparello J,
Finotti A, Chilin A, Marzaro G, Gambari R, Bian ZX, Kwok WM, et al:
Targeting DNA binding for NF-κB as an anticancer approach in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cells. 7:1772018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhou Y, Zhou Z, Chan D, Chung PY, Wang Y,
Chan ASC, Law S, Lam KH and Tang JCO: The Anticancer effect of a
novel quinoline derivative 91b1 through downregulation of Lumican.
Int J Mol Sci. 23:131812022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li T, Fu J, Zeng Z, Cohen D, Li J, Chen Q,
Li B and Liu XS: TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune
cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 48(W1): W509–W514. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu T, Hu E, Xu S, Chen M, Guo P, Dai Z,
Feng T, Zhou L, Tang W, Zhan L, et al: clusterProfiler 4.0: A
universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation
(Camb). 2:1001412021.
|
|
30
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Nastou KC, Lyon D,
Kirsch R, Pyysalo S, Doncheva NT, Legeay M, Fang T, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks,
and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement
sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 49(D1): D605–D612. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shimada Y, Imamura M, Wagata T, Yamaguchi
N and Tobe T: Characterization of 21 newly established esophageal
cancer cell lines. Cancer. 69:277–284. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tang JC, Wan TS, Wong N, Pang E, Lam KY,
Law SY, Chow LM, Ma ES, Chan LC, Wong J and Srivastava G:
Establishment and characterization of a new xenograft-derived human
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell line SLMT-1 of Chinese
origin. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 124:36–41. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheung LC, Tang JC, Lee PY, Hu L, Guan XY,
Tang WK, Srivastava G, Wong J, Luk JM and Law S: Establishment and
characterization of a new xenograft-derived human esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma cell line HKESC-4 of Chinese origin. Cancer
Genet Cytogenet. 178:17–25. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang H, Jin Y, Chen X, Jin C, Law S, Tsao
SW and Kwong YL: Cytogenetic aberrations in immortalization of
esophageal epithelial cells. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 165:25–35.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Graham FL, Smiley J, Russell WC and Nairn
R: Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from
human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 36:59–74. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou C, Liu S, Zhou X, Xue L, Quan L, Lu
N, Zhang G, Bai J, Wang Y, Liu Z, et al: Overexpression of human
pituitary tumor transforming gene (hPTTG), is regulated by
beta-catenin/TCF pathway in human esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 113:891–898. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kumar S, Bawa S and Gupta H: Biological
activities of quinoline derivatives. Mini Rev Med Chem.
9:1648–1654. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Li S, Shen XY, Ouyang T, Qu Y, Luo T and
Wang HQ: Synergistic anticancer effect of combined crocetin and
cisplatin on KYSE-150 cells via p53/p21 pathway. Cancer Cell Int.
17:982017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cesna V, Sukovas A, Jasukaitiene A,
Naginiene R, Barauskas G, Dambrauskas Z, Paskauskas S and Gulbinas
A: Narrow line between benefit and harm: Additivity of hyperthermia
to cisplatin cytotoxicity in different gastrointestinal cancer
cells. World J Gastroenterol. 24:1072–1083. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kryczka J, Kryczka J, Czarnecka-Chrebelska
KH and Brzeziańska-Lasota E: Molecular mechanisms of
chemoresistance induced by cisplatin in NSCLC cancer therapy. Int J
Mol Sci. 22:88852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Martin L, Blanpain C, Garnier P, Wittamer
V, Parmentier M and Vita C: Structural and functional analysis of
the RANTES-glycosaminoglycans interactions. Biochemistry.
40:6303–6318. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Singh SK, Mishra MK, Rivers BM, Gordetsky
JB, Bae S and Singh R: Biological and clinical significance of the
CCR5/CCL5 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel).
12:8832020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Chen D, Yang K, Mei J, Zhang G, Lv X and
Xiang L: Screening the pathogenic genes and pathways related to
DMBA (7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene)-induced transformation of
hamster oral mucosa from precancerous lesions to squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2:637–642. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
González-Arriagada WA, Coletta RD,
Lozano-Burgos C, García C, Maripillán J, Alcayaga-Miranda F,
Godínez-Pacheco B, Oyarce-Pezoa S, Martínez-Flores R and García IE:
CR5/CCL5 axis is linked to a poor outcome, and inhibition reduces
metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 149:17335–17346. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Karmakar S and Mukherjee R: Integrin
receptors and ECM proteins involved in preferential adhesion of
colon carcinoma cells to lung cells. Cancer Lett. 196:217–227.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Langley RR and Fidler IJ: The seed and
soil hypothesis revisited-the role of tumor-stroma interactions in
metastasis to different organs. Int J Cancer. 128:2527–2535. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang C, Zhou H, Kurboniyon MS, Tang Y, Cai
Z, Ning S, Zhang L and Liang X: Chemodynamic PtMn nanocubes for
effective photothermal ROS storm a key anti-tumor therapy in-vivo.
Int J Nanomedicine. 19:5045–5056. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bordbar-Khiabani A and Gasik M: Smart
hydrogels for advanced drug delivery systems. Int J Mol Sci.
23:36652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|