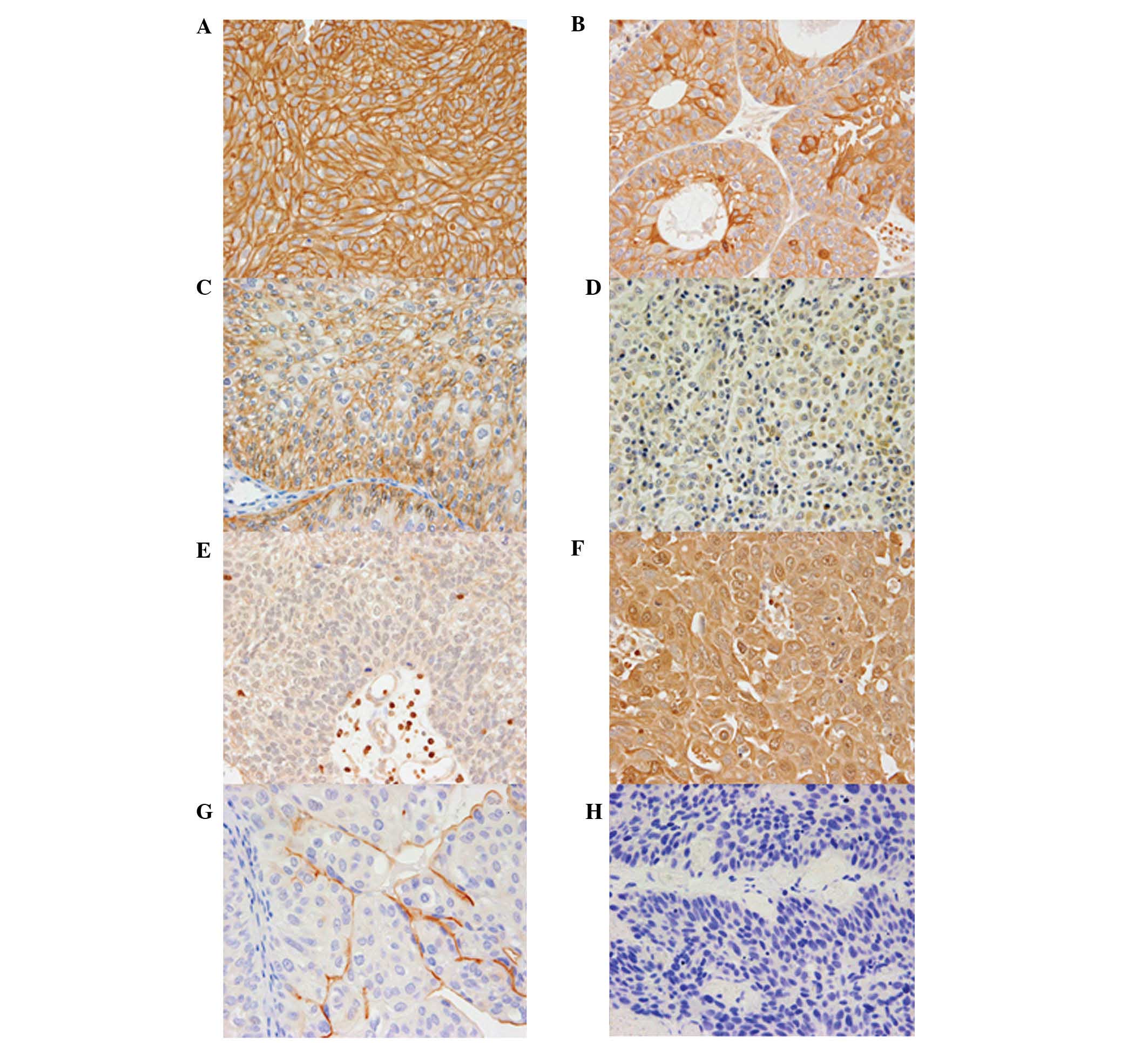
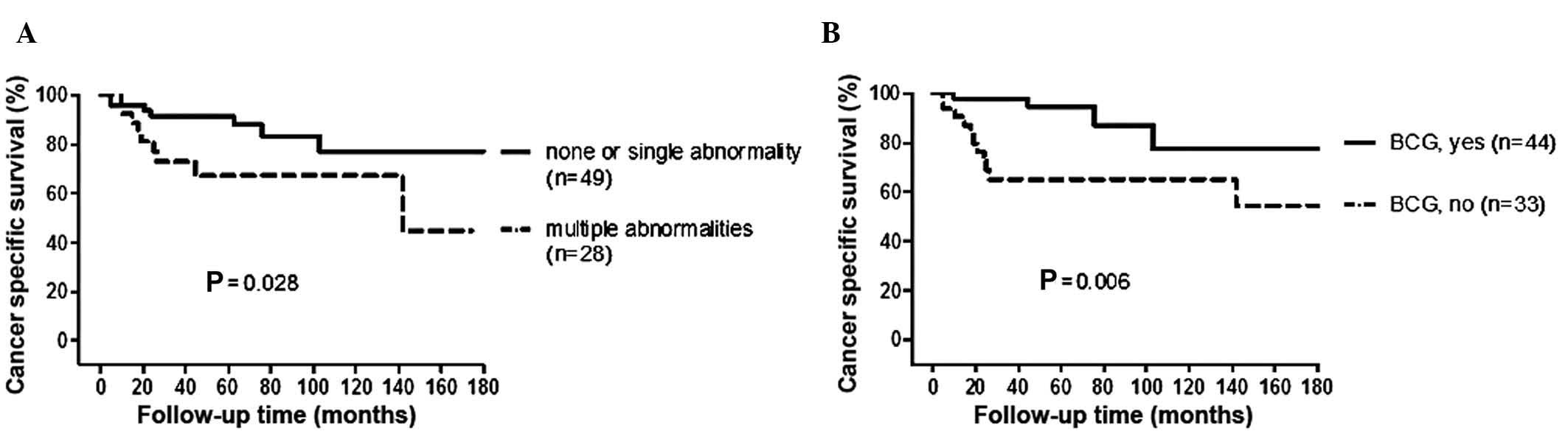
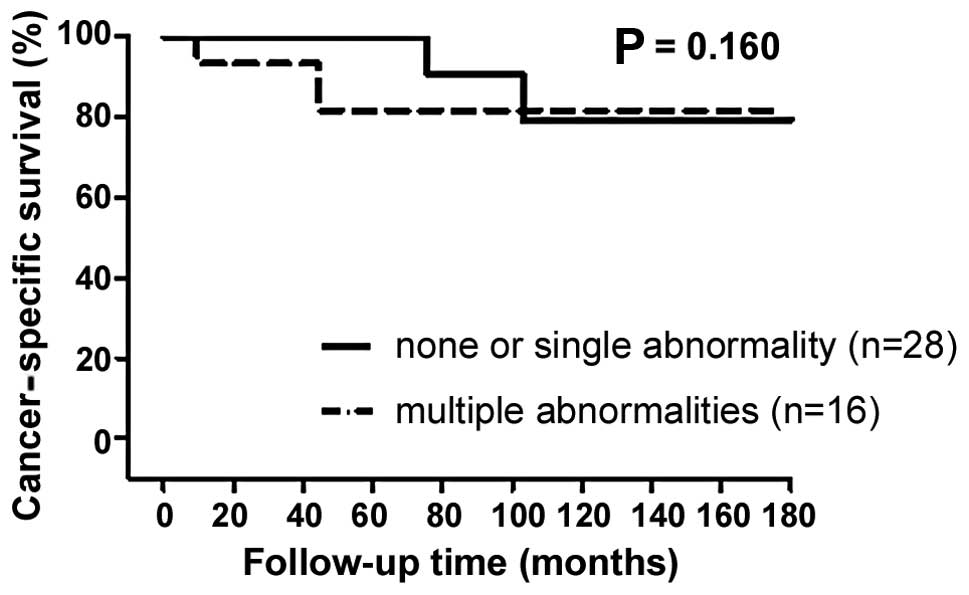
|
1.
|
Shahin O, Thalmann GN, Rentsch C,
Mazzucchelli L and Studer UE: A retrospective analysis of 153
patients treated with or without intravesical bacillus
Calmette-Guerin for primary stage T1 grade 3 bladder cancer:
recurrence, progression and survival. J Urol. 169:96–100. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP,
Oosterlinck W, et al: Predicting recurrence and progression in
individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC
risk tables: a combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC
trials. Eur Urol. 49:466–465. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Malavaud B: T1G3 bladder tumours: the case
for radical cystectomy. Eur Urol. 45:406–410. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Turner W: T1G3 bladder tumours: the case
for conservative treatment. Eur Urol. 45:401–405. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Agerbaek M, Alsner J, Marcussen N,
Lundbeck F and Von der Maase H: Focal S100A4 protein expression is
an independent predictor of development of metastatic disease in
cystectomized bladder cancer patients. Eur Urol. 50:777–785. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Matsumoto K, Irie A, Satoh T, et al:
Expression of S100A2 and S100A4 predicts for disease progression
and patient survival in bladder cancer. Urology. 70:602–607. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Matsumoto K, Satoh T, Irie A, et al: Loss
expression of uroplakin III is associated with clinicopathologic
features of aggressive bladder cancer. Urology. 72:444–449. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Heimann R, Lan F, McBride R and Hellman S:
Separating favorable from unfavorable prognostic markers in breast
cancer: the role of E-cadherin. Cancer Res. 60:298–304.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Andersen K, Nesland JM, Holm R, Florenes
VA, Fodstad O and Maelandsmo GM: Expression of S100A4 combined with
reduced E-cadherin expression predicts patient outcome in malignant
melanoma. Mod Pathol. 17:990–997. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Okegawa T, Pong RC, Li Y, Bergelson JM,
Sagalowsky AI and Hsieh JT: The mechanism of the growth-inhibitory
effect of coxsackie and adenovirus receptor (CAR) on human bladder
cancer: a functional analysis of car protein structure. Cancer Res.
61:6592–6600. 2001.
|
|
11.
|
Sherbet GV and Lakshmi MS: S100A4 (MTS1)
calcium binding protein in cancer growth, invasion and metastasis.
Anticancer Res. 18:2415–2421. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Huang HY, Shariat SF, Sun TT, et al:
Persistent uroplakin expression in advanced urothelial carcinomas:
implications in urothelial tumor progression and clinical outcome.
Hum Pathol. 38:1703–1713. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Matsumoto K, Shariat SF, Ayala GE, Rauen
KA and Lerner SP: Loss of coxsackie and adenovirus receptor
expression is associated with features of aggressive bladder
cancer. Urology. 66:441–446. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Matsumoto K, Kikuchi E, Horiguchi Y, et
al: Late recurrence and progression in non-muscle-invasive bladder
cancers after 5-year tumor-free periods. Urology. 75:1385–1390.
2010.
|
|
15.
|
Zieger K, Wolf H, Olsen PR and Hojgaard K:
Long-term survival of patients with bladder tumours: the
significance of risk factors. Br J Urol. 82:667–672. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Millan-Rodriguez F, Chechile-Toniolo G,
Salvador-Bayarri J, Palou J, Algaba F and Vicente-Rodriguez J:
Primary superficial bladder cancer risk groups according to
progression, mortality and recurrence. J Urol. 164:680–684. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
van den Bosch S and Alfred Witjes J:
Long-term cancer-specific survival in patients with high-risk,
non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer and tumour progression: a
systematic review. Eur Urol. 60:493–500. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Herr HW and Sogani PC: Does early
cystectomy improve the survival of patients with high risk
superficial bladder tumors? J Urol. 166:1296–1299. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Park J, Song C, Shin E, Hong JH, Kim CS
and Ahn H: Do molecular biomarkers have prognostic value in primary
T1G3 bladder cancer treated with bacillus Calmette-Guerin
intravesical therapy? Urol Oncol. Jul 20–2011, (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
20.
|
Lacombe L, Dalbagni G, Zhang ZF, et al:
Overexpression of p53 protein in a high-risk population of patients
with superficial bladder cancer before and after bacillus
Calmette-Guerin therapy: correlation to clinical outcome. J Clin
Oncol. 14:2646–2652. 1996.
|
|
21.
|
Schmitz-Drager BJ, Goebell PJ, Ebert T and
Fradet Y: p53 immunohistochemistry as a prognostic marker in
bladder cancer. Playground for urology scientists? Eur Urol.
38:691–699. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Alvarez-Mugica M, Cebrian V,
Fernandez-Gomez JM, Fresno F, Escaf S and Sanchez-Carbayo M:
Myopodin methylation is associated with clinical outcome in
patients with T1G3 bladder cancer. J Urol. 184:1507–1513. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Lamm DL, Blumenstein BA, Crissman JD, et
al: Maintenance bacillus Calmette-Guerin immunotherapy for
recurrent TA, T1 and carcinoma in situ transitional cell carcinoma
of the bladder: a randomized Southwest Oncology Group Study. J
Urol. 163:1124–1129. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Herr HW and Donat SM: A re-staging
transurethral resection predicts early progression of superficial
bladder cancer. BJU Int. 97:1194–1198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Schwaibold HE, Sivalingam S, May F and
Hartung R: The value of a second transurethral resection for T1
bladder cancer. BJU Int. 97:1199–1201. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Decobert M, LaRue H, Harel F, Meyer F,
Fradet Y and Lacombe L: Maintenance bacillus Calmette-Guerin in
high-risk nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer: how much is enough?
Cancer. 113:710–716. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|