|
1
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer: Global Cancer Observatory. Cancer Today. Accessed on
September 22, 2024https://gco.iarc.fr/today/online-analysis-multi-bars.
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Arnold M, Morgan E, Rumgay H, Mafra A,
Singh D, Laversanne M, Vignat J, Gralow JR, Cardoso F, Siesling S
and Soerjomataram I: Current and future burden of breast cancer:
Global statistics for 2020 and 2040. Breast. 66:15–23. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee MS, 'Azmiyaty Amar Ma' Ruf C, Nadhirah
Izhar DP, Nafisah Ishak S, Wan Jamaluddin WS, Ya'acob SNM and
Kamaluddin MN: Awareness on breast cancer screening in Malaysia: A
cross sectional study. Biomedicine (Taipei). 9:182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Momenimovahed Z and Salehiniya H:
Epidemiological characteristics of and risk factors for breast
cancer in the world. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 11:151–164.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
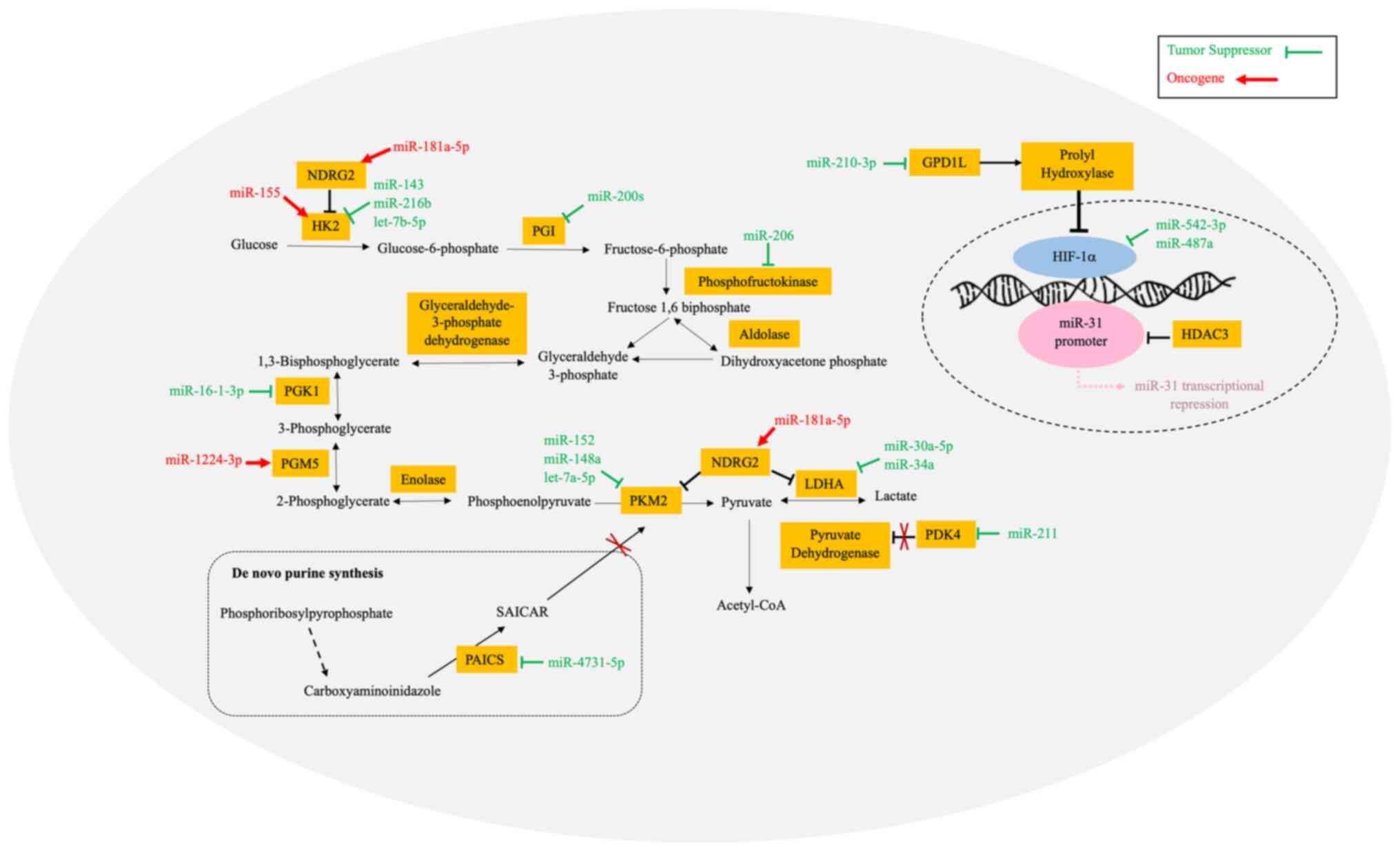
Malhotra GK, Zhao X, Band H and Band V:
Histological, molecular and functional subtypes of breast cancers.
Cancer Biol Ther. 10:955–960. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Watkins EJ: Overview of breast cancer.
JAAPA. 32:13–17. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Posner MC and Wolmark N: Non-invasive
breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 21:155–164. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Corben AD: Pathology of invasive breast
disease. Surg Clin North Am. 93:363–392. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sharma GN, Dave R, Sanadya J, Sharma P and
Sharma KK: Various types and management of breast cancer: An
overview. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 1:109–126. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yip CH and Rhodes A: Estrogen and
progesterone receptors in breast cancer. Future Oncol.
10:2293–2301. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iqbal N and Iqbal N: Human epidermal
growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) in cancers: Overexpression and
therapeutic implications. Mol Biol Int. 2014:8527482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Derakhshan F and Reis-Filho JS:
Pathogenesis of triple-negative breast cancer. Annu Rev Pathol.
17:181–204. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan J and Le A: The heterogeneity of
breast cancer metabolism. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1311:89–101. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ahn S, Woo JW, Lee K and Park SY: HER2
status in breast cancer: Changes in guidelines and complicating
factors for interpretation. J Pathol Transl Med. 54:34–44. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hanahan D: Hallmarks of cancer: New
dimensions. Cancer Discov. 12:31–46. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Serrano-Carbajal EA, Espinal-Enríquez J
and Hernández-Lemus E: Targeting metabolic deregulation landscapes
in breast cancer subtypes. Front Oncol. 10:972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
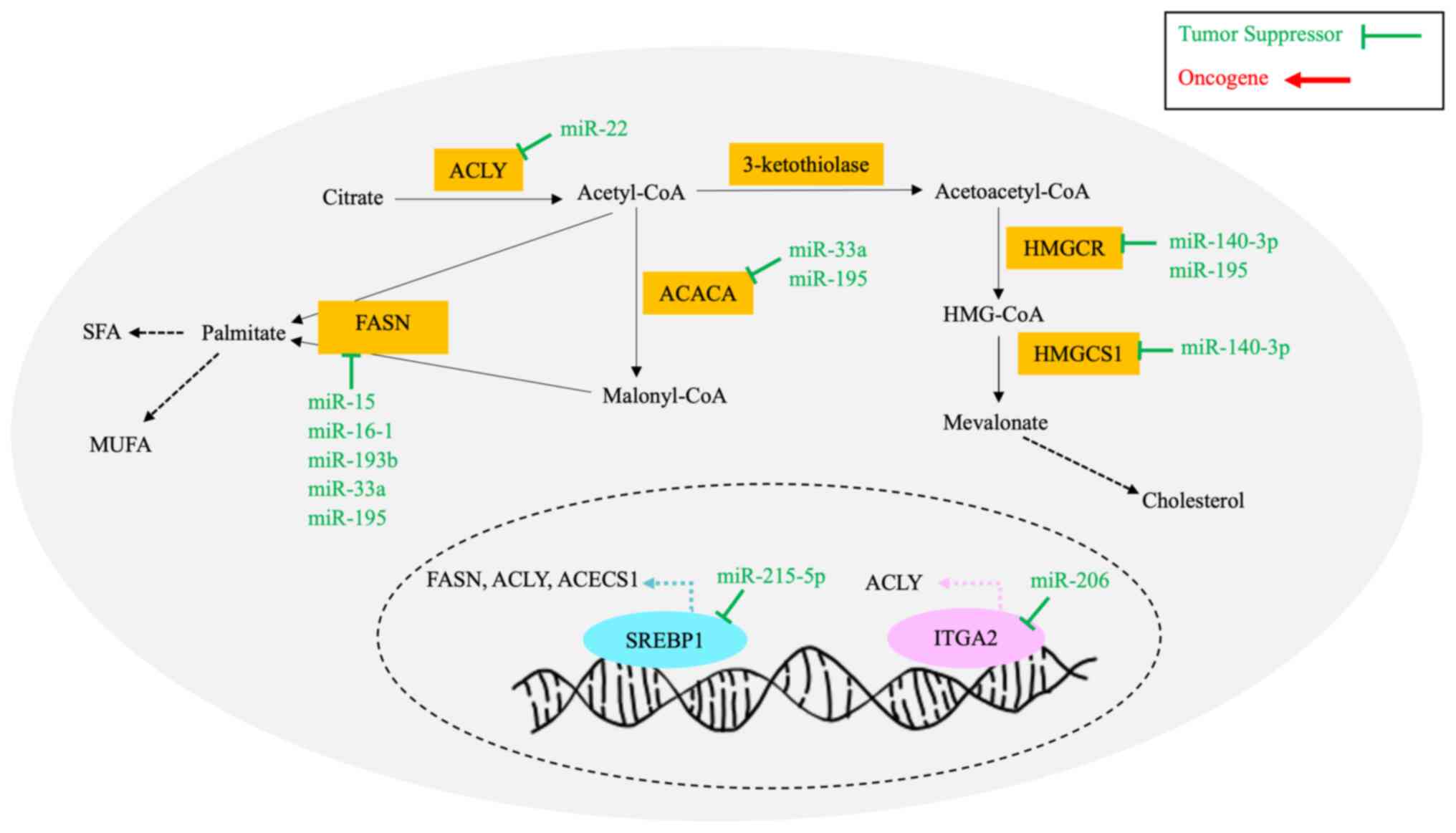
|
Wang L, Zhang S and Wang X: The metabolic
mechanisms of breast cancer metastasis. Front Oncol. 10:6024162021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chan B, Manley J, Lee J and Singh SR: The
emerging roles of microRNAs in cancer metabolism. Cancer Lett.
356:301–308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: Causes and
consequences of microRNA dysregulation. Cancer J. 18:215–222. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Muñoz JP, Pérez-Moreno P, Pérez Y and
Calaf GM: The role of MicroRNAs in breast cancer and the challenges
of their clinical application. Diagnostics (Basel). 13:30722023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Suriya Muthukumaran N, Velusamy P, Akino
Mercy CS, Langford D, Natarajaseenivasan K and Shanmughapriya S:
MicroRNAs as regulators of cancer cell energy metabolism. J Pers
Med. 12:13292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR,
Soleymani Fard S and Ghaffari SH: An overview of microRNAs:
Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell
Physiol. 234:5451–5465. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Diener C, Keller A and Meese E: The
miRNA-target interactions: An underestimated intricacy. Nucleic
Acids Res. 52:1544–1557. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu L, He J, Wei X, Wan G, Lao Y, Xu W, Li
Z, Hu H, Hu Z, Luo X, et al: MicroRNA-20a-mediated loss of
autophagy contributes to breast tumorigenesis by promoting genomic
damage and instability. Oncogene. 36:5874–5884. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ma F, Li W, Liu C, Li W, Yu H, Lei B, Ren
Y, Li Z, Pang D and Qian C: MiR-23a promotes TGF-β1-induced EMT and
tumor metastasis in breast cancer cells by directly targeting CDH1
and activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncotarget. 8:69538–69550.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gao F and Tian J: FOXK1, regulated by
miR-365-3p, promotes cell growth and EMT indicates unfavorable
prognosis in breast cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 13:623–634. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ali Syeda Z, Langden SSS, Munkhzul C, Lee
M and Song SJ: Regulatory mechanism of MicroRNA expression in
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21:17232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nakrani MN, Wineland RH and Anjum F:
Physiology, glucose metabolism. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls
Publishing; Treasure Island, FL: 2023
|
|
31
|
Paredes-Flores MA and Mohiuddin SS:
Biochemistry, glycogenolysis. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls
Publishing; Treasure Island, FL: 2022
|
|
32
|
Patino SC and Orrick JA: Biochemistry,
glycogenesis. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing;
Treasure Island, FL: 2023
|
|
33
|
Dunn J and Grider MH: Physiology,
adenosine triphosphate. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls
Publishing; Treasure Island, FL: 2023
|
|
34
|
Pavlova NN, Zhu J and Thompson CB: The
hallmarks of cancer metabolism: Still emerging. Cell Metab.
34:355–377. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Warburg O: On the origin of cancer cells.
Science. 123:309–314. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liberti MV and Locasale JW: The warburg
effect: How does it benefit cancer cells? Trends Biochem Sci.
41:211–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pascale RM, Calvisi DF, Simile MM, Feo CF
and Feo F: The Warburg effect 97 years after its discovery. Cancers
(Basel). 12:28192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu L, Chen X, Wang L and Chen S: The sweet
trap in tumors: Aerobic glycolysis and potential targets for
therapy. Oncotarget. 7:38908–38926. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nong S, Han X, Xiang Y, Qian Y, Wei Y,
Zhang T, Tian K, Shen K, Yang J and Ma X: Metabolic reprogramming
in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutics. MedComm (2020). 4:e2182023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNA
dysregulation in cancer: Diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics.
A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med. 4:143–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chaudhry R and Varacallo M: Biochemistry,
glycolysis. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure
Island, FL: 2023
|
|
42
|
Lenzen S: A fresh view of glycolysis and
glucokinase regulation: History and current status. J Biol Chem.
289:12189–12194. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Roberts DJ and Miyamoto S: Hexokinase II
integrates energy metabolism and cellular protection: Akting on
mitochondria and TORCing to autophagy. Cell Death Differ.
22:248–257. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Jiang S, Zhang LF, Zhang HW, Hu S, Lu MH,
Liang S, Li B, Li Y, Li D, Wang ED and Liu MF: A novel
miR-155/miR-143 cascade controls glycolysis by regulating
hexokinase 2 in breast cancer cells. EMBO J. 31:1985–1998. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu T, Ye P, Ye Y and Han B: MicroRNA-216b
targets HK2 to potentiate autophagy and apoptosis of breast cancer
cells via the mTOR signaling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 17:2970–2983.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li L, Zhang X, Lin Y, Ren X, Xie T, Lin J,
Wu S and Ye Q: Let-7b-5p inhibits breast cancer cell growth and
metastasis via repression of hexokinase 2-mediated aerobic
glycolysis. Cell Death Discov. 9:1142023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li L, Peng G, Liu X, Zhang Y, Han H and
Liu ZR: Pyruvate kinase M2 coordinates metabolism switch between
glycolysis and glutaminolysis in cancer cells. iScience.
23:1016842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hsu MC and Hung WC: Pyruvate kinase M2
fuels multiple aspects of cancer cells: From cellular metabolism,
transcriptional regulation to extracellular signaling. Mol Cancer.
17:352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Park B, Kim JY, Riffey OF, Dowker-Key P,
Bruckbauer A, McLoughlin J, Bettaieb A and Donohoe DR: Pyruvate
kinase M1 regulates butyrate metabolism in cancerous colonocytes.
Sci Rep. 12:87712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Schormann N, Hayden KL, Lee P, Banerjee S
and Chattopadhyay D: An overview of structure, function, and
regulation of pyruvate kinases. Protein Sci. 28:1771–1784. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Amin S, Yang P and Li Z: Pyruvate kinase
M2: A multifarious enzyme in non-canonical localization to promote
cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1871:331–341.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Israelsen WJ and Vander Heiden MG:
Pyruvate kinase: Function, regulation and role in cancer. Semin
Cell Dev Biol. 43:43–51. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wen YY, Liu WT, Sun HR, Ge X, Shi ZM, Wang
M, Li W, Zhang JY, Liu LZ and Jiang BH: IGF-1-mediated
PKM2/β-catenin/miR-152 regulatory circuit in breast cancer. Sci
Rep. 7:158972017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Xu Q, Liu LZ, Yin Y, He J, Li Q, Qian X,
You Y, Lu Z, Peiper SC, Shu Y and Jiang BH: Regulatory circuit of
PKM2/NF-κB/miR-148a/152-modulated tumor angiogenesis and cancer
progression. Oncogene. 34:5482–5493. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yao A, Xiang Y, Si YR, Fan LJ, Li JP, Li
H, Guo W, He HX, Liang XJ, Tan Y, et al: PKM2 promotes glucose
metabolism through a let-7a-5p/Stat3/hnRNP-A1 regulatory feedback
loop in breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 120:6542–6554. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Chen Y, Cen L, Guo R, Huang S and Chen D:
Roles and mechanisms of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 in cancer. Bull
Cancer. 109:1298–1307. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ye T, Liang Y, Zhang D and Zhang X:
MicroRNA-16-1-3p represses breast tumor growth and metastasis by
inhibiting PGK1-mediated warburg effect. Front Cell Dev Biol.
8:6151542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ran F, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Liu J, Li H, Ding L
and Ye Q: miR-1224-3p promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and
migration through PGM5-mediated aerobic glycolysis. J Oncol.
2021:55297702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li L, Kang L, Zhao W, Feng Y, Liu W, Wang
T, Mai H, Huang J, Chen S, Liang Y, et al: miR-30a-5p suppresses
breast tumor growth and metastasis through inhibition of
LDHA-mediated Warburg effect. Cancer Lett. 400:89–98. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Xiao X, Huang X, Ye F, Chen B, Song C, Wen
J, Zhang Z, Zheng G, Tang H and Xie X: The miR-34a-LDHA axis
regulates glucose metabolism and tumor growth in breast cancer. Sci
Rep. 6:217352016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ge X, Lyu P, Cao Z, Li J, Guo G, Xia W and
Gu Y: Overexpression of miR-206 suppresses glycolysis,
proliferation and migration in breast cancer cells via PFKFB3
targeting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 463:1115–1121. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Telang S, Yalcin A, Clem AL, Bucala R,
Lane AN, Eaton JW and Chesney J: Ras transformation requires
metabolic control by 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase. Oncogene.
25:7225–7234. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kim JW and Dang CV: Multifaceted roles of
glycolytic enzymes. Trends Biochem Sci. 30:142–150. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ahmad A, Aboukameel A, Kong D, Wang Z,
Sethi S, Chen W, Sarkar FH and Raz A: Phosphoglucose
isomerase/autocrine motility factor mediates epithelial-mesenchymal
transition regulated by miR-200 in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
71:3400–3409. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Guda MR, Asuthkar S, Labak CM, Tsung AJ,
Alexandrov I, Mackenzie MJ, Prasad DV and Velpula KK: Targeting
PDK4 inhibits breast cancer metabolism. Am J Cancer Res.
8:1725–1738. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lu H, Forbes RA and Verma A:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation by aerobic glycolysis
implicates the Warburg effect in carcinogenesis. J Biol Chem.
277:23111–23115. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhai Z, Mu T, Zhao L, Li Y, Zhu D and Pan
Y: MiR-181a-5p facilitates proliferation, invasion, and glycolysis
of breast cancer through NDRG2-mediated activation of PTEN/AKT
pathway. Bioengineered. 13:83–95. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
68
|
Lang L, Tao J, Yang C and Li W: Tumor
suppressive role of microRNA-4731-5p in breast cancer through
reduction of PAICS-induced FAK phosphorylation. Cell Death Discov.
8:1542022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ziello JE, Jovin IS and Huang Y:
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-1 regulatory pathway and its
potential for therapeutic intervention in malignancy and ischemia.
Yale J Biol Med. 80:51–60. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1: Upstream and downstream
of cancer metabolism. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 20:51–56. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
71
|
Du Y, Wei N, Ma R, Jiang SH and Song D: A
miR-210-3p regulon that controls the Warburg effect by modulating
HIF-1α and p53 activity in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell
Death Dis. 11:7312020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Jiang Y, Zhang M, Yu D, Hou G, Wu J and Li
F: CircRBM33 downregulation inhibits hypoxia-induced glycolysis and
promotes apoptosis of breast cancer cells via a
microRNA-542-3p/HIF-1α axis. Cell Death Discov. 8:1262022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Cao L, Wang M, Dong Y, Xu B, Chen J, Ding
Y, Qiu S, Li L, Karamfilova Zaharieva E, Zhou X and Xu Y: Circular
RNA circRNF20 promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis and Warburg
effect through miR-487a/HIF-1α/HK2. Cell Death Dis. 11:1452020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Zhao Y, He J, Yang L, Luo Q and Liu Z:
Histone deacetylase-3 modification of MicroRNA-31 promotes cell
proliferation and aerobic glycolysis in breast cancer and is
predictive of poor prognosis. J Breast Cancer. 21:112–123. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kurmi K and Haigis MC: Nitrogen metabolism
in cancer and immunity. Trends Cell Biol. 30:408–424. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Wang S, Tsun ZY, Wolfson RL, Shen K, Wyant
GA, Plovanich ME, Yuan ED, Jones TD, Chantranupong L, Comb W, et
al: Metabolism. Lysosomal amino acid transporter SLC38A9 signals
arginine sufficiency to mTORC1. Science. 347:188–194. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Yeon A, You S, Kim M, Gupta A, Park MH,
Weisenberger DJ, Liang G and Kim J: Rewiring of cisplatin-resistant
bladder cancer cells through epigenetic regulation of genes
involved in amino acid metabolism. Theranostics. 8:4520–4534. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Gao M, Monian P, Quadri N, Ramasamy R and
Jiang X: Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Mol
Cell. 59:298–308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wei Z, Liu X, Cheng C, Yu W and Yi P:
Metabolism of amino acids in cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol.
8:6038372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yan W, Wu X, Zhou W, Fong MY, Cao M, Liu
J, Liu X, Chen CH, Fadare O, Pizzo DP, et al: Cancer-cell-secreted
exosomal miR-105 promotes tumour growth through the MYC-dependent
metabolic reprogramming of stromal cells. Nat Cell Biol.
20:597–609. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Cruzat V, Macedo Rogero M, Noel Keane K,
Curi R and Newsholme P: Glutamine: Metabolism and immune function,
supplementation and clinical translation. Nutrients. 10:15642018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Choi YK and Park KG: Targeting glutamine
metabolism for cancer treatment. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 26:19–28.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Wise DR and Thompson CB: Glutamine
addiction: A new therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci.
35:427–433. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Jin J, Byun JK, Choi YK and Park KG:
Targeting glutamine metabolism as a therapeutic strategy for
cancer. Exp Mol Med. 55:706–715. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Jin L, Alesi GN and Kang S: Glutaminolysis
as a target for cancer therapy. Oncogene. 35:3619–3625. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Haikala HM, Marques E, Turunen M and
Klefström J: Myc requires RhoA/SRF to reprogram glutamine
metabolism. Small GTPases. 9:274–282. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
87
|
Budczies J, Pfitzner BM, Györffy B, Winzer
KJ, Radke C, Dietel M, Fiehn O and Denkert C: Glutamate enrichment
as new diagnostic opportunity in breast cancer. Int J Cancer.
136:1619–1628. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Herner A, Sauliunaite D, Michalski CW,
Erkan M, De Oliveira T, Abiatari I, Kong B, Esposito I, Friess H
and Kleeff J: Glutamate increases pancreatic cancer cell invasion
and migration via AMPA receptor activation and Kras-MAPK signaling.
Int J Cancer. 129:2349–2359. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Mukha A, Kahya U, Linge A, Chen O, Löck S,
Lukiyanchuk V, Richter S, Alves TC, Peitzsch M, Telychko V, et al:
GLS-driven glutamine catabolism contributes to prostate cancer
radiosensitivity by regulating the redox state, stemness and
ATG5-mediated autophagy. Theranostics. 11:7844–7868. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Xiong J, Wang N, Zhong HJ, Cui BW, Cheng
S, Sun R, Chen JY, Xu PP, Cai G, Wang L, et al: SLC1A1 mediated
glutamine addiction and contributed to natural killer T-cell
lymphoma progression with immunotherapeutic potential.
EBioMedicine. 72:1036142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Cluntun AA, Lukey MJ, Cerione RA and
Locasale JW: Glutamine metabolism in cancer: Understanding the
heterogeneity. Trends Cancer. 3:169–180. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
El Ansari R, McIntyre A, Craze ML, Ellis
IO, Rakha EA and Green AR: Altered glutamine metabolism in breast
cancer; subtype dependencies and alternative adaptations.
Histopathology. 72:183–190. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Lieu EL, Nguyen T, Rhyne S and Kim J:
Amino acids in cancer. Exp Mol Med. 52:15–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Kung HN, Marks JR and Chi JT: Glutamine
synthetase is a genetic determinant of cell type-specific glutamine
independence in breast epithelia. PLoS Genet. 7:e10022292011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Lampa M, Arlt H, He T, Ospina B, Reeves J,
Zhang B, Murtie J, Deng G, Barberis C, Hoffmann D, et al:
Glutaminase is essential for the growth of triple-negative breast
cancer cells with a deregulated glutamine metabolism pathway and
its suppression synergizes with mTOR inhibition. PLoS One.
12:e01850922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Thewes V, Simon R, Hlevnjak M, Schlotter
M, Schroeter P, Schmidt K, Wu Y, Anzeneder T, Wang W, Windisch P,
et al: The branched-chain amino acid transaminase 1 sustains growth
of antiestrogen-resistant and ERα-negative breast cancer. Oncogene.
36:4124–4134. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Craze ML, El-Ansari R, Aleskandarany MA,
Cheng KW, Alfarsi L, Masisi B, Diez-Rodriguez M, Nolan CC, Ellis
IO, Rakha EA and Green AR: Glutamate dehydrogenase (GLUD1)
expression in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 174:79–91.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Cao Y, Lin SH, Wang Y, Chin YE, Kang L and
Mi J: Glutamic pyruvate transaminase GPT2 promotes tumorigenesis of
breast cancer cells by activating sonic hedgehog signaling.
Theranostics. 7:3021–3033. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zhang L and Han J: Branched-chain amino
acid transaminase 1 (BCAT1) promotes the growth of breast cancer
cells through improving mTOR-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis and
function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 486:224–231. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Masisi BK, El Ansari R, Alfarsi L, Craze
ML, Jewa N, Oldfield A, Cheung H, Toss M, Rakha EA and Green AR:
The biological and clinical significance of glutaminase in luminal
breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 13:39632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Kandasamy P, Gyimesi G, Kanai Y and
Hediger MA: Amino acid transporters revisited: New views in health
and disease. Trends Biochem Sci. 43:752–789. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Yadav P, Sharma P, Sundaram S, Venkatraman
G, Bera AK and Karunagaran D: SLC7A11/xCT is a target of miR-5096
and its restoration partially rescues miR-5096-mediated ferroptosis
and anti-tumor effects in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
522:211–224. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Liu Y, Hu Y, Jiang Y, Bu J and Gu X:
Targeting ferroptosis, the achilles' heel of breast cancer: A
review. Front Pharmacol. 13:10361402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Liu XX, Li XJ, Zhang B, Liang YJ, Zhou CX,
Cao DX, He M, Chen GQ, He JR and Zhao Q: MicroRNA-26b is
underexpressed in human breast cancer and induces cell apoptosis by
targeting SLC7A11. FEBS Lett. 585:1363–1367. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Sun D, Li YC and Zhang XY: Lidocaine
promoted ferroptosis by targeting miR-382-5p/SLC7A11 axis in
ovarian and breast cancer. Front Pharmacol. 12:6812232021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Wang J, Yang K, Cao J and Li L: Knockdown
of circular RNA septin 9 inhibits the malignant progression of
breast cancer by reducing the expression of solute carrier family 1
member 5 in a microRNA-149-5p-dependent manner. Bioengineered.
12:10624–10637. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
van Geldermalsen M, Wang Q, Nagarajah R,
Marshall AD, Thoeng A, Gao D, Ritchie W, Feng Y, Bailey CG, Deng N,
et al: ASCT2/SLC1A5 controls glutamine uptake and tumour growth in
triple-negative basal-like breast cancer. Oncogene. 35:3201–3108.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
108
|
Kinslow CJ, Tang A, Chaudhary KR and Cheng
SK: Prevalence of estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) somatic mutations
in breast cancer. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 6:pkac0602022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Msheik ZS, Nassar FJ, Chamandi G, Itani
AR, Gadaleta E, Chalala C, Alwan N and Nasr RR: miR-126 decreases
proliferation and mammosphere formation of MCF-7 and predicts
prognosis of ER+ breast cancer. Diagnostics (Basel). 12:7452022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Yanagida O, Kanai Y, Chairoungdua A, Kim
DK, Segawa H, Nii T, Cha SH, Matsuo H, Fukushima J, Fukasawa Y, et
al: Human L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1): Characterization
of function and expression in tumor cell lines. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1514:291–302. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Saito Y and Soga T: Amino acid
transporters as emerging therapeutic targets in cancer. Cancer Sci.
112:2958–2965. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Li Y, Wang W, Wu X, Ling S, Ma Y and Huang
P: SLC7A5 serves as a prognostic factor of breast cancer and
promotes cell proliferation through activating AKT/mTORC1 signaling
pathway. Ann Transl Med. 9:8922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Kurozumi S, Kaira K, Matsumoto H, Kurosumi
M, Yokobori T, Kanai Y, Sekine C, Honda C, Katayama A, Furuya M, et
al: Association of L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) with the
immune system and prognosis in invasive breast cancer. Sci Rep.
12:27422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Törnroos R, Tina E and Göthlin Eremo A:
SLC7A5 is linked to increased expression of genes related to
proliferation and hypoxia in estrogen-receptor-positive breast
cancer. Oncol Rep. 47:172022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Bacci M, Lorito N, Ippolito L, Ramazzotti
M, Luti S, Romagnoli S, Parri M, Bianchini F, Cappellesso F, Virga
F, et al: Reprogramming of amino acid transporters to support
aspartate and glutamate dependency sustains endocrine resistance in
breast cancer. Cell Rep. 28:104–118.e8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Delgir S, Ilkhani K, Safi A, Rahmati Y,
Montazari V, Zaynali-Khasraghi Z, Seif F, Bastami M and Alivand MR:
The expression of miR-513c and miR-3163 was downregulated in tumor
tissues compared with normal adjacent tissue of patients with
breast cancer. BMC Med Genomics. 14:1802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Fong MY, Zhou W, Liu L, Alontaga AY,
Chandra M, Ashby J, Chow A, O'Connor STF, Li S, Chin R, et al:
Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in
premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nat Cell Biol.
17:183–194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Figueira I, Godinho-Pereira J, Galego S,
Maia J, Haskó J, Molnár K, Malhó R, Costa-Silva B, Wilhelm I,
Krizbai IA and Brito MA: MicroRNAs and extracellular vesicles as
distinctive biomarkers of precocious and advanced stages of breast
cancer brain metastases development. Int J Mol Sci. 22:52142021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Lu C, Zhao Y, Wang J, Shi W, Dong F, Xin
Y, Zhao X and Liu C: Breast cancer cell-derived extracellular
vesicles transfer miR-182-5p and promote breast carcinogenesis via
the CMTM7/EGFR/AKT axis. Mol Med. 27:782021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Yang M, Zhang Y, Li M, Liu X and Darvishi
M: The various role of microRNAs in breast cancer angiogenesis,
with a special focus on novel miRNA-based delivery strategies.
Cancer Cell Int. 23:242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Guo L, Kong D, Liu J, Zhan L, Luo L, Zheng
W, Zheng Q, Chen C and Sun S: Breast cancer heterogeneity and its
implication in personalized precision therapy. Exp Hematol Oncol.
12:32023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Muciño-Olmos EA, Vázquez-Jiménez A,
López-Esparza DE, Maldonado V, Valverde M and Resendis-Antonio O:
MicroRNAs regulate metabolic phenotypes during multicellular tumor
spheroids progression. Front Oncol. 10:5823962020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Fu Y, Zou T, Shen X, Nelson PJ, Li J, Wu
C, Yang J, Zheng Y, Bruns C, Zhao Y, et al: Lipid metabolism in
cancer progression and therapeutic strategies. MedComm (2020).
2:27–59. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Gyamfi D, Ofori Awuah E and Owusu S:
Chapter 2-lipid metabolism: An overview. Patel VB: The Molecular
Nutrition of Fats. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: pp. 17–32.
2019
|
|
125
|
Burdge GC and Calder PC: Introduction to
fatty acids and lipids. World Rev Nutr Diet. 112:1–16. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Zechner R, Zimmermann R, Eichmann TO,
Kohlwein SD, Haemmerle G, Lass A and Madeo F: FAT SIGNALS-lipases
and lipolysis in lipid metabolism and signaling. Cell Metab.
15:279–291. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Monaco ME: Fatty acid metabolism in breast
cancer subtypes. Oncotarget. 8:29487–29500. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Park JK, Coffey NJ, Limoges A and Le A:
The Heterogeneity of lipid metabolism in cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1063:33–55. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Vasseur S and Guillaumond F: Lipids in
cancer: A global view of the contribution of lipid pathways to
metastatic formation and treatment resistance. Oncogenesis.
11:462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Koundouros N and Poulogiannis G:
Reprogramming of fatty acid metabolism in cancer. Br J Cancer.
122:4–22. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
131
|
Menendez JA and Lupu R: Fatty acid
synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat
Rev Cancer. 7:763–777. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Alo' PL, Visca P, Marci A, Mangoni A,
Botti C and Di Tondo U: Expression of fatty acid synthase (FAS) as
a predictor of recurrence in stage I breast carcinoma patients.
Cancer. 77:474–482. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Chajès V, Cambot M, Moreau K, Lenoir GM
and Joulin V: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase alpha is essential to breast
cancer cell survival. Cancer Res. 66:5287–5294. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Mashima T, Seimiya H and Tsuruo T: De novo
fatty-acid synthesis and related pathways as molecular targets for
cancer therapy. Br J Cancer. 100:1369–1372. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Xu S, Chen T, Dong L, Li T, Xue H, Gao B,
Ding X, Wang H and Li H: Fatty acid synthase promotes breast cancer
metastasis by mediating changes in fatty acid metabolism. Oncol
Lett. 21:272021.
|
|
136
|
Wang J, Zhang X, Shi J, Cao P, Wan M,
Zhang Q, Wang Y, Kridel SJ, Liu W, Xu J, et al: Fatty acid synthase
is a primary target of MiR-15a and MiR-16-1 in breast cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:78566–78576. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Wahdan-Alaswad RS, Cochrane DR, Spoelstra
NS, Howe EN, Edgerton SM, Anderson SM, Thor AD and Richer JK:
Metformin-induced killing of triple-negative breast cancer cells is
mediated by reduction in fatty acid synthase via miRNA-193b. Horm
Cancer. 5:374–389. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Chen Y, Li K, Gong D, Zhang J, Li Q, Zhao
G and Lin P: ACLY: A biomarker of recurrence in breast cancer.
Pathol Res Pract. 216:1530762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Liu H, Huang X and Ye T: MiR-22
down-regulates the proto-oncogene ATP citrate lyase to inhibit the
growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Am J Transl Res.
10:659–669. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Adorno-Cruz V, Hoffmann AD, Liu X,
Dashzeveg NK, Taftaf R, Wray B, Keri RA and Liu H: ITGA2 promotes
expression of ACLY and CCND1 in enhancing breast cancer stemness
and metastasis. Genes Dis. 8:493–508. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Daniëls VW, Smans K, Royaux I, Chypre M,
Swinnen JV and Zaidi N: Cancer cells differentially activate and
thrive on de novo lipid synthesis pathways in a low-lipid
environment. PLoS One. 9:e1069132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Simeone P, Tacconi S, Longo S, Lanuti P,
Bravaccini S, Pirini F, Ravaioli S, Dini L and Giudetti AM:
Expanding roles of De Novo lipogenesis in breast cancer. Int J
Environ Res Public Health. 18:35752021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Singh R, Yadav V, Kumar S and Saini N:
MicroRNA-195 inhibits proliferation, invasion and metastasis in
breast cancer cells by targeting FASN, HMGCR, ACACA and CYP27B1.
Sci Rep. 5:174542015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Yang Z, Qin W, Chen Y, Yuan B, Song X,
Wang B, Shen F, Fu J and Wang H: Cholesterol inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis by promoting CD44
localization in lipid rafts. Cancer Lett. 429:66–77. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Yang YF, Jan YH, Liu YP, Yang CJ, Su CY,
Chang YC, Lai TC, Chiou J, Tsai HY, Lu J, et al: Squalene synthase
induces tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 enrichment in lipid rafts
to promote lung cancer metastasis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
190:675–687. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Vona R, Iessi E and Matarrese P: Role of
cholesterol and lipid rafts in cancer signaling: A promising
therapeutic opportunity? Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:6229082021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Bhardwaj A, Singh H, Trinidad CM,
Albarracin CT, Hunt KK and Bedrosian I: The isomiR-140-3p-regulated
mevalonic acid pathway as a potential target for prevention of
triple negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 20:1502018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
DeBose-Boyd RA and Ye J: SREBPs in lipid
metabolism, insulin signaling, and beyond. Trends Biochem Sci.
43:358–368. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Wu CL, Xu LL, Peng J and Zhang DH: Al-MPS
obstructs EMT in breast cancer by inhibiting lipid metabolism via
miR-215-5p/SREBP1. Endocrinology. 163:bqac0402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Zhao J, Xu L, Sun J, Song M, Wang L, Yuan
S, Zhu Y, Wan Z, Larsson S, Tsilidis K, et al: Global trends in
incidence, death, burden and risk factors of early-onset cancer
from 1990 to 2019. BMJ Oncol. 2:e0000492023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Ellsworth RE, Blackburn HL, Shriver CD,
Soon-Shiong P and Ellsworth DL: Molecular heterogeneity in breast
cancer: State of the science and implications for patient care.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 64:65–72. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Ho TQH, Bissell MCS, Kerlikowske K,
Hubbard RA, Sprague BL, Lee CI, Tice JA, Tosteson ANA and
Miglioretti DL: Cumulative probability of false-positive results
after 10 years of screening with digital breast tomosynthesis vs
digital mammography. JAMA Netw Open. 5:e2224402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
El Hachem Z, Zoghbi M and Hallit S:
Psychosocial consequences of false-positive results in screening
mammography. J Family Med Prim Care. 8:419–425. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Park S, Ahn S, Kim JY, Kim J, Han HJ,
Hwang D, Park J, Park HS, Park S, Kim GM, et al: Blood test for
breast cancer screening through the detection of tumor-associated
circulating transcripts. Int J Mol Sci. 23:91402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Gilson Sena IF, Fernandes LL, Lorandi LL,
Santana TV, Cintra L, Lima IF, Iwai LK, Kramer JM, Birbrair A and
Heller D: Identification of early biomarkers in saliva in
genetically engineered mouse model C(3)1-TAg of breast cancer. Sci
Rep. 12:115442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Giró Benet J, Seo M, Khine M, Gumà Padró
J, Pardo Martnez A and Kurdahi F: Breast cancer detection by
analyzing the volatile organic compound (VOC) signature in human
urine. Sci Rep. 12:148732022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Zhang L, Xiao H, Karlan S, Zhou H, Gross
J, Elashoff D, Akin D, Yan X, Chia D, Karlan B and Wong DT:
Discovery and preclinical validation of salivary transcriptomic and
proteomic biomarkers for the non-invasive detection of breast
cancer. PLoS One. 5:e155732010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Garrido-Palacios A, Rojas Carvajal AM,
Núñez-Negrillo AM, Cortés-Martín J, Sánchez-García JC and
Aguilar-Cordero MJ: MicroRNA dysregulation in early breast cancer
diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci.
24:82702023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Kashyap D and Kaur H: Cell-free miRNAs as
non-invasive biomarkers in breast cancer: Significance in early
diagnosis and metastasis prediction. Life Sci. 246:1174172020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Papadaki C, Stoupis G, Tsalikis L,
Monastirioti A, Papadaki M, Maliotis N, Stratigos M, Mastrostamatis
G, Mavroudis D and Agelaki S: Circulating miRNAs as a marker of
metastatic disease and prognostic factor in metastatic breast
cancer. Oncotarget. 10:966–981. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Chen X, Wang YW, Zhu WJ, Li Y, Liu L, Yin
G and Gao P: A 4-microRNA signature predicts lymph node metastasis
and prognosis in breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 76:122–132. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Gong C, Tan W, Chen K, You N, Zhu S, Liang
G, Xie X, Li Q, Zeng Y, Ouyang N, et al: Prognostic value of a
BCSC-associated MicroRNA signature in hormone receptor-positive
HER2-negative breast cancer. EBioMedicine. 11:199–209. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Fu Z, Wang L, Li S, Chen F, Au-Yeung KK
and Shi C: MicroRNA as an important target for anticancer drug
development. Front Pharmacol. 12:7363232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Chakrabortty A, Patton DJ, Smith BF and
Agarwal P: miRNAs: Potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets
for cancer. Genes (Basel). 14:13752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Hsieh TH, Hsu CY, Tsai CF, Long CY, Chai
CY, Hou MF, Lee JN, Wu DC, Wang SC and Tsai EM: miR-125a-5p is a
prognostic biomarker that targets HDAC4 to suppress breast
tumorigenesis. Oncotarget. 6:494–509. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
167
|
Søkilde R, Persson H, Ehinger A, Pirona
AC, Fernö M, Hegardt C, Larsson C, Loman N, Malmberg M, Rydén L, et
al: Refinement of breast cancer molecular classification by miRNA
expression profiles. BMC Genomics. 20:5032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Wang H, Tan Z, Hu H, Liu H, Wu T, Zheng C,
Wang X, Luo Z, Wang J, Liu S, et al: microRNA-21 promotes breast
cancer proliferation and metastasis by targeting LZTFL1. BMC
Cancer. 19:7382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Arisan ED, Rencuzogullari O,
Cieza-Borrella C, Miralles Arenas F, Dwek M, Lange S and
Uysal-Onganer P: MiR-21 is required for the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci.
22:15572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Wang J, Wang Q, Guan Y, Sun Y, Wang X,
Lively K, Wang Y, Luo M, Kim JA, Murphy E, et al: Breast cancer
cell-derived microRNA-155 suppresses tumor progression via
enhancing immune cell recruitment and antitumor function. J Clin
Invest. 132:e1572482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Xu W, Song C, Wang X, Li Y, Bai X, Liang
X, Wu J and Liu J: Downregulation of miR-155-5p enhances the
anti-tumor effect of cetuximab on triple-negative breast cancer
cells via inducing cell apoptosis and pyroptosis. Aging (Albany
NY). 13:228–240. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Schmidt DR, Patel R, Kirsch DG, Lewis CA,
Vander Heiden MG and Locasale JW: Metabolomics in cancer research
and emerging applications in clinical oncology. CA Cancer J Clin.
71:333–358. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Rossi C, Cicalini I, Cufaro MC, Consalvo
A, Upadhyaya P, Sala G, Antonucci I, Del Boccio P, Stuppia L and De
Laurenzi V: Breast cancer in the era of integrating 'Omics'
approaches. Oncogenesis. 11:172022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Danzi F, Pacchiana R, Mafficini A, Scupoli
MT, Scarpa A, Donadelli M and Fiore A: To metabolomics and beyond:
A technological portfolio to investigate cancer metabolism. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 8:1372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Fan S, Shahid M, Jin P, Asher A and Kim J:
Identification of metabolic alterations in breast cancer using mass
spectrometry-based metabolomic analysis. Metabolites. 10:1702020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Subramani R, Poudel S, Smith KD, Estrada A
and Lakshmanaswamy R: Metabolomics of breast cancer: A review.
Metabolites. 12:6432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Budczies J, Brockmöller SF, Müller BM,
Barupal DK, Richter-Ehrenstein C, Kleine-Tebbe A, Griffin JL,
Orešič M, Dietel M, Denkert C and Fiehn O: Comparative metabolomics
of estrogen receptor positive and estrogen receptor negative breast
cancer: Alterations in glutamine and beta-alanine metabolism. J
Proteomics. 94:279–288. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Amiri-Dashatan N, Yekta RF, Koushki M,
Arefi Oskouie A, Esfahani H, Taheri S and Kazemian E: Metabolomic
study of serum in patients with invasive ductal breast carcinoma
with LC-MS/MS approach. Int J Biol Markers. 37:349–359. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Shestakova KM, Moskaleva NE, Boldin AA,
Rezvanov PM, Shestopalov AV, Rumyantsev SA, Zlatnik EY, Novikova
IA, Sagakyants AB, Timofeeva SV, et al: Targeted metabolomic
profiling as a tool for diagnostics of patients with non-small-cell
lung cancer. Sci Rep. 13:110722023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Gold A, Choueiry F, Jin N, Mo X and Zhu J:
The application of metabolomics in recent colorectal cancer
studies: A state-of-the-art review. Cancers (Basel). 14:7252022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Nam M, Seo SS, Jung S, Jang SY, Lee J,
Kwon M, Khan I, Ryu DH, Kim MK and Hwang GS: Comparable plasma
lipid changes in patients with high-grade cervical intraepithelial
neoplasia and patients with cervical cancer. J Proteome Res.
20:740–750. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
182
|
Granit A, Mishra K, Barasch D,
Peretz-Yablonsky T, Eyal S and Kakhlon O: Metabolomic profiling of
triple negative breast cancer cells suggests that valproic acid can
enhance the anticancer effect of cisplatin. Front Cell Dev Biol.
10:10147982022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Xiao Y, Ma D, Yang YS, Yang F, Ding JH,
Gong Y, Jiang L, Ge LP, Wu SY, Yu Q, et al: Comprehensive
metabolomics expands precision medicine for triple-negative breast
cancer. Cell Res. 32:477–490. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Iyer A, Hamers AAJ and Pillai AB:
CyTOF® for the masses. Front Immunol. 13:8158282022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
185
|
Fogazzi V, Kapahnke M, Cataldo A,
Plantamura I, Tagliabue E, Di Cosimo S, Cosentino G and Iorio MV:
The role of MicroRNAs in HER2-positive breast cancer: Where we are
and future prospective. Cancers (Basel). 14:53262022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Cappelletti V, Iorio E, Miodini P,
Silvestri M, Dugo M and Daidone MG: Metabolic footprints and
molecular subtypes in breast cancer. Dis Markers. 2017:76878512017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|