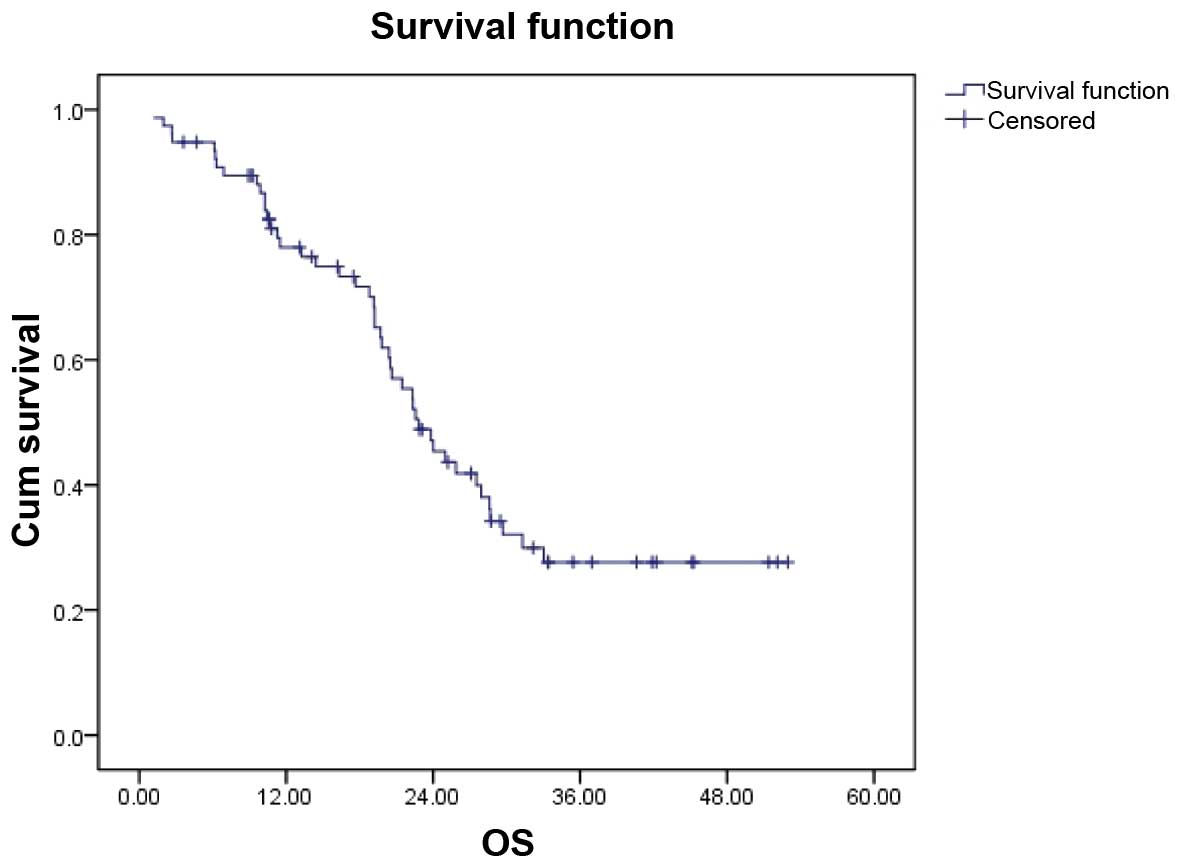
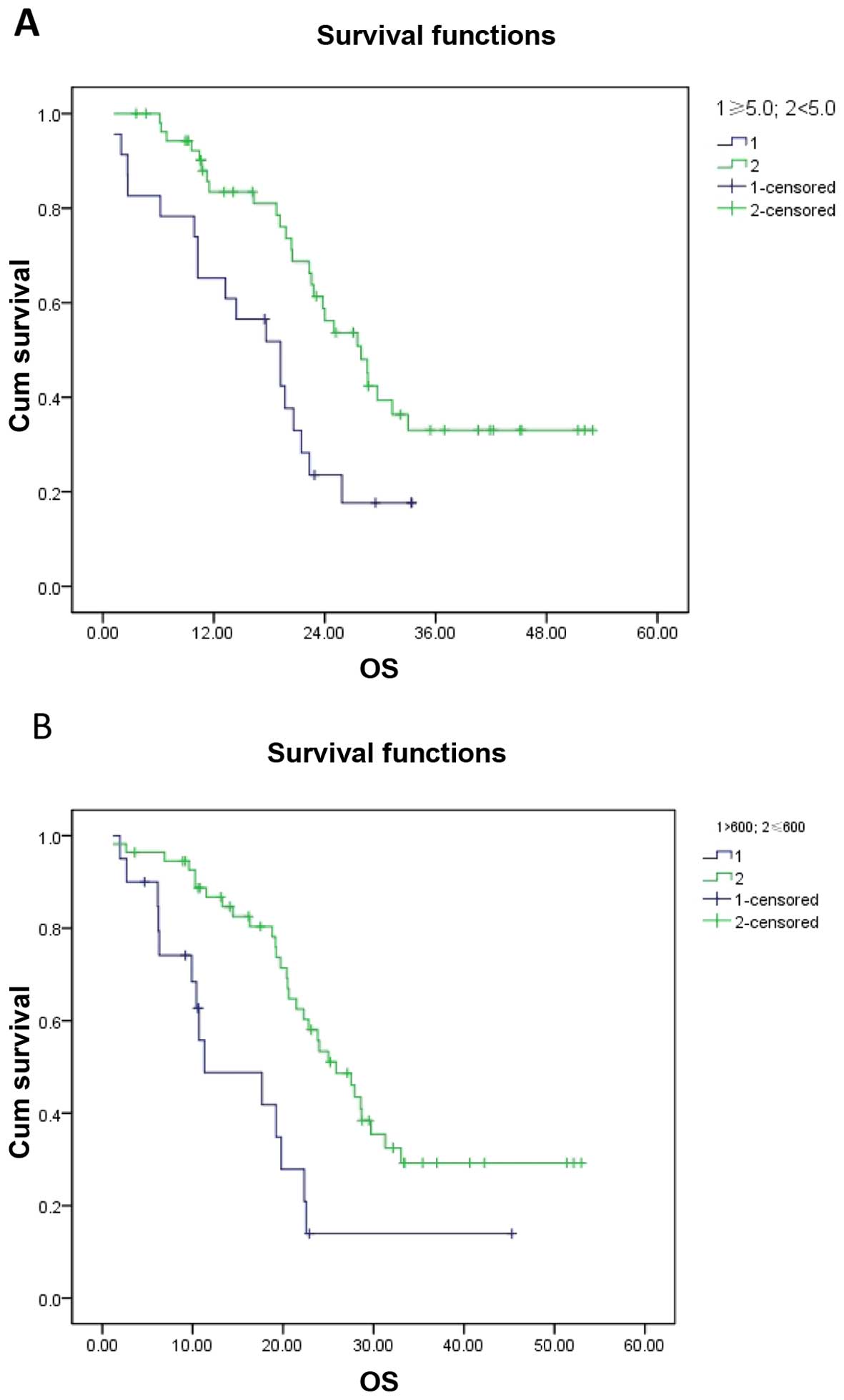
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pfister DG, Johnson DH, Azzoli CG, Sause
W, Smith TJ, Baker S Jr, Olak J, Stover D, Strawn JR, Turrisi AT,
et al: American society of clinical oncology treatment of
unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer guideline: Update 2003. J
Clin Oncol. 22:330–353. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rengan R, Maity AM, Stevenson JP and Hahn
SM: New strategies in non-small cell lung cancer: Improving
outcomes in chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced disease. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:4192–4199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Curran WJ Jr, Paulus R, Langer CJ, Komaki
R, Lee JS, Hauser S, Movsas B, Wasserman T, Rosenthal SA, Gore E,
et al: Sequential vs. concurrent chemoradiation for stage III
non-small cell lung cancer: Randomized phase III trial RTOG 9410. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 103:1452–1460. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J,
Schiller JH, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R and Johnson DH:
Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:2542–2550. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Han B, Xiu Q, Wang H, Shen J, Gu A, Luo Y,
Bai C, Guo S, Liu W, Zhuang Z, et al: A multicenter, randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy of
paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with endostar for advanced
non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 6:1104–1109. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mu H, Shen C and Feng Y: Clinical
observation on the target therapy of rh-endostatin, combined with
chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Lung
Cancer. 12:780–784. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Rong B, Yang S, Li W, Zhang W and Ming Z:
Systematic review and meta-analysis of Endostar (rh-endostatin)
combined with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treating
advanced non-small cell lung cancer. World J Surg Oncol.
10:1702012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao X, Mei K, Cai X, Chen J, Yu J, Zhou C
and Li Q: A randomized phase II study of recombinant human
endostatin plus gemcitabine/cisplatin compared with
gemcitabine/cisplatin alone as first-line therapy in advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer. Invest New Drugs. 30:1144–1149. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang XD, Dai P, Wu J, Song DA and Yu JM:
Effect of recombinant human endostatin on radiosensitivity in
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 83:1272–1277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bao Y, Peng F, Zhou QC, Yu ZH, Li JC,
Cheng ZB, Chen L, Hu X, Chen YY, Wang J, et al: Phase II trial of
recombinant human endostatin in combination with concurrent
chemoradiotherapy in patients with stage III non-small-cell lung
cancer. Radiother Oncol. 114:161–166. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ribatti D, Crivellato E and Vacca A:
Inflammation and antiangiogenesis in cancer. Curr Med Chem.
19:955–960. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Albini A, Tosetti F, Benelli R and Noonan
DM: Tumor inflammatory angiogenesis and its chemoprevention. Cancer
Res. 65:10637–10641. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Keizman D, Ish-Shalom M, Huang P,
Eisenberger MA, Pili R, Hammers H and Carducci MA: The association
of pre-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio with response rate,
progression free survival and overall survival of patients treated
with sunitinib for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer.
48:202–208. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Botta C, Barbieri V, Ciliberto D, Rossi A,
Rocco D, Addeo R, Staropoli N, Pastina P, Marvaso G, Martellucci I,
et al: Systemic inflammatory status at baseline predicts
bevacizumab benefit in advanced non-small cell lung cancer
patients. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:469–475. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D and
Verweij J: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pinato DJ, Shiner RJ, Seckl MJ, Stebbing
J, Sharma R and Mauri FA: Prognostic performance of
inflammation-based prognostic indices in primary operable non-small
cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 110:1930–1935. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Coffelt SB, Tal AO, Scholz A, De Palma M,
Patel S, Urbich C, Biswas SK, Murdoch C, Plate KH, Reiss Y and
Lewis CE: Angiopoietin-2 regulates gene expression in
TIE2-expressing monocytes and augments their inherent proangiogenic
functions. Cancer Res. 70:5270–5280. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Coffelt SB, Chen YY, Muthana M, Welford
AF, Tal AO, Scholz A, Plate KH, Reiss Y, Murdoch C, De Palma M and
Lewis CE: Angiopoietin 2 stimulates TIE2-expressing monocytes to
suppress T cell activation and to promote regulatory T cell
expansion. J Immunol. 186:4183–4190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kao SC, Pavlakis N, Harvie R, Vardy JL,
Boyer MJ, van Zandwijk N and Clarke SJ: High blood
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is an indicator of poor prognosis in
malignant mesothelioma patients undergoing systemic therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:5805–5813. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kishi Y, Kopetz S, Chun YS, Palavecino M,
Abdalla EK and Vauthey JN: Blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
predicts survival in patients with colorectal liver metastases
treated with systemic chemotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:614–622.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cho H, Hur HW, Kim SW, Kim SH, Kim JH, Kim
YT and Lee K: Pre-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is
elevated in epithelial ovarian cancer and predicts survival after
treatment. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 58:15–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liao W, Zhang J, Zhu Q, Qin L, Yao W, Lei
B, Shi W, Yuan S, Tahir SA, Jin J and He S: Preoperative
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a new prognostic marker in
hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. Transl Oncol.
7:248–255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
An X, Ding PR, Li YH, Wang FH, Shi YX,
Wang ZQ, He YJ, Xu RH and Jiang WQ: Elevated neutrophil to
lymphocyte ratio predicts survival in advanced pancreatic cancer.
Biomarkerss. 15:516–522. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yamanaka T, Matsumoto S, Teramukai S,
Ishiwata R, Nagai Y and Fukushima M: The baseline ratio of
neutrophils to lymphocytes is associated with patient prognosis in
advanced gastric cancer. Oncology. 73:215–220. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ohno Y, Nakashima J, Ohori M, Hatano T and
Tachibana M: Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an
independent predictor of recurrence in patients with nonmetastatic
renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 184:873–878. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yao Y, Yuan D, Liu H, Gu X and Song Y:
Pretreatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is associated with
response to therapy and prognosis of advanced non-small cell lung
cancer patients treated with first-line platinum-based
chemotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 62:471–479. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cedrés S, Torrejon D, Martínez A, Martinez
P, Navarro A, Zamora E, Mulet-Margalef N and Felip E: Neutrophil to
lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as an indicator of poor prognosis in stage
IV non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 14:864–869. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sarraf KM, Belcher E, Raevsky E, Nicholson
AG, Goldstraw P and Lim E: Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and its
association with survival after complete resection in non-small
cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 137:425–428. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Unal D, Eroglu C, Kurtul N, Oguz A and
Tasdemir A: Are neutrophil/lymphocyte and platelet/lymphocyte rates
in patients with non-small cell lung cancer associated with
treatment response and prognosis? Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
14:5237–5242. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang J, Huang SH, Li H, Li Y, Chen XL,
Zhang WQ, Chen HG and Gu LJ: Preoperative lymphocyte count is a
favorable prognostic factor of disease-free survival in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Med Oncol. 30:3522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kobayashi N, Usui S, Kikuchi S, Goto Y,
Sakai M, Onizuka M and Sato Y: Preoperative lymphocyte count is an
independent prognostic factor in node-negative non-small cell lung
cancer. Lung Cancer. 75:223–227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sakai T, Tsushima T, Kimura D, Hatanaka R,
Yamada Y and Fukuda I: A clinical study of the prognostic factors
for postoperative early recurrence in patients who underwent
complete resection for pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Ann Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 17:539–543. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Erler JT, Bennewith KL, Cox TR, Lang G,
Bird D, Koong A, Le QT and Giaccia AJ: Hypoxia-induced lysyl
oxidase is a critical mediator of bone marrow cell recruitment to
form the premetastatic niche. Cancer Cell. 15:35–44. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang L, DeBusk LM, Fukuda K, Fingleton B,
Green-Jarvis B, Shyr Y, Matrisian LM, Carbone DP and Lin PC:
Expansion of myeloid immune suppressor Gr+CD11b+ cells in
tumor-bearing host directly promotes tumor angiogenesis. Cancer
Cell. 6:409–421. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|