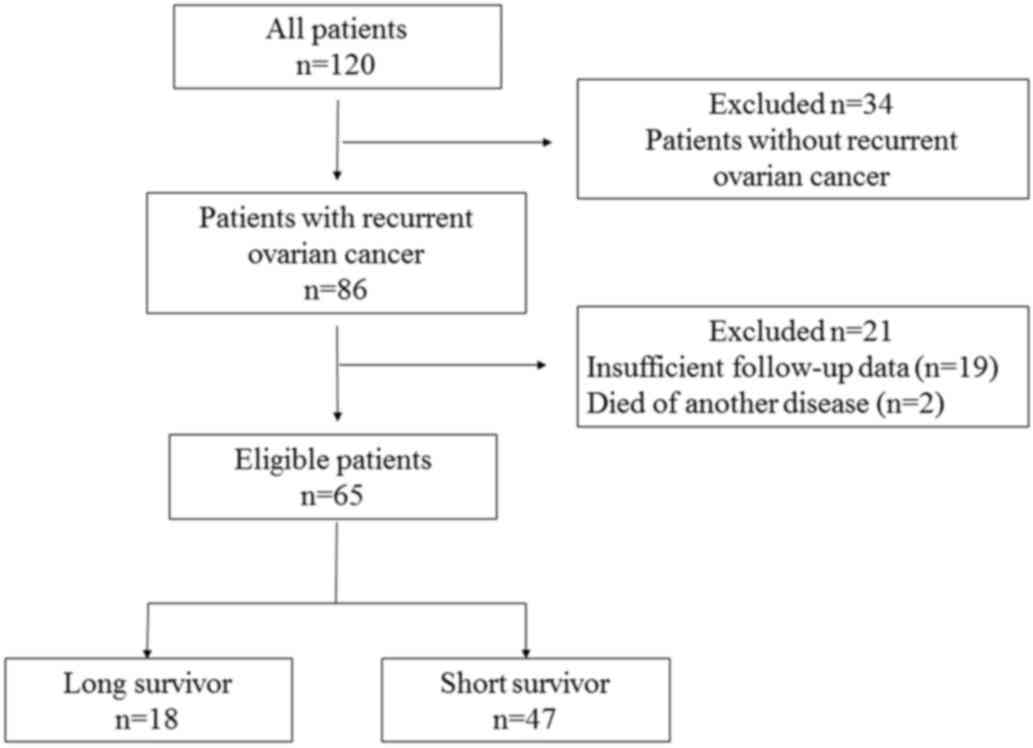
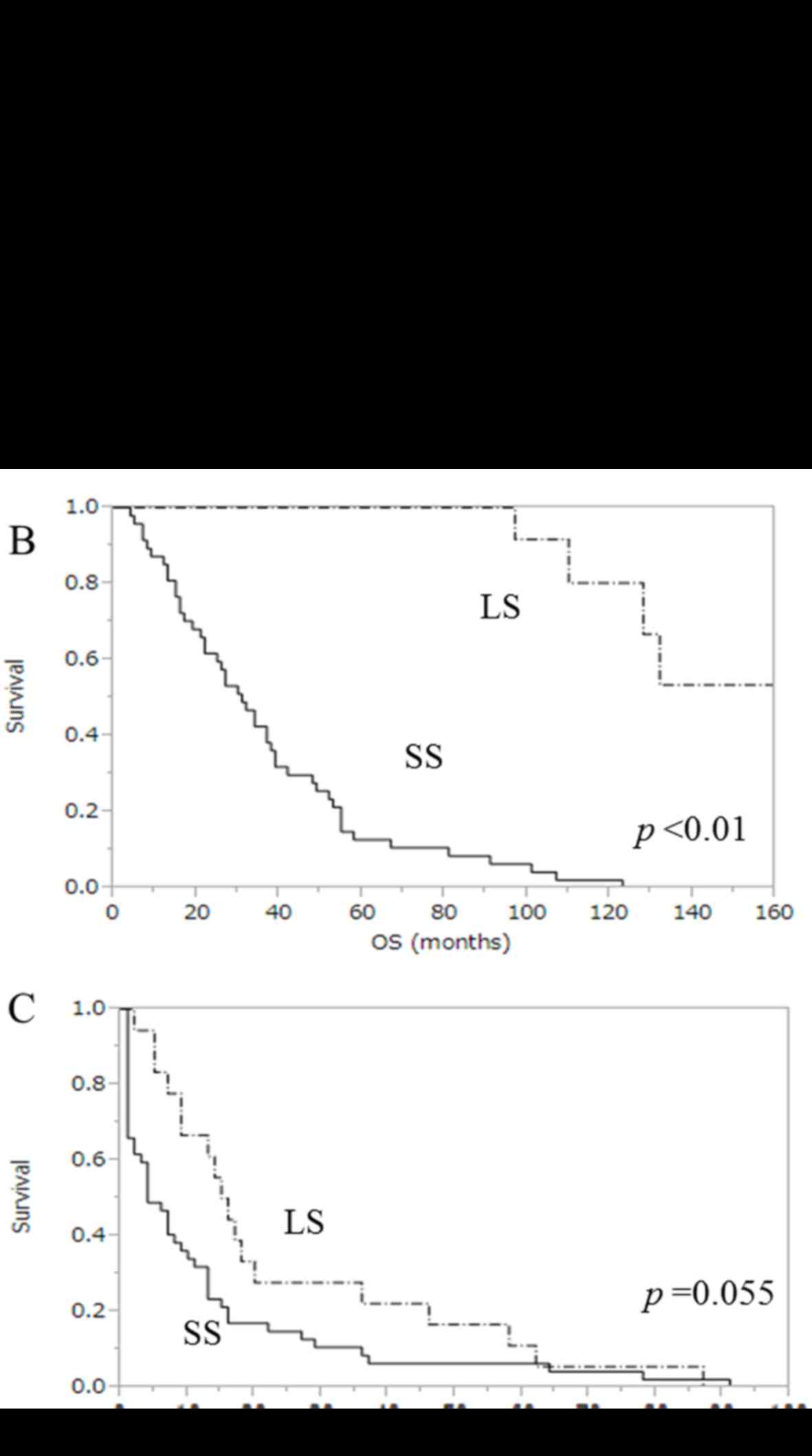
|
1
|
Ozols RF: Systemic therapy for ovarian
cancer: Current status and new treatment. Semin Oncol. 33 2 Suppl
6:S3–S11. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sundar S, Wu J, Hillaby K, Yap J and
Lilford R: A systematic review evaluating the relationship between
progression free survival and post progression survival in advanced
ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 125:493–499. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van der Burg ME, De Wit R, van Putten WL,
Logmans A, Kruit WH, Stoter G and Verweij J: Weekly cisplatin and
daily oral etoposide is highly effective in platinum pretreated
ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 86:19–25. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zang RY, Zhand ZY, Li ZT, Cai SM, Tang MQ,
Chen J and Liu Q: Impact of secondary cytoreductive surgery on
survival of patients with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. Eur J
Surg Oncol. 26:798–804. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rustin GJ, Vergote I, Eisenhauer E,
Pujade-Lauraine E, Quinn M, Thigpen T, du Bois A, Kristensen G,
Jakobsen A, Sagae S, et al: Definitions for response and
progression in ovarian cancer clinical trials incorporating RECIST
1.1 and CA 125 agreed by the Gynecological Cancer Intergroup
(GCIG). Int J Gynecol Cancer. 21:419–423. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shimokawa M, Ohki M and Kaku T:
Correlation of progression-free and post-progression survival with
overall survival in phase III trials of first-line chemotherapy for
advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol.
36:370–375. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vidal F, Guerby P, Luyckx M, Haddad P,
Stoeckle E, Morice P, Leblanc E, Lecuru F, Daraï E, Classe JM, et
al: Are early relapses in advanced-stage ovarian cancer doomed to a
poor prognosis? PLoS One. 11:e01477872016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Petrillo M, Anchora L Pedone, Tortorella
L, Fanfani F, Gallotta V, Pacciani M, Scambia G and Fagotti A:
Secondary cytoreductive surgery in patients with isolated
platinum-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer: A retrospective
analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 134:257–261. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bristow RE, Puri I and Chi DS:
Cytoreductive surgery for recurrent ovarian cancer: A
meta-analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 112:265–274. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Salani R, Santillan A, Zahurak ML,
Giuntoli RL II, Gardner GJ, Armstrong DK and Bristow RE: Secondary
cytoreductive surgery for localized, recurrent epithelial ovarian
cancer: Analysis of prognostic factors and survival outcome.
Cancer. 109:685–691. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Laas E, Luyckx M, De Cuypere M, Selle F,
Daraï E, Querleu D, Rouzier R and Chéreau E: Secondary complete
cytoreduction in recurrent ovarian cancer: Benefit of optimal
patient selection using scoring system. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
24:238–246. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
van de Laar R, Massuger LF, van Gorp T,
IntHout J, Zusterzeel PL and Kruitwagen RF: External validation of
two prediction models of complete secondary cytoreductive surgery
in patients with recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 137:210–215. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Harter P, du Bois A, Hahmann M, Hasenburg
A, Burges A, Loibl S, Gropp M, Huober J, Fink D, Schröder W, et al:
Surgery in recurrent ovarian cancer: The arbeitsgemeinchaft
gynaekologische onkologie (AGO) DESKTOP OVAR trial. Ann Surg Oncol.
13:1702–1710. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tian WJ, Chi DS, Sehouli J, Tropé CG,
Jiang R, Ayhan A, Cormio G, Xing Y, Breitbach GP, Braicu EI, et al:
A risk model for secondary cytoreductive surgery in recurrent
ovarian cancer: An evidence-based proposal for patient selection.
Ann Surg Oncol. 19:597–604. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vergote IB, Garcia A, Micha J, Pippitt C,
Bendell J, Spitz D, Reed N, Dark G, Fracasso PM, Ibrahim EN, et al:
Randomized multicenter phase II trial comparing two schedules of
etirinotecan pegol (NKTR-102) in women with recurrent
platinum-resistant/refractory epithelial ovarian cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 31:4060–4066. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Markman M, Markman J, Webster K, Zanotti
K, Kulp B, Peterson G and Belinson J: Duration of response to
second-line, platinum-based chemotherapy for ovarian cancer:
Implications for patient management and clinical trial design. J
Clin Oncol. 22:3120–3125. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hoskins PJ and Le N: Identifying patients
unlikely to benefit from further chemotherapy: A descriptive study
of outcome at each relapse in ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
97:862–869. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Griffiths RW, Zee YK, Evans S, Mitchell
CL, Kumaran GC, Welch RS, Jayson GC, Clamp AR and Hasan J: Outcomes
after multiple lines of chemotherapy for platinum-resistant
epithelial cancers of the ovary, peritoneum, and fallopian tube.
Int J Gynecol Cancer. 21:58–65. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun C, Li N, Ding D, Weng D, Meng L, Chen
G and Ma D: The role of BRCA status on the prognosis of patients
with epithelial ovarian cancer: A systematic review of the
literature with a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e952852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|