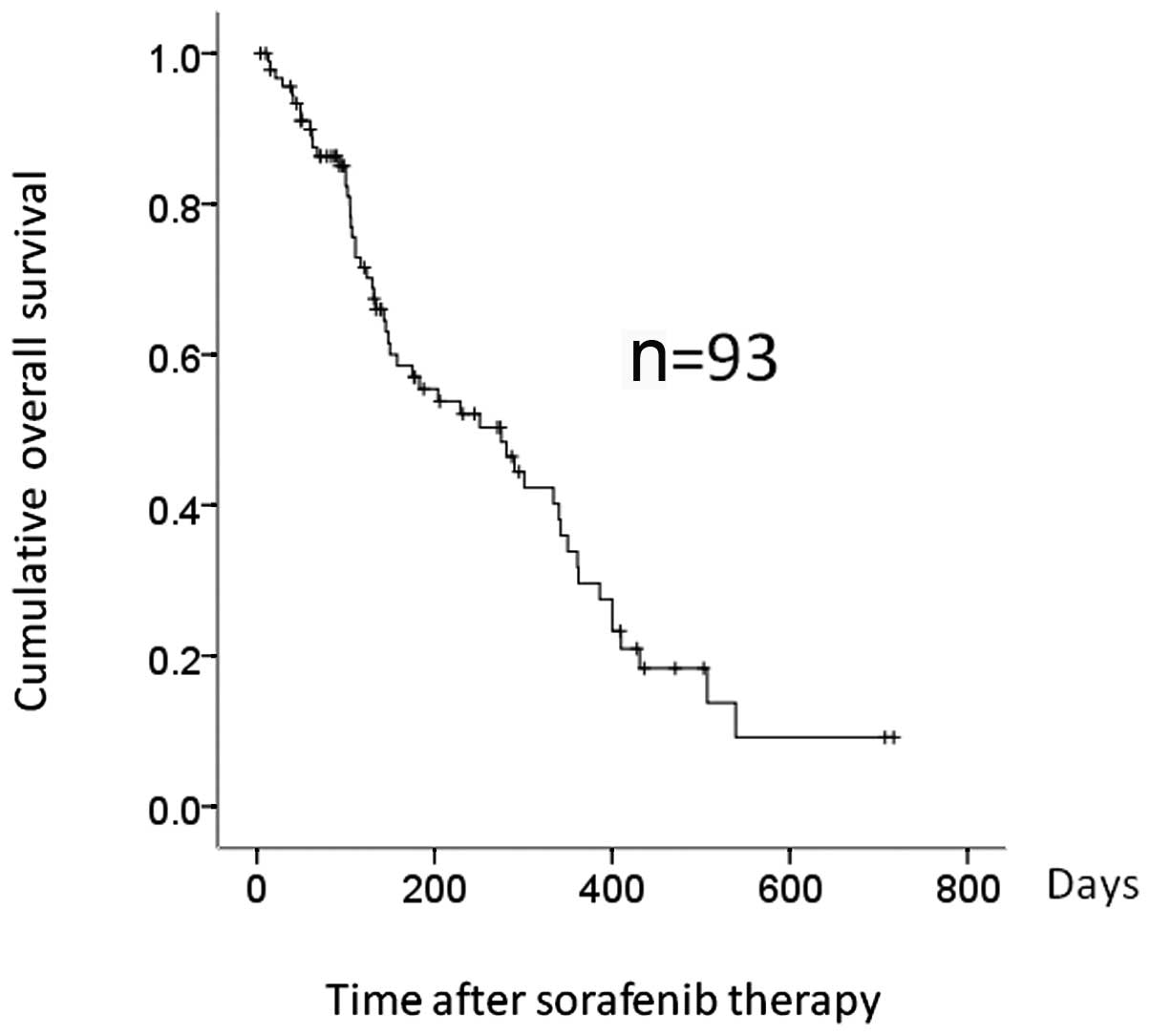
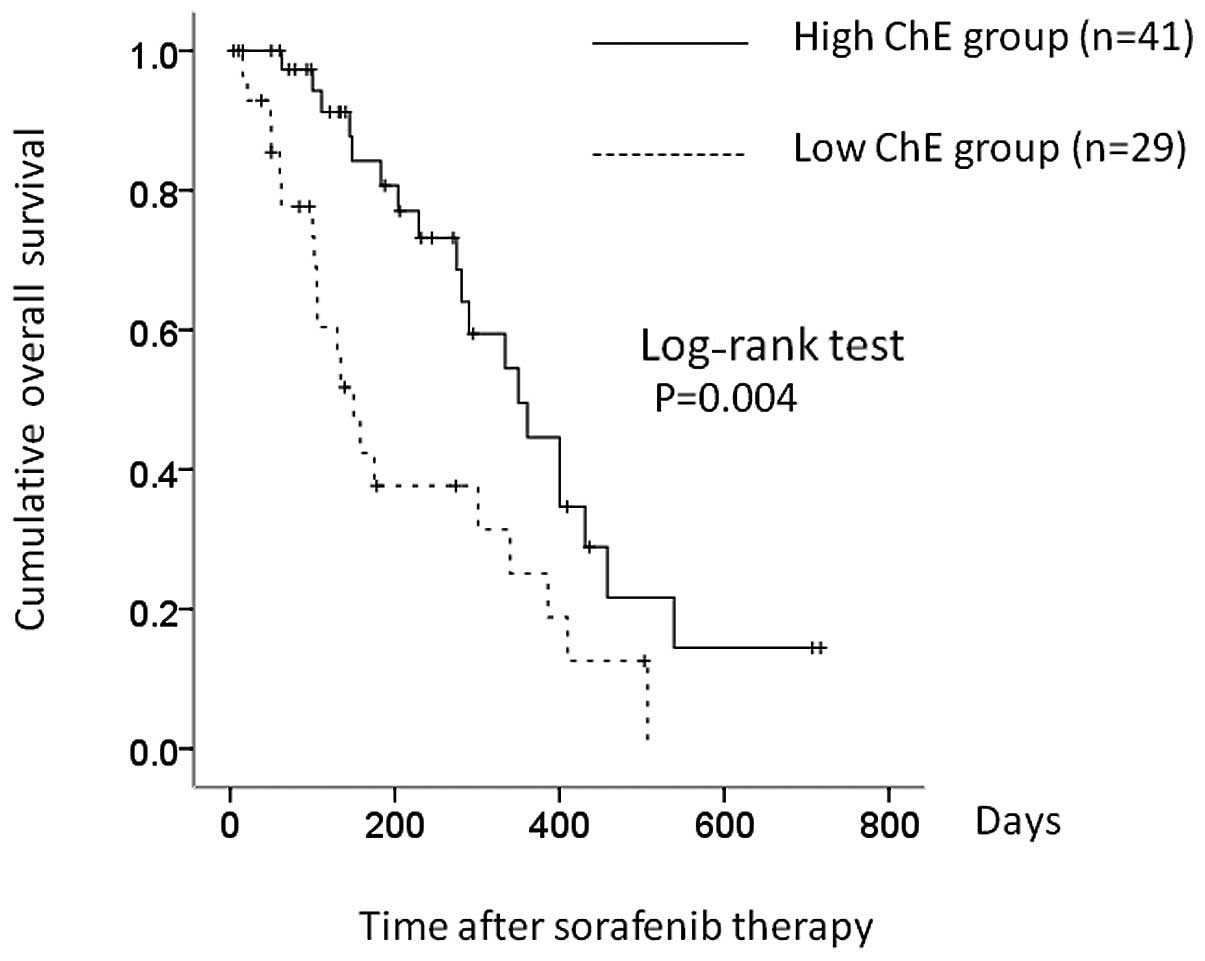
|
1
|
Nishikawa H, Osaki Y, Kita R and Kimura T:
Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma in Japan. Cancers. 4:165–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR,
Seitz JF, Borbath I, Häussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici
M, Voliotis D and Bruix J; SHARP Investigators Study Group:
Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med.
359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abou-Alfa GK, Schwartz L, Ricci S, Amadori
D, Santoro A, Figer A, De Greve J, Douillard JY, Lathia C, Schwartz
B, Taylor I, Moscovici M and Saltz LB: Phase II study of sorafenib
in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol.
24:4293–4300. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S,
Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, Xu J, Sun Y, Liang H, Liu J,
Wang J, Tak WY, Pan H, Burock K, Zou J, Voliotis D and Guan Z:
Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific
region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III
randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol.
10:25–34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D,
McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, Cao Y,
Shujath J, Gawlak S, Eveleigh D, Rowley B, Liu L, Adnane L, Lynch
M, Auclair D, Taylor I, Gedrich R, Voznesensky A, Riedl B, Post LE,
Bollag G and Trail PA: BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral
antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor
tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis.
Cancer Res. 64:7099–7109. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baek KK, Kim JH, Uhm JE, Park SH, Lee J,
Parl JO, Park YS, Kang WK and Lim HY: Prognostic factors in
patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with
sorafenib: a retrospective comparison with previously known
prognostic models. Oncology. 80:167–174. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Llovet JM, Peña CE, Lathia CD, Shan M,
Meinhardt G and Bruix J; Investigators SHARP Study Group: Plasma
biomarkers as predictors of outcome in patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 18:2290–2300. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Raoul JL, Bruix J, Greten TF, Sherman M,
Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Scherubl H, Scheulen ME, Germanidis G,
Dominguez S, Ricci S, Nadel A, Moscovici M, Voliotis D and Llovet
JM: Relationship between baseline hepatic status and outcome, and
effect of sorafenib on liver function: SHARP trial subanalyses. J
Hepatol. 56:1080–1088. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng AL, Guan Z, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S,
Kim JS, Yang TS, Tak WY, Pan H, Yu S, Xu J, Fang F, Zou J, Lentini
G, Voliotis D and Kang YK: Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in
patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma according to
baseline status: subset analyses of the phase III sorafenib
Asia-Pacific trial. Eur J Cancer. 48:1456–1465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ezzoukhry Z, Louandre C, Trécherel E,
Godin C, Chauffert B, Dupont S, Diouf M, Barbare JC, Mazière JC and
Galmiche A: EGFR activation is a potential determinant of primary
resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib. Int J
Cancer. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tsukui Y, Mochizuki H, Hoshino Y, Kawakami
S, Kuno T, Fukasawa Y, Iwamoto F, Hirose S, Yoshida T, Hosoda K,
Suzuki Y, Hosoda K, Kojima Y, Hirose Y, Shindou K, Matsuda M,
Yagawa S, Tawara A, Kobayashi M, Konishi T, Yamazaki T, Takahashi
S, Fujii H, Enomoto N and Omata M: Factors contributing to the
overall survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated
by sorafenib. Hepatogastroenterology. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Morimoto M, Numata K, Moriya S, Kondo M,
Nozaki A, Morioka Y, Maeda S and Tanaka K: Inflammation-based
prognostic score for hepatocellular carcinoma patients on sorafenib
treatment. Anticancer Res. 32:619–623. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mohri Y, Tanaka K, Ohi M, Yokoe T, Miki C
and Kusunoki M: Prognostic significance of host- and tumor-related
factors in patients with gastric cancer. World J Surg. 34:285–290.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Battisti V, Bagatini MD, Maders LD, Chiesa
J, Santos KF, Gonçalves JF, Abdalla FH, Battisti IE, Schetinger MR
and Morsch VM: Cholinesterase activities and biochemical
determinations in patients with prostate cancer: influence of
Gleason score, treatment and bone metastasis. Biomed Pharmacother.
66:249–255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mitsunaga S, Kinoshita T, Hasebe T,
Nakagohri T, Konishi M, Takahashi S, Gotohda N and Ochiai A: Low
serum level of cholinesterase at recurrence of pancreatic cancer is
a poor prognostic factor and relates to systemic disorder and nerve
plexus invasion. Pancreas. 36:241–248. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Morera Ocón FJ, Ripoll Orts F,
García-Granero Ximénez M, Pastor MJ and Bernal Sprekelsen JC:
Decrease of serum cholinesterase in colorectal cancer. Med Clin
(Barc). 129:729–730. 2007.(In Spanish).
|
|
17
|
Chougule A, Hussain S and Agarwal DP:
Prognostic and diagnostic value of serum pseudocholinesterase,
serum aspartate transaminase, and serum alinine transaminase in
malignancies treated by radiotherapy. J Cancer Res Ther. 4:21–25.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hamamoto Y, Niino K, Ishiyama H and Hosoya
T: Impact of pretreatment cholinesterase level on survival of
inoperable intrahepatic or hepatic-hilar carcinomas treated with
three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy. Radiat Med. 22:316–323.
2004.
|
|
19
|
Nishikawa H, Osaki Y, Inuzuka T, Takeda H,
Nakajima J, Matsuda F, Henmi S, Sakamoto A, Ishikawa T, Saito S,
Kita R and Kimura T: Branched-chain amino acid treatment before
transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular
carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 18:1379–1384. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kaibori M, Matsui K, Saito T and Kamiyama
Y: Risk factors for early death due to recurrence after resection
of large hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatogastroenterology.
55:2151–2156. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Weismüller TJ, Prokein J, Becker T,
Barg-Hock H, Klempnauer J, Manns MP and Strassburg CP: Prediction
of survival after liver transplantation by pre-transplant
parameters. Scand J Gastroenterol. 43:736–746. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Motta M, Giugno I, Ruello P, Pistone G, Di
Fazio I and Malaguarnera M: Lipoprotein (a) behaviour in patients
with hepatocellular carcinoma. Minerva Med. 92:301–305.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fernández Prieto RM, Ramallo Bravo A,
Carmona Carmona G and Carrasco Jiménez MS: Update on the current
role of plasma cholinesterase. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim.
58:508–516. 2011.(In Spanish).
|
|
24
|
Lencioni R and Llovet JM: Modified RECIST
(mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Seminars in
Liver Dis. 30:52–60. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA,
Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Van Glabbeke M, van
Oosterom AT, Christian MC and Gwyther SG: New guidelines to
evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors European
Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer
Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of
Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:205–216. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D and
Verweij J: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumors:
revised RECIST guideline (ver.1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Edeline J, Boucher E, Rolland Y, Vauléon
E, Pracht M, Perrin C, Le Roux C and Raoul JL: Comparison of tumor
response by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST)
and modified RECIST in patients treated with sorafenib for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 118:147–156. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Abbadessa G, Rimassa L, Pressiani T,
Carrillo-Infante C, Cucchi E and Santoro A: Optimized management of
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: four long-lasting responses to
sorafenib. World J Gastroenterol. 17:2450–2453. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Inuzuka T, Nishikawa H, Sekikawa A, Takeda
H, Henmi S, Sakamoto A, Saito S, Kita R, Kimura T, Osaki Y and Kudo
M: Complete response of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with
multiple lung metastases treated with sorafenib: case report.
Oncology. 81:152–157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sacco R, Bargellini I, Gianluigi G,
Bertini M, Bozzi E, Altomare E, Battaglia V, Romano A, Bertoni M,
Capria A, Bresci G and Bartolozzi C: Complete response for advanced
liver cancer during sorafenib therapy: case report. BMC
Gastroenterol. 11:42011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shao YY, Lin ZZ, Hsu C, Shen YC, Hsu CH
and Cheng AL: Early alpha-fetoprotein response predicts treatment
efficacy of antiangiogenic systemic therapy in patients with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 116:4590–4596. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Vincenzi B, Santini D, Russo A, Addeo R,
Giuliani F, Montella L, Rizzo S, Venditti O, Frezza AM, Caraglia M,
Colucci G, Del Prete S and Tonini G: Early skin toxicity as a
predictive factor for tumor control in hepatocellular carcinoma
patients treated with sorafenib. Oncologist. 15:85–92. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xiang ZL, Zeng ZC, Tang ZY, Fan J, He J,
Zeng HY and Zhu XD: Potential prognostic biomarkers for bone
metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncologist. 16:1028–1039.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|