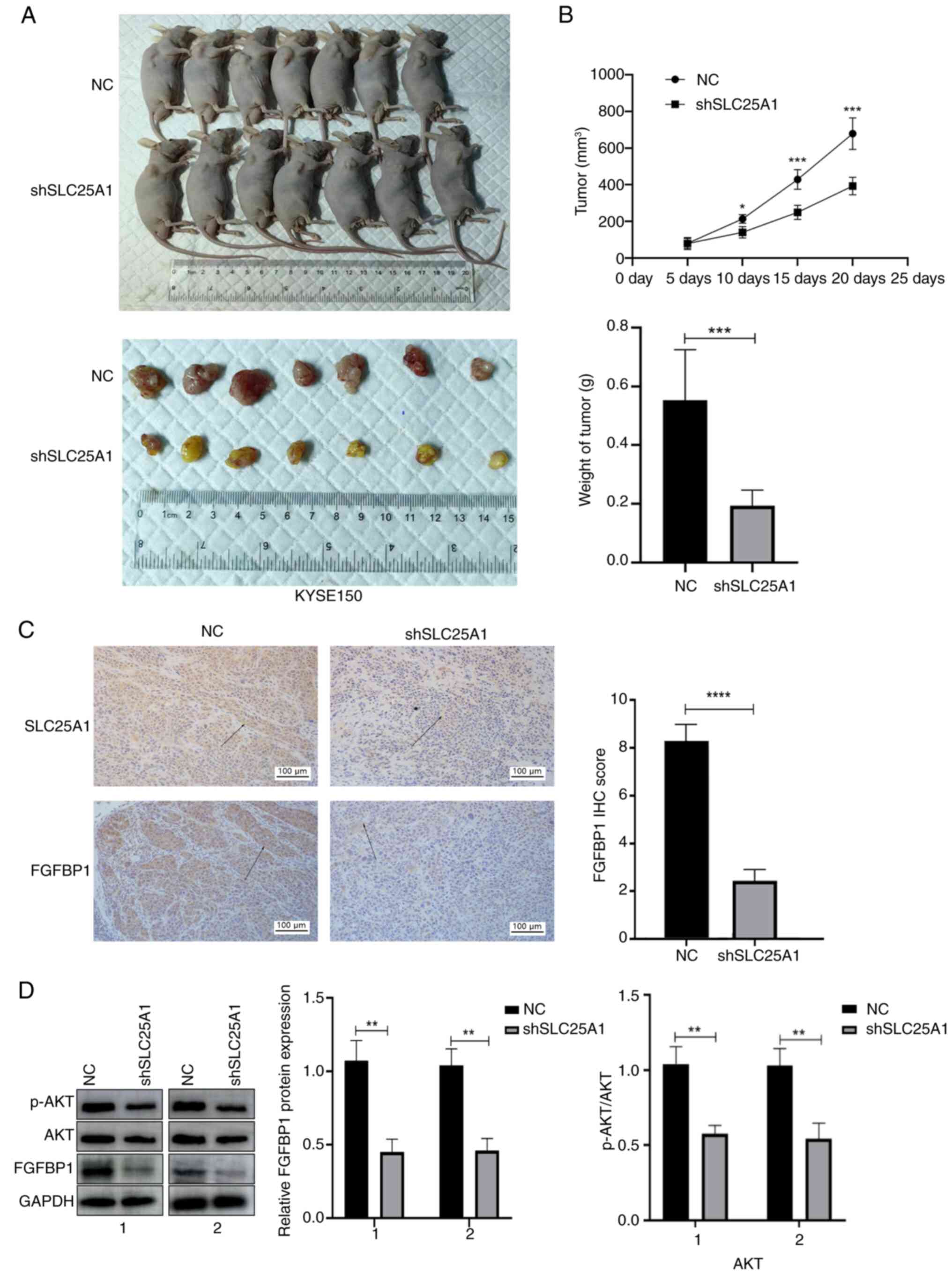
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
De Gouw DJJM, Klarenbeek BR, Driessen M,
Bouwense SAW, van Workum F, Fütterer JJ, Rovers MM, Ten Broek RPG
and Rosman C: Detecting pathological complete response in
esophageal cancer after neoadjuvant therapy based on imaging
techniques: A diagnostic systematic review and meta-analysis. J
Thorac Oncol. 14:1156–1171. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 72:7–33. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen K, Wang X, Yang L and Chen Z: The
Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy for gastric esophageal cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis and literature review. Cancer
Control. 28:10732748219974302021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun J, Aluvila S, Kotaria R, Mayor JA,
Walters DE and Kaplan RS: Mitochondrial and plasma membrane citrate
transporters: Discovery of selective inhibitors and application to
structure/function analysis. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 2:101–110.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rochette L, Meloux A, Zeller M, Malka G,
Cottin Y and Vergely C: Mitochondrial SLC25 carriers: Novel targets
for cancer therapy. Molecules. 25:24172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Palmieri F: The mitochondrial transporter
family SLC25: Identification, properties and physiopathology. Mol
Aspects Med. 34:465–484. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ma C, Gerhard E, Lu D and Yang J: Citrate
chemistry and biology for biomaterials design. Biomaterials.
178:383–400. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rohrig F and Schulze A: The multifaceted
roles of fatty acid synthesis in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
16:732–749. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pope ED III, Kimbrough EO, Vemireddy LP,
Surapaneni PK, Copland JA III and Mody K: Aberrant lipid metabolism
as a therapeutic target in liver cancer. Expert Opin therapeutic
targets. 23:473–483. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ding X, Zhang W, Li S and Yang H: The role
of cholesterol metabolism in cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 9:219–227.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kuzu OF, Noory MA and Robertson GP: The
role of cholesterol in cancer. Cancer Res. 76:2063–2070. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Beckwitt CH, Brufsky A, Oltvai ZN and
Wells A: Statin drugs to reduce breast cancer recurrence and
mortality 11. Breast Cancer Res. 20:1442018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu W, Chakraborty B, Safi R, Kazmin D,
Chang CY and McDonnell DP: Dysregulated cholesterol homeostasis
results in resistance to ferroptosis increasing tumorigenicity and
metastasis in cancer. Nat Commun. 12:51032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baek AE, Yu YA, He S, Wardell SE, Chang
CY, Kwon S, Pillai RV, McDowell HB, Thompson JW, Dubois LG, et al:
The cholesterol metabolite 27 hydroxycholesterol facilitates breast
cancer metastasis through its actions on immune cells. Nat Commun.
8:8642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou X, Huang F, Ma G, Wei W, Wu N and Liu
Z: Dysregulated ceramides metabolism by fatty acid 2-hydroxylase
exposes a metabolic vulnerability to target cancer metastasis.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:3702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fernandez HR, Gadre SM, Tan M, Graham GT,
Mosaoa R, Ongkeko MS, Kim KA, Riggins RB, Parasido E, Petrini I, et
al: The mitochondrial citrate carrier, SLC25A1, drives stemness and
therapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death
Differ. 25:1239–1258. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang Y, He J, Zhang B, Zhang Z, Jia G, Liu
S, Wu T, He X and Wang N: SLC25A1 promotes tumor growth and
survival by reprogramming energy metabolism in colorectal cancer.
Cell Death Dis. 12:11082021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li EC, Du P, Ji KZ and Wang Z: Chinese
ethics review system and Chinese medicine ethical review: past,
present, and future. Chin J Integr Med. 17:867–872. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
Clusterprofiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tomayko MM and Reynolds CP: Determination
of subcutaneous tumor size in athymic (nude) mice. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 24:148–154. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Z, Qin Y, Ji S, Xu W, Liu M, Hu Q,
Ye Z, Fan G, Yu X, Liu W and Xu X: FGFBP1-mediated crosstalk
between fibroblasts and pancreatic cancer cells via FGF22/FGFR2
promotes invasion and metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 53:997–1008. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li J, Xu J, Zheng Y, Gao Y, He S, Li H,
Zou K, Li N, Tian J, Chen W and He J: Esophageal cancer:
Epidemiology, risk factors and screening. Chin J Cancer Res.
33:535–547. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Merkow RP, Bilimoria KY, Keswani RN, Chung
J, Sherman KL, Knab LM, Posner MC and Bentrem DJ: Treatment trends,
risk of lymph node metastasis, and outcomes for localized
esophageal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106:dju1332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lagergren Jand Lagergren P: Oesophageal
cancer. BMJ. 341:c62802010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Harada K, Rogers JE, Iwatsuki M, Yamashita
K, Baba H and Ajani JA: Recent advances in treating oesophageal
cancer. F1000Res. 9:F1000Faculty Rev-1189. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Peng R, Zhang M, Wang H, Lin J, Wang H,
Wang F, Liu L, Zhao Q and Liu J: Advances into understanding the
vital role of the mitochondrial citrate carrier (CIC) in metabolic
diseases. Pharmacol Res. 161:1051322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Palmieri F and Monné M: Discoveries,
metabolic roles and diseases of mitochondrial carriers: A review.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:2362–2378. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tan M, Mosaoa R, Graham GT,
Kasprzyk-Pawelec A, Gadre S, Parasido E, Catalina-Rodriguez O,
Foley P, Giaccone G, Cheema A, et al: Inhibition of the
mitochondrial citrate carrier, Slc25a1, reverts steatosis, glucose
intolerance, and inflammation in preclinical models of NAFLD/NASH.
Cell Death Differ. 27:2143–2157. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang R, Peng X, Du JX, Boohaker R,
Estevao IL, Grajeda BI, Cox MB, Almeida IC and Lu W: Oncogenic
KRASG12D reprograms lipid metabolism by upregulating SLC25A1 to
drive pancreatic tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 83:3739–3752. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Morigny P, Boucher J, Arner P and Langin
D: Lipid and glucose metabolism in white adipocytes: Pathways,
dysfunction and therapeutics. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 17:276–295. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cheng C, Geng F, Cheng X and Guo D: Lipid
metabolism reprogramming and its potential targets in cancer.
Cancer Commun (Lond). 38:272018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Currie E, Schulze A, Zechner R, Walther TC
and Farese RV Jr: Cellular fatty acid metabolism and cancer. Cell
Metab. 18:153–161. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gouirand V, Guillaumond F and Vasseur S:
Influence of the tumor microenvironment on cancer cells metabolic
reprogramming. Front Oncol. 8:1172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Merino Salvador M, Gómez De Cedrón M,
Moreno Rubio J, Falagán Martínez S, Sánchez Martínez R, Casado E,
Ramírez de Molina A and Sereno M: Lipid metabolism and lung cancer.
Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 112:31–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Saikia S, Ahmed F, Prajapati BG, Padma VV,
Chorawala MR, Postwala HI and Bhattacharya S: Reprogramming of
lipid metabolism in cancer: New insight into pathogenesis and
therapeutic strategies. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 24:1847–1858. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Palmieri F, Scarcia P and Monné M:
Diseases caused by mutations in mitochondrial carrier genes SLC25:
A review. Biomolecules. 10:6552020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kunji S, King MS, Ruprecht JJ and
Thangaratnarajah C: The SLC25 carrier family: Important transport
proteins in mitochondrial physiology and pathology. Physiology
(Bethesda). 35:302–327. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Van Schaftingen E and Hers HG: Inhibition
of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by fructose 2,6-biphosphate. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 78:2861–2863. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jiang L, Shestov AA, Swain P, Yang C,
Parker SJ, Wang QA, Terada LS, Adams ND, McCabe MT, Pietrak B, et
al: Reductive carboxylation supports redox homeostasis during
anchorage-independent growth. Nat Cell Biol. 532:255–258. 2016.
|
|
45
|
Beer HD, Bittner M, Niklaus G, Munding C,
Max N, Goppelt A and Werner S: The fibroblast growth factor binding
protein is a novel interaction partner of FGF-7, FGF-10 and FGF-22
and regulates FGF activity: Implications for epithelial repair.
Oncogene. 24:5269–5277. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tassi E and Wellstein A: The angiogenic
switch molecule, secreted FGF-binding protein, an indicator of
early stages of pancreatic and colorectal adenocarcinoma. Semin
Oncol. 33(6 Suppl 11): S50–S56. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Taetzsch T, Brayman VL and Valdez G: FGF
binding proteins (FGFBPs): Modulators of FGF signaling in the
developing, adult, and stressed nervous system. Biochim Biophys
Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1864(9 Pt B): 2983–2991. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Abuharbeid S, Czubayko F and Aigner A: The
fibroblast growth factor-binding protein FGF-BP. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 38:1463–1468. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Tassi E, Henke RT, Bowden ET, Swift MR,
Kodack DP, Kuo AH, Maitra A and Wellstein A: Expression of a
fibroblast growth factor-binding protein during the development of
adenocarcinoma of the pancreas and colon. Cancer Res. 66:1191–1198.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rosli SN, Shintani T, Toratani S, Usui E
and Okamoto T: 1α,25 (OH)2D3 inhibits FGF-2
release from oral squamous cell carcinoma cells through
down-regulation of HBp17/FGFBP-1. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.
50:802–806. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Glaviano A, Foo ASC, Lam HY, Yap KCH,
Jacot W, Jones RH, Eng H, Nair MG, Makvandi P, Geoerger B, et al:
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies
in cancer. Mol Cancer. 22:1382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L,
Gulluni F and Hirsch E: PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: an
updated review. Ann Med. 46:372–383. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li B, Xu WW, Lam AKY, Wang Y, Hu HF, Guan
XY, Qin YR, Saremi N, Tsao SW, He QY and Cheung ALM: Significance
of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in metastasis of esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma and its potential as a target for anti-metastasis
therapy. Oncotarget. 8:38755–38766. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Koundouros N and Poulogiannis G:
Reprogramming of fatty acid metabolism in cancer. Br J Cancer.
122:4–22. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
55
|
Tian LY, Smit DJ and Jücker M: The role of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma metabolism. Int
J Mol Sci. 24:26522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu LZ, Wang B, Zhang R, Wu Z, Huang Y,
Zhang X, Zhou J, Yi J, Shen J, Li MY and Dong M: The activated
CD36-Src axis promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and
actin remodeling-involved metastasis in high-fat environment. Cell
Death Dis. 14:5482023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang D, Wei Y, Huang Q, Chen Y, Zeng K,
Yang W and Chen J and Chen J: Important hormones regulating lipid
metabolism. Molecules. 27:70522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bu L, Zhang Z, Chen J, Fan Y, Guo J, Su Y,
Wang H, Zhang X, Wu X, Jiang Q, et al: High-fat diet promotes liver
tumorigenesis via palmitoylation and activation of AKT. Gut.
73:1156–1168. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Xie Y, Su N, Yang J, Tan Q, Huang S, Jin
M, Ni Z, Zhang B, Zhang D, Luo F, et al: FGF/FGFR signaling in
health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:1812020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|