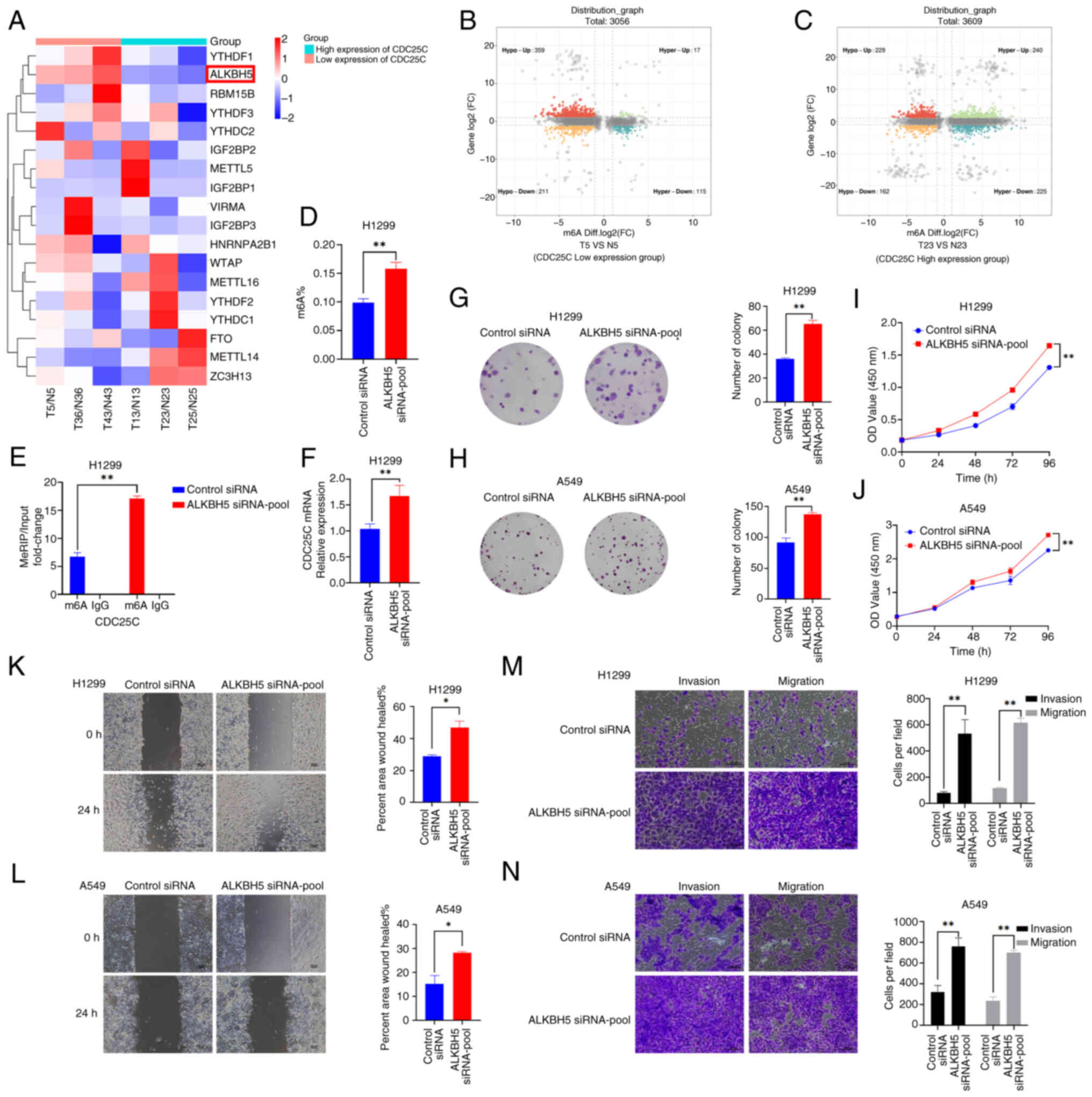
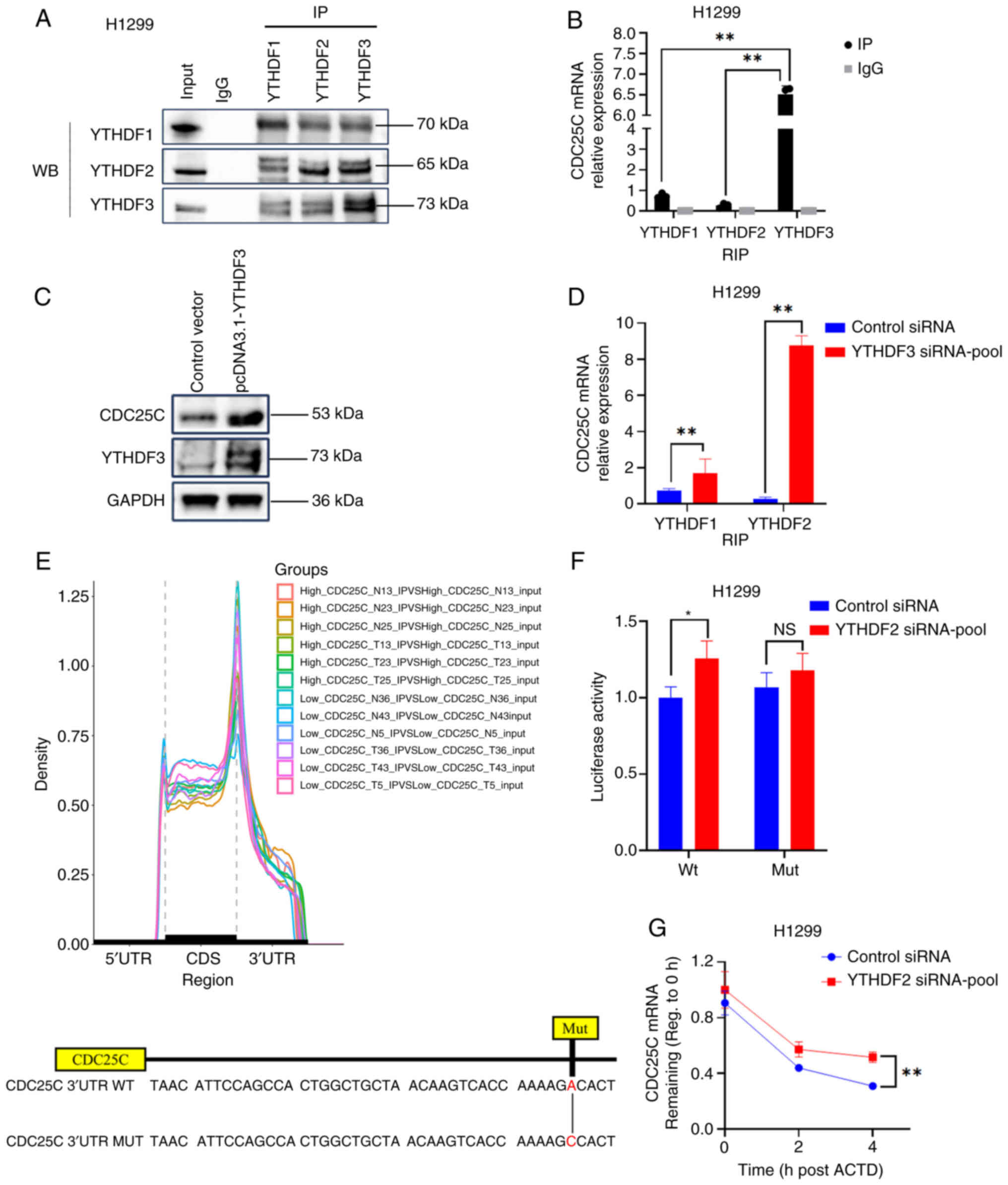
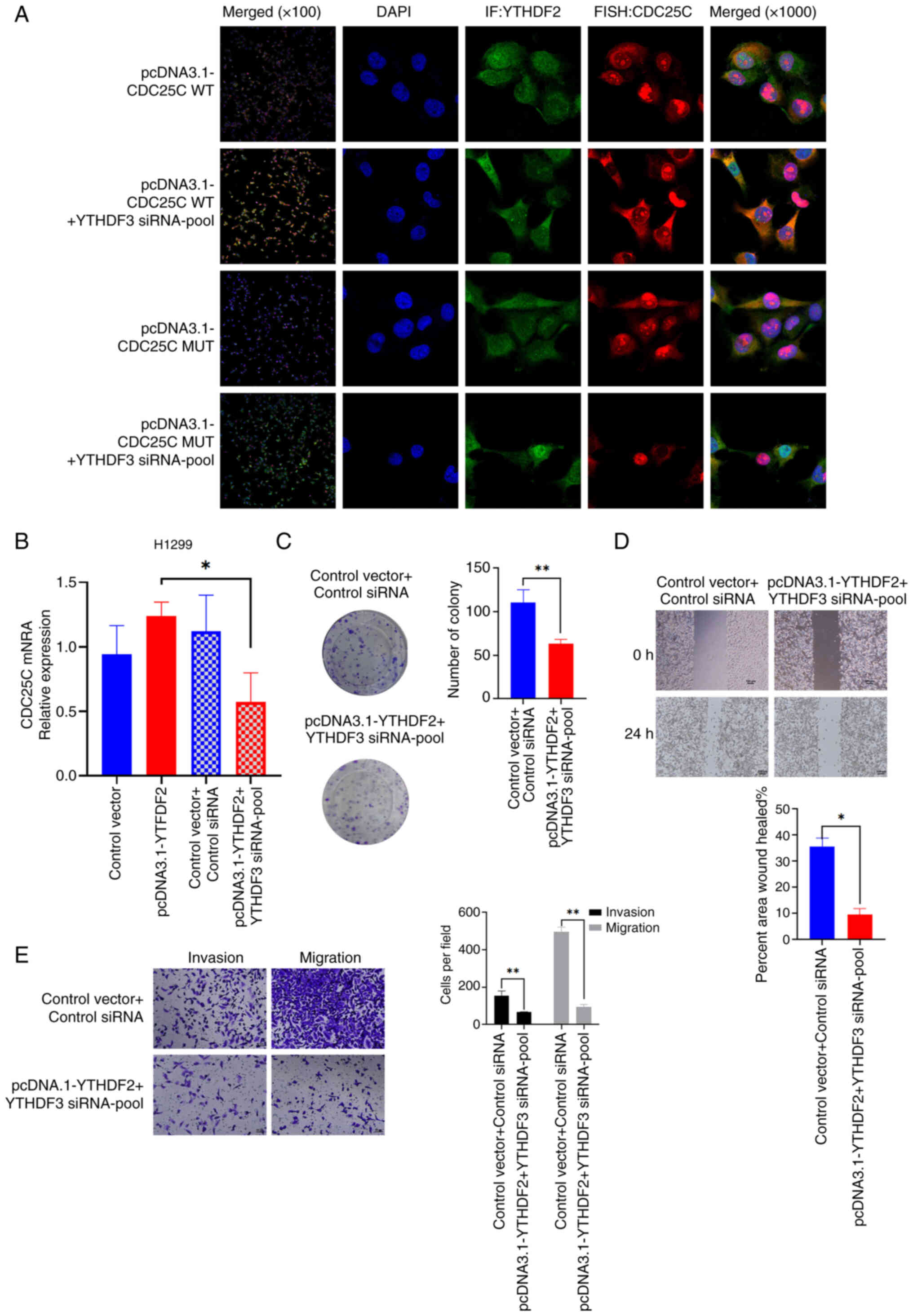
|
1
|
Del Campo JM, Maroto S, Sebastian L,
Sebastian L, Vaillo X, Bolufer S, Lirio F, Sesma J and Galvez C:
Uniportal VATS for diagnosis and staging in non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC). Diagnostics (Basel). 13:8262023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mathieu LN, Larkins E, Sinha AK,
Mishra-Kalyani PS, Jafri S, Kalavar S, Ghosh S, Goldberg KB, Pazdur
R, Beaver JA and Singh H: FDA approval summary: Atezolizumab as
adjuvant treatment following surgical resection and platinum-based
chemotherapy for stage II TO IIIA NSCLC. Clin Cancer Res.
29:2973–2978. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen Y, Li H, Zhang W, Qi W, Lu C, Huang
H, Yang Z, Liu B and Zhang L: Sesamin suppresses NSCLC cell
proliferation through cyclin D1 inhibition-dependent cell cycle
arrest via Akt/p53 pathway [Toxicology and applied pharmacology,
387 (2020) 114848]. Toxicol Appl Pharm. 400:1150482020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yang T, Xiao Y, Liu S, Luo F, Tang D, Yu Y
and Xie Y: Isorhamnetin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by
triggering DNA damage and regulating the AMPK/mTOR/p70S6K signaling
pathway in doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer. Phytomedicine.
114:1547802023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li R, Zheng C, Shiu PH, Rangsinth P, Wang
W, Kwan YW, Wong ES, Zhang Y, Li J and Leung GP: Garcinone E
triggers apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human colorectal cancer
cells by mediating a reactive oxygen species-dependent JNK
signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 162:1146172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bazzaz R, Bijanpour H, Pirouzpanah SMB,
Yaghmaei P and Rashtchizadeh N: Adjuvant therapy with
γ-tocopherol-induce apoptosis in HT-29 colon cancer via
cyclin-dependent cell cycle arrest mechanism. J Biochem Mol Toxic.
33:e223992019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tao L, Cao YZ, Wei ZH, Jia Q, Yu S, Zhong
J, Wang A, Woodgett JR and Lu Y: Xanthatin triggers Chk1-mediated
DNA damage response and destabilizes Cdc25C lysosomal degradation
in lung cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharm. 337:85–94. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang JN, Zhang ZR, Che Y, Yuan ZY, Lu ZL,
Li Y, Li N, Wan J, Sun HD, Sun N, et al: Acetyl-macrocalin B, an
-kaurane diterpenoid, initiates apoptosis through the
ROS-p38-caspase 9-dependent pathway and induces G2/M phase arrest
via the Chk1/2-Cdc25C-Cdc2/cyclin B axis in non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 19:609–621. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Senju M, Sueoka N, Sato A, Iwanaga K,
Sakao Y, Tomimitsu S, Tominaga M, Irie K, Hayashi S and Sueoka E:
Hsp90 inhibitors cause G2/M arrest associated with the reduction of
Cdc25C and Cdc2 in lung cancer cell lines. J Cancer Res Clin.
132:150–158. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhou Q and Chen T: BI6727, a polo-like
kinase 1 inhibitor, synergizes with gefitinib to suppress
hepatocellular carcinoma cells via a G2/M arrest mechanism.
Pharmazie. 77:230–235. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao Y, Wu Z, Zhang Y and Zhu L: HY-1
induces G2/M cell cycle arrest in human colon cancer cells through
the ATR-Chk1-Cdc25C and weel pathways. Cancer Sci. 104:1062–1066.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu K, Zheng MY, Lu R, Du J, Zhao Q, Li Z,
Li Y and Zhang S: The role of CDC25C in cell cycle regulation and
clinical cancer therapy: A systematic review. Cancer Cell Int.
20:2132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang M, Hu X, Tang B and Deng FM:
Exploring the interplay between methylation patterns and non-coding
RNAs in non-small cell lung cancer: Implications for pathogenesis
and therapeutic targets. Heliyon. 10:e248112024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
He Y, Hu H, Wang YD, Yuan H, Lu Z, Wu P,
Liu D, Tian L, Yin J, Jiang K and Miao Y: ALKBH5 inhibits
pancreatic cancer motility by decreasing long non-coding RNA
KCNK15-AS1 methylation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:838–846. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang P, Wang Q, Liu A, Zhu J and Feng J:
ALKBH5 holds prognostic values and inhibits the metastasis of colon
cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 26:1615–1623. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gao Y, Pei G, Li D, Li R, Shao Y, Zhang QC
and Li P: Multivalent m6A motifs promote phase
separation of YTHDF proteins. Cell Res. 29:767–769. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sheikhshabani SH, Modarres P,
Ghafouri-Fard S, Amini-Farsani Z, Khodaee L, Shaygan N,
Amini-Farsani Z and Omrani MD: Meta-analysis of microarray data to
determine gene indicators involved in cisplatin resistance in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 7:e19702024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Koh YW, Han JH, Haam S and Lee HW:
Prognostic and predictive value of YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 and their
correlation with tumor-infiltrating immune cells in non-small cell
carcinoma. Front Oncol. 12:9966342022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wen J, Xue L, Wei Y, Liang J, Jia W, Yong
T, Chu T, Li H, Han S, Liao J, et al: YTHDF2 is a therapeutic
target for HCC by suppressing immune evasion and angiogenesis
through ETV5/PD-L1/VEGFA Axis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e23072422024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun S, Liu Y, Zhou M, Wen J, Xue L, Han S,
Liang J, Wang Y, Wei Y, Yu J, et al: PA2G4 promotes the metastasis
of hepatocellular carcinoma by stabilizing FYN mRNA in a
YTHDF2-dependent manner. Cell Biosci. 12:552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fang Y, Wu X, Gu Y, Shi R, Yu T, Pan Y,
Zhang J, Jing X, Ma P and Shu Y: LINC00659 cooperated with ALKBH5
to accelerate gastric cancer progression by stabilising JAK1 mRNA
in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Clin Transl Med.
13:e12052023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang M, Liu Z, Fang X, Cong X and Hu Y:
The emerging role of m6A modification of non-coding RNA
in gastrointestinal cancers: A comprehensive review. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 11:12645522023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Jin Z, Sheng J, Hu Y, Zhang Y, Wang X and
Huang Y: Shining a spotlight on m6A and the vital role
of RNA modification in endometrial cancer: A review. Front Genet.
14:12473092023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Devarajan E and Huang S: STAT3 as a
central regulator of tumor metastases. Curr Mol Med. 9:626–633.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee H, Jeong AJ and Ye SK: Highlighted
STAT3 as a potential drug target for cancer therapy. BMB Rep.
52:415–423. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Egusquiaguirre SP, Yeh JE, Walker SR, Liu
S and Frank DA: The STAT3 target gene TNFRSF1A modulates the NF-κB
pathway in breast cancer cells. Neoplasia. 20:489–498. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ren Y, Li S, Zhu R, Wan C, Song D, Zhu J,
Cai G, Long S, Kong L and Yu L: Discovery of STAT3 and histone
deacetylase (HDAC) dual-pathway inhibitors for the treatment of
solid cancer. J Med Chem. 64:7468–7482. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen H, Zhou W, Bian A, Zhang Q, Miao Y,
Yin X, Ye J, Xu S, Ti C, Sun Z, et al: Selectively targeting STAT3
using a small molecule inhibitor is a potential therapeutic
strategy for pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 29:815–830. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bai W, Xiao G, Xie G, Chen Z, Xu X, Zeng J
and Xie J: METTL3/IGF2BP1 influences the development of
non-small-cell lung cancer by mediating m6A methylation
modification of TRPV1. Thorac Cancer. 15:1871–1881. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ji X, Wan X, Sun H, Deng Q, Meng S, Xie B
and Zhou S: METTL14 enhances the m6A modification level
of lncRNA MSTRG.292666.16 to promote the progression of non-small
cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 24:612024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lu H, Ai J, Zheng Y, Zhou W, Zhang L, Zhu
Z, Zhang H and Wang S: IGFBP2/ITGA5 promotes gefitinib resistance
via activating STAT3/CXCL1 axis in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell
Death Dis. 15:4472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang KL, Yeh TY, Hsu PC, Wong TH, Liu JR,
Chern JW, Lin MH and Yu CW: Discovery of novel anaplastic lymphoma
kinase (ALK) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) dual inhibitors
exhibiting antiproliferative activity against non-small cell lung
cancer. J Enzym Inhib Med Chem. 39:23186452024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yu HS, Liu J, Bu X, Ma Z, Yao Y, Li J,
Zhang T, Song W, Xiao X, Sun Y, et al: Targeting METTL3 reprograms
the tumor microenvironment to improve cancer immunotherapy. Cell
Chem Biol. 31:776–791.e7. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang Q, Huang YF, Jiang M, Tang Y, Wang Q,
Bai L, Yu C, Yang X, Ding K, Wang W, et al: The demethylase ALKBH5
mediates ZKSCAN3 expression through the m6A modification
to activate VEGFA transcription and thus participates in
MNNG-induced gastric cancer progression. J Hazard Mater.
473:1346902024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Song K, Cao Q, Yang Y, Zuo Y and Wu X:
ALKBH5 modulates bone cancer pain in a rat model by suppressing
NR2B expression. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 71:1105–1115. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang S, Zhu X, Hao Y, Su TT and Shi W:
ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification of circFOXP1 promotes
gastric cancer progression by regulating SOX4 expression and
sponging miR-338-3p. Commun Biol. 7:5652024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Tang B, Yang Y, Kang M, Wang Y, Wang Y, Bi
Y, He S and Shimamoto F: m6A demethylase ALKBH5 inhibits
pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis by decreasing WIF-1 RNA methylation
and mediating Wnt signaling. Mol Cancer. 19:32020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang C, Samanta D, Lu H, Bullen JW, Zhang
H, Chen I, He X and Semenza GL: Hypoxia induces the breast cancer
stem cell phenotype by HIF-dependent and ALKBH5-mediated
m6 A-demethylation of NANOG mRNA. P Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:E2047–E2056. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang S, Zhao BS, Zhou A, Lin K, Zheng S,
Lu Z, Chen Y, Sulman EP, Xie K, Bögler O, et al: The m6A
hallmark of cancer: RNA demethylase ALKBH5 maintains tumorigenicity
of glioblastoma stem-like cells by sustaining FOXM1 expression and
cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 31:591–606.e6. 2017.
|
|
41
|
Jin D, Guo J, Wu Y, Yang L, Wang X, Du J,
Dai J, Chen W, Gong K, Miao S, et al: m6A demethylase
ALKBH5 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by reducing
YTHDFs-mediated YAP expression and inhibiting
miR-107/LATS2-mediated YAP activity in NSCLC. Mol Cancer.
19:402020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Luo Y, Zeng C, Ouyang Z, Zhu W, Wang J,
Chen Z, Xiao C, Wu G, Li L, Qian Y, et al: YTH domain family
protein 3 accelerates non-small cell lung cancer immune evasion
through targeting CD8+ T lymphocytes. Cell Death Discov.
10:3202024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lin Y, Jin X, Nie Q, Chen M, Guo W, Chen
L, Li Y, Chen X, Zhang W, Chen H, et al: YTHDF3 facilitates
triple-negative breast cancer progression and metastasis by
stabilizing ZEB1 mRNA in an m6 A-dependent manner. Ann
Transl Med. 10:832022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Chen J, Sun Y, Xu X, Wang D, He J, Zhou H,
Lu Y, Zeng J, Du F, Gong A and Xu M: YTH domain family 2
orchestrates epithelial-mesenchymal transition/proliferation
dichotomy in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 16:2259–2271.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wan F, Qiu F, Deng Y, Hu H, Zhang Y, Zhang
JY, Kuang P, Tian H, Wu D, Min H, et al: Knockdown of YTHDF2
initiates ERS induced apoptosis and cancer stemness suppression by
sustaining GLI2 stability in cervical cancer. Trans Oncol.
46:1019942024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zhao X, Lv S, Li N, Zou Q, Sun L and Song
T: YTHDF2 protein stabilization by the deubiquitinase OTUB1
promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation via PRSS8 mRNA
degradation. J Biol Chem. 300:107–152. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Yoon SH, Lee S, Kim HS, Song J, Baek M,
Ryu S, Lee HB, Moon HG, Noh DY, Jon S and Han W: NSDHL contributes
to breast cancer stem-like cell maintenance and tumor-initiating
capacity through TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in MCF-7 tumor
spheroid. BMC Cancer. 24:13702024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Qian J, Jiao Y, Wang G, Liu H, Cao X and
Yang H: Mechanism of TGF-β1 inhibiting Kupffer cell immune
responses in cholestatic cirrhosis. Exp Ther Med. 20:1541–1549.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zeng Q, Shi W, Xie L, Dai Y and Wei C:
TGF-β1/miR-30d-5p axis regulating the expression of EMT key factors
to induce apoptosis of lung cancer cells. Heliyon. 10:e378012024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Naik A and Thakur N: Epigenetic regulation
of TGF-βand vice versa in cancers-A review on recent developments.
Biochem Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1879:1892192024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Hu Z, Liu Y, Liu M, Zhang Y and Wang C:
Roles of TGF-β signalling pathway-related lncRNAs in cancer
(Review). Oncol Lett. 25:1072023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
da Silva Correia J, Miranda Y,
Austin-Brown N, Hsu J, Mathison J, Xiang R, Zhou H, Li Q, Han J and
Ulevitch RJ: Nod1-dependent control of tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:1840–1845. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Couturier-Maillard A, Secher T, Rehman A,
Normand S, De Arcangelis A, Haesler R, Huot L, Grandjean T,
Bressenot A, Delanoye-Crespin A, et al: NOD2-mediated dysbiosis
predisposes mice to transmissible colitis and colorectal cancer. J
Clin Invest. 123:700–711. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|