|
1
|
Janes SM, Alrifai D and Fennell DA:
Perspectives on the Treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma. N
Engl J Med. 385:1207–1218. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bridda A, Padoan I, Mencarelli R and Frego
M: Peritoneal mesothelioma: A review. MedGenMed.
9:322007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Attanoos RL and Gibbs AR: Pathology of
malignant mesothelioma. Histopathology. 30:403–418. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Scherpereel A, Opitz I, Berghmans T,
Psallidas I, Glatzer M, Rigau D, Astoul P, Bölükbas S, Boyd J,
Coolen J, et al: ERS/ESTS/EACTS/ESTRO guidelines for the management
of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Eur Respir J. 55:19009532020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
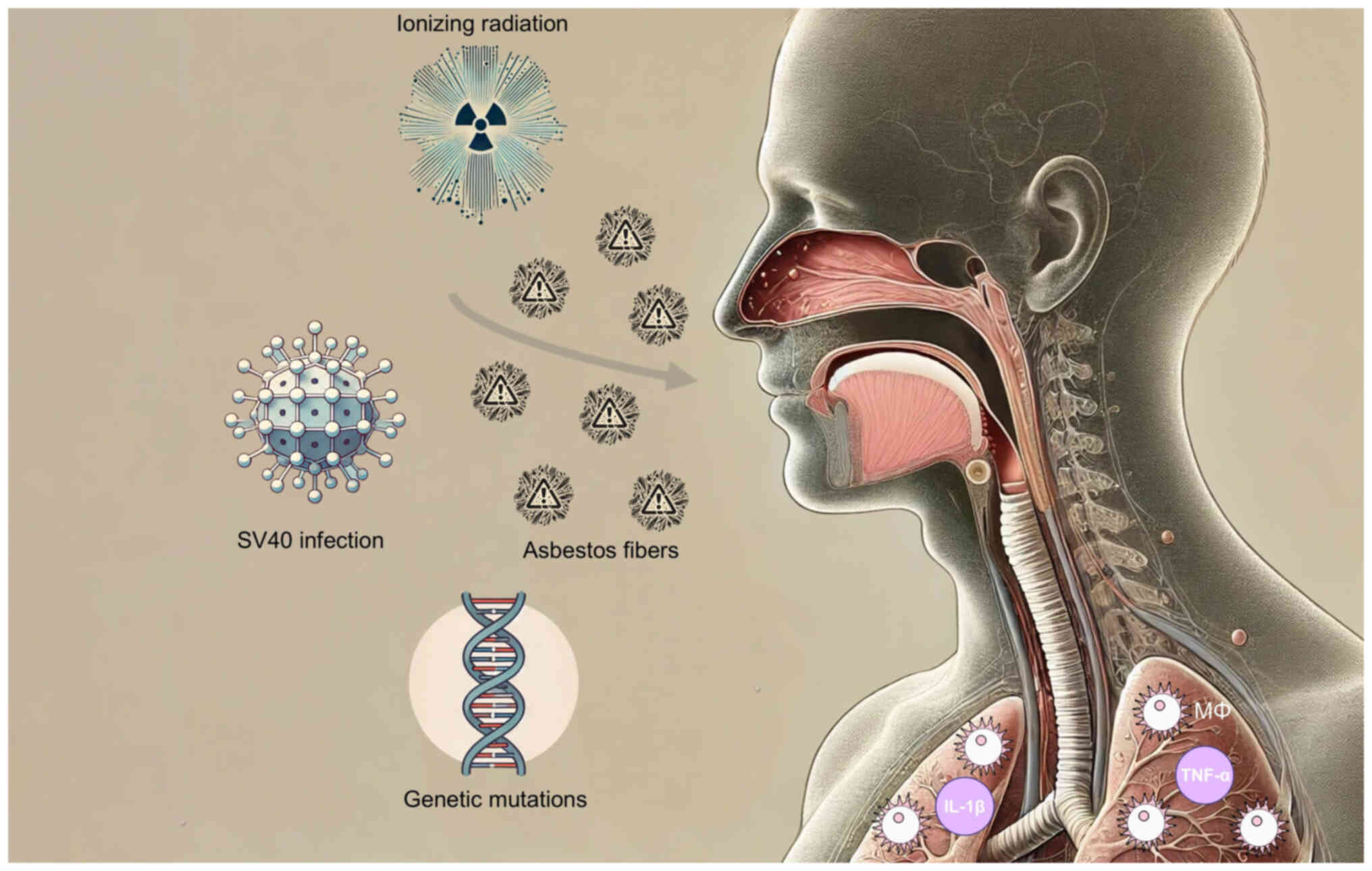
Husain AN, Colby TV, Ordóñez NG, Allen TC,
Attanoos RL, Beasley MB, Butnor KJ, Chirieac LR, Churg AM, Dacic S,
et al: Guidelines for pathologic diagnosis of malignant
mesothelioma 2017 update of the consensus statement from the
International Mesothelioma Interest Group. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
142:89–108. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Robinson BW and Lake RA: Advances in
malignant mesothelioma. N Engl J Med. 353:1591–1603. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moore AJ, Parker RJ and Wiggins J:
Malignant mesothelioma. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 3:342008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gloeckler Ries LA, Reichman ME, Lewis DR,
Hankey BF and Edwards BK: Cancer survival and incidence from the
surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) program.
Oncologist. 8:541–552. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Z, Li VR, Chu FI, Yu V, Lee A, Low D,
Moghanaki D, Lee P and Qi XS: Predicting overall survival for
patients with malignant mesothelioma following radiotherapy via
interpretable machine learning. Cancers (Basel). 15:39162023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meyerhoff RR, Yang CFJ, Speicher PJ,
Gulack BC, Hartwig MG, D'Amico TA, Harpole DH and Berry MF: Impact
of mesothelioma histologic subtype on outcomes in the surveillance,
epidemiology, and end results database. J Surg Res. 196:23–32.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moon IK and Jarstfer MB: The human
telomere and its relationship to human disease, therapy, and tissue
engineering. Front Biosci. 12:4595–4620. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Blackburn EH, Epel ES and Lin J: Human
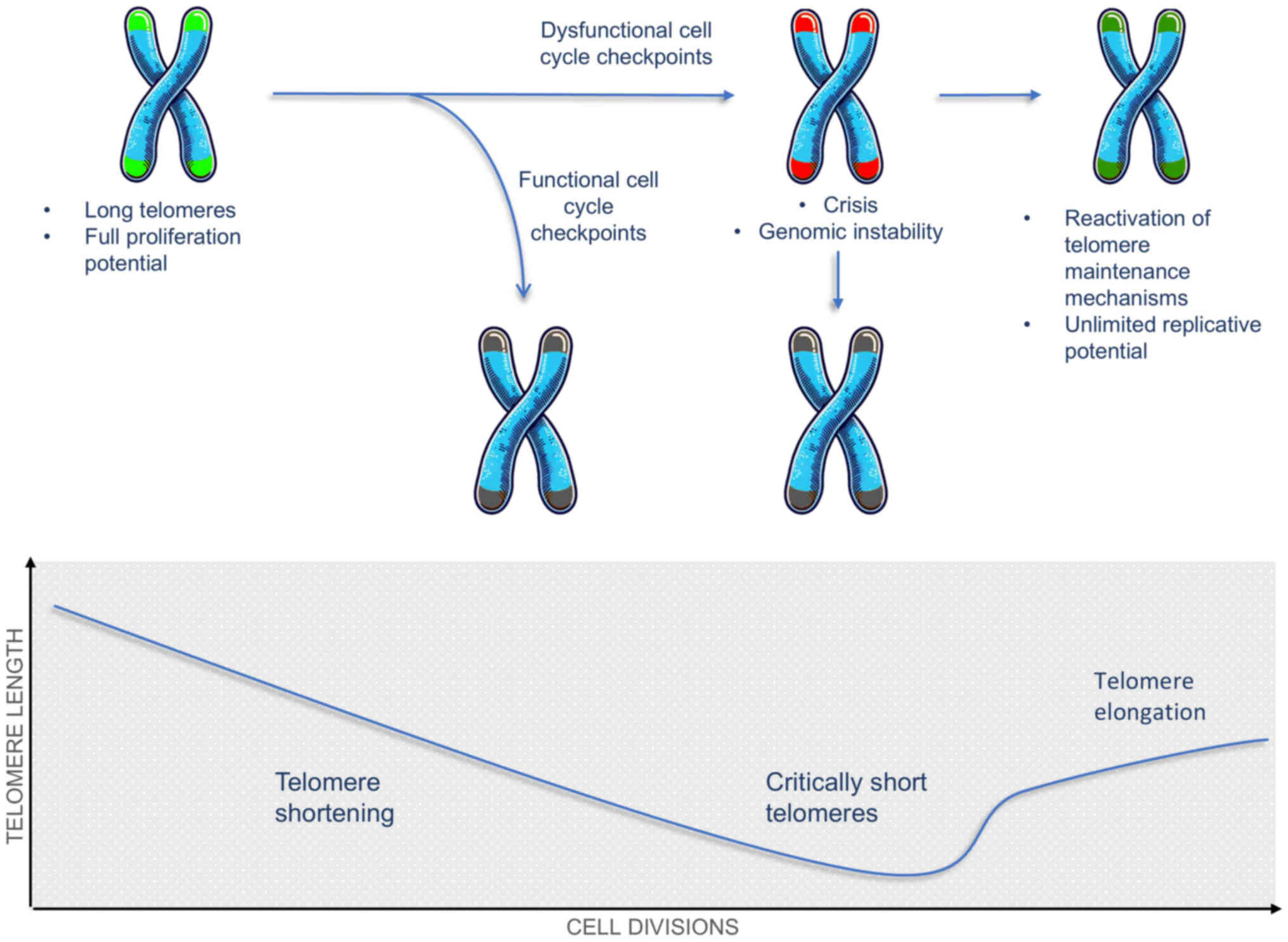
telomere biology: A contributory and interactive factor in aging,
disease risks, and protection. Science. 350:1193–1198. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
O'Sullivan RJ and Karlseder J: Telomeres:
protecting chromosomes against genome instability. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 11:171–181. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Artandi SE and DePinho RA: Telomeres and
telomerase in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 31:9–18. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Shay JW and Bacchetti S: A survey of
telomerase activity in human cancer. Eur J Cancer. 33:787–791.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Robinson NJ and Schiemann WP: Telomerase
in cancer: Function, regulation, and clinical translation. Cancers
(Basel). 14:8082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maciejowski J and de Lange T: Telomeres in
cancer: Tumour suppression and genome instability. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 18:175–186. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fan HC, Chang FW, Tsai JD, Lin KM, Chen
CM, Lin SZ, Liu CA and Harn HJ: Telomeres and Cancer. Life (Basel).
11:14052021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu Y and Goldkorn A: Telomere and
telomerase therapeutics in cancer. Genes (Basel). 7:222016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dratwa M, Wysoczańska B, Łacina P, Kubik T
and Bogunia-Kubik K: TERT-Regulation and roles in cancer formation.
Front Immunol. 11:5899292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tsatsakis A, Oikonomopoulou T,
Nikolouzakis TK, Vakonaki E, Tzatzarakis M, Flamourakis M, Renieri
E, Fragkiadaki P, Iliaki E, Bachlitzanaki M, et al: Role of
telomere length in human carcinogenesis (Review). Int J Oncol.
63:782023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu X, Han W, Xue W, Zou Y, Xie C, Du J
and Jin G: The association between telomere length and cancer risk
in population studies. Sci Rep. 6:222432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma H, Zhou Z, Wei S, Liu Z, Pooley KA,
Dunning AM, Svenson U, Roos G, Hosgood HD III, Shen M and Wei Q:
Shortened telomere length is associated with increased risk of
cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. 6:e204662011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shay JW and Wright WE: Role of telomeres
and telomerase in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 21:349–353. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bibby AC, Tsim S, Kanellakis N, Ball H,
Talbot DC, Blyth KG, Maskell NA and Psallidas I: Malignant pleural
mesothelioma: An update on investigation, diagnosis and treatment.
Eur Respir Rev. 25:472–486. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gilham C, Rake C, Burdett G, Nicholson AG,
Davison L, Franchini A, Carpenter J, Hodgson J, Darnton A and Peto
J: Pleural mesothelioma and lung cancer risks in relation to
occupational history and asbestos lung burden. Occup Environ Med.
73:290–299. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Nicholson WJ: Comparative dose-response
relationships of asbestos fiber types: Magnitudes and
uncertainties. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 643:74–84. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mott FE: Mesothelioma: A review. Ochsner
J. 12:70–79. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Alpert N, van Gerwen M and Taioli E:
Epidemiology of mesothelioma in the 21st century in Europe and the
United States, 40 years after restricted/banned asbestos use.
Transl Lung Cancer Res. 9(Suppl 1): S28–S38. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lempesis IG, Georgakopoulou VE, Papalexis
P, Chrousos GP and Spandidos DA: Role of stress in the pathogenesis
of cancer (Review). Int J Oncol. 63:1242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Slominski RM, Raman C, Chen JY and
Slominski AT: How cancer hijacks the body's homeostasis through the
neuroendocrine system. Trends Neurosci. 46:263–275. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Teta MJ, Lau E, Sceurman BK and Wagner ME:
Therapeutic radiation for lymphoma: Risk of malignant mesothelioma.
Cancer. 109:1432–1438. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Galateau-Salle F, Bidet P, Iwatsubo Y,
Gennetay E, Renier A, Letourneux M, Pairon JC, Moritz S, Brochard
P, Jaurand MC and Freymuth F: SV40-like DNA sequences in pleural
mesothelioma, bronchopulmonary carcinoma, and non-malignant
pulmonary diseases. J Pathol. 184:252–257. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Carbone M, Gazdar A and Butel JS: SV40 and
human mesothelioma. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 9(Suppl 1): S47–S59.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Betti M, Aspesi A, Sculco M, Matullo G,
Magnani C and Dianzani I: Genetic predisposition for malignant
mesothelioma: A concise review. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 781:1–10.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang H, Testa JR and Carbone M:
Mesothelioma epidemiology, carcinogenesis, and pathogenesis. Curr
Treat Options in Oncol. 9:147–157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kamp DW and Weitzman SA: The molecular
basis of asbestos induced lung injury. Thorax. 54:638–652. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shukla A, Gulumian M, Hei TK, Kamp D,
Rahman Q and Mossman BT: Multiple roles of oxidants in the
pathogenesis of asbestos-induced diseases. Free Radic Biol Med.
34:1117–1129. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Spandidos DA: A unified theory for the
development of cancer. Biosci Rep. 6:691–708. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Testa JR, Cheung M, Pei J, Below JE, Tan
Y, Sementino E, Cox NJ, Dogan AU, Pass HI, Trusa S, et al: Germline
BAP1 mutations predispose to malignant mesothelioma. Nat Genet.
43:1022–1025. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bianchi AB, Mitsunaga SI, Cheng JQ, Klein
WM, Jhanwar SC, Seizinger B, Kley N, Klein-Szanto AJ and Testa JR:
High frequency of inactivating mutations in the neurofibromatosis
type 2 gene (NF2) in primary malignant mesotheliomas. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 92:10854–10858. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sekido Y and Sato T: NF2 alteration in
mesothelioma. Front Toxicol. 5:11619952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sekido Y: Molecular pathogenesis of
malignant mesothelioma. Carcinogenesis. 34:1413–1419. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Janssen-Heininger YM, Mossman BT, Heintz
NH, Forman HJ, Kalyanaraman B, Finkel T, Stamler JS, Rhee SG and
van der Vliet A: Redox-based regulation of signal transduction:
Principles, pitfalls, and promises. Free Radic Biol Med. 45:1–17.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yap TA, Aerts JG, Popat S and Fennell DA:
Novel insights into mesothelioma biology and implications for
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:475–488. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang H, Hall SRR, Sun B, Zhao L, Gao Y,
Schmid RA, Tan ST, Peng RW and Yao F: NF2 and Canonical Hippo-YAP
pathway define distinct tumor subsets characterized by different
immune deficiency and treatment implications in human pleural
mesothelioma. Cancers (Basel). 13:15612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhou S, Liu L, Li H, Eilers G, Kuang Y,
Shi S, Yan Z, Li X, Corson JM, Meng F, et al: Multipoint targeting
of the PI3K/mTOR pathway in mesothelioma. Br J Cancer.
110:2479–2488. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Uematsu K, Kanazawa S, You L, He B, Xu Z,
Li K, Peterlin BM, McCormick F and Jablons DM: Wnt pathway
activation in mesothelioma: Evidence of Dishevelled overexpression
and transcriptional activity of beta-catenin. Cancer Res.
63:4547–4551. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Anani W, Bruggeman R and Zander DS:
β-catenin expression in benign and malignant pleural disorders. Int
J Clin Exp Pathol. 4:742–747. 2011.
|
|
50
|
McLoughlin KC, Kaufman AS and Schrump DS:
Targeting the epigenome in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Transl
Lung Cancer Res. 6:350–365. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Destro A, Ceresoli GL, Baryshnikova E,
Garassino I, Zucali PA, De Vincenzo F, Bianchi P, Morenghi E,
Testori A, Alloisio M, et al: Gene methylation in pleural
mesothelioma: Correlations with clinico-pathological features and
patient's follow-up. Lung Cancer. 59:369–376. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kubo T, Toyooka S, Tsukuda K, Sakaguchi M,
Fukazawa T, Soh J, Asano H, Ueno T, Muraoka T, Yamamoto H, et al:
Epigenetic silencing of MicroRNA-34b/c plays an important role in
the pathogenesis of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Clin Cancer
Res. 17:4965–4974. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Perera ND and Mansfield AS: The evolving
therapeutic landscape for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Curr
Oncol Rep. 24:1413–1423. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lapidot M and Sattler M: The role of
surgery in pleural mesothelioma. Cancers (Basel). 16:17192024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Vogelzang NJ, Rusthoven JJ, Symanowski J,
Denham C, Kaukel E, Ruffie P, Gatzemeier U, Boyer M, Emri S,
Manegold C, et al: Phase III study of pemetrexed in combination
with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant
pleural mesothelioma. J Clin Oncol. 21:2636–2644. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ziółkowska B, Cybulska-Stopa B,
Papantoniou D and Suwiński R: Systemic treatment in patients with
malignant pleural mesothelioma - real life experience. BMC Cancer.
22:4322022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Price A: What is the role of radiotherapy
in malignant pleural mesothelioma? Oncologist. 16:359–365. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hanna GG, John T and Ball DL:
Controversies in the role of radiotherapy in pleural mesothelioma.
Transl Lung Cancer Res. 10:2079–2087. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhang Y and Zhang Z: The history and
advances in cancer immunotherapy: understanding the characteristics
of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic
implications. Cell Mol Immunol. 17:807–821. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cantini L, Hassan R, Sterman DH and Aerts
JGJV: Emerging treatments for malignant pleural mesothelioma: Where
are we heading? Front Oncol. 10:3432022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Gray SG and Mutti L: Immunotherapy for
mesothelioma: A critical review of current clinical trials and
future perspectives. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 9(Suppl 1): S100–S119.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Baas P, Scherpereel A, Nowak AK, Fujimoto
N, Peters S, Tsao AS, Mansfield AS, Popat S, Jahan T, Antonia S, et
al: First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant
pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): A multicentre, randomised,
open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 397:375–386. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nakajima EC, Vellanki PJ, Larkins E,
Chatterjee S, Mishra-Kalyani PS, Bi Y, Qosa H, Liu J, Zhao H,
Biable M, et al: FDA approval summary: Nivolumab in combination
with ipilimumab for the treatment of unresectable malignant pleural
mesothelioma. Clin Cancer Res. 28:446–451. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
64
|
Uddin F, Rudin CM and Sen T: CRISPR Gene
Therapy: Applications, limitations, and implications for the
future. Front Oncol. 10:13872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cross D and Burmester JK: Gene therapy for
cancer treatment: Past, present and future. Clin Med Res.
4:218–227. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Vachani A, Moon E, Wakeam E and Albelda
SM: Gene therapy for mesothelioma and lung cancer. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 42:385–393. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Pease DF and Kratzke RA: Oncolytic viral
therapy for mesothelioma. Front Oncol. 7:1792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang T, Jou TH, Hsin J, Wang Z, Huang K,
Ye J, Yin H and Xing Y: Talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC): A review
of the recent advances in cancer therapy. J Clin Med. 12:10982023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Dagogo-Jack I: Targeted approaches to
treatment of pleural mesothelioma: A review. JCO Precis Oncol.
7:e23003442023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zalcman G, Mazieres J, Margery J,
Greillier L, Audigier-Valette C, Moro-Sibilot D, Molinier O, Corre
R, Monnet I, Gounant V, et al: Bevacizumab for newly diagnosed
pleural mesothelioma in the Mesothelioma Avastin Cisplatin
Pemetrexed Study (MAPS): A randomised, controlled, open-label,
phase 3 trial. Lancet. 387:1405–1414. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ceresoli GL, Zucali PA, Mencoboni M, Botta
M, Grossi F, Cortinovis D, Zilembo N, Ripa C, Tiseo M, Favaretto
AG, et al: Phase II study of pemetrexed and carboplatin plus
bevacizumab as first-line therapy in malignant pleural
mesothelioma. Br J Cancer. 109:552–558. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zucali PA, Perrino M, De Vincenzo F,
Giordano L, Cordua N, D'Antonio F and Santoro A: A phase II study
of the combination of gemcitabine and imatinib mesylate in
pemetrexed-pretreated patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma.
Lung Cancer. 142:132–137. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Tsao AS, Harun N, Lee JJ, Heymach J,
Pisters K, Hong WK, Fujimoto J and Wistuba I: Phase I trial of
cisplatin, pemetrexed, and imatinib mesylate in chemonaive patients
with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma. Clin Lung Cancer.
15:197–201. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Govindan R, Kratzke RA, Herndon JE II,
Niehans GA, Vollmer R, Watson D, Green MR and Kindler HL; Cancer
and Leukemia Group B (CALGB 30101): Gefitinib in patients with
malignant mesothelioma: A phase II study by the cancer and leukemia
group B. Clin Cancer Res. 11:2300–2304. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
De Paepe A, Vermaelen KY, Cornelissen R,
Germonpre PR, Janssens A, Lambrechts M, Bootsma G, Van Meerbeeck J
and Surmont VF: Cetuximab plus platinum-based chemotherapy in
patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: A single arm phase II
trial. J Chin Oncol. 35(15_suppl): e200302017.
|
|
76
|
Haakensen VD, Öjlert ÅK, Thunold S,
Farooqi S, Nowak AK, Chin WL, Grundberg O, Szejniuk WM, Cedres S,
Sørensen JB, et al: UV1 telomerase vaccine with ipilimumab and
nivolumab as second line treatment for pleural mesothelioma-A phase
II randomised trial. Eur J Cancer. 202:1139732024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
De Lange T: How telomeres solve the
end-protection problem. Science. 326:948–952. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
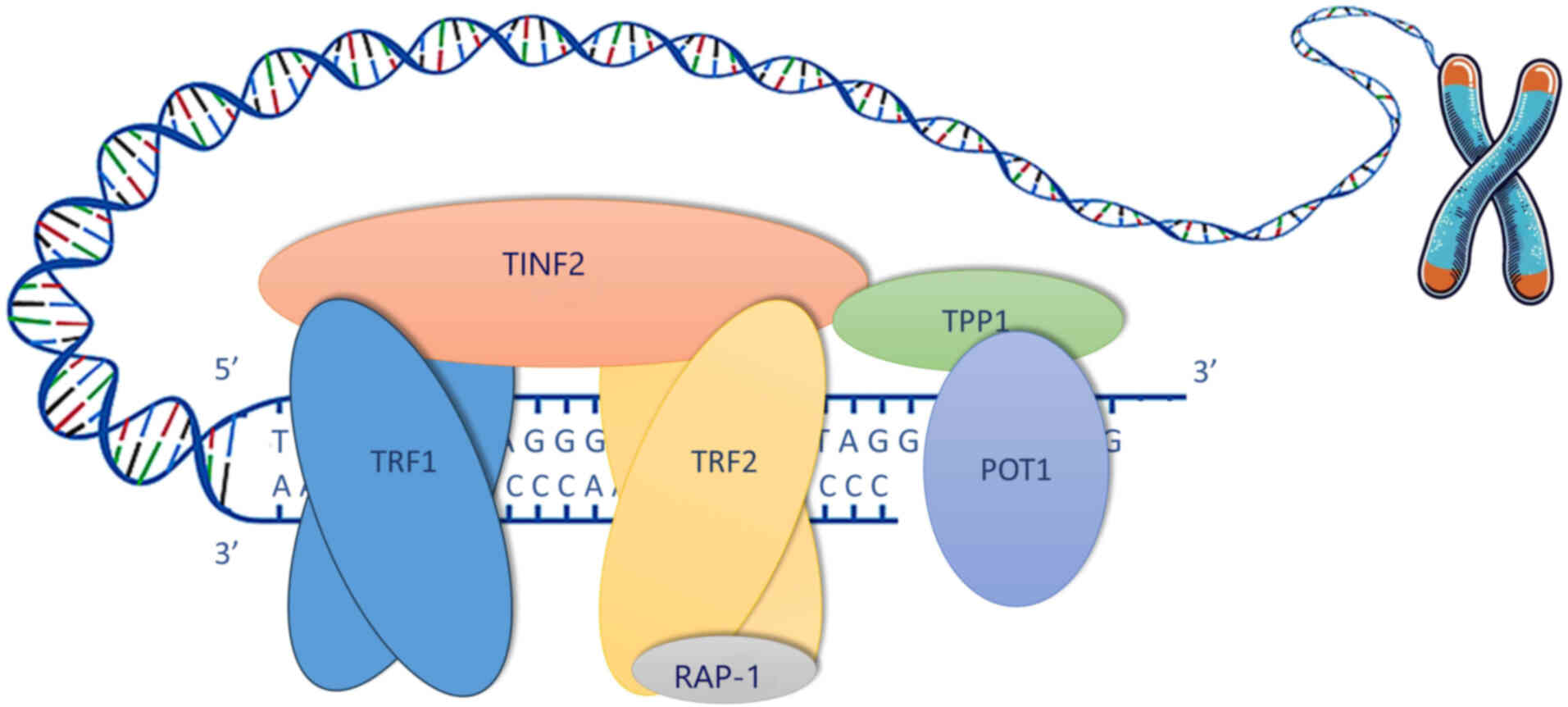
Palm W and de Lange T: How shelterin
protects mammalian telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 42:301–334. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Martínez P and Blasco MA: Telomere-driven
diseases and telomere-targeting therapies. J Cell Biol.
216:875–887. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Greider CW and Blackburn EH: A telomeric
sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere
repeat synthesis. Nature. 337:331–337. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Shay JW and Wright WE: Hayflick, his
limit, and cellular ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 1:72–76. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Deng Y, Chan SS and Chang S: Telomere
dysfunction and tumour suppression: The senescence connection. Nat
Rev Cancer. 8:450–458. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Bryan TM, Englezou A, Dalla-Pozza L,
Dunham MA and Reddel RR: Evidence for an alternative mechanism for
maintaining telomere length in human tumors and tumor-derived cell
lines. Nat Med. 3:1271–1274. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Bryan TM, Englezou A, Gupta J, Bacchetti S
and Reddel RR: Telomere elongation in immortal human cells without
detectable telomerase activity. EMBO J. 14:4240–4248. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zvereva MI, Shcherbakova DM and Dontsova
OA: Telomerase: Structure, functions, and activity regulation.
Biochemistry (Mosc). 75:1563–1583. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Nandakumar J and Cech TR: Finding the end:
Recruitment of telomerase to telomeres. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
14:69–82. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Xin ZT, Beauchamp AD, Calado RT, Bradford
JW, Regal JA, Shenoy A, Liang Y, Lansdorp PM, Young NS and Ly H:
Functional characterization of natural telomerase mutations found
in patients with hematologic disorders. Blood. 109:524–532. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
de Lange T: Shelterin-mediated telomere
protection. Annu Rev Genet. 52:223–247. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Chen H, Majumdar A, Wang L, Kar S, Brown
KM, Feng H, Turman C, Dennis J, Easton D, Michailidou K, et al:
Large-scale cross-cancer fine-mapping of the 5p15.33 region reveals
multiple independent signals. HGG Adv. 2:1000412021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Okamoto K and Seimiya H: Revisiting
telomere shortening in cancer. Cells. 8:1072019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Blasco MA, Lee HW, Hande MP, Samper E,
Lansdorp PM, DePinho RA and Greider CW: Telomere shortening and
tumor formation by mouse cells lacking telomerase RNA. Cell.
91:25–34. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Karimi B, Yunesian M, Nabizadeh R,
Mehdipour P and Aghaie A: Is leukocyte telomere length related with
lung cancer risk?: A meta-analysis. Iran Biomed J. 21:142–153.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
94
|
Naing C, Aung K, Lai PK and Mak JW:
Association between telomere length and the risk of colorectal
cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies. BMC Cancer.
17:242017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Benites-Zapata VA, Ulloque-Badaracco JR,
Alarcón-Braga EA, Fernández-Alonso AM, López-Baena MT and
Pérez-López FR: Telomerase activity and telomere length in women
with breast cancer or without malignancy: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Maturitas. 180:1078822024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Caini S, Raimondi S, Johansson H, De
Giorgi V, Zanna I, Palli D and Gandini S: Telomere length and the
risk of cutaneous melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer: A review
of the literature and meta-analysis. J Dermatol Sci. 80:168–174.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Wentzensen IM, Mirabello L, Pfeiffer RM
and Savage SA: The association of telomere length and cancer: A
meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 20:1238–1250.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Holesova Z, Krasnicanova L, Saade R, Pös
O, Budis J, Gazdarica J, Repiska V and Szemes T: Telomere length
changes in cancer: Insights on carcinogenesis and potential for
non-invasive diagnostic strategies. Genes (Basel). 14:7152023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Chen S, Hu S, Zhou B, Cheng B, Tong H, Su
D, Li X, Chen Y and Zhang G: Telomere-related prognostic biomarkers
for survival assessments in pancreatic cancer. Sci Rep.
13:105862023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Wang J, Xie LY, Allan S, Beach D and
Hannon GJ: Myc activates telomerase. Genes Dev. 12:1769–1774. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Liu M, Zhang Y, Jian Y, Gu L, Zhang D,
Zhou H, Wang Y and Xu ZX: The regulations of telomerase reverse
transcriptase (TERT) in cancer. Cell Death Dis. 15:902024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Kim NW, Piatyszek MA, Prowse KR, Harley
CB, West MD, Ho PL, Coviello GM, Wright WE, Weinrich SL and Shay
JW: Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal
cells and cancer. Science. 266:2011–2015. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Kim NW and Wu F: Advances in
quantification and characterization of telomerase activity by the
telomeric repeat amplification protocol (TRAP). Nucleic Acids Res.
25:2595–2597. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
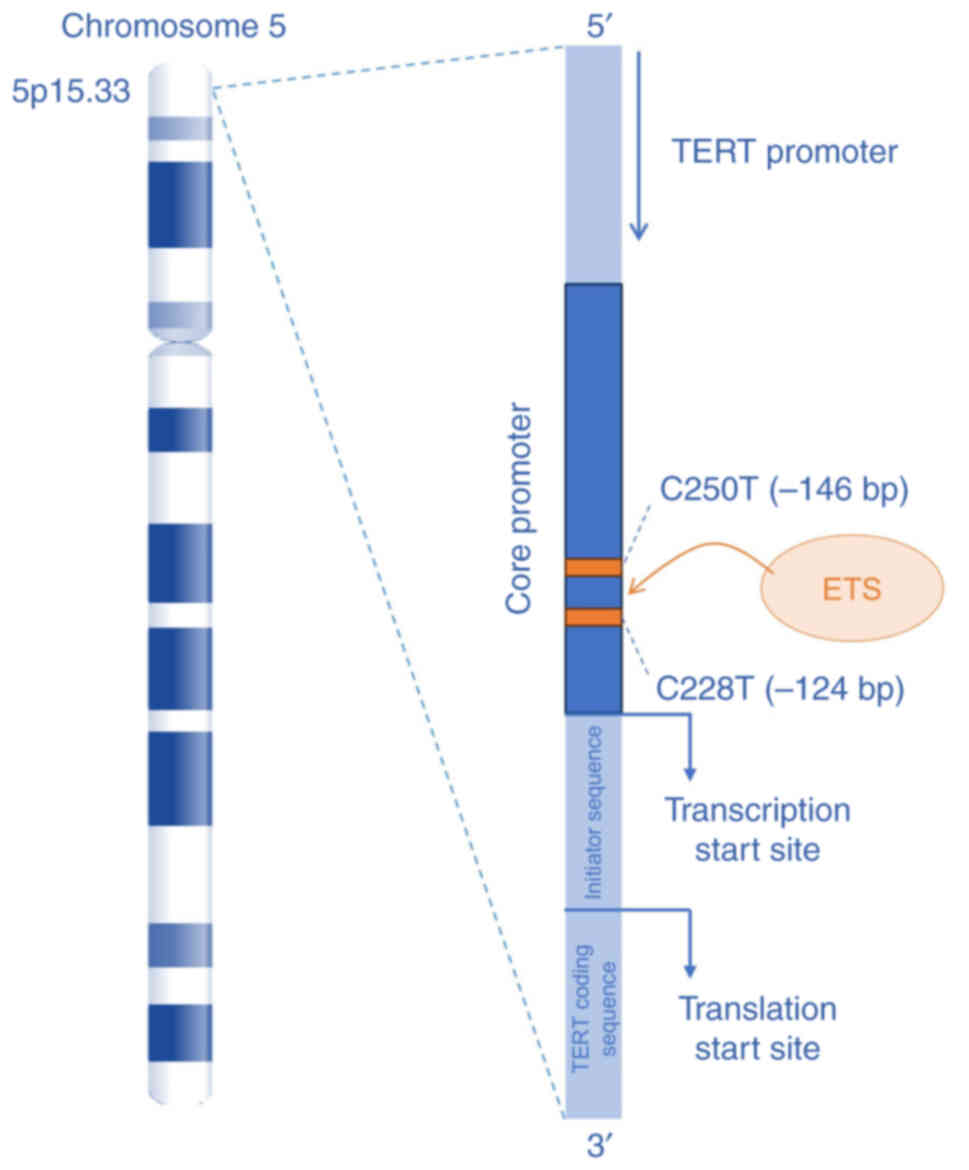
Horn S, Figl A, Rachakonda PS, Fischer C,
Sucker A, Gast A, Kadel S, Moll I, Nagore E, Hemminki K, et al:
TERT promoter mutations in familial and sporadic melanoma. Science.
339:959–961. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Vinagre J, Almeida A, Pópulo H, Batista R,
Lyra J, Pinto V, Coelho R, Celestino R, Prazeres H, Lima L, et al:
Frequency of TERT promoter mutations in human cancers. Nat Commun.
4:21852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Hiyama E and Hiyama K: Telomere and
telomerase in stem cells. Br J Cancer. 96:1020–1024. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Park JI, Venteicher AS, Hong JY, Choi J,
Jun S, Shkreli M, Chang W, Meng Z, Cheung P, Ji H, et al:
Telomerase modulates Wnt signalling by association with target gene
chromatin. Nature. 460:66–72. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Colebatch AJ, Dobrovic A and Cooper WA:
TERT gene: Its function and dysregulation in cancer. J Clin Pathol.
72:281–284. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Powter B, Jeffreys SA, Sareen H, Cooper A,
Brungs D, Po J, Roberts T, Koh ES, Scott KF, Sajinovic M, et al:
Human TERT promoter mutations as a prognostic biomarker in glioma.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 147:1007–1017. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Marczyk VR, Maia AL and Goemann IM:
Distinct transcriptional and prognostic impacts of TERT promoter
mutations C228T and C250T in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Endocr
Relat Cancer. 31:e2400582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Xu Y, Ren X, Jiang T, Lv S, Gao K, Liu Y
and Yan Y: Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and hTERT gene expression
in CTCs for radiotherapy effect with lung cancer. BMC Cancer.
23:4752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Killela PJ, Reitman ZJ, Jiao Y, Bettegowda
C, Agrawal N, Diaz LA Jr, Friedman AH, Friedman H, Gallia GL,
Giovanella BC, et al: TERT promoter mutations occur frequently in
gliomas and a subset of tumors derived from cells with low rates of
self-renewal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:6021–6026. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Castelo-Branco P, Leão R, Lipman T,
Campbell B, Lee D, Price A, Zhang C, Heidari A, Stephens D, Boerno
S, et al: A cancer specific hypermethylation signature of the TERT
promoter predicts biochemical relapse in prostate cancer: A
retrospective cohort study. Oncotarget. 7:57726–57736. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Asai A, Oshima Y, Yamamoto Y, Uochi TA,
Kusaka H, Akinaga S, Yamashita Y, Pongracz K, Pruzan R, Wunder E,
et al: A novel telomerase template antagonist (GRN163) as a
potential anticancer agent. Cancer Res. 63:3931–3939.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Tefferi A, Lasho TL, Begna KH, Patnaik MM,
Zblewski DL, Finke CM, Laborde RR, Wassie E, Schimek L, Hanson CA,
et al: A pilot study of the telomerase inhibitor imetelstat for
myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med. 373:908–919. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Wang X, Hu CS, Petersen B, Qiu J, Ye F,
Houldsworth J, Eng K, Huang F and Hoffman R: Imetelstat, a
telomerase inhibitor, is capable of depleting myelofibrosis stem
and progenitor cells. Blood Adv. 2:2378–2388. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Olschok K, Altenburg B, De Toledo MAS,
Maurer A, Abels A, Beier F, Gezer D, Isfort S, Paeschke K,
Brümmendorf TH, et al: The telomerase inhibitor imetelstat
differentially targets JAK2V617F versus CALR mutant
myeloproliferative neoplasm cells and inhibits JAK-STAT signaling.
Front Oncol. 13:12774532023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Zhang JM and Zou L: Alternative
lengthening of telomeres: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic
outlooks. Cell Biosci. 10:302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
De Vitis M, Berardinelli F and Sgura A:
Telomere length maintenance in cancer: At the crossroad between
telomerase and alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT). Int J
Mol Sci. 19:6062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Flynn RL, Cox KE, Jeitany M, Wakimoto H,
Bryll AR, Ganem NJ, Bersani F, Pineda JR, Suvà ML, Benes CH, et al:
Alternative lengthening of telomeres renders cancer cells
hypersensitive to ATR inhibitors. Science. 347:273–277. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Afshari N, Al-Gazally ME, Rasulova I,
Jalil AT, Matinfar S and Momeninejad M: Sensitive bioanalytical
methods for telomerase activity detection: A cancer biomarker. Anal
Methods. 14:4174–4184. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Kyo S, Takakura M and Inoue M: Telomerase
activity in cancer as a diagnostic and therapeutic target. Histol
Histopathol. 15:813–824. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Mervic A, Goricar K, Blagus T, Franko A,
Trebusak-Podkrajsek K, Fikfak MD, Dolzan V and Kovac V: Telomere
length and TERT polymorphisms as biomarkers in asbestos-related
diseases. Radiol Oncol. 58:87–98. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Aida S, Aida J, Naoi M, Kato M, Tsuura Y,
Natsume I and Takubo K: Measurement of telomere length in cells
from pleural effusion: Asbestos exposure causes telomere shortening
in pleural mesothelial cells. Pathol Int. 68:503–508. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Pirker C, Bilecz A, Grusch M, Mohr T,
Heidenreich B, Laszlo V, Stockhammer P, Lötsch-Gojo D, Gojo J,
Gabler L, et al: Telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter
mutations identify a genomically defined and highly aggressive
human pleural mesothelioma subgroup. Clin Cancer Res. 26:3819–3830.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Au AY, Hackl T, Yeager TR, Cohen SB, Pass
HI, Harris CC and Reddel RR: Telomerase activity in pleural
malignant mesotheliomas. Lung Cancer. 73:283–288. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Andreikos D, Kyrodimos E, Kotsinas A,
Chrysovergis A and Papacharalampous GX: The association between
telomere length and head and neck cancer risk: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 25:90002024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Yuan X, Dai M and Xu D: Telomere-related
markers for cancer. Curr Top Med Chem. 20:410–432. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Borges G, Criqui M and Harrington L:
Tieing together loose ends: Telomere instability in cancer and
aging. Mol Oncol. 16:3380–3396. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Cigan SS, Meredith JJ, Kelley AC, Yang T,
Langer EK, Hooten AJ, Lane JA, Cole BR, Krailo M, Frazier AL, et
al: Predicted leukocyte telomere length and risk of germ cell
tumours. Br J Cancer. 127:301–312. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Lagniau S, Lamote K, van Meerbeeck JP and
Vermaelen KY: Biomarkers for early diagnosis of malignant
mesothelioma: Do we need another moonshot? Oncotarget.
8:53751–53762. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Nabeshima K, Matsumoto S, Hamasaki M, Hida
T, Kamei T, Hiroshima K, Tsujimura T and Kawahara K: Use of p16
FISH for differential diagnosis of mesothelioma in smear
preparations. Diagn Cytopathol. 44:774–780. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Hiroshima K, Wu D, Hasegawa M, Koh E,
Sekine Y, Ozaki D, Yusa T, Walts AE, Marchevsky AM, Nabeshima K, et
al: Cytologic differential diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma and
reactive mesothelial cells with FISH analysis of p16. Diagn
Cytopathol. 44:591–598. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Jaouen A, Thivolet-Bejui F, Chalabreysse
L, Piaton E, Traverse-Glehen A, Isaac S, Decaussin-Petrucci M,
Depaepe L, Fontaine J, Remy I, et al: BRCA1 associated protein 1
(BAP1) expression in pleural diffuse malignant mesothelioma: A
comparative cytological and histological analyses on 50 patients.
Ann Pathol. 36:111–119. 2016.In French. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Hjerpe A, Ascoli V, Bedrossian C, Boon M,
Creaney J, Davidson B, Dejmek A, Dobra K, Fassina A, Field A, et
al: Guidelines for cytopathologic diagnosis of epithelioid and
mixed type malignant mesothelioma. Complementary statement from the
International Mesothelioma Interest Group, also endorsed by the
International Academy of Cytology and the Papanicolaou Society of
Cytopathology. CytoJournal. 12:262015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Minato H, Kurose N, Fukushima M, Nojima T,
Usuda K, Sagawa M, Sakuma T, Ooi A, Matsumoto I, Oda M, et al:
Comparative immunohistochemical analysis of IMP3, GLUT1, EMA,
CD146, and desmin for distinguishing malignant mesothelioma from
reactive mesothelial cells. Am J Clin Pathol. 141:85–93. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Levstek T, Redenšek S, Trošt M, Dolžan V
and Podkrajšek KT: Assessment of the telomere length and its effect
on the symptomatology of Parkinson's disease. Antioxidants (Basel).
10:1372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Lulkiewicz M, Bajsert J, Kopczynski P,
Barczak W and Rubis B: Telomere length: How the length makes a
difference. Mol Biol Rep. 47:7181–7188. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Havas A, Yin S and Adams PD: The role of
aging in cancer. Mol Oncol. 16:3213–3219. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Kusamura S, Baratti D, De Simone M,
Pasqual EM, Ansaloni L, Marrelli D, Robella M, Accarpio F, Valle M,
Scaringi S, et al: Diagnostic and therapeutic pathway in diffuse
malignant peritoneal mesothelioma. Cancers (Basel). 15:6622023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Benitez-Buelga C, Sanchez-Barroso L,
Gallardo M, Apellániz-Ruiz M, Inglada-Pérez L, Yanowski K, Carrillo
J, Garcia-Estevez L, Calvo I, Perona R, et al: Impact of
chemotherapy on telomere length in sporadic and familial breast
cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 149:385–394. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Schneider CV, Schneider KM, Teumer A,
Rudolph KL, Hartmann D, Rader DJ and Strnad P: Association of
telomere length with risk of disease and mortality. JAMA Intern
Med. 182:291–300. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Hamada T, Yuan C, Bao Y, Zhang M, Khalaf
N, Babic A, Morales-Oyarvide V, Cochrane BB, Gaziano JM,
Giovannucci EL, et al: Prediagnostic leukocyte telomere length and
pancreatic cancer survival. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
28:1868–1875. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Pauleck S, Gigic B, Cawthon RM, Ose J,
Peoples AR, Warby CA, Sinnott JA, Lin T, Boehm J, Schrotz-King P,
et al: Association of circulating leukocyte telomere length with
survival in patients with colorectal cancer. J Geriatr Oncol.
13:480–485. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Dhaene K, Hübner R, Kumar-Singh S, Weyn B
and Van Marck E: Telomerase activity in human pleural mesothelioma.
Thorax. 53:915–918. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Cesare AJ and Reddel RR: Alternative
lengthening of telomeres: Models, mechanisms and implications. Nat
Rev Genet. 11:319–330. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Kumaki F, Kawai T, Hiroi S, Shinomiya N,
Ozeki Y, Ferrans VJ and Torikata C: Telomerase activity and
expression of human telomerase RNA component and human telomerase
reverse transcriptase in lung carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 32:188–195.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Hansson M, Zendehrokh N, Ohyashiki J,
Ohyashiki K, Westman UB, Roos G and Dejmek A: Telomerase activity
in effusions: A comparison between telomere repeat amplification
protocol in situ and conventional telomere repeat amplification
protocol assay. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 132:1896–1902. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Villa R, Daidone MG, Motta R, Venturini L,
De Marco C, Vannelli A, Kusamura S, Baratti D, Deraco M, Costa A,
et al: Multiple mechanisms of telomere maintenance exist and
differentially affect clinical outcome in diffuse malignant
peritoneal mesothelioma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:4134–4140. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Trupiano JK, Geisinger KR, Willingham MC,
Manders P, Zbieranski N, Case D and Levine EA: Diffuse malignant
mesothelioma of the peritoneum and pleura, analysis of markers. Mod
Pathol. 17:476–481. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Foddis R, De Rienzo A, Broccoli D,
Bocchetta M, Stekala E, Rizzo P, Tosolini A, Grobelny JV, Jhanwar
SC, Pass HI, et al: SV40 infection induces telomerase activity in
human mesothelial cells. Oncogene. 21:1434–1442. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Heaphy CM, Subhawong AP, Hong SM, Goggins
MG, Montgomery EA, Gabrielson E, Netto GJ, Epstein JI, Lotan TL,
Westra WH, et al: Prevalence of the alternative lengthening of
telomeres telomere maintenance mechanism in human cancer subtypes.
Am J Pathol. 179:1608–1615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Hahn WC, Counter CM, Lundberg AS,
Beijersbergen RL, Brooks MW and Weinberg RA: Creation of human
tumour cells with defined genetic elements. Nature. 400:464–468.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Zendehrokh N and Dejmek A: Telomere repeat
amplification protocol (TRAP) in situ reveals telomerase activity
in three cell types in effusions: Malignant cells, proliferative
mesothelial cells, and lymphocytes. Mod Pathol. 18:189–196. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Counter CM, Gupta J, Harley CB, Leber B
and Bacchetti S: Telomerase activity in normal leukocytes and in
hematologic malignancies. Blood. 85:2315–2320. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Norrback KF, Dahlenborg K, Carlsson R and
Roos G: Telomerase activation in normal B lymphocytes and
non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Blood. 88:222–229. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Lee WY: Limitations of detection of
malignancy in pleural effusions using ELISA-based TRAP assay:
comparison with cytological examination. Cytopathology. 16:227–232.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Tangkijvanich P, Tresukosol D,
Sampatanukul P, Sakdikul S, Voravud N, Mahachai V and Mutirangura
A: Telomerase assay for differentiating between malignancy-related
and nonmalignant ascites. Clin Cancer Res. 5:2470–2475.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Braunschweig R, Yan P, Guilleret I,
Delacretaz F, Bosman FT, Mihaescu A and Benhattar J: Detection of
malignant effusions: Comparison of a telomerase assay and cytologic
examination. Diagn Cytopathol. 24:174–180. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Gül I, Dündar O, Bodur S, Tunca Y and
Tütüncü L: The status of telomerase enzyme activity in benign and
malignant gynaecologic pathologies. Balkan Med J. 30:287–292. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Miracco C, de Santi MM, Pacenti L,
Schürfeld K, Laurini L, Pirtoli L, Luzi P and Ninfo V: Telomerase
activity, Ki-67, cyclin D1 and A expression, and apoptosis in
solitary fibrous tumors: Additional features of a predictable
course? Pathol Res Pract. 197:475–481. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Adell E and Dejmek A: Telomerase activity
analyzed with TRAP in situ provides additional information in
effusions remaining equivocal after immunocytochemistry and
hyaluronan analysis. Diagn Cytopathol. 42:1051–1057. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Cakir C, Gulluoglu MG and Yilmazbayhan D:
Cell proliferation rate and telomerase activity in the differential
diagnosis. Pathology. 38:10–15. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Lantuejoul S, Soria JC, Moro-Sibilot D,
Morat L, Veyrenc S, Lorimier P, Brichon PY, Sabatier L, Brambilla C
and Brambilla E: Differential expression of telomerase reverse
transcriptase (hTERT) in lung tumours. Br J Cancer. 90:1222–1229.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Henson JD, Neumann AA, Yeager TR and
Reddel RR: Alternative lengthening of telomeres in mammalian cells.
Oncogene. 21:598–610. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Hiyama E and Hiyama K: Telomerase as tumor
marker. Cancer Lett. 194:221–233. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Montgomery E, Argani P, Hicks JL, DeMarzo
AM and Meeker AK: Telomere lengths of translocation-associated and
nontranslocation-associated sarcomas differ dramatically. Am J
Pathol. 164:1523–1529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Hakin-Smith V, Jellinek DA, Levy D,
Carroll T, Teo M, Timperley WR, McKay MJ, Reddel RR and Royds JA:
Alternative lengthening of telomeres and survival in patients with
glioblastoma multiforme. Lancet. 361:836–838. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Ulaner GA, Huang HY, Otero J, Zhao Z,
Ben-Porat L, Satagopan JM, Gorlick R, Meyers P, Healey JH, Huvos
AG, et al: Absence of a telomere maintenance mechanism as a
favorable prognostic factor in patients with osteosarcoma. Cancer
Res. 63:1759–1763. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Johnson JE, Varkonyi RJ, Schwalm J, Cragle
R, Klein-Szanto A, Patchefsky A, Cukierman E, von Mehren M and
Broccoli D: Multiple mechanisms of telomere maintenance exist in
liposarcomas. Clin Cancer Res. 11:5347–5355. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Costa A, Daidone MG, Daprai L, Villa R,
Cantù S, Pilotti S, Mariani L, Gronchi A, Henson JD, Reddel RR and
Zaffaroni N: Telomere maintenance mechanisms in liposarcomas:
Association with histologic subtypes and disease progression.
Cancer Res. 66:8918–8924. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Claude E and Decottignies A: Telomere
maintenance mechanisms in cancer: Telomerase, ALT or lack thereof.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 60:1–8. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Seger YR, García-Cao M, Piccinin S,
Cunsolo CL, Doglioni C, Blasco MA, Hannon GJ and Maestro R:
Transformation of normal human cells in the absence of telomerase
activation. Cancer Cell. 2:401–413. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Shay JW and Wright WE: Telomerase: A
target for cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell. 2:257–265. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Folini M and Zaffaroni N: Targeting
telomerase by antisense-based approaches: Perspectives for new
anti-cancer therapies. Curr Pharm Des. 11:1105–1117. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Jiang WQ, Zhong ZH, Henson JD and Reddel
RR: Identification of candidate alternative lengthening of
telomeres genes by methionine restriction and RNA interference.
Oncogene. 26:4635–4647. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Quetel L, Meiller C, Assié JB, Blum Y,
Imbeaud S, Montagne F, Tranchant R, de Wolf J, Caruso S, Copin MC,
et al: Genetic alterations of malignant pleural mesothelioma:
Association with tumor heterogeneity and overall survival. Mol
Oncol. 14:1207–1223. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Zhou M, Jiang B, Xiong M and Zhu X:
Association between TERT rs2736098 polymorphisms and cancer risk-A
meta-analysis. Front Physiol. 9:3772018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Wang M and Sun Y: Telomerase reverse
transcriptase rs2736098 polymorphism is associated with lung
cancer: A meta-analysis. J Int Med Res. 48:3000605209361732020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
He G, Song T, Zhang Y, Chen X, Xiong W,
Chen H, Sun C, Zhao C, Chen Y and Wu H: TERT rs10069690
polymorphism and cancers risk: A meta-analysis. Mol Genet Genomic
Med. 7:e009032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Li H, Xu Y, Mei H, Peng L, Li X and Tang
J: The TERT rs2736100 polymorphism increases cancer risk: A
meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 8:38693–38705. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Ma R, Liu C, Lu M, Yuan X, Cheng G, Kong
F, Lu J, Strååt K, Björkholm M, Ma L and Xu D: The TERT locus
genotypes of rs2736100-CC/CA and rs2736098-AA predict shorter
survival in renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol. 37:301.e1–301.e10.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Pandith AA, Wani ZA, Qasim I, Afroze D,
Manzoor U, Amin I, Baba SM, Koul A, Anwar I, Mohammad F, et al:
Association of strong risk of hTERT gene polymorphic variants to
malignant glioma and its prognostic implications with respect to
different histological types and survival of glioma cases. J Gene
Med. 22:e32602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Dratwa M, Łacina P, Butrym A, Porzuczek D,
Mazur G and Bogunia-Kubik K: Telomere length and hTERT genetic
variants as potential prognostic markers in multiple myeloma. Sci
Rep. 13:157922023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Zins K, Peka E, Miedl H, Ecker S, Abraham
D and Schreiber M: Association of the telomerase reverse
transcriptase rs10069690 polymorphism with the risk, age at onset
and prognosis of triple negative breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
24:18252023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Nie X, Shang J and Wang W: TERT genetic
polymorphism rs2736100 is associated with an aggressive
manifestation of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Front Surg.
9:10191802023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Pu RT, Sheng ZM, Michael CW, Rhode MG,
Clark DP and O'Leary TJ: Methylation profiling of mesothelioma
using real-time methylation-specific PCR: A pilot study. Diagn
Cytopathol. 35:498–502. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Guilleret I and Benhattar J: Demethylation
of the human telomerase catalytic subunit (hTERT) gene promoter
reduced hTERT expression and telomerase activity and shortened
telomeres. Exp Cell Res. 289:326–334. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Guilleret I and Benhattar J: Unusual
distribution of DNA methylation within the hTERT CpG island in
tissues and cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 325:1037–1043.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Tallet A, Nault JC, Renier A, Hysi I,
Galateau-Sallé F, Cazes A, Copin MC, Hofman P, Andujar P, Le
Pimpec-Barthes F, et al: Overexpression and promoter mutation of
the TERT gene in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Oncogene.
33:3748–3752. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
191
|
Campanella NC, Silva EC, Dix G, de Lima
Vazquez F, Escremim de Paula F, Berardinelli GN and Balancin M:
Mutational profiling of driver tumor suppressor and oncogenic genes
in Brazilian malignant pleural mesotheliomas. Pathobiology.
87:208–216. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Pestana A, Vinagre J, Sobrinho-Simões M
and Soares P: TERT biology and function in cancer: Beyond
immortalisation. J Mol Endocrinol. 58:R129–R146. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Sato T and Sekido Y: NF2/Merlin
inactivation and potential therapeutic targets in mesothelioma. Int
J Mol Sci. 19:9882018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Huang DS, Wang Z, He XJ, Diplas BH, Yang
R, Killela PJ, Meng Q, Ye ZY, Wang W, Jiang XT, et al: Recurrent
TERT promoter mutations identified in a large-scale study of
multiple tumour types are associated with increased TERT expression
and telomerase activation. Eur J Cancer. 51:969–976. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Rachakonda PS, Hosen I, de Verdier PJ,
Fallah M, Heidenreich B, Ryk C, Wiklund NP, Steineck G, Schadendorf
D, Hemminki K and Kumar R: TERT promoter mutations in bladder
cancer affect patient survival and disease recurrence through
modification by a common polymorphism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:17426–17431. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Borah S, Xi L, Zaug AJ, Powell NM, Dancik
GM, Cohen SB, Costello JC, Theodorescu D and Cech TR: Cancer. TERT
promoter mutations and telomerase reactivation in urothelial
cancer. Science. 347:1006–1010. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Lu VM, Goyal A, Lee A, Jentoft M,
Quinones-Hinojosa A and Chaichana KL: The prognostic significance
of TERT promoter mutations in meningioma: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Neurooncol. 142:1–10. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
198
|
Yang H, Park H, Ryu HJ, Heo J, Kim JS, Oh
YL, Choe JH, Kim JH, Kim JS, Jang HW, et al: Frequency of TERT
promoter mutations in real-world analysis of 2,092 thyroid
carcinoma patients. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 37:652–663. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Ramlee MK, Wang J, Toh WX and Li S:
Transcription regulation of the human telomerase reverse
transcriptase (hTERT) Gene. Genes (Basel). 7:502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Hannen R and Bartsch JW: Essential roles
of telomerase reverse transcriptase hTERT in cancer stemness and
metastasis. FEBS Lett. 592:2023–2031. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Heidenreich B, Rachakonda PS, Hosen I,
Volz F, Hemminki K, Weyerbrock A and Kumar R: TERT promoter
mutations and telomere length in adult malignant gliomas and
recurrences. Oncotarget. 6:10617–10633. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Ivanov SV, Miller J, Lucito R, Tang C,
Ivanova AV, Pei J, Carbone M, Cruz C, Beck A, Webb C, et al:
Genomic events associated with progression of pleural malignant
mesothelioma. Int J Cancer. 124:589–599. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
203
|
Chiba K, Lorbeer FK, Shain AH, McSwiggen
DT, Schruf E, Oh A, Ryu J, Darzacq X, Bastian BC and Hockemeyer D:
Mutations in the promoter of the telomerase gene TERT contribute to
tumorigenesis by a two-step mechanism. Science. 357:1416–1420.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Nickerson ML, Dancik GM, Im KM, Edwards
MG, Turan S, Brown J, Ruiz-Rodriguez C, Owens C, Costello JC, Guo
G, et al: Concurrent alterations in TERT, KDM6A, and the BRCA
pathway in bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:4935–4948. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Fujimoto A, Furuta M, Shiraishi Y, Gotoh
K, Kawakami Y, Arihiro K, Nakamura T, Ueno M, Ariizumi S, Nguyen
HH, et al: Whole-genome mutational landscape of liver cancers
displaying biliary phenotype reveals hepatitis impact and molecular
diversity. Nat Commun. 6:61202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Kwon J, Lee D and Lee SA: BAP1 as a
guardian of genome stability: Implications in human cancer. Exp Mol
Med. 55:745–754. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Carbone M, Adusumilli PS, Alexander HR Jr,
Baas P, Bardelli F, Bononi A, Bueno R, Felley-Bosco E,
Galateau-Salle F, Jablons D, et al: Mesothelioma: Scientific clues
for prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. CA Cancer J Clin.
69:402–429. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Baumann F, Flores E, Napolitano A, Kanodia
S, Taioli E, Pass H, Yang H and Carbone M: Mesothelioma patients
with germline BAP1 mutations have 7-fold improved long-term
survival. Carcinogenesis. 36:76–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
209
|
Bueno R, Stawiski EW, Goldstein LD,
Durinck S, De Rienzo A, Modrusan Z, Gnad F, Nguyen TT, Jaiswal BS,
Chirieac LR, et al: Comprehensive genomic analysis of malignant
pleural mesothelioma identifies recurrent mutations, gene fusions
and splicing alterations. Nat Genet. 48:407–416. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Johanns TM, Fu Y, Kobayashi DK, Mei Y,
Dunn IF, Mao DD, Kim AH and Dunn GP: High incidence of TERT
mutation in brain tumor cell lines. Brain Tumor Pathol. 33:222–227.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Landa I, Ganly I, Chan TA, Mitsutake N,
Matsuse M, Ibrahimpasic T, Ghossein RA and Fagin JA: Frequent
somatic TERT promoter mutations in thyroid cancer: Higher
prevalence in advanced forms of the disease. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 98:E1562–E1566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Spiegl-Kreinecker S, Lötsch D, Neumayer K,
Kastler L, Gojo J, Pirker C, Pichler J, Weis S, Kumar R, Webersinke
G, et al: TERT promoter mutations are associated with poor
prognosis and cell immortalization in meningioma. Neuro Oncol.
20:1584–1593. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Zanetti M: A second chance for telomerase
reverse transcriptase in anticancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 14:115–128. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
214
|
Watanabe Y, Kojima T, Kagawa S, Uno F,
Hashimoto Y, Kyo S, Mizuguchi H, Tanaka N, Kawamura H, Ichimaru D,
et al: A novel translational approach for human malignant pleural
mesothelioma: Heparanase-assisted dual virotherapy. Oncogene.
29:1145–1154. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
215
|
Sterman DH, Recio A, Vachani A, Sun J,
Cheung L, DeLong P, Amin KM, Litzky LA, Wilson JM, Kaiser LR and
Albelda SM: Long-term follow-up of patients with malignant pleural
mesothelioma receiving high-dose adenovirus herpes simplex
thymidine kinase/ganciclovir suicide gene therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
11:7444–7453. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Molnar-Kimber KL, Sterman DH, Chang M,
Kang EH, ElBash M, Lanuti M, Elshami A, Gelfand K, Wilson JM,
Kaiser LR and Albelda SM: Impact of preexisting and induced humoral
and cellular immune responses in an adenovirus-based gene therapy
phase I clinical trial for localized mesothelioma. Hum Gene Ther.
9:2121–2133. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Sterman DH, Recio A, Carroll RG, Gillespie
CT, Haas A, Vachani A, Kapoor V, Sun J, Hodinka R, Brown JL, et al:
A phase I clinical trial of single-dose intrapleural IFN-beta gene
transfer for malignant pleural mesothelioma and metastatic pleural
effusions: High rate of antitumor immune responses. Clin Cancer
Res. 13(15 Pt 1): 4456–4466. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Kawashima T, Kagawa S, Kobayashi N,
Shirakiya Y, Umeoka T, Teraishi F, Taki M, Kyo S, Tanaka N and
Fujiwara T: Telomerase-specific replication-selective virotherapy
for human cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10(1 Pt 1): 285–292. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Taki M, Kagawa S, Nishizaki M, Mizuguchi
H, Hayakawa T, Kyo S, Nagai K, Urata Y, Tanaka N and Fujiwara T:
Enhanced oncolysis by a tropism-modified telomerase-specific
replication-selective adenoviral agent OBP-405 ('Telomelysin-RGD').
Oncogene. 24:3130–3140. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Lin D, Shen Y and Liang T: Oncolytic
virotherapy: Basic principles, recent advances and future
directions. Sig Transduct Target Ther. 8:1562023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
221
|
Nemunaitis J, Tong AW, Nemunaitis M,
Senzer N, Phadke AP, Bedell C, Adams N, Zhang YA, Maples PB, Chen
S, et al: A phase I study of telomerase-specific replication
competent oncolytic adenovirus (telomelysin) for various solid
tumors. Mol Ther. 18:429–434. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
222
|
Kishimoto H, Zhao M, Hayashi K, Urata Y,
Tanaka N, Fujiwara T, Penman S and Hoffman RM: In vivo internal
tumor illumination by telomerase-dependent adenoviral GFP for
precise surgical navigation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:14514–14517. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Uno F, Fujiwara T, Takata Y, Ohtani S,
Katsuda K, Takaoka M, Ohkawa T, Naomoto Y, Nakajima M and Tanaka N:
Antisense-mediated suppression of human heparanase gene expression
inhibits pleural dissemination of human cancer cells. Cancer Res.
61:7855–7860. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Kiyokawa J, Kawamura Y, Ghouse SM, Acar S,
Barçın E, Martínez-Quintanilla J, Martuza RL, Alemany R, Rabkin SD,
Shah K and Wakimoto H: Modification of extracellular matrix
enhances oncolytic adenovirus immunotherapy in glioblastoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 27:889–902. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
225
|
Eikenes L, Bruland ØS, Brekken C and
Davies Cde L: Collagenase increases the transcapillary pressure
gradient and improves the uptake and distribution of monoclonal
antibodies in human osteosarcoma xenografts. Cancer Res.
64:4768–4773. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
McKenzie EA: Heparanase: A target for drug
discovery in cancer and inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 151:1–14.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Blackburn JS, Rhodes CH, Coon CI and
Brinckerhoff CE: RNA interference inhibition of matrix
metalloproteinase-1 prevents melanoma metastasis by reducing tumor
collagenase activity and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 67:10849–10858.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Fitzgerald M, Hayward IP, Thomas AC,
Campbell GR and Campbell JH: Matrix metalloproteinase can
facilitate the heparanase-induced promotion of phenotype change in
vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis. 145:97–106. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Shirakawa Y, Tazawa H, Tanabe S, Kanaya N,
Noma K, Koujima T, Kashima H, Kato T, Kuroda S, Kikuchi S, et al:
Phase I dose-escalation study of endoscopic intratumoral injection
of OBP-301 (Telomelysin) with radiotherapy in oesophageal cancer
patients unfit for standard treatments. Eur J Cancer. 153:98–108.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Heo J, Liang JD, Kim CW, Woo HY, Shih IL,
Su TH, Lin ZZ, Yoo SY, Chang S, Urata Y and Chen PJ: Safety and
dose escalation of the targeted oncolytic adenovirus OBP-301 for
refractory advanced liver cancer: Phase I clinical trial. Mol Ther.
31:2077–2088. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Yamada N, Oizumi S, Kikuchi E, Shinagawa
N, Konishi-Sakakibara J, Ishimine A, Aoe K, Gemba K, Kishimoto T,
Torigoe T and Nishimura M: CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
predict favorable prognosis in malignant pleural mesothelioma after
resection. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 59:1543–1549. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Ranki T, Joensuu T, Jäger E, Karbach J,
Wahle C, Kairemo K, Alanko T, Partanen K, Turkki R, Linder N, et
al: Local treatment of a pleural mesothelioma tumor with ONCOS-102
induces a systemic antitumor CD8+ T-cell response,
prominent infiltration of CD8+ lymphocytes and Th1 type
polarization. OncoImmunology. 3:e9589372014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
233
|
Alley EW, Lopez J, Santoro A, Morosky A,
Saraf S, Piperdi B and van Brummelen E: Clinical safety and
activity of pembrolizumab in patients with malignant pleural
mesothelioma (KEYNOTE-028): Preliminary results from a
non-randomised, open-label, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol.
18:623–630. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Quispel-Janssen J, van der Noort V, de
Vries JF, Zimmerman M, Lalezari F, Thunnissen E, Monkhorst K,
Schouten R, Schunselaar L, Disselhorst M, et al: Programmed death 1
blockade with nivolumab in patients with recurrent malignant
pleural mesothelioma. J Thorac Oncol. 13:1569–1576. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Sharma P, Hu-Lieskovan S, Wargo JA and
Ribas A: Primary, adaptive, and acquired resistance to cancer
immunotherapy. Cell. 168:707–723. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Wang L, Geng H, Liu Y, Liu L, Chen Y, Wu
F, Liu Z, Ling S, Wang Y and Zhou L: Hot and cold tumors:
Immunological features and the therapeutic strategies. MedComm
(2020). 4:e3432023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Harber J, Kamata T, Pritchard C and
Fennell D: Matter of TIME: The tumor-immune microenvironment of
mesothelioma and implications for checkpoint blockade efficacy. J
Immunother Cancer. 9:e0030322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Nasti TH and Eberhardt CS: Vaccination
against cancer or infectious agents during checkpoint inhibitor
therapy. Vaccines (Basel). 9:13962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Negrini S, De Palma R and Filaci G:
Anti-cancer immunotherapies targeting telomerase. Cancers (Basel).
12:22602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Middleton G, Silcocks P, Cox T, Valle J,
Wadsley J, Propper D, Coxon F, Ross P, Madhusudan S, Roques T, et
al: Gemcitabine and capecitabine with or without telomerase peptide
vaccine GV1001 in patients with locally advanced or metastatic
pancreatic cancer (TeloVac): An open-label, randomised, phase 3
trial. Lancet Oncol. 15:829–840. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Hunger RE, Kernland Lang K, Markowski CJ,
Trachsel S, Møller M, Eriksen JA, Rasmussen AM, Braathen LR and
Gaudernack G: Vaccination of patients with cutaneous melanoma with
telomerase-specific peptides. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
60:1553–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Collins JM, Redman JM and Gulley JL:
Combining vaccines and immune checkpoint inhibitors to prime,
expand, and facilitate effective tumor immunotherapy. Expert Rev
Vaccines. 17:697–705. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Fan T, Zhang M, Yang J, Zhu Z, Cao W and
Dong C: Therapeutic cancer vaccines: Advancements, challenges and
prospects. Sig Transduct Target Ther. 8:4502023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
244
|
Tumeh PC, Harview CL, Yearley JH, Shintaku
IP, Taylor EJM, Robert L, Chmielowski B, Spasic M, Henry G, Ciobanu
V, et al: PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive
immune resistance. Nature. 515:568–571. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
245
|
Haakensen VD, Nowak AK, Ellingsen EB,
Farooqi SJ, Bjaanæs MM, Horndalsveen H, Mcculloch T, Grundberg O,
Cedres SM and Helland Å: NIPU: A randomised, open-label, phase II
study evaluating nivolumab and ipilimumab combined with UV1
vaccination as second line treatment in patients with malignant
mesothelioma. J Transl Med. 19:2322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Lorigan P, Medina T, Nyakas M, Rutten A,
Feun LG, Cowey CL, Payne M, Hussain I, Kuze T, O'Day S, et al:
Ipilimumab and nivolumab plus UV1, an anticancer vaccination
against telomerase, in advanced melanoma. J Chin Oncol.
42(17_suppl): LBA95192024.
|
|
247
|
Buchbinder EI and Desai A: CTLA-4 and PD-1
pathways: Similarities, differences, and implications of their
inhibition. Am J Clin Oncol. 39:98–106. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
248
|
Wei SC, Sharma R, Anang NAS, Levine JH,
Zhao Y, Mancuso JJ, Setty M, Sharma P, Wang J, Pe'er D and Allison
JP: Negative Co-stimulation constrains T cell differentiation by
imposing boundaries on possible cell states. Immunity.
50:1084–1098.e10. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Wei SC, Levine JH, Cogdill AP, Zhao Y,
Anang NAS, Andrews MC, Sharma P, Wang J, Wargo JA, Pe'er D and
Allison JP: Distinct cellular mechanisms underlie Anti-CTLA-4 and
Anti-PD-1 checkpoint blockade. Cell. 170:1120–1133.e17. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Lilleby W, Gaudernack G, Brunsvig PF,
Vlatkovic L, Schulz M, Mills K, Hole KH and Inderberg EM: Phase
I/IIa clinical trial of a novel hTERT peptide vaccine in men with
metastatic hormone-naive prostate cancer. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 66:891–901. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Brunsvig PF, Guren TK, Nyakas M,
Steinfeldt-Reisse CH, Rasch W, Kyte JA, Juul HV, Aamdal S,
Gaudernack G and Inderberg EM: Long-term outcomes of a phase I
study with UV1, a second generation telomerase based vaccine, in
patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Front Immunol.
11:5721722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
Aamdal E, Jacobsen KD, Straume O, Kersten
C, Herlofsen O, Karlsen J, Hussain I, Amundsen A, Dalhaug A, Nyakas
M, et al: Ipilimumab in a real-world population: A prospective
phase IV trial with long-term follow-up. Int J Cancer. 150:100–111.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
253
|
Labby ZE, Straus C, Caligiuri P, MacMahon
H, Li P, Funaki A, Kindler HL and Armato SG III: Variability of
tumor area measurements for response assessment in malignant
pleural mesothelioma. Med Phys. 40:0819162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
254
|
Thunold S, Hernes E, Farooqi S, Öjlert ÅK,
Francis RJ, Nowak AK, Szejniuk WM, Nielsen SS, Cedres S, Perdigo
MS, et al: Outcome prediction based on [18F]FDG PET/CT in patients
with pleural mesothelioma treated with ipilimumab and nivolumab +/−
UV1 telomerase vaccine. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 52:693–707.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
255
|
Creff G, Devillers A, Depeursinge A,
Palard-Novello X, Acosta O, Jegoux F and Castelli J: Evaluation of
the prognostic value of FDG PET/CT parameters for patients with
surgically treated head and neck cancer: A systematic review. JAMA
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 146:471–479. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
256
|
Im HJ, Oo S, Jung W, Jang JY, Kim SW,
Cheon GJ, Kang KW, Chung JK, Kim EE and Lee DS: Prognostic value of
metabolic and volumetric parameters of preoperative FDG-PET/CT in
patients with resectable pancreatic cancer. Medicine (Baltimore).
95:e36862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
257
|
Yenigün BM, Kahya Y, Soydal Ç, Ata Tutkun
N, Kocaman G, Koçak EM, Özkan E, Dizbay Sak S and Kayı Cangır A:
The prognostic value of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission
tomography/computed tomography parameters in patients with
malignant pleural mesothelioma. Turk Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi
Derg. 29:92–100. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
258
|
Bagchi S, Yuan R and Engleman EG: Immune
checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of cancer: Clinical impact
and mechanisms of response and resistance. Annu Rev Pathol.
16:223–249. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|