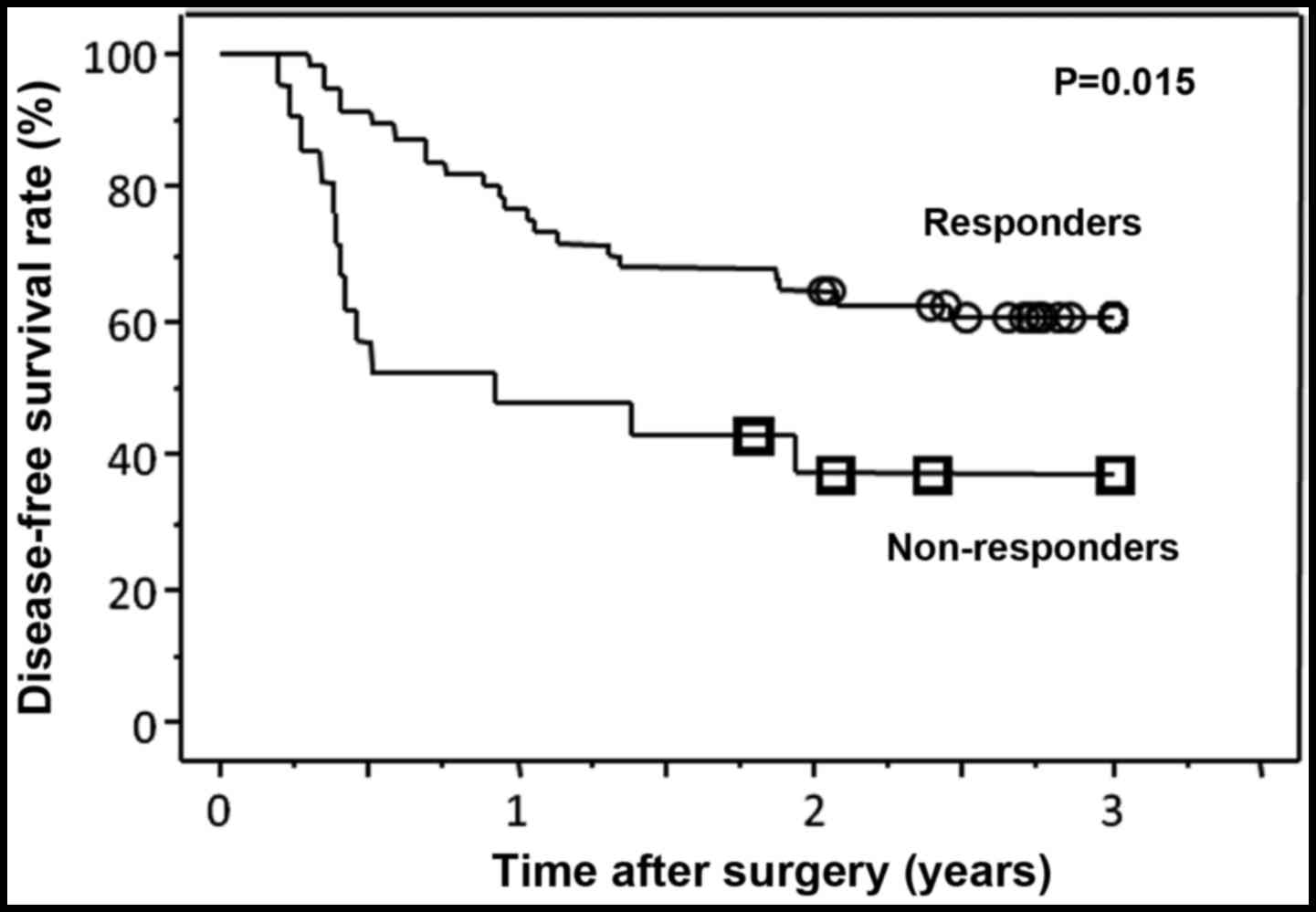
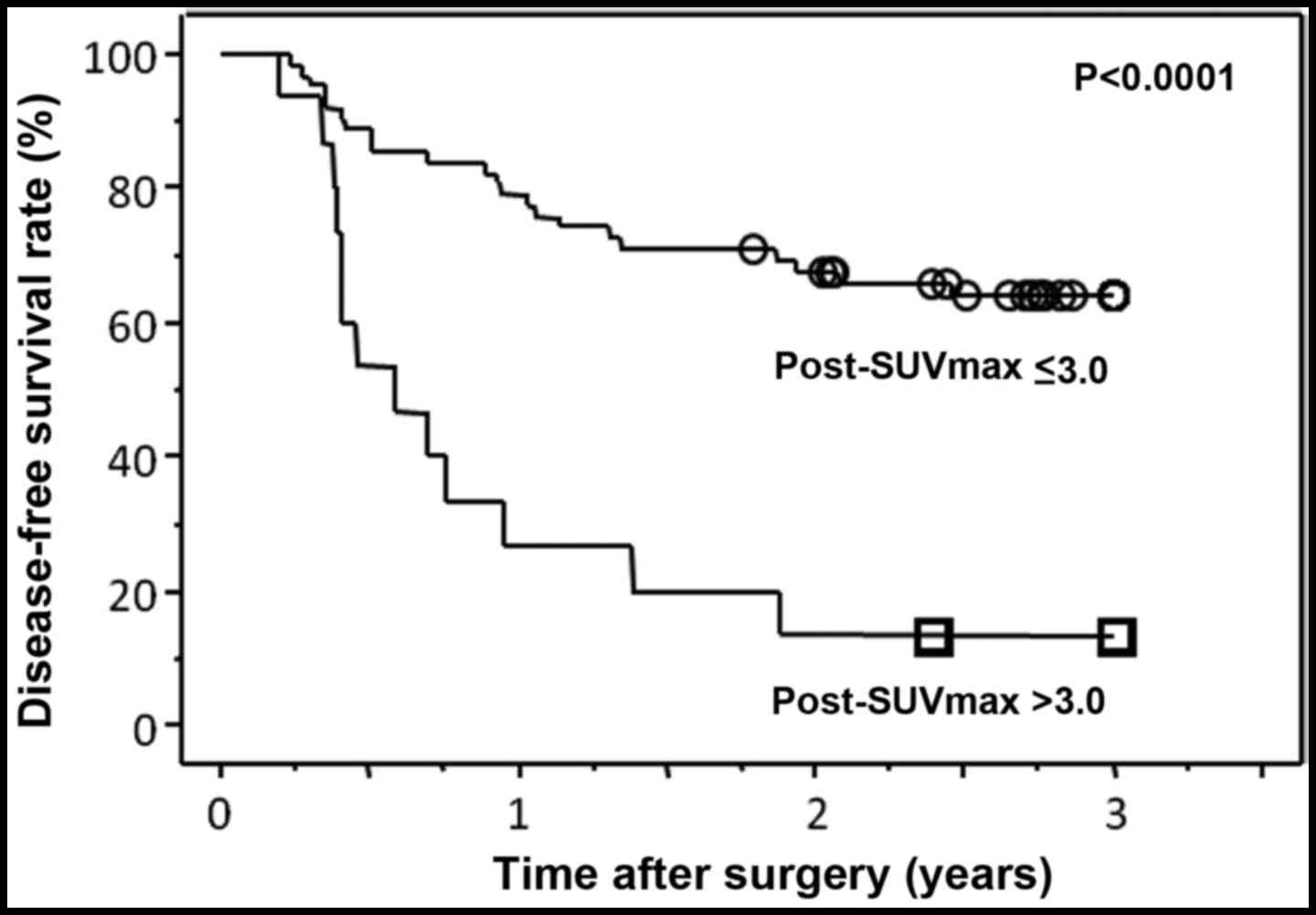
|
1
|
Isono K, Sato H and Nakayama K: Results of
a nationwide study on the three-field lymph node dissection of
esophageal cancer. Oncology. 48:411–420. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Akiyama H, Tsurumaru M, Udagawa H and
Kajiyama Y: Radical lymph node dissection for cancer of the
thoracic esophagus. Ann Surg. 220:364–372; discussion 372–373.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Allum WH, Stenning SP, Bancewicz J, Clark
PI and Langley RE: Long-term results of a randomized trial of
surgery with or without preoperative chemotherapy in esophageal
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:5062–5067. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP,
Thompson JN, Van de Velde CJ, Nicolson M, Scarffe JH, Lofts FJ,
Falk SJ, Iveson TJ, et al: Perioperative chemotherapy versus
surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal cancer. N Eng J Med.
355:11–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Medical Research Council Oesophageal
Cancer Working Group, . Surgical resection with or without
preoperative chemotherapy in oesophageal cancer: A randomised
controlled trial. Lancet. 359:1727–1733. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gebski V, Burmeister B, Smithers BM, Foo
K, Zalcberg J and Simes J; Australasian Gastro-Intestinal Trials
Group, : Survival benefits from neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy or
chemotherapy in oesophageal carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Lancet
Oncol. 8:226–234. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kaklamanos IG, Walker GR, Ferry K,
Franceschi D and Livingstone AS: Neoadjuvant treatment for
resectable cancer of the esophagus and the gastroesophageal
junction: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Ann Surg
Oncol. 10:754–761. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Law S, Fok M, Chow S, Chu KM and Wong J:
Preoperative chemotherapy versus surgical therapy alone for
squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: A prospective randomized
trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 114:210–217. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ancona E, Ruol A, Santi S, Merigliano S,
Sileni VC, Koussis H, Zaninotto G, Bonavina L and Peracchia A: Only
pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy improves
significantly the long term survival of patients with resectable
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Final report of a randomized,
controlled trial of preoperative chemotherapy versus surgery alone.
Cancer. 91:2165–2174. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Block MI, Patterson GA, Sundaresan RS,
Bailey MS, Flanagan FL, Dehdashti F, Siegel BA and Cooper JD:
Improvement in staging of esophageal cancer with the addition of
positron emission tomography. Ann Thorac Surg. 64:770–776;
discussion 776–777. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Luketich JD, Schauer PR, Meltzer CC,
Landreneau RJ, Urso GK, Townsend DW, Ferson PF, Keenan RJ and
Belani CP: Role of positron emission tomography in staging
esophageal cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 64:765–769. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Flanagan FL, Dehdashti F, Siegel BA, Trask
DD, Sundaresan SR, Patterson GA and Cooper JD: Staging of
esophageal cancer with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron
emission tomography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 168:417–424. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Flamen P, Lerut A, Van Custem E, De Wever
W, Peeters M, Stroobants S, Dupont P, Bormans G, Hiele M, De Leyn
P, et al: Utility of positron emission tomography for the staging
of patients with potentially operable esophageal carcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 18:3202–3210. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brücher BL, Weber W, Bauer M, Fink U,
Avril N, Stein HJ, Werner M, Zimmerman F, Siewert JR and Schwaiger
M: Neoadjuvant therapy of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma:
Response evaluation by positron emission tomography. Ann Surg.
233:300–309. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Weber WA, Ott K, Becker K, Dittler HJ,
Helmberger H, Avril NE, Meisetschläger G, Busch R, Siewert JR,
Schwaiger M and Fink U: Prediction of response to preoperative
chemotherapy in adenocarcinomas of the esophagogastric junction by
metabolic imaging. J Clin Oncol. 19:3058–3065. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Flamen P, Van Cutsem E, Lerut A, Cambier
JP, Haustermans K, Bormans G, De Leyn P, Van Raemdonck D, De Wever
W, Ectors N, et al: Positron emission tomography for assessment of
the response to induction radiochemotherapy in locally advanced
oesophageal cancer. Ann Oncol. 13:361–368. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Higuchi I, Yasuda T, Yano M, Doki Y,
Miyata H, Tatsumi M, Fukunaga H, Takiguchi S, Fujiwara Y, Hatazawa
J and Monden M: Lack of fludeoxyglucose F 18 uptake in
posttreatment positron emission tomography as a significant
predictor of survival after subsequent surgery in multimodality
treatment for patients with locally advanced esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 136:205–212. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yuan S, Yu Y, Chao KS, Fu Z, Yin Y, Liu T,
Chen S, Yang X, Yang G, Guo H and Yu J: Additional value of PET/CT
over PET in assessment of locoregional lymph nodes in thoracic
esophageal squamous cell cancer. J Nucl Med. 47:1255–1259.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sobin LH and Wittekind C: TNM
Classification of Malignant Tumors. 6th. Wiley; New York: 2002
|
|
20
|
Kelsen DP, Heelan R, Coonley C, Bains M,
Martini N, Hilaris B and Golbey RB: Clinical and pathological
evaluation of response to chemotherapy in patients with esophageal
carcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 6:539–546. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ishihara R, Yamamoto S, Iishi H, Nagai K,
Matui F, Kawada N, Ohta T, Kanzaki H, Hanafusa M, Hanaoka N, et al:
Predicting the effects of chemoradiotherapy for squamous cell
carcinoma of the esophagus by induction chemotherapy response
assessed by positron emission tomography: Toward
PET-response-guided selection of chemoradiotherapy or
esophagectomy. Int J Clin Oncol. 17:225–232. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kawahara K, Maekawa T, Okabayashi K,
Shiraishi T, Yoshinaga Y, Yoneda S, Hideshima T and Shirakusa T:
The number of lymph node metastases influences survival in
esophageal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 67:160–163. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tachibana M, Kinugasa S, Dhar DK, Kotoh T,
Shibakita M, Ohno S, Masunaga R, Kubota H, Kohno H and Nagasue N:
Prognostic factors after extended esophagectomy for squamous cell
carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus. J Surg Oncol. 72:88–93. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rizk N, Venkatraman E, Park B, Flores R,
Bains MS and Rusch V; American Joint Committee on Cancer staging
system, : The prognostic importance of the number of involved lymph
nodes in esophageal cancer: Implications for revisions of the
American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 132:1374–1381. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Akutsu Y, Shuto K, Kono T, Uesato M,
Hoshino I, Shiratori T, Isozaki Y, Akanuma N, Uno T and Matsubara
H: The number of pathologic lymph nodes involved is still a
significant prognostic factor even after neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Surg
Oncol. 105:756–760. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gu Y, Swisher SG, Ajani JA, Correa AM,
Hofstetter WL, Liao Z, Komaki RR, Rashid A, Hamilton SR and Wu TT:
The number of lymph nodes with metastasis predicts survival in
patients with esophageal or esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma
who receive preoperative chemoradiation. Cancer. 106:1017–1025.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dhar DK, Tachibana M, Kinukawa N, Riruke
M, Kohno H, Little AG and Nagasue N: The prognostic significance of
lymph node size in patients with squamous esophageal cancer. Ann
Surg Oncol. 9:1010–1016. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Komori T, Doki Y, Kabuto T, Ishikawa O,
Hiratsuka M, Sasaki Y, Ohigashi H, Murata K, Yamada T, Miyashiro I,
et al: Prognostic significance of the size of cancer nests in
metastatic lymph nodes in human esophageal cancers. J Surg Oncol.
82:19–27. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Doi N, Imada T, Aoyama N, Kameda Y and
Koizumi H: Prognostic significance of the carcinoma area in the
thickest part of the lymph node. Hepatogastroenterology.
47:728–732. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vesselle H, Schmidt RA, Pugsley JM, Li M,
Kohlmyer SG, Vallires E and Wood DE: Lung cancer proliferation
correlates with [F-18]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake by positron
emission tomography. Clin Cancer Res. 6:3837–3844. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jacob R, Welkoborsky HJ, Mann WJ, Jauch M
and Amedee R: [Fluorine-18]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission
tomography, DNA ploidy and growth fraction in squamous-cell
carcinomas of the head and neck. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec.
63:307–313. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Strauss LG, Koczan D, Klippel S, Pan L,
Cheng C, Willis S and Haberkorn U: Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss A:
Impact of angiogenesis-related gene expression on the tracer
kinetics of 18F-FDG in colorectal tumors. J Nucl Med.
49:1238–1244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kaira K, Oriuchi N, Sunaga N, Ishizuka T,
Shimizu K and Yamamoto N: A systemic review of PET and biology in
lung cancer. Am J Transl Res. 3:383–391. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rebollo Aguirre AC, Ramos-Font C, Villegas
Portero R, Cook GJ, Llamas Elvira JM and Tabares AR:
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for
the evaluation of neoadjuvant therapy response in esophageal
cancer: Systematic review of the literature. Ann Surg. 250:247–254.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kwee RM: Prediction of tumor response to
neoadjuvant therapy in patients with esophageal cancer with use of
18F FDG PET: A systematic review. Radiology.
254:707–717. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Smith JW, Moreira J, Abood G, Aranha GV,
Nagda S, Wagner RH and Shoup M: The influence of
(18)flourodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography on the
management of gastroesophageal junction carcinoma. Am J Surg.
197:308–312. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Port JL, Lee PC, Korst RJ, Liss Y,
Meherally D, Christos P, Mazumdar M and Altorki NK: Positron
emission tomographic scanning predicts survival after induction
chemotherapy for esophageal carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 84:393–400;
discussion 400. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Roedl JB, Harisinghani MG, Colen RR,
Fischman AJ, Blake MA, Mathisen DJ and Mueller PR: Assessment of
treatment response and recurrence in esophageal carcinoma based on
tumor length and standardized uptake value on positron emission
tomography-computed tomography. Ann Thorac Surg. 86:1131–1138.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Suzuki A, Xiao L, Hayashi Y, Macapinlac
HA, Welsh J, Lin SH, Lee JH, Bhutani MS, Maru DM, Hofstetter WL, et
al: Prognostic significance of baseline positron emission
tomography and importance of clinical complete response in patients
with esophageal or gastroesophageal junction cancer treated with
definitive chemoradiotherapy. Cancer. 117:4823–4833. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|