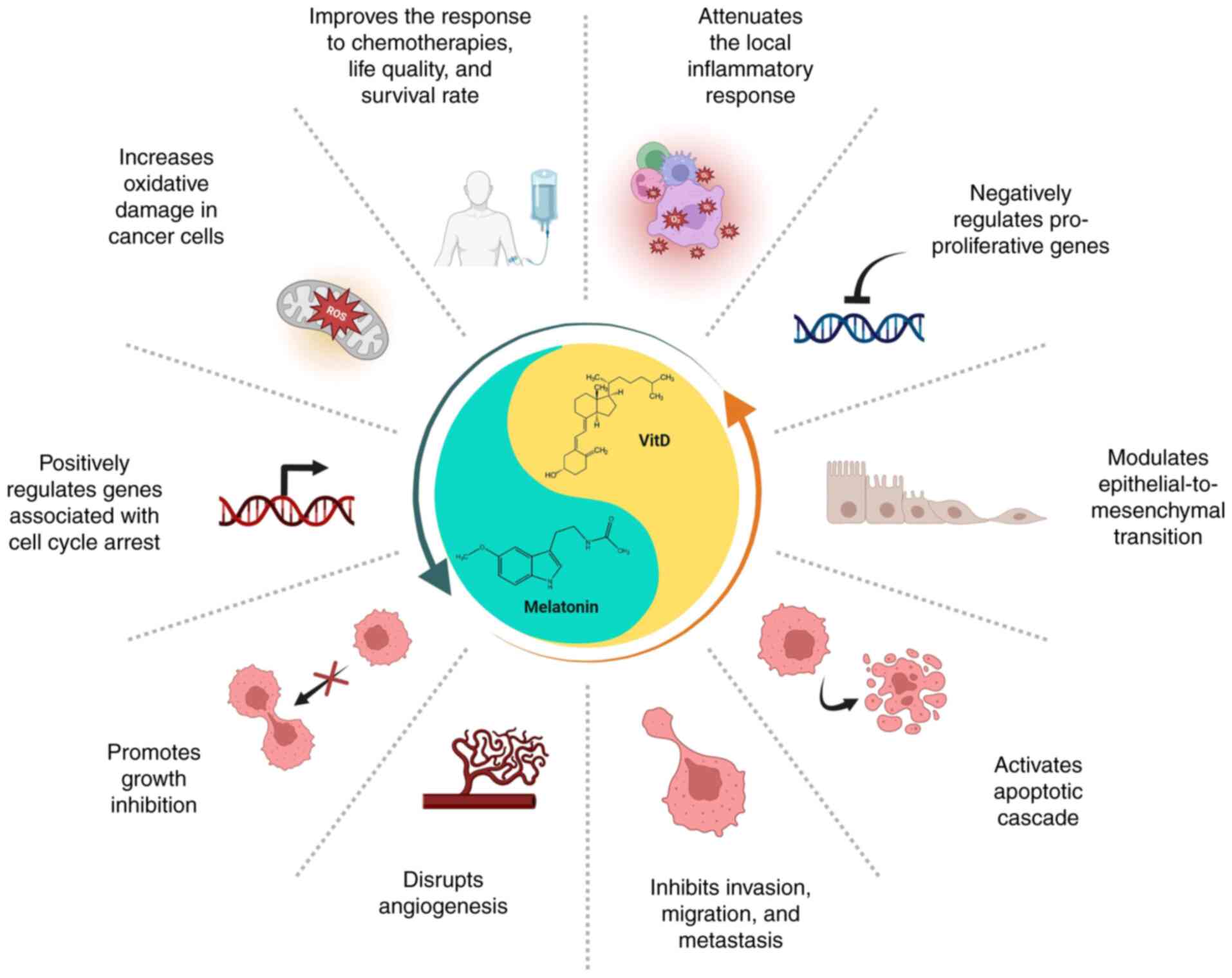
Introduction
Connecting cancer with melatonin and
vitamin D (VitD)
Cancer is a devasting disease that affects millions
of individuals worldwide annually (1). Current cancer treatments include
surgical removal accompanied by chemo- and radiotherapy,
immunotherapy, and the use of molecular inhibitors (2). Despite the technological advances
being made in early detection and successful therapy, achieving
remission, the risk of cancer recurrence often persists. Under
specific circumstances, dormant residual cancer cells can
reactivate their aggressive state to disseminate tumor cells from
the primary lesion to distant organs emerging as a recurrent
disease (3). The etiology and
plasticity of cancerous states have recently been revisited
concerning epigenetic and gene regulation landscapes in addition to
the conditions of entropy and attractor states (4). Under the influence of genetic
mutations, epigenetic modifications and microenvironmental
perturbations, tumor cell phenotypes dynamically change over time,
thereby favoring intratumor heterogeneity (5). This may confer adaptability to
cancer cells due to therapy resistance, metastasis, and clonal
evolution. Cancer cell fitness includes a multitude of evolutionary
and ecological features that determine cell fate and tumor behavior
(6). A more precise recognition
of this classification system holds promise for clinicians to
personalize therapeutic interventions according to the evolvability
of the cancer of a patient.
The use of functional adjunctive agents with
antitumor activities and high tolerability, whose formation has
been reported even in early life forms (7), such as melatonin and VitD represents
an additional opportunity for cancer treatment. There is a plethora
of evidence demonstrating that melatonin and VitD participate at
different levels in complex signaling pathways and biological
functions of cancer, most of which will be addressed in the present
review. For instance, melatonin has been documented to counteract
tumor development and growth via several physiological, molecular
and atomic mechanisms in addition to alleviating the adverse
effects of chemo- and radiotherapy in a number of types of cancer
(8-11). As regards VitD, previous in
vitro and in vivo studies have disclosed its
immunomodulatory and antitumor properties (12-14). Similar to melatonin, VitD has been
shown to exert anti-angiogenic, antiproliferative (15) and anti-inflammatory effects on
cancer cells (16). What is of
great value is the association of their serum levels with the
cellular state; in other words, high levels of melatonin and VitD
are strongly associated with reduced incidence rates of various
malignancies and vice versa (17-21). Taken together, this evidence
should encourage some clinical trials using melatonin and VitD as
adjuvant therapy or even protective agents alone. The present
review comprehensively evaluates individual mechanistic aspects
whereby melatonin and VitD function in the context of cancer, with
particular focus on their synergistic effects preventing cancer
progression (Fig. 1).
General aspects of melatonin and its major
association with cancer
Molecular pathways involved in the
synthesis and action of melatonin
Melatonin (N-acetyl-methoxytryptamine) is an
indoleamine produced at night by the pineal gland, but also by
'perhaps' all organismal cells in a continuous non-circadian manner
(22). It is synthesized from the
5-hydroxytryptophan, which is catalyzed to serotonin by the enzyme
aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (23). Serotonin is then converted into
N-acetylserotonin by the alkylamine N-acetyltransferase, a rate
limiting enzyme for melatonin synthesis. The final stage of
melatonin biosynthesis occurs with the participation of the enzyme
acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase and S-adenosyl methionine, a
coenzyme involved in methylation reactions (24).
Due to its chemical structure and low molecular
weight, melatonin easily crosses the cell membrane and interacts
with multiple intracellular components. Melatonin exerts its
effects through membrane G protein-coupled receptors (MT1 and MT2),
as well as via cytosolic MT3 and calmodulin. Notably, melatonin is
not a direct ligand for nuclear receptors (RZR/RORα) as previously
documented (25). A recent study
utilizing functional assays demonstrated that melatonin and its
metabolites are promising candidates for interacting with both aryl
hydrocarbon receptor and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
γ. Their docking scores, comparable to those of the receptors'
natural ligands, suggest a potential role in modulating these
signaling pathways (26). The
widespread detection of MT1 and MT2 receptors in various tissues
underscores the broad spectrum of melatonin's activity,
encompassing the blood vessels, adipocytes, liver, kidneys, retina,
ovaries, testes, mammary glands, gallbladder, immune cells,
cardiovascular system, brain sites and skin (26,27). There are also receptor-independent
actions of melatonin by directly interfering with intracellular
substrates of cancer cells. Of note, a myriad of internal
regulatory mechanisms has already been proposed for a number of
types of cancer, such as ovarian, breast and pancreatic cancer
(18,28-30).
Another key site for melatonin synthesis and
metabolism is the skin (31),
particularly the mitochondria of skin cells. Under ultraviolet
radiation, melatonin can be converted into different photoproducts
without the involvement of enzymatic activities (32). Notably, metabolites, including
N-acetyl-N2-formyl-5-methoxykynuramine (AFMK), 6-hydroxymelatonin
(6-OHM), 2-hydroxymelatonin and 4-hydroxymelatonin (4-OHM) can be
produced in the epidermis through UVB-induced non-enzymatic
transformations of melatonin to maintain homeostasis through
multiple mechanisms of action. The pathways for melatonin
metabolism, including the indolic and kynurenine pathways, vary
based on cell type and function. For example, in melanocytes,
keratinocytes and fibroblasts, melatonin is transformed into AFMK
and 5-methoxytryptamine, whereas in melanoma cells, 6-OHM and AFMK
are produced endogenously (33).
While the central circadian clock regulates
melatonin secretion, melatonin itself can also influence both the
central circadian clock and peripheral oscillators in various
tissues and organs, establishing it as a circadian rhythm marker
(34). Melatonin levels typically
increase at night and decrease during the day. Increased levels of
melatonin during nighttime can signal to the cells and organs in
the body that it is night, aiding in organizing target organs and
organ systems into appropriate homeostatic metabolic rhythms
(35). Consequently, exposure to
light at night (LAN) may disrupt circadian rhythms and melatonin
production (36), potentially
contributing to the development, promotion and progression of
cancers. Concurrently, although melatonin levels are generally
lower in cancer cells (37),
advanced tumors may still produce melatonin, potentially altering
body homeostasis and conferring a protective effect following
therapeutic interventions (38).
Mechanisms through which melatonin
inhibits cancer growth and metastasis
Melatonin has long been reported to influence a
variety of physiological processes in cancer and it would be a
difficult task to mention all of them in detail. There is no
consensus on how and why melatonin behaves distinctively on various
oncogenic molecules and culture medium conditions; its effects may
be dependent on specific concentrations or dosages, cell type or
animal models, exposure time, routes, and period of treatment.
Reiter et al compiled the molecular mechanisms by which
melatonin restrains cancer at the initiation, progression and
metastasis stages (39); in
general, vast evidence exists pointing to melatonin as a regulator
of DNA damage and inhibitor of oncogenic signaling pathways related
to tumor progression and metastasis. In this scenario, melatonin
largely intervenes in the hallmarks of cancer, including
fundamental actions in genomic instability, sustained proliferative
signaling, resistance to apoptosis, replicative immortality,
dysregulated metabolism, inflammation, angiogenesis, tissue
invasion and metastasis (40).
The anticancer effects of melatonin target common pathways shared
with a majority of established anti-cancer agents, suggesting that
indoleamine exhibits pleiotropic characteristics akin to other
antineoplastic drugs in terms of their mechanisms of action.
Some of these mechanisms of action include the
regulation of major intracellular pathways, such as
mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), extracellular
signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and protein kinase B (AKT/PKB)
signaling. Critical mediators affected by melatonin encompass
cyclins, nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), heat shock proteins (HSPs) and
c-Myc, which are potential targets for cancer drugs (41). Additionally, melatonin also exerts
its anticancer effects by inducing epigenetic modifications, DNA
damage, and mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum alterations in
neoplastic cells. The regulation of these mediators by melatonin
mitigates tumor growth and invasiveness through modulation of
differential expression of genes, protein secretion and activity,
angiogenic factors, in addition to regulating structural molecules
involved in metastasis. The role of melatonin in different cancer
types has recently been documented and differentially expressed
genes strongly linked to cancer hallmarks have been identified
(42). Interconnecting gene
subsets have exhibited a close association among breast,
hepatocellular, prostate and oral cancers, as well as neuroblastoma
and osteosarcoma, in terms of alterations in melatonin-related
signaling pathways. Some of these genes have been already shown to
be regulated by miRNAs potentially targeted by melatonin in a
variety of cancers (43).
Understanding the role of melatonin in intricate molecular
signaling at the gene level is crucial for guiding appropriate
therapeutic interventions.
As a considerable number of reviews that summarize
the anticancer effects of melatonin are currently available, the
present review focuses on the general aspects involving the
aforementioned cancer categories which reinforce the use of the
indole in clinical settings.
Genomic instability in cancer and the
role of melatonin
Cancer initiation is often associated with
chromosomal instability by creating aneuploidy nuclei due to the
failures in cell cycle checkpoint machinery (44). This is associated with the poor
prognosis of patients as a result of metastasis, therapeutic
resistance and inflammatory signaling by introducing
double-stranded DNA into the cytosol (45). A previous study demonstrated that
the oral supplementation of melatonin (50 mg/kg body weight) in
mice with Ehrlich carcinoma promoted a reduction in the aneuploidy
status associated with reduced DNA synthesis and delayed
progression of cells to S-phase of the cell cycle (46). Melatonin is considered to protect
DNA functioning as an antioxidant molecule capable of increasing
the activity of other antioxidants, stimulating glutathione
synthesis, inhibiting pro-oxidative processes, and enhancing the
activity of the mitochondrial electron transport chain (47).
It has been recently documented the role of
melatonin acting in different DNA repair systems, especially by
preventing DNA from damage and ameliorating its repair processes
(48). Of note, melatonin,
including its metabolites (AMK, AFMK, c3-OHM, 4- and 6-OHM)
regulate a variety of DNA repair pathways having a more precise
effect on the factors governing the repair of double-stranded DNA
breaks by homologous recombination (HR) and non-HR mechanisms. By
preventing DNA oxidative damage, melatonin may act by activating
antioxidant enzymes, inhibiting metal-induced DNA damage and
pro-oxidative enzymes, protecting against non-radical DNA
oxidation, and boosting DNA repair machinery (49). When used as a chemical adjuvant,
melatonin has revealed various radio-protective and radio-sensitive
effects following ionizing radiation in many cancer types (48,50-52). These actions indicate the
potential of melatonin as a tumor initiation protector in addition
to avoiding the deleterious side effects arising from radiotherapy
(Table I).
 | Table IMajor results regarding genomic
instability in cancer and the role of melatonin. |
Table I
Major results regarding genomic
instability in cancer and the role of melatonin.
| Cell lineage | Type of cancer | Dosage and period
of treatment | Relevant
effects | (Refs.) |
|---|
| ECC (Ehrlich
carcinoma cells) | Ascites | 10−9,
10−6 and 10−3 M melatonin for 24 h in
vitro assays; 50 mg/kg b.w. for 7-21 days, orally | Melatonin reduced
DNA synthesis and delayed the progression of cells from
G0/G1 phase to S-phase of the cell cycle,
also depressed the aneuploidy status in mice | (46) |
| Leukocytes | N.A. | A single oral dose
of 100 mg melatonin to healthy human volunteers. Blood collected
1-2 h after melatonin ingestion | Melatonin
effectively promoted radioprotection against ionizing
radiation-induced DNA damage in human lymphocytes | (51) |
Cell proliferation and apoptosis in
melatonin-treated cancers
Sustained proliferative signaling and resistance to
apoptosis represent a common characteristic of cancers by which
they can develop and progress. There is vast literature available
demonstrating that melatonin effectively alters the expression
pattern of proteins and active signaling pathways related to the
cell cycle of different types of cancer cells (Table II). For instance, in vitro
studies have documented anti-proliferative actions of melatonin
(varying from nano to millimolar concentrations) by arresting the
cell cycle in the G1 phase, delaying G1/S transition and preventing
the mitosis of breast cancer (MCF-7 cells) (53), ovarian cancer (SKOV-3 cells)
(28), melanoma (SK-MEL-1 cells)
(54), osteosarcoma (hFOB 1.19)
(55) and glioma (C6 cells)
(56).
 | Table IIMajor results regarding cell
proliferation and apoptosis in melatonin-treated cancers. |
Table II
Major results regarding cell
proliferation and apoptosis in melatonin-treated cancers.
| Cell lineage | Type of cancer | Dosage and period
of treatment | Relevant
effects | (Refs.) |
|---|
| MCF-7 | Human breast
carcinoma | 10−9 M
melatonin during 0-40 h | Melatonin added to
the culture medium, increase the duration of the cell cycle from
20.36 to 23.48 h. | (53) |
| SKOV-3 | Human ovarian
cancer | 1.6, 3.2 and 4.0 mM
melatonin for 48 h | Melatonin induced
cell cycle arrest by reducing DNA content in the S and G2/M
phases. | (28) |
| SK-MEL-1 | Human melanoma | 0.1, 0.3 and 1.0 mM
melatonin for 24, 48 and 72 h | Melatonin at 1 mM
significantly arrested the cell cycle in the G1 phase (after 24 h)
and in the S and G2-M phase (after 48-h incubation period). | (54) |
| hFOB 1.19 | Normal human fetal
osteoblastic cell line | 1 nM to 1.0 mM
melatonin for 24 h | Melatonin
significantly increased the fraction of cells in G0/G1 phase, while
simultaneously reducing the proportion of cells in the G2/M phase
rather than the S phase. | (55) |
| C6 | Glioma cells | 1 nM to 1.0 mM
melatonin 48 and 72 h in vitro assays | Melatonin
inhibiting cell progression from G0/G1 to S phase of the cell
cycle. | (56) |
| B65 | Neuroblastoma cell
line | 0.1 to 1 mM
melatonin for 24 h | Melatonin increased
the percentage of cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. It also
downregulated the transcriptional activity of cdk4, cdk2 and cyclin
D1. | (59) |
| Bel7402,
SMMC-7721 | Human
hepatocellular carcinoma | 0.2 to 2 mM
melatonin for 48 and 72 h | Combined treatment
with melatonin and sorafenib enhanced the cell cycle arrest of
cancer cells at the G0/G1 phase. It also upregulated p27, and
downregulated p-AKT, c-myc, cyclin D1 and CDK4/6 protein
expression. | (60) |
| H1975 and
HCC827 | Non-small-cell lung
cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma | 0.1 to 10 mM
melatonin for 24 and 48 h | Melatonin treatment
significantly increased the sub-G1 populations in H1975 cells.
Melatonin downregulated the survivin, p-Bad, Bcl-xL and Bcl-2
levels, but did not affect the evels of Mcl-1. | (61) |
| HCT116 | Human colorectal
adenocarcinoma | 10 µM
melatonin for a 12-h period in 2 days | Melatonin exposure
for 48 h induced cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase. Melatonin also
markedly reduced the expression of cyclin A and cyclin E at 48 h
after the second treatment. | (62) |
| MG-63 | Osteosarcoma | 1 nM to 10 mM
melatonin for 24, 48, or 72 h | Melatonin
significantly increased the fraction of cells in the G0/G1phase,
reducing the proportion in the S and G2/M phases of the cell cycle
by the downregulation of cyclin D1, CDK4, cyclin B1 and CDK1. | (63) |
| OVCAR-429 and
PA-1 | Ovarian cancer | 400, 600 and 800
µM melatonin for 24,48 and 72 h | Melatonin promoted
the accumulation of the treated cells in the G1 phase with the
downregulation of CDK 2/4. | (57) |
| LNCaP | Prostate
cancer | 0.25 to 3.0 mM
melatonin for 6, 12, 24 and 48 h | Melatonin markedly
activated Bax expression and decreased Bcl-2 expression in a dose-
and time-dependent manner. Melatonin also increased the expression
of p53, p21 and p27. | (84) |
| Ovarian tissue | Rat ovarian
cancer | 200 µg
melatonin/100 g body weight per day for 60 days | Melatonin therapy
promoted apoptosis along with the upregulation of p53, BAX and
cleaved caspase 3. | (72) |
| PANC-1 | Human pancreatic
carcinoma | 10−9 and
10−12 M melatonin for 24 and 48 h | Melatonin
interfered with the Bax/Bcl-2 protein balance and promoted
caspase-9 expression. These effects were reversed by treatment with
the melatonin receptor antagonist, luzindole. | (77) |
| HL-60 | Human leukemia | 1 nM, 1 µM
and 1 mM for 1, 6, 12, 24, 48 and 72 h | Melatonin at 1 mm
induced a significant increase in caspase-3 and -9 activities, and
also evoked cell death by mitochondrial membrane depolarization and
permeability transition pore induction. | (82) |
| RAMOS-1 | Human leukemia | 2 mM melatonin for
12, 24, 48 and 72 h | Apoptotic effect of
melatonin was associated with cell-cycle arrest, the activation of
caspase-3, the downregulation of Bcl-2, mitochondrial membrane
depolarization and cytochrome c release. | (83) |
| HepG2 | Human
hepatocellular carcinoma | 2 and 4 mM
melatonin for 24 and 48 h | Melatonin increased
the transcriptional activity of the forkhead-responsive element
FoxO3a which binds to a specific sequence in the Bim promoter,
leading to apoptosis. | (85) |
| HepG2 and
SMMC-7721 | Human
hepatocellular carcinoma | 10−3 to
10−9 M melatonin for 24 and 48 h | Melatonin promoted
apoptosis and the downregulation of XIAP and survivin levels.
Melatonin also reduced the expression of COX-2 and inhibited AKT
activation. | (86) |
Mechanistically, melatonin affects the cell cycle
mainly through the inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs),
CDK inhibitors (CDI) and cyclins (for further details please see
the compiled information in the review by Targhazeh et al
(57). In ovarian cancer cells
(OVCAR-429 and PA-1), melatonin has been shown to promote a delay
in the G1 phase by downregulating CDK2/4 gene expression and its
protein levels (58). Similarly,
Liu et al (55) revealed a
significant reduction in the expression of CDK1/4 in osteosarcoma
by melatonin (1 mM), and this was responsible for the prevention of
ERK activation. Other studies have also reported the role of
melatonin in inhibiting the expression of CDK2 in neuroblastoma
(59), CDK4/6 in hepatocellular
carcinoma (60) and CDK4 in
non-small lung cancer cells (61). Melatonin is further able to
inversely regulate the expression of cyclins, thus affecting the
proliferation of cancer cells. In colon cancer cells, melatonin (10
µM) has been shown to cause a marked reduction in both the
cyclins A and E (62), whereas in
osteosarcoma, it significantly downregulated cyclin B1 and D1
(63). Another study revealed
that melatonin completely abolished the growth of breast cancer
cells induced by estradiol by suppressing cyclin D1 possibly
interfering with G1 to S transition (64). By combining melatonin with other
chemotherapeutics, an effective downregulation of cyclin D1, A and
B was observed varying in pancreatic ductal carcinoma (65), breast cancer (66), and lung cancer cells (61).
Melatonin has also been shown to exert a positive
effect on CDI (tumor suppressors) in different cancer types. In
HepG2 liver cancer cells, melatonin promotes the high expression of
the p21 protein, which negatively reduces cell proliferation by
increasing G2/M arresting (67).
An augmentation in the expression of p21wafl, p16, p21 and p27KIP1
levels by melatonin was also evidenced in breast, colorectal and
ovarian cancer cells, respectively (58,62,68). p53 is another target by which
melatonin may exert tumor-suppressive effects, acting by altering
both protein expression and phosphorylation. The concentration of
p53 protein was identified at high levels after melatonin treatment
in hepatoma (69), breast
(68), prostate (70), cervical and endometrial (71) cancer cells, and further in animal
models of ovarian carcinoma (72)
and hepatocellular carcinoma (73). These melatonin-mediated increases
in p53 levels are regulated by different signaling mechanisms
[e.g., p38 MAPK, sirtuin (SIRT)1, MT1/2 receptors, MDM2/MDMX/p300]
(57).
As a 'smart killer' molecule, melatonin can induce
anti-apoptotic effects in healthy cells while triggering
proapoptotic signals in cancer cells. Bizzarri et al
(74) compiled the extensive
molecular mechanisms of the pro-apoptotic actions of melatonin; it
can activate the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways
depending on cancer cell type, particularly through the increase in
the p53/MDM2 ratio and decrease of SIRT1. Cancer cells evade
apoptosis by overexpressing anti-apoptotic molecules, whereas under
expressing pro-apoptotic messages thus resisting apoptosis
(75). There is a multitude of
studies that document a reduction of B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2)
levels and the upregulation of Bax and caspases (pro-apoptotic
proteins) by melatonin treatment in different cancer models as
outlined by Rubio et al (76), Leja-Szpak et al (77), Xu et al (78) and Chuffa et al (79).
Although the mitochondria are strongly involved in
apoptosis, they also participate in other types of cell death, such
as necrosis, autophagy, necroptosis, ferroptosis and pyroptosis
(80,81). Mitochondria are involved in the
control of the intrinsic pathway by releasing and activating some
pro-apoptotic factors (e.g., cytochrome c and caspase
activators). Experimental data concerning major apoptotic pathways
and mitochondrial processes have been demonstrated based on
melatonin treatment. In leukemia HL-60 cells, it has been shown
that melatonin induces apoptosis with a significant increase in
caspase-3 and -9 levels accompanied by the depolarization of the
mitochondrial membrane and the augmentation of the mitochondrial
permeability transition pore (82). Another study using HL-60 cells
revealed activation of the Bcl-2 members (Bid and Bax) followed by
the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria (76). In lymphoblastic RAMOS-1 cells,
melatonin lowered the mitochondrial membrane potential resulting in
the release of cytochrome c and the activation of apoptosis
(83).
Alternative pathways whereby melatonin indirectly
regulates cancer cell apoptosis include MAPK, forkhead box class
O3a (FoxO3a), cycloxygenase-2 (COX-2) and NF-κB signaling (57). Melatonin is capable of increasing
p38 MAPK and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) thereby
triggering apoptosis in prostate cancer LNCaP cells (84); this activated pathway in turn
increases Bax and Bad in addition to cytochrome c and
caspase-9. The activation and nuclear translocation of FoxO3a is
mediated by melatonin in HepG2 cells, which leads to apoptosis
through an increase in the pro-apoptotic protein Bim and Fas ligand
(85). Melatonin has also the
ability to overcome apoptosis resistance of HepG2 and SMMC-7721
cells by promoting downregulation of survivin and XIAP
(anti-apoptotic members); these mechanisms were associated with
reduced expression of COX-2 and AKT activation (86).
Reactive oxygen species (ROS),
dysregulated metabolism and the interference of melatonin in cancer
cells
ROS play a crucial significant role in the
etiopathogenesis of cancer. ROS are signal transducers involved
with angiogenesis, apoptosis, ferroptosis, necroptosis, autophagy,
cell migration and invasion and proliferation (87). An increasing number of studies has
explored immunotherapies and anticancer agents that lead to ROS
generation or inhibition and disrupt oxidative stress balance
(e.g., natural extracts and nutraceuticals); thus, targeting cancer
with effective design of ROS-mediated therapies in clinical trials
is expected (88). Notably, while
the production of ROS can result in DNA damage and cancer
initiation, a massive production of ROS inhibits tumor growth via
basically two mechanisms: i) Blocking cell proliferation by
altering signaling pathways associated with cell cycle and
biosynthesis of nucleotides and ATP; and ii) activating ferroptosis
and apoptotic signaling related to endoplasmic reticulum stress,
mitochondria and the p53 pathway (88). Through this perspective, a newly
proposed mechanism of action of melatonin inducing ROS generation
in cancer cells reiterates its clinical use as an anti-neoplastic
therapeutic (89). Florido et
al (89) emphasized the role
of melatonin in SIRT signaling, AKT pathways and the anti-Warburg
effect; of particular interest is the melatonin-mediated ROS
production via the activation of reverse electron transport (RET)
in the mitochondria of cancer cells. This finding was particularly
evidenced in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (Cal-27 and
SCC-9 cell lines) treated with 0.5 or 1 mM melatonin, and also in
mice with Cal-27 tumor xenografts (89). In these experimental models,
melatonin led to increased mitochondrial activity, thus inducing
ROS-dependent mitochondrial uncoupling via RET in addition to
increasing the membrane potential and CoQ10 H2/CoQ10 ratio
associated with mitochondrial ROS.
The induction of oxidative stress can also be
regulated by SIRT3 and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α)
activities. As SIRT3 activates superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), an
antioxidant enzyme, its suppression substantively increases
ROS-mediated oxidative damage (90). In HeLa cancer cells, melatonin has
been shown to induce oxidative stress by inhibiting SIRT3/SOD2
activities, which potentially stimulates the release of cytochrome
c, resulting in apoptosis (91). Otherwise, a high SIRT3 activity
has been found to be associated with the apoptosis of lung cancer
cells by elevating ROS production due to an increase in oxidative
phosphorylation (92). In this
case, melatonin-induced SIRT3 contributes to the deacetylation of
pyruvate dehydrogenase followed by the enhancement of mitochondrial
complex I and IV activities, finally inducing ROS while reversing
the Warburg-type metabolism. Melatonin has been proven not only to
reverse the Warburg effect via SIRTs and ROS production, but also
by inhibiting HIF-1α (93). The
activation of HIF-1 stimulates mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase
kinase, which in turn prevents pyruvate from entering the
mitochondria and its conversion to acetyl coenzyme A by pyruvate
dehydrogenase complex. Notably, melatonin directly or indirectly
inhibits HIF-1 in cancer cells (94), thereby favoring the reversal of
the Warburg effect while inducing ROS generation and apoptosis
(11,95). These anti-Warburg effects of
melatonin are presented in Table
III.
 | Table IIIMajor results regarding metabolism
and the interference of melatonin in cancer cells. |
Table III
Major results regarding metabolism
and the interference of melatonin in cancer cells.
| Cell lineage | Type of cancer | Dosage and period
of treatment | Relevant
effects | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Various cell
lines | Various types of
cancer | 0.5, 1 and 2 mM
melatonin in combination or not with shikonin for 6 or 24 h | Melatonin
potentiates the cytotoxic effects of shikonin on cancer cells by
inducing oxidative stress via inhibition of the SIRT3/SOD2-AKT
pathway | (91) |
| HCT116 | Human colon
cancer | 1 mM melatonin for
16 h under hypoxic conditions | Under hypoxia,
melatonin suppressed HIF-1 transcriptional activity, leading to a
decrease in VEGF expression | (94) |
Inflammation and angiogenesis in the
context of melatonin in cancer
The association between inflammation and cancer
progression has been widely documented. Several factors serve as
crucial targets that can be adjusted to regulate the detrimental
effects of inflammation, including COX-2, NF-κB, TNF-α,
prostaglandins and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS).
Melatonin has been shown to have the ability to reduce these
inflammatory mediators through multiple signaling pathways in
various types of cancer, such as hepatocellular carcinoma, ovarian,
pulmonary and breast cancer (60,96-98). Studies have indicated that
attenuating the local inflammatory response through NF-κB
inhibition can help restrict tumor expansion (39,99). Melatonin has been frequently
observed to modulate NF-κB translocation into the nucleus and its
binding to DNA (96,100,101). These actions may be pertinent to
the ability of melatonin to impede tumor progression, as they could
influence the redox status and immune microenvironment of the
tumor.
Hypoxia (low levels of O2) is linked to
metastatic disease and increased mortality due to its capacity to
promote the development of blood vessels (angiogenesis) and
lymphatic vessels (lymphangiogenesis), enabling cancer cells to
evade the adverse tumor microenvironment and spread to secondary
sites (102). HIF-1 and vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) are pivotal factors that mediate
the angiogenic process. There is a plethora of experimental studies
proving the anti-angiogenic role of melatonin in different tumors
(33,103-105). Among the actions of melatonin,
it commonly inhibits the expression of VEGF and its receptors
(VEGFRs) at the protein and gene levels, in addition to the HIF-1α
activity (106). Some of these
actions of melatonin are summarized in Table IV.
 | Table IVMajor results regarding inflammation
and angiogenesis in the context of melatonin in cancer. |
Table IV
Major results regarding inflammation
and angiogenesis in the context of melatonin in cancer.
| Cell lineage | Type of cancer | Dosage and period
of treatment | Relevant
effects | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Ovarian tissue | Rat ovarian
cancer | 200 µg
melatonin/100 g body weight per day for 60 days | Melatonin
significantly decreased the expression of IkBα, NFκB p65, TRIF and
IRF-3, which are implicated in TLR4-mediated signaling | (96) |
| H1299 and A549 | Human lung
cancer | 1 mM melatonin for
48 h associated or not with berberine | Melatonin improved
the antitumor activity of berberine by stimulating caspase/Cyto C
and inhibiting AP-2β/hTERT, NF-κB/COX-2 and Akt/ERK signaling
pathways | (97) |
| MDA-MB-361 | Human breast
cancer | 0.1 to 1.0 mM
melatonin for 72 h | Melatonin inhibited
COX-2 expression and PGE2 production, abrogated p300 histone
acetyltransferase activity and p300-mediated NF-κB acetylation,
thereby blocking NF-κB binding and p300 employment to COX-2
promoter | (98) |
| HepG2 | Human
hepatocellular carcinoma | 1 mM melatonin for
24 and 48 h under normoxic and hypoxic conditions | Melatonin reduced
the expression of proangiogenic proteins VEGF and HIF-1α in cells
treated with 1 mM melatonin for 24 h in both normoxic and hypoxic
conditions | (103) |
| Renal tissue | Mouse renal
adenocarcinoma | 1 mM melatonin for
16 h under hypoxic conditions with or without luzindole (1
µM) for in vitro studies and in vivo with 20
mg melatonin/kg body weight per day for 7 days | Melatonin inhibited
tumor growth and blocked tumor angiogenesis in mice and diminished
the expression of the HIF-1α protein | (33) |
Tissue invasion, metastasis and the role
of melatonin in cancer
Evidence suggests that disseminated cells interact
with a variety of proteins and cells to colonize other sites
(107). In doing this, a
metastatic cell loses cell-to-cell contact to invade tissue and
promote intravasation, transportation, and extravasation to the
secondary tumor site (108).
Cell adhesion molecules play pivotal roles in cellular processes,
and melatonin has been shown to inhibit cancer invasion by
influencing the expression of tight and adherent junction proteins.
For instance, melatonin treatment modulates
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by increasing epithelial
markers (e.g., E-cadherin expression), while decreasing mesenchymal
markers (e.g., N-cadherin, Snail and vimentin) in different cancer
types (109-111); the mechanisms related to these
regulations involved the participation of ERK1/2 and NF-κB
pathways. Concurrently, melatonin upregulated occludin expression,
a transmembrane protein in tight junctions, inhibiting the
migration of human lung adenocarcinoma cells (112). Additionally, melatonin is
capable of regulating integrin expression, thereby inhibiting the
invasion of glioma, prostate and breast cancer cells (113-115).
Extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling is another
essential mechanism occurring in the tumor microenvironment, and
changes in ECM stiffness and degradation contribute to tumor growth
and progression (116). Several
factors, including integrin signaling, cancer associated
fibroblasts (CAFs), the TGF pathway and MMPs are featured as key
players (116). An endless body
of evidence has mentioned the role of melatonin in regulating ECM.
Of note, melatonin has been shown to inhibit chondrosarcoma cell
proliferation, migration and anoikic resistance by suppressing MMP7
expression via miR-520f-3p activity (117). In addition, melatonin indirectly
reduces gastric cell proliferation and invasion through the
inhibition of ROS and CAFs followed by a consecutive reduction of
MMP2 and MMP9 in the CAFs; these effects have been proven to be
involved in NF-κB signaling (118). The inhibition of
melatonin-induced MMPs associated with the invasive potential of
cancer has been further documented in chondrosarcoma (118), liver (119), ovarian (120), renal (121), glioblastoma (122) and bladder cancer cells (123). The anti-metastatic effects of
melatonin on different types of cancer are presented in Table V.
 | Table VMajor results regarding tissue
invasion, metastasis and the role of melatonin in cancer. |
Table V
Major results regarding tissue
invasion, metastasis and the role of melatonin in cancer.
| Cell lineage | Type of cancer | Dosage and period
of treatment | Relevant
effects | (Refs.) |
|---|
| GBC-SD | Human gallbladder
cancer | 0.25, 0.50, 1.00,
2.00 and 3.00 mM for 24 or 48 h | Melatonin increased
the protein levels of the epithelial marker, E-cadherin, while the
expression levels of the mesenchymal markers, N-cadherin, Snail and
vimentin decreased | (109) |
| MGC80-3 and
SGC-7901 | adenocarcinoma | 0.1, 0.5 and 1.5 mM
for 24 h | Melatonin reduced
cell invasion and migration, increased E-cadherin and β-catenin
expression, and downregulated fibronectin, vimentin, Snail, MMP-2
and MMP-9 expression | (110) |
| A549 | Human lung
adenocarcinoma | 0.1, 0.5, 0.75,
1.0, 2.5 and 5.0 mM melatonin for 12 and 24 h or 7 days | Melatonin inhibits
the migration by down-regulation of the expression of osteopontin
and myosin light chainkinase and upregulation of occludin involving
in JNK/MAPK pathway | (112) |
| C4-2 and LNCaP | Human o steoblastic
prostate cancer | 1, 0.3 and 1.0 mM
0melatonin for 24 and 48 h under normoxic and hypoxic
conditions | Melatonin inhibits
FAK, c-Src, and NF-κB transcriptional activity via the melatonin
MT1 receptor, which inhibits integrin α2β1 expression | (114) |
| U251 | Human glioma | 1 nM and 1.0 mM
melatonin for 12 and 24 h under normoxic and hypoxic
conditions | Melatonin
suppressed the migratory and invasive capacity by reducing the
phosphorylation of FAK and Pyk2, and decreasing expression of
alphav beta 3 (αvβ3) integrin | (115) |
| JJ012 and
SW1353 | Human
chondrosarcoma | 0.1, 0.3 and 1 mM
melatonin for 18 and 24 h or 1, 2, 3, and 4 days | Melatonin reduced
MMP-7 synthesis by promoting increased levels of miR-520f-3p
expression, which were downregulated in human chondrosarcoma tissue
samples | (117) |
| SKOV-3 and CSC | Human ovarian
carcinoma | 1 to 10 mM
melatonin for 24, 48 or 72 h with or without luzindole | Melatonin decreased
genes related with EMT including ZEB1, ZEB2, Snail and vimentin,
whereas increase E-cadherin; melatonin also decreased MMP-9
expression and inhibited PI3K and MAPK | (120) |
| Achn, Caki-1, and
HL-60 | Human renal
adenocarcinoma and human leukemia | 0.5 to 2 mM
melatonin for 24 and 48 h | Melatonin
transcriptionally inhibited MMP-9 by reducing p65- and
p52-DNA-binding activities | (121) |
| HT1197, HT1376,
T24, and | Human bladder
carcinoma | 1 mM melatonin for
24 h or 10 days | Melatonin treatment
suppressed the growth, migration, and invasion through
downregulating ZNF746-regulated MMP-9/MMP-2 signaling | (123) |
Clinical trials for the melatonin-based
prevention and treatment of cancers
There is credible evidence demonstrating the use of
melatonin in clinical trials. A previous systematic review of
randomized controlled trials of melatonin in 643 patients suffering
from solid tumors revealed a reduced risk of mortality at 1 year
(relative risk, 0.66; 95% confidence interval, 0.59-0.73;
I2, 0%; heterogeneity, P<0.56); treatment with
melatonin had no adverse events and the majority of the effects
were dose- and cancer type-dependent (124). A few years later, the same
research group evaluated 21 clinical trials associating the use of
melatonin with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, supportive care and
palliative care on the 1-year survival of patients with solid
tumors (125). They observed
improvements in complete and partial response to treatment in
addition to the stabilization of disease. Notably, melatonin
combined with chemotherapy decreased the mortality rate of patients
while ameliorating all chemotherapy-related side-effects.
The prophylactic effects of melatonin in reducing
the toxicity of chemotherapy and radiotherapy have been widely
documented (40,126,127). Ma et al (106) highlighted that melatonin plays a
protective role in mitigating mitochondrial damage induced by
chemotherapeutic drugs. These protective effects of melatonin
against the harmful effects induced by various chemotherapeutic
categories and agents encompass anthracyclines, alkylating agents,
platinum compounds, antimetabolites, mitotic inhibitors and
molecular-targeted agents. By combining melatonin with other
chemotherapeutic agents used to treat 250 patients with metastatic
solid cancers (104 patients with lung cancer, 77 patients with
breast cancer; 42 patients with gastrointestinal tract neoplasms,
and 27 patients with head and neck cancers), Lissoni et al
(128) observed a significant
tumor regression rate in patients who underwent melatonin (20
mg/day orally every day) and chemotherapy compared to those
receiving chemotherapy alone. In addition, the administration of
adjunctive melatonin further reduced cardiotoxicity, neurotoxicity,
thrombocytopenia, stomatitis and asthenia. Hence, the potential
advantages of melatonin appear noteworthy; thus, it may be
reasonable to consider implementing melatonin therapy in the early
stages of cancer with the prospect of enhanced benefits. Research
has demonstrated that the anticancer effects of melatonin are not
tissue-specific, and its therapeutic and preventive properties have
been reported in cancers originating from various tissues (129). In addition to augmenting the
therapeutic effects of other anticancer drugs, melatonin improves
the sleep and quality of life of patients with cancer. Although
further research is warranted to fully establish the indole as an
ally in the clinical setting, evidence suggests its potential
benefits and warrants further exploration. For more detailed
information on the particular effectiveness of melatonin in
specific cancer types in human trials, please consult the review by
Talib et al (129).
Vitamin D and cancer
Metabolic pathways involved in the
production and action of VitD
VitD plays a critical role in the metabolism of
calcium and phosphorus, which are essential for bone health and
various other biological functions. Pathologies due to VitD
deficiency are characterized by hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, and
dental and skeletal alterations. For several decades, it has been
shown that VitD, in addition to maintaining bone and tooth health,
has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties,
as well as stimulating the growth of hematopoietic tissue (130-136). The two main inactive precursors
of VitD are VitD2 and VitD3. VitD2 (ergocalciferol) can be derived
from dietary sources (20%), and some of its hydroxy-derivatives may
be produced in several types of cells (137), while VitD3 (cholecalciferol) is
produced when the cholesterol precursor, 7-dehydrocholesterol
located in the epidermis, is exposed to the UVB radiation (80%)
(138-140). Both undergo the same activation
process (141), and synthesized
VitD is transported by binding to VitD binding protein (DBP) in
serum. However, there is a greater amount of knowledge available
about the synthesis and action of 1,25(OH)2 D3 (calcitriol), as the
active form of VitD (142). To
activate both forms, they must be metabolized, and the liver is the
organ where hydroxylation to 25OHD3 (calcifediol) mainly occurs. In
the liver, the microsomal and mitochondrial 25-hydroxylase enzymes,
CYP2R1 and CYP27A1 respectively, convert VitD to 25OHD3 (141,142). CYP27A1 is widely distributed in
different tissues with the highest levels found in the liver and
muscles, while CYP27R1 is mainly expressed in the liver, skin and
testes (143). Finally, in the
kidneys, there are transmembrane proteins, megalin and cubilin
(144), which function as DBP
receptors in the proximal renal tubules where a mitochondrial
oxidase as CYP27B1, also known as 1α-hydroxylase, acts on 25OHD3 to
synthesize 1,25(OH)2 D3 (145).
This is considered the most potent metabolite of VitD, which
mediates many of its hormonal actions (135). Notably, new pathways of VitD
activation by CYP11A1 have also been established, with the
production of various hydroxy-derivatives in vivo and their
presence in human serum (146-149).
As previously mentioned, VitD metabolites are
transported in the blood bound mainly to DBP (85-88%), a transport
protein homologous to albumin and α-fetoprotein (150) produced mainly in the liver.
25OHD3 is the form that predominates in the circulation, and it is
used as a clinical marker to determine VitD status, by identifying
reserve levels. Moreover, the concentration in serum is very
similar to the levels of VitD stored in adipose and muscle tissue
(151,152). The average concentration in
blood is 30 ng/ml, and it has a half-life of 15 days (153). Under normal conditions, the
concentration of DBP is markedly higher than the concentrations of
VitD metabolites, and the affinity of DBP for 25OHD3 is markedly
greater than that of 1,25(OH)2D3; thus, in physiological
situations, a very low percentage of 25OHD3 and 1,25(OH)2 D3 is
free in the blood (154).
Mechanisms by which VitD may inhibit
cancer growth and metastasis
The majority of the effects of 1,25(OH)2 D3 are
mediated primarily by its binding to the VitD receptor (VDR), which
is a member of the superfamily of nuclear receptors with homology
to the receptors for retinoic acid (RXR), thyroid hormone, sex
hormones and adrenal steroids. VDR is a phosphoprotein and the
binding of 1,25(OH)2D3 induces phosphorylation on serine residues,
stabilizing the receptor and setting the stage for a cascade of
multiple events that intricately modulate cancer pathways (155,156). Within the cancer cell, VDR can
be located both in the cytosol and in the nucleus, influencing
genomic and non-genomic signaling pathways that play crucial roles
in cancer growth and metastasis (157,158).
Genomic actions of VitD to counteract
cancer development and progression to metastasis
Once 1,25(OH)2 D3 and other VitD hydroxy-derivatives
(159-163) cross the target cell membrane,
they bind to the cytoplasmic VDR and this complex binds the RXR,
increasing the affinity for specific DNA sequences known VitD
response elements located in the promoter regions of target genes
(164,165). Following this interaction,
several coactivators (e.g., SRC-1, SRC-2, SRC-3, P300 and CBP,
RIP140, etc.) and corepressors (e.g., NCoR and SMRT, HDACs, etc.)
influence the transcription of different genes involved in the
control of cancer (166,167). The genomic mechanisms of VitD
are not immediate, since a time interval is necessary to obtain the
functional proteins that mediate the anticancer actions.
These genomic effects of VitD exert a profound
influence on pathways crucial to cancer cell proliferation. Through
precise modulation of gene expression, VitD disrupts the delicate
balance that sustains uncontrolled tumor growth (168). By downregulating
pro-proliferative genes, such as CDK, c-Myc, EGFR, KRAS, NF-κB,
etc. (16,168,169), and upregulating those associated
with cell cycle arrest, including CDKN1A and CDKN1B, GADD45A, BTG2,
IGFBP3, CDH1, PTEN, among others, VitD emerges as a potent genomic
modulator, halting cancer cell to attenuate their ability to
proliferate uncontrollably (170,171).
Among the main features of the genomic actions of
VitD, is its ability to induce the apoptosis, or programmed cell
death, of cancer cells. Through the targeted regulation of pro- and
anti-apoptotic genes, including BCL2, BAX, caspases 3 and 8, p53,
etc., VitD promotes the elimination of damaged or malignant cells
(172). This genomic modulation
not only impedes cancer development, but also serves as a critical
barrier against the survival and dissemination of cells poised for
metastasis (173).
The genomic influence of VitD also extends to
pathways governing cellular differentiation. By favorably
modulating gene expression associated with this process, VitD
promotes a cellular environment that discourages the maintenance of
a stem cell-like state in cancer cells (174). This not only impedes
tumorigenesis, but also disrupts the acquisition of the aggressive
traits necessary for metastatic progression (175).
In addition, the genomic actions of VitD extend to
the inhibition of angiogenesis, which, as previously mentioned,
constitutes a process vital for sustained tumor growth (176). Through the modulation of pro-
and anti-angiogenic genes, such as VEGF, FGF-2, MMPs, ANGPT2,
THBS1, among others, VitD disrupts the formation of new blood
vessels that nourish tumors (177). Thus, this genomic interference
serves as a strategic impediment to the establishment of a robust
blood supply, critically hindering the expansion and metastatic
potential of cancer cells.
In addition to its direct genomic actions, VitD
engages in crosstalk with inflammatory signaling pathways,
contributing to its inhibitory effect on cancer development
(178). By modulating the
expression of genes involved in inflammation and immune regulation,
VitD creates an anti-inflammatory milieu that hampers the
pro-tumorigenic environment often associated with chronic
inflammation (179).
As is known, the genomic modulation by VitD tends to
extend its protective influence to counteract metastatic pathways
(180). By selectively up- or
downregulating genes involved in cellular motility, extracellular
matrix degradation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition, VitD
exerts genomic control over the migration, invasion, and
colonization of cancer cells intending to spread to distant sites
(181). Therefore, VitD emerges
as a potential guardian against the formidable challenge of
metastasis, especially during advanced cancer stages.
Non-genomic actions of VitD in the battle
against cancer and metastasis
One of the hallmark features of non-genomic actions
of VitD in cancer inhibition is its ability to rapidly modulate
cell signaling cascades. Through interactions with
membrane-associated receptors, VitD orchestrates fast responses
that impact cellular processes such as proliferation, survival and
apoptosis (182). Hence, this
non-genomic modulation serves as an immediate brake on the aberrant
signaling often associated with cancer cells (183). These rapid responses have been
studied for different steroids and can be induced by the binding of
the hormone to a protein associated with the membrane (184), which involves a classic receptor
such as VDR, but associated with the caveolae of the bilayer lipid,
or a non-classical steroid receptor specific for rapid responses
called membrane-associated rapid response steroid binding protein
(185). The interaction of
1,25(OH)2 D3 with these receptors promotes the activation of
signaling molecules, such as phospholipase C, increasing the
synthesis of second messengers including inositol triphosphate
(IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). IP3 in turn stimulates the release
of Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum into the
cytoplasm and DAG activates protein kinase C (PKC). Both
Ca2+ and PKC regulate Ca2+ entry into the
cell through voltage-gated channels (186). Thus, it is clear that VitD, in
its non-genomic capacity, plays a crucial role in maintaining
cellular calcium homeostasis (187). Hence, by swiftly regulating
calcium influx and efflux across the cell membrane, VitD
contributes to the normalization of calcium levels, disrupting the
signaling pathways that sustain uncontrolled cell growth (188). Additionally, some of the second
messengers mentioned can also interact with the nucleus to modulate
gene expression, whereby under certain circumstances, both genomic
and non-genomic actions of VitD may collaborate to fight against
cancer and metastasis (189).
Similar to genomic mechanisms, non-genomic pathways
of VitD also extend to the inhibition of angiogenesis, albeit
through rapid responses (179,190). By directly influencing
endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells, VitD disrupts
the formation of new blood vessels crucial for tumor sustenance
(191). This rapid interference
with angiogenesis contributes to the containment of cancer growth
and metastasis.
The non-genomic actions of VitD also have a
profound effect on immune cells, influencing their functions in the
tumor microenvironment (192).
The rapid modulation of immune responses, such as enhanced
phagocytosis and cytokine production, contributes to an antitumor
environment. This rapid immune regulation represents a critical
non-genomic strategy employed by VitD to inhibit cancer progression
(132).
VitD also swiftly interferes with cellular
processes involved in migration and invasion, essential steps in
cancer metastasis. Through non-genomic mechanisms, VitD hampers the
reorganization of the cytoskeleton and disrupts focal adhesion,
thereby impeding the ability of cancer cells to migrate and invade
surrounding tissues (193). A
compilation of in vitro and in vivo studies related
to the antitumor actions of VitD is presented in Table VI.
 | Table VIMajor results regarding the effects
of vitamin D in various types of cancer. |
Table VI
Major results regarding the effects
of vitamin D in various types of cancer.
| Cell lineage | Type of cancer | Dosage and period
of treatment | Relevant
effects | (Refs.) |
|---|
| LS180 CRC | N.A. | 10−7 M
1,25(OH)2D3 for 3 h | During
1,25(OH)2D3 activation the coactivator SRC-1
was correlated with VDR/RXR activity, while corepressors NCoR and
SMRT were also recruited to activation of complexes near genes
stimulated by 1,25(OH)2D3 | (167) |
| MM96L, Sk-Mel-28,
1205Lu, WM164, and C8161 | Human melanoma | 10 nM
1,25(OH)2D3 for 24, 48 and 72 h |
1,25(OH)2D3
inhibition of melanoma growth was dependent on PTEN and VDR;
1,25(OH)2D3 also inhibited the PI3K-AKT-mTOR
and RAS-ERK signaling pathways, while increasing caspase
levels | (171) |
| HCT116 | Human colorectal
carcinoma | 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10,
15, 20, 40 µM 1,25(OH)2D3 for 24
h | Treatment with
1,25(OH)2D3 exerted a dose-dependent effect
on the expression of caspase-3, but did not have any effect on
NF-κB expression | (172) |
| MCF-7 and
MDA-MB-231 | Human breast
cancer | 100 nM
1,25(OH)2D3 for 24 and 48 h | Treatment with
calcitriol (1,25(OH)2D3) increased the
expression of TIMPs 1 and 2 and decreased MMPs 2 and 9); it also
reduced the expression of VEGF, TGF-β1 and amphiregulin | (176) |
| 4T1 | Murine breast
cancer | 0.001 to 100
µM 1,25 (OH)2D3 for 12, 24 and 48 h
for in vitro assays and 10 mg per kg-1 every 3 days for six
times | MMP-2 and MMP-9
were downregulated by 1,25(OH)2D3, while
paxillin, a key component of the focal adhesion complex, was
upregulated | (180) |
| MCF-7 and
MDA-MB-231 | Human breast
cancer | 0.5 and 1 µM
1,25 (OH)2D3 for 24 h |
1,25(OH)2D3 impaired
migration by increasing E-cadherin, and F-actin and reducing
vimentin expression; it also induced apoptosis by decreasing mTOR
expression and increasing AMPK activation | (193) |
| Fragment of human
leiomyoma | Human leiomyoma in
xenograft model | 0.5
µg/kg/day or 1 µg/kg/day vitamin D for 21 or 60
days |
1,25(OH)2D3 at 1
µg/kg for 60 days significantly reduced proliferation,
collagen-I, plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and TGF-β3 expression
in the xenograft tissue; it also increased apoptosis in the animal
model | (194) |
| EO771 | Mouse breast
adenocarcinoma | 40 IU/day
1,25(OH)2D3 per mouse seven times in 2
weeks | Vitamin D was able
to modulate the tumor growth and the inflammation in the
microenvironment by recruitment of CD8+ cells; this
effect was reversed in high-fat diet conditions | (195) |
| BT-474, MCF-7,
T47D, MDA-MB 453, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468, and A549 | Human breast and
lung cancer | 7.78, 15.62, 31.25,
62.5, 125.0, 250, and 500.0 µM
1,25(OH)2D3 for 24, 48, and 72 h |
1,25(OH)2D3 induced
cell growth arrest mediated by the upregulation of p53 and the
downregulation of Bcl2 and cyclin-D1 expression levels; 1,25
(OH)2D3 also decreased cell migration and
inhibited blood vessel growth in vitro | (196) |
| MMTV-PyMT | Mouse breast
cancer | 10−10,
10−9, 10−8, and 10−7 M
1,25(OH)2D3 for 48 h for in vitro
studies and 25 IU/kg or 1,000 IU/kg for in vivo studies for
10 weeks | Vitamin D treatment
inhibited p-STAT3, Zeb1 and vimentin, and increased E-cadherin
levels; epithelial-mesenchymal transition and CXCL12/CXCR4
signaling were favored for metastases in a condition of vitamin D
deficiency (25 IU/kg) | (198) |
Evidence from animal and human studies on
the effects of VitD in cancer treatment and prevention
Numerous animal studies have demonstrated that
adequate VitD levels contribute to the suppression of tumor growth.
Experimental models, ranging from mice to rats, consistently show a
reduction in tumor size and incidence when VitD is administered
(194-197). Animal experiments also suggest
that VitD plays a role in inhibiting metastasis. Studies utilizing
metastatic models demonstrate that VitD supplementation can impede
the spread of cancer cells to distant organs, highlighting its
potential as a modulator of metastatic pathways (198). Likewise, VitD has been
implicated in the modulation of immune responses in animal studies.
Enhanced immune surveillance and increased activity of immune cells
contribute to a microenvironment less conducive to tumorigenesis
(199).
Notably, epidemiological studies have consistently
associated higher VitD levels with a reduced risk of developing
certain types of cancer. Thus, populations with increased sun
exposure or VitD supplementation tend to exhibit lower incidences
of colorectal, breast and prostate cancers (200). Human studies have also explored
the impact of VitD on cancer survival rates, as well as both the
genomic and non-genomic effects of VitD in these patients. In this
regard, some research suggests that patients with cancer with
higher VitD levels at the time of diagnosis may experience improved
outcomes and an increased overall survival. In fact, studies
examining gene expression patterns indicate that VitD may influence
key pathways associated with cell proliferation, apoptosis and
differentiation (201-203). Emerging evidence even suggests
that the VitD status may influence the response to cancer
treatments such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy.
Therefore, patients with optimal VitD levels may exhibit better
responses to therapeutic interventions (204-206).
As regards the prevention of cancer, some clinical
trials have also explored the potential of VitD supplementation in
reducing the risk of developing several types of cancer, including
colorectal, breast and prostate cancer. In addition, findings from
observational studies and meta-analyses have suggested an
association between higher VitD levels and a lower incidence of
developing certain types of cancer, such as pancreatic, colorectal,
gastric, prostatic, liver, bladder and lung cancer (207,208).
Establishing the optimal VitD dosage for cancer
prevention and treatment remains a challenge. The dose-response
association is complex, and individual variations in metabolism and
absorption add layers of intricacy to this value. Furthermore, the
effects of VitD appear to be cancer-type specific (209). In this sense, while there is
evidence to support its protective role in certain malignancies,
the association with other cancer types remains less clear,
highlighting the need for targeted research in diverse cancer types
(210).
Synergistic effects of melatonin and vitamin
D in cancer
Potential mechanisms by which melatonin
and VitD interact to produce synergistic effects in the prevention
and treatment of cancer
The authors have previously documented an inverse
association between melatonin and VitD deficiencies with the
pathogenesis of multiple diseases, including cancer (211). Since the synthesis of both VitD
and melatonin tend to be depressed during aging, the proper
functioning of some biological systems is disrupted resulting in
excessive oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial
malfunction. It is known that the mitochondria are the preferential
site for both melatonin and VitD actions; thus, they may play
cooperative roles in ensuring the maintenance of cellular
homeostasis (211). Common
signaling pathways associated with the mitochondrial functions
regulated by melatonin and VitD include the downregulation of mTOR,
FOXO1, iNOS, NF-κB and RAAS, as well as the upregulation of Klotho,
SIRT-, AMPK, Nrf2 and HSP70. The regulatory events mediated by
these targeted molecules in association with mitochondrial-related
processes (e.g., apoptosis and resistance to chemotherapy) are
promising biological mechanisms to be addressed in future or
ongoing studies using melatonin and VitD as adjunctive agents.
In this regard, a complementary therapeutic
strategy using melatonin and VitD has been highly recommended for
patients with breast cancer (212). While in vitro studies hae
revealed the capacity of melatonin to regulate the transcriptional
activity of VDR in human breast cancer cells, higher levels of VitD
have exhibited a negative regulation with melatonin secretion
(211). Notably, Bizzarri et
al (213) exposed
estrogen-responsive rat breast cancer cells (RM4 line) to combined
treatment with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (VitD3, the active form of
VitD) at low concentrations with melatonin (10−9 M).
Melatonin markedly increased the sensitivity of RM4 cells to VitD3
and the combination treatment further enhanced the release of
TGF-β1 compared to either melatonin or VitD3 alone; increasing
TGF-β1 secretion is considered to promote the growth inhibition of
breast cancer cells and to activate the apoptotic cascade (213). To more completely understand the
anti-proliferative effect of TGF-β1-dependent signaling on breast
cancer cells, the same research group investigated the role of
melatonin and VitD3 considering the activities of proteins involved
with cell cycle, tumor suppression, and cell growth (214). Melatonin synergistically
interacted with VitD3 to induce a complete cell growth arrest at
144 h following incubation. This TGF-β1-activated blockade was
accompanied by increased levels of Smad4 and phosphorylated Smad3.
Moreover, the combination of melatonin and VitD3 significantly
reduced the Akt phosphorylation and MDM2 levels, with a consequent
increase in the p53/MDM2 ratio. These events can be completely
reversed by the addition of a monoclonal anti-TGF-β1 antibody to
the culture medium, which reinforces the TGF-β1 dependence in
downregulating critical molecules involved with cell growth
(214). The main actions by
which melatonin and VitD synergistically interact to exert
antitumor effects are illustrated in Fig. 2.
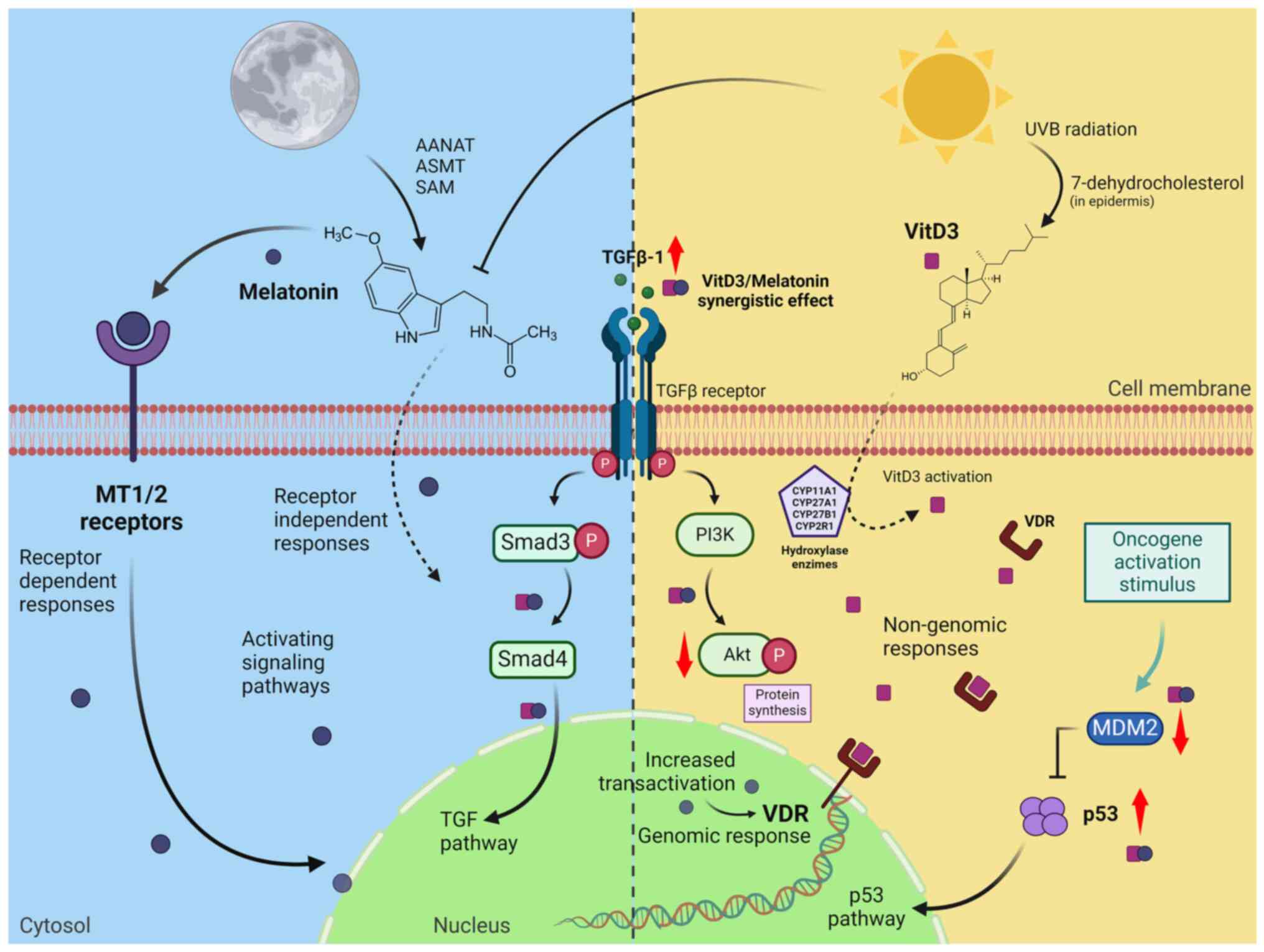 | Figure 2Illustration of the synthesis and
potential synergistic effects of melatonin and VitD3
(cholecalciferol) in a cancer cell. During the night, melatonin is
synthesized in the pineal gland from the precursor serotonin which
is converted into N-acetyl-serotonin by AANAT. With the action of
ASMT and SAM the final stage of melatonin production is achieved.
Light inhibits the synthesis of melatonin, while increasing the
levels of VitD3, which is activated with different tissue-specific
hydroxylase enzymes. Melatonin can easily cross the cell membrane
to act in a receptor independent response thus activating signaling
pathways in the cytosol or mainly binding through their G
protein-coupled receptors MT1 and MT2 to mediate numerous
biological actions. The effects of VitD3 are primarily genomic and
mediated by its interaction with nuclear VDR, and melatonin is
documented to increase VDR transactivation. In the cytosol, VDR and
VitD3 can trigger non-genomic responses by modulating various cell
signaling cascades. Treatment with melatonin and VitD3 may act
synergistically to inhibit cancer cell growth by increasing the
levels of TGFβ-1, Smad4 and phosphorylated Smad3, thus enhancing
the TGF pathway. This combination can also promote a reduction in
Akt phosphorylation and MDM2 levels, thereby leading to an increase
in p53 pathway and consequently causing tumor suppression and
apoptosis. AANAT, alkylamine acetyltransferase; ASMT,
acetyl-serotonin O-methyltransferase; SAM, S-adenosyl methionine;
VDR, vitamin D receptor; TGFβ-1, transforming growth factor beta 1;
Smad3, suppressors of mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3;
Smad4, suppressors of mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4;
MDM2, mouse double minute 2 homolog; p53, tumor protein p53. |
In vivo and in vitro experiments have
also documented that inflammation and oxidative processes represent
the main mechanisms of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver
cancer (71,215). For this reason, Özerkan et
al (216) evaluated the
hepato-protective activity of melatonin and VitD3 on CCl4-induced
cytotoxicity in human hepatoma (HepG2 and Hep3B cell lines).
Efficiently, the co-administration of melatonin (10−8 M)
and VitD3 (2.5×10−6 M) protected liver cells from
oxidative damage by diminishing lipid peroxidation and augmenting
glutathione levels similar to that of the control groups. Given
that there are several means by which ROS compromise cancer cell
survival, it is hypothesized that melatonin and VitD may
synergistically act to intensify oxidative damage in a more
advanced stage of cancer.
Evidence from studies on patients with
cancer on the effects of the combined use of melatonin and
VitD
According to the Clinical Practice Committee of The
Society of Integrative Oncology, composed of leading researchers
and clinicians, melatonin and VitD are among the supplements that
have evidenced effectiveness against different types of cancer
(217). Although clinical trials
(Clinical trial no. NCT01965522) focusing on the potential benefits
and realistic expectations of this combination are far from
optimal, they are of significant value to ease the burden of
patients afflicted with this disease.
The pathogenesis of lip, oral cavity and pharyngeal
cancers (LOCP), which are categorized as rare neoplasms, is still
unclear; however, it is considered to involve oxidative stress, the
immune system and components of the extracellular matrix (217-219). Recently, a study conducted with
45 patients diagnosed with LOCP and classified according to their
age (younger vs. older cancer groups) demonstrated the link between
the serum levels of melatonin and VitD with the oxidant-antioxidant
status of patients (218).
Regardless of age, patients with LOCP exhibited a decrease in VitD
and catalase levels in contrast to an increase in osteopontin and
malondialdehyde levels. In the older LOCP group, melatonin levels
were diminished in addition to the variations in the antioxidant
status (218).
Previous clinical studies using melatonin and
vitamins including VitD as therapy have been conducted on patients
with breast, head and neck cancer. While in patients with breast
cancer a significant tumor regression rate followed with no
recurrence rate and a 5-year survival of 50% at stage IV was
commonly observed (220),
patients with head and neck cancer exhibited a greater response to
therapy and an improved survival rate (221). More recently, a retrospective
observational study by Di Bella et al (222) observed the effectiveness of
treating patients with malignant anaplastic brain cancer with a
combination of components (including melatonin and VitD) that
exhibit anti-proliferative, cytostatic, antioxidant and
anti-metastatic features. Notably, they observed the antitumor
actions of the treatment and a longer survival rate of patients (5
to 8 years after commencing the therapy). Aligned with these
findings, the same group retrospectively analyzed 15 cases of
osteosarcomas treated with a multitherapy composed of melatonin and
VitD, among other active principles, and observed an increased
patient survival rate and life quality without overt toxicity
compared to the standard therapy for osteosarcoma (223).
Other effects of these biotherapeutic agents, have
been used to treat a total of 28 patients with advanced
non-small-cell-lung cancer (NSCLC) (stage IIIB or stage IV NSCLC)
receiving cyclophosphamide as therapy. Patients who experienced a
low-performance status and prognosis benefited from the
complementary therapy in terms of survival rate [(overall survival
rate was 51.2% (at 1 year) and 21.1% (at 2 years)] and quality of
life. The majority of patients improved their respiratory
conditions (e.g., dyspnea and cough) and general symptoms such as
fatigue, insomnia, and pain (224). Of note, 1 year later, Norsa and
Martino (225) investigated the
effect of the melatonin and VitD combination in patients with
advanced-stage lung cancer in whom the disease had progressed
following standard chemotherapy. Among the disease-related
benefits, there were improvements in respiratory symptoms, which
was even more evident in patients surviving for >95 days after
commencing the protocol regimen.
Additionally, the radioprotective actions of
melatonin and VitD, whose synthesis is dependent on appropriate
light wavelengths, have been broadly recognized since various
studies with animals and humans supported their protective effects
against ionizing radiation (IR)-induced damage (226). In the course of the ever-growing
use of IR in medical practice, a number of individuals are
continuously exposed to different IR sources and doses,
particularly patients undergoing radiotherapy. In this regard,
melatonin and VitD show promise in selectively enhancing the
sensitivity of cancer cells to radiotherapy, rendering them
potential adjuncts to improve anticancer effects and therapeutic
outcomes. Considering existing research on their antioxidant
effects, these substances may be beneficial for protecting
individuals exposed to radiation and those undergoing radiation
treatments. However, further human studies are required to
determine optimal and safe doses, which requires clinical trials
for validation.
Conclusions and future perspectives
It is well-known that melatonin and VitD share
similarities, with a significant impact on human health, acting
through multiple systems due to their anti-inflammatory and
antioxidant actions, immune enhancer responses and oncostatic
properties. A notable and paradoxical fact concerning both agents
is that VitD deficiency could be caused by 'low sunlight exposure',
whereas a reduction in melatonin secretion occurs when a 'darkness
deficiency' arises, among other conditions, from overexposure to
artificial blue light (227).
Previous research has shown the representation of low daytime UVB
or high LAN exposure on circadian disruption and related disorders
(e.g., cancer risk) (228).
Although epidemiological investigations on the deleterious
consequences of the combined suppression of VitD and melatonin are
lacking, it appears likely that they negatively affect the
physiology of cancerous cells or tissue, while protecting
non-damaged cells.
As regards the central discussion of the present
review, VitD and melatonin supplementation exhibit efficacy against
several types of cancer. Clinical trials on this combination are
still limited but are valuable in improving the quality of life of
cancer patients. Specifically, human studies involving
osteosarcoma, as well as lip, oral cavity, pharynx, breast, head,
neck, brain and lung cancers are examples of these improvements.
VitD and melatonin also have radioprotective potential, which could
improve the effectiveness of radiotherapy and protect patients from
its side-effects. The use of synthetic radioprotective compounds is
restricted due to the occurrence of undesirable health
consequences, particularly when higher doses are required for
maximum radioprotection. Considering the prevalent deficiencies of
melatonin and VitD in modern societies, supplementing with both
substances would be crucial, given that such deficiencies may
exacerbate the adverse effects of radiotherapy (e.g., ionizing
radiation) and chemotherapy. In this sense, further studies are
warranted to determine optimal doses when these agents are used in
combination.
In addition to reducing the growth of cancer cells
and improving the life quality of patients, this combination may
improve sleep quality providing an indirect benefit on the cancer
mediated by the connections between sleep and the immune system
(229).
Finally, to determine the efficacy of both agents
in ameliorating the life quality of patients with cancer, large
controlled trials comparing the effects of combined therapy with
melatonin and VitD with a single agent or even placebo are
warranted, in order to investigate their potential synergistic
effects. This intervention is easy to follow, since melatonin and
VitD are inexpensive compounds and do not produce organic toxicity,
dependence and/or chemoresistance.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors' contributions
All authors (RJR, LGDAC, VAS, VMMG, NDLH, DAS and
WM) contributed equally to the conception and design of the review,
with substantial input on the data, content analysis and
interpretation, writing, and critical review of the article for its
intellectual content. All authors have read and approved the final
manuscript. Data authentication is not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
DAS is the Editor-in-Chief for the journal, but had
no personal involvement in the re-viewing process, or any influence
in terms of adjudicating on the final decision, for this article.
The other authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr Vinícius Augusto
Simão from the Department of Structural and Functional Biology,
UNESP, São Paulo State University, Institute of Biosciences,
Botucatu, São Paulo, Brazil, for his participation in the design
and elaboration of the figures of the manuscript.
Funding
The present study work has been partially supported by grants
from Instituto de Salud Carlos III (FIS PI22/01608) and the
Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (PID2021-1230760B-100). The
present study also received grant funding PICT 2020 Seria A 4000
from Agencia Nacional de Promoción de la Investigación, el
Desarrollo Tecnológico y la Innovación (FONCyT), and Fundación
Florencio Fiorini (Academia Nacional de Medicina, 2024).
References
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 73:17–48. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zaimy MA, Saffarzadeh N, Mohammadi A,
Pourghadamyari H, Izadi P, Sarli A, Moghaddam LK, Paschepari SR,
Azizi H, Torkamandi S and Tavakkoly-Bazzaz J: New methods in the
diagnosis of cancer and gene therapy of cancer based on
nanoparticles. Cancer Gene Ther. 24:233–243. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Heidrich I, Deitert B, Werner S and Pantel
K: Liquid biopsy for monitoring of tumor dormancy and early
detection of disease recurrence in solid tumors. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 42:161–182. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Feinberg AP and Levchenko A: Epigenetics
as a mediator of plasticity in cancer. Science. 379:eaaw38352023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Biswas A and De S: Drivers of dynamic
intratumor heterogeneity and phenotypic plasticity. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 320:C750–C760. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maley CC, Aktipis A, Graham TA, Sottoriva
A, Boddy AM, Janiszewska M, Silva AS, Gerlinger M, Yuan Y, Pienta
KJ, et al: Classifying the evolutionary and ecological features of
neoplasms. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:605–619. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim TK, Slominski RM, Pyza E, Kleszczynski
K, Tuckey RC, Reiter RJ, Holick MF and Slominski AT: Evolutionary
formation of melatonin and vitamin D in early life forms: Insects
take centre stage. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 99:1772–1790. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
de Almeida Chuffa LG, Seiva FRF, Cucielo
MS, Silveira HS, Reiter RJ and Lupi LA: Mitochondrial functions and
melatonin: A tour of the reproductive cancers. Cell Mol Life Sci.
76:837–863. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li Y, Li S, Zhou Y, Meng X, Zhang JJ, Xu
DP and Li HB: Melatonin for the prevention and treatment of cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:39896–39921. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rafiyan M, Davoodvandi A, Reiter RJ,
Mansournia MA, Rasooli Manesh SM, Arabshahi V and Asemi Z:
Melatonin and cisplatin co-treatment against cancer: A mechanistic
review of their synergistic effects and melatonin's protective
actions. Pathol Res Pract. 253:1550312024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Reiter RJ, Sharma R, Rosales-Corral S,
Manucha W, Chuffa LGA and Zuccari DAPC: Melatonin and pathological
cell interactions: mitochondrial glucose processing in cancer
cells. Int J Mol Sci. 22:124942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Koll L, Gül D, Elnouaem MI, Raslan H,
Ramadan OR, Knauer SK, Strieth S, Hagemann J, Stauber RH and Khamis
A: Exploiting vitamin D receptor and its ligands to target squamous
cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Int J Mol Sci. 24:46752023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang W, Hu W, Xue S, Chen Q, Jiang Y,
Zhang H and Zuo W: Vitamin D and lung cancer; association,
prevention, and treatment. Nutr Cancer. 73:2188–2200. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
You W, Liu X, Tang H, Lu B, Zhou Q, Li Y,
Chen M, Zhao J, Xu Y, Wang M, et al: Vitamin D status is associated
with immune checkpoint inhibitor efficacy and immune-related
adverse event severity in lung cancer patients: A prospective
cohort study. J Immunother. 46:236–243. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hassan HT, Eliopoulos A, Maurer HR and
Spandidos DA: Recombinant human GM-CSF enhances the
anti-proliferative activity of vitamin D in MCF-7 human breast
cancer clonogenic cells. Eur J Cancer. 28A:1588–1589. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jeon SM and Shin EA: Exploring vitamin D
metabolism and function in cancer. Exp Mol Med. 50:1–14. 2018.
|
|
17
|
Bellerba F, Serrano D, Johansson H, Pozzi
C, Segata N, NabiNejad A, Piperni E, Gnagnarella P, Macis D,
Aristarco V, et al: Colorectal cancer, vitamin D and microbiota: A
double-blind phase II randomized trial (ColoViD) in colorectal
cancer patients. Neoplasia. 34:1008422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cucielo MS, Cesário RC, Silveira HS,
Gaiotte LB, Dos Santos SAA, de Campos Zuccari DAP, Seiva FRF,
Reiter RJ and de Almeida Chuffa LG: Melatonin reverses the
warburg-type metabolism and reduces mitochondrial membrane
potential of ovarian cancer cells independent of MT1 receptor
activation. Molecules. 27:43502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Garland CF, Garland FC, Gorham ED, Lipkin
M, Newmark H, Mohr SB and Holick MF: The role of vitamin D in
cancer prevention. Am J Public Health. 96:252–261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang L, Wang S, Che X and Li X: Vitamin D
and lung cancer risk: A comprehensive review and meta-analysis.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:299–305. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao M, Wan J, Zeng K, Tong M, Lee AC,
Ding J and Chen Q: The reduction in circulating melatonin level may
contribute to the pathogenesis of ovarian cancer: A retrospective
study. J Cancer. 7:831–836. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Reiter RJ, Sharma R, Ma Q, Rosales-Corral
S and Manucha W: Circadian and non-circadian melatonin: Influences
on glucose metabolism in cancer cells. J Curr Sci Technol.
10:85–98. 2020.
|
|
23
|
Cipolla-Neto J and Amaral FGD: Melatonin
as a hormone: New physiological and clinical insights. Endocr Rev.
39:990–1028. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Claustrat B and Leston J: Melatonin:
Physiological effects in humans. Neurochirurgie. 61:77–84. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Emet M, Ozcan H, Ozel L, Yayla M, Halici Z
and Hacimuftuoglu A: A review of melatonin, its receptors and
drugs. Eurasian J Med. 48:135–141. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu J, Clough SJ, Hutchinson AJ,
Adamah-Biassi EB, Popovska-Gorevski M and Dubocovich ML: MT1 and
MT2 melatonin receptors: A therapeutic perspective. Annu Rev
Pharmacol Toxicol. 56:361–383. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Ng KY, Leong MK, Liang H and Paxinos G:
Melatonin receptors: Distribution in mammalian brain and their
respective putative functions. Brain Struct Funct. 222:2921–2939.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cucielo MS, Freire PP, Emílio-Silva MT,
Romagnoli GG, Carvalho RF, Kaneno R, Hiruma-Lima CA, Delella FK,
Reiter RJ and Chuffa LGA: Melatonin enhances cell death and
suppresses the metastatic capacity of ovarian cancer cells by
attenuating the signaling of multiple kinases. Pathol Res Pract.
248:1546372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Franco PIR, do Carmo Neto JR, Milhomem AC,
Machado JR and Miguel MP: Antitumor effect of melatonin on breast
cancer in experimental models: A systematic review. Biochim Biophys
Acta Rev Cancer. 1878:1888382023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Tamtaji OR, Mirhosseini N, Reiter RJ,
Behnamfar M and Asemi Z: Melatonin and pancreatic cancer: Current
knowledge and future perspectives. J Cell Physiol. 234:5372–5378.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Slominski AT, Semak I, Fischer TW, Kim TK,
Kleszczyński K, Hardeland R and Reiter RJ: Metabolism of melatonin
in the skin: Why is it important? Exp Dermatol. 26:563–568. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Slominski AT, Zmijewski MA, Semak I, Kim
TK, Janjetovic Z, Slominski RM and Zmijewski JW: Melatonin,
mitochondria, and the skin. Cell Mol Life Sci. 74:3913–3925. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim KJ, Choi JS, Kang I, Kim KW, Jeong CH
and Jeong JW: Melatonin suppresses tumor progression by reducing
angiogenesis stimulated by HIF-1 in a mouse tumor model. J Pineal
Res. 54:264–270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Stehle JH, von Gall C and Korf HW:
Melatonin: A clock-output, a clock-input. J Neuroendocrinol.
15:383–389. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Slominski RM, Reiter RJ,
Schlabritz-Loutsevitch N, Ostrom RS and Slominski AT: Melatonin
membrane receptors in peripheral tissues: Distribution and
functions. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 351:152–166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stevens RG, Brainard GC, Blask DE, Lockley
SW and Motta ME: Breast cancer and circadian disruption from
electric lighting in the modern world. CA Cancer J Clin.
64:207–218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gaiotte LB, Cesário RC, Silveira HS, de
Morais Oliveira DA, Cucielo MS, Romagnoli GG, Kaneno R, de Campos
Zuccari AP, Reiter RJ and de Almeida Chuffa LG: Combination of
melatonin with paclitaxel reduces the TLR4-mediated inflammatory
pathway, PD-L1 levels, and survival of ovarian carcinoma cells.
Melatonin Res. 5:34–51. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Slominski RM, Raman C, Chen JY and
Slominski AT: How cancer hijacks the body's homeostasis through the
neuroendocrine system. Trends Neurosci. 46:263–275. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Reiter RJ, Rosales-Corral SA, Tan DX,
Acuna-Castroviejo D, Qin L, Yang SF and Xu K: Melatonin, a full
service anti-cancer agent: Inhibition of initiation, progression
and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 18:8432017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Talib WH: Melatonin and cancer hallmarks.
Molecules. 23:5182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Moloudizargari M, Moradkhani F, Hekmatirad
S, Fallah M, Asghari MH and Reiter RJ: Therapeutic targets of
cancer drugs: Modulation by melatonin. Life Sci. 267:1189342021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chuffa L, Carvalho R, Camargo VL, Cury S,
Domeniconi R, Zuccari DA and Seiva FR: Melatonin and cancer:
Exploring gene networks and functional categories. Melatonin Res.
6:431–451. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
de Almeida Chuffa LG, Carvalho RF,
Justulin LA, Cury SS, Seiva FRF, Jardim-Perassi BV, Zuccari DAPC
and Reiter RJ: A meta-analysis of microRNA networks regulated by
melatonin in cancer: Portrait of potential candidates for breast
cancer treatment. J Pineal Res. 69:e126932020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Ben-David U and Amon A: Context is
everything: Aneuploidy in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 21:44–62. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Bakhoum SF and Cantley LC: The
multifaceted role of chromosomal instability in cancer and its
microenvironment. Cell. 174:1347–1360. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
El-Missiry MA and Abd El-Aziz AF:
Influence of melatonin on proliferation and antioxidant system in
Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 151:119–125. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Reiter RJ, Mayo JC, Tan DX, Sainz RM,
Alatorre-Jimenez M and Qin L: Melatonin as an antioxidant: Under
promises but over delivers. J Pineal Res. 61:253–278. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mir SM, Aliarab A, Goodarzi G, Shirzad M,
Jafari SM, Qujeq D, Samavarchi Tehrani S and Asadi J: Melatonin: A
smart molecule in the DNA repair system. Cell Biochem Funct.
40:4–16. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Galano A, Tan DX and Reiter RJ: Melatonin:
A versatile protector against oxidative DNA damage. Molecules.
23:5302018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Alonso-González C, González A,
Menéndez-Menéndez J, Martínez-Campa C and Cos S: Melatonin as a
radio-sensitizer in cancer. Biomedicines. 8:2472020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Esmaely F, Mahmoudzadeh A, Cheki M and
Shirazi A: The radioprotective effect of melatonin against
radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in radiology. J Cancer
Res Ther. 16(Suppl 1): S59–S63. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Farhood B, Goradel NH, Mortezaee K,
Khanlarkhani N, Salehi E, Nashtaei MS, Mirtavoos-Mahyari H,
Motevaseli E, Shabeeb D, Musa AE and Najafi M: Melatonin as an
adjuvant in radiotherapy for radioprotection and
radiosensitization. Clin Transl Oncol. 21:268–279. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Cos S, Recio J and Sánchez-Barceló EJ:
Modulation of the length of the cell cycle time of MCF-7 human
breast cancer cells by melatonin. Life Sci. 58:811–816. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cabrera J, Negrín G, Estévez F, Loro J,
Reiter RJ and Quintana J: Melatonin decreases cell proliferation
and induces melanogenesis in human melanoma SK-MEL-1 cells. J
Pineal Res. 49:45–54. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu L, Zhu Y, Xu Y and Reiter RJ:
Melatonin delays cell proliferation by inducing G1 and G2/M phase
arrest in a human osteoblastic cell line hFOB 1.19. J Pineal Res.
50:222–231. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Martín V, Herrera F, Carrera-Gonzalez P,
García-Santos G, Antolín I, Rodriguez-Blanco J and Rodriguez C:
Intracellular signaling pathways involved in the cell growth
inhibition of glioma cells by melatonin. Cancer Res. 66:1081–1088.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Targhazeh N, Reiter RJ, Rahimi M, Qujeq D,
Yousefi T, Shahavi MH and Mir SM: Oncostatic activities of
melatonin: Roles in cell cycle, apoptosis, and autophagy.
Biochimie. 202:34–48. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Shen CJ, Chang CC, Chen YT, Lai CS and Hsu
YC: Melatonin suppresses the growth of ovarian cancer cell lines
(OVCAR-429 and PA-1) and potentiates the effect of G1 arrest by
targeting CDKs. Int J Mol Sci. 17:1762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Pizarro JG, Yeste-Velasco M, Esparza JL,
Verdaguer E, Pallàs M, Camins A and Folch J: The antiproliferative
activity of melatonin in B65 rat dopaminergic neuroblastoma cells
is related to the downregulation of cell cycle-related genes. J
Pineal Res. 45:8–16. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Long F, Dong C, Jiang K, Xu Y, Chi X, Sun
D, Gao Z, Shao S and Wang L: Melatonin enhances the anti-tumor
effect of sorafenib via AKT/p27-mediated cell cycle arrest in
hepatocarcinoma cell lines†. RSC Adv. 7:21342–21351. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Yun M, Kim EO, Lee D, Kim JH, Kim J, Lee
H, Lee J and Kim SH: Melatonin sensitizes H1975 non-small-cell lung
cancer cells harboring a T790M-targeted epidermal growth factor
receptor mutation to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 34:865–872. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hong Y, Won J, Lee Y, Lee S, Park K, Chang
KT and Hong Y: Melatonin treatment induces interplay of apoptosis,
autophagy, and senescence in human colorectal cancer cells. J
Pineal Res. 56:264–274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Liu L, Xu Y and Reiter RJ: Melatonin
inhibits the proliferation of human osteosarcoma cell line MG-63.
Bone. 55:432–438. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Cini G, Neri B, Pacini A, Cesati V,
Sassoli C, Quattrone S, D'Apolito M, Fazio A, Scapagnini G,
Provenzani A and Quattrone A: Antiproliferative activity of
melatonin by transcriptional inhibition of cyclin D1 expression: A
molecular basis for melatonin-induced oncostatic effects. J Pineal
Res. 39:12–20. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ju HQ, Li H, Tian T, Lu YX, Bai L, Chen
LZ, Sheng H, Mo HY, Zeng JB, Deng W, et al: Melatonin overcomes
gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by
abrogating nuclear factor-κB activation. J Pineal Res. 60:27–38.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Margheri M, Pacini N, Tani A, Nosi D,
Squecco R, Dama A, Masala E, Francini F, Zecchi-Orlandini S and
Formigli L: Combined effects of melatonin and all-trans retinoic
acid and somatostatin on breast cancer cell proliferation and
death: Molecular basis for the anticancer effect of these
molecules. Eur J Pharmacol. 681:34–43. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Carbajo-Pescador S, Martín-Renedo J,
García-Palomo A, Tuñón MJ, Mauriz JL and González-Gallego J:
Changes in the expression of melatonin receptors induced by
melatonin treatment in hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells. J Pineal Res.
47:330–338. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Mediavilla MD, Cos S and Sánchez-Barceló
EJ: Melatonin increases p53 and p21WAF1 expression in MCF-7 human
breast cancer cells in vitro. Life Sci. 65:415–420. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
She MH, Chen BB, Wang XM and He SS:
p53-dependent antiproliferation and apoptosis of H22 cell induced
by melatonin. Ai Zheng. 23:803–807. 2004.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kim CH and Yoo YM: Melatonin induces
apoptotic cell death via p53 in LNCaP cells. Korean J Physiol
Pharmacol. 14:365–369. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Hong RT, Xu JM and Mei Q: Melatonin
ameliorates experimental hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon
tetrachloride in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 15:1452–1458. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Chuffa LG, Alves MS, Martinez M, Camargo
IC, Pinheiro PF, Domeniconi RF, Júnior LA and Martinez FE:
Apoptosis is triggered by melatonin in an in vivo model of ovarian
carcinoma. Endocr Relat Cancer. 23:65–76. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Sánchez DI, González-Fernández B, Crespo
I, San-Miguel B, Álvarez M, González-Gallego J and Tuñón MJ:
Melatonin modulates dysregulated circadian clocks in mice with
diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Pineal Res.
65:e125062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Bizzarri M, Proietti S, Cucina A and
Reiter RJ: Molecular mechanisms of the pro-apoptotic actions of
melatonin in cancer: A review. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
17:1483–1496. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Carneiro BA and El-Deiry WS: Targeting
apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:395–417. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Rubio S, Estévez F, Cabrera J, Reiter RJ,
Loro J and Quintana J: Inhibition of proliferation and induction of
apoptosis by melatonin in human myeloid HL-60 cells. J Pineal Res.
42:131–138. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Leja-Szpak A, Jaworek J, Pierzchalski P
and Reiter RJ: Melatonin induces pro-apoptotic signaling pathway in
human pancreatic carcinoma cells (PANC-1). J Pineal Res.
49:248–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Xu L, Jin QD, Gong X, Liu H and Zhou RX:
Anti-gastric cancer effect of melatonin and Bcl-2, Bax, p21 and p53
expression changes. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 66:723–729. 2014.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chuffa LGA, Reiter RJ and Lupi LA:
Melatonin as a promising agent to treat ovarian cancer: Molecular
mechanisms. Carcinogenesis. 38:945–952. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Bock FJ and Tait SWG: Mitochondria as
multifaceted regulators of cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
21:85–100. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Tian C, Liu Y, Li Z, Zhu P and Zhao M:
Mitochondria related cell death modalities and disease. Front Cell
Dev Biol. 10:8323562022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Bejarano I, Redondo PC, Espino J, Rosado
JA, Paredes SD, Barriga C, Reiter RJ, Pariente JA and Rodríguez AB:
Melatonin induces mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in human myeloid
HL-60 cells. J Pineal Res. 46:392–400. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Trubiani O, Recchioni R, Moroni F,
Pizzicannella J, Caputi S and Di Primio R: Melatonin provokes cell
death in human B-lymphoma cells by mitochondrial-dependent
apoptotic pathway activation. J Pineal Res. 39:425–431. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Joo SS and Yoo YM: Melatonin induces
apoptotic death in LNCaP cells via p38 and JNK pathways:
Therapeutic implications for prostate cancer. J Pineal Res.
47:8–14. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Carbajo-Pescador S, Steinmetz C, Kashyap
A, Lorenz S, Mauriz JL, Heise M, Galle PR, González-Gallego J and
Strand S: Melatonin induces transcriptional regulation of Bim by
FoxO3a in HepG2 cells. Br J Cancer. 108:442–449. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
86
|
Fan L, Sun G, Ma T, Zhong F and Wei W:
Melatonin overcomes apoptosis resistance in human hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting survivin and XIAP. J Pineal Res. 55:174–183.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Verma P, Rishi B, George NG, Kushwaha N,
Dhandha H, Kaur M, Jain A, Jain A, Chaudhry S, Singh A, et al:
Recent advances and future directions in etiopathogenesis and
mechanisms of reactive oxygen species in cancer treatment. Pathol
Oncol Res. 29:16114152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Huang R, Chen H, Liang J, Li Y, Yang J,
Luo C, Tang Y, Ding Y, Liu X, Yuan Q, et al: Dual role of reactive
oxygen species and their application in cancer therapy. J Cancer.
12:5543–5561. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Florido J, Martinez-Ruiz L,
Rodriguez-Santana C, López-Rodríguez A, Hidalgo-Gutiérrez A,
Cottet-Rousselle C, Lamarche F, Schlattner U, Guerra-Librero A,
Aranda-Martínez P, et al: Melatonin drives apoptosis in head and
neck cancer by increasing mitochondrial ROS generated via reverse
electron transport. J Pineal Res. 73:e128242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Florido J, Rodriguez-Santana C,
Martinez-Ruiz L, López-Rodríguez A, Acuña-Castroviejo D, Rusanova I
and Escames G: Understanding the mechanism of action of melatonin,
which induces ROS production in cancer cells. Antioxidants (Basel).
11:16212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Li M, Wu C, Muhammad JS, Yan D, Tsuneyama
K, Hatta H, Cui ZG and Inadera H: Melatonin sensitises
shikonin-induced cancer cell death mediated by oxidative stress via
inhibition of the SIRT3/SOD2-AKT pathway. Redox Biol.
36:1016322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Chen X, Hao B, Li D, Reiter RJ, Bai Y,
Abay B, Chen G, Lin S, Zheng T, Ren Y, et al: Melatonin inhibits
lung cancer development by reversing the Warburg effect via
stimulating the SIRT3/PDH axis. J Pineal Res. 71:e127552021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Reiter RJ, Sharma R, Rodriguez C, Martin
V, Rosales-Corral S, Zuccari DAPC and Chuffa LGA: Part-time cancers
and role of melatonin in determining their metabolic phenotype.
Life Sci. 278:1195972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Park SY, Jang WJ, Yi EY, Jang JY, Jung Y,
Jeong JW and Kim YJ: Melatonin suppresses tumor angiogenesis by
inhibiting HIF-1alpha stabilization under hypoxia. J Pineal Res.
48:178–184. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Reiter RJ, Sharma R, Ma Q, Rorsales-Corral
S and de Almeida Chuffa LG: Melatonin inhibits Warburg-dependent
cancer by redirecting glucose oxidation to the mitochondria: A
mechanistic hypothesis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:2527–2542. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Chuffa LGA, Fioruci-Fontanelli BA, Mendes
LO, Ferreira Seiva FR, Martinez M, Fávaro WJ, Domeniconi RF,
Pinheiro PF, Delazari Dos Santos L and Martinez FE: Melatonin
attenuates the TLR4-mediated inflammatory response through MyD88-
and TRIF-dependent signaling pathways in an in vivo model of
ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. 15:342015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Lu JJ, Fu L, Tang Z, Zhang C, Qin L, Wang
J, Yu Z, Shi D, Xiao X, Xie F, et al: Melatonin inhibits
AP-2β/hTERT, NF-κB/COX-2 and Akt/ERK and activates caspase/Cyto C
signaling to enhance the antitumor activity of berberine in lung
cancer cells. Oncotarget. 7:2985–3001. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Wang J, Xiao X, Zhang Y, Shi D, Chen W, Fu
L, Liu L, Xie F, Kang T, Huang W and Deng W: Simultaneous
modulation of COX-2, p300, Akt, and Apaf-1 signaling by melatonin
to inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis in breast cancer
cells. J Pineal Res. 53:77–90. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Pikarsky E, Porat RM, Stein I, Abramovitch
R, Amit S, Kasem S, Gutkovich-Pyest E, Urieli-Shoval S, Galun E and
Ben-Neriah Y: NF-kappaB functions as a tumour promoter in
inflammation-associated cancer. Nature. 431:461–466. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Chuang JI, Mohan N, Meltz ML and Reiter
RJ: Effect of melatonin on NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity in the
rat spleen. Cell Biol Int. 20:687–692. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Niranjan R, Nath C and Shukla R: The
mechanism of action of MPTP-induced neuroinflammation and its
modulation by melatonin in rat astrocytoma cells, C6. Free Radic
Res. 44:1304–1316. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Schito L: Hypoxia-dependent angiogenesis
and lymphangiogenesis in cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1136:71–85.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Colombo J, Maciel JMW, Ferreira LC, DA
Silva RF and Zuccari DAP: Effects of melatonin on HIF-1α and VEGF
expression and on the invasive properties of hepatocarcinoma cells.
Oncol Lett. 12:231–237. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Jardim-Perassi BV, Arbab AS, Ferreira LC,
Borin TF, Varma NR, Iskander AS, Shankar A, Ali MM and de Campos
Zuccari DA: Effect of melatonin on tumor growth and angiogenesis in
xenograft model of breast cancer. PLoS One. 9:e853112014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Zonta YR, Martinez M, Camargo ICC,
Domeniconi RF, Lupi Júnior LAL, Pinheiro PFF, Reiter RJ, Martinez
FE and Chuffa LGA: Melatonin reduces angiogenesis in serous
papillary ovarian carcinoma of ethanol-preferring rats. Int J Mol
Sci. 18:7632017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Ma Q, Reiter RJ and Chen Y: Role of
melatonin in controlling angiogenesis under physiological and
pathological conditions. Angiogenesis. 23:91–104. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Sulekha Suresh D and Guruvayoorappan C:
Molecular principles of tissue invasion and metastasis. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 324:C971–C991. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Gupta GP and Massagué J: Cancer
metastasis: Building a framework. Cell. 127:679–695. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Tang H, Shi X, Zhu P, Guo W, Li J, Yan B
and Zhang S: Melatonin inhibits gallbladder cancer cell migration
and invasion via ERK-mediated induction of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Lett. 22:6092021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Wang X, Wang B, Xie J, Hou D, Zhang H and
Huang H: Melatonin inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
gastric cancer cells via attenuation of IL-1β/NF-κB/MMP2/MMP9
signaling. Int J Mol Med. 42:2221–2228. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Wang X, Wang B, Zhan W, Kang L, Zhang S,
Chen C, Hou D, You R and Huang H: Melatonin inhibits lung
metastasis of gastric cancer in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother.
117:1090182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Zhou Q, Gui S, Zhou Q and Wang Y:
Melatonin inhibits the migration of human lung adenocarcinoma A549
cell lines involving JNK/MAPK pathway. PLoS One. 9:e1011322014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Cos S, Fernández R, Güézmes A and
Sánchez-Barceló EJ: Influence of melatonin on invasive and
metastatic properties of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 58:4383–4390. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Tai HC, Wang SW, Swain S, Lin LW, Tsai HC,
Liu SC, Wu HC, Guo JH, Liu CL, Lai YW, et al: Melatonin suppresses
the metastatic potential of osteoblastic prostate cancers by
inhibiting integrin α2 β1 expression. J
Pineal Res. 72:e127932022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Xu CS, Wang ZF, Huang XD, Dai LM, Cao CJ
and Li ZQ: Involvement of ROS-alpha v beta 3 integrin-FAK/Pyk2 in
the inhibitory effect of melatonin on U251 glioma cell migration
and invasion under hypoxia. J Transl Med. 13:952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Najafi M, Farhood B and Mortezaee K:
Extracellular matrix (ECM) stiffness and degradation as cancer
drivers. J Cell Biochem. 120:2782–2790. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Nguyen BT, Lin CY, Chang TK, Fong YC,
Thadevoos LA, Lai CY, Huang YL, Tsai CH, Ko CY, Liu JF, et al:
Melatonin inhibits chondrosarcoma cell proliferation and metastasis
by enhancing miR-520f-3p production and suppressing MMP7
expression. J Pineal Res. 75:e128722023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Liu D, Shi K, Fu M and Chen F: Melatonin
indirectly decreases gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion
via effects on cancer-associated fibroblasts. Life Sci.
277:1194972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Ordoñez R, Carbajo-Pescador S,
Prieto-Dominguez N, García-Palomo A, González-Gallego J and Mauriz
JL: Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and nuclear factor
kappa B contribute to melatonin prevention of motility and
invasiveness in HepG2 liver cancer cells. J Pineal Res. 56:20–30.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Akbarzadeh M, Movassaghpour AA, Ghanbari
H, Kheirandish M, Fathi Maroufi N, Rahbarghazi R, Nouri M and
Samadi N: The potential therapeutic effect of melatonin on human
ovarian cancer by inhibition of invasion and migration of cancer
stem cells. Sci Rep. 7:170622017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Lin YW, Lee LM, Lee WJ, Chu CY, Tan P,
Yang YC, Chen WY, Yang SF, Hsiao M and Chien MH: Melatonin inhibits
MMP-9 transactivation and renal cell carcinoma metastasis by
suppressing Akt-MAPKs pathway and NF-κB DNA-binding activity. J
Pineal Res. 60:277–290. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Doğanlar O, Doğanlar ZB, Delen E and Doğan
A: The role of melatonin in angio-miR-associated inhibition of
tumorigenesis and invasion in human glioblastoma tumour spheroids.
Tissue Cell. 73:1016172021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Chen YT, Yang CC, Shao PL, Huang CR and
Yip HK: Melatonin-mediated downregulation of ZNF746 suppresses
bladder tumorigenesis mainly through inhibiting the AKT-MMP-9
signaling pathway. J Pineal Res. 66:e125362019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Mills E, Wu P, Seely D and Guyatt G:
Melatonin in the treatment of cancer: A systematic review of
randomized controlled trials and meta-analysis. J Pineal Res.
39:360–366. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Seely D, Wu P, Fritz H, Kennedy DA, Tsui
T, Seely AJ and Mills E: Melatonin as adjuvant cancer care with and
without chemotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
randomized trials. Integr Cancer Ther. 11:293–303. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Favero G, Moretti E, Bonomini F, Reiter
RJ, Rodella LF and Rezzani R: Promising antineoplastic actions of
melatonin. Front Pharmacol. 9:10862018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Oz E, Erbaş D, Sürücü HS and Düzgün E:
Prevention of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by melatonin. Mol
Cell Biochem. 282:31–37. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Lissoni P, Barni S, Mandalà M, Ardizzoia
A, Paolorossi F, Vaghi M, Longarini R, Malugani F and Tancini G:
Decreased toxicity and increased efficacy of cancer chemotherapy
using the pineal hormone melatonin in metastatic solid tumour
patients with poor clinical status. Eur J Cancer. 35:1688–1692.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Talib WH, Alsayed AR, Abuawad A, Daoud S
and Mahmod AI: Melatonin in cancer treatment: Current knowledge and
future opportunities. Molecules. 26:25062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Bouillon R, Manousaki D, Rosen C,
Trajanoska K, Rivadeneira F and Richards JB: The health effects of
vitamin D supplementation: Evidence from human studies. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 18:96–110. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Carlberg C: Vitamin D in the context of
evolution. Nutrients. 14:30182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Holick MF, Mazzei L, García Menéndez S,
Martín Giménez VM, Al Anouti F and Manucha W: Genomic or
non-genomic? A question about the pleiotropic roles of vitamin D in
inflammatory-based diseases. Nutrients. 15:7672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Khazai N, Judd SE and Tangpricha V:
Calcium and vitamin D: Skeletal and extraskeletal health. Curr
Rheumatol Rep. 10:110–117. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Martín Giménez VM, Lahore H, Ferder L,
Holick MF and Manucha W: The little-explored therapeutic potential
of nanoformulations of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its
active analogs in prevalent inflammatory and oxidative disorders.
Nanomedicine (Lond). 16:2327–2330. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Mazzaferro S, Goldsmith D, Larsson TE,
Massy ZA and Cozzolino M: Vitamin D metabolites and/or analogs:
Which D for which patient? Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 12:339–349. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Ysmail-Dahlouk L, Nouari W and Aribi M:
1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 down-modulates the production
of proinflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide and enhances the
phosphorylation of monocyte-expressed STAT6 at the recent-onset
type 1 diabetes. Immunol Lett. 179:122–130. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Slominski AT, Kim TK, Shehabi HZ, Tang EK,
Benson HA, Semak I, Lin Z, Yates CR, Wang J, Li W and Tuckey RC: In
vivo production of novel vitamin D2 hydroxy-derivatives by human
placentas, epidermal keratinocytes, Caco-2 colon cells and the
adrenal gland. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 383:181–192. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Christakos S, Dhawan P, Verstuyf A,
Verlinden L and Carmeliet G: Vitamin D: Metabolism, molecular
mechanism of action, and pleiotropic effects. Physiol Rev.
96:365–408. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
139
|
Jones G, Strugnell SA and DeLuca HF:
Current understanding of the molecular actions of vitamin D.
Physiol Rev. 78:1193–1231. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
van den Heuvel EG, Lips P, Schoonmade LJ,
Lanham-New SA and van Schoor NM: Comparison of the effect of daily
vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 supplementation on serum
25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration (total 25(OH)D, 25(OH)D2, and
25(OH) D3) and importance of body mass index: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Adv Nutr. 15:1001332024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Haussler MR, Haussler CA, Jurutka PW,
Thompson PD, Hsieh JC, Remus LS, Selznick SH and Whitfield GK: The
vitamin D hormone and its nuclear receptor: Molecular actions and
disease states. J Endocrinol. 154(Suppl 1): S57–S73.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Norlin M and Wikvall K: Enzymatic
activation in vitamin D signaling-past, present and future. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 742:1096392023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Araya Z, Hosseinpour F, Bodin K and
Wikvall K: Metabolism of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 by microsomal and
mitochondrial vitamin D3 25-hydroxylases (CYP2D25 and CYP27A1): A
novel reaction by CYP27A1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1632:40–47. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Kaseda R, Hosojima M, Sato H and Saito A:
Role of megalin and cubilin in the metabolism of vitamin D(3). Ther
Apher Dial. 15(Suppl 1): S14–S17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Slominski AT, Kim TK, Shehabi HZ, Semak I,
Tang EK, Nguyen MN, Benson HA, Korik E, Janjetovic Z, Chen J, et
al: In vivo evidence for a novel pathway of vitamin D3
metabolism initiated by P450scc and modified by CYP27B1. FASEB J.
26:3901–3915. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Slominski AT, Kim TK, Janjetovic Z,
Slominski RM, Li W, Jetten AM, Indra AK, Mason RS and Tuckey RC:
Biological effects of CYP11A1-derived vitamin D and lumisterol
metabolites in the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 144:2145–2161. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Qayyum S, Slominski RM, Raman C and
Slominski AT: Novel CYP11A1-derived vitamin D and lumisterol
biometabolites for the management of COVID-19. Nutrients.
14:47792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Slominski AT, Kim TK, Li W, Postlethwaite
A, Tieu EW, Tang EKY and Tuckey RC: Detection of novel
CYP11A1-derived secosteroids in the human epidermis and serum and
pig adrenal gland. Sci Rep. 5:148752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Slominski AT, Li W, Kim TK, Semak I, Wang
J, Zjawiony JK and Tuckey RC: Novel activities of CYP11A1 and their
potential physiological significance. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
151:25–37. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
McLeod JF and Cooke NE: The vitamin
D-binding protein, alpha-fetoprotein, albumin multigene family:
Detection of transcripts in multiple tissues. J Biol Chem.
264:21760–21769. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Girgis CM and Brennan-Speranza TC: Vitamin
D and skeletal muscle: Current concepts from preclinical studies.
JBMR Plus. 5:e105752021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Park CY and Han SN: The role of vitamin D
in adipose tissue biology: Adipocyte differentiation, energy
metabolism, and inflammation. J Lipid Atheroscler. 10:130–144.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Sempos CT, Heijboer AC, Bikle DD,
Bollerslev J, Bouillon R, Brannon PM, DeLuca HF, Jones G, Munns CF,
Bilezikian JP, et al: Vitamin D assays and the definition of
hypovitaminosis D: Results from the first international conference
on controversies in vitamin D. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 84:2194–2207.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Bouillon R, Schuit F, Antonio L and
Rastinejad F: Vitamin D binding protein: A historic overview. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 10:9102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Deeb KK, Trump DL and Johnson CS: Vitamin
D signalling pathways in cancer: Potential for anticancer
therapeutics. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:684–700. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Nezbedova P and Brtko J:
1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inducible transcription factor and
its role in the vitamin D action. Endocr Regul. 38:29–38.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Falzone L, Gattuso G, Candido S, Tomaselli
A, Fagone S, Spandidos DA and Libra M: Vitamin D and microRNAs:
Role in the pathogenesis and prognosis of breast cancer (Review).
Int J Epigenetics. 3:52023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Fleet JC, DeSmet M, Johnson R and Li Y:
Vitamin D and cancer: A review of molecular mechanisms. Biochem J.
441:61–76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Slominski AT, Chaiprasongsuk A, Janjetovic
Z, Kim TK, Stefan J, Slominski RM, Hanumanthu VS, Raman C, Qayyum
S, Song Y, et al: Photoprotective properties of vitamin D and
lumisterol hydroxyderivatives. Cell Biochem Biophys. 78:165–180.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Slominski AT, Kim TK, Janjetovic Z,
Brożyna AA, Żmijewski MA, Xu H, Sutter TR, Tuckey RC, Jetten AM and
Crossman DK: Differential and overlapping effects of
20,23(OH)2D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 on gene
expression in human epidermal keratinocytes: Identification of AhR
as an alternative receptor for 20,23(OH)2D3. Int J Mol
Sci. 19:30722018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Slominski AT, Kim TK, Qayyum S, Song Y,
Janjetovic Z, Oak ASW, Slominski RM, Raman C, Stefan J,
Mier-Aguilar CA, et al: Vitamin D and lumisterol derivatives can
act on liver X receptors (LXRs). Sci Rep. 11:80022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Slominski AT, Kim TK, Slominski RM, Song
Y, Janjetovic Z, Podgorska E, Reddy SB, Song Y, Raman C, Tang EKY,
et al: Metabolic activation of tachysterol3 to
biologically active hydroxyderivatives that act on VDR, AhR, LXRs,
and PPARγ receptors. Faseb J. 36:e224512022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Song Y, Slominski RM, Qayyum S, Kim TK,
Janjetovic Z, Raman C, Tuckey RC, Song Y and Slominski AT:
Molecular and structural basis of interactions of vitamin D3
hydroxyderivatives with aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR): An
integrated experimental and computational study. Int J Biol
Macromol. 209:1111–1123. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Escriva H, Bertrand S and Laudet V: The
evolution of the nuclear receptor superfamily. Essays Biochem.
40:11–26. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Gil Á, Plaza-Diaz J and Mesa MD: Vitamin
D: Classic and novel actions. Ann Nutr Metab. 72:87–95. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Flach KD and Zwart W: The first decade of
estrogen receptor cistromics in breast cancer. J Endocrinol.
229:R43–R56. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Meyer MB and Pike JW: Corepressors (NCoR
and SMRT) as well as coactivators are recruited to positively
regulated 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-responsive genes. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 136:120–124. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Negri M, Gentile A, de Angelis C, Montò T,
Patalano R, Colao A, Pivonello R and Pivonello C: Vitamin D-induced
molecular mechanisms to potentiate cancer therapy and to reverse
drug-resistance in cancer cells. Nutrients. 12:17982020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Starska-Kowarska K: Role of vitamin D in
head and neck cancer-immune function, anti-tumour effect, and its
impact on patient prognosis. Nutrients. 15:25922023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Bhoora S and Punchoo R: Policing cancer:
Vitamin D arrests the cell cycle. Int J Mol Sci. 21:92962020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Shariev A, Painter N, Reeve VE, Haass NK,
Rybchyn MS, Ince FA, Mason RS and Dixon KM: PTEN: A novel target
for vitamin D in melanoma. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
218:1060592022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Varghese JE, Shanmugam V, Rengarajan RL,
Meyyazhagan A, Arumugam VA, Al-Misned FA and El-Serehy HA: Role of
vitamin D3 on apoptosis and inflammatory-associated gene 528 in
colorectal cancer: An in vitro approach. J King Saud Univ Sci.
32:2786–2789. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
173
|
Seraphin G, Rieger S, Hewison M,
Capobianco E and Lisse TS: The impact of vitamin D on cancer: A
mini review. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 231:1063082023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Samuel S and Sitrin MD: Vitamin D's role
in cell proliferation and differentiation. Nutr Rev. 66(Suppl 2):
S116–S124. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Fernández-Barral A, Bustamante-Madrid P,
Ferrer-Mayorga G, Barbáchano A, Larriba MJ and Muñoz A: Vitamin D
effects on cell differentiation and stemness in cancer. Cancers
(Basel). 12:24132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Bajbouj K, Al-Ali A, Shafarin J, Sahnoon
L, Sawan A, Shehada A, Elkhalifa W, Saber-Ayad M, Muhammad JS,
Elmoselhi AB, et al: Vitamin D exerts significant antitumor effects
by suppressing vasculogenic mimicry in breast cancer cells. Front
Oncol. 12:9183402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Kalkunte S, Brard L, Granai CO and Swamy
N: Inhibition of angiogenesis by vitamin D-binding protein:
Characterization of anti-endothelial activity of DBP-maf.
Angiogenesis. 8:349–360. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Liu W, Zhang L, Xu HJ, Li Y, Hu CM, Yang
JY and Sun MY: The anti-inflammatory effects of vitamin D in
tumorigenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 19:27362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
El-Sharkawy A and Malki A: Vitamin D
signaling in inflammation and cancer: Molecular mechanisms and
therapeutic implications. Molecules. 25:32192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Liu J, Shen J, Mu C, Liu Y, He D, Luo H,
Wu W, Zheng X, Liu Y, Chen S, et al: High-dose vitamin D metabolite
delivery inhibits breast cancer metastasis. Bioeng Transl Med.
7:e102632021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Zhuravel E, Efanova O, Shestakova T,
Glushko N, Mezhuev O, Soldatkina M and Pogrebnoy P: Administration
of vitamin D3 improves antimetastatic efficacy of cancer vaccine
therapy of Lewis lung carcinoma. Exp Oncol. 32:33–39.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Zmijewski MA: Vitamin D and human health.
Int J Mol Sci. 20:1452019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Hii CS and Ferrante A: The non-genomic
actions of vitamin D. Nutrients. 8:1352016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Levin ER: Rapid signaling by steroid
receptors. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 295:R1425–R1430.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Doroudi M, Schwartz Z and Boyan BD:
Membrane-mediated actions of 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3: A review of
the roles of phospholipase A2 activating protein and
Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Steroid Biochem
Mol Biol. 147:81–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
186
|
Sirajudeen S, Shah I and Al Menhali A: A
Narrative role of vitamin d and its receptor: With current evidence
on the gastric tissues. Int J Mol Sci. 20:38322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Lajdova I, Spustova V, Oksa A, Kaderjakova
Z, Chorvat D Jr, Morvova M Jr, Sikurova L and Marcek Chorvatova A:
The impact of vitamin D3 supplementation on mechanisms of cell
calcium signaling in chronic kidney disease. Biomed Res Int.
2015:8076732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Sergeev IN: Calcium signaling in cancer
and vitamin D. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 97:145–151. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Norman AW: Minireview: Vitamin D receptor:
New assignments for an already busy receptor. Endocrinology.
147:5542–5548. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Mantell DJ, Owens PE, Bundred NJ, Mawer EB
and Canfield AE: 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) inhibits
angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Circ Res. 87:214–220. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Jamali N, Sorenson CM and Sheibani N:
Vitamin D and regulation of vascular cell function. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 314:H753–H765. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Wu X, Hu W, Lu L, Zhao Y, Zhou Y, Xiao Z,
Zhang L, Zhang H, Li X, Li W, et al: Repurposing vitamin D for
treatment of human malignancies via targeting tumor
microenvironment. Acta Pharm Sin B. 9:203–219. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Santos JM, Khan ZS, Munir MT, Tarafdar K,
Rahman SM and Hussain F: Vitamin D3 decreases glycolysis
and invasiveness, and increases cellular stiffness in breast cancer
cells. J Nutr Biochem. 53:111–120. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
194
|
Corachán A, Ferrero H, Escrig J, Monleon
J, Faus A, Cervelló I and Pellicer A: Long-term vitamin D treatment
decreases human uterine leiomyoma size in a xenograft animal model.
Fertil Steril. 113:205–216.e4. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
195
|
Karkeni E, Morin SO, Bou Tayeh B, Goubard
A, Josselin E, Castellano R, Fauriat C, Guittard G, Olive D and
Nunès JA: Vitamin D controls tumor growth and CD8+ T cell
infiltration in breast cancer. Front Immunol. 10:13072019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Veeresh PKM, Basavaraju CG, Dallavalasa S,
Anantharaju PG, Natraj SM, Sukocheva OA and Madhunapantula SV:
Vitamin D3 inhibits the viability of breast cancer cells in vitro
and ehrlich ascites carcinomas in mice by promoting apoptosis and
cell cycle arrest and by impeding tumor angiogenesis. Cancers
(Basel). 15:48332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Welsh J: Vitamin D and breast cancer:
Insights from animal models. Am J Clin Nutr. 80(Suppl 6):
1721S–1724S. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Li J, Luco AL, Camirand A, St-Arnaud R and
Kremer R: Vitamin D regulates CXCL12/CXCR4 and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in a model of breast cancer
metastasis to lung. Endocrinology. 162:bqab0492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Reid C, Flores-Villalva S, Remot A,
Kennedy E, O'Farrelly C and Meade KG: Long-term in vivo vitamin
D3 supplementation modulates bovine IL-1 and chemokine
responses. Sci Rep. 13:108462023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
200
|
Muñoz A and Grant WB: Vitamin D and
cancer: An historical overview of the epidemiology and mechanisms.
Nutrients. 14:14482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Chandler PD, Chen WY, Ajala ON, Hazra A,
Cook N, Bubes V, Lee IM, Giovannucci EL, Willett W, Buring JE, et
al: Effect of vitamin D3 supplements on development of advanced
cancer: A secondary analysis of the VITAL randomized clinical
trial. JAMA Netw Open. 3:e20258502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Keum N, Lee DH, Greenwood DC, Manson JE
and Giovannucci E: Vitamin D supplementation and total cancer
incidence and mortality: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled
trials. Ann Oncol. 30:733–743. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Talib WH, Ahmed Jum'AH DA, Attallah ZS,
Jallad MS, Al Kury LT, Hadi RW and Mahmod AI: Role of vitamins A,
C, D, E in cancer prevention and therapy: Therapeutic potentials
and mechanisms of action. Front Nutr. 10:12818792024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
El-Bassiouny NA, Helmy MW, Hassan MAE and
Khedr GA: The Cardioprotective effect of vitamin D in breast cancer
patients receiving adjuvant doxorubicin based chemotherapy. Clin
Breast Cancer. 22:359–366. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Galus Ł, Michalak M, Lorenz M,
Stoińska-Swiniarek R, Tusień Małecka D, Galus A, Kolenda T,
Leporowska E and Mackiewicz J: Vitamin D supplementation increases
objective response rate and prolongs progression-free time in
patients with advanced melanoma undergoing anti-PD-1 therapy.
Cancer. 129:2047–2055. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Yu X, Liu B, Zhang N, Wang Q and Cheng G:
Immune response: A missed opportunity between vitamin D and
radiotherapy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:6469812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Arayici ME, Basbinar Y and Ellidokuz H:
Vitamin D intake, serum 25-hydroxyvitamin-D (25(OH)D) levels, and
cancer risk: A comprehensive meta-meta-analysis including
meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials and observational
epidemiological studies. Nutrients. 15:27222023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Krasanakis T, Nikolouzakis TK, Sgantzos M,
Mariolis-Sapsakos T, Souglakos J, Spandidos DA, Tsitsimpikou C,
Tsatsakis A and Tsiaoussis J: Role of anabolic agents in colorectal
carcinogenesis: Myths and realities (Review). Oncol Rep.
42:2228–2244. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Dimitrakopoulou VI, Tsilidis KK, Haycock
PC, Dimou NL, Al-Dabhani K, Martin RM, Lewis SJ, Gunter MJ, Mondul
A, Shui IM, et al: Circulating vitamin D concentration and risk of
seven cancers: Mendelian randomisation study. BMJ. 359:j47612017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Young MRI and Xiong Y: Influence of
vitamin D on cancer risk and treatment: Why the variability? Trends
Cancer Res. 13:43–53. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Mocayar Marón FJ, Ferder L, Reiter RJ and
Manucha W: Daily and seasonal mitochondrial protection: Unraveling
common possible mechanisms involving vitamin D and melatonin. J
Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 199:1055952020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Vitti-Ruela BV, Dokkedal-Silva V, Hachul
H, Tufik S and Andersen ML: Melatonin and vitamin D: Complementary
therapeutic strategies for breast cancer. Support Care Cancer.
29:3433–3434. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Bizzarri M, Cucina A, Valente MG,
Tagliaferri F, Borrelli V, Stipa F and Cavallaro A: Melatonin and
vitamin D3 increase TGF-beta1 release and induce growth inhibition
in breast cancer cell cultures. J Surg Res. 110:332–337. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Proietti S, Cucina A, D'Anselmi F,
Dinicola S, Pasqualato A, Lisi E and Bizzarri M: Melatonin and
vitamin D3 synergistically down-regulate Akt and MDM2 leading to
TGFβ-1-dependent growth inhibition of breast cancer cells. J Pineal
Res. 50:150–158. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
215
|
Wang H, Wei W, Wang NP, Gui SY, Wu L, Sun
WY and Xu SY: Melatonin ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced
hepatic fibrogenesis in rats via inhibition of oxidative stress.
Life Sci. 77:1902–1915. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Özerkan D, Özsoy N and Yılmaz E: Vitamin D
and melatonin protect the cell's viability and ameliorate the CCl4
induced cytotoxicity in HepG2 and Hep3B hepatoma cell lines.
Cytotechnology. 67:995–1002. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
217
|
Frenkel M, Abrams DI, Ladas EJ, Deng G,
Hardy M, Capodice JL, Winegardner MF, Gubili JK, Yeung KS, Kussmann
H and Block KI: Integrating dietary supplements into cancer care.
Integr Cancer Ther. 12:369–384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Nuszkiewicz J, Czuczejko J, Maruszak M,
Pawłowska M, Woźniak A, Małkowski B and Szewczyk-Golec K:
Parameters of oxidative stress, vitamin D, osteopontin, and
melatonin in patients with lip, oral cavity, and pharyngeal cancer.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021:23649312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Rai V, Bose S, Saha S and Chakraborty C:
Evaluation of oxidative stress and the microenvironment in oral
submucous fibrosis. Heliyon. 5:e015022019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Di Bella G: The Di Bella Method (DBM)
improved survival, objective response and performance status in a
retrospective observational clinical study on 122 cases of breast
cancer. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 32:751–762. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Di Bella G and Colori B: The Di Bella
Method (DBM) improved survival, objective response and performance
status in a retrospective observational clinical study on 23
tumours of the head and neck. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 33:249–256.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Di Bella G, Borghetto V and Costanzo E: A
retrospective observational study on cases of anaplastic brain
tumors treated with the Di Bella Method: A rationale and
effectiveness. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 42:464–483. 2021.
|
|
223
|
Di Bella G, Di Bella L, Borghetto V,
Moscato I and Costanzo E: A retrospective observational study on
cases of osteosarcomas treated with a multitherapy: The rationale
and effectiveness. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 43:173–179.
2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Norsa A and Martino V: Somatostatin,
retinoids, melatonin, vitamin D, bromocriptine, and
cyclophosphamide in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients
with low performance status. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 21:68–73.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Norsa A and Martino V: Somatostatin,
retinoids, melatonin, vitamin D, bromocriptine, and
cyclophosphamide in chemotherapy-pretreated patients with advanced
lung adenocarcinoma and low performance status. Cancer Biother
Radiopharm. 22:50–55. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Nuszkiewicz J, Woźniak A and
Szewczyk-Golec K: Ionizing radiation as a source of oxidative
stress-the protective role of melatonin and vitamin D. Int J Mol
Sci. 21:58042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Minich DM, Henning M, Darley C, Fahoum M,
Schuler CB and Frame J: Is Melatonin the 'Next vitamin D'?: A
review of emerging science, clinical uses, safety, and dietary
supplements. Nutrients. 14:39342022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
228
|
Smolensky MH, Sackett-Lundeen LL and
Portaluppi F: Nocturnal light pollution and underexposure to
daytime sunlight: Complementary mechanisms of circadian disruption
and related diseases. Chronobiol Int. 32:1029–1048. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Besedovsky L, Lange T and Haack M: The
sleep-immune crosstalk in health and disease. Physiol Rev.
99:1325–1380. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|