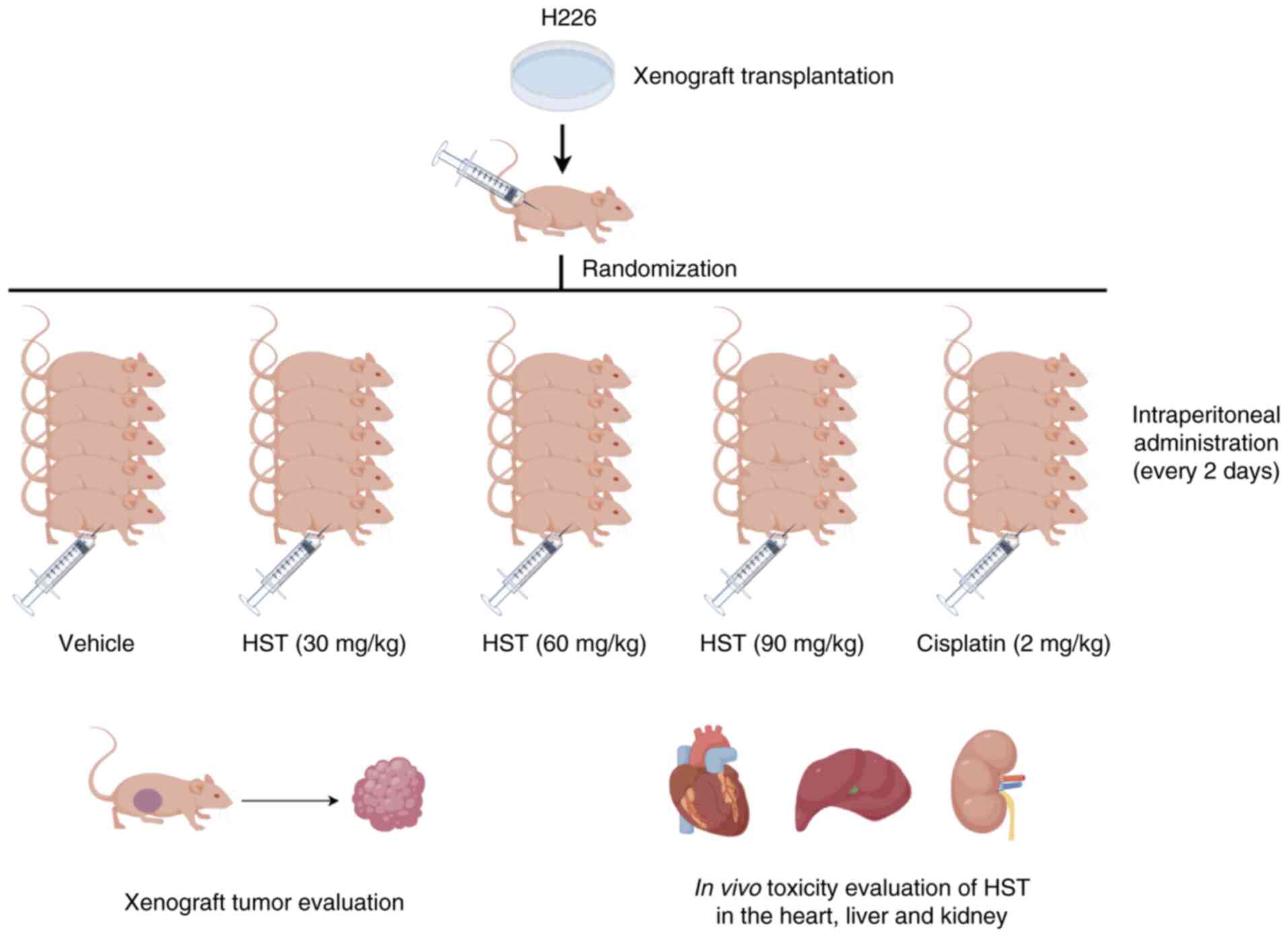
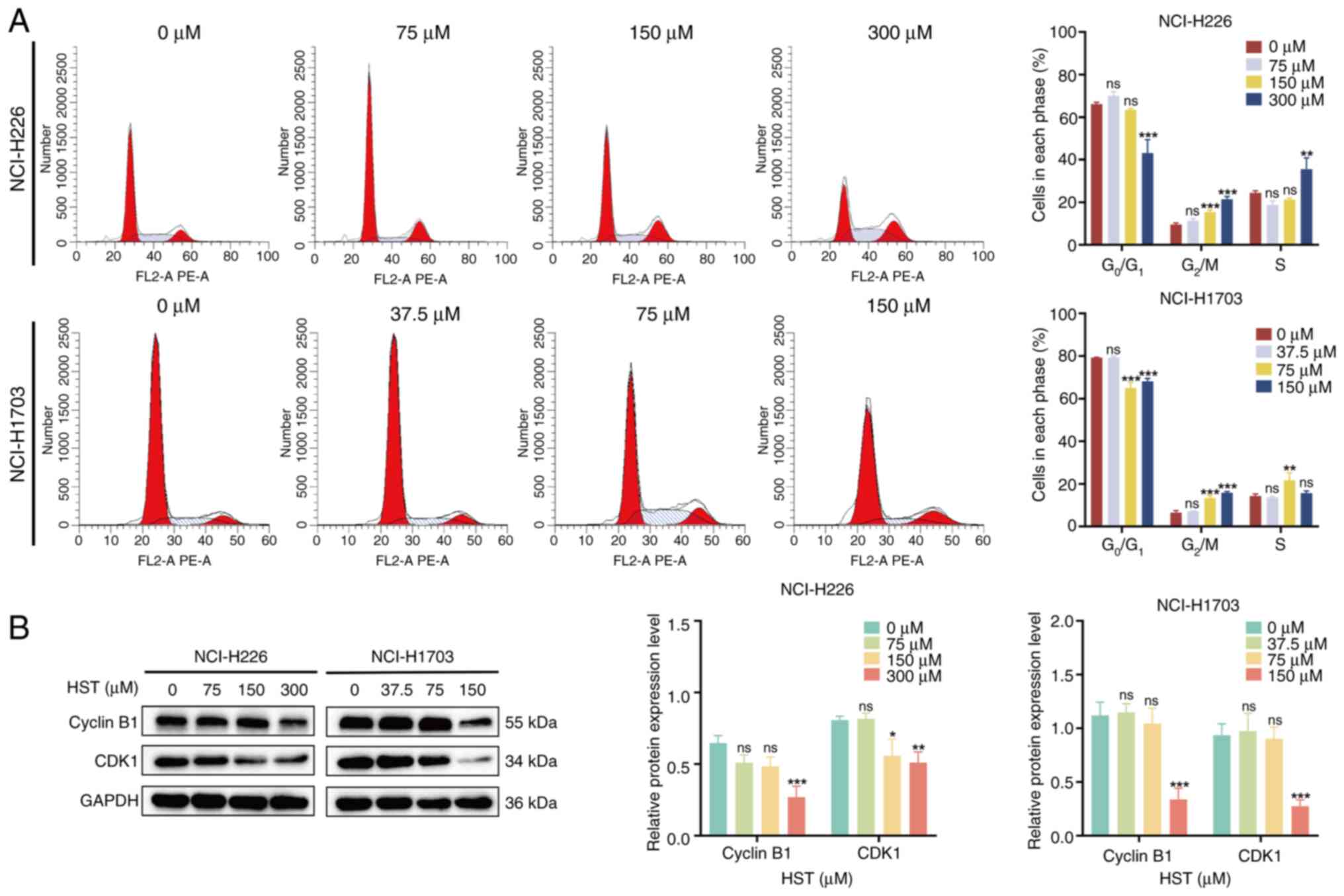
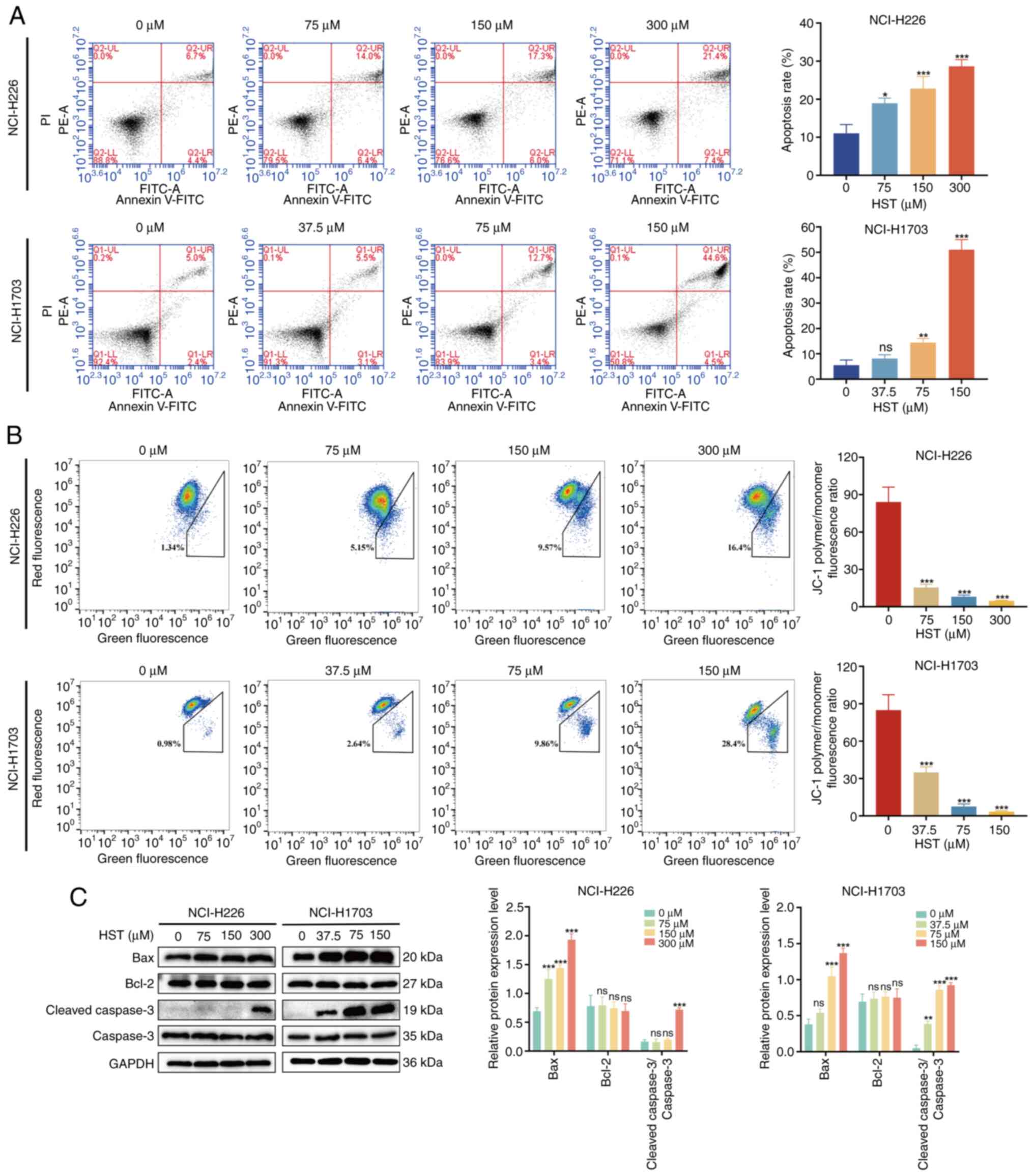
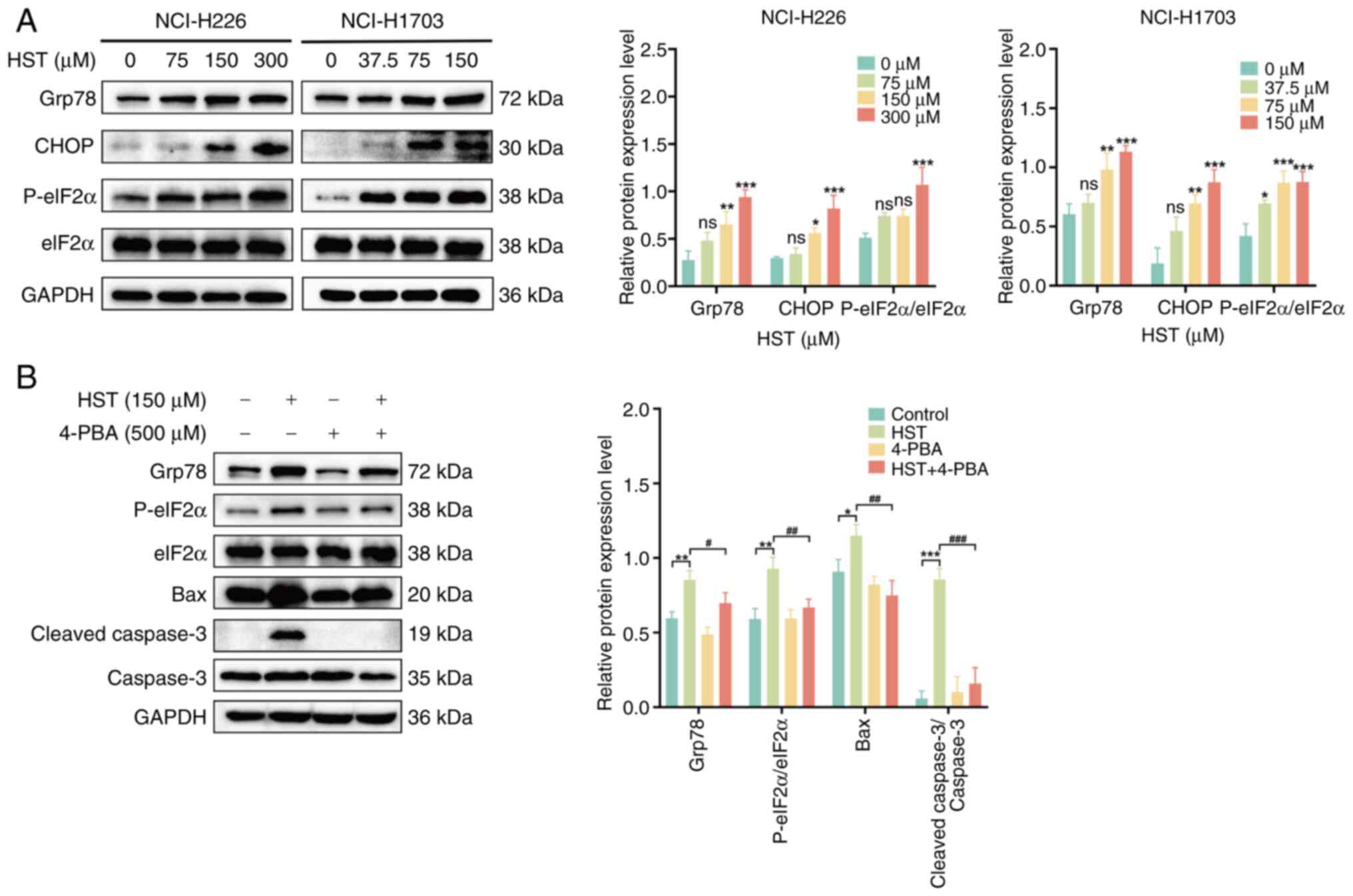
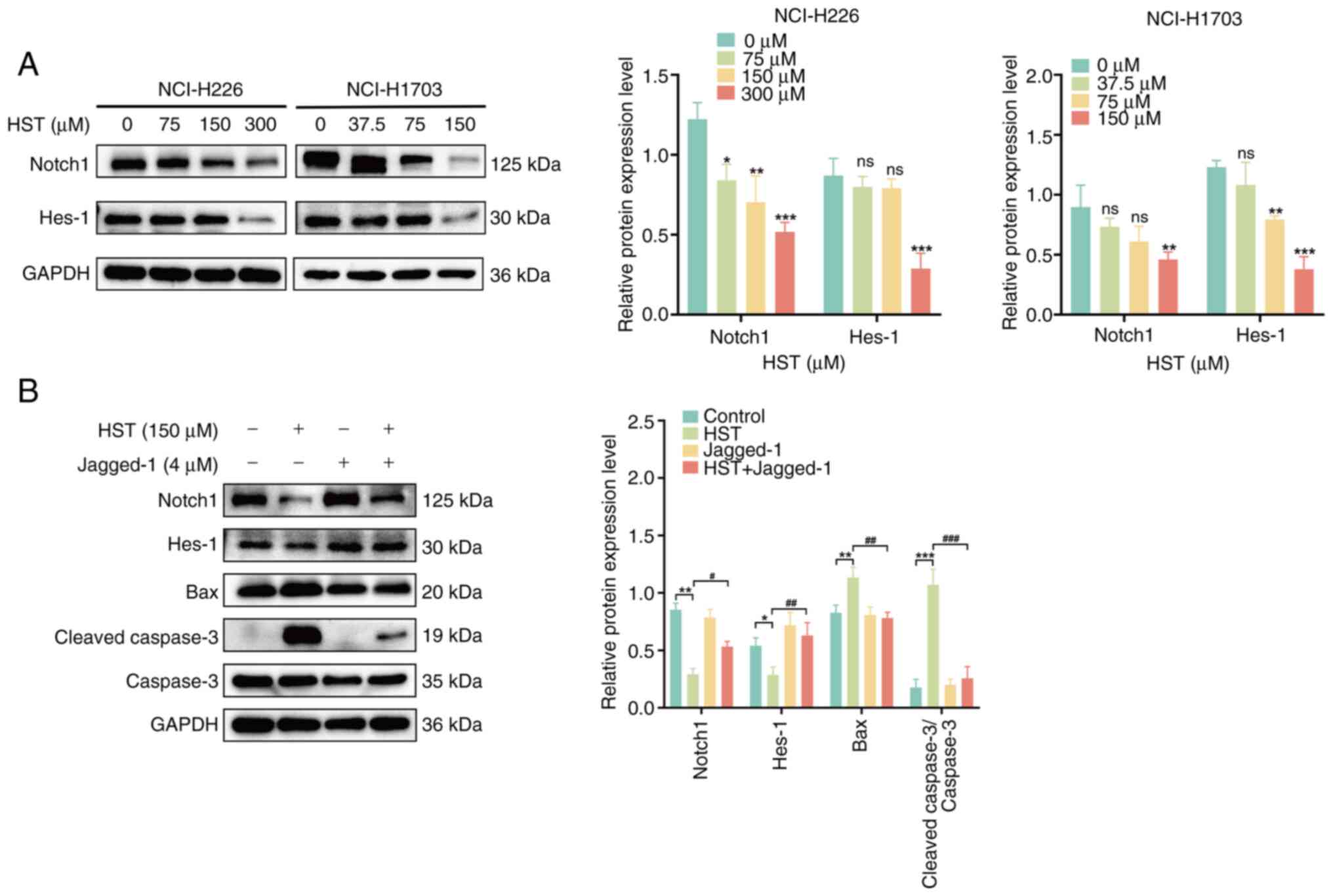
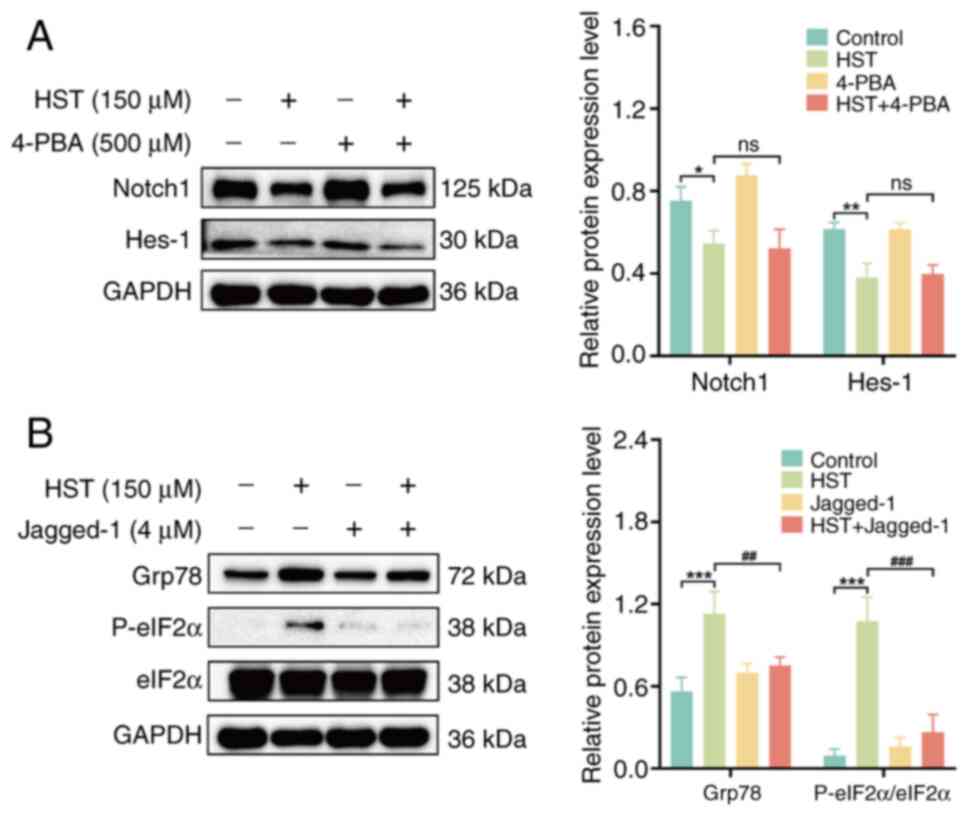
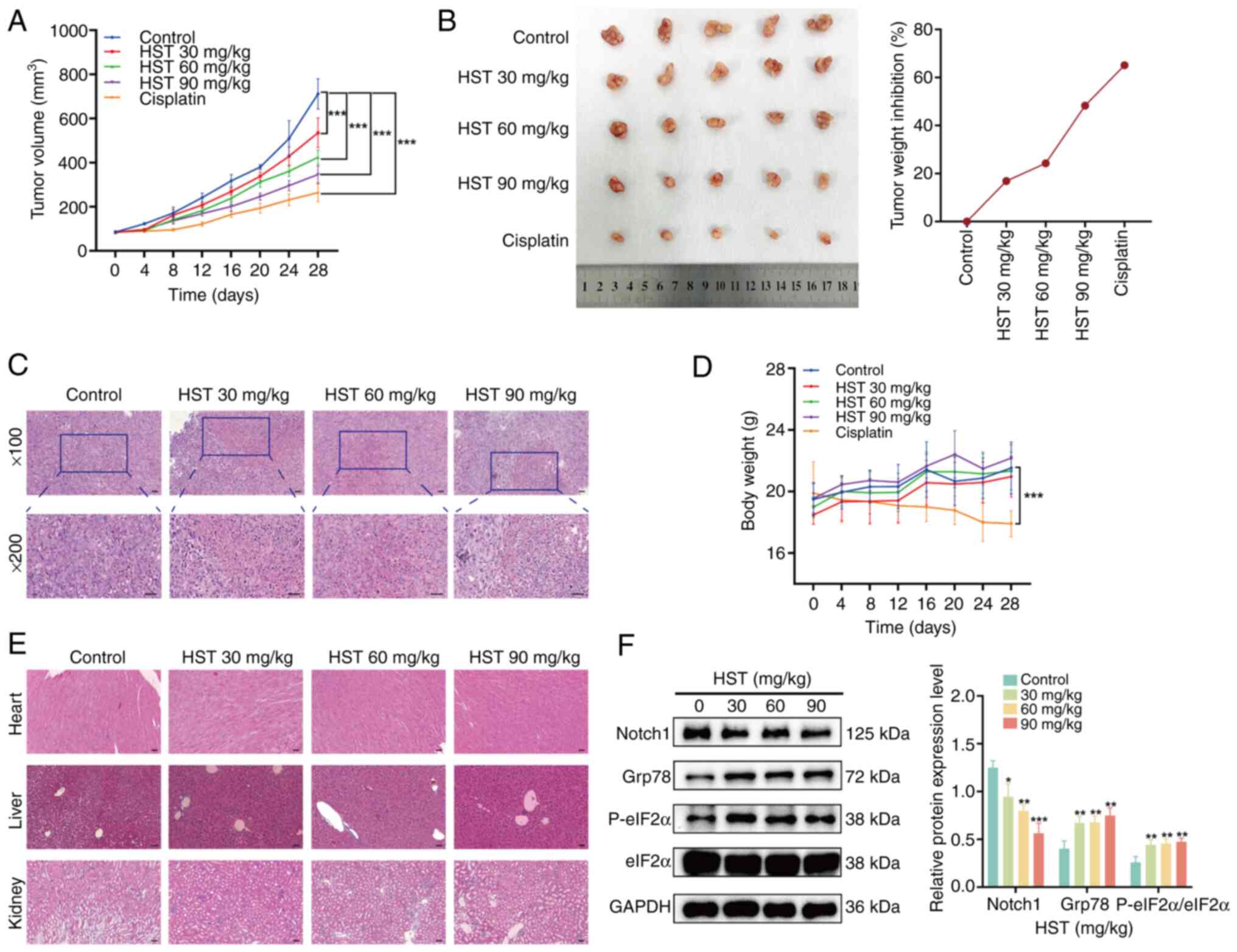
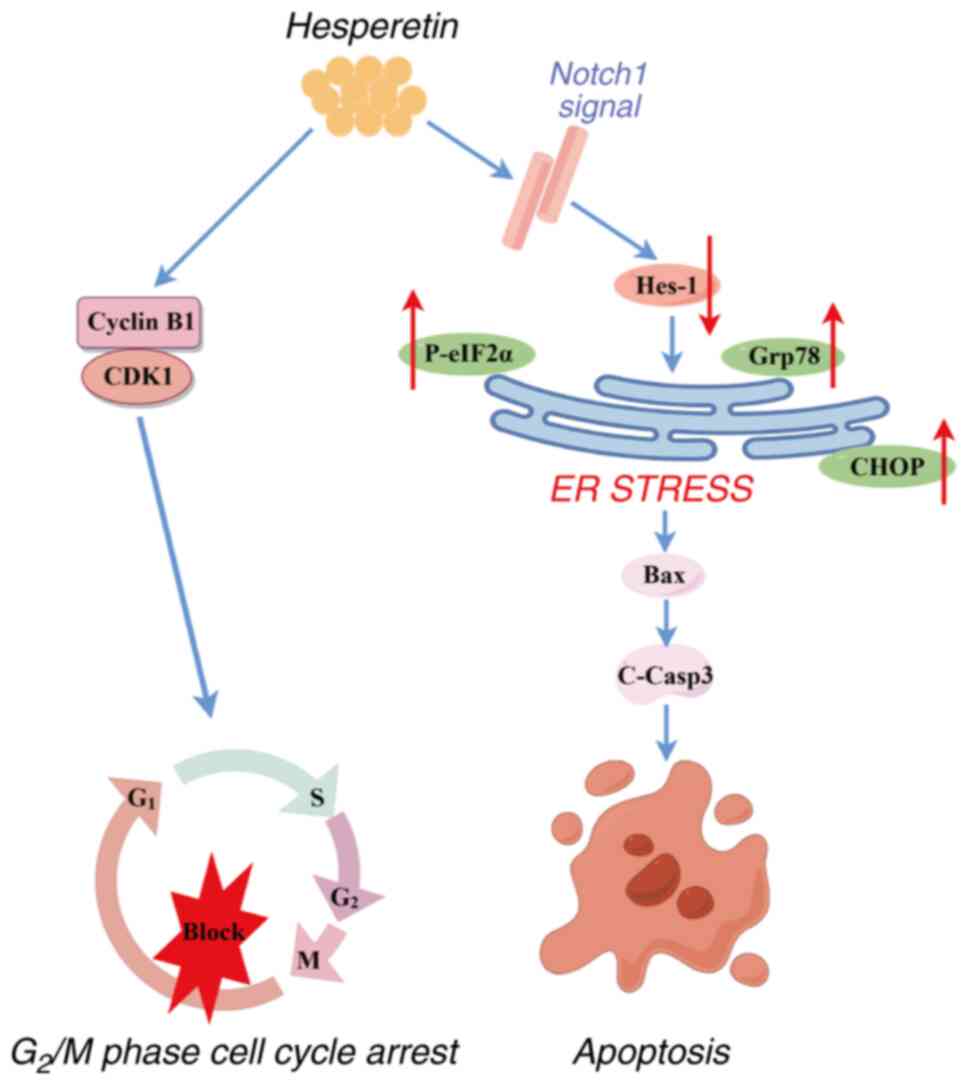
|
1
|
Li C, Lei S, Ding L, Xu Y, Wu X, Wang H,
Zhang Z, Gao T, Zhang Y and Li L: Global burden and trends of lung
cancer incidence and mortality. Chin Med J (Engl). 136:1583–1590.
2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oncology Society of Chinese Medical
Association; Chinese Medical Association Publishing House: Chinese
Medical Association guideline for clinical diagnosis and treatment
of lung cancer (2023 edition). Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.
103:2037–2074. 2023.In Chinese.
|
|
3
|
Wang J, Shen Q, Shi Q, Yu B, Wang X, Cheng
K, Lu G and Zhou X: Detection of ALK protein expression in lung
squamous cell carcinomas by immunohistochemistry. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 33:1092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arora S, Sheoran S, Baniya B, Subbarao N,
Singh H, Prabhu D, Kumar N, Pawar SC and Vuree S: Hesperidin's role
in the treatment of lung cancer: In-silico and In-vitro findings.
In Silico Pharmacol. 12:1042024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Drilon A, Rekhtman N, Ladanyi M and Paik
P: Squamous-cell carcinomas of the lung: Emerging biology,
controversies, and the promise of targeted therapy. Lancet Oncol.
13:e418–e426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sohel M, Sultana H, Sultana T, Al Amin M,
Aktar S, Ali MC, Rahim ZB, Hossain MA, Al Mamun A, Amin MN and Dash
R: Chemotherapeutic potential of hesperetin for cancer treatment,
with mechanistic insights: A comprehensive review. Heliyon.
8:e088152022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li L, Ren Z, Zhao P and Liu X: Research
progress in antitumor pharmacological activities of hesperidin and
hesperetin. Acta Chin Med. 33:2304–2308. 2018.In Chinese.
|
|
8
|
Elango R, Athinarayanan J, Subbarayan VP,
Lei DKY and Alshatwi AA: Hesperetin induces an apoptosis-triggered
extrinsic pathway and a p53-independent pathway in human lung
cancer H522 cells. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 20:559–569. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wolfram J, Scott B, Boom K, Shen J, Borsoi
C, Suri K, Grande R, Fresta M, Celia C, Zhao Y, et al: Hesperetin
liposomes for cancer therapy. Curr Drug Deliv. 13:711–719. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ramteke P and Umesh CSY: Hesperetin, a
Citrus bioflavonoid, prevents IL-1β-induced inflammation and cell
proliferation in lung epithelial A549 cells. Indian J Exp Biol.
57:7–14. 2019.
|
|
11
|
Chaudhari A, Seol JW, Kim SJ, Lee YJ, Kang
HS, Kim IS, Kim NS and Park SY: Reactive oxygen species regulate
Bax translocation and mitochondrial transmembrane potential, a
possible mechanism for enhanced TRAIL-induced apoptosis by CCCP.
Oncol Rep. 18:71–76. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shi Q, Xue C, Zeng Y, Yuan X, Chu Q, Jiang
S, Wang J, Zhang Y, Zhu D and Li L: Notch signaling pathway in
cancer: From mechanistic insights to targeted therapies. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 9:1282024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Babukumar S, Vinothkumar V and
Ramachandhiran D: Modulating effect of hesperetin on the molecular
expression pattern of apoptotic and cell proliferative markers in
7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced oral carcinogenesis. Arch
Physiol Biochem. 126:430–439. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Canaud G and Bonventre JV: Cell cycle
arrest and the evolution of chronic kidney disease from acute
kidney injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 30:575–583. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Jiang L, Liu Y, Tumbath S, Boudreau MW,
Chatkewitz LE, Wang J, Su X, Zahid KR, Li K, Chen Y, et al:
Isopentyl-deoxynboquinone induces mitochondrial dysfunction and
G2/M phase cell cycle arrest to selectively kill NQO1-positive
pancreatic cancer cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 41:74–92. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zou X, Qu Z, Gao P, Sun S and Ji Y:
Effects of Sulforaphane on G2/M phase arrest in HepG-2 cells and
the expression of Cdk1 and CyclinB1. Acta Chin Med Pharmacol.
38:8–12. 2010.In Chinese.
|
|
17
|
Krueger A, Baumann S, Krammer PH and
Kirchhoff S: FLICE-inhibitory proteins: Regulators of death
receptor-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 21:8247–8254. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Walensky LD: BCL-2 in the crosshairs:
Tipping the balance of life and death. Cell Death Differ.
13:1339–1350. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kato H and Nishitoh H: Stress responses
from the endoplasmic reticulum in cancer. Front Oncol. 5:932015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Faitova J, Krekac D, Hrstka R and Vojtesek
B: Endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
11:488–505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park SH, Park HS, Lee JH, Chi GY, Kim GY,
Moon SK, Chang YC, Hyun JW, Kim WJ and Choi YH: Induction of
endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis and non-canonical
autophagy by luteolin in NCI-H460 lung carcinoma cells. Food Chem
Toxicol. 56:100–109. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qiu C, Zhang T, Zhang W, Zhou L, Yu B,
Wang W, Yang Z, Liu Z, Zou P and Liang G: Licochalcone a inhibits
the proliferation of human lung cancer cell lines A549 and H460 by
inducing G2/M cell cycle arrest and ER stress. Int J Mol Sci.
18:17612017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen S, Wu Z, Ke Y, Shu P, Chen C, Lin R
and Shi Q: Wogonoside inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in
endometrial cancer via ER stress-Hippo signaling axis. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 51:1096–1105. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Saran U, Chandrasekaran B, Tyagi A, Shukla
V, Singh A, Sharma AK and Damodaran C: Corrigendum: A small
molecule inhibitor of Notch1 modulates stemness and suppresses
breast cancer cell growth. Front Pharmacol. 14:12075892023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun J, Dong M, Xiang X, Zhang S and Wen D:
Notch signaling and targeted therapy in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Lett. 585:2166472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Anusewicz D, Orzechowska M and Bednarek
AK: Lung squamous cell carcinoma and lung adenocarcinoma
differential gene expression regulation through pathways of Notch,
Hedgehog, Wnt, and ErbB signalling. Sci Rep. 10:211282020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zong D, Ouyang R, Li J, Chen Y and Chen P:
Notch signaling in lung diseases: Focus on Notch1 and Notch3. Ther
Adv Respir Dis. 10:468–484. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou L, Wu S, Yu L, Gong X, Song W and
Cheng Z: Expression of CD133 and Notch1 in non-small cell lung
cancer and the clinicopathological significance. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da
Xue Xue Bao. 35:196–201, In Chinese.
|
|
29
|
Yuan X, Wu H, Xu H, Han N, Chu Q, Yu S,
Chen Y and Wu K: Meta-analysis reveals the correlation of Notch
signaling with non-small cell lung cancer progression and
prognosis. Sci Rep. 5:103382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cao H, Hu Y, Wang P, Zhou J, Deng Z and
Wen J: Down-regulation of Notch receptor signaling pathway induces
caspase-dependent and caspase-independent apoptosis in lung
squamous cell carcinoma cells. APMIS. 120:441–450. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lu CJ, He YF, Yuan WZ, Xiang LJ, Zhang J,
Liang YR, Duan J, He YH and Li MY: Dihydromyricetin-mediated
inhibition of the Notch1 pathway induces apoptosis in QGY7701 and
HepG2 hepatoma cells. World J Gastroenterol. 23:6242–6251. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Khan F, Pandey P, Jha NK, Khalid M and
Ojha S: Rutin mediated apoptotic cell death in caski cervical
cancer cells via Notch-1 and Hes-1 downregulation. Life (Basel).
11:7612021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kunnimalaiyaan S, Sokolowski KM,
Balamurugan M, Gamblin TC and Kunnimalaiyaan M: Xanthohumol
inhibits Notch signaling and induces apoptosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01274642015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tremblay I, Paré E, Arsenault D, Douziech
M and Boucher MJ: The MEK/ERK pathway promotes NOTCH signalling in
pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e855022013.
|
|
35
|
Zhang M, Yu LM, Zhao H, Zhou XX, Yang Q,
Song F, Yan L, Zhai ME, Li BY, Zhang B, et al:
2,3,5,4′-Tetrahydroxystilbe ne-2-O-β-D-glucoside protects murine
hearts against ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating
Notch1/Hes1 signaling and attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:317–330. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gan L, Liu Z, Wu T, Feng F and Sun C: αMSH
promotes preadipocyte proliferation by alleviating ER
stress-induced leptin resistance and by activating Notch1 signal in
mice. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:231–238. 2017.
|
|
37
|
Silva Barcelos EC, Rompietti C, Adamo FM,
Dorillo E, De Falco F, Del Papa B, Baldoni S, Nogarotto M, Esposito
A, Capoccia S, et al: NOTCH1-mutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia
displays high endoplasmic reticulum stress response with druggable
potential. Front Oncol. 13:12189892023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Barcelos ECS, Rompietti C, Adamo FM,
Dorillo E, De Falco F, Del Papa B, Baldoni S, Nogarotto M, Esposito
A, Capoccia SJ, et al: NOTCH1-mutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia
displays high endoplasmic reticulum stress response with druggable
potential. Front Oncol. 13:12189892023.
|
|
39
|
Bodduluru LN, Kasala ER, Barua CC, Karnam
KC, Dahiya V and Ellutla M: Antiproliferative and antioxidant
potential of hesperetin against benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung
carcinogenesis in Swiss albino mice. Chem Biol Interact.
242:345–352. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|