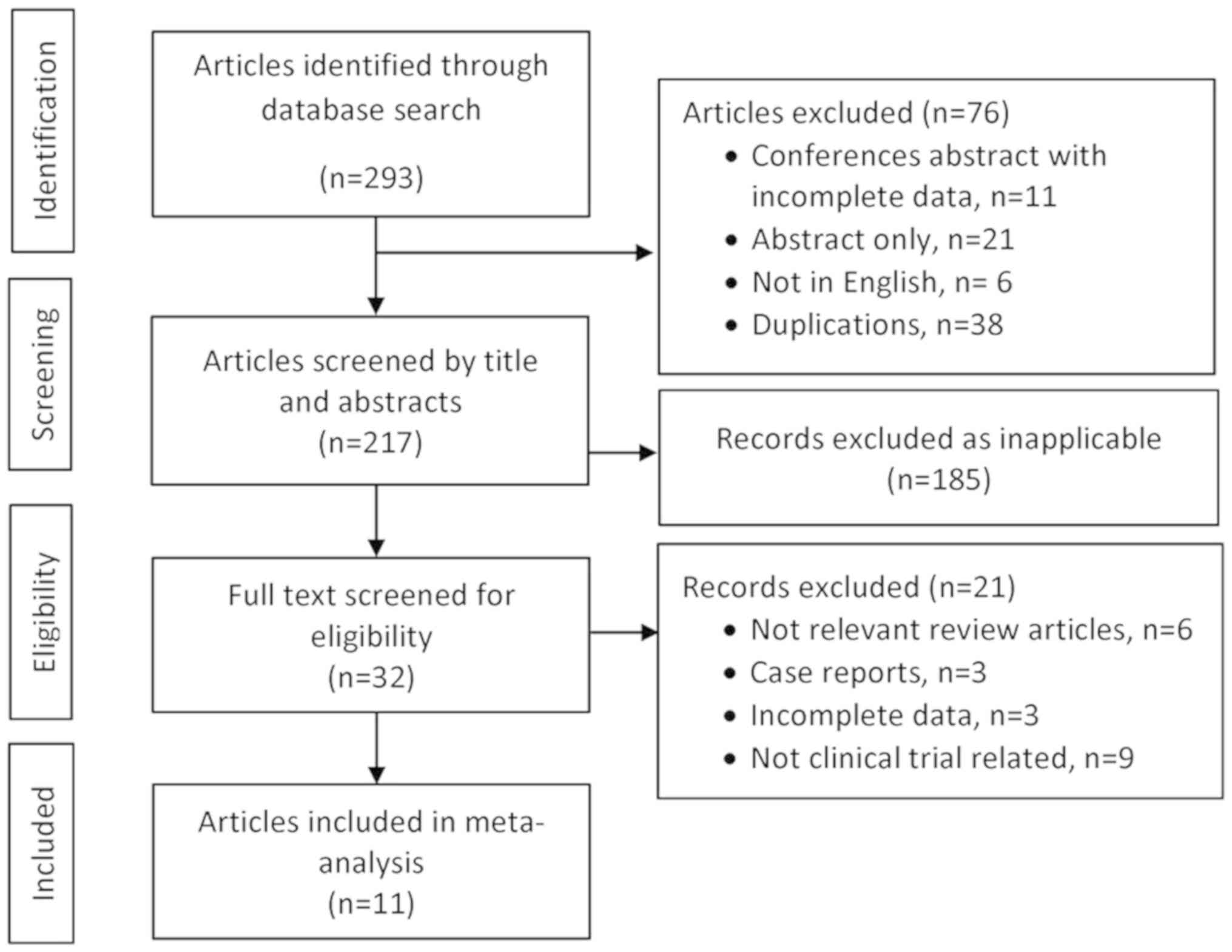
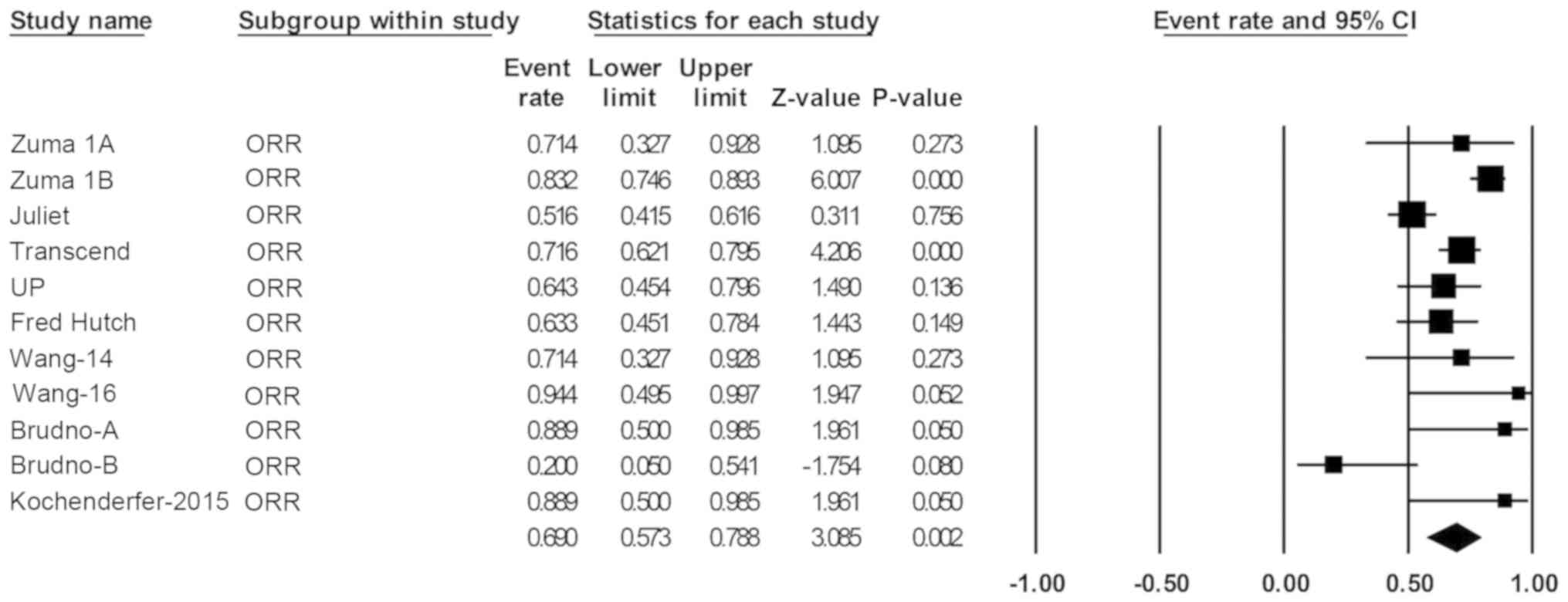
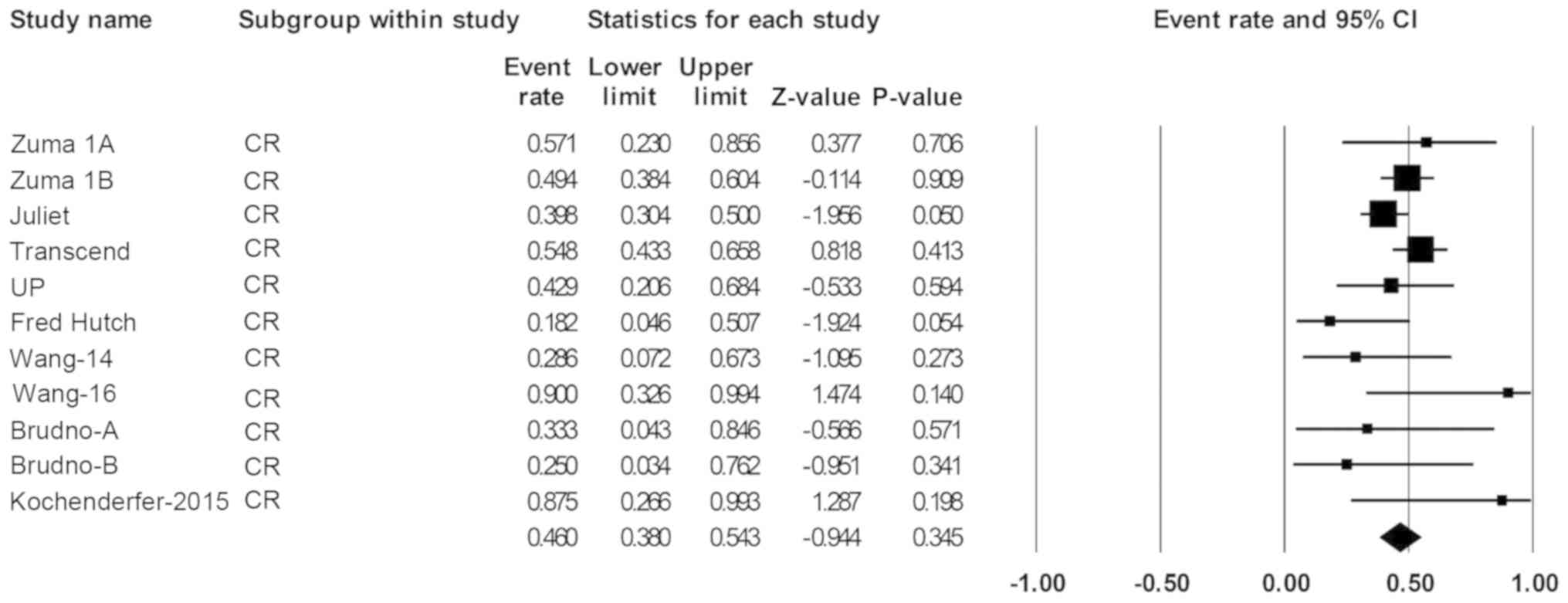
|
1
|
Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H and Isaacson
PG: Classification of lymphoid neoplasms: The microscope as a tool
for disease discovery. Blood. 112:4384–4399. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sehn LH, Donaldson J, Chhanabhai M,
Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Klasa R, MacPherson N, O'Reilly S, Spinelli
JJ, Sutherland J, et al: Introduction of combined CHOP plus
rituximab therapy dramatically improved outcome of diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma in British Columbia. J Clin Oncol. 223:5027–5033.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Coiffier B: Rituximab in the treatment of
diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Semin Oncol. 29:30–35.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Habermann TM, Weller EA, Morrison VA,
Gascoyne RD, Cassileth PA, Cohn JB, Dakhil SR, Woda B, Fisher RI,
Peterson BA and Horning SJ: Rituximab-CHOP versus CHOP alone or
with maintenance rituximab in older patients with diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 24:3121–3127. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sarkozy C and Sehn LH: Management of
relapsed/refractory DLBCL. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol.
31:209–216. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Damaj G, Bernard M, Legouill S, Cartron G,
Le Mevel A, Dubus C, Berthou C, Colombat P, Milpied N, Marolleau
JP, et al: Late relapse of localized high-grade non-hodgkin's
lymphoma: Clinical and biological features. Blood. 112:2603.
2008.
|
|
7
|
Larouche JF, Berger F, Chassagne-Clément
C, Ffrench M, Callet-Bauchu E, Sebban C, Ghesquières H,
Broussais-Guillaumot F, Salles G and Coiffier B: Lymphoma
recurrence 5 years or later following diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma: Clinical characteristics and outcome. J Clin Oncol.
28:2094–2100. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang J, Medeiros LJ and Young KH: Cancer
immunotherapy in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Front Oncol.
10(351)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Martin P: The use of CAR T cells in
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma. Clin Adv
Hematol Oncol. 15:247–249. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
US Food and Drug Administration: FDA
approves CAR-T cell therapy to treat adults with certain types of
large B-cell lymphoma. Accessed on November 13, 2018 at https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-car-t-cell-therapy-treat-adults-certain-types-large-b-cell-lymphoma.
|
|
11
|
Neelapu SS, Locke FL, Bartlett NL, Lekakis
LJ, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, Braunschweig I, Oluwole OO, Siddiqi T,
Lin Y, et al: Axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T-cell therapy in
refractory large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 377:2531–2544.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
US Food and Drug Administration: FDA
approves tisagenlecleucel for adults with relapsed or refractory
large B-cell lymphoma. Accessed on November 13, 2018 at https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-tisagenlecleucel-adults-relapsed-or-refractory-large-b-cell-lymphoma.
|
|
13
|
Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, Waller EK,
Borchmann P, McGuirk JP, Jäger U, Jaglowski S, Andreadis C, Westin
JR, et al: Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 380:45–56. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Borchmann P, Tam CS, Jäger U, McGuirk JP,
Holte H, Waller EK, Jaglowski SM, Bishop MR, Andreadis C, Foley SR,
et al: An updated analysis of JULIET, a global pivotal Phase
2 trial of tisagenlecleucel in adult patients with relapsed or
refractory (r/r) diffuse large b-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Presented
at 2018 EHA Congress (abstract S799), 2018. https://library.ehaweb.org/eha/2018/stockholm/214521/peter.borchmann.an.updated.analysis.of.juliet.a.global.pivotal.phase.2.trial.html.
|
|
15
|
Abramson JS, Gordon LI, Palomba ML,
Lunning MA, Arnason JE, Forero-Torres A, Wang M, Maloney DG, Sehgal
A, Andreadis C, et al: Updated safety and long term clinical
outcomes in TRANSCEND NHL 001, pivotal trial of lisocabtagene
maraleucel (JCAR017) in R/R aggressive NHL. J Clin Oncol.
36(7505)2018.
|
|
16
|
Lee DW, Gardner R, Porter DL, Louis CU,
Ahmed N, Jensen M, Grupp SA and Mackall CL: Current concepts in the
diagnosis and management of cytokine release syndrome. Blood.
124:188–195. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow
C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J
and Moher D: The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews
and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care
interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med.
151:W65–W94. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
DerSimonian R and Laird N: Meta-analysis
in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 7:177–188. 1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Locke FL, Neelapu SS, Bartlett NL, Siddiqi
T, Chavez JC, Hosing CM, Ghobadi A, Budde LE, Bot A, Rossi JM, et
al: Phase 1 results of ZUMA-1: A multicenter study of KTE-C19
anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy in refractory aggressive lymphoma. Mol
Ther. 25:285–295. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, Waller EK,
Borchmann P, McGuirk JP, Jäger U, Jaglowski S, Andreadis C, Westin
JR, et al: Primary analysis of Juliet: A global, pivotal, phase 2
trial of CTL019 in adult patients with relapsed or refractory
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 130(577)2017.
|
|
21
|
Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam C, Waller EK,
Borchmann P, McGuirk J, Jäger U, Jaglowski S, Andreadis C, Westin
J, et al: Global pivotal phase 2 trial of the CD19-targeted therapy
CTL019 in adult patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)-an interim analysis. Hematol Oncol.
35(27)2017.
|
|
22
|
Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon LI,
Lunning MA, Arnason JE, Wang M, Forero A, Maloney DG, Albertson T,
Garcia J, et al: High durable CR rates in relapsed/refractory (R/R)
aggressive B-NHL treated with the CD19-directed CAR T cell product
JCAR017 (TRANSCEND NHL 001): Defined composition allows for
dose-finding and definition of pivotal cohort. Blood.
130(58)2017.
|
|
23
|
Schuster SJ, Svoboda J, Chong EA, Nasta
SD, Mato AR, Anak Ö, Brogdon JL, Pruteanu-Malinici I, Bhoj V,
Landsburg D, et al: Chimeric antigen receptor T cells in refractory
B-cell lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 377:2545–2554. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Turtle CJ, Hanafi LA, Berger C, Hudecek M,
Pender B, Robinson E, Hawkins R, Chaney C, Cherian S, Chen X, et
al: Immunotherapy of non-hodgkin's lymphoma with a defined ratio of
CD8+ and CD4+ CD19-specific chimeric antigen
receptor-modified T cells. Sci Transl Med.
8(355ra116)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang Y, Zhang Wy, Han Qw, Liu Y, Dai Hr,
Guo Yl, Bo J, Fan H, Zhang Y, Zhang Yj, et al: Effective response
and delayed toxicities of refractory advanced diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma treated by CD20-directed chimeric antigen
receptor-modified T cells. Clin Immunol. 155:160–175.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Popplewell LL, Wagner JR, Naranjo
A, Blanchard MS, Mott MR, Norris AP, Wong CW, Urak RZ, Chang WC, et
al: Phase 1 studies of central memory-derived CD19 CAR T-cell
therapy following autologous HSCT in patients with B-cell NHL.
Blood. 127:2980–2990. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Brudno JN, Shi V, Stroncek D, Pittaluga S,
Kanakry JA, Curtis LM, Gea-Banacloche JC, Pavletic S, Bagheri MH,
Rose JJ, et al: T cells expressing a novel fully-human anti-CD19
chimeric antigen receptor induce remissions of advanced lymphoma in
a first-in-humans clinical trial. Blood. 128(999)2016.
|
|
28
|
Brudno JN, Somerville RP, Shi V, Rose JJ,
Halverson DC, Fowler DH, Gea-Banacloche JC, Pavletic SZ, Hickstein
DD, Lu TL, et al: Allogeneic T cells that express an anti-CD19
chimeric antigen receptor induce remissions of B-cell malignancies
that progress after allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell
transplantation without causing graft-versus-host disease. J Clin
Oncol. 34:1112–1121. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kochenderfer JN, Dudley ME, Kassim SH,
Somerville RP, Carpenter RO, Stetler-Stevenson M, Yang JC, Phan GQ,
Hughes MS, Sherry RM, et al: Chemotherapy-Refractory diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma and indolent B-cell malignancies can be effectively
treated with autologous T cells expressing an anti-CD19 chimeric
antigen receptor. J Clin Oncol. 33:540–549. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kochenderfer JN, Somerville RPT, Lu T,
Yang JC, Sherry RM, Feldman SA, McIntyre L, Bot A, Rossi J, Lam N
and Rosenberg SA: Long-Duration complete remissions of diffuse
large B cell lymphoma after anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T
cell therapy. Mol Ther. 25:2245–2253. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kochenderfer JN and Rosenberg SA: Treating
B-cell cancer with T cells expressing anti-CD19 chimeric antigen
receptors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 10:267–276. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Jensen MC, Popplewell L, Cooper LJ,
DiGiusto D, Kalos M, Ostberg JR and Forman SJ: Antitransgene
rejection responses contribute to attenuated persistence of
adoptively transferred CD20/CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptor
redirected T cells in humans. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant.
16:1245–1256. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Savoldo B, Ramos CA, Liu E, Mims MP,
Keating MJ, Carrum G, Kamble RT, Bollard CM, Gee AP, Mei Z, et al:
CD28 costimulation improves expansion and persistence of chimeric
antigen receptor-modified T cells in lymphoma patients. J Clin
Invest. 121:1822–1826. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Till BG, Jensen MC, Wang J, Chen EY, Wood
BL, Greisman HA, Qian X, James SE, Raubitschek A, Forman SJ, et al:
Adoptive immunotherapy for indolent non-hodgkin lymphoma and mantle
cell lymphoma using genetically modified autologous CD20-specific T
cells. Blood. 112:2261–2271. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Crump M, Neelapu SS, Farooq U, Van Den
Neste E, Kuruvilla J, Westin J, Link BK, Hay A, Cerhan JR, Zhu L,
et al: Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma:
Results from the international SCHOLAR-1 study. Blood.
130:1800–1808. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kawalekar OU, O'Connor RS, Fraietta JA,
Guo L, McGettigan SE, Posey AD Jr, Patel PR, Guedan S, Scholler J,
Keith B, et al: Distinct signaling of coreceptors regulates
specific metabolism pathways and impacts memory development in CAR
T cells. Immunity. 44:380–390. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhao Z, Condomines M, van der Stegen SJC,
Perna F, Kloss CC, Gunset G, Plotkin J and Sadelain M: Structural
design of engineered costimulation determines tumor rejection
kinetics and persistence of CAR T cells. Cancer Cell. 28:415–428.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Park JH and Brentjens RJ: Are all chimeric
antigen receptors created equal? J Clin Oncol. 33:651–653.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Siddiqi T, Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon
LI, Lunning MA, Arnason JE, Wang M, Forero-Torres A, Maloney DG,
Heipel M, et al: Correlation of patient characteristics and
biomarkers with clinical outcomes of JCAR017 in R/R aggressive BNHL
(TRANSCEND NHL 001 study). J Clin Oncol. 36(5)2018.
|
|
40
|
Kochenderfer JN, Dudley ME, Feldman SA,
Wilson WH, Spaner DE, Maric I, Stetler-Stevenson M, Phan GQ, Hughes
MS, Sherry RM, et al: B-cell depletion and remissions of malignancy
along with cytokine-associated toxicity in a clinical trial of
anti-CD19 chimeric-antigen-receptor-transduced T cells. Blood.
119:2709–2720. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|