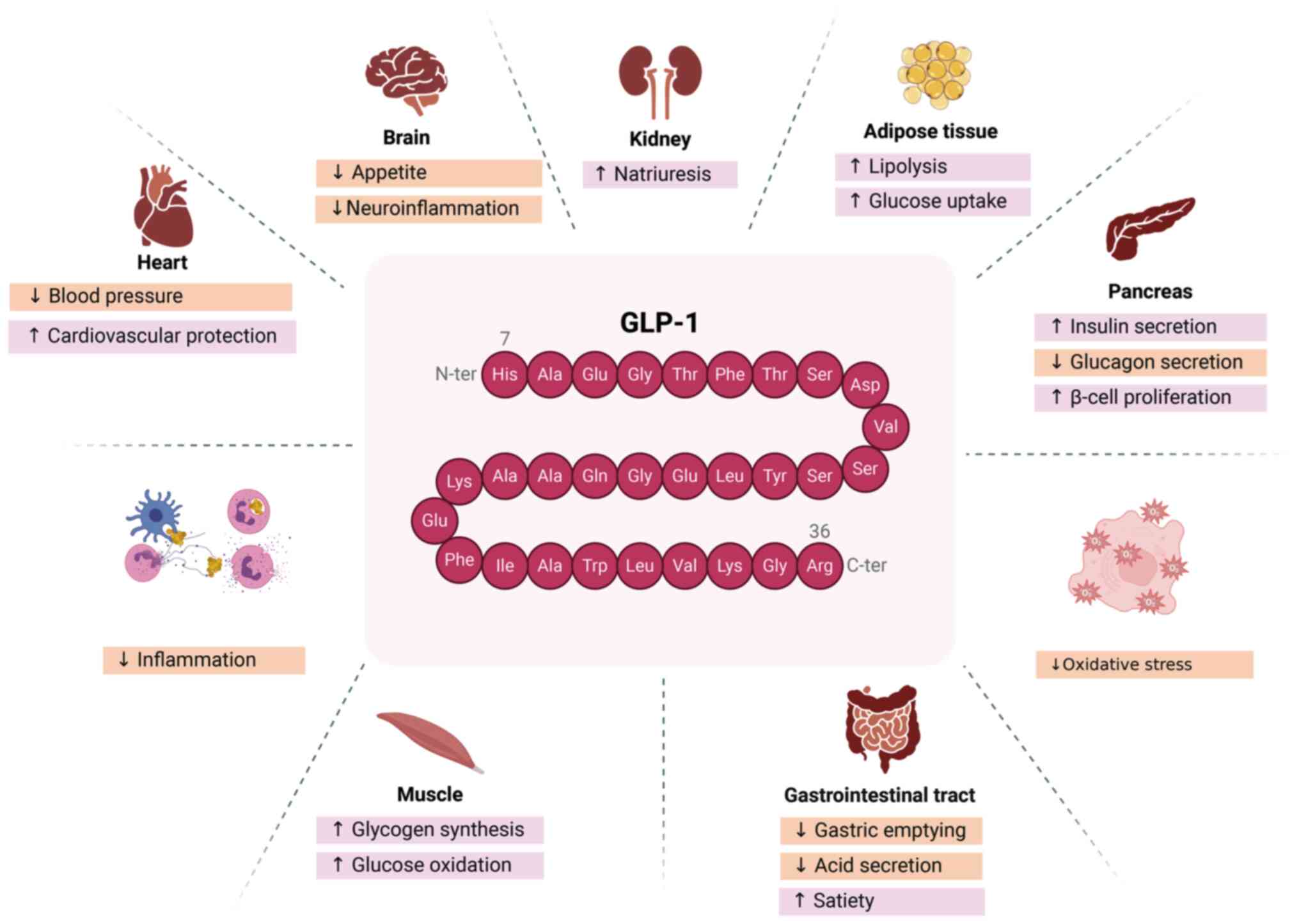
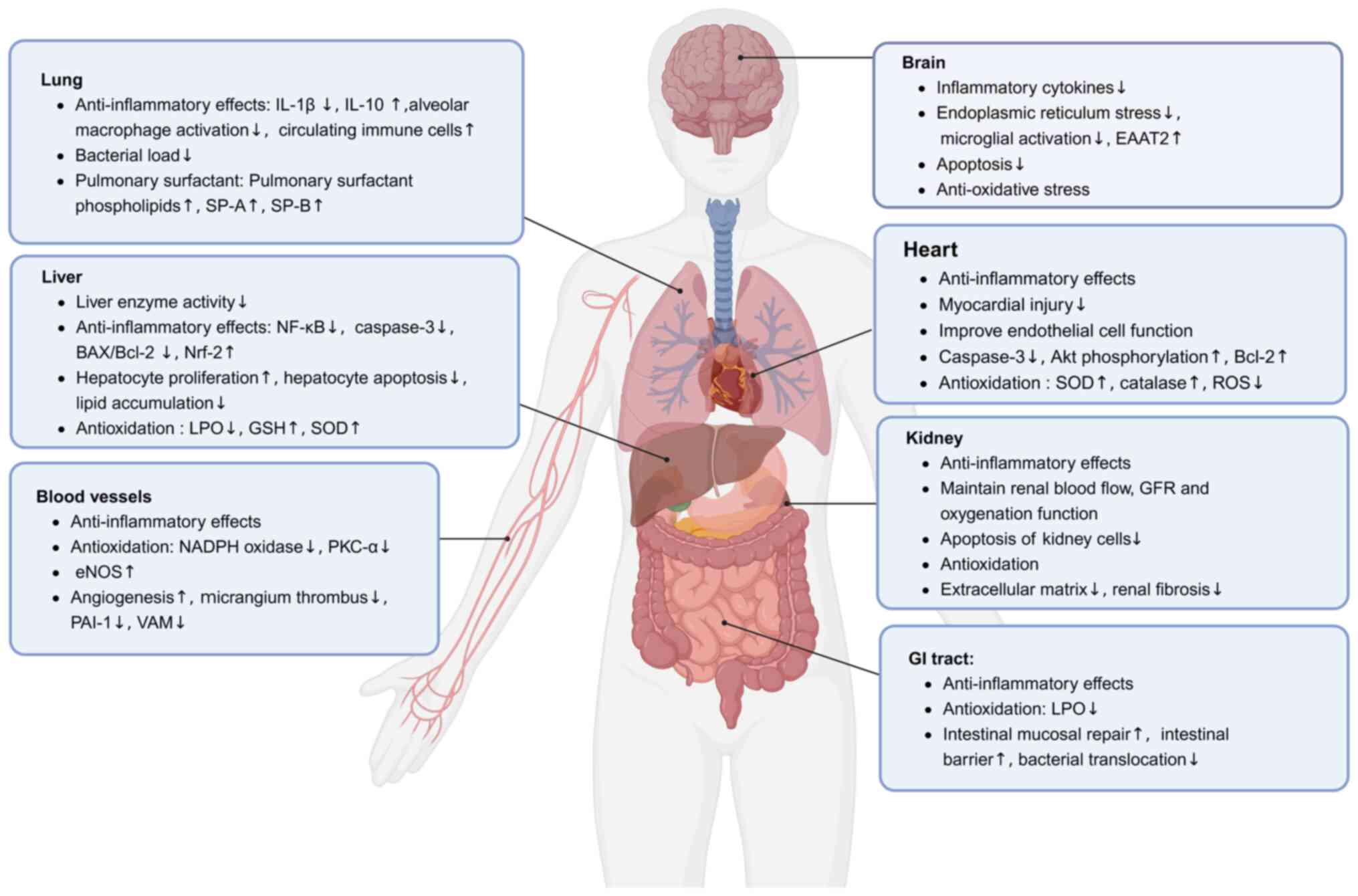
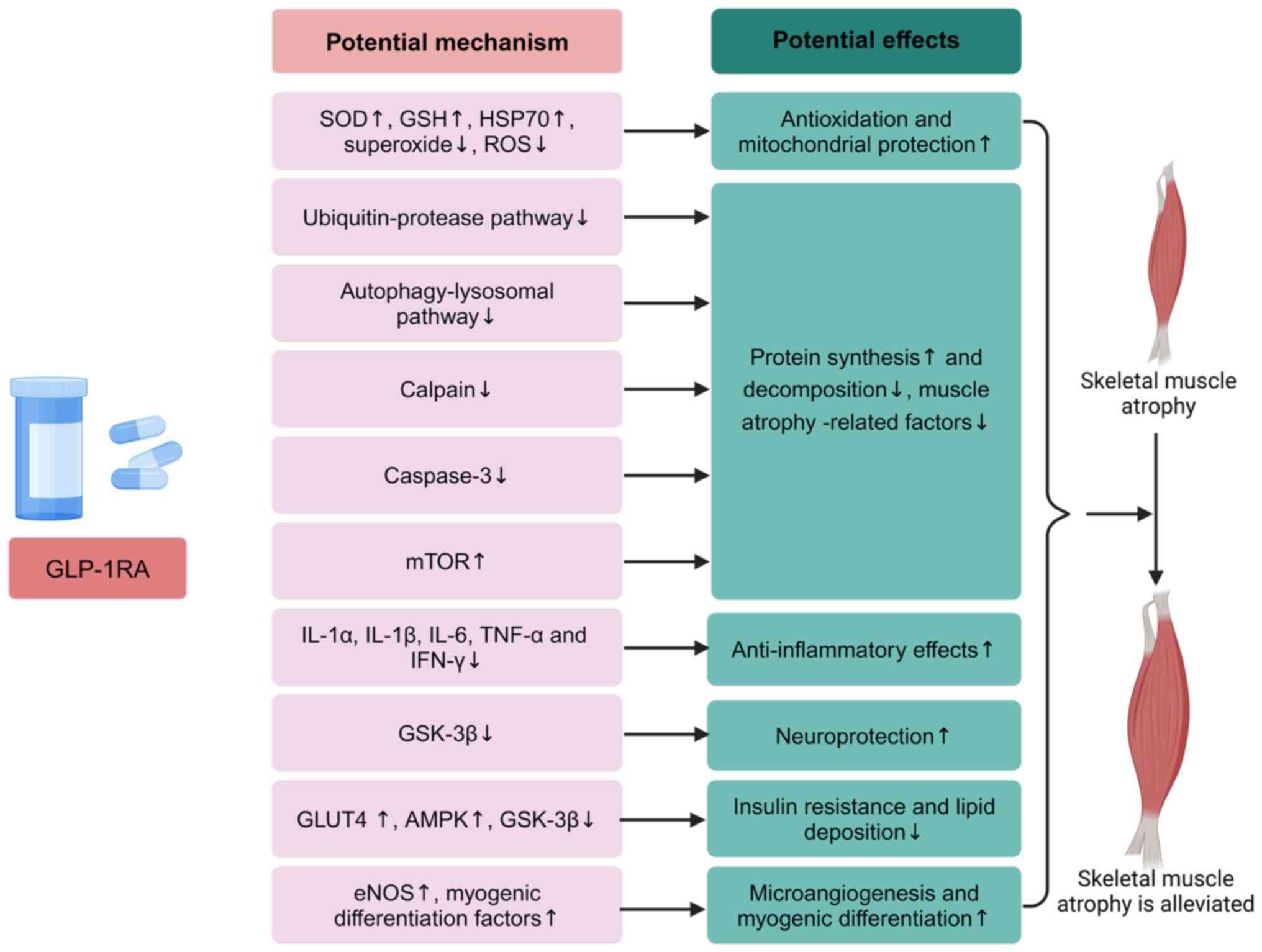
|
1
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mushtaq A and Kazi F: Updates in sepsis
management. Lancet Infect Dis. 22:242022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Vincent JL, Jones G, David S, Olariu E and
Cadwell KK: Frequency and mortality of septic shock in Europe and
North America: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care.
23:1962019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abraham E: New definitions for sepsis and
septic shock: Continuing evolution but with much still to be done.
JAMA. 315:757–759. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bracht H, Hafner S and Weiß M: Sepsis
update: Definition and epidemiology. Anasthesiol Intensivmed
Notfallmed Schmerzther. 54:10–20. 2019.In German. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vincent JL: Current sepsis therapeutics.
EBioMedicine. 86:1043182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Leviner S: Post-sepsis syndrome. Crit Care
Nurs Q. 44:182–186. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Callahan LA and Supinski GS:
Sepsis-induced myopathy. Crit Care Med. 37(10 Suppl): S354–S367.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gardner AK, Ghita GL, Wang Z,
Ozrazgat-Baslanti T, Raymond SL, Mankowski RT, Brumback BA, Efron
PA, Bihorac A, Moore FA, et al: The development of chronic critical
illness determines physical function, quality of life, and
long-term survival among early survivors of sepsis in surgical
ICUs. Crit Care Med. 47:566–573. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu Y, Wang D, Li T, Xu L, Li Z, Bai X,
Tang M and Wang Y: Melatonin: A potential adjuvant therapy for
septic myopathy. Biomed Pharmacother. 158:1142092023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu W, Hu C and Zhao S: Sarcopenia and
mortality risk of patients with sepsis: A meta-analysis. Int J Clin
Pract. 2022:49744102022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mankowski RT, Laitano O, Clanton TL and
Brakenridge SC: Pathophysiology and treatment strategies of acute
myopathy and muscle wasting after sepsis. J Clin Med. 10:18742021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen J and Huang M: Intensive care
unit-acquired weakness: Recent insights. J Intensive Med. 4:73–80.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Piva S, Fagoni N and Latronico N:
Intensive care unit-acquired weakness: Unanswered questions and
targets for future research. F1000Res. 8:F1000Faculty Rev-508.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Latronico N, Herridge M, Hopkins RO, Angus
D, Hart N, Hermans G, Iwashyna T, Arabi Y, Citerio G, Ely EW, et
al: The ICM research agenda on intensive care unit-acquired
weakness. Intensive Care Med. 43:1270–1281. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schefold JC, Bierbrauer J and
Weber-Carstens S: Intensive care unit-acquired weakness (ICUAW) and
muscle wasting in critically ill patients with severe sepsis and
septic shock. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 1:147–157. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Farhan H, Moreno-Duarte I, Latronico N,
Zafonte R and Eikermann M: Acquired muscle weakness in the surgical
intensive care unit: Nosology, epidemiology, diagnosis, and
prevention. Anesthesiology. 124:207–234. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Graaf Cd, Donnelly D, Wootten D, Lau J,
Sexton PM, Miller LJ, Ahn JM, Liao J, Fletcher MM, Yang D, et al:
Glucagon-like peptide-1 and its class B G protein-coupled
receptors: A long march to therapeutic successes. Pharmacol Rev.
68:954–1013. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI,
Blonde L, Bloomgarden ZT, Bush MA, Dagogo-Jack S, Davidson MB,
Einhorn D, Garvey WT, et al: AACE comprehensive diabetes management
algorithm 2013. Endocr Pract. 19:327–336. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB,
Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R,
Matthews DR, et al: Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes:
A patient-centered approach: position statement of the American
diabetes association (ADA) and the European association for the
study of diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 35:1364–1379. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gutzwiller JP, Drewe J, Göke B, Schmidt H,
Rohrer B, Lareida J and Beglinger C: Glucagon-like peptide-1
promotes satiety and reduces food intake in patients with diabetes
mellitus type 2. Am J Physiol. 276:R1541–R1544. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao X, Wang M, Wen Z, Lu Z, Cui L, Fu C,
Xue H, Liu Y and Zhang Y: GLP-1 receptor agonists: Beyond their
pancreatic effects. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
12:7211352021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang F, Zeng F, Luo X, Lei Y, Li J, Lu S,
Huang X, Lan Y and Liu R: GLP-1 receptor: A new target for sepsis.
Front Pharmacol. 12:7069082021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Iwai S, Kaji K, Nishimura N, Kubo T,
Tomooka F, Shibamoto A, Suzuki J, Tsuji Y, Fujinaga Y, Kitagawa K,
et al: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, semaglutide
attenuates chronic liver disease-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in
diabetic mice. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1869:1667702023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sandoval DA and D'Alessio DA: Physiology
of proglucagon peptides: Role of glucagon and GLP-1 in health and
disease. Physiol Rev. 95:513–548. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nian M, Drucker DJ and Irwin D: Divergent
regulation of human and rat proglucagon gene promoters in vivo. Am
J Physiol. 277:G829–G837. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jin SL, Han VK, Simmons JG, Towle AC,
Lauder JM and Lund PK: Distribution of glucagonlike peptide I
(GLP-I), glucagon, and glicentin in the rat brain: An
immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol. 271:519–532.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Han VK, Hynes MA, Jin C, Towle AC, Lauder
JM and Lund PK: Cellular localization of proglucagon/glucagon-like
peptide I messenger RNAs in rat brain. J Neurosci Res. 16:97–107.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Drucker DJ and Nauck MA: The incretin
system: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl
peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 368:1696–1705.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sharma D, Verma S, Vaidya S, Kalia K and
Tiwari V: Recent updates on GLP-1 agonists: Current advancements
& challenges. Biomed Pharmacother. 108:952–962. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kreymann B, Williams G, Ghatei MA and
Bloom SR: Glucagon-like peptide-1 7-36: A physiological incretin in
man. Lancet. 2:1300–1304. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Deacon CF, Johnsen AH and Holst JJ:
Degradation of glucagon-like peptide-1 by human plasma in vitro
yields an N-terminally truncated peptide that is a major endogenous
metabolite in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 80:952–957.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Müller TD, Finan B, Bloom SR, D'Alessio D,
Drucker DJ, Flatt PR, Fritsche A, Gribble F, Grill HJ, Habener JF,
et al: Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol Metab. 30:72–130. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hansen L, Deacon CF, Orskov C and Holst
JJ: Glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36)amide is transformed to
glucagon-like peptide-1-(9-36)amide by dipeptidyl peptidase IV in
the capillaries supplying the L cells of the porcine intestine.
Endocrinology. 140:5356–5363. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Meier JJ, Nauck MA, Kranz D, Holst JJ,
Deacon CF, Gaeckler D, Schmidt WE and Gallwitz B: Secretion,
degradation, and elimination of glucagon-like peptide 1 and gastric
inhibitory polypeptide in patients with chronic renal insufficiency
and healthy control subjects. Diabetes. 53:654–662. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Leech CA, Chepurny OG and Holz GG:
Epac2-dependent rap1 activation and the control of islet insulin
secretion by glucagon-like peptide-1. Vitam Horm. 84:279–302. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Göke R, Larsen PJ, Mikkelsen JD and Sheikh
SP: Distribution of GLP-1 binding sites in the rat brain: Evidence
that exendin-4 is a ligand of brain GLP-1 binding sites. Eur J
Neurosci. 7:2294–2300. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Campos RV, Lee YC and Drucker DJ:
Divergent tissue-specific and developmental expression of receptors
for glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1 in the mouse.
Endocrinology. 134:2156–2164. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cantini G, Mannucci E and Luconi M:
Perspectives in GLP-1 research: New targets, new receptors. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 27:427–438. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Holz GG: Epac: A new cAMP-binding protein
in support of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor-mediated signal
transduction in the pancreatic beta-cell. Diabetes. 53:5–13. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Drucker DJ, Philippe J, Mojsov S, Chick WL
and Habener JF: Glucagon-like peptide I stimulates insulin gene
expression and increases cyclic AMP levels in a rat islet cell
line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 84:3434–3438. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fehmann HC and Habener JF: Galanin
inhibits proinsulin gene expression stimulated by the
insulinotropic hormone glucagon-like peptide-I(7-37) in mouse
insulinoma beta TC-1 cells. Endocrinology. 130:2890–2896. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Arakawa M, Ebato C, Mita T, Hirose T,
Kawamori R, Fujitani Y and Watada H: Effects of exendin-4 on
glucose tolerance, insulin secretion, and beta-cell proliferation
depend on treatment dose, treatment duration and meal contents.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 390:809–814. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hare KJ, Vilsbøll T, Asmar M, Deacon CF,
Knop FK and Holst JJ: The glucagonostatic and insulinotropic
effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 contribute equally to its
glucose-lowering action. Diabetes. 59:1765–1770. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Beiroa D, Imbernon M, Gallego R, Senra A,
Herranz D, Villarroya F, Serrano M, Fernø J, Salvador J, Escalada
J, et al: GLP-1 agonism stimulates brown adipose tissue
thermogenesis and browning through hypothalamic AMPK. Diabetes.
63:3346–3358. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Halim MA, Degerblad M, Sundbom M, Karlbom
U, Holst JJ, Webb DL and Hellström PM: Glucagon-like peptide-1
inhibits prandial gastrointestinal motility through myenteric
neuronal mechanisms in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
103:575–585. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
McKay NJ, Kanoski SE, Hayes MR and Daniels
D: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists suppress water intake
independent of effects on food intake. Am J Physiol Regul Integr
Comp Physiol. 301:R1755–R1764. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Herman JP: Regulation of
hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical responses to stressors by the
nucleus of the solitary tract/dorsal vagal complex. Cell Mol
Neurobiol. 38:25–35. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Ghosal S, Packard AEB, Mahbod P, McKlveen
JM, Seeley RJ, Myers B, Ulrich-Lai Y, Smith EP, D'Alessio DA and
Herman JP: Disruption of glucagon-like peptide 1 signaling in sim1
neurons reduces physiological and behavioral reactivity to acute
and chronic stress. J Neurosci. 37:184–193. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Perry T, Lahiri DK, Chen D, Zhou J, Shaw
KT, Egan JM and Greig NH: A novel neurotrophic property of
glucagon-like peptide 1: A promoter of nerve growth factor-mediated
differentiation in PC12 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 300:958–966.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
During MJ, Cao L, Zuzga DS, Francis JS,
Fitzsimons HL, Jiao X, Bland RJ, Klugmann M, Banks WA, Drucker DJ
and Haile CN: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is involved in
learning and neuroprotection. Nat Med. 9:1173–1179. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K,
Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, Nissen SE, Pocock S, Poulter NR,
Ravn LS, et al: Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2
diabetes. N Engl J Med. 375:311–322. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mann JFE, Ørsted DD, Brown-Frandsen K,
Marso SP, Poulter NR, Rasmussen S, Tornøe K, Zinman B and Buse JB;
LEADER Steering Committee and Investigators: Liraglutide and renal
outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 377:839–848.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Teramoto S, Miyamoto N, Yatomi K, Tanaka
Y, Oishi H, Arai H, Hattori N and Urabe T: Exendin-4, a
glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, provides neuroprotection
in mice transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 31:1696–1705. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Aravindhan K, Bao W, Harpel MR, Willette
RN, Lepore JJ and Jucker BM: Cardioprotection resulting from
glucagon-like peptide-1 administration involves shifting metabolic
substrate utilization to increase energy efficiency in the rat
heart. PLoS One. 10:e01308942015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lebrun LJ, Lenaerts K, Kiers D, Pais de
Barros JP, Le Guern N, Plesnik J, Thomas C, Bourgeois T, Dejong
CHC, Kox M, et al: Enteroendocrine L cells sense LPS after gut
barrier injury to enhance GLP-1 secretion. Cell Rep. 21:1160–1168.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Guo J, Zhang X, Pan R, Zheng Y, Chen W and
Wang L: Liraglutide alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by
regulating pulmonary surfactant through inhibiting autophagy.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 46:573–582. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Armstrong MJ, Gaunt P, Aithal GP, Barton
D, Hull D, Parker R, Hazlehurst JM, Guo K; LEAN trial team; Abouda
G, et al: Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with
non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): A multicentre, double-blind,
randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet. 387:679–690.
2016.
|
|
59
|
Pan HC, Chen JY, Chen HY, Yeh FY, Sun CY,
Huang TT and Wu VC: GLP-1 receptor agonists' impact on cardio-renal
outcomes and mortality in T2D with acute kidney disease. Nat
Commun. 15:59122024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Guo J, Chen X, Wang C, Ruan F, Xiong Y,
Wang L, Abdel-Razek O, Meng Q, Shahbazov R, Cooney RN and Wang G:
Liraglutide alleviates acute lung injury and mortality in
pneumonia-induced sepsis through regulating surfactant protein
expression and secretion. Shock. 61:601–610. 2024.
|
|
61
|
Yi H, Duan Y, Song R, Zhou Y, Cui Y, Liu
C, Mao Z, Hu J and Zhou F: Activation of glucagon-like peptide-1
receptor in microglia exerts protective effects against
sepsis-induced encephalopathy via attenuating endoplasmic reticulum
stress-associated inflammation and apoptosis in a mouse model of
sepsis. Exp Neurol. 363:1143482023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Atef MM, Abou Hashish NA, Hafez YM, Selim
AF, Ibrahim HA, Eltabaa EF, Rizk FH, Shalaby AM, Ezzat N, Alabiad
MA and Elshamy AM: The potential protective effect of liraglutide
on valproic acid induced liver injury in rats: Targeting HMGB1/RAGE
axis and RIPK3/MLKL mediated necroptosis. Cell Biochem Funct.
41:1209–1219. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Seufert J and Gallwitz B: The
extra-pancreatic effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists: A focus on the
cardiovascular, gastrointestinal and central nervous systems.
Diabetes Obes Metab. 16:673–688. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Glorie LLF, Verhulst A, Matheeussen V,
Baerts L, Magielse J, Hermans N, D'Haese PC, De Meester I and De
Beuf A: DPP4 inhibition improves functional outcome after renal
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
303:F681–F688. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM,
Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, Martin FC, Michel JP, Rolland Y,
Schneider SM, et al: Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition
and diagnosis: Report of the European working group on sarcopenia
in older people. Age Ageing. 39:412–423. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Cohen S, Nathan JA and Goldberg AL: Muscle
wasting in disease: Molecular mechanisms and promising therapies.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 14:58–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Preiser JC, Ichai C, Orban JC and
Groeneveld AB: Metabolic response to the stress of critical
illness. Br J Anaesth. 113:945–954. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Bloch S, Polkey MI, Griffiths M and Kemp
P: Molecular mechanisms of intensive care unit-acquired weakness.
Eur Respir J. 39:1000–1011. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Kanova M and Kohout P: Molecular
mechanisms underlying intensive care unit-acquired weakness and
sarcopenia. Int J Mol Sci. 23:83962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK,
Nunez L, Clarke BA, Poueymirou WT, Panaro FJ, Na E, Dharmarajan K,
et al: Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal
muscle atrophy. Science. 294:1704–1708. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Csibi A, Cornille K, Leibovitch MP, Poupon
A, Tintignac LA, Sanchez AM and Leibovitch SA: The translation
regulatory subunit eIF3f controls the kinase-dependent mTOR
signaling required for muscle differentiation and hypertrophy in
mouse. PLoS One. 5:e89942010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Tintignac LA, Lagirand J, Batonnet S,
Sirri V, Leibovitch MP and Leibovitch SA: Degradation of MyoD
mediated by the SCF (MAFbx) ubiquitin ligase. J Biol Chem.
280:2847–2856. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Cai D, Frantz JD, Tawa NE Jr, Melendez PA,
Oh BC, Lidov HG, Hasselgren PO, Frontera WR, Lee J, Glass DJ and
Shoelson SE: IKKbeta/NF-kappaB activation causes severe muscle
wasting in mice. Cell. 119:285–298. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Klaude M, Fredriksson K, Tjäder I,
Hammarqvist F, Ahlman B, Rooyackers O and Wernerman J: Proteasome
proteolytic activity in skeletal muscle is increased in patients
with sepsis. Clin Sci (Lond). 112:499–506. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Supinski GS and Callahan LA: Calpain
activation contributes to endotoxin-induced diaphragmatic
dysfunction. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 42:80–87. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
76
|
Smith IJ, Lecker SH and Hasselgren PO:
Calpain activity and muscle wasting in sepsis. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 295:E762–E771. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Supinski GS and Callahan LA: Caspase
activation contributes to endotoxin-induced diaphragm weakness. J
Appl Physiol (1985). 100:1770–1777. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hussain SN, Mofarrahi M, Sigala I, Kim HC,
Vassilakopoulos T, Maltais F, Bellenis I, Chaturvedi R, Gottfried
SB, Metrakos P, et al: Mechanical ventilation-induced diaphragm
disuse in humans triggers autophagy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
182:1377–1386. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Franco-Romero A and Sandri M: Role of
autophagy in muscle disease. Mol Aspects Med. 82:1010412021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Latres E, Amini AR, Amini AA, Griffiths J,
Martin FJ, Wei Y, Lin HC, Yancopoulos GD and Glass DJ: Insulin-like
growth factor-1 (IGF-1) inversely regulates atrophy-induced genes
via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of
rapamycin (PI3K/Akt/mTOR) pathway. J Biol Chem. 280:2737–2744.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Sandri M, Sandri C, Gilbert A, Skurk C,
Calabria E, Picard A, Walsh K, Schiaffino S, Lecker SH and Goldberg
AL: Foxo transcription factors induce the atrophy-related ubiquitin
ligase atrogin-1 and cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Cell.
117:399–412. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Lang CH and Frost RA: Role of growth
hormone, insulin-like growth factor-I, and insulin-like growth
factor binding proteins in the catabolic response to injury and
infection. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 5:271–279. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Nystrom G, Pruznak A, Huber D, Frost RA
and Lang CH: Local insulin-like growth factor I prevents
sepsis-induced muscle atrophy. Metabolism. 58:787–797. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Showkat M, Beigh MA and Andrabi KI: mTOR
signaling in protein translation regulation: Implications in cancer
genesis and therapeutic interventions. Mol Biol Int.
2014:6869842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Lang CH, Frost RA and Vary TC: Regulation
of muscle protein synthesis during sepsis and inflammation. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 293:E453–E459. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Frost RA and Lang CH: mTor signaling in
skeletal muscle during sepsis and inflammation: Where does it all
go wrong? Physiology (Bethesda). 26:83–96. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Ferri E, Marzetti E, Calvani R, Picca A,
Cesari M and Arosio B: Role of age-related mitochondrial
dysfunction in sarcopenia. Int J Mol Sci. 21:52362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wu Y, Yao YM and Lu ZQ: Mitochondrial
quality control mechanisms as potential therapeutic targets in
sepsis-induced multiple organ failure. J Mol Med (Berl).
97:451–462. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Preau S, Vodovar D, Jung B, Lancel S,
Zafrani L, Flatres A, Oualha M, Voiriot G, Jouan Y, Joffre J, et
al: Energetic dysfunction in sepsis: A narrative review. Ann
Intensive Care. 11:1042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Friedrich O, Hund E, Weber C, Hacke W and
Fink RH: Critical illness myopathy serum fractions affect membrane
excitability and intracellular calcium release in mammalian
skeletal muscle. J Neurol. 251:53–65. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zink W, Kaess M, Hofer S, Plachky J,
Zausig YA, Sinner B, Weigand MA, Fink RH and Graf BM: Alterations
in intracellular Ca2+-homeostasis of skeletal muscle fibers during
sepsis. Crit Care Med. 36:1559–1563. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Bolton CF: Neuromuscular manifestations of
critical illness. Muscle Nerve. 32:140–163. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Friedrich O, Reid MB, Van den Berghe G,
Vanhorebeek I, Hermans G, Rich MM and Larsson L: The sick and the
weak: Neuropathies/myopathies in the critically Ill. Physiol Rev.
95:1025–1109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, Antonelli
M, Coopersmith CM, French C, Machado FR, Mcintyre L, Ostermann M,
Prescott HC, et al: Surviving sepsis campaign: International
guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021.
Intensive Care Med. 47:1181–1247. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Bos LDJ and Ware LB: Acute respiratory
distress syndrome: Causes, pathophysiology, and phenotypes. Lancet.
400:1145–1156. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Baer B, Putz ND, Riedmann K, Gonski S, Lin
J, Ware LB, Toki S, Peebles RS Jr, Cahill KN and Bastarache JA:
Liraglutide pretreatment attenuates sepsis-induced acute lung
injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 325:L368–L384. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Wang D, Xu L, Liu Y, Wang C, Qi S, Li Z,
Bai X, Liao Y and Wang Y: Role of mesenchymal stem cells in sepsis
and their therapeutic potential in sepsis-associated myopathy
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 54:922024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
99
|
Martin GS and Bernard GR; International
Sepsis Forum: Airway and lung in sepsis. Intensive Care Med.
27(Suppl 1): S63–S79. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Mazeraud A, Righy C, Bouchereau E,
Benghanem S, Bozza FA and Sharshar T: Septic-associated
encephalopathy: A comprehensive review. Neurotherapeutics.
17:392–403. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Catarina AV, Branchini G, Bettoni L, De
Oliveira JR and Nunes FB: Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: From
pathophysiology to progress in experimental studies. Mol Neurobiol.
58:2770–2779. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Li Y, Yin L, Fan Z, Su B, Chen Y, Ma Y,
Zhong Y, Hou W, Fang Z and Zhang X: Microglia: A potential
therapeutic target for sepsis-associated encephalopathy and
sepsis-associated chronic pain. Front Pharmacol. 11:6004212020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Fang Y, Jiang D, Wang Y, Wang Q, Lv D, Liu
J and Liu C: Neuroprotection of rhGLP-1 in diabetic rats with
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via regulation of oxidative
stress, EAAT2, and apoptosis. Drug Dev Res. 79:249–259. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Bi CF, Liu J, Yang LS and Zhang JF:
Research progress on the mechanism of sepsis induced myocardial
injury. J Inflamm Res. 15:4275–4290. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Aneman A and Vieillard-Baron A: Cardiac
dysfunction in sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 42:2073–2076. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Sharma A and Verma S: Mechanisms by which
glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose
cotransporter-2 inhibitors reduce cardiovascular risk in adults
with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Can J Diabetes. 44:93–102. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Noyan-Ashraf MH, Momen MA, Ban K, Sadi AM,
Zhou YQ, Riazi AM, Baggio LL, Henkelman RM, Husain M and Drucker
DJ: GLP-1R agonist liraglutide activates cytoprotective pathways
and improves outcomes after experimental myocardial infarction in
mice. Diabetes. 58:975–983. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Timmers L, Henriques JP, de Kleijn DP,
Devries JH, Kemperman H, Steendijk P, Verlaan CW, Kerver M, Piek
JJ, Doevendans PA, et al: Exenatide reduces infarct size and
improves cardiac function in a porcine model of ischemia and
reperfusion injury. J Am Coll Cardiol. 53:501–510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Bose AK, Mocanu MM, Carr RD, Brand CL and
Yellon DM: Glucagon-like peptide 1 can directly protect the heart
against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Diabetes. 54:146–151. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Chang G, Zhang D, Yu H, Zhang P, Wang Y,
Zheng A and Qin S: Cardioprotective effects of exenatide against
oxidative stress-induced injury. Int J Mol Med. 32:1011–1020. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Gómez H and Kellum JA: Sepsis-induced
acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Crit Care. 22:546–553. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Zarjou A and Agarwal A: Sepsis and acute
kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22:999–1006. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Wan L, Bagshaw SM, Langenberg C, Saotome
T, May C and Bellomo R: Pathophysiology of septic acute kidney
injury: What do we really know? Crit Care Med. 36(4 Suppl):
S198–S203. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Xiang L, Thompson MS, Clemmer JS, Mittwede
PN, Khan T and Hester RL: Early treatment with GLP-1 after severe
trauma preserves renal function in obese Zucker rats. Am J Physiol
Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 316:R621–R627. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Elkhoely A: Liraglutide ameliorates
gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury in rats via PGC-1α-mediated
mitochondrial biogenesis: Involvement of PKA/CREB and Notch/Hes-1
signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 114:1095782023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Xu C, Lu C, Wang Z, Hu X, Li S, Xie Y, Qiu
Y, Cao R, Li Y and Yang J: Liraglutide abrogates nephrotoxic
effects of chemotherapies. Pharmacol Res. 189:1066802023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Li YK, Ma DX, Wang ZM, Hu XF, Li SL, Tian
HZ, Wang MJ, Shu YW and Yang J: The glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)
analog liraglutide attenuates renal fibrosis. Pharmacol Res.
131:102–111. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Kasper P, Tacke F, Steffen HM and Michels
G: Hepatic dysfunction in sepsis. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed.
115:609–619. 2020.In German. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Horvatits T, Drolz A, Trauner M and
Fuhrmann V: Liver injury and failure in critical illness.
Hepatology. 70:2204–2215. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Strnad P, Tacke F, Koch A and Trautwein C:
Liver-guardian, modifier and target of sepsis. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14:55–66. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Milani L, Galindo CM, Turin de Oliveira
NM, Corso CR, Adami ER, Stipp MC, Beltrame OC and Acco A: The GLP-1
analog liraglutide attenuates acute liver injury in mice. Ann
Hepatol. 18:918–928. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Zhang WY, Hu XF, Wan N, Zhang JF, Yang P,
Wen Q, Chen WJ, Zhu F, Liang ML, Cheng LX and Shu YW: Protective
effect of the glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue liraglutide on
carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 514:386–392. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Abdelaziz AI, Mantawy EM, Gad AM, Fawzy HM
and Azab SS: Activation of pCREB/Nrf-2 signaling mediates
re-positioning of liraglutide as hepato-protective for
methotrexate-induced liver injury (MILI). Food Chem Toxicol.
132:1107192019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Zhu CG, Luo Y, Wang H, Li JY, Yang J, Liu
YX, Qu HQ, Wang BL and Zhu M: Liraglutide ameliorates
lipotoxicity-induced oxidative stress by activating the NRF2
pathway in HepG2 cells. Horm Metab Res. 52:532–539. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Fay KT, Ford ML and Coopersmith CM: The
intestinal microenvironment in sepsis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol
Basis Dis. 1863:2574–2583. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Mittal R and Coopersmith CM: Redefining
the gut as the motor of critical illness. Trends Mol Med.
20:214–223. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
127
|
Haseeb MA and Salwen MJ: Collateral
damage: Sepsis-induced gut injury. Crit Care Med. 33:2439–2440.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Deniz M, Atasoy BM, Dane F, Can G, Erzik
C, Çetinel Ş and Yeğen BÇ: Radiation-induced oxidative injury of
the ileum and colon is alleviated by glucagon-like peptide-1 and
-2. J Radiat Res Appl Sci. 8:234–242. 2015.
|
|
129
|
Semeraro N, Ammollo CT, Semeraro F and
Colucci M: Coagulopathy of acute sepsis. Semin Thromb Hemost.
41:650–658. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Bonetti PO, Lerman LO and Lerman A:
Endothelial dysfunction: A marker of atherosclerotic risk.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:168–175. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Gaspari T, Liu H, Welungoda I, Hu Y,
Widdop RE, Knudsen LB, Simpson RW and Dear AE: A GLP-1 receptor
agonist liraglutide inhibits endothelial cell dysfunction and
vascular adhesion molecule expression in an ApoE−/− mouse model.
Diab Vasc Dis Res. 8:117–124. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Shiraki A, Oyama J, Komoda H, Asaka M,
Komatsu A, Sakuma M, Kodama K, Sakamoto Y, Kotooka N, Hirase T and
Node K: The glucagon-like peptide 1 analog liraglutide reduces
TNF-α-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in endothelial
cells. Atherosclerosis. 221:375–382. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Erdogdu Ö, Eriksson L, Nyström T, Sjöholm
Å and Zhang Q: Exendin-4 restores glucolipotoxicity-induced gene
expression in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 419:790–795. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Steven S, Jurk K, Kopp M, Kröller-Schön S,
Mikhed Y, Schwierczek K, Roohani S, Kashani F, Oelze M, Klein T, et
al: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor signalling reduces
microvascular thrombosis, nitro-oxidative stress and platelet
activation in endotoxaemic mice. Br J Pharmacol. 174:1620–1632.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Gurjar AA, Kushwaha S, Chattopadhyay S,
Das N, Pal S, China SP, Kumar H, Trivedi AK, Guha R, Chattopadhyay
N and Sanyal S: Long acting GLP-1 analog liraglutide ameliorates
skeletal muscle atrophy in rodents. Metabolism. 103:1540442020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Hong Y, Lee JH, Jeong KW, Choi CS and Jun
HS: Amelioration of muscle wasting by glucagon-like peptide-1
receptor agonist in muscle atrophy. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle.
10:903–918. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Bonaldo P and Sandri M: Cellular and
molecular mechanisms of muscle atrophy. Dis Model Mech. 6:25–39.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
138
|
Choi DH, Yang J and Kim YS: Rapamycin
suppresses postnatal muscle hypertrophy induced by
myostatin-inhibition accompanied by transcriptional suppression of
the Akt/mTOR pathway. Biochem Biophys Rep. 17:182–190.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Lee SJ and McPherron AC: Regulation of
myostatin activity and muscle growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:9306–9311. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Sartori R, Milan G, Patron M, Mammucari C,
Blaauw B, Abraham R and Sandri M: Smad2 and 3 transcription factors
control muscle mass in adulthood. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
296:C1248–C1257. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Amirouche A, Durieux AC, Banzet S,
Koulmann N, Bonnefoy R, Mouret C, Bigard X, Peinnequin A and
Freyssenet D: Down-regulation of Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin
signaling pathway in response to myostatin overexpression in
skeletal muscle. Endocrinology. 150:286–294. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Silveira WA, Gonçalves DA, Graça FA,
Andrade-Lopes AL, Bergantin LB, Zanon NM, Godinho RO, Kettelhut IC
and Navegantes LC: Activating cAMP/PKA signaling in skeletal muscle
suppresses the ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent proteolysis:
Implications for sympathetic regulation. J Appl Physiol (1985).
117:11–19. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Le Grand F and Rudnicki MA: Skeletal
muscle satellite cells and adult myogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
19:628–633. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Stewart R, Flechner L, Montminy M and
Berdeaux R: CREB is activated by muscle injury and promotes muscle
regeneration. PLoS One. 6:e247142011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Fan D, Wang Y, Liu B and Yin F:
Hypoglycemic drug liraglutide alleviates low muscle mass by
inhibiting the expression of MuRF1 and MAFbx in diabetic muscle
atrophy. J Chin Med Assoc. 86:166–175. 2023.
|
|
146
|
Sandireddy R, Yerra VG, Areti A,
Komirishetty P and Kumar A: Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress
in diabetic neuropathy: Futuristic strategies based on these
targets. Int J Endocrinol. 2014:6749872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Ma J, Shi M, Zhang X, Liu X, Chen J, Zhang
R, Wang X and Zhang H: GLP-1R agonists ameliorate peripheral nerve
dysfunction and inflammation via p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways
in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int J Mol Med.
41:2977–2985. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Krasner NM, Ido Y, Ruderman NB and
Cacicedo JM: Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analog liraglutide
inhibits endothelial cell inflammation through a calcium and AMPK
dependent mechanism. PLoS One. 9:e975542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Mitchell PD, Salter BM, Oliveria JP,
El-Gammal A, Tworek D, Smith SG, Sehmi R, Gauvreau GM, Butler M and
O'Byrne PM: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor expression on human
eosinophils and its regulation of eosinophil activation. Clin Exp
Allergy. 47:331–338. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Yanay O, Bailey AL, Kernan K, Zimmerman JJ
and Osborne WR: Effects of exendin-4, a glucagon like peptide-1
receptor agonist, on neutrophil count and inflammatory cytokines in
a rat model of endotoxemia. J Inflamm Res. 8:129–135. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Powers SK, Hudson MB, Nelson WB, Talbert
EE, Min K, Szeto HH, Kavazis AN and Smuder AJ:
Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants protect against mechanical
ventilation-induced diaphragm weakness. Crit Care Med.
39:1749–1759. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Romanello V, Guadagnin E, Gomes L, Roder
I, Sandri C, Petersen Y, Milan G, Masiero E, Del Piccolo P, Foretz
M, et al: Mitochondrial fission and remodelling contributes to
muscle atrophy. EMBO J. 29:1774–1785. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Luna-Marco C, Iannantuoni F, Hermo-Argibay
A, Devos D, Salazar JD, Víctor VM and Rovira-Llopis S:
Cardiovascular benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor
agonists through effects on mitochondrial function and oxidative
stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 213:19–35. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Xie S, Zhang M, Shi W, Xing Y, Huang Y,
Fang WX, Liu SQ, Chen MY, Zhang T, Chen S, et al: Long-term
activation of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor by dulaglutide
prevents diabetic heart failure and metabolic remodeling in type 2
diabetes. J Am Heart Assoc. 11:e0267282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Helmstädter J, Frenis K, Filippou K, Grill
A, Dib M, Kalinovic S, Pawelke F, Kus K, Kröller-Schön S, Oelze M,
et al: Endothelial GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor
mediates cardiovascular protection by liraglutide in mice with
experimental arterial hypertension. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
40:145–158. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
156
|
Timper K, Del Río-Martín A, Cremer AL,
Bremser S, Alber J, Giavalisco P, Varela L, Heilinger C, Nolte H,
Trifunovic A, et al: GLP-1 receptor signaling in astrocytes
regulates fatty acid oxidation, mitochondrial integrity, and
function. Cell Metab. 31:1189–1205.e13. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Menconi M, Fareed M, O'Neal P, Poylin V,
Wei W and Hasselgren PO: Role of glucocorticoids in the molecular
regulation of muscle wasting. Crit Care Med. 35(9 Suppl):
S602–S608. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Combaret L, Taillandier D, Dardevet D,
Béchet D, Rallière C, Claustre A, Grizard J and Attaix D:
Glucocorticoids regulate mRNA levels for subunits of the 19 S
regulatory complex of the 26 S proteasome in fast-twitch skeletal
muscles. Biochem J. 378:239–246. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Turturici G, Sconzo G and Geraci F: Hsp70
and its molecular role in nervous system diseases. Biochem Res Int.
2011:6181272011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Petry ÉR, Dresch DF, Carvalho C, Medeiros
PC, Rosa TG, de Oliveira CM, Martins LAM, Schemitt E, Bona S, Guma
FCR, et al: Oral glutamine supplementation attenuates inflammation
and oxidative stress-mediated skeletal muscle protein content
degradation in immobilized rats: Role of 70 kDa heat shock protein.
Free Radic Biol Med. 145:87–102. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Hutchison KA, Dittmar KD, Stancato LF and
Pratt WB: Ability of various members of the hsp70 family of
chaperones to promote assembly of the glucocorticoid receptor into
a functional heterocomplex with hsp90. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
58:251–258. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Senf SM, Dodd SL, McClung JM and Judge AR:
Hsp70 overexpression inhibits NF-kappaB and Foxo3a transcriptional
activities and prevents skeletal muscle atrophy. FASEB J.
22:3836–3845. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Sadek MA, Kandil EA, El Sayed NS, Sayed HM
and Rabie MA: Semaglutide, a novel glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist,
amends experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis-induced multiple
sclerosis in mice: Involvement of the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 115:1096472023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
164
|
Ribeiro CB, Christofoletti DC, Pezolato
VA, de Cássia Marqueti Durigan R, Prestes J, Tibana RA, Pereira EC,
de Sousa Neto IV, Durigan JL and da Silva CA: Leucine minimizes
denervation-induced skeletal muscle atrophy of rats through
akt/mtor signaling pathways. Front Physiol. 6:732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Mohiuddin MS, Himeno T, Inoue R,
Miura-Yura E, Yamada Y, Nakai-Shimoda H, Asano S, Kato M, Motegi M,
Kondo M, et al: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist protects
dorsal root ganglion neurons against oxidative insult. J Diabetes
Res. 2019:94260142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Bell KE, von Allmen MT, Devries MC and
Phillips SM: Muscle disuse as a pivotal problem in
sarcopenia-related muscle loss and dysfunction. J Frailty Aging.
5:33–41. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Govers R: Molecular mechanisms of GLUT4
regulation in adipocytes. Diabetes Metab. 40:400–410. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Andreozzi F, Raciti GA, Nigro C, Mannino
GC, Procopio T, Davalli AM, Beguinot F, Sesti G, Miele C and Folli
F: The GLP-1 receptor agonists exenatide and liraglutide activate
glucose transport by an AMPK-dependent mechanism. J Transl Med.
14:2292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Purves T, Middlemas A, Agthong S, Jude EB,
Boulton AJ, Fernyhough P and Tomlinson DR: A role for
mitogen-activated protein kinases in the etiology of diabetic
neuropathy. FASEB J. 15:2508–2514. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Lluís F, Perdiguero E, Nebreda AR and
Muñoz-Cánoves P: Regulation of skeletal muscle gene expression by
p38 MAP kinases. Trends Cell Biol. 16:36–44. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Montessuit C, Rosenblatt-Velin N,
Papageorgiou I, Campos L, Pellieux C, Palma T and Lerch R:
Regulation of glucose transporter expression in cardiac myocytes:
p38 MAPK is a strong inducer of GLUT4. Cardiovasc Res. 64:94–104.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Guebre-Egziabher F, Alix PM, Koppe L,
Pelletier CC, Kalbacher E, Fouque D and Soulage CO: Ectopic lipid
accumulation: A potential cause for metabolic disturbances and a
contributor to the alteration of kidney function. Biochimie.
95:1971–1979. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Ruderman N and Prentki M: AMP kinase and
malonyl-CoA: Targets for therapy of the metabolic syndrome. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 3:340–351. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Cao HY, Xu F, Chen ZL, Lin BS, Zheng XB,
Yuan SH, Liang H and Weng JP: Effect of exendin-4 on lipid
deposition in skeletal muscle of diet-induced obese mice and its
underlying mechanism. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 97:131–136. 2017.In
Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Smits MM, Muskiet MH, Tonneijck L, Kramer
MH, Diamant M, van Raalte DH and Serné EH: GLP-1 receptor agonist
exenatide increases capillary perfusion independent of nitric oxide
in healthy overweight men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
35:1538–1543. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Montagnani M, Chen H, Barr VA and Quon MJ:
Insulin-stimulated activation of eNOS is independent of
Ca2+ but requires phosphorylation by Akt at Ser(1179). J
Biol Chem. 276:30392–30398. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Subaran SC, Sauder MA, Chai W, Jahn LA,
Fowler DE, Aylor KW, Basu A and Liu Z: GLP-1 at physiological
concentrations recruits skeletal and cardiac muscle
microvasculature in healthy humans. Clin Sci (Lond). 127:163–170.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Chai W, Dong Z, Wang N, Wang W, Tao L, Cao
W and Liu Z: Glucagon-like peptide 1 recruits microvasculature and
increases glucose use in muscle via a nitric oxide-dependent
mechanism. Diabetes. 61:888–896. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Tobaiqy M: A review of serious adverse
events linked with GLP-1 agonists in type 2 diabetes mellitus and
obesity treatment. Pharmacol Rep. 76:981–990. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S,
Davies M, Van Gaal LF, Lingvay I, McGowan BM, Rosenstock J, Tran
MTD, Wadden TA, et al: Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with
overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 384:989–1002. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Huang HH, Wang YJ, Jiang HY, Yu HW, Chen
YQ, Chiou A and Kuo JC: Sarcopenia-related changes in serum GLP-1
level affect myogenic differentiation. J Cachexia Sarcopenia
Muscle. 15:1708–1721. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Sargeant JA, Henson J, King JA, Yates T,
Khunti K and Davies MJ: A review of the effects of glucagon-like
peptide-1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2
inhibitors on lean body mass in humans. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul).
34:247–262. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|