|
1
|
Reis-Filho JS and Tutt AN: Triple negative
tumours: a critical review. Histopathology. 52:108–118. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Masuda H, Masuda N, Kodama Y, et al:
Predictive factors for the effectiveness of neoadjuvant
chemotherapy and prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer
patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 67:911–917. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chang HR, Glaspy J, Allison MA, et al:
Differential response of triple-negative breast cancer to a
docetaxel and carboplatin-based neoadjuvant treatment. Cancer.
116:4227–4237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheang MC, Voduc D, Bajdik C, et al:
Basal-like breast cancer defined by five biomarkers has superior
prognostic value than triple-negative phenotype. Clin Cancer Res.
14:1368–1376. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, et al:
Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of
recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4429–4434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tassone P, Di Martino MT, Ventura M, et
al: Loss of BRCA1 function increases the antitumor activity of
cisplatin against human breast cancer xenografts in vivo. Cancer
Biol Ther. 8:648–653. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bhattacharyya A, Ear US, Koller BH,
Weichselbaum RR and Bishop DK: The breast cancer susceptibility
gene BRCA1 is required for subnuclear assembly of Rad51 and
survival following treatment with the DNA cross-linking agent
cisplatin. J Biol Chem. 275:23899–23903. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Quinn JE, Kennedy RD, Mullan PB, et al:
BRCA1 functions as a differential modulator of chemotherapy-induced
apoptosis. Cancer Res. 63:6221–6228. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kennedy RD, Quinn JE, Mullan PB, Johnston
PG and Harkin DP: The role of BRCA1 in the cellular response to
chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 96:1659–1668. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moynahan ME, Chiu JW, Koller BH and Jasin
M: Brca1 controls homology-directed DNA repair. Mol Cell.
4:511–518. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rodler E, Korde L and Gralow J: Current
treatment options in triple negative breast cancer. Breast Dis.
32:99–122. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chacón RD and Costanzo MV: Triple-negative
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 12 Suppl 2:32010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Andre F and Zielinski CC: Optimal
strategies for the treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast
cancer with currently approved agents. Ann Oncol. 23 Suppl
6:vi46–vi51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Foulkes WD, Smith IE and Reis-Filho JS:
Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1938–1948. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Byrski T, Gronwald J, Huzarski T, et al:
Pathologic complete response rates in young women with
brca1-positive breast cancers after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J
Clin Oncol. 28:375–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Byrski T, Huzarski T, Dent R, et al:
Response to neoadjuvant therapy with cisplatin in BRCA1-positive
breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 115:359–363. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livasy CA, Perou CM, Karaca G, et al:
Identification of a basal-like subtype of breast ductal carcinoma
in situ. Hum Pathol. 38:197–204. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
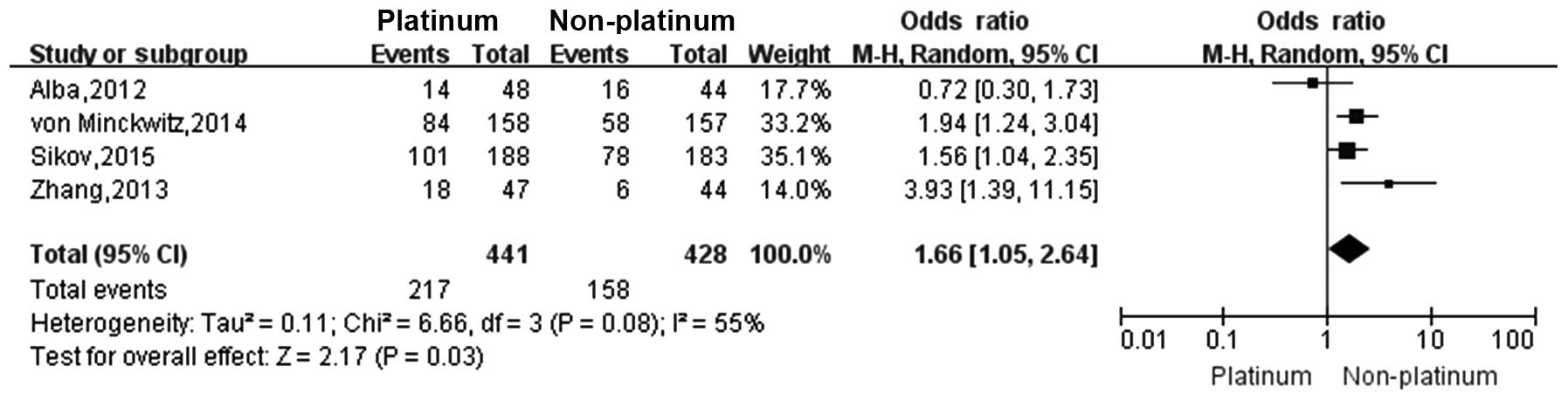
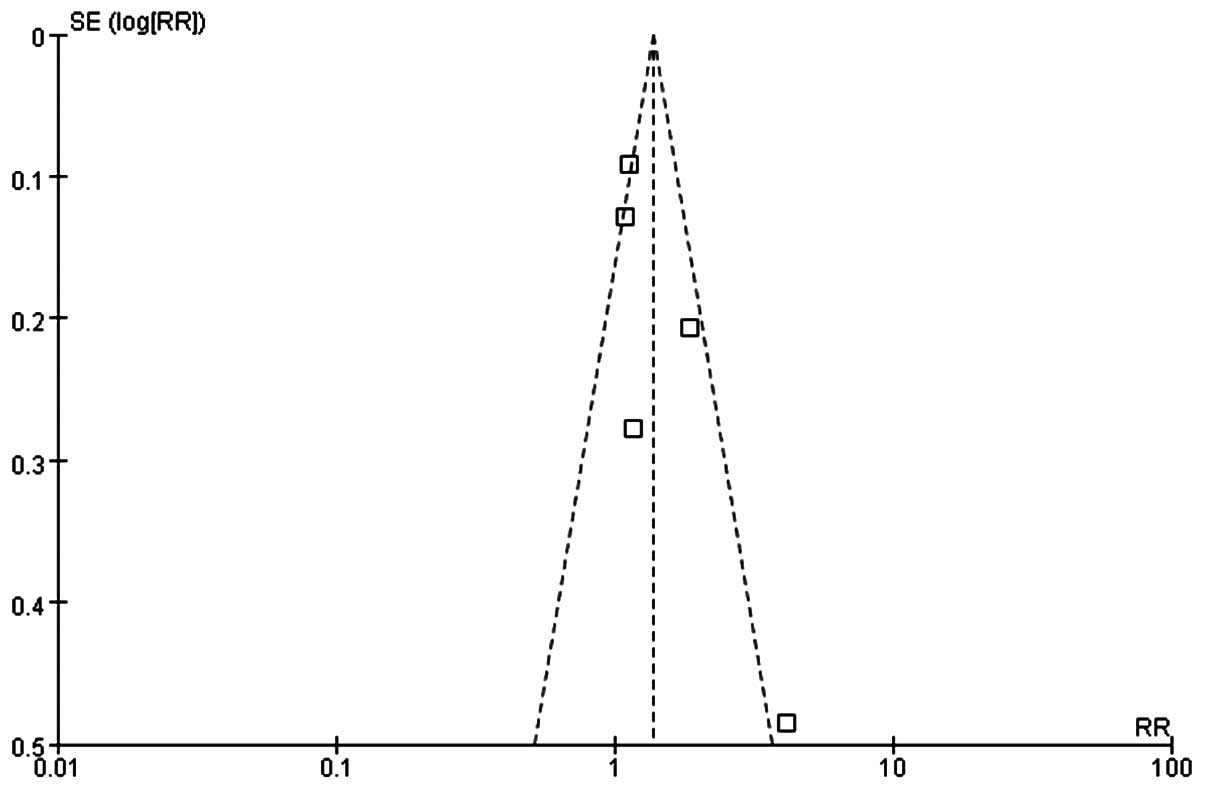
Alba E, Chacon JI, Lluch A, et al: A
randomized phase II trial of platinum salts in basal-like breast
cancer patients in the neoadjuvant setting. Results from the
GEICAM/2006-03, multicenter study. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
136:487–493. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
von Minckwitz G, Schneeweiss A, Loibl S,
Salat C, Denkert C, Rezai M, et al: Neoadjuvant carboplatin in
patients with triple-negative and HER2-positive early breast cancer
(geparsixto; GBG 66): a randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol.
15:747–756. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sikov WM, Berry DA, Perou CM, et al:
Impact of the addition of carboplatin and/or bevacizumab to
neoadjuvant once-per-week paclitaxel followed by dose-dense
doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide on pathologic complete response
rates in stage II to III triple-negative breast cancer: CALGB 40603
(alliance). J Clin Oncol. 33:13–21. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang P, Yin Y, Xu B, et al: Carboplatin
plus paclitaxel compared with epirubicin plus paclitaxel as
neoadjuvant chemotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer – a
phase ii clinical trial. Cancer Res. 73:P3-14-072013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fan Y, Xu BH, Yuan P, et al:
Docetaxel-cisplatin might be superior to docetaxel-capecitabine in
the first-line treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast
cancer. Ann Oncol. 24:1219–1225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu Sk, Zhao X, Meng XY, et al: Analysis of
chemotherapeutic efficacies in metastatic triple-negative breast
cancer. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 13:3001–3003. 2012.
|
|
24
|
Bhattacharyya GS, Basu S, Agarwal V, et
al: Single institute phase ii study of weekly cisplatinum and
metronomic dosing of cyclophosphamide and methotrexate in second
line metastatic breast cancer triple-negative. Eur J Cancer (Abstr
41LBA, presented data-ECCO 15-ESMO 34 2009). 7:2009.
|
|
25
|
Villarreal-Garza C, Khalaf D, Bouganim N,
Clemons M, Pena-Curiel O, Baez-Revueltas B, et al: Platinum-based
chemotherapy in triple-negative advanced breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 146:567–572. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Turner NC, Reis-Filho JS, Russell AM, et
al: BRCA1 dysfunction in sporadic basal-like breast cancer.
Oncogene. 26:2126–2132. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leong CO, Vidnovic N, DeYoung MP, Sgroi D
and Ellisen LW: The p63/p73 network mediates chemosensitivity to
cisplatin in a biologically defined subset of primary breast
cancers. J Clin Invest. 117:1370–1380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tun NM, Villani G, Ong K, Yoe L and Bo ZM:
Risk of having BRCA1 mutation in high-risk women with
triple-negative breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Clin Genet.
85:43–48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu M, Mo QG, Wei CY, Qin QH, Huang Z and
He J: Platinum-based chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer:
a meta-analysis. Oncol Lett. 5:983–991. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
ISRCTN Registry: Triple Negative Trial: a
randomised phase III trial of carboplatin compared to docetaxel for
patients with advanced oestrogen receptor-progesterone
receptor-human epidermal growth factor receptor two-breast cancer.
https://www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN97330959Accessed. July
4–2014
|
|
31
|
ClinicalTrials.gov, . Platinum for
triple-negative metastatic breast cancer and evaluation of p63/p73
as a biomarker of response. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00483223Accessed.
July 4–2014
|