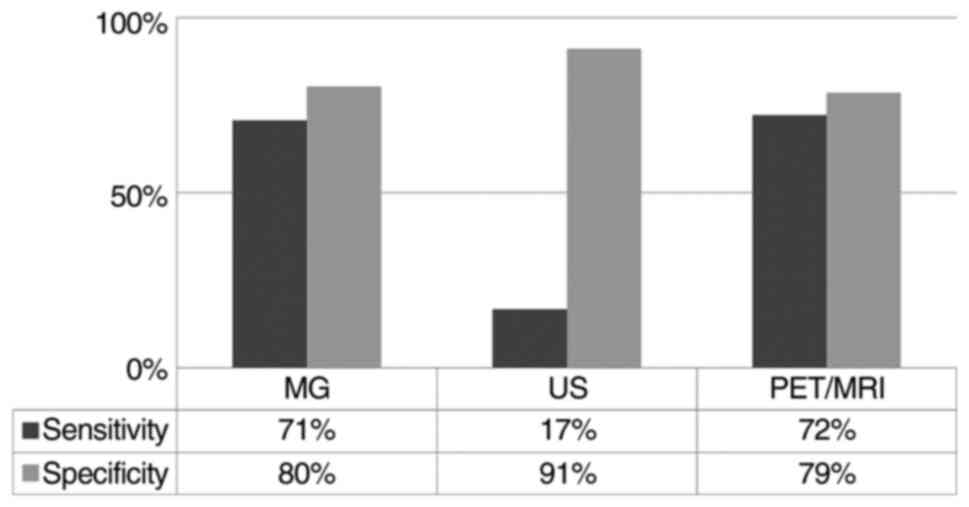
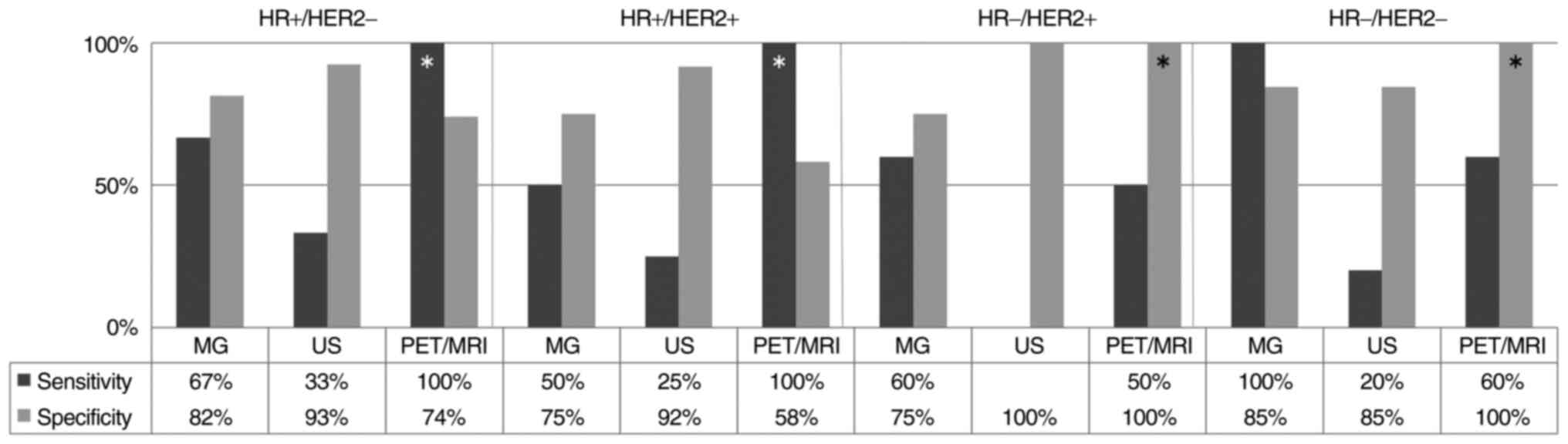
|
1
|
Balu-Maestro C, Chapellier C, Bleuse A,
Chanalet I, Chauvel C and Largillier R: Imaging in evaluation of
response to neoadjuvant breast cancer treatment benefits of MRI.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 72:145–152. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Drew PJ, Kerin MJ, Mahapatra T, Malone C,
Monson JR, Turnbull LW and Fox JN: Evaluation of response to
neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced breast cancer
with dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of the breast. Eur J Surg Oncol.
27:617–620. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Shin HJ, Kim HH, Ahn JH, Kim SB, Jung KH,
Gong G, Son BH and Ahn SH: Comparison of mammography, sonography,
MRI and clinical examination in patients with locally advanced or
inflammatory breast cancer who underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Br J Radiol. 84:612–620. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Atkins JJ, Appleton CM, Fisher CS, Gao F
and Margenthaler JA: Which imaging modality is superior for
prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with
triple negative breast cancer? J Oncol. 2013(964863)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Dialani D, Chadashxili T and Slanetz P:
Role of imaging in neoadjuvant therapy for breast cancer. Ann Surg
Oncol. 22:1416–1424. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Pengel KE, Koolen BB, Loo CE, Vogel WV,
Wesseling J, Lips EH, Rutgers EJ, Valdés Olmos RA, Vrancken Peeters
MJ, Rodenhuis S and Gilhuijs KG: Combined use of 18F-FDG PET/CT and
MRI for response monitoring of breast cancer during neoadjuvant
chemotherapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 41:1515–524.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li H, Yao L, Jin P, Hu L, Li X, Guo T and
Yang K: MRI and PET/CT for evaluation of the pathological response
to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Breast. 40:106–115. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Pahk K, Kim S and Choe KG: Early
prediction of pathological complete response in luminal B type
neoadjuvant chemotherapy-treated breast cancer patients: Comparison
between interim 18F-FDG PET/CT and MRI. Nucl Med Commun.
36:887–891. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Melsaether A and Moy L: Breast PET/MR
imaging. Radiol Clin North Am. 55:579–589. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Rice SL and Friedman KP: Clinical PET-MR
imaging in breast cancer and lung cancer. PET Clin. 11:387–402.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Catalano OA, Horn GL, Signore A, Iannace
C, Lepore M, Vangel M, Luongo A, Catalano M, Lehman C, Salvatore M,
et al: PET/MR in invasive ductal breast cancer: Correlation between
imaging markers and histological phenotype. Br J Cancer.
116:893–902. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Heys SD and Chaturvedi S: Primary
chemotherapy in breast cancer: The beginning of the end or the end
of the beginning for the surgical oncologist? World J Surg Oncol.
1(14)2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rea D, Tomlins A and Francis A: Time to
stop operating on breast cancer patients with pathological complete
response? Eur J Surg Oncol. 39:924–930. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mamounas EP: Impact of neoadjuvant
chemotherapy on locoregional surgical treatment of breast cancer.
Ann Surg Oncol. 22:1425–1433. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Masuda N, Lee SJ, Ohtani S, Im YH, Lee ES,
Yokota I, Kuroi K, Im SA, Park BW, Kim SB, et al: Adjuvant
capecitabine for breast cancer after preoperative chemotherapy. N
Engl J Med. 376:2147–2159. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
De Los Santos J, Bernreuter W, Keene K,
Krontiras H, Carpenter J, Bland K, Cantor A and Forero A: Accuracy
of breast magnetic resonance imaging in predicting pathologic
response in patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Clin
Breast Cancer. 11:312–319. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Marinovich ML, Houssami N, Macaskill P,
Sardanelli F, Irwig L, Mamounas EP, von Minckwitz G, Brennan ME and
Ciatto S: Meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging in detecting
residual breast cancer after neoadjuvant therapy. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 105:321–333. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gu YL, Pan SM, Ren J, Yang ZX and Jiang
GQ: Role of magnetic resonance imaging in detection of pathologic
complete remission in breast cancer patients treated with
neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A meta-analysis. Clin Breast Cancer.
17:245–255. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Akimoto E, Kadoya T, Kajitani K, Emi A,
Shigematsu H, Ohara M, Masumoto N and Okada M: Role of
18F-PET/CT in predicting prognosis of patients with
breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Clin Breast Cancer.
1:45–52. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liu Q, Wang C, Li P, Liu J, Huang G and
Song S: The role of (18)F-FDG PET/CT and MRI in assessing
pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in
patients with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Biomed Res Int. 2016(3746232)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lee HJ, Song IH, Seo AN, Lim B, Kim JY,
Lee JJ, Park IA, Shin J, Yu JH, Ahn JH and Gong G: Correlations
between molecular subtypes and pathologic response patterns of
breast cancers after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Sug Oncol.
22:392–400. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Loo CE, Straver ME, Rodenhuis S, Muller
SH, Wesseling J, Vrancken Peeters MJ and Gilhuijs KG: Magnetic
resonance imaging response monitoring of breast cancer during
neoadjuvant chemotherapy: Relevance of breast cancer subtype. J
Clin Oncol. 29:660–666. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Koolen BB, Pengel KE, Wesseling J, Vogel
WV, Vrancken Peeters MJ, Vincent AD, Gilhuijs KG, Rodenhuis S,
Rutgers EJ and Valdés Olmos RA: FDG PET/CT during neoadjuvant
chemotherapy may predict response in ER-positive/HER2-negative and
triple negative, but not in HER2-positive breast cancer. Breast.
22:691–697. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tsunoda-Shimizu H, Hayashi N, Hamaoka T,
Kawasaki T, Tsugawa K, Yagata H, Kikuchi M, Suzuki K and Nakamura
S: Determining the morphological features of breast cancer and
predicting the effects of neoadjuvant chemotherapy via diagnostic
breast imaging. Breast Cancer. 15:133–140. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kim TH, Yoon JK, Kang DK, Kang SY, Jung
YS, Han S, Kim JY, Yim H and An YS: Value of volume-based metabolic
parameters for predicting survival in breast cancer patients
treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Medicine (Baltimore).
95(e4605)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Croshaw R, Shapira-Wright H, Svensson E,
Erb K and Julian T: Accuracy of clinical examination, digital
mammogram, ultrasound, and MRI in determining postneoadjuvant
pathologic tumor response in operable breast cancer patients. Ann
Surg Oncol. 18:3160–3163. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Uchiyama N, Kinoshita T, Hojo T, Asaga S,
Suzuki J, Kawawa Y and Otsuka K: Usefulness of adjunction of
digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) to full-field digital
mammography (FFDM) in evaluation of pathological response after
neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for breast cancer. Breast Imaging.
7361:354–361. 2012.
|
|
28
|
Jones RL, Lakhani SR, Ring AE, Ashley S,
Walsh G and Smith IE: Pathological complete response and residual
DCIS following neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast carcinoma. Br J
Cancer. 94:358–362. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kaufmann M, Hortobagyi GN, Goldhirsch A,
Scholl S, Makris A, Valagussa P, Blohmer JU, Eiermann W, Jackesz R,
Jonat W, et al: Recommendations from an international expert panel
on the use of neoadjuvant (primary) systemic treatment of operable
breast cancer: An update. J Clin Oncol. 24:1940–1949.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mazouni C, Peintinger F, Wan-Kau S, Andre
F, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Symmans WF, Meric-Bernstam F, Valero V,
Hortobagyi GN and Pusztai L: Residual ductal carcinoma in situ in
patients with complete eradication of invasive breast cancer after
neoadjuvant chemotherapy does not adversely affect patient outcome.
J Clin Oncol. 25:2650–2655. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Symmans WF, Peintinger F, Hatzis C, Rajan
R, Kuerer H, Valero V, Assad L, Poniecka A, Hennessy B, Green M, et
al: Measurement of residual breast cancer burden to predict
survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol.
25:4414–4422. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|