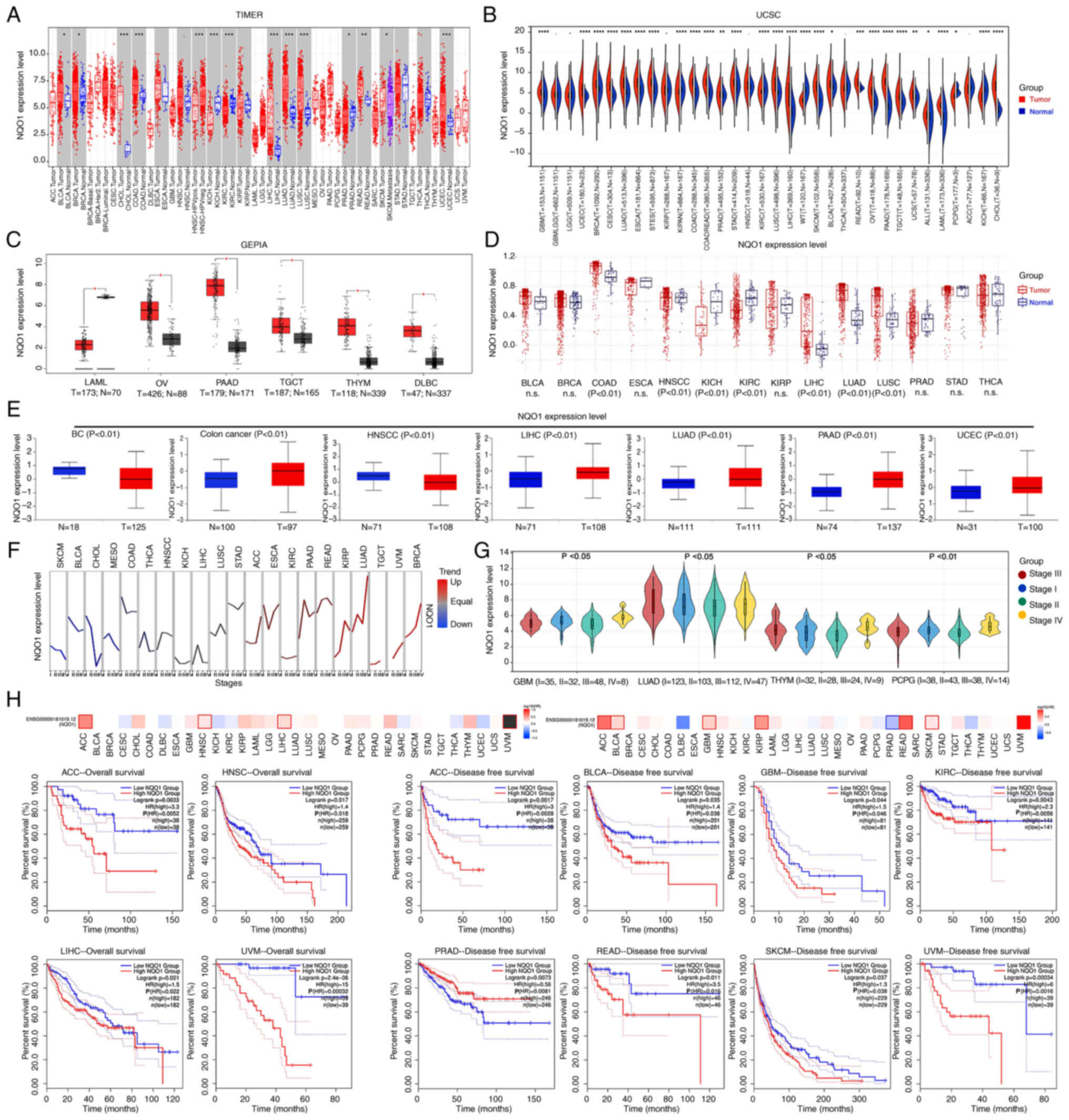
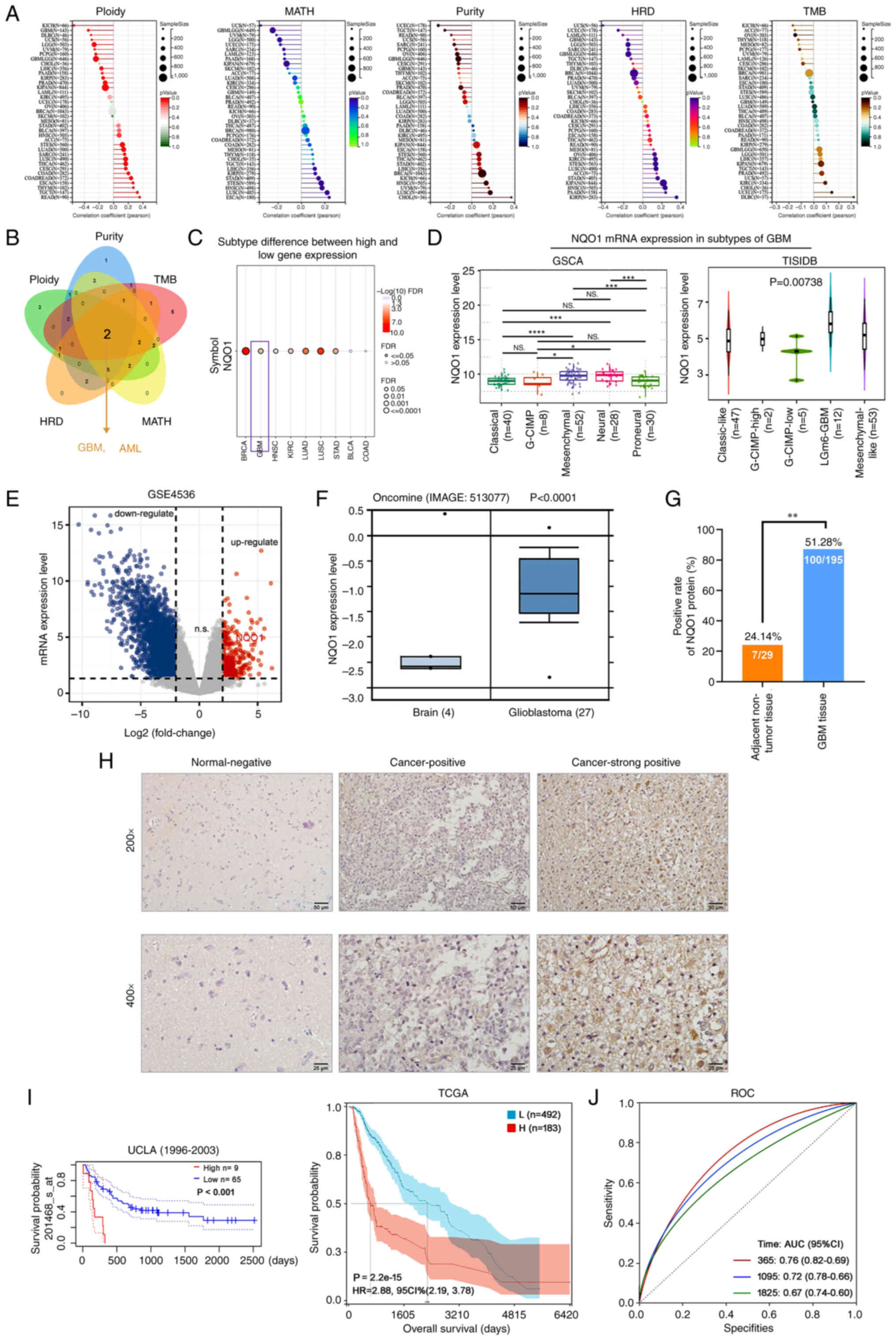
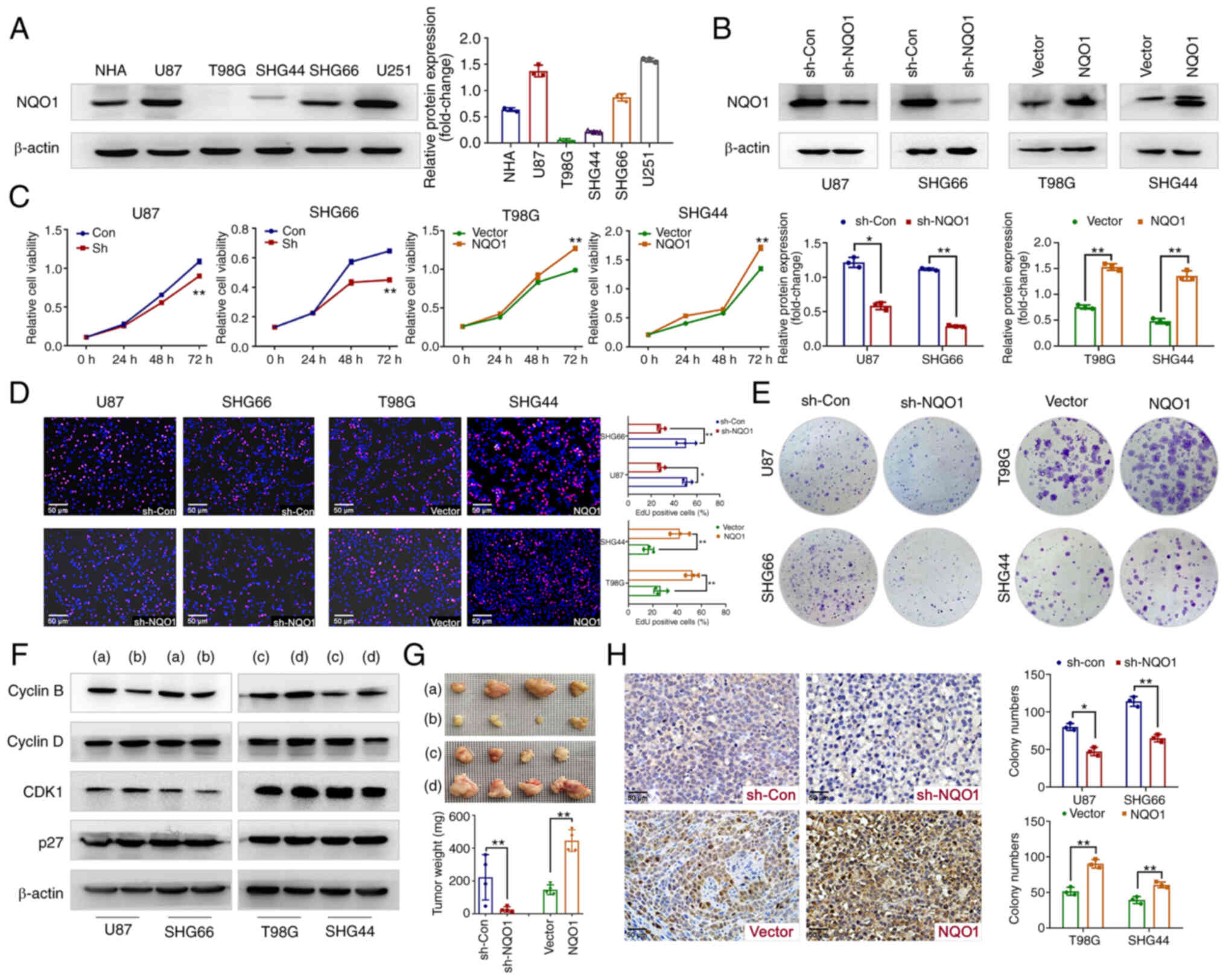
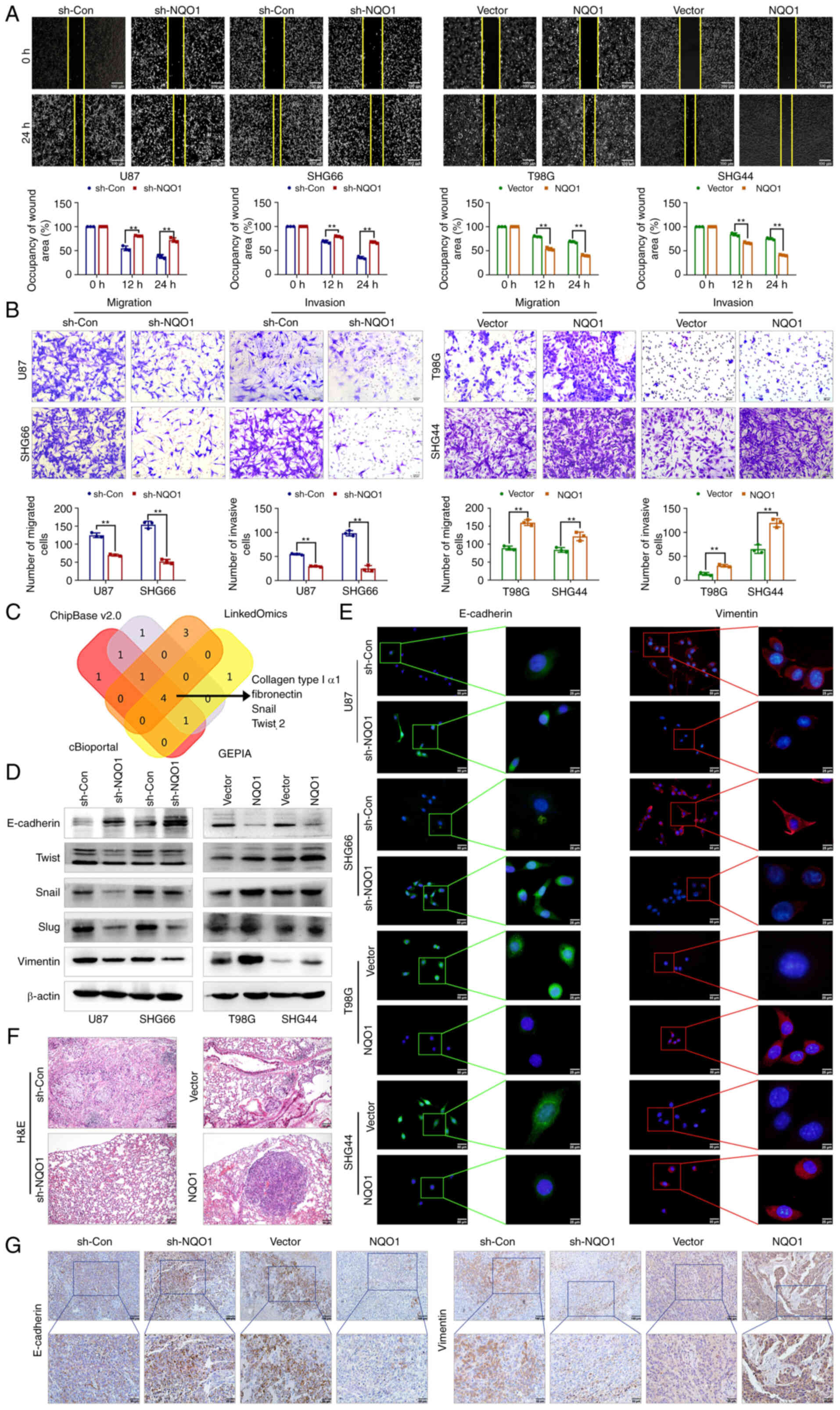
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 72:7–33. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fang R, Chen X, Zhang S, Shi H, Ye Y, Shi
H, Zou Z, Li P, Guo Q, Ma L, et al: EGFR/SRC/ERK-stabilized YTHDF2
promotes cholesterol dysregulation and invasive growth of
glioblastoma. Nat Commun. 12:1772021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Chan DT, Hsieh SY, Kam MK, Cheung TCY, Ng
SCP and Poon WS: Pattern of recurrence and factors associated with
cerebrospinal fluid dissemination of glioblastoma in Chinese
patients. Surg Neurol Int. 7:922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Verhaak RG, Hoadley KA, Purdom E, Wang V,
Qi Y, Wilkerson MD, Miller CR, Ding L, Golub T, Mesirov JP, et al:
Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes
of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1,
EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell. 17:98–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Z, Shi Y, Ying C, Jiang Y and Hu J:
Hypoxia-induced PLOD1 overexpression contributes to the malignant
phenotype of glioblastoma via NF-κB signaling. Oncogene.
40:1458–1475. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Wang X, Qi S, Gao L, Huang G, Ren Z,
Li K, Peng Y, Yi G, Guo J, et al: Spliceosome-regulated
RSRP1-dependent NF-κB activation promotes the glioblastoma
mesenchymal phenotype. Neuro Oncol. 23:1693–1708. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang G, Luo L, Zhang J, Zhai D, Huang D,
Yin J, Zhou Q, Zhang Q and Zheng G: lncRNA LINC01057 promotes
mesenchymal differentiation by activating NF-κB signaling in
glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 498:152–164. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Amicone L, Marchetti A and Cicchini C:
Exosome-associated circRNAs as key regulators of EMT in cancer.
Cells. 11:17162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu Y, Guo G, Lu Y, Chen X, Zhu L, Zhao L,
Li C, Zhang Z, Jin X, Dong J, et al: Silencing IKBKE inhibits the
migration and invasion of glioblastoma by promoting Snail1
degradation. Clin Transl Oncol. 24:816–828. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yun EJ, Kim D, Hsieh JT and Baek ST:
Stanniocalcin 2 drives malignant transformation of human
glioblastoma cells by targeting SNAI2 and matrix
Metalloproteinases. Cell Death Discov. 8:3082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhong C, Li X, Tao B, Peng L, Peng T, Yang
X, Xia X and Chen L: LIM and SH3 protein 1 induces glioma growth
and invasion through PI3K/AKT signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Biomed Pharmacother. 116:1090132019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nan Y, Guo L, Lu Y, Guo G, Hong R, Zhao L,
Wang L, Ren B, Yu K, Zhong Y and Huang Q: miR-451 suppresses EMT
and metastasis in glioma cells. Cell Cycle. 20:1270–1278. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ernster L and Lindberg O: Animal
mitochondria. Annu Rev Physiol. 20:13–42. 1958. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yadav U, Kumar P and Rai V: NQO1 gene
C609T polymorphism (dbSNP: rs1800566) and digestive tract cancer
risk: A meta-analysis. Nutr Cancer. 70:557–568. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang Y, Zhang Y, Wu Q, Cui X, Lin Z, Liu S
and Chen L: Clinical implications of high NQO1 expression in breast
cancers. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Z, Zhang Y, Jin T, Men J, Lin Z, Qi P,
Piao Y and Yan G: NQO1 protein expression predicts poor prognosis
of non-small cell lung cancers. BMC Cancer. 15:2072015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin L, Sun J, Tan Y, Li Z, Kong F, Shen Y,
Liu C and Chen L: Prognostic implication of NQO1 overexpression in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 69:31–37. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Madajewski B, Boatman MA, Chakrabarti G,
Boothman DA and Bey EA: Depleting tumor-NQO1 potentiates anoikis
and inhibits growth of NSCLC. Mol Cancer Res. 14:14–25. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Yang Y, Zhu G, Dong B, Piao J, Chen L and
Lin Z: The NQO1/PKLR axis promotes lymph node metastasis and breast
cancer progression by modulating glycolytic reprogramming. Cancer
Lett. 453:170–183. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Thapa D, Huang SB, Muñoz AR, Yang X,
Bedolla RG, Hung CN, Chen CL, Huang THM, Liss MA, Reddick RL, et
al: Attenuation of NAD[P]H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 aggravates
prostate cancer and tumor cell plasticity through enhanced TGFβ
signaling. Commun Biol. 3:122020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Shimokawa M, Yoshizumi T, Itoh S, Iseda N,
Sakata K, Yugawa K, Toshima T, Harada N, Ikegami T and Mori M:
Modulation of Nqo1 activity intercepts anoikis resistance and
reduces metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Sci. 111:1228–1240. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu W, Klockow JL, Zhang M, Lafortune F,
Chang E, Jin L, Wu Y and Daldrup-Link HE: Glioblastoma multiforme
(GBM): An overview of current therapies and mechanisms of
resistance. Pharmacol Res. 171:1057802021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Liu YL, Selenica P, Zhou Q, Iasonos A,
Callahan M, Feit NZ, Boland J, Vazquez-Garcia I, Mandelker D, Zehir
A, et al: BRCA Mutations, homologous DNA repair deficiency, tumor
mutational burden, and response to immune checkpoint inhibition in
recurrent ovarian cancer. JCO Precis Oncol.
4:PO.20.000692020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shahcheraghi SH, Tchokonte-Nana V, Lotfi
M, Lotfi M, Ghorbani A and Sadeghnia HR: Wnt/beta-catenin and
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in glioblastoma: Two main targets
for drug design: A review. Curr Pharm Des. 26:1729–1741. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang X, Liu Y, Han A, Tang C, Xu R, Feng
L, Yang Y, Chen L and Lin Z: The NQO1/p53/SREBP1 axis promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis by regulating
Snail stability. Oncogene. 41:5107–5120. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Begleiter A and Fourie J: Induction of
NQO1 in cancer cells. Methods Enzymol. 382:320–351. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pradubyat N, Sakunrangsit N, Mutirangura A
and Ketchart W: NADPH: Quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) mediated
anti-cancer effects of plumbagin in endocrine resistant MCF7 breast
cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 66:1531332020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yang Y, Zheng J, Wang M, Zhang J, Tian T,
Wang Z, Yuan S, Liu L, Zhu P, Gu F, et al: NQO1 promotes an
aggressive phenotype in hepatocellular carcinoma via amplifying
ERK-NRF2 signaling. Cancer Sci. 112:641–654. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhou HZ, Zeng HQ, Yuan D, Ren JH, Cheng
ST, Yu HB, Ren F, Wang Q, Qin YP, Huang AL and Chen J: NQO1
potentiates apoptosis evasion and upregulates XIAP via inhibiting
proteasome-mediated degradation SIRT6 in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cell Commun Signal. 17:1682019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Precilla SD, Biswas I, Kuduvalli SS and
Anitha TS: Crosstalk between PI3K/AKT/mTOR and WNT/β-Catenin
signaling in GBM-could combination therapy checkmate the collusion?
Cell Signal. 95:1103502022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Courtney KD, Corcoran RB and Engelman JA:
The PI3K pathway as drug target in human cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:1075–1083. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Wojtas B, Gielniewski B, Wojnicki K,
Maleszewska M, Mondal SS, Nauman P, Grajkowska W, Glass R, Schüller
U, Herold-Mende C and Kaminska B: Gliosarcoma is driven by
alterations in PI3K/Akt, RAS/MAPK pathways and characterized by
collagen gene expression signature. Cancers (Basel). 11:2842019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Burris HA III: Overcoming acquired
resistance to anticancer therapy: Focus on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathway. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 71:829–842. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ahn YJ, Lim JW and Kim H: Docosahexaenoic
acid induces expression of NAD(P)H: Quinone oxidoreductase and heme
oxygenase-1 through Activation of Nrf2 in cerulein-stimulated
pancreatic acinar cells. Antioxidants (Basel). 9:10842020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liang S, Guo H, Ma K, Li X, Wu D, Wang Y,
Wang W, Zhang S, Cui Y, Liu Y, et al: A PLCB1-PI3K-akt signaling
axis activates EMT to promote cholangiocarcinoma progression.
Cancer Res. 81:5889–5903. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee S, Choi EJ, Cho EJ, Lee YB, Lee JH, Yu
SJ, Yoon JH and Kim YJ: Inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling suppresses
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma
through the Snail/GSK-3/beta-catenin pathway. Clin Mol Hepatol.
26:529–539. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tian H, Lian R, Li Y, Liu C, Liang S, Li
W, Tao T, Wu X, Ye Y, Yang X, et al: AKT-induced lncRNA VAL
promotes EMT-independent metastasis through diminishing
Trim16-dependent Vimentin degradation. Nat Commun. 11:51272020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Zhong C, Chen Y, Tao B, Peng L, Peng T,
Yang X, Xia X and Chen L: LIM and SH3 protein 1 regulates cell
growth and chemosensitivity of human glioblastoma via the PI3K/AKT
pathway. BMC Cancer. 18:7222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Katikireddy KR, White TL, Miyajima T,
Vasanth S, Raoof D, Chen Y, Price MO, Price FW and Jurkunas UV:
NQO1 downregulation potentiates menadione-induced
endothelial-mesenchymal transition during rosette formation in
Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Free Radic Biol Med.
116:19–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|