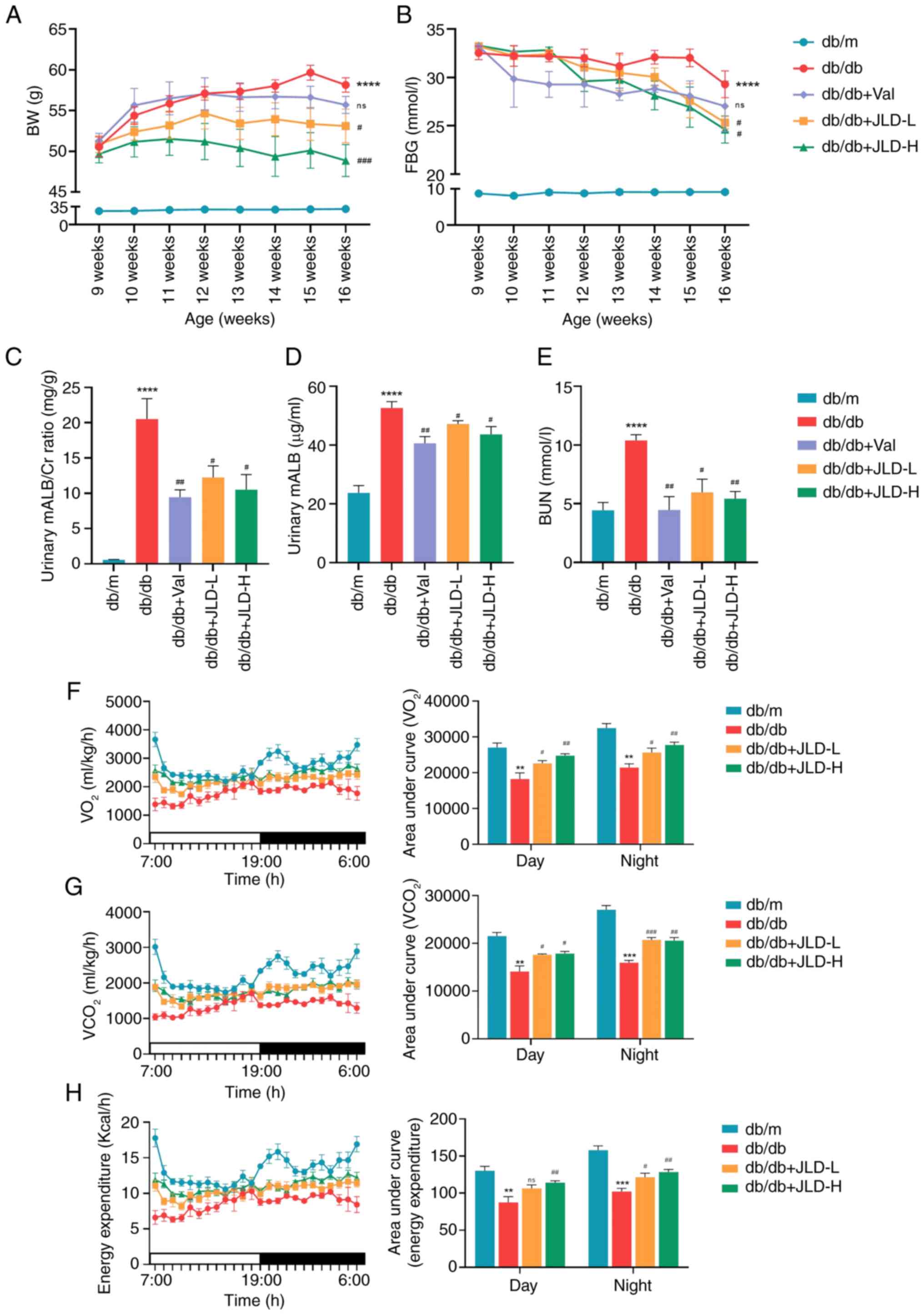
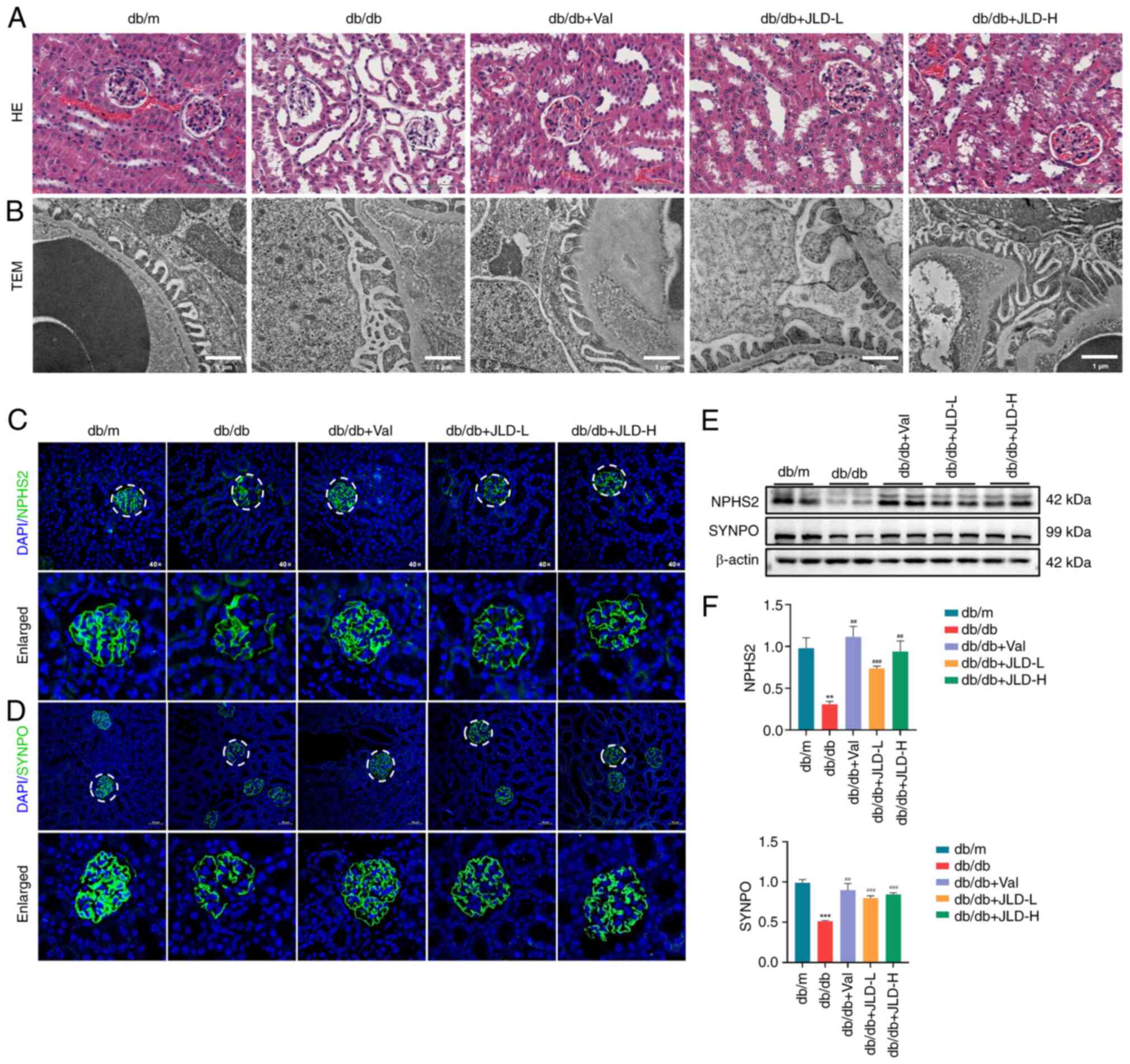
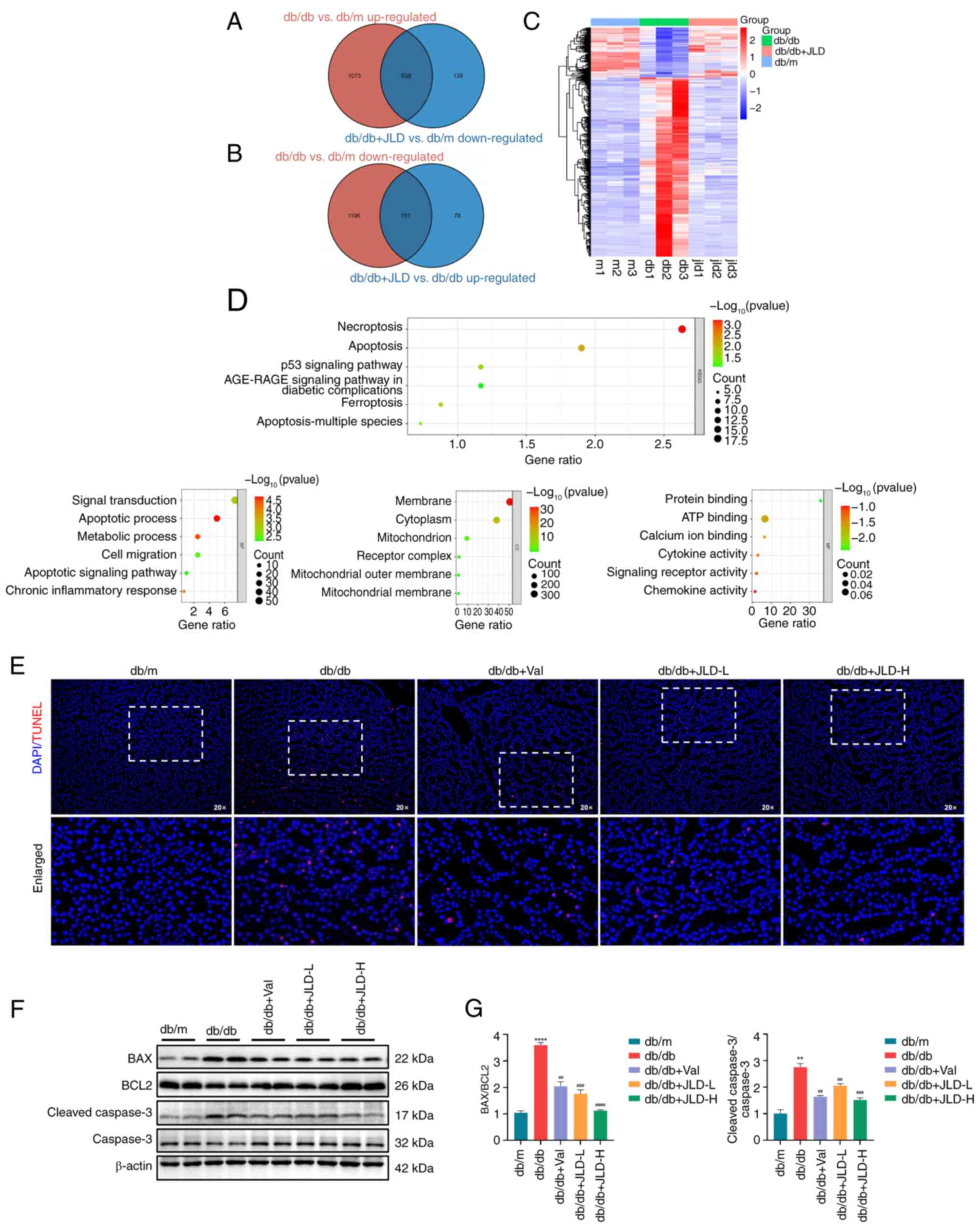
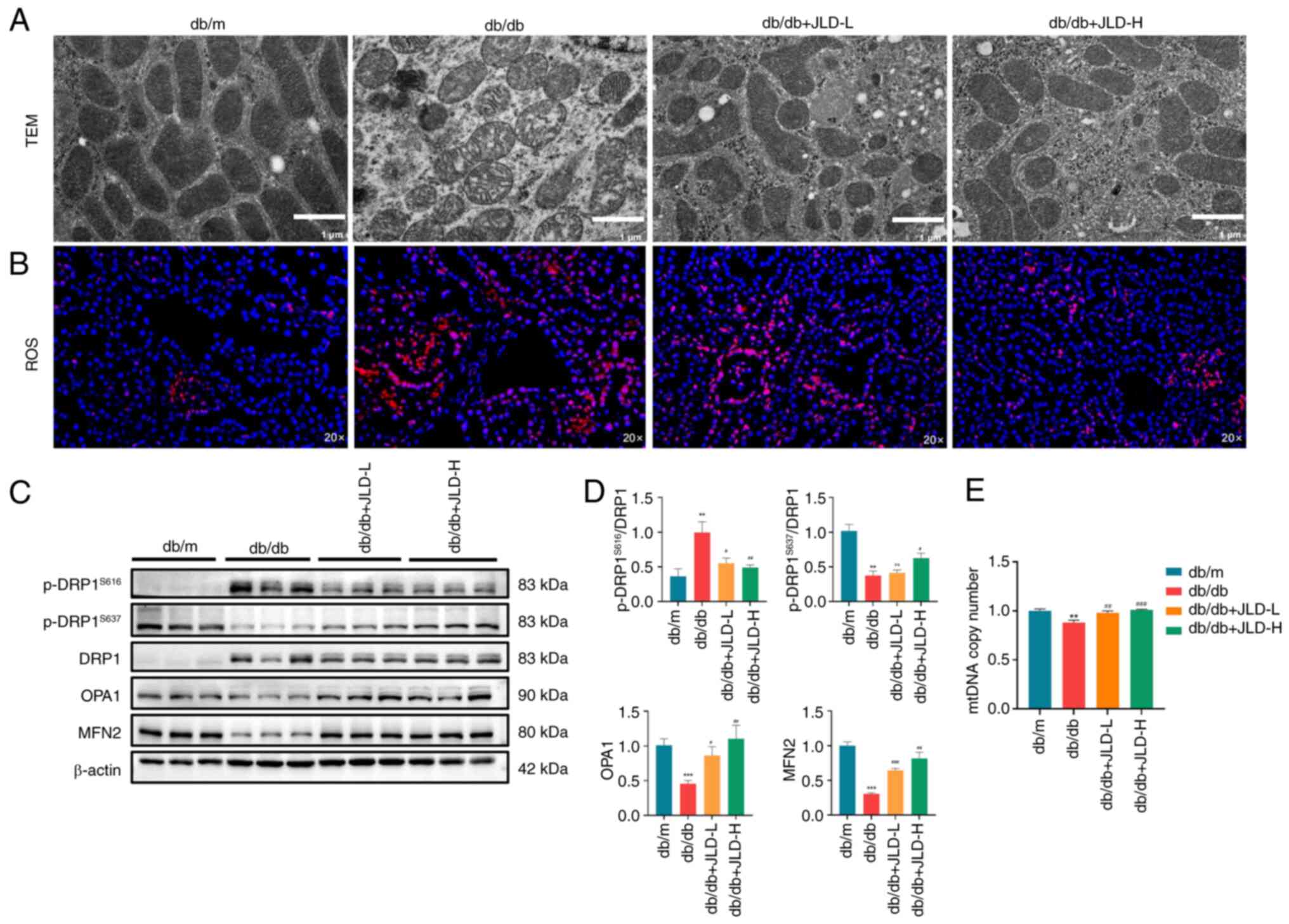
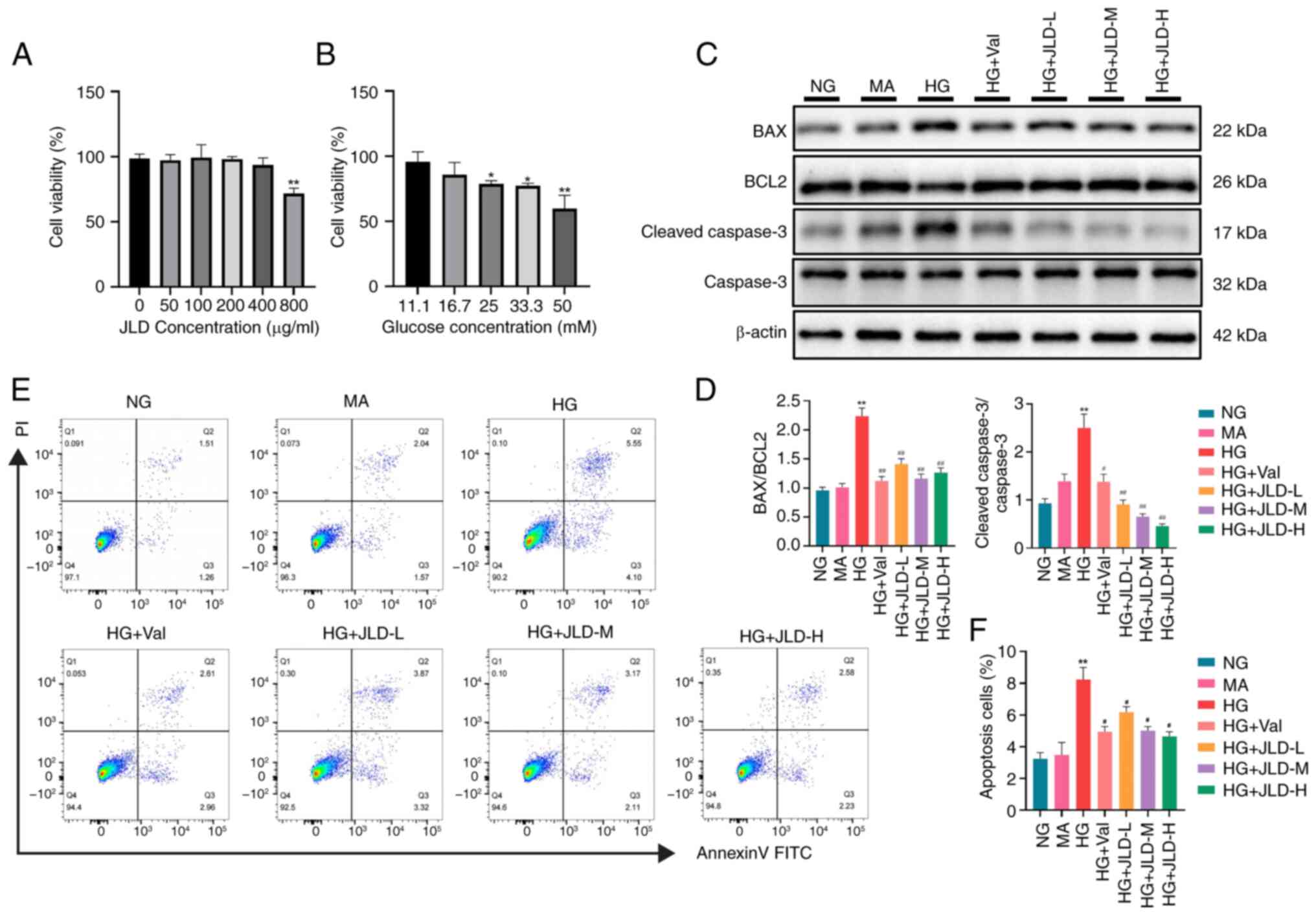
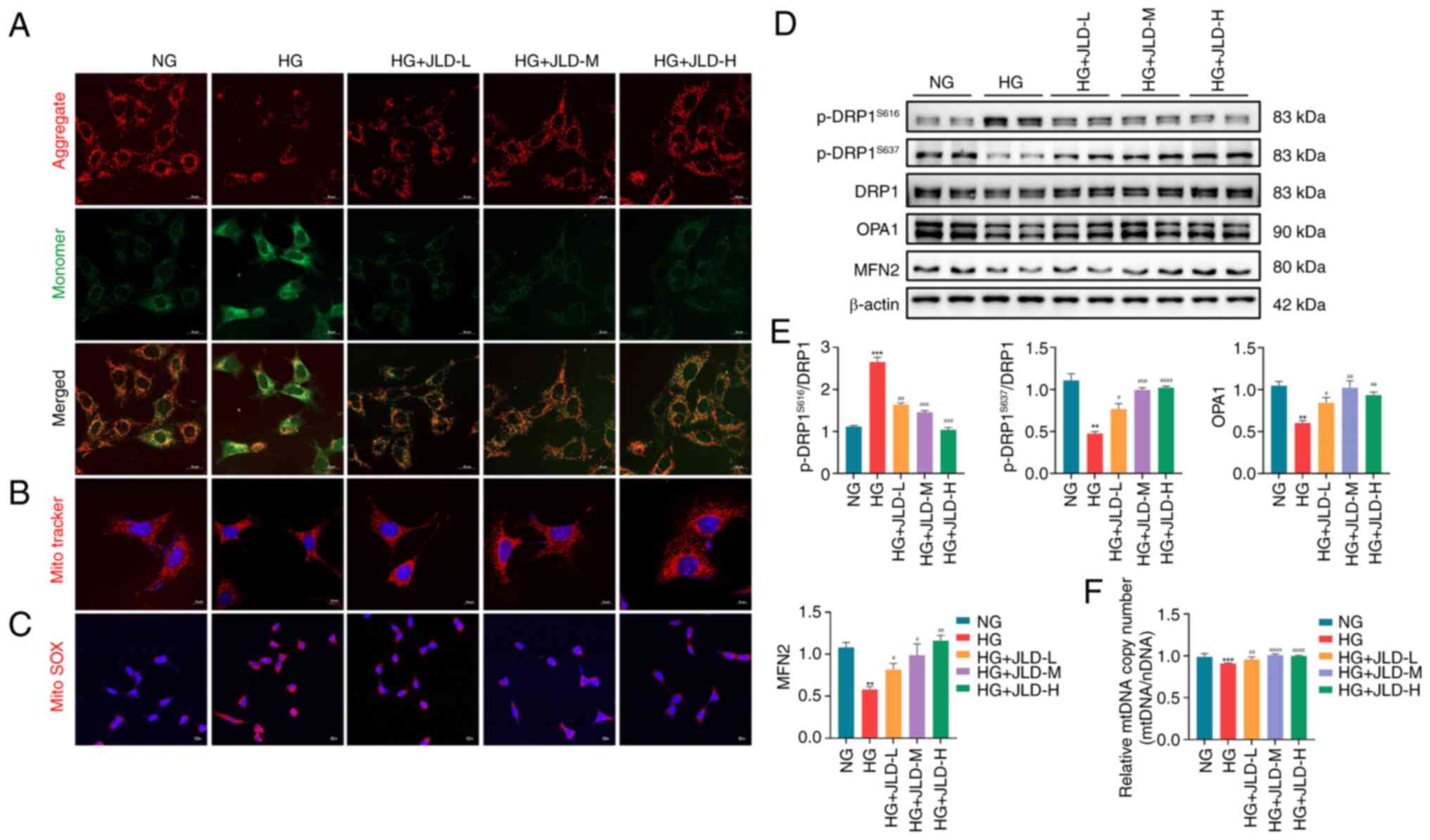
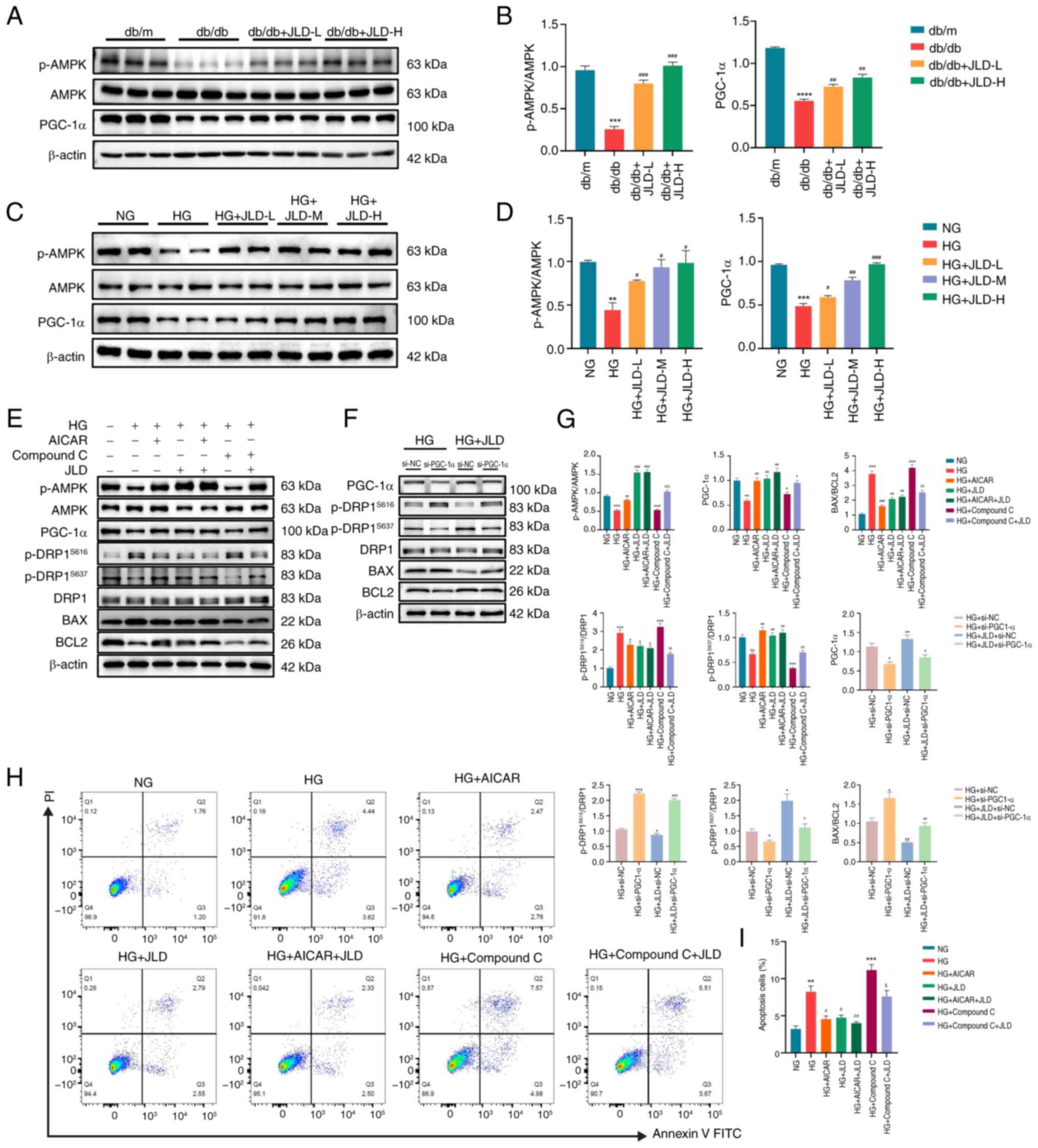
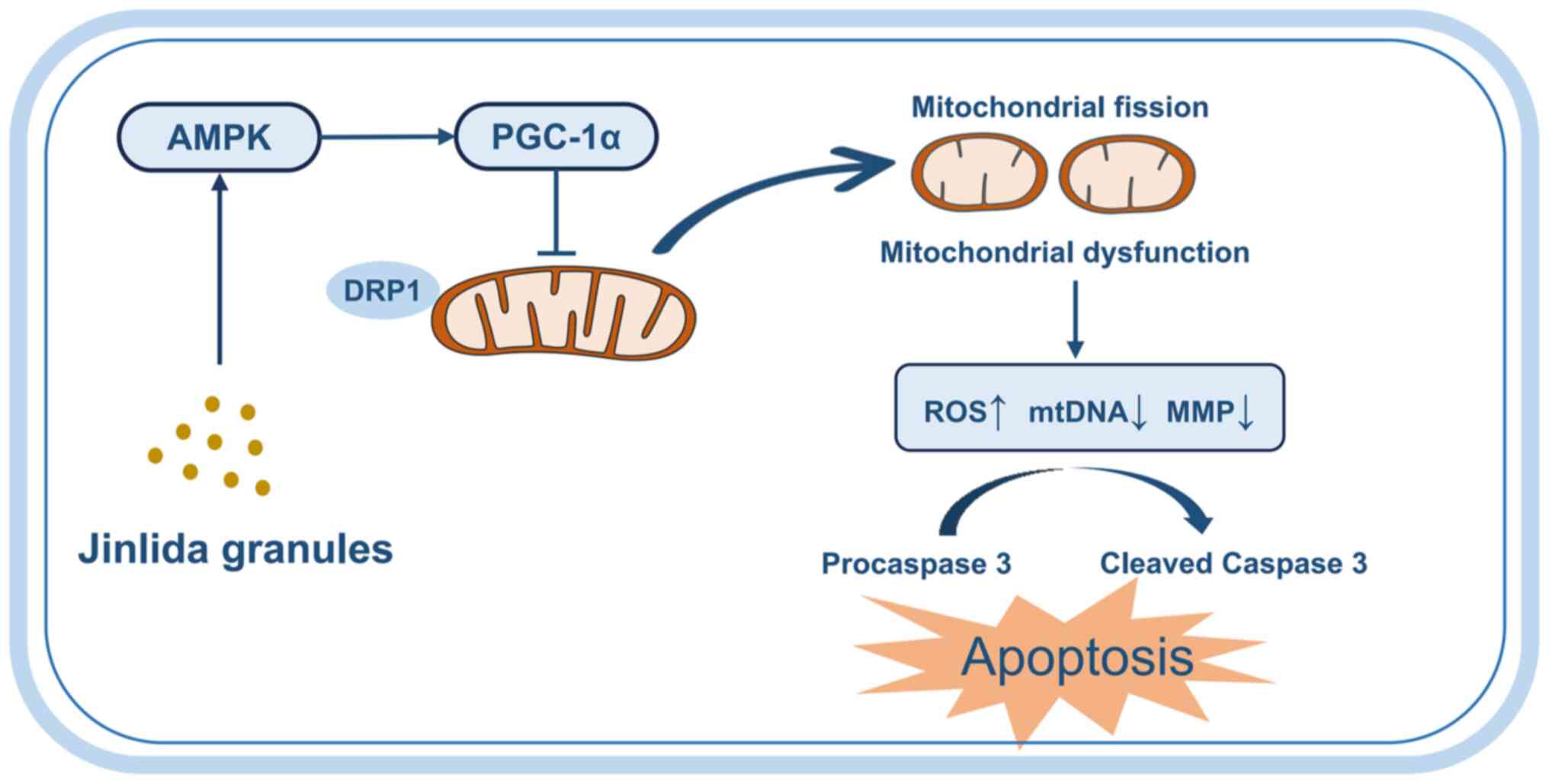
|
1
|
Tuttle KR, Agarwal R, Alpers CE, Bakris
GL, Brosius FC, Kolkhof P and Uribarri J: Molecular mechanisms and
therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int.
102:248–260. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Magliano DJ and Boyko EJ: IDF Diabetes
Atlas 10th edition Scientific Committee: Idf Diabetes Atlas.
International Diabetes Federation © International Diabetes
Federation; Brussels: 2021
|
|
3
|
Cleveland KH and Schnellmann RG:
Pharmacological targeting of mitochondria in diabetic kidney
disease. Pharmacol Rev. 75:250–262. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Petrazzuolo A, Sabiu G, Assi E, Maestroni
A, Pastore I, Lunati ME, Montefusco L, Loretelli C, Rossi G, Nasr
MB, et al: Broadening horizons in mechanisms, management, and
treatment of diabetic kidney disease. Pharmacol Res.
190:1067102023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dimmer KS and Scorrano L: (De)constructing
mitochondria: What for? Physiology (Bethesda). 21:233–241.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bhargava P and Schnellmann RG:
Mitochondrial energetics in the kidney. Nat Rev Nephrol.
13:629–646. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Flemming N, Pernoud L, Forbes J and Gallo
L: Mitochondrial dysfunction in individuals with diabetic kidney
disease: A systematic review. Cells. 11:24812022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Meyer JN, Leuthner TC and Luz AL:
Mitochondrial fusion, fission, and mitochondrial toxicity.
Toxicology. 391:42–53. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mishra P, Carelli V, Manfredi G and Chan
DC: Proteolytic cleavage of Opa1 stimulates mitochondrial inner
membrane fusion and couples fusion to oxidative phosphorylation.
Cell Metab. 19:630–641. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Forbes JM and Thorburn DR: Mitochondrial
dysfunction in diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol.
14:291–312. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang X, Jiang L, Liu XQ, Huang YB, Wang
AL, Zeng HX, Gao L, Zhu QJ, Xia LL and Wu YG: Paeoniflorin binds to
VEGFR2 to restore autophagy and inhibit apoptosis for podocyte
protection in diabetic kidney disease through PI3K-AKT signaling
pathway. Phytomedicine. 106:1544002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gong M, Guo Y, Dong H, Wu F, He Q, Gong J
and Lu F: Modified Hu-lu-ba-wan protects diabetic glomerular
podocytes via promoting PKM2-mediated mitochondrial dynamic
homeostasis. Phytomedicine. 123:1552472024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shen Z, Cui T, Liu Y, Wu S, Han C and Li
J: Astragalus membranaceus and Salvia miltiorrhiza ameliorate
diabetic kidney disease via the 'gut-kidney axis'. Phytomedicine.
121:1551292023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ji H, Zhao X, Chen X, Fang H, Gao H, Wei
G, Zhang M, Kuang H, Yang B, Cai X, et al: Jinlida for diabetes
prevention in impaired glucose tolerance and multiple metabolic
abnormalities: The FOCUS randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern
Med. 184:727–735. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang D, Tian M, Qi Y, Chen G, Xu L, Zou X,
Wang K, Dong H and Lu F: Jinlida granule inhibits palmitic acid
induced-intracellular lipid accumulation and enhances autophagy in
NIT-1 pancreatic β cells through AMPK activation. J Ethnopharmacol.
161:99–107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang H, Hao Y, Wei C, Yao B, Liu S, Zhou
H, Huang D, Zhang C and Wu Y: Chinese medicine Jinlida granules
improve high-fat-diet induced metabolic disorders via activation of
brown adipose tissue in mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 114:1087812019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Susztak K, Raff AC, Schiffer M and
Böttinger EP: Glucose-induced reactive oxygen species cause
apoptosis of podocytes and podocyte depletion at the onset of
diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 55:225–233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Qin X, Zhao Y, Gong J, Huang W, Su H, Yuan
F, Fang K, Wang D, Li J, Zou X, et al: Berberine protects
glomerular podocytes via inhibiting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial
fission and dysfunction. Theranostics. 9:1698–1713. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Steinberg GR and Hardie DG: New insights
into activation and function of the AMPK. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
24:255–272. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Handschin C and Spiegelman BM: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 coactivators,
energy homeostasis, and metabolism. Endocr Rev. 27:728–735. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mohandes S, Doke T, Hu H, Mukhi D, Dhillon
P and Susztak K: Molecular pathways that drive diabetic kidney
disease. J Clin Invest. 133:e1656542023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tervaert TW, Mooyaart AL, Amann K, Cohen
AH, Cook HT, Drachenberg CB, Ferrario F, Fogo AB, Haas M, de Heer
E, et al: Pathologic classification of diabetic nephropathy. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 21:556–563. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mukhi D and Susztak K: The transcriptomic
signature of the aging podocyte. Kidney Int. 98:1079–1081. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu S, Yuan Y, Xue Y, Xing C and Zhang B:
Podocyte injury in diabetic kidney disease: A focus on
mitochondrial dysfunction. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:8328872022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Audzeyenka I, Bierżyńska A and Lay AC:
Podocyte bioenergetics in the development of diabetic nephropathy:
The role of mitochondria. Endocrinology. 163:bqab2342022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Haroon S and Vermulst M: Linking
mitochondrial dynamics to mitochondrial protein quality control.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 38:68–74. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Song M and Dorn GW II: Mitoconfusion:
Noncanonical functioning of dynamism factors in static mitochondria
of the heart. Cell Metab. 21:195–205. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sabouny R and Shutt TE: Reciprocal
regulation of mitochondrial fission and fusion. Trends Biochem Sci.
45:564–577. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu Q, Zhang H, Cortés NG, Wu D, Wang P,
Zhang J, Mattison JA, Smith E, Bettcher LF, Wang M, et al:
Increased Drp1 acetylation by lipid overload induces cardiomyocyte
death and heart dysfunction. Circ Res. 126:456–470. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tilokani L, Nagashima S, Paupe V and
Prudent J: Mitochondrial dynamics: Overview of molecular
mechanisms. Essays Biochem. 62:341–360. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huynh C, Ryu J, Lee J, Inoki A and Inoki
K: Nutrient-sensing mTORC1 and AMPK pathways in chronic kidney
diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. 19:102–122. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Juszczak F, Caron N, Mathew AV and
Declèves AE: Critical role for AMPK in metabolic disease-induced
chronic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci. 21:79942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rogacka D, Audzeyenka I and Piwkowska A:
Regulation of podocytes function by AMP-activated protein kinase.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 692:1085412020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Eid AA, Ford BM, Bhandary B, de Cassia
Cavaglieri R, Block K, Barnes JL, Gorin Y, Choudhury GG and Abboud
HE: Mammalian target of rapamycin regulates Nox4-mediated podocyte
depletion in diabetic renal injury. Diabetes. 62:2935–2947. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li SY and Susztak K: The role of
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α
(PGC-1α) in kidney disease. Semin Nephrol. 38:121–126. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fontecha-Barriuso M, Lopez-Diaz AM,
Guerrero-Mauvecin J, Miguel V, Ramos AM, Sanchez-Niño MD,
Ruiz-Ortega M, Ortiz A and Sanz AB: Tubular mitochondrial
dysfunction, oxidative stress, and progression of chronic kidney
disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 11:13562022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Halling JF and Pilegaard H:
PGC-1α-mediated regulation of mitochondrial function and
physiological implications. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 45:927–936.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu H, Deng X, Shi Y, Su Y, Wei J and Duan
H: PGC-1α, glucose metabolism and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J
Endocrinol. 229:R99–R115. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ji JL, Li JY, Liang JX, Zhou Y, Liu CC,
Zhang Y, Zhang AQ, Liu H, Ma RX and Li ZL: Tubular TMEM16A promotes
tubulointerstitial fibrosis by suppressing PGC-1α-mediated
mitochondrial homeostasis in diabetic kidney disease. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 80:3472023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Fontecha-Barriuso M, Martin-Sanchez D,
Martinez-Moreno JM, Monsalve M, Ramos AM, Sanchez-Niño MD,
Ruiz-Ortega M, Ortiz A and Sanz AB: The role of PGC-1α and
mitochondrial biogenesis in kidney diseases. Biomolecules.
10:3472020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hou S, Zhang T, Li Y, Guo F and Jin X:
Glycyrrhizic acid prevents diabetic nephropathy by activating
AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling in db/db Mice. J Diabetes Res.
2017:28659122017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Dugan LL, You YH, Ali SS, Diamond-Stanic
M, Miyamoto S, DeCleves AE, Andreyev A, Quach T, Ly S, Shekhtman G,
et al: AMPK dysregulation promotes diabetes-related reduction of
superoxide and mitochondrial function. J Clin Invest.
123:4888–4899. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gu H, Zhong L, Zhang Y, Sun J, Liu L and
Liu Z: Exploring the mechanism of Jinlida granules against type 2
diabetes mellitus by an integrative pharmacology strategy. Sci Rep.
14:102862024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu Y, Li Y, Xu L, Shi J, Yu X, Wang X, Li
X, Jiang H, Yang T, Yin X, et al: Quercetin attenuates podocyte
apoptosis of diabetic nephropathy through targeting EGFR signaling.
Front Pharmacol. 12:7927772022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
He JY, Hong Q, Chen BX, Cui SY, Liu R, Cai
GY, Guo J and Chen XM: Ginsenoside Rb1 alleviates diabetic kidney
podocyte injury by inhibiting aldose reductase activity. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 43:342–353. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Li X, Wang J, Yan J, He JC, Li Y and Zhong
Y: Additive renal protective effects between arctigenin and
puerarin in diabetic kidney disease. Biomed Pharmacother.
171:1161072024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|