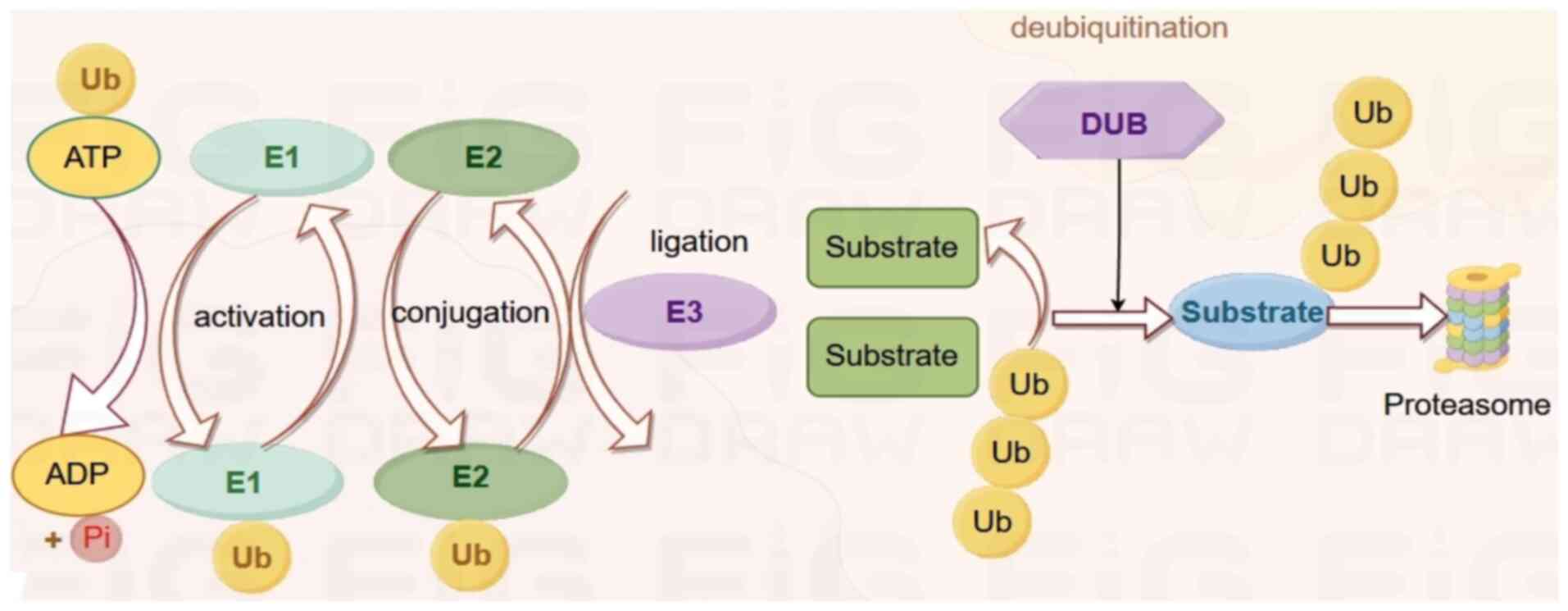
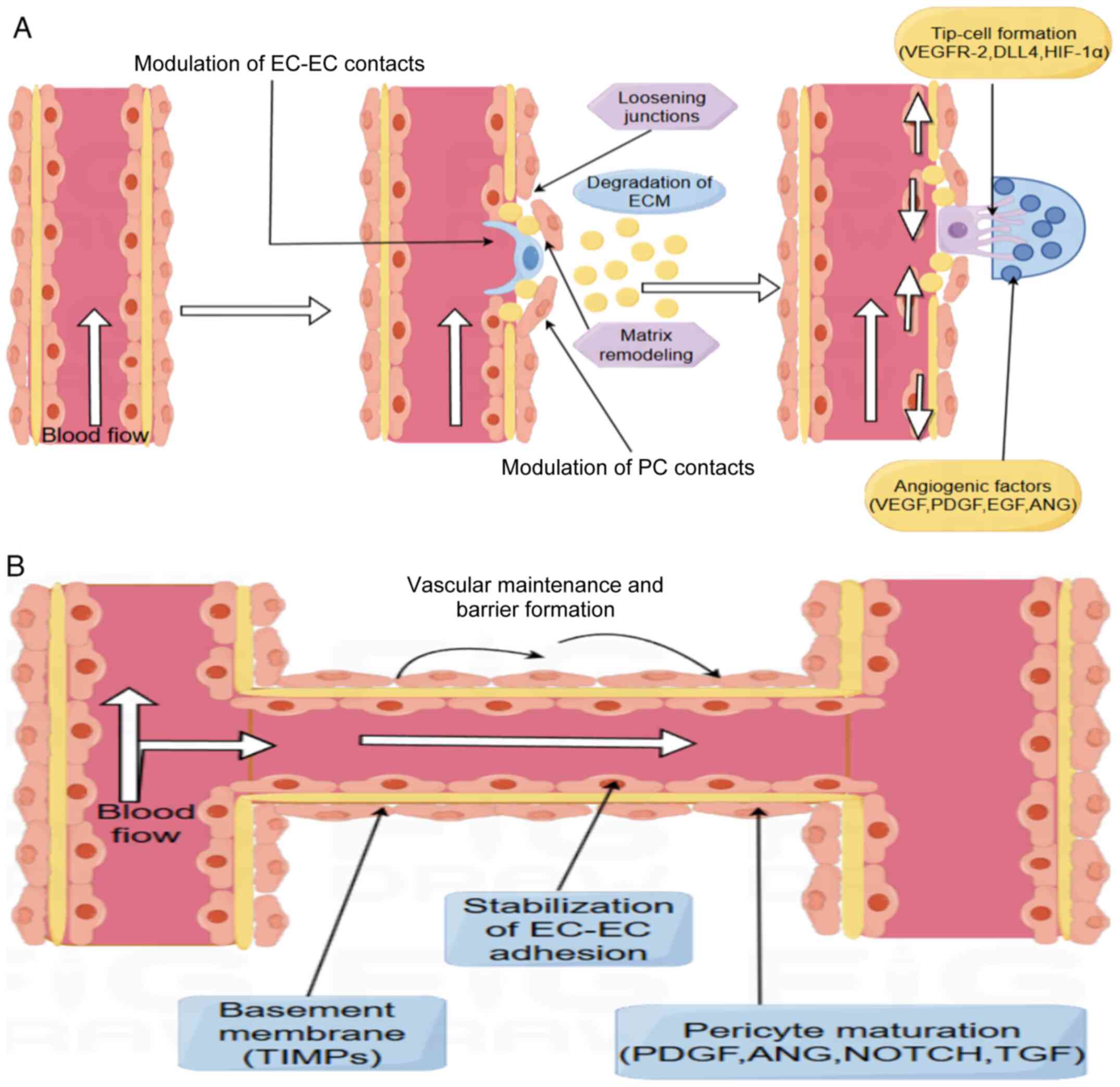
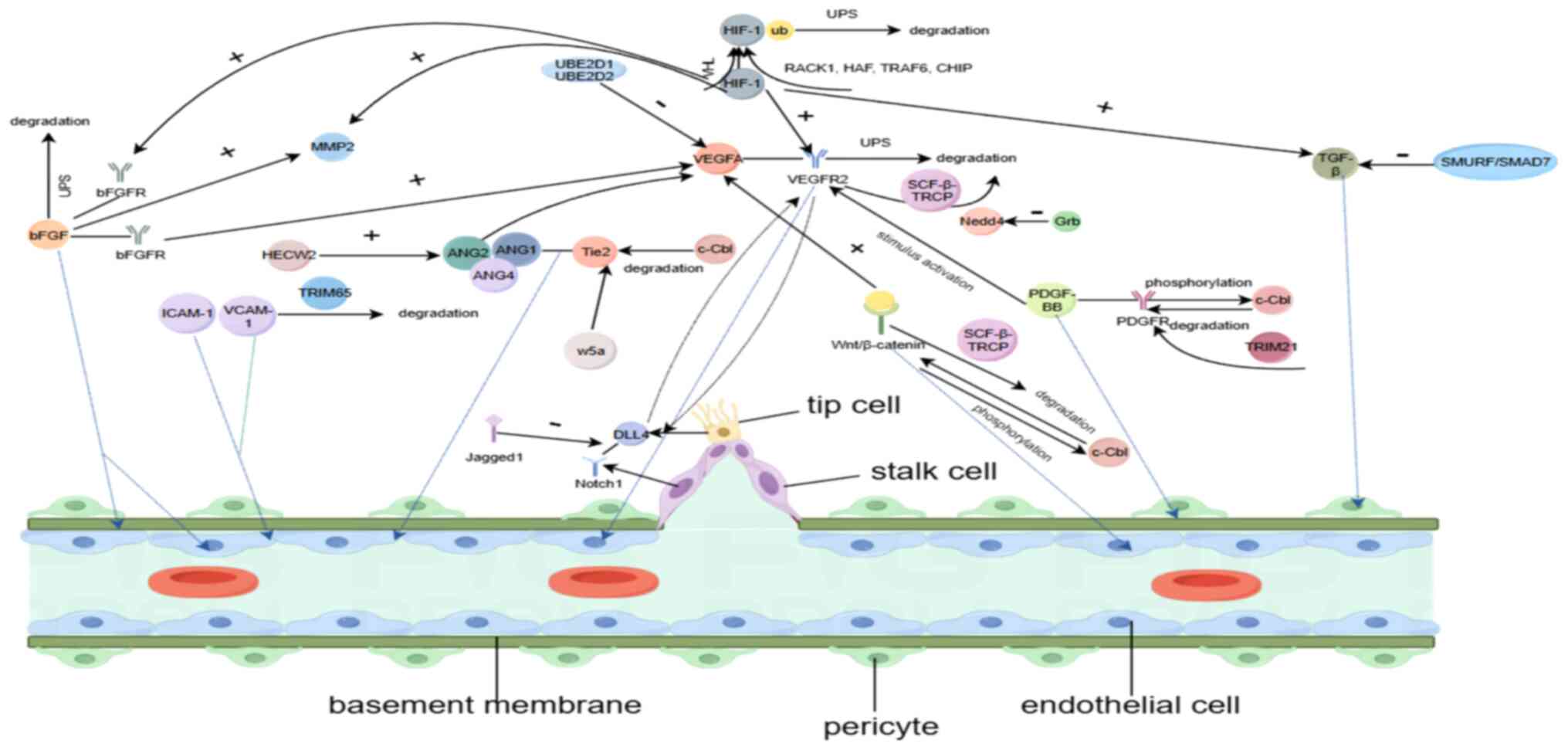
|
1
|
Qin W, Steinek C, Kolobynina K, Forné I,
Imhof A, Cardoso MC and Leonhardt H: Probing protein ubiquitination
in live cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 50:e1252022.
|
|
2
|
Popovic D, Vucic D and Dikic I:
Ubiquitination in disease pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Med.
20:1242–1253. 2014.
|
|
3
|
Xu G and Jaffrey SR: The new landscape of
protein ubiquitination. Nat Biotechnol. 29:1098–1100. 2011.
|
|
4
|
Lacoursiere RE, Hadi D and Shaw GS:
Acetylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination (Oh My!): Following
post-translational modifications on the ubiquitin road.
Biomolecules. 12:4672022.
|
|
5
|
Rape M: Ubiquitylation at the crossroads
of development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 19:59–70.
2018.
|
|
6
|
Rieger J, Kaessmeyer S, Al Masri S,
Hünigen H and Plendl J: Endothelial cells and angiogenesis in the
horse in health and disease-A review. Anat Histol Embryol.
49:656–678. 2020.
|
|
7
|
Akbarian M, Bertassoni LE and Tayebi L:
Biological aspects in controlling angiogenesis: current progress.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 79:3492022.
|
|
8
|
Francescone R and Vendramini-Costa DB: In
vitro models to study angiogenesis and vasculature. Methods Mol
Biol. 2514:15–28. 2022.
|
|
9
|
Ahmad A and Nawaz MI: Molecular mechanism
of VEGF and its role in pathological angiogenesis. J Cell Biochem.
123:1938–1965. 2022.
|
|
10
|
Mezu-Ndubuisi OJ and Maheshwari A: The
role of integrins in inflammation and angiogenesis. Pediatr Res.
89:1619–1626. 2021.
|
|
11
|
Li W, Wen L, Rathod B, Gingras AC, Ley K
and Lee HS: Kindlin2 enables EphB/ephrinB bi-directional signaling
to support vascular development. Life Sci Alliance.
6:e2022018002022.
|
|
12
|
Rabquer BJ, Amin MA, Teegala N, Shaheen
MK, Tsou PS, Ruth JH, Lesch CA, Imhof BA and Koch AE: Junctional
adhesion molecule-C is a soluble mediator of angiogenesis. J
Immunol. 185:1777–1785. 2010.
|
|
13
|
Rizzi A, Benagiano V and Ribatti D:
Angiogenesis versus arteriogenesis. Rom J Morphol Embryol.
58:15–19. 2017.
|
|
14
|
Ashraf JV and Al Haj Zen A: Role of
vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype switching in arteriogenesis.
Int J Mol Sci. 22:105852021.
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, Yang Y, Wang Z, Fu X, Chu XM, Li Y,
Wang Q, He X, Li M, Wang K, et al: Insights into the regulatory
role of circRNA in angiogenesis and clinical implications.
Atherosclerosis. 298:14–26. 2020.
|
|
16
|
Lugano R, Ramachandran M and Dimberg A:
Tumor angiogenesis: Causes, consequences, challenges and
opportunities. Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:1745–1770. 2020.
|
|
17
|
Liu ZL, Chen HH, Zheng LL, Sun LP and Shi
L: Angiogenic signaling pathways and anti-angiogenic therapy for
cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:1982023.
|
|
18
|
Anderson NM and Simon MC: The tumor
microenvironment. Curr Biol. 30:R921–R925. 2020.
|
|
19
|
Maxwell PH and Ratcliffe PJ: Oxygen
sensors and angiogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 13:29–37. 2002.
|
|
20
|
Bui QT, Hong JH, Kwak M, Lee JY and Lee
PC: Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes in cancer. Cells.
10:13832021.
|
|
21
|
Omorphos NP, Gao C, Tan SS and Sangha MS:
Understanding angiogenesis and the role of angiogenic growth
factors in the vascularization of engineered tissues. Mol Biol Rep.
48:941–950. 2021.
|
|
22
|
Hicklin DJ and Ellis LM: Role of the
vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and
angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 23:1011–1027. 2005.
|
|
23
|
Ferrara N: Vascular endothelial growth
factor: Basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev.
25:581–611. 2004.
|
|
24
|
Shah AA, Kamal MA and Akhtar S: Tumor
Angiogenesis and VEGFR-2: Mechanism, pathways and current
biological therapeutic interventions. Curr Drug Metab. 22:50–59.
2021.
|
|
25
|
Rahimi N and Costello CE: Emerging roles
of post-translational modifications in signal transduction and
angiogenesis. Proteomics. 15:300–309. 2015.
|
|
26
|
Rahimi N: The ubiquitin-proteasome system
meets angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:538–548. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Han D, Wang L, Jiang S and Yang Q: The
ubiquitin-proteasome system in breast cancer. Trends Mol Med.
29:599–621. 2023.
|
|
28
|
Meissner M, Reichenbach G, Stein M,
Hrgovic I, Kaufmann R and Gille J: Down-regulation of vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor 2 is a major molecular
determinant of proteasome inhibitor-mediated antiangiogenic action
in endothelial cells. Cancer Res. 69:1976–1984. 2009.
|
|
29
|
Meyer RD, Srinivasan S, Singh AJ, Mahoney
JE, Gharahassanlou KR and Rahimi N: PEST motif serine and tyrosine
phosphorylation controls vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor 2 stability and downregulation. Mol Cell Biol.
31:2010–2025. 2011.
|
|
30
|
Xu D, Wu J, Dong L, Luo W, Li L, Tang D
and Liu J: Serpinc1 acts as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular
carcinoma through inducing apoptosis and blocking macrophage
polarization in an ubiquitin-proteasome manner. Front Oncol.
11:7386072021.
|
|
31
|
Wiszniak S and Schwarz Q: Exploring the
intracrine functions of VEGF-A. Biomolecules. 11:1282021.
|
|
32
|
Wang Y and Yang C: Enhanced VEGF-A
expression and mediated angiogenic differentiation in human
gingival fibroblasts by stimulating with TNF-α in vitro. J Dent
Sci. 17:876–881. 2022.
|
|
33
|
Watari K, Shibata T, Fujita H, Shinoda A,
Murakami Y, Abe H, Kawahara A, Ito H, Akiba J, Yoshida S, et al:
NDRG1 activates VEGF-A-induced angiogenesis through PLCγ1/ERK
signaling in mouse vascular endothelial cells. Commun Biol.
3:1072020.
|
|
34
|
Husain A, Khadka A, Ehrlicher A,
Saint-Geniez M and Krishnan R: Substrate stiffening promotes VEGF-A
functions via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 586:27–33. 2022.
|
|
35
|
Critchley WR, Smith GA, Zachary IC,
Harrison MA and Ponnambalam S: The E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes
UBE2D1 and UBE2D2 regulate VEGFR2 dynamics and endothelial
function. J Cell Sci. 136:jcs2606572023.
|
|
36
|
Smith GA, Fearnley GW, Abdul-Zani I,
Wheatcroft SB, Tomlinson DC, Harrison MA and Ponnambalam S:
Ubiquitination of basal VEGFR2 regulates signal transduction and
endothelial function. Biol Open. 6:1404–1415. 2017.
|
|
37
|
Murakami T, Felinski EA and Antonetti DA:
Occludin phosphorylation and ubiquitination regulate tight junction
trafficking and vascular endothelial growth factor-induced
permeability. J Biol Chem. 284:21036–21046. 2009.
|
|
38
|
Shaik S, Nucera C, Inuzuka H, Gao D,
Garnaas M, Frechette G, Harris L, Wan L, Fukushima H, Husain A, et
al: SCF(β-TRCP) suppresses angiogenesis and thyroid cancer cell
migration by promoting ubiquitination and destruction of VEGF
receptor 2. J Exp Med. 209:1289–1307. 2012.
|
|
39
|
Tian X, Chen Y, Peng Z, Lin Q and Sun A:
NEDD4 E3 ubiquitin ligases: Promising biomarkers and therapeutic
targets for cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 214:1156412023.
|
|
40
|
Murdaca J, Treins C, Monthouël-Kartmann
MN, Pontier-Bres R, Kumar S, Van Obberghen E and Giorgetti-Peraldi
S: Grb10 prevents Nedd4-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor-2 degradation. J Biol Chem. 279:26754–26761. 2004.
|
|
41
|
Wu R, Gandhi S, Tokumaru Y, Asaoka M, Oshi
M, Yan L, Ishikawa T and Takabe K: Intratumoral PDGFB gene
predominantly expressed in endothelial cells is associated with
angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis, but not with metastasis in
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 195:17–31. 2022.
|
|
42
|
Liu W, Guo S, Tang Z, Wei X, Gao P, Wang
N, Li X and Guo Z: Magnesium promotes bone formation and
angiogenesis by enhancing MC3T3-E1 secretion of PDGF-BB. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 528:664–670. 2020.
|
|
43
|
Kim DY, Park G, Hong HS, Kim S and Son Y:
Platelet-derived growth factor-BB priming enhances vasculogenic
capacity of bone marrow-derived endothelial precursor like cells.
Tissue Eng Regen Med. 20:695–704. 2023.
|
|
44
|
Pinilla-Macua I and Sorkin A: Cbl and
Cbl-b independently regulate EGFR through distinct receptor
interaction modes. Mol Biol Cell. 34:ar1342023.
|
|
45
|
Tang R, Langdon WY and Zhang J: Negative
regulation of receptor tyrosine kinases by ubiquitination: Key
roles of the Cbl family of E3 ubiquitin ligases. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 13:9711622022.
|
|
46
|
Rorsman C, Tsioumpekou M, Heldin CH and
Lennartsson J: The ubiquitin ligases c-Cbl and Cbl-b negatively
regulate platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) BB-induced
chemotaxis by affecting PDGF receptor β (PDGFRβ) internalization
and signaling. J Biol Chem. 291:11608–11618. 2016.
|
|
47
|
Wang K, Papadopoulos N, Hamidi A,
Lennartsson J and Heldin CH: SUMOylation of PDGF receptor α affects
signaling via PLCγ and STAT3, and cell proliferation. BMC Mol Cell
Biol. 24:192023.
|
|
48
|
Tsioumpekou M, Cunha SI, Ma H, Åhgren A,
Cedervall J, Olsson AK, Heldin CH and Lennartsson J: Specific
targeting of PDGFRβ in the stroma inhibits growth and angiogenesis
in tumors with high PDGF-BB expression. Theranostics. 10:1122–1135.
2020.
|
|
49
|
Lv F, Li X and Wang Y: Lycorine inhibits
angiogenesis by docking to PDGFRα. BMC Cancer. 22:8732022.
|
|
50
|
Sang BT, Wang CD, Liu X, Guo JQ, Lai JY
and Wu XM: PDGF-BB/PDGFRβ induces tumour angiogenesis via enhancing
PKM2 mediated by the PI3K/AKT pathway in Wilms' tumour. Med Oncol.
40:2402023.
|
|
51
|
Miyake S, Lupher ML Jr, Druker B and Band
H: The tyrosine kinase regulator Cbl enhances the ubiquitination
and degradation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor
alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:7927–7932. 1998.
|
|
52
|
Hatakeyama S: TRIM family proteins: Roles
in autophagy, immunity, and carcinogenesis. Trends Biochem Sci.
42:297–311. 2017.
|
|
53
|
Sarri N, Papadopoulos N, Lennartsson J and
Heldin CH: The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM21 regulates basal levels of
PDGFRβ. Int J Mol Sci. 24:77822023.
|
|
54
|
Zahra FT, Sajib MS and Mikelis CM: Role of
bFGF in acquired resistance upon anti-VEGF therapy in cancer.
Cancers (Basel). Cancer (Basel). 13:14222021.
|
|
55
|
Lei X, Li Z, Huang M, Huang L, Huang Y, Lv
S, Zhang W, Chen Z, Ke Y, Li S, et al: Gli1-mediated tumor
cell-derived bFGF promotes tumor angiogenesis and pericyte coverage
in non-small cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
43:832024.
|
|
56
|
Przybylski M: A review of the current
research on the role of bFGF and VEGF in angiogenesis. J Wound
Care. 18:516–519. 2009.
|
|
57
|
Li L, Ma Q, Mou J, Wang M, Ye J and Sun G:
Basic fibroblast growth factor gel preparation induces angiogenesis
during wound healing. Int J Artif Organs. 46:171–181. 2023.
|
|
58
|
Yu Y, Chen Y, Zheng YJ, Weng QH, Zhu SP
and Zhou DS: LncRNA TUG1 promoted osteogenic differentiation
through promoting bFGF ubiquitination. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.
56:42–48. 2020.
|
|
59
|
Sukhthankar M, Yamaguchi K, Lee SH,
McEntee MF, Eling TE, Hara Y and Baek SJ: A green tea component
suppresses post-translational expression of basic fibroblast growth
factor in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 134:1972–1980.
2008.
|
|
60
|
Wang R, Ma Y, Zhan S, Zhang G, Cao L,
Zhang X, Shi T and Chen W: B7-H3 promotes colorectal cancer
angiogenesis through activating the NF-κB pathway to induce VEGFA
expression. Cell Death Dis. 11:552020.
|
|
61
|
Xiong Z, Xu X, Zhang Y, Ma C, Hou C, You
Z, Shu L, Ke Y and Liu Y: IFITM3 promotes glioblastoma stem
cell-mediated angiogenesis via regulating JAK/STAT3/bFGF signaling
pathway. Cell Death Dis. 15:452024.
|
|
62
|
Akwii RG, Sajib MS, Zahra FT and Mikelis
CM: Role of Angiopoietin-2 in vascular physiology and
pathophysiology. Cells. 8:4712019.
|
|
63
|
Skóra JP, Antkiewicz M, Kupczyńska D,
Kulikowska K, Strzelec B, Janczak D and Barć P: Local intramuscular
administration of ANG1 and VEGF genes using plasmid vectors
mobilizes CD34+ cells to peripheral tissues and promotes
angiogenesis in an animal model. Biomed Pharmacother.
143:1121862021.
|
|
64
|
Zhou H, Chen T, Li Y, You J, Deng X, Chen
N, Li T, Zheng Y, Li R, Luo M, et al: Glycation of Tie-2 inhibits
angiopoietin-1 signaling activation and angiopoietin-1-induced
angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 23:71372022.
|
|
65
|
Pan L, Liu Z, Chen Y, Yang B and Cheng B:
Angiopoietin-1: Can be produced by endothelial cells and act in an
autocrine agonistic manner? Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 74:341–345.
2020.
|
|
66
|
Scholz A, Plate KH and Reiss Y:
Angiopoietin-2: A multifaceted cytokine that functions in both
angiogenesis and inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1347:45–51.
2015.
|
|
67
|
Felcht M, Luck R, Schering A, Seidel P,
Srivastava K, Hu J, Bartol A, Kienast Y, Vettel C, Loos EK, et al:
Angiopoietin-2 differentially regulates angiogenesis through TIE2
and integrin signaling. J Clin Invest. 122:1991–2005. 2012.
|
|
68
|
Vimalraj S: A concise review of VEGF,
PDGF, FGF, Notch, angiopoietin, and HGF signalling in tumor
angiogenesis with a focus on alternative approaches and future
directions. Int J Biol Macromol. 221:1428–1438. 2022.
|
|
69
|
Chaube B, Citrin KM, Sahraei M, Singh AK,
de Urturi DS, Ding W, Pierce RW, Raaisa R, Cardone R, Kibbey R, et
al: Suppression of angiopoietin-like 4 reprograms endothelial cell
metabolism and inhibits angiogenesis. Nat Commun. 14:82512023.
|
|
70
|
Thien CB and Langdon WY: Negative
regulation of PTK signalling by Cbl proteins. Growth Factors.
23:161–167. 2005.
|
|
71
|
Mohapatra B, Ahmad G, Nadeau S, Zutshi N,
An W, Scheffe S, Dong L, Feng D, Goetz B, Arya P, et al: Protein
tyrosine kinase regulation by ubiquitination: critical roles of
Cbl-family ubiquitin ligases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:122–139.
2013.
|
|
72
|
Wehrle C, Van Slyke P and Dumont DJ:
Angiopoietin-1-induced ubiquitylation of Tie2 by c-Cbl is required
for internalization and degradation. Biochem J. 423:375–380.
2009.
|
|
73
|
Augustin HG, Koh GY, Thurston G and
Alitalo K: Control of vascular morphogenesis and homeostasis
through the angiopoietin-Tie system. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
10:165–177. 2009.
|
|
74
|
Choi KS, Choi HJ, Lee JK, Im S, Zhang H,
Jeong Y, Park JA, Lee IK, Kim YM and Kwon YG: The endothelial E3
ligase HECW2 promotes endothelial cell junctions by increasing
AMOTL1 protein stability via K63-linked ubiquitination. Cell
Signal. 28:1642–1651. 2016.
|
|
75
|
Chiaverina G, di Blasio L, Monica V,
Accardo M, Palmiero M, Peracino B, Vara-Messler M, Puliafito A and
Primo L: Dynamic interplay between pericytes and endothelial cells
during sprouting angiogenesis. Cells. 8:11092019.
|
|
76
|
Armulik A, Genové G and Betsholtz C:
Pericytes: Developmental, physiological, and pathological
perspectives, problems, and promises. Dev Cell. 21:193–215.
2011.
|
|
77
|
Lee HW, Xu Y, He L, Choi W, Gonzalez D,
Jin SW and Simons M: Role of venous endothelial cells in
developmental and pathologic angiogenesis. Circulation.
144:1308–1322. 2021.
|
|
78
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Molecular
mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature.
473:298–307. 2011.
|
|
79
|
van Splunder H, Villacampa P,
Martínez-Romero A and Graupera M: Pericytes in the disease
spotlight. Trends Cell Biol. 34:58–71. 2024.
|
|
80
|
Rustenhoven J, Jansson D, Smyth LC and
Dragunow M: Brain pericytes as mediators of neuroinflammation.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 38:291–304. 2017.
|
|
81
|
Stevenson TJ, Johnson RH, Savistchenko J,
Rustenhoven J, Woolf Z, Smyth LCD, Murray HC, Faull RLM, Correia J,
Schweder P, et al: Pericytes take up and degrade α-synuclein but
succumb to apoptosis under cellular stress. Sci Rep.
12:173142022.
|
|
82
|
Chen CJ, Ou YC, Li JR, Chang CY, Pan HC,
Lai CY, Liao SL, Raung SL and Chang CJ: Infection of pericytes in
vitro by Japanese encephalitis virus disrupts the integrity of the
endothelial barrier. J Virol. 88:1150–1161. 2014.
|
|
83
|
Yang X, Chang L, Liu Z, Geng X, Wang R,
Yin X, Fan W and Zhao BQ: Neddylation in the chronically
hypoperfused corpus callosum: MLN4924 reduces blood-brain barrier
injury via ERK5/KLF2 signaling. Exp Neurol. 371:1145872024.
|
|
84
|
Huang F, Feng Y, Peterlin BM and Fujinaga
K: P-TEFb is degraded by Siah1/2 in quiescent cells. Nucleic Acids
Res. 50:5000–5013. 2022.
|
|
85
|
Suarez S, McCollum GW, Jayagopal A and
Penn JS: High glucose-induced retinal pericyte apoptosis depends on
association of GAPDH and Siah1. J Biol Chem. 290:28311–28320.
2015.
|
|
86
|
Liu C, Billadeau DD, Abdelhakim H, Leof E,
Kaibuchi K, Bernabeu C, Bloom GS, Yang L, Boardman L, Shah VH and
Kang N: IQGAP1 suppresses TβRII-mediated myofibroblastic activation
and metastatic growth in liver. J Clin Invest. 123:1138–1156.
2013.
|
|
87
|
Mosaddeghzadeh N and Ahmadian MR: The RHO
family GTPases: mechanisms of regulation and signaling. Cells.
10:18312021.
|
|
88
|
Majolée J, Kovačević I and Hordijk PL:
Ubiquitin-based modifications in endothelial cell-cell contact and
inflammation. J Cell Sci. 132:jcs2277282019.
|
|
89
|
Majolée J, Podieh F, Hordijk PL and
Kovačević I: The interplay of Rac1 activity, ubiquitination and GDI
binding and its consequences for endothelial cell spreading. PLoS
One. 16:e02543862021.
|
|
90
|
Jin Q, Lin L, Zhao T, Yao X, Teng Y, Zhang
D, Jin Y and Yang M: Overexpression of E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl
attenuates endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus by
inhibiting the JAK2/STAT4 signaling and Runx3-mediated H3K4me3. J
Transl Med. 19:4692021.
|
|
91
|
Qian H, Zhang N, Wu B, Wu S, You S, Zhang
Y and Sun Y: The E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 regulates PARP1
stability to alleviate oxidative stress-induced injury in human
umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Cell Mol Med. 24:4600–4611.
2020.
|
|
92
|
Zou J, Zhou L, Le Y, Fang Z, Zhong M, Nie
F, Wei X, Zhang X, Chen Z, Cai L, et al: WWP2 drives the
progression of gastric cancer by facilitating the ubiquitination
and degradation of LATS1 protein. Cell Commun. Signal.
21:382023.
|
|
93
|
Zhang N, Zhang Y, Wu B, You S and Sun Y:
Role of WW domain E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 2 in modulating
ubiquitination and Degradation of Septin4 in oxidative stress
endothelial injury. Redox Biol. 30:1014192020.
|
|
94
|
You S, Xu J, Yin Z, Wu B, Wang P, Hao M,
Cheng C, Liu M, Zhao Y, Jia P, et al: Down-regulation of WWP2
aggravates type 2 diabetes mellitus-induced vascular endothelial
injury through modulating ubiquitination and degradation of DDX3X.
Cardiovasc Diabetol. 22:1072023.
|
|
95
|
Qian Y, Wang Z, Lin H, Lei T, Zhou Z,
Huang W, Wu X, Zuo L, Wu J, Liu Y, et al: TRIM47 is a novel
endothelial activation factor that aggravates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice via K63-linked
ubiquitination of TRAF2. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
7:1482022.
|
|
96
|
Liu J, Lu S, Zheng L, Guo Q, Cao L, Xiao
Y, Chen D, Zou Y, Liu X, Deng C, et al: ATM-CHK2-TRIM32 axis
regulates ATG7 ubiquitination to initiate autophagy under oxidative
stress. Cell Rep. 42:1134022023.
|
|
97
|
Cockram PE, Kist M, Prakash S, Chen SH,
Wertz IE and Vucic D: Ubiquitination in the regulation of
inflammatory cell death and cancer. Cell Death Differ. 28:591–605.
2021.
|
|
98
|
Ullah K, Chen S, Lu J, Wang X, Liu Q,
Zhang Y, Long Y, Hu Z and Xu G: The E3 ubiquitin ligase STUB1
attenuates cell senescence by promoting the ubiquitination and
degradation of the core circadian regulator BMAL1. J Biol Chem.
295:4696–4708. 2020.
|
|
99
|
Li X, Wang T, Tao Y, Wang X, Li L and Liu
J: Inhibition of USP7 suppresses advanced glycation end-induced
cell cycle arrest and senescence of human umbilical vein
endothelial cells through ubiquitination of p53. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 54:311–320. 2022.
|
|
100
|
Mason DE, Collins JM, Dawahare JH, Nguyen
TD, Lin Y, Voytik-Harbin SL, Zorlutuna P, Yoder MC and Boerckel JD:
YAP and TAZ limit cytoskeletal and focal adhesion maturation to
enable persistent cell motility. J Cell Biol. 218:1369–1389.
2019.
|
|
101
|
Uematsu A, Kido K, Takahashi H, Takahashi
C, Yanagihara Y, Saeki N, Yoshida S, Maekawa M, Honda M, Kai T, et
al: The E3 ubiquitin ligase MIB2 enhances inflammation by degrading
the deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD. J Biol Chem. 294:14135–14148.
2019.
|
|
102
|
Li R, Shao J, Jin YJ, Kawase H, Ong YT,
Troidl K, Quan Q, Wang L, Bonnavion R, Wietelmann A, et al:
Endothelial FAT1 inhibits angiogenesis by controlling YAP/TAZ
protein degradation via E3 ligase MIB2. Nat Commun.
14:19802023.
|
|
103
|
Gallemit PEM, Yoodee S, Malaitad T and
Thongboonkerd V: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate plays more predominant
roles than caffeine for inducing actin-crosslinking,
ubiquitin/proteasome activity and glycolysis, and suppressing
angiogenesis features of human endothelial cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 141:1118372021.
|
|
104
|
Goyani S, Roy M and Singh R: TRIM-NHL as
RNA binding ubiquitin E3 Ligase (RBUL): Implication in development
and disease pathogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1867:1660662021.
|
|
105
|
Zhou ZX, Ma XF, Xiong WH, Ren Z, Jiang M,
Deng NH, Zhou BB, Liu HT, Zhou K, Hu HJ, et al: TRIM65 promotes
vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic transformation by activating
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling during atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis.
390:1174302024.
|
|
106
|
Hu Z, Song Q, Ma H, Guo Y, Zhang T, Xie H
and Luo X: TRIM32 inhibits the proliferation and migration of
pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells through the inactivation of
PI3K/Akt pathway in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Bioenerg
Biomembr. 53:309–320. 2021.
|
|
107
|
Liu Y, Zhu L, Ming Y, Wu Z, Zhang L, Chen
Q and Qi Y: A role of TRIM59 in pulmonary hypertension: Modulating
the protein ubiquitylation modification. J Transl Med.
21:8212023.
|
|
108
|
Wang Q, Shi W, Zhang Q, Feng W, Wang J,
Zhai C, Yan X and Li M: Inhibition of Siah2 ubiquitin ligase
ameliorates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial remodeling
through inactivation of YAP. Life Sci. 242:1171592020.
|
|
109
|
Kitamura H: Ubiquitin-specific proteases
(USPs) and metabolic disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 24:32192023.
|
|
110
|
Zhu Y, Zhang Q, Yan X, Liu L, Zhai C, Wang
Q, Chai L and Li M: Ubiquitin-specific protease 7 mediates
platelet-derived growth factor-induced pulmonary arterial smooth
muscle cells proliferation. Pulm Circ.
11:204589402110461312021.
|
|
111
|
Zhou ZX, Ren Z, Yan BJ, Qu SL, Tang ZH,
Wei DH, Liu LS, Fu MG and Jiang ZS: The role of ubiquitin E3 ligase
in atherosclerosis. Curr Med Chem. 28:152–168. 2021.
|
|
112
|
Matsumura Y, Sakai J and Skach WR:
Endoplasmic reticulum protein quality control is determined by
cooperative interactions between Hsp/c70 protein and the CHIP E3
ligase. J Biol Chem. 288:31069–31079. 2013.
|
|
113
|
Cai Z, He X, Liu S, Bai Y, Pan B and Wu K:
Linear ubiquitination modification of NR6A1 by LUBAC inhibits RIPK3
kinase activity and attenuates apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle
cells. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 36:e230912022.
|
|
114
|
Dai Y, Li Y, Cheng R, Gao J, Li Y and Lou
C: TRIM37 inhibits PDGF-BB-induced proliferation and migration of
airway smooth muscle cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 101:24–29.
2018.
|
|
115
|
Dong LH, Li L, Song Y, Duan ZL, Sun SG,
Lin YL, Miao SB, Yin YJ, Shu YN, Li H, et al: TRAF6-mediated SM22α
K21 ubiquitination promotes G6PD activation and NADPH production,
contributing to GSH homeostasis and VSMC survival in vitro and in
vivo. Circ Res. 117:684–694. 2015.
|
|
116
|
Marchand M, Monnot C, Muller L and Germain
S: Extracellular matrix scaffolding in angiogenesis and capillary
homeostasis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 89:147–156. 2019.
|
|
117
|
Neve A, Cantatore FP, Maruotti N, Corrado
A and Ribatti D: Extracellular matrix modulates angiogenesis in
physiological and pathological conditions. Biomed Res Int.
2014:7560782014.
|
|
118
|
Mongiat M, Andreuzzi E, Tarticchio G and
Paulitti A: Extracellular matrix, a hard player in angiogenesis.
Int J Mol Sci. 17:18222016.
|
|
119
|
Pai FC, Huang HW, Tsai YL, Tsai WC, Cheng
YC, Chang HH and Chen Y: Inhibition of FABP6 reduces tumor cell
invasion and angiogenesis through the decrease in MMP-2 and VEGF in
human glioblastoma cells. Cells. 10:27822021.
|
|
120
|
Chen Y, Huang Y, Huang Y, Xia X, Zhang J,
Zhou Y, Tan Y, He S, Qiang F, Li A, et al: JWA suppresses tumor
angiogenesis via Sp1-activated matrix metalloproteinase-2 and its
prognostic significance in human gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis.
35:442–451. 2014.
|
|
121
|
Chen Y, Huang Y, Hou P, Zhang Z, Zhang Y,
Wang W, Sun G, Xu L, Zhou J, Bai J and Zheng J: ING4 suppresses
tumor angiogenesis and functions as a prognostic marker in human
colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 7:79017–79031. 2016.
|
|
122
|
Chen JJ, Ren YL, Shu CJ, Zhang Y, Chen MJ,
Xu J, Li J, Li AP, Chen DY, He JD, et al: JP3, an antiangiogenic
peptide, inhibits growth and metastasis of gastric cancer through
TRIM25/SP1/MMP2 axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:1182020.
|
|
123
|
Yang X, Rothman VL, L'Heureux DZ and
Tuszynski G: Reduction of angiocidin expression in human umbilical
vein endothelial cells via siRNA silencing inhibits angiogenesis.
Exp Mol Pathol. 81:108–114. 2006.
|
|
124
|
Huang MT, Mason JC, Birdsey GM, Amsellem
V, Gerwin N, Haskard DO, Ridley AJ and Randi AM: Endothelial
intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-2 regulates angiogenesis.
Blood. 106:1636–1643. 2005.
|
|
125
|
Kitazume S, Imamaki R, Ogawa K and
Taniguchi N: Sweet role of platelet endothelial cell adhesion
molecule in understanding angiogenesis. Glycobiology. 24:1260–1264.
2014.
|
|
126
|
Kummer D and Ebnet K: Junctional adhesion
molecules (JAMs): The JAM-integrin connection. Cells. 7:252018.
|
|
127
|
Kaur G, Sharma D, Bisen S, Mukhopadhyay
CS, Gurdziel K and Singh NK: Vascular cell-adhesion molecule 1
(VCAM-1) regulates JunB-mediated IL-8/CXCL1 expression and
pathological neovascularization. Commun Biol. 6:5162023.
|
|
128
|
Hoer S, Smith L and Lehner PJ: MARCH-IX
mediates ubiquitination and downregulation of ICAM-1. FEBS Lett.
581:45–51. 2007.
|
|
129
|
Li Y, Huang X, Guo F, Lei T, Li S,
Monaghan-Nichols P, Jiang Z, Xin HB and Fu M: TRIM65 E3 ligase
targets VCAM-1 degradation to limit LPS-induced lung inflammation.
J Mol Cell Biol. 12:190–201. 2020.
|
|
130
|
Park S, Sorenson CM and Sheibani N:
PECAM-1 isoforms, eNOS and endoglin axis in regulation of
angiogenesis. Clin Sci (Lond). 129:217–234. 2015.
|
|
131
|
Liu J, Yao Q, Xiao L, Li F, Ma W, Zhang Z,
Xie X, Yang C, Cui Q, Tian Y, et al: APC/Cdh1 targets PECAM-1 for
ubiquitination and degradation in endothelial cells. J Cell
Physiol. 235:2521–2531. 2020.
|
|
132
|
Wu L, Xiao J, Yi D, Ding H, Wang R, Duan
Z, Liu Z, Shi X, Shen M and Sang J: Cytosolic Cadherin 4 promotes
angiogenesis and metastasis in papillary thyroid cancer by
suppressing the ubiquitination/degradation of β-catenin. J Transl
Med. 22:2012024.
|
|
133
|
Zimna A and Kurpisz M: Hypoxia-Inducible
Factor-1 in physiological and pathophysiological angiogenesis:
Applications and therapies. Biomed Res Int. 2015:5494122015.
|
|
134
|
Tirpe AA, Gulei D, Ciortea SM, Crivii C
and Berindan-Neagoe I: Hypoxia: Overview on hypoxia-mediated
mechanisms with a focus on the role of HIF Genes. Int J Mol Sci.
20:61402019.
|
|
135
|
Chen L, Endler A and Shibasaki F: Hypoxia
and angiogenesis: Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factors via novel
binding factors. Exp Mol Med. 41:849–857. 2009.
|
|
136
|
Wicks EE and Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible
factors: Cancer progression and clinical translation. J Clin
Invest. 132:e1598392022.
|
|
137
|
Ke Q and Costa M: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1 (HIF-1). Mol Pharmacol. 70:1469–1480. 2006.
|
|
138
|
Kubaichuk K and Kietzmann T: Involvement
of E3 ligases and deubiquitinases in the control of HIF-α subunit
abundance. Cells. 8:5982019.
|
|
139
|
Ajani JA, Xu Y, Huo L, Wang R, Li Y, Wang
Y, Pizzi MP, Scott A, Harada K, Ma L, et al: YAP1 mediates gastric
adenocarcinoma peritoneal metastases that are attenuated by YAP1
inhibition. Gut. 70:55–66. 2021.
|
|
140
|
Koyasu S, Kobayashi M, Goto Y, Hiraoka M
and Harada H: Regulatory mechanisms of hypoxia-inducible factor 1
activity: Two decades of knowledge. Cancer Sci. 109:560–571.
2018.
|
|
141
|
Bora-Singhal N, Saha B, Mohankumar D,
Padmanabhan J, Coppola D and Chellappan S: A novel
PHD2/VHL-mediated regulation of YAP1 contributes to VEGF expression
and angiogenesis. Cancer Res Commun. 2:624–638. 2022.
|
|
142
|
Kim YJ, Zhao Y, Myung JK, Yi JM, Kim MJ
and Lee SJ: Suppression of breast cancer progression by FBXL16 via
oxygen-independent regulation of HIF1α stability. Cell Rep.
37:1099962021.
|
|
143
|
Yueyang M, Yaqin H, Guolian X, Wenjian Z,
Yang J, Chen L, Haiyan C, Min C, Jianping D, Penggao D, et al:
Glioma angiogenesis is boosted by ELK3 activating the
HIF-1[Formula: See text]/VEGF-A signaling axis. BMC Cancer.
23:6622023.
|
|
144
|
Chen P, Duan X, Li X, Li J, Ba Q and Wang
H: HIPK2 suppresses tumor growth and progression of hepatocellular
carcinoma through promoting the degradation of HIF-1α. Oncogene.
39:2863–2876. 2012.
|
|
145
|
Chen C, Wei M, Wang C, Sun D, Liu P, Zhong
X, He Q and Yu W: The histone deacetylase HDAC1 activates
HIF1α/VEGFA signal pathway in colorectal cancer. Gene.
754:1448512020.
|
|
146
|
Hu L, Lv X, Li D, Zhang W, Ran G, Li Q and
Hu J: The anti-angiogenesis role of FBXW7 in diabetic retinopathy
by facilitating the ubiquitination degradation of c-Myc to
orchestrate the HDAC2. J Cell Mol Med. 25:2190–2202. 2021.
|
|
147
|
Deng Y, Li S, Li S, Yu C, Huang D, Chen H
and Yin X: CircPDE4B inhibits retinal pathological angiogenesis via
promoting degradation of HIF-1α though targeting miR-181c. IUBMB
Life. 72:1920–1929. 2020.
|
|
148
|
Pitulescu ME, Schmidt I, Giaimo BD,
Antoine T, Berkenfeld F, Ferrante F, Park H, Ehling M, Biljes D,
Rocha SF, et al: Dll4 and Notch signalling couples sprouting
angiogenesis and artery formation. Nat Cell Biol. 19:915–927.
2017.
|
|
149
|
Parmalee NL and Kitajewski J: Wnt
signaling in angiogenesis. Curr Drug Targets. 9:558–564. 2008.
|
|
150
|
Shaw P, Dwivedi SKD, Bhattacharya R,
Mukherjee P and Rao G: VEGF signaling: Role in angiogenesis and
beyond. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1879:1890792024.
|
|
151
|
Dutta D, Sharma V, Mutsuddi M and
Mukherjee A: Regulation of notch signaling by E3 ubiquitin ligases.
FEBS J. 289:937–954. 2022.
|
|
152
|
Zhang B and Ma JX: Wnt pathway antagonists
and angiogenesis. Protein Cell. 1:898–906. 2010.
|
|
153
|
Choi HJ, Park H, Lee HW and Kwon YG: The
Wnt pathway and the roles for its antagonists, DKKS, in
angiogenesis. IUBMB Life. 64:724–731. 2012.
|
|
154
|
Zerlin M, Julius MA and Kitajewski J:
Wnt/Frizzled signaling in angiogenesis. Angiogenesis. 11:63–69.
2008.
|
|
155
|
Dejana E: The role of wnt signaling in
physiological and pathological angiogenesis. Circ Res. 107:943–952.
2010.
|
|
156
|
Shi YN, Zhu N, Liu C, Wu HT, Gui Y, Liao
DF and Qin L: Wnt5a and its signaling pathway in angiogenesis. Clin
Chim Acta. 471:263–269. 2017.
|
|
157
|
Mankuzhy P, Dharmarajan A, Perumalsamy LR,
Sharun K, Samji P and Dilley RJ: The role of Wnt signaling in
mesenchymal stromal cell-driven angiogenesis. Tissue Cell.
85:1022402023.
|
|
158
|
van Loon K, Huijbers EJM and Griffioen AW:
Secreted frizzled-related protein 2: A key player in noncanonical
Wnt signaling and tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
40:191–203. 2021.
|
|
159
|
Park HB, Kim JW and Baek KH: Regulation of
Wnt signaling through ubiquitination and deubiquitination in
cancers. Int J Mol Sci. 21:39042020.
|
|
160
|
Kikuchi A: Modulation of Wnt signaling by
Axin and Axil. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 10:255–265. 1999.
|
|
161
|
Huang SM, Mishina YM, Liu S, Cheung A,
Stegmeier F, Michaud GA, Charlat O, Wiellette E, Zhang Y, Wiessner
S, et al: Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt
signalling. Nature. 461:614–620. 2009.
|
|
162
|
Law SM and Zheng JJ: Premise and peril of
Wnt signaling activation through GSK-3β inhibition. iScience.
25:1041592022.
|
|
163
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009.
|
|
164
|
Li Q, Luo H, Dai FQ, Wang RT, Fan XQ, Luo
YY, Deng MS, Wang Y, Long T, Guo W, et al: SAMD9 promotes
postoperative recurrence of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by
stimulating MYH9-Mediated GSK3β/β-Catenin signaling. Adv Sci
(Weinh). 10:e22035732023.
|
|
165
|
Lyle CL, Belghasem M and Chitalia VC:
c-Cbl: An important regulator and a target in angiogenesis and
tumorigenesis. Cells. 8:4982019.
|
|
166
|
Shivanna S, Harrold I, Shashar M, Meyer R,
Kiang C, Francis J, Zhao Q, Feng H, Edelman ER, Rahimi N and
Chitalia VC: The c-Cbl ubiquitin ligase regulates nuclear β-catenin
and angiogenesis by its tyrosine phosphorylation mediated through
the Wnt signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 290:12537–12546. 2015.
|
|
167
|
Chitalia V, Shivanna S, Martorell J, Meyer
R, Edelman E and Rahimi N: c-Cbl, a ubiquitin E3 ligase that
targets active β-catenin: A novel layer of Wnt signaling
regulation. J Biol Chem. 288:23505–23517. 2013.
|
|
168
|
Kumaradevan S, Lee SY, Richards S, Lyle C,
Zhao Q, Tapan U, Jiangliu Y, Ghumman S, Walker J, Belghasem M, et
al: c-Cbl expression correlates with human colorectal cancer
survival and Its Wnt/β-catenin suppressor function is regulated by
Tyr371 phosphorylation. Am J Pathol. 188:1921–1933. 2018.
|
|
169
|
Wang H, Deng G, Ai M, Xu Z, Mou T, Yu J,
Liu H, Wang S and Li G: Hsp90ab1 stabilizes LRP5 to promote
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via activating of AKT and
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in gastric cancer progression.
Oncogene. 38:1489–1507. 2019.
|
|
170
|
Chen C, Zhu D, Zhang H, Han C, Xue G, Zhu
T, Luo J and Kong L: YAP-dependent ubiquitination and degradation
of β-catenin mediates inhibition of Wnt signalling induced by
Physalin F in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 9:5912018.
|
|
171
|
Harper JA, Yuan JS, Tan JB, Visan I and
Guidos CJ: Notch signaling in development and disease. Clin Genet.
64:461–472. 2003.
|
|
172
|
Hasan SS and Fischer A: Notch signaling in
the vasculature: Angiogenesis and angiocrine functions. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Med. 13:a0411662023.
|
|
173
|
Tetzlaff F and Fischer A: Control of blood
vessel formation by notch signaling. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1066:319–338. 2018.
|
|
174
|
Luo Z, Shang X, Zhang H, Wang G, Massey
PA, Barton SR, Kevil CG and Dong Y: Notch signaling in
osteogenesis, osteoclastogenesis, and angiogenesis. Am J Pathol.
189:1495–1500. 2019.
|
|
175
|
Sainson RC and Harris AL: Regulation of
angiogenesis by homotypic and heterotypic notch signalling in
endothelial cells and pericytes: From basic research to potential
therapies. Angiogenesis. 11:41–51. 2008.
|
|
176
|
Jiang N, Hu Y, Wang M, Zhao Z and Li M:
The notch signaling pathway contributes to angiogenesis and tumor
immunity in breast cancer. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press).
14:291–309. 2022.
|
|
177
|
Benedito R, Roca C, Sörensen I, Adams S,
Gossler A, Fruttiger M and Adams RH: The notch ligands Dll4 and
Jagged1 have opposing effects on angiogenesis. Cell. 137:1124–1135.
2009.
|
|
178
|
Garcia A and Kandel JJ: Notch: A key
regulator of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Histol Histopathol.
27:151–156. 2012.
|
|
179
|
Ferrante F, Giaimo BD, Friedrich T, Sugino
T, Mertens D, Kugler S, Gahr BM, Just S, Pan L, Bartkuhn M, et al:
Hydroxylation of the NOTCH1 intracellular domain regulates Notch
signaling dynamics. Cell Death Dis. 13:6002022.
|
|
180
|
Zhou B, Lin W, Long Y, Yang Y, Zhang H, Wu
K and Chu Q: Notch signaling pathway: architecture, disease, and
therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:952022.
|
|
181
|
Revici R, Hosseini-Alghaderi S, Haslam F,
Whiteford R and Baron M: E3 ubiquitin ligase regulators of notch
receptor endocytosis: From flies to humans. Biomolecules.
12:2242022.
|
|
182
|
Le Bras S, Loyer N and Le Borgne R: The
multiple facets of ubiquitination in the regulation of notch
signaling pathway. Traffic. 12:149–161. 2011.
|
|
183
|
Koo BK, Yoon KJ, Yoo KW, Lim HS, Song R,
So JH, Kim CH and Kong YY: Mind bomb-2 is an E3 ligase for Notch
ligand. J Biol Chem. 280:22335–22342. 2005.
|
|
184
|
Izumi N, Helker C, Ehling M, Behrens A,
Herzog W and Adams RH: Fbxw7 controls angiogenesis by regulating
endothelial Notch activity. PLoS One. 7:e411162012.
|
|
185
|
Ohnuki H, Inoue H, Takemori N, Nakayama H,
Sakaue T, Fukuda S, Miwa D, Nishiwaki E, Hatano M, Tokuhisa T, et
al: BAZF, a novel component of cullin3-based E3 ligase complex,
mediates VEGFR and Notch cross-signaling in angiogenesis. Blood.
119:2688–2698. 2012.
|