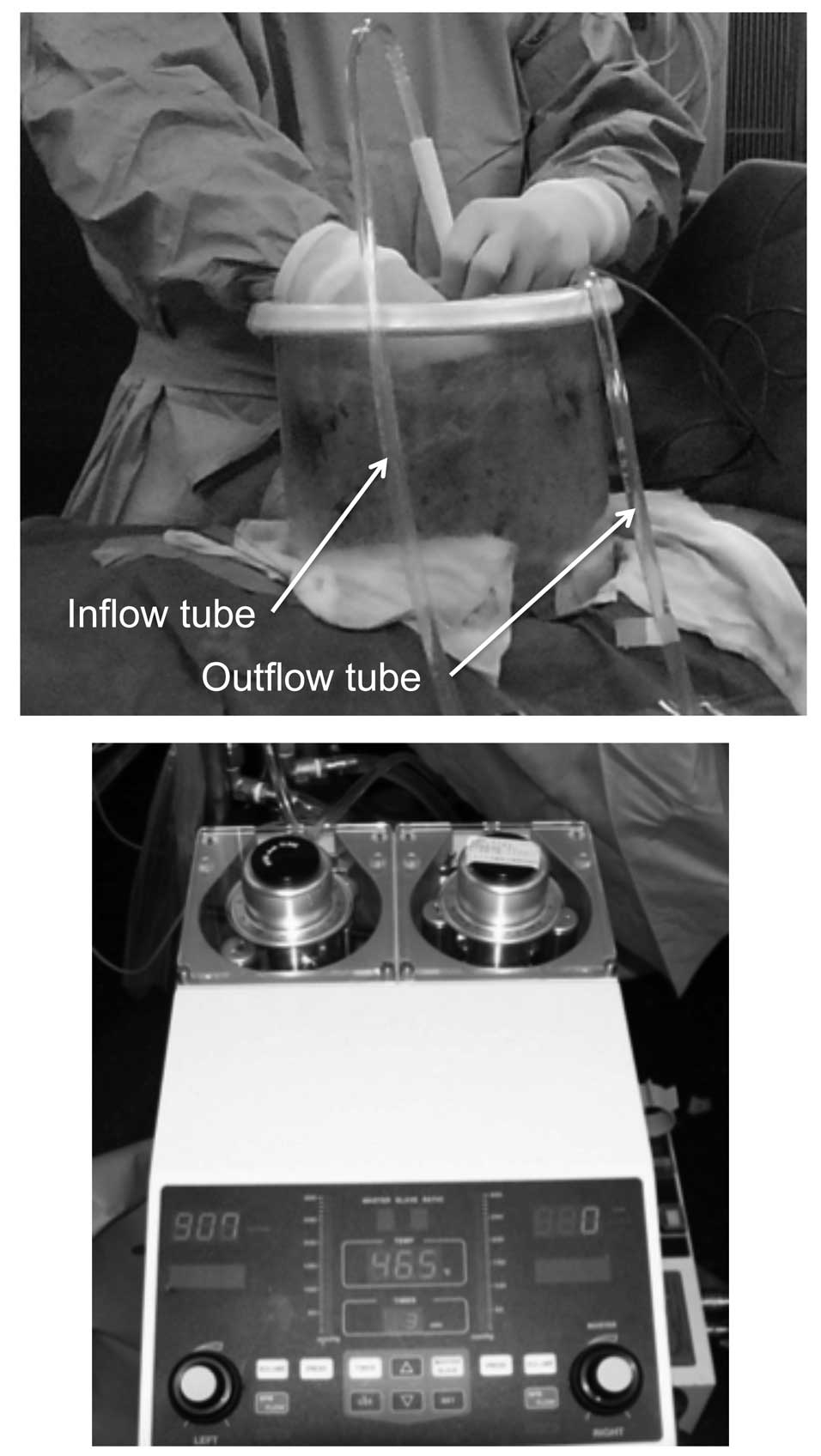
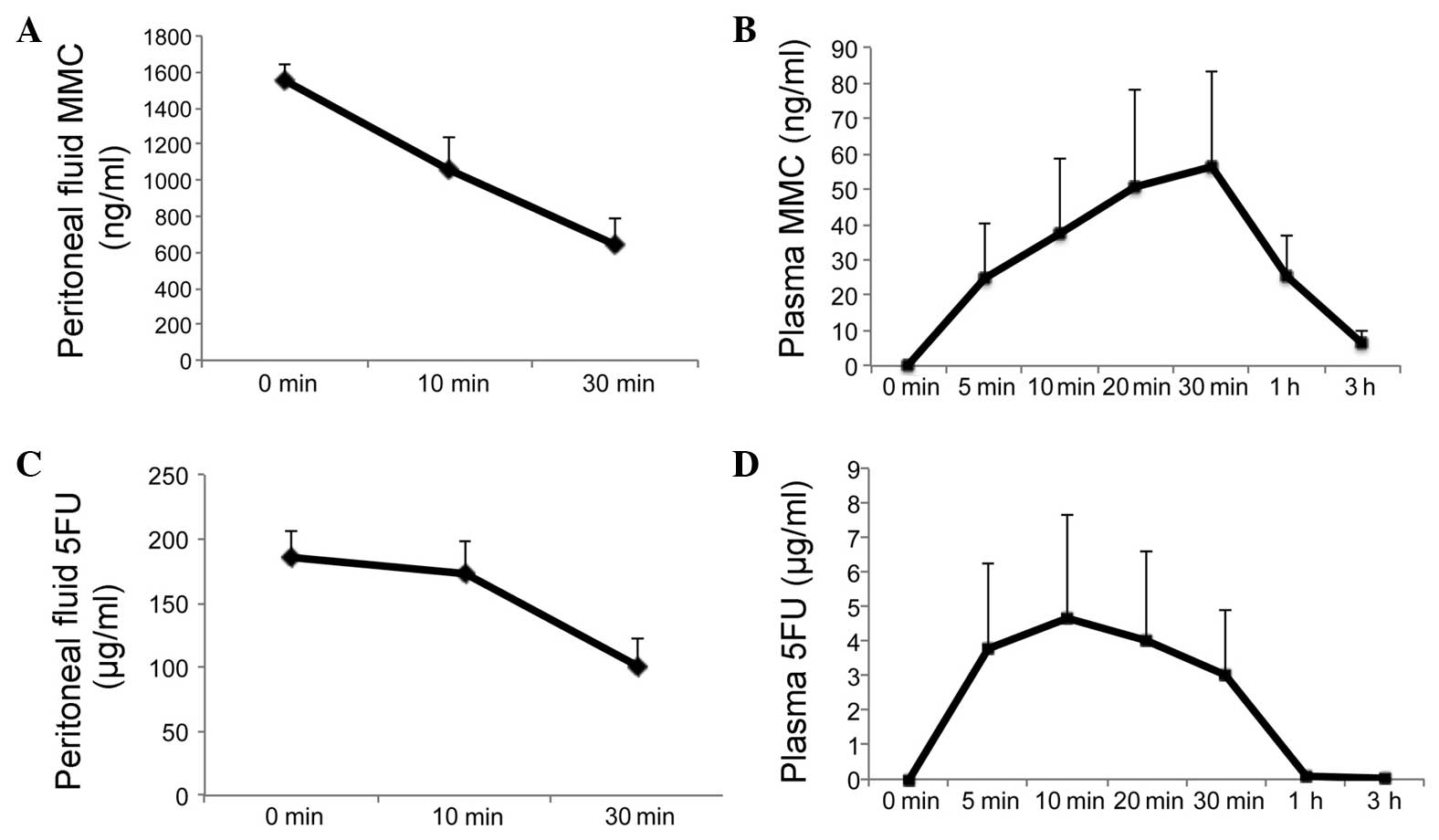
|
1.
|
Stewart JH IV, Shen P and Levine EA:
Intraperitoneal hyperthermic chemotherapy for peritoneal surface
malignancy: current status and future directions. Ann Surg Oncol.
12:765–777. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Chua TC, Esquivel J, Pelz JO and Morris
DL: Summary of current therapeutic options for peritoneal
metastases from colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 107:566–573. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Mohr Z, Hirche C, Liebeskind U, Rau B and
Hunerbein M: Feasibility of delayed hyperthermic intraperitoneal
chemotherapy in case of unforeseen complications. Eur Surg Res.
47:19–25. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Yonemura Y, Elnemr A, Endou Y, et al:
Multidisciplinary therapy for treatment of patients with peritoneal
carcinomatosis from gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol.
2:85–97. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Imano M, Imamoto H, Itoh T, et al: Impact
of intraperitoneal chemotherapy after gastrectomy with positive
cytological findings in peritoneal washings. Eur Surg Res.
47:254–259. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Fujishima Y, Goi T, Kimura Y, Hirono Y,
Katayama K and Yamaguchi A: MUC2 protein expression status is
useful in assessing the effects of hyperthermic intraperitoneal
chemotherapy for peritoneal dissemination of colon cancer. Int J
Oncol. 40:960–964. 2012.
|
|
7.
|
Bosanquet DC, Harris DA, Evans MD and
Beynon J: Systematic review and meta-analysis of intraoperative
peritoneal lavage for colorectal cancer staging. Br J Surg.
100:853–862. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Mohan HM, O’Connor DB, O’Riordan JM and
Winter DC: Prognostic significance of detection of microscopic
peritoneal disease in colorectal cancer: a systematic review. Surg
Oncol. 22:e1–e6. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Glockzin G, Rochon J, Arnold D, et al: A
prospective multicenter phase II study evaluating multimodality
treatment of patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis arising from
appendiceal and colorectal cancer: the COMBATAC trial. BMC Cancer.
13:672013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Koppe MJ, Boerman OC, Oyen WJ and
Bleichrodt RP: Peritoneal carcinomatosis of colorectal origin:
incidence and current treatment strategies. Ann Surg. 243:212–222.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Klaver YL, Hendriks T, Lomme RM, Rutten
HJ, Bleichrodt RP and de Hingh IH: Intraoperative versus early
postoperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy after cytoreduction for
colorectal peritoneal carcinomatosis: an experimental study. Ann
Surg Oncol. 19(Suppl 3): S475–S482. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12.
|
Weber T, Roitman M and Link KH: Current
status of cytoreductive surgery with hyperthermic intraperitoneal
chemotherapy in patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis from
colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 11:167–176. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Kobayashi H, Tanisaka K, Doi O, et al: An
in vitro chemosensitivity test for solid human tumors using
collagen gel droplet embedded cultures. Int J Oncol. 11:449–455.
1997.
|
|
14.
|
Okumura K, Shiomi H, Mekata E, et al:
Correlation between chemosensitivity and mRNA expression level of
5-fluorouracil-related metabolic enzymes during liver metastasis of
colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 15:875–882. 2006.
|
|
15.
|
Muller M, Cherel M, Dupre PF, Gouard S,
Collet M and Classe JM: The cytotoxic effect of combined
hyperthermia and taxane chemotherapy on ovarian cancer cells:
results of an in vitro study. Eur Surg Res. 48:55–63. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Sugarbaker PH: Intraperitoneal
chemotherapy and cytoreductive surgery for the prevention and
treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis and sarcomatosis. Semin Surg
Oncol. 14:254–261. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Kuzuya T, Yamauchi M, Ito A, Hasegawa M,
Hasegawa T and Nabeshima T: Pharmacokinetic characteristics of
5-fluorouracil and mitomycin C in intraperitoneal chemotherapy. J
Pharm Pharmacol. 46:685–689. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Pestieau SR, Marchettini P, Stuart OA,
Chang D and Sugarbaker PH: Prevention of intraperitoneal adhesions
by intraperitoneal lavage and intraperitoneal 5-fluorouracil:
experimental studies. Int Surg. 87:195–200. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Sugarbaker PH and Jablonski KA: Prognostic
features of 51 colorectal and 130 appendiceal cancer patients with
peritoneal carcinomatosis treated by cytoreductive surgery and
intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Ann Surg. 221:124–132. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Sugarbaker PH: Cytoreductive surgery plus
hyperthermic perioperative chemotherapy for selected patients with
peritoneal metastases from colorectal cancer: a new standard of
care or an experimental approach? Gastroenterol Res Pract.
2012:3094172012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21.
|
Wyatt MD and Wilson DM III: Participation
of DNA repair in the response to 5-fluorouracil. Cell Mol Life Sci.
66:788–799. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
De Roover A, Detroz B, Detry O, et al:
Adjuvant hyperthermic intraperitoneal peroperative chemotherapy
(HIPEC) associated with curative surgery for locally advanced
gastric carcinoma. An initial experience. Acta Chir Belg.
106:297–301. 2006.
|
|
23.
|
Tentes AA, Spiliotis ID, Korakianitis OS,
Vaxevanidou A and Kyziridis D: Adjuvant perioperative
intraperitoneal chemotherapy in locally advanced colorectal
carcinoma: preliminary results. ISRN Surg. 2011:5298762011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Raue W, Tsilimparis N, Bloch A, Menenakos
C and Hartmann J: Volume therapy and cardiocircular function during
hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Eur Surg Res.
43:365–372. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Mizumoto A, Canbay E, Hirano M, et al:
Morbidity and mortality outcomes of cytoreductive surgery and
hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy at a single institution
in Japan. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012:8364252012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|