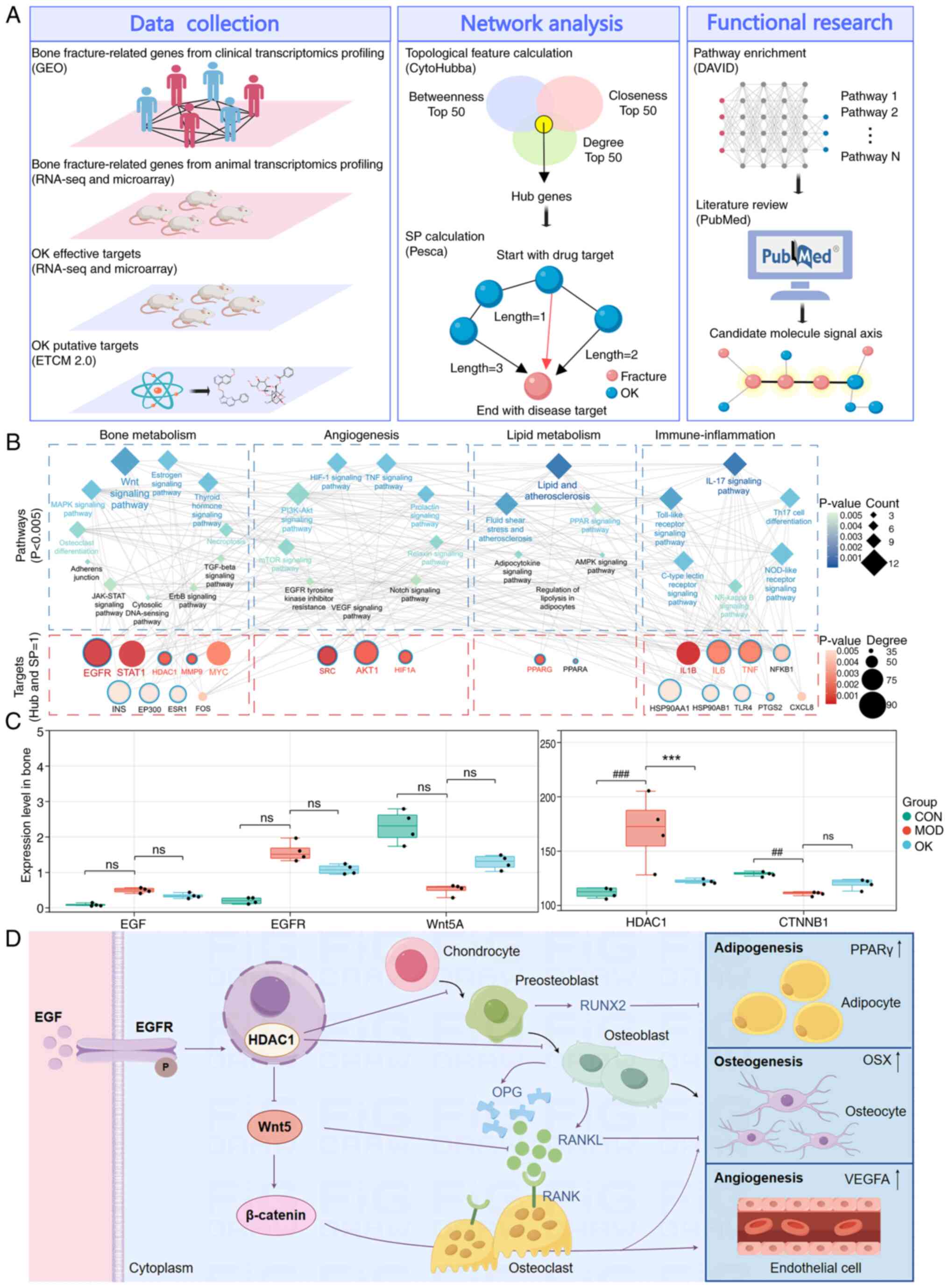
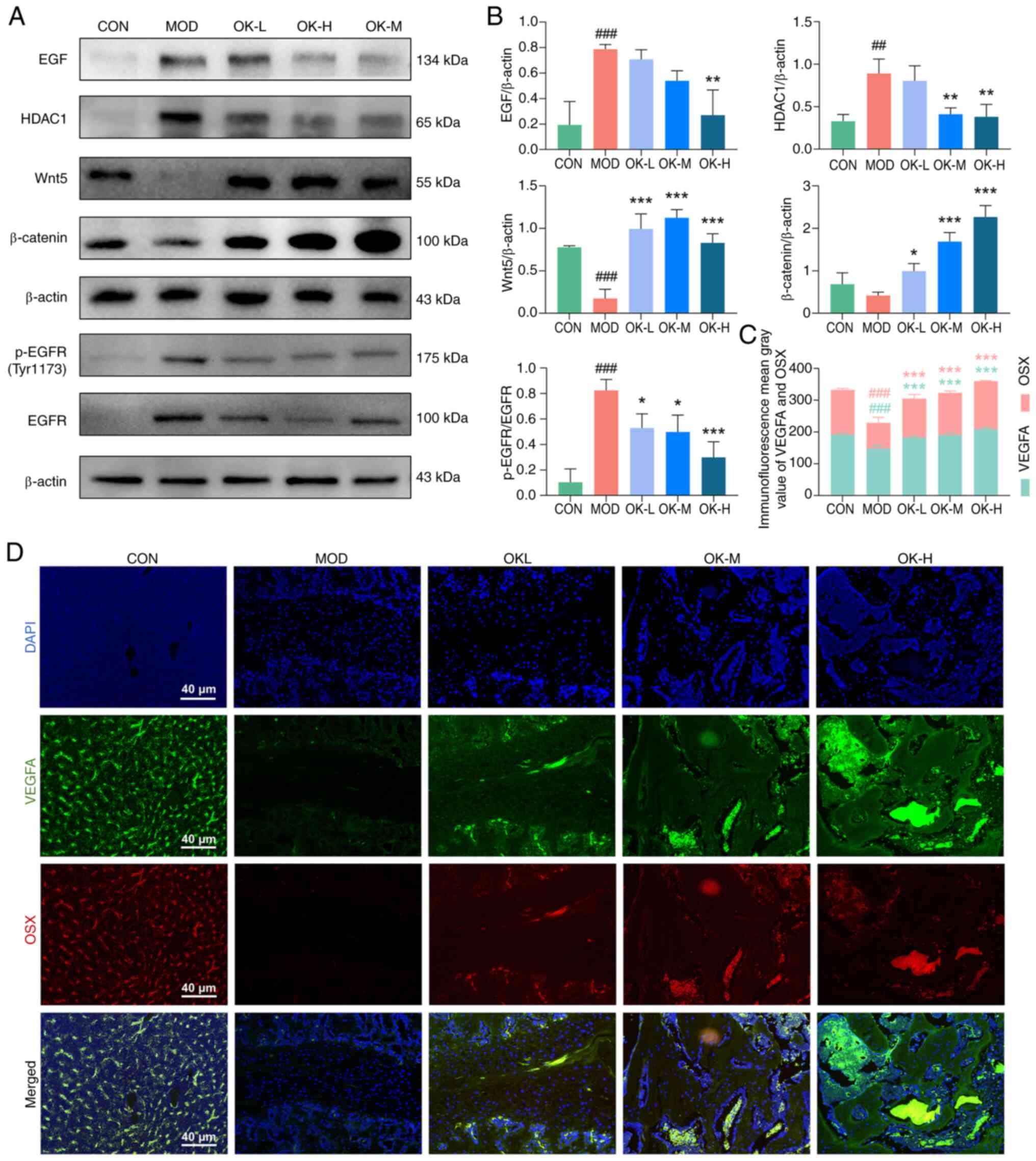
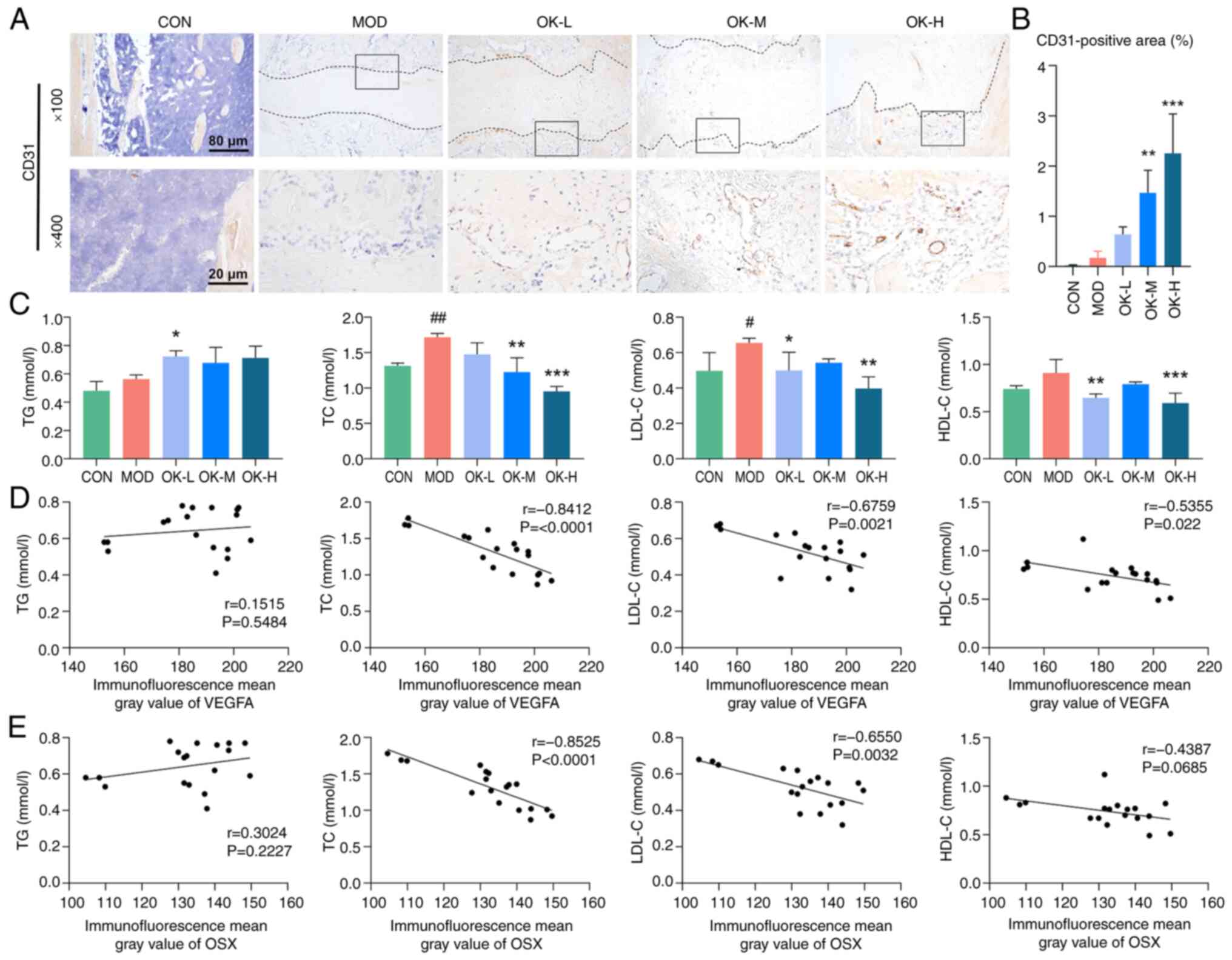
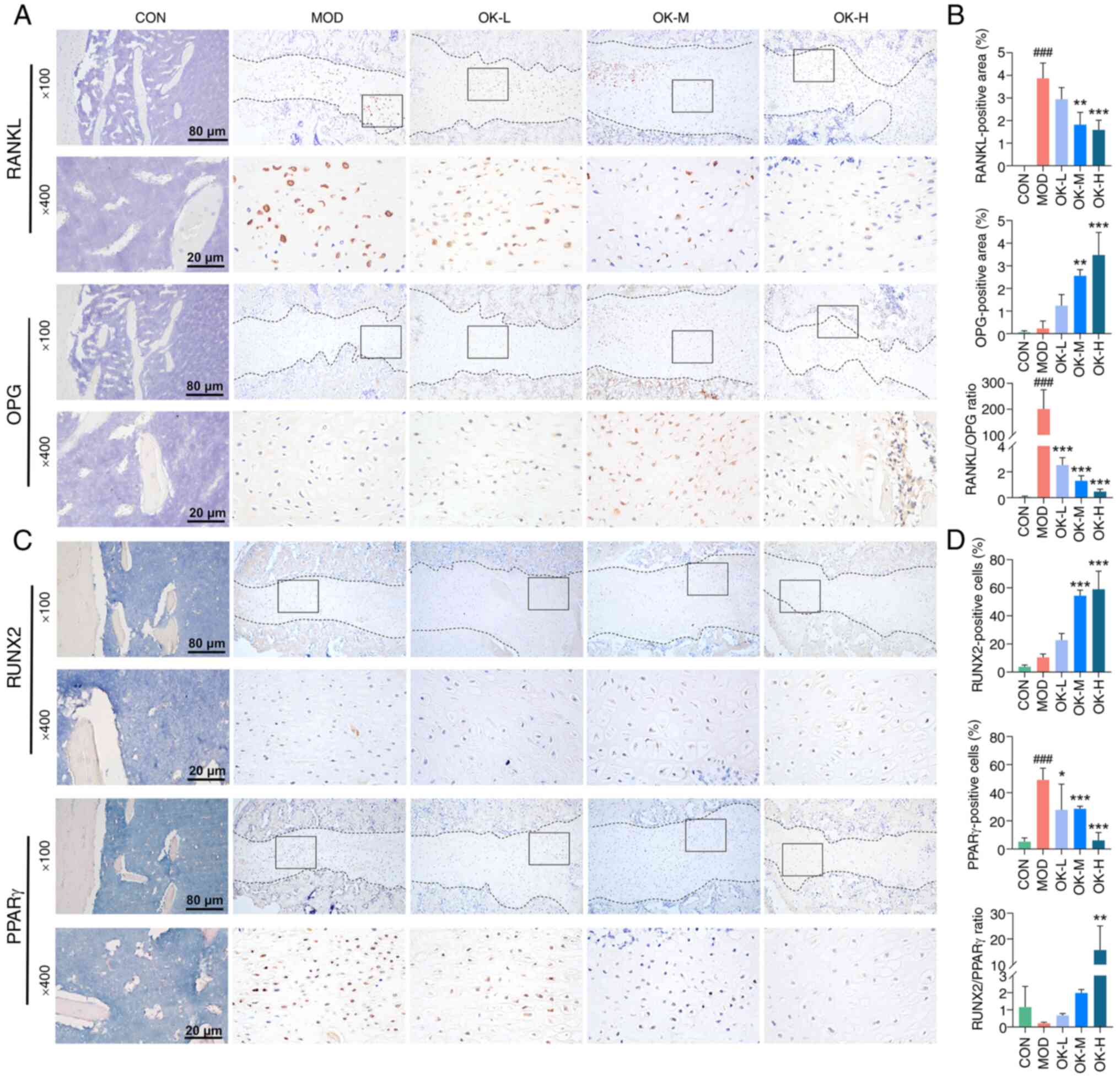
|
1
|
GBD 2019 Fracture Collaborators: Global,
regional, and national burden of bone fractures in 204 countries
and territories, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis from the global
burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2:e580–e592.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zura R, Xiong Z, Einhorn T, Watson JT,
Ostrum RF, Prayson MJ, Della Rocca GJ, Mehta S, McKinley T, Wang Z
and Steen RG: Epidemiology of fracture nonunion in 18 human bones.
JAMA Surg. 151:e1627752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ekegren CL, Edwards ER, de Steiger R and
Gabbe BJ: Incidence, costs and predictors of non-union, delayed
union and mal-union following long bone fracture. Int J Environ Res
Public Health. 15:28452018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hendrickx LAM, Virgin J, van den Bekerom
MPJ, Doornberg JN, Kerkhoffs GMMJ and Jaarsma RL: Complications and
subsequent surgery after intra-medullary nailing for tibial shaft
fractures: Review of 8110 patients. Injury. 51:1647–1654. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tian R, Zheng F, Zhao W, Zhang Y, Yuan J,
Zhang B and Li L: Prevalence and influencing factors of nonunion in
patients with tibial fracture: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
J Orthop Surg Res. 15:3772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Antonova E, Le TK, Burge R and Mershon J:
Tibia shaft fractures: Costly burden of nonunions. BMC
Musculoskelet Disord. 14:422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Davis S, Martyn-St James M, Sanderson J,
Stevens J, Goka E, Rawdin A, Sadler S, Wong R, Campbell F,
Stevenson M, et al: A systematic review and economic evaluation of
bisphosphonates for the prevention of fragility fractures. Health
Technol Assess. 20:1–406. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Hegde V, Jo JE, Andreopoulou P and Lane
JM: Effect of osteoporosis medications on fracture healing.
Osteoporos Int. 27:861–871. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Davis S, Simpson E, Hamilton J, James MMS,
Rawdin A, Wong R, Goka E, Gittoes N and Selby P: Denosumab,
raloxifene, romosozumab and teriparatide to prevent osteoporotic
fragility fractures: A systematic review and economic evaluation.
Health Technol Assess. 24:1–314. 2020. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Petrova NL, Donaldson NK, Bates M, Tang W,
Jemmott T, Morris V, Dew T, Meacock L, Elias DA, Moniz CF and
Edmonds ME: Effect of recombinant human parathyroid hormone (1-84)
on resolution of active charcot neuro-osteoarthropathy in diabetes:
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes
Care. 44:1613–1621. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Aro HT, Govender S, Patel AD, Hernigou P,
de Gregorio AP, Popescu GI, Golden JD, Christensen J and Valentin
A: Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: A randomized
trial in open tibial fractures treated with reamed nail fixation. J
Bone Joint Surg Am. 93:801–808. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ding W, Ji R, Yao S, Ruan P, Ye F, Lou X,
Ni L, Ji Y, Chen J and Ji W: Hu'po Anshen decoction promotes
fracture healing in mice with traumatic brain injury through
BMP2-COX2-ATF4 signaling pathway. FASEB J. 37:e229522023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Z, Li Y, Liu C, Gu Y and Han G:
Research progress of the mechanisms and applications of
ginsenosides in promoting bone formation. Phytomedicine.
129:1556042024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qian D, Zhang Q, He CX, Guo J, Huang XT,
Zhao J, Zhang H, Xu C and Peng W: Hai-Honghua medicinal liquor is a
reliable remedy for fracture by promotion of osteogenic
differentiation via activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. J
Ethnopharmacol. 330:1182342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang L, Kuang H, Zhang Z, Rong K, Yuan Y,
Peng Z, Zhao H, Liu K, Ou L and Kuang J: Efficacy and safety of
Osteoking on fracture healing: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 15:13634212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie L, Song X, Lei L, Chen C, Zhao H, Hu
J, Yu Y, Bai X, Wu X, Li X, et al: Exploring the potential
mechanism of Heng-Gu-Gu-Shang-Yu-He-Ji therapy for osteoporosis
based on network pharmacology and transcriptomics. J
Ethnopharmacol. 321:1174802024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Luo X, Liu J, Wang X, Chen Q, Lei Y, He Z,
Wang X, Ye Y, Na Q, Lao C, et al: Mechanism exploration of
Osteoking in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation based on
network pharmacology and molecular docking. J Orthop Surg Res.
19:882024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun Y, Chen R, Zhu D, Shen ZQ, Zhao HB and
Lee WH: Osteoking improves OP rat by enhancing HSP90-β expression.
Int J Mol Med. 45:1543–1553. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou J, Zheng Z, Luo Y, Dong Y, Yan Y,
Zhang Y, Tang K, Quan R, Lin J, Zhang K, et al: Clinical efficacy
of Osteoking in knee osteoarthritis therapy: A prospective,
multicenter, non-randomized controlled study in China. Front
Pharmacol. 15:13819362024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ling H, Zeng Q, Ge Q, Chen J, Yuan W, Xu
R, Shi Z, Xia H, Hu S, Jin H, et al: Osteoking decelerates
cartilage degeneration in dmm-induced osteoarthritic mice model
through TGF-β/smad-dependent manner. Front Pharmacol.
12:6788102021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang S, Liu Y, Ma Z, Gao S, Chen L, Zhong
H, Zhang C, Li T, Chen W, Zhang Y and Lin N: Osteoking promotes
bone formation and bone defect repair through
ZBP1-STAT1-PKR-MLKL-mediated necroptosis. Chin Med. 19:132024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun Z, Jin H, Zhou H, Yu L, Wan H and He
Y: Guhong Injection promotes fracture healing by activating
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Biomed
Pharmacother. 120:1094362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Alentado VJ, Knox AM, Staut CA, McGuire
AC, Chitwood JR, Mostardo SL, Shaikh MZ, Blosser RJ, Dadwal UC, Chu
TMG, et al: Validation of the modified radiographic union score for
tibia fractures (mRUST) in murine femoral fractures. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:9110582022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu X, Mao X, Liu Y, Chen W, Li W, Lin N
and Zhang Y: Preclinical efficacy of TZG in myofascial pain
syndrome by impairing PI3K-RAC2 signaling-mediated neutrophil
extracellular traps. iScience. 26:1080742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Garrick JM, Costa LG, Cole TB and
Marsillach J: Evaluating gait and locomotion in rodents with the
CatWalk. Curr Protoc. 1:e2202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Wang X, Ding Z, Lin N and Zhang
Y: Enhanced efficacy with reduced toxicity of tripterygium
glycoside tablet by compatibility with total glucosides of paeony
for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Biomed Pharmacother.
166:1154172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li W, Wang K, Liu Y, Wu H, He Y, Li C,
Wang Q, Su X, Yan S, Su W, et al: A novel drug combination of
mangiferin and cinnamic acid alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by
inhibiting TLR4/NFκB/NLRP3 activation-induced pyroptosis. Front
Immunol. 13:9129332022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang Y, Li X, Shi Y, Chen T, Xu Z, Wang
P, Yu M, Chen W, Li B, Jing Z, et al: ETCM v2.0: An update with
comprehensive resource and rich annotations for traditional Chinese
medicine. Acta Pharm Sin B. 13:2559–2571. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Scardoni G, Tosadori G, Pratap S, Spoto F
and Laudanna C: Finding the shortest path with PesCa: A tool for
network reconstruction. F1000Res. 4:4842015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma Z, Chen W, Liu Y, Yu L, Mao X, Guo X,
Jiang F, Guo Q, Lin N and Zhang Y: Artesunate Sensitizes human
hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib via exacerbating
AFAP1L2-SRC-FUNDC1 axis-dependent mitophagy. Autophagy. 20:541–556.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Li W, Mao X, Wu H, Guo M, Su X, Lu J, Guo
Q, Li T, Wang X, Su W, et al: Deciphering the chemical profile and
pharmacological mechanisms of Baihu-Guizhi decoction using
ultra-fast liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight tandem
mass spectrometry coupled with network pharmacology-based
investigation. Phytomedicine. 67:1531562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mao X, Li W, Chen W, Li Y, Wang Q, Wang X,
Pi Z, Wang D, Xu H, Guo Q, et al: Exploring and characterizing a
novel combination of paeoniflorin and talatizidine for the
treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacol Res. 153:1046582020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fu R, Liu C, Yan Y, Li Q and Huang RL:
Bone defect reconstruction via endochondral ossification: A
developmental engineering strategy. J Tissue Eng.
12:204173142110042112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Min R: Analysis of therapeutic effect of
henggu gushang healing agent combined with PFNA on
intertrochanteric fracture of femur. J JIANGXI Univ CM. 35:43–46.
2023.
|
|
35
|
He P, Yue C, Chen J, Ma M, Yang G, Wang Q
and Liu Y: Observation on the curative effect of Henggu Gushangyu
Mixture in the treatment of femoral intertrochanteric fracture
after internal fixation. Fujian J TCM. 53:60–62. 2022.
|
|
36
|
Liu Z, Zhao X, Luo W and Wang L: The
effect of osteoking on postoperative fracture healing of femoral
neck fracture. Int J Trad Chin Med. 44:1122–1126. 2022.
|
|
37
|
Einhorn TA and Gerstenfeld LC: Fracture
healing: Mechanisms and interventions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 11:45–54.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Menger MM, Laschke MW, Nussler AK, Menger
MD and Histing T: The vascularization paradox of non-union
formation. Angiogenesis. 25:279–290. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bixel MG, Sivaraj KK, Timmen M,
Mohanakrishnan V, Aravamudhan A, Adams S, Koh BI, Jeong HW, Kruse
K, Stange R and Adams RH: Angiogenesis is uncoupled from
osteogenesis during calvarial bone regeneration. Nat Commun.
15:45752024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Maes C, Kobayashi T, Selig MK, Torrekens
S, Roth SI, Mackem S, Carmeliet G and Kronenberg HM: Osteoblast
precursors, but not mature osteoblasts, move into developing and
fractured bones along with invading blood vessels. Dev Cell.
19:329–344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Huang C, Ness VP, Yang X, Chen H, Luo J,
Brown EB and Zhang X: Spatiotemporal analyses of osteogenesis and
angiogenesis via intravital imaging in cranial bone defect repair.
J Bone Miner Res. 30:1217–1230. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhu S, Chen W, Masson A and Li YP: Cell
signaling and transcriptional regulation of osteoblast lineage
commitment, differentiation, bone formation, and homeostasis. Cell
Discov. 10:712024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Burger MG, Grosso A, Briquez PS, Born GME,
Lunger A, Schrenk F, Todorov A, Sacchi V, Hubbell JA, Schaefer DJ,
et al: Robust coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by
VEGF-decorated matrices for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater.
149:111–125. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rauch A, Haakonsson AK, Madsen JGS, Larsen
M, Forss I, Madsen MR, Van Hauwaert EL, Wiwie C, Jespersen NZ,
Tencerova M, et al: Osteogenesis depends on commissioning of a
network of stem cell transcription factors that act as repressors
of adipogenesis. Nat Genet. 51:716–727. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ambrosi TH, Scialdone A, Graja A, Gohlke
S, Jank AM, Bocian C, Woelk L, Fan H, Logan DW, Schürmann A, et al:
Adipocyte accumulation in the bone marrow during obesity and aging
impairs stem cell-based hematopoietic and bone regeneration. Cell
Stem Cell. 20:771–784.e6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Schubert J, Lindahl B, Melhus H, Renlund
H, Leosdottir M, Yari A, Ueda P, Jernberg T and Hagström E:
Elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol: An inverse marker of
morbidity and mortality in patients with myocardial infarction. J
Intern Med. 294:616–627. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Poiana C, Radoi V, Carsote M and
Bilezikian JP: New clues that may link osteoporosis to the
circulating lipid profile. Bone Res. 1:260–266. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mandal CC: High Cholesterol deteriorates
bone health: New insights into molecular mechanisms. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 6:1652015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chang PY, Gold EB, Cauley JA, Johnson WO,
Karvonen-Gutierrez C, Jackson EA, Ruppert KM and Lee JS:
Triglyceride levels and fracture risk in midlife women: Study of
women's health across the nation (SWAN). J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
101:3297–3305. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fang L, Choi SH, Baek JS, Liu C, Almazan
F, Ulrich F, Wiesner P, Taleb A, Deer E, Pattison J, et al: Control
of angiogenesis by AIBP-mediated cholesterol efflux. Nature.
498:118–122. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen H, Shao Z, Gao Y, Yu X, Huang S and
Zeng P: Are blood lipids risk factors for fracture? Integrative
evidence from instrumental variable causal inference and mediation
analysis using genetic data. Bone. 131:1151742020.
|
|
52
|
Barzilay JI, Buzkova P, Kuller LH, Cauley
JA, Fink HA, Sheets K, Robbins JA, Carbone LD, Elam RE and Mukamal
KJ: The association of lipids and lipoproteins with hip fracture
risk: The cardiovascular health study. Am J Med. 135:1101–1108.e1.
2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Baek WY and Kim JE: Transcriptional
regulation of bone formation. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 3:126–135.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim HY, Jang HJ, Muthamil S, Shin UC, Lyu
JH, Kim SW, Go Y, Park SH, Lee HG and Park JH: Novel insights into
regulators and functional modulators of adipogenesis. Biomed
Pharmacother. 177:1170732024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Huang X, Chen W, Gu C, Liu H, Hou M, Qin
W, Zhu X, Chen X, Liu T, Yang H and He F: Melatonin suppresses bone
marrow adiposity in ovariectomized rats by rescuing the imbalance
between osteogenesis and adipogenesis through SIRT1 activation. J
Orthop Translat. 38:84–97. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dong Y, Zhou H, Alhaskawi A, Wang Z, Lai
J, Abdullah Ezzi SH, Kota VG, Abdulla Hasan Abdulla MH, Sun Z and
Lu H: Alterations in bone fracture healing associated with TNFRSF
signaling pathways. Front Pharmacol. 13:9055352022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yu G, Fu X, Gong A, Gu J, Zou H, Yuan Y,
Song R, Ma Y, Bian J, Liu Z and Tong X: Oligomeric
proanthocyanidins ameliorates osteoclastogenesis through reducing
OPG/RANKL ratio in chicken's embryos. Poult Sci.
103:1037062024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhu J, Shimizu E, Zhang X, Partridge NC
and Qin L: EGFR signaling suppresses osteoblast differentiation and
inhibits expression of master osteoblastic transcription factors
Runx2 and osterix. J Cell Biochem. 112:1749–1760. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lees-Shepard JB, Flint K, Fisher M, Omi M,
Richard K, Antony M, Chen PJ, Yadav S, Threadgill D, Maihle NJ and
Dealy CN: Cross-talk between EGFR and BMP signals regulates
chondrocyte maturation during endochondral ossification. Dev Dyn.
251:75–94. 2022.
|
|
60
|
Yi T, Lee HL, Cha JH, Ko SI, Kim HJ, Shin
HI, Woo KM, Ryoo HM, Kim GS and Baek JH: Epidermal growth factor
receptor regulates osteoclast differentiation and survival through
cross-talking with RANK signaling. J Cell Physiol. 217:409–422.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Haberland M, Carrer M, Mokalled MH,
Montgomery RL and Olson EN: Redundant control of adipogenesis by
histone deacetylases 1 and 2. J Biol Chem. 285:14663–14670.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Vishal M, Ajeetha R, Keerthana R and
Selvamurugan N: Regulation of Runx2 by histone deacetylases in
bone. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 17:343–351. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhong YT, Liao HB, Ye ZQ, Jiang HS, Li JX,
Ke LM, Hua JY, Wei B, Wu X and Cui L: Eurycomanone stimulates bone
mineralization in zebrafish larvae and promotes osteogenic
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by upregulating
AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling. J Orthop Translat. 40:132–146.
2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kramer I, Halleux C, Keller H, Pegurri M,
Gooi JH, Weber PB, Feng JQ, Bonewald LF and Kneissel M: Osteocyte
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is required for normal bone homeostasis.
Mol Cell Biol. 30:3071–3085. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Albers J, Keller J, Baranowsky A, Beil FT,
Catala-Lehnen P, Schulze J, Amling M and Schinke T: Canonical Wnt
signaling inhibits osteoclastogenesis independent of
osteoprotegerin. J Cell Biol. 200:537–549. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Takada I, Kouzmenko AP and Kato S: Wnt and
PPARgamma signaling in osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis. Nat Rev
Rheumatol. 5:442–447. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Takada I, Kouzmenko AP and Kato S:
Molecular switching of osteoblastogenesis versus adipogenesis:
Implications for targeted therapies. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
13:593–603. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Olsen JJ, Pohl SÖG, Deshmukh A,
Visweswaran M, Ward NC, Arfuso F, Agostino M and Dharmarajan A: The
role of Wnt signalling in angiogenesis. Clin Biochem Rev.
38:131–142. 2017.
|