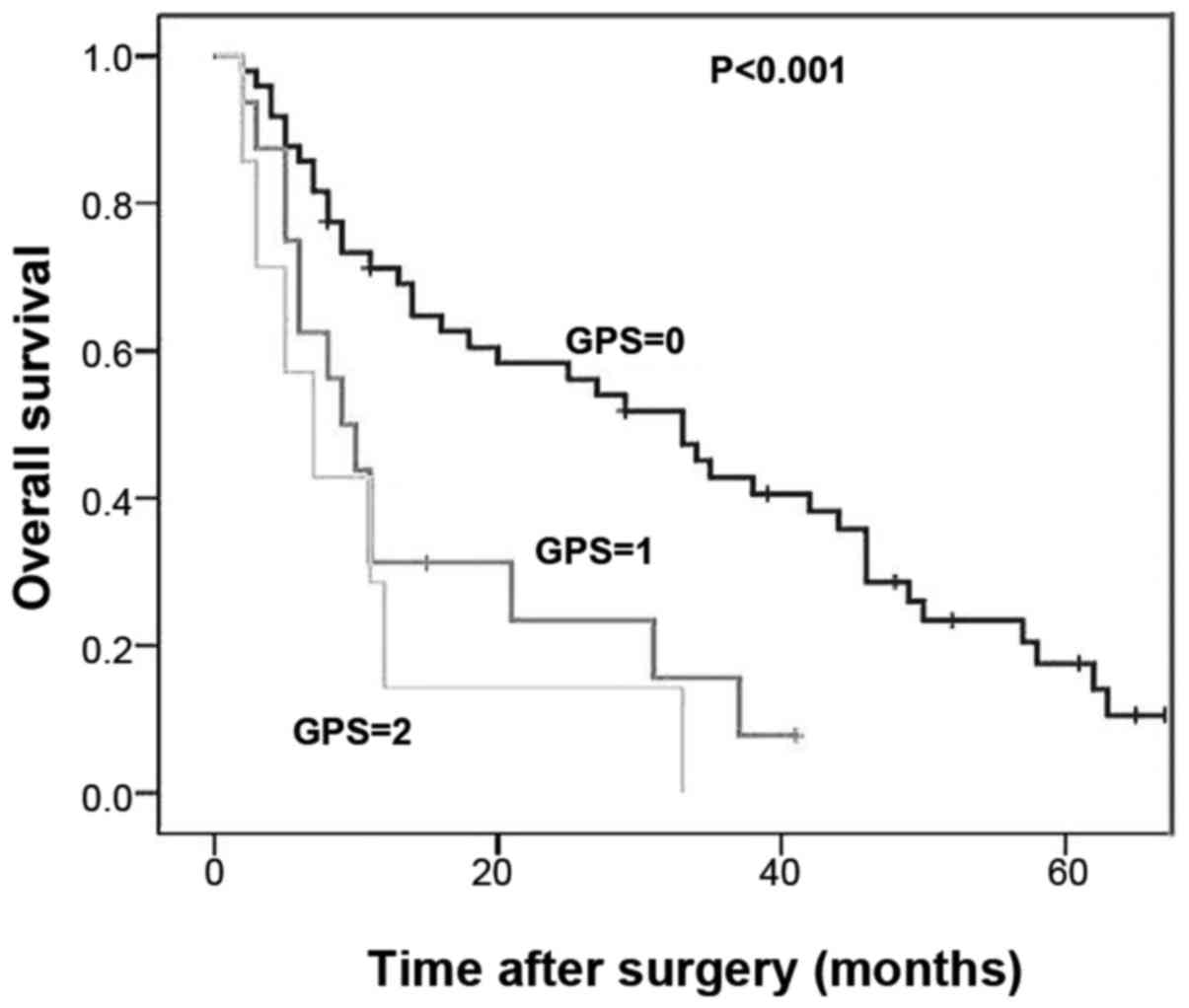
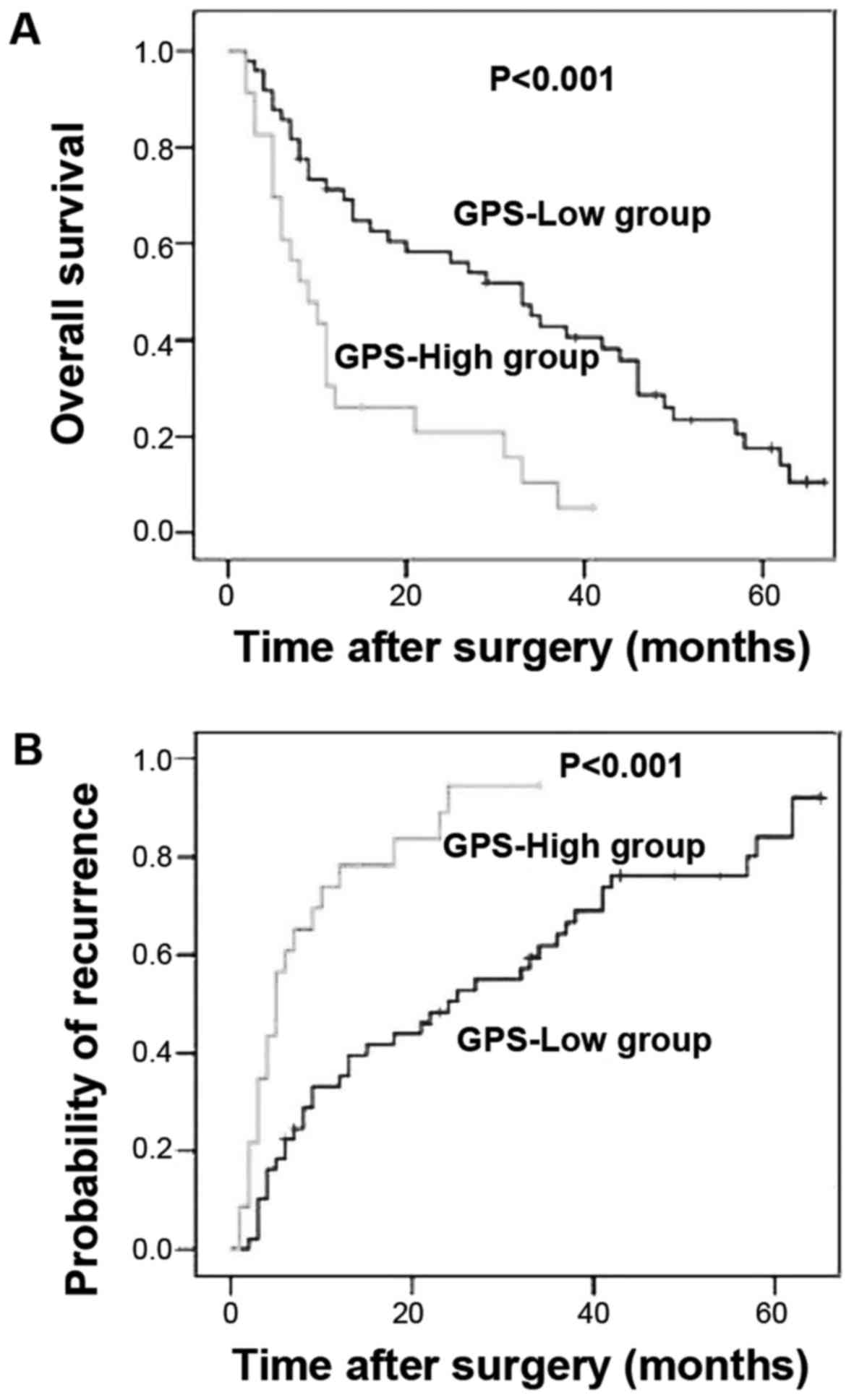
|
1
|
Guest RV, Boulter L, Kendall TJ,
Minnis-Lyons SE, Walker R, Wigmore SJ, Sansom OJ and Forbes SJ:
Cell lineage tracing reveals a biliary origin of intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 74:1005–1010. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nakanuma Y, Sripa B, Batanasapt V, Leong
ASY, Ponchon T and Ishak KG: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Digestive SystemWorld
Health Organization of Tumours. Hamilton SR and Aaltonen LA: IARC;
Lyon: pp. 173–180. 2000
|
|
3
|
Farges O, Fuks D, Le Treut YP, et al: AJCC
7th edition of TNM staging accurately discriminates outcomes of
patients with resectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma:by the
AFC-IHCC-2009 study group. Cancer. 117:2170–2177. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zou S, Li J, Zhou H, Frech C, Jiang X, Chu
JS, Zhao X, Li Y, Li Q, Wang H, et al: Mutational landscape of
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Nat Commun. 5:56962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang JD and Quan ZW: The molecular
mechanism of cholangiocarcinoma. J Pract Oncol Chin. 22:96–98.
2007.
|
|
6
|
de Jong MC, Nathan H, Sotiropoulos GC,
Paul A, Alexandrescu S, Marques H, Pulitano C, Barroso E, Clary BM,
Aldrighetti L, et al: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: An
international multi-institutional analysis of prognostic factors
and lymph node assessment. J Clin Oncol. 29:3140–3145. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
de Groen PC, Gores GJ, LaRusso NF,
Gunderson LL and Nagorney DM: Biliary tract cancers. N Engl J Med.
341:1368–1378. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li T, Qin LX, Zhou J, Sun HC, Qiu SJ, Ye
QH, Wang L, Tang ZY and Fan J: Staging, prognostic factors and
adjuvant therapy of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma after curative
resection. Liver Int. 34:953–960. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li H, Wu JS, Wang XT, Lv P, Gong LS, Liu
G, Tian BN, Li YY and Jiang B: Factors predicting surgical
resection in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and
cirrhosis. J Invest Surg. 27:219–225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Li J, Xia Y, Gong R, Wang K, Yan
Z, Wan X, Liu G, Wu D, Shi L, et al: Prognostic nomogram for
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma after partial hepatectomy. J Clin
Oncol. 31:1188–1195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Paik KY, Jung JC, Heo JS, Choi SH, Choi DW
and Kim YI: What prognostic factors are important for resected
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma? J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
23:766–770. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kinoshita A, Onoda H, Imai N, Iwaku A,
Oishi M, Tanaka K, Fushiya N, Koike K, Nishino H, Matsushima M, et
al: The Glasgow Prognostic Score, an inflammation based prognostic
score, predicts survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
BMC Cancer. 13:522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Roxburgh CS and McMillan DC: Role of
systemic inflammatory response in predicting survival in patients
with primary operable cancer. Future Oncol. 6:149–163. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Argilés JM, Busquets S, Toledo M and
López-Soriano FJ: The role of cytokines in cancer cachexia. Curr
Opin Support Palliat Care. 3:263–268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kusumanto YH, Dam WA, Hospers GA, Meijer C
and Mulder NH: Platelets and granulocytes in particular the
neutrophils from important compartments for circulating vascular
endothelial growth factor. Angiogenesis. 6:283–287. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ulich TR, Del Castillo J and Guo KZ: In
vivo hematologic effects of recombinant interleukin-6 on
hematopoiesis and circulating numbers of RBCs and WBCs. Blood.
73:108–110. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Philip M, Rowley DA and Schreiber H:
Inflammation as a tumor promoter in cancer induction. Semin Cancer
Biol. 14:433–439. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Heikkilä KK, Ebrahim S and Lawlor DA: A
systematic review of the association between circulating
concentrations of C reactive protein and cancer. Epidemiol
Community Health. 61:824–833. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kulbe H, Chakravarty P, Leinster DA,
Charles KA, Kwong J, Thompson RG, et al: A dynamic inflammatory
cytokine network in the human ovarian cancer microenvironment.
Cancer Res. 72:66–75. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Coward J, Kulbe H, Chakravarty P, Leader
D, Vassileva V, Leinster DA, Thompson R, Schioppa T, Nemeth J,
Vermeulen J, et al: Interleukin-6 as a therapeutic target in human
ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:6083–6096. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tomita M, Ayabe T, Chosa E and Nakamura K:
Prognostic significance of pre- and postoperative glasgow
prognostic score for patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
Anticancer Res. 34:3137–3140. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang AG, Chen HL and Lu HY: Comparison of
Glasgow prognostic score and prognostic index in patients with
advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
141:563–568. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sharma R, Hook J, Kumar M and Gabra H:
Evaluation of an inflammation-based prognostic score in patients
with advanced ovarian cancer. Eur J Cancer. 44:251–256. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ikeguchi M, Urushibara S, Shimoda R,
Yamamoto M, Maeta Y and Ashida K: Inflammation-based prognostic
scores and nutritional prognostic index in patients with
locally-advanced unresectable colorectal cancer. World J Surg
Oncol. 12:2102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ramsey S, Lamb GW, Aitchison M, Graham J
and McMillan DC: Evaluation of an inflammation-based prognostic
score in patients with metastatic renal cancer. Cancer.
109:205–212. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pan QX, Zhang JH, Su ZJ, Wang CR and Ke
SY: The Glasgow Prognostic Score is an independent prognostic
predictor of hepatocellular carcinoma following radical resection.
Oncol Res Treat. 37:192–197. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ishizuka M, Kubota K, Kita J, Shimoda M,
Kato M and Sawada T: Impact of an inflammation-based prognostic
system on patients undergoing surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma:
A retrospective study of 398 Japanese patients. Am J Surg.
203:101–106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kaneko M, Nozawa H, Sasaki K, Hongo K,
Hiyoshi M, Tada N, Murono K, Nirei T, Kawai K, Sunami E, et al:
Elevated neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio predicts poor prognosis in
advanced colorectal cancer patients receiving oxaliplatin-based
chemotherapy. Oncology. 82:261–268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oh BS, Jang JW, Kwon JH, You CR, Chung KW,
Kay CS, Jung HS and Lee S: Prognostic value of C-reactive protein
and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 13:782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kwon HC, Kim SH, Oh SY, Lee S, Lee JH,
Choi HJ, Park KJ, Roh MS, Kim SG, Kim HJ, et al: Clinical
significance of preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte versus
platelet-lymphocyte ratio in patients with operable colorectal
cancer. Biomarkers. 17:216–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Smith RA, Bosonnet L, Raraty M, Sutton R,
Neoptolemos JP, Campbell F and Ghaneh P: Preoperative
platelet-lymphocyte ratio is an independent significant prognostic
marker in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg.
197:466–472. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kasymjanova G, MacDonald N, Agulnik JS,
Cohen V, Pepe C, Kreisman H, Sharma R and Small D: The predictive
value of pre-treatment inflammatory markers in advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer. Curr Oncol. 17:52–58. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Proctor MJ, Morrison DS, Talwar D, Balmer
SM, Fletcher CD, O'Reilly DS, Foulis AK, Horgan PG and McMillan DC:
A comparison of inflammation-based prognostic scores in patients
with cancer. A Glasgow Inflammation Outcome Study. Eur J Cancer.
47:2633–2641. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pinato DJ, North BV and Sharma R: A novel,
externally validated inflammation-based prognostic algorithm in
hepatocellular carcinoma: The prognostic nutritional index (PNI).
Br J Cancer. 106:1439–1445. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gomez D, Morris-Stiff G, Toogood GJ, Lodge
JP and Prasad KR: Impact of systemic inflammation on outcome
following resection for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Surg
Oncol. 97:513–518. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Oshiro Y, Sasaki R, Fukunaga K, Kondo T,
Oda T, Takahashi H and Ohkohchi N: Inflammation-based prognostic
score is a useful predictor of postoperative outcome in patients
with extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci.
20:389–395. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hiraoka A, Kawamura T, Aibiki T, Okudaira
T, Toshimori A, Yamago H, Nakahara H, Suga Y, Azemoto N, Miyata H,
et al: Prognosis and therapy for ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma:
Problems with staging and treatment strategy. Eur J Radiol.
84:366–371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Edmondson HA and Steiner PE: Primary
carcinoma of the liver: A study of 100 cases among 48,900
necropsies. Cancer. 7:462–503. 1954. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Leyva-Illades D, McMillin M, Quinn M and
Demorrow S: Cholangiocarcinoma pathogenesis: Role of the tumor
microenvironment. Transl Gastrointest Cancer. 1:71–80.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dutta S, Crumley AB, Fullarton GM, Horgan
PG and McMillan DC: Comparison of the prognostic value of tumour
and patient related factors in patients undergoing potentially
curative resection of gastric cancer. Am J Surg. 204:294–299. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang DS, Ren C, Qiu MZ, Luo HY, Wang ZQ,
Zhang DS, Wang FH, Li YH and Xu RH: Comparison of the prognostic
value of various preoperative inflammation-based factors in
patients with stage III gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 33:749–756.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Glen P, Jamieson NB, McMillan DC, Carter
R, Imrie CW and McKay CJ: Evaluation of an inflammation-based
prognostic score in patients with inoperable pancreatic cancer.
Pancreatology. 6:450–453. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Allin KH and Nordestgaard BG: Elevated
C-reactive protein in the diagnosis, prognosis, and cause of
cancer. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 48:155–170. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Johnson C, Han Y, Hughart N, McCarra J,
Alpini G and Meng F: Interleukin-6 and its receptor, key players in
hepatobiliary inflammation and cancer. Transl Gastrointest Cancer.
1:58–70. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wehbe H, Henson R, Meng F, Mize-Berge J
and Patel T: Interleukin-6 contributes to growth in
cholangiocarcinoma cells by aberrant promoter methylation and gene
expression. Cancer Res. 66:10517–10524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Park J, Tadlock L, Gores GJ and Patel T:
Inhibition of interleukin 6-mediated mitogen-activated protein
kinase activation attenuates growth of a cholangiocarcinoma cell
line. Hepatology. 30:1128–1133. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Meng F, Yamagiwa Y, Ueno Y and Patel T:
Over-expression of interleukin-6 enhances cell survival and
transformed cell growth in human malignant cholangiocytes. J
Hepatol. 44:1055–1065. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Heimbach JK, Gores GJ, Haddock MG, Alberts
SR, Nyberg SL, Ishitani MB and Rosen CB: Liver transplantation for
unresectable perihilar cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis.
24:201–207. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Jarnagin WR, Fong Y, DeMatteo RP, Gonen M,
Burke EC, BS J Bodniewicz, BA M Youssef, Klimstra D and Blumgart
LH: Staging, resectability, and outcome in 225 patients with hilar
cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg. 234:507–517, discussion 517–519.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yamada D, Rizvi S, Razumilava N, Bronk SF,
Davila JI, Champion MD, Borad MJ, Bezerra JA, Chen X and Gores GJ:
IL-33 facilitates oncogene-induced cholangiocarcinoma in mice by an
interleukin-6-sensitive mechanism. Hepatology. 61:1627–1642. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jaiswal M, LaRusso NF, Burgart LJ and
Gores GJ: Inflammatory cytokines induce DNA damage and inhibit DNA
repair in cholangiocarcinoma cells by a nitric oxide-dependent
mechanism. Cancer Res. 60:184–190. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Maemura K, Natsugoe S and Takao S:
Molecular mechanism of cholangiocarcinoma carcinogenesis. J
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 21:754–760. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gupta D and Lis CG: Pretreatment serum
albumin as a predictor of cancer survival: A systematic review of
the epidemiological literature. Nutr J. 9:692010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lien YC, Hsieh CC, Wu YC, Hsu HS, Hsu WH,
Wang LS, Huang MH and Huang BS: Preoperative serum albumin level is
a prognostic indicator for adenocarcinoma of the gastric cardia. J
Gastrointest Surg. 8:1041–1048. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
McMillan DC, Watson WSO, O'Gorman P,
Preston T, Scott HR and McArdle CS: Albumin concentrations are
primarily determined by the body cell mass and the systemic
inflammatory response in cancer patients with weight loss. Nutr
Cancer. 39:210–213. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ohki S, Shibata M, Gonda K, Machida T,
Shimura T, Nakamura I, Ohtake T, Koyama Y, Suzuki S, Ohto H, et al:
Circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells are increased and
correlate to immune suppression, inflammation and hypoproteinemia
in patients with cancer. Oncol Rep. 28:453–458. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Nakeeb A, Pitt HA, Sohn TA, Coleman J,
Abrams RA, Piantadosi S, Hruban RH, Lillemoe KD, Yeo CJ and Cameron
JL: Cholangiocarcinoma. A spectrum of intrahepatic, perihilar, and
distal tumors. Ann Surg. 224:463–473, discussion 473–475. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Tanaka M, Tanaka H, Tsukuma H, Ioka A,
Oshima A and Nakahara T: Risk factors for intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma: A possible role of hepatitis B virus. J Viral
Hepat. 17:742–748. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Donato F, Gelatti U, Tagger A, Favret M,
Ribero ML, Callea F, Martelli C, Savio A, Trevisi P and Nardi G:
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatitis C and B virus
infection, alcohol intake, and hepatolithiasis: A case-control
study in Italy. Cancer Causes Control. 12:959–964. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wu Y, Wang T, Ye S, Zhao R, Bai X, Wu Y,
Abe K and Jin X: Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in
paraffin-embedded intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
tissue in the northern Chinese population. Hum Pathol. 43:56–61.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Perumal V, Wang J, Thuluvath P, Choti M
and Torbenson M: Hepatitis C and hepatitis B nucleic acids are
present in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas from the United States.
Hum Pathol. 37:1211–1216. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhou Y, Zhao Y, Li B, Huang J, Wu L, Xu D,
Yang J and He J: Hepatitis viruses infection and risk of
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Evidence from a meta-analysis. BMC
Cancer. 12:2892012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhou HB, Wang H, Li YQ, Li SX, Wang H,
Zhou DX, Tu QQ, Wang Q, Zou SS, Wu MC, et al: Hepatitis B virus
infection: A favorable prognostic factor for intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma after resection. World J Gastroenterol.
17:1292–1303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhang L, Cai JQ, Zhao JJ, Bi XY, Tan XG,
Yan T, Li C and Zhao P: Impact of hepatitis B virus infection on
outcome following resection for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J
Surg Oncol. 101:233–238. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Peng NF, Li LQ, Qin X, Guo Y, Peng T, Xiao
KY, Chen XG, Yang YF, Su ZX, Chen B, et al: Evaluation of risk
factors and clinicopathologic features for intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma in Southern China: A possible role of hepatitis
B virus. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:1258–1266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhou H, Wang H, Zhou D, Wang H, Wang Q,
Zou S, Tu Q, Wu M and Hu H: Hepatitis B virus-associated
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma may
hold common disease process for carcinogenesis. Eur J Cancer.
46:1056–1061. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Llovet JM, Brú C and Bruix J: Prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma: The BCLC staging classification. Semin
Liver Dis. 19:329–338. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ding FX, Wang F, Lu YM, Li K, Wang KH, He
XW and Sun SH: Multiepitope peptide-loaded virus-like particles as
a vaccine against hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 49:1492–1502. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ward SM, Phalora P, Bradshaw D,
Leyendeckers H and Klenerman P: Direct ex vivo evaluation of
long-lived protective antiviral memory B cell responses against
hepatitis B virus. J Infect Dis. 198:813–817. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
No authors listed: A new prognostic system
for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 435
patients: the Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP)
investigators. Hepatology. 28:751–755. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|